Fourier transforms. Definition F(ω) = - should know these! f(t).e -jωt.dt. ω = 2πf. other definitions exist. f(t) = - F(ω).e jωt.
|
|
|
- Claud Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fourier transforms This is intended to be a practical exposition, not fully mathematically rigorous ref The Fourier Transform and its Applications R. Bracewell (McGraw Hill) Definition F(ω) = - f(t).e -jωt.dt ω = 2πf should know these! f(t) = - F(ω).e jωt.df = (1/2π) - F(ω).e jωt.dω other definitions exist Conventions f: function to be transformed F: Fourier transform of f F = FT[f] so inverse transform is f = FT -1 [F] there will be a few exceptions to upper/lower case rule g.hall@ic.ac.uk 1
2 What is the importance? widely used in many branches of science some problems solved more easily by a transform to another domain eg algebra just becomes simpler but sometimes understanding too.. in instruments decomposition of signals in the time domain into frequency, and vice versa, is a valuable tool this will be the main interest here (ie t & f) Both time development f(t) and spectral density F(ω) are observables Should note that not all functions have FT Formally, require (i) - f(t).e -jωt.dt < (ii) f(t) has finite maxima and minima within any finite interval (iii) f(t) has finite number of discontinuities within any finite interval g.hall@ic.ac.uk 2
3 Impulse A common signal in physics is an impulse - a la Dirac ie δ(t-t 0 ) = 0 t t 0 - δ(t-t 0 ) = 1 or if range of integration includes t 0 Such a definition is comparable to many detector signals eg. a scintillation detector measures ionisation of a cosmic ray particle a pulse from a photomultiplier converts light into electrical signal the signal is fast (very short duration, typically ~ns) the total charge in the pulse is fixed other examples: fast laser pulse, most ionisation even if the signal is not a genuine impulse, it can be considered as a sum of many consecutive impulses or the subsequent processing may be long in comparison with the signal duration for the approximation to be valid g.hall@ic.ac.uk 3
4 FT of impulse F(ω) = - δ(t).e -jωt.dt = 1 ie an impulse contains a uniform mixture of all frequencies an important general comment is that short duration pulses have a wide range of frequencies, as do pulses with fast edges (like steps). Real instruments do not support infinite frequency ranges. Note on inverting FTs f(t) = - F(ω).e jωt.df = (1/2π) - F(ω). e jωt.dω Many inversions are straightforward integrations others need care eg inverse of δ function (1/2π) - 1. e jωt.dω = (1/2π)[e jωt /jt ] -??? often simpler to recognise the function from experience (practice!) g.hall@ic.ac.uk 4
5 Some theorems F(ω) = FT[f(t)] = - f(t).e -jωt.dt Linearity FT[a.f(t)+b.g(t)] = a.f(ω) + b.g(ω) Translation in time (Shift theorem) FT[f(t+t 0 )] = - f(t+t 0 ).e -jωt.dt = - f(u).e -jω(u-t 0 ).du = e jωt 0 - f(u).e -jωu.du = e jωt 0 F(ω) different frequency components of waveform suffer different phase shifts to maintain pulse shape Similarity - scale by factor a > 0 FT[f(at)] = - f(at).e -jωt.dt = - f(u).e -jωu/a.du/a = - f(u).e -j(ω/a)u.du/a Modulation = (1/ a )F(ω/a) FT[f(t)cosαt] = (1/2) - f(t).[e jαt + e -jαt ]. e -jωt dt = (1/2){ - f(t).e -j(ω-α)t.dt + - f(t).e -j(ω+α)t.dt} = (1/2){F(ω-α) + F(ω+α)} compression of time scale= expansion of frequency scale g.hall@ic.ac.uk 5
6 and tricks sometimes the symmetry can be exploited to ease calculation F(ω) = - f(t).e -jωt.dt 2πf(t) = - F(ω).e jωt.dω FT pair interchange and t => 2πf(ω) = - F(t).e jωt.dt example so - F(t).e -jωt.dt = 2πf(-ω) FT[δ(t)] = 1 so FT[1] = 2πδ(-ω) = 2πδ(ω) We will very often be dealing with real functions in time ie. f(t) = Re[f(t)] + j Im[f(t)] = Re[f(t)] so complex conjugate f*(t) = f(t) then F(-ω) = F*(ω) g.hall@ic.ac.uk 6
7 Some examples (i) (1) f(t) = 0 t < 0 = e -at t 0 F(ω) = 0 e -at.e -jωt.dt = 0 e -(jω+a)t.dt = 1/(jω+a) (2) f(t) = e -a t F(ω) = - 0 e at.e -jωt.dt + 0 e -at.e -jωt.dt =-1/(jω-a) +1/(jω+a) = 2a/(ω 2 +a 2 ) 1 (3) f(t)= 0 t < 0 = 1 t 0 rewrite as limit a->0 (1/2)[1 + e-at [t 0]-e at [t<0]] F(ω) = limit a->0 (1/2)[2πδ(ω) + 1/(jω+a) + 1/(jω-a)] = πδ(ω) + 1/jω = 1/jω ω > this function is often called H(t) g.hall@ic.ac.uk 7
8 Some examples (ii) (4) f(t) = 0 t < 0 = 1-e -at t 0 F(ω) = a/[jω(jω+a)] ω > 0 (5) f(t) = 0 t < 0 = ate -at t 0 F(ω) = a/(jω+a) 2 (6) f(t) = exp(-a 2 t 2 ) F(ω) = ( π/a)exp(-ω 2 /4a 2 ) (7) top-hat function Π(t) f(t) = 1 -a < t a = 0 elsewhere F(ω) = 2sin(ωa)/ω -a a g.hall@ic.ac.uk 8
9 Fourier pairs top hat function -a a F(ω) = 2sin(ωa)/ω what value does a have? g.hall@ic.ac.uk 9
10 Bandpass filter Low pass + high pass filters equal time constants are often chosen F(ω) = jωτ/(1+jωτ) 2 H(f) τ = 1µs (degrees) φ f (Hz) f (Hz) H(f) 0.01 f 0 = 1/2πτ g.hall@ic.ac.uk 10 f (Hz)
11 Integrator + Bandpass filter Commonly encountered pulse shape in amplifier systems integrator response = 1/jωC F(ω) = A/(1+jωτ) f(t) = e 1 (t/τ)e -t/τ τ = 2 F(f) τ = 1µs f (Hz) (degrees) φ g.hall@ic.ac.uk f (Hz)
12 Differentiation and integration FT[f (t)] = - f (t).e -jωt.dt = - lim[ f(t+ t)-f(t)].e -jωt.dt t limit at t -> 0 = - lim[ f(t+ t)]e -jωt.dt - - lim[ f(t)].e -jωt.dt t t = lim[e jω t F(ω) -F(ω)] = jωf(ω) t use Shift theorem FT[ -t f(t)dt] = - { -t f(u)du.}e -jωt.dt let -t f(u)du = g(t) - { -t f(u)du.}e -jωt.dt = - g(t)e -jωt.dt = [g(t) e -jωt /(-jω)] - + (1/jω) - g (t)e -jωt.dt = F(ω)/jω Formally, subject to constraints on g(±) g.hall@ic.ac.uk 12
13 Fourier transforms of repetitive functions typically give line spectra, instead of continuous ie series of discrete frequency components dominate obvious for sin( 0 t) and combinations Recall Modulation theorem FT[f(t)cosω 0 t] = (1/2){F(ω-ω 0 ) + F(ω+ω 0 )} so f(t) = 1 F(ω) = 2πδ(ω) FT[cosω 0 t] = (1/2){δ(ω-ω 0 ) + δ(ω+ω 0 )} single freqency component at ω= ω 0 (and -ω = ω 0 ) FT[cos(ω 0 t)cos(ω 1 t)] = (1/4){δ(ω-ω 0 -ω 1 ) + δ(ω-ω 0 +ω 1 ) + δ(ω+ω 0 -ω 1 )+ δ(ω+ω 0 +ω 1 )} components at ω= ω 0 -ω 1 and ω= ω 0 +ω 1 (and -ω =...) What is the meaning of negative frequencies? g.hall@ic.ac.uk 13
14 Negative frequencies Can consider them as a formal mathematical consequence of the Fourier integral which has an elegant symmetry but doesn t interfere with practical applications We are always concerned with functions which are real since measured quantities must be For real functions F(-ω) = F*(ω) and we always encounter combinations like - F(ω) e jωt dω - F(ω) e jωt dω = -0 F(ω) e jωt dω + 0 F(ω) e jωt dω = 0 -F( υ) e -jυt dυ + 0 F(ω) e jωt dω = 0 F*(ω) e -jωt dω + 0 F(ω) e jωt dω if F(ω) = F 0 e jθ then F*(ω) e -jωt + F(ω) e jωt = F 0 [e -j(ωt+θ) + e j(ωt+θ) ] so - F(ω) e jωt dω = 2 0 F 0 cos(ωt+θ) dω purely real integral g.hall@ic.ac.uk 14
15 Sequence of pulses General case g(t) = n=- f(t+n t) f(t+2 t) + f(t+ t) + f(t) + f(t- t) + f(t-2 t) + f(t-n t) + from Shift theorem G(ω) = F (ω) n=- e jωn t = F (ω) [1+ n=1 2cos(ωn t)] n=- e jωn t = n=- e jθ = n=0 e jθ + n=0 e -jθ - 1 Geometric series S = 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + x n + = 1/(1-x) n=- e jθ = 1/(1- e jθ ) + 1/(1- e -jθ ) - 1 = 1 so G(ω) = F (ω) frequency content unchanged - as seems logical but normally can t observe waveform for infinite time If f(t) is truly periodic ie duration < t we'll later find it more convenient to work with Fourier series exploit the natural harmonics of the system g.hall@ic.ac.uk 15
16 Real sequences If observe for a duration T, the lowest freqency which can be observed is ~1/T ie partial cycles should be included with random phase and would be expected not to contribute so convolute periodic waveform with top-hat duration T to make it finite g(t) = n=- f(t+n t) * Π(t,T) G(ω) = F (ω).2sin(ωt/2)/ω this has peaks at ωt/2 = (π/2)(2k+1) k = 1, 2, 3, ie multiples of ω 0 = (π/t)(2k+1) Train of rectangular pulses, duration a G(ω) = [2sin(ωa/2)/ω]. [2sin(ωT/2)/ω] = (4/ω 2 )sin(ωa/2).sin(ωt/2) will return to this later g.hall@ic.ac.uk 16
Signals & Systems. Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform. Alp Ertürk
 Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Signal and systems. Linear Systems. Luigi Palopoli. Signal and systems p. 1/5
 Signal and systems p. 1/5 Signal and systems Linear Systems Luigi Palopoli palopoli@dit.unitn.it Wrap-Up Signal and systems p. 2/5 Signal and systems p. 3/5 Fourier Series We have see that is a signal
Signal and systems p. 1/5 Signal and systems Linear Systems Luigi Palopoli palopoli@dit.unitn.it Wrap-Up Signal and systems p. 2/5 Signal and systems p. 3/5 Fourier Series We have see that is a signal
X. Chen More on Sampling
 X. Chen More on Sampling 9 More on Sampling 9.1 Notations denotes the sampling time in second. Ω s = 2π/ and Ω s /2 are, respectively, the sampling frequency and Nyquist frequency in rad/sec. Ω and ω denote,
X. Chen More on Sampling 9 More on Sampling 9.1 Notations denotes the sampling time in second. Ω s = 2π/ and Ω s /2 are, respectively, the sampling frequency and Nyquist frequency in rad/sec. Ω and ω denote,
Review of Fourier Transform
 Review of Fourier Transform Fourier series works for periodic signals only. What s about aperiodic signals? This is very large & important class of signals Aperiodic signal can be considered as periodic
Review of Fourier Transform Fourier series works for periodic signals only. What s about aperiodic signals? This is very large & important class of signals Aperiodic signal can be considered as periodic
Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4.1
 Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4. A large class of aperiodic CT signals can be represented by the CT Fourier transform (CTFT). The (CT) Fourier transform (or spectrum)
Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4. A large class of aperiodic CT signals can be represented by the CT Fourier transform (CTFT). The (CT) Fourier transform (or spectrum)
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Let x(t) be a CT periodic signal with period T, i.e., xt ( + T) = xt ( ), t R Example: the rectangular
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Let x(t) be a CT periodic signal with period T, i.e., xt ( + T) = xt ( ), t R Example: the rectangular
ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Chap 2.1 2.5: Signal Classifications Fourier Transform Dirac Delta Function
ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Chap 2.1 2.5: Signal Classifications Fourier Transform Dirac Delta Function
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II
 27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
Figure 3.1 Effect on frequency spectrum of increasing period T 0. Consider the amplitude spectrum of a periodic waveform as shown in Figure 3.2.
 3. Fourier ransorm From Fourier Series to Fourier ransorm [, 2] In communication systems, we oten deal with non-periodic signals. An extension o the time-requency relationship to a non-periodic signal
3. Fourier ransorm From Fourier Series to Fourier ransorm [, 2] In communication systems, we oten deal with non-periodic signals. An extension o the time-requency relationship to a non-periodic signal
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Representation of Signals in Terms of Frequency Components Consider the CT signal defined by N xt () = Acos( ω t+ θ ), t k = 1 k k k The frequencies `present
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Representation of Signals in Terms of Frequency Components Consider the CT signal defined by N xt () = Acos( ω t+ θ ), t k = 1 k k k The frequencies `present
Series FOURIER SERIES. Graham S McDonald. A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis
 Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC37 Communications Systems : Fourier Representations School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Outline Chap..5: Signal Classiications Fourier Transorm Dirac Delta Function Unit Impulse Fourier
ENSC37 Communications Systems : Fourier Representations School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Outline Chap..5: Signal Classiications Fourier Transorm Dirac Delta Function Unit Impulse Fourier
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9
 Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
Homework 4. May An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt
 Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
Homework 5 EE235, Summer 2013 Solution
 Homework 5 EE235, Summer 23 Solution. Fourier Series. Determine w and the non-zero Fourier series coefficients for the following functions: (a f(t 2 cos(3πt + sin(πt + π 3 w π f(t e j3πt + e j3πt + j2
Homework 5 EE235, Summer 23 Solution. Fourier Series. Determine w and the non-zero Fourier series coefficients for the following functions: (a f(t 2 cos(3πt + sin(πt + π 3 w π f(t e j3πt + e j3πt + j2
ECE-700 Review. Phil Schniter. January 5, x c (t)e jωt dt, x[n]z n, Denoting a transform pair by x[n] X(z), some useful properties are
![ECE-700 Review. Phil Schniter. January 5, x c (t)e jωt dt, x[n]z n, Denoting a transform pair by x[n] X(z), some useful properties are ECE-700 Review. Phil Schniter. January 5, x c (t)e jωt dt, x[n]z n, Denoting a transform pair by x[n] X(z), some useful properties are](/thumbs/89/98815129.jpg) ECE-7 Review Phil Schniter January 5, 7 ransforms Using x c (t) to denote a continuous-time signal at time t R, Laplace ransform: X c (s) x c (t)e st dt, s C Continuous-ime Fourier ransform (CF): ote that:
ECE-7 Review Phil Schniter January 5, 7 ransforms Using x c (t) to denote a continuous-time signal at time t R, Laplace ransform: X c (s) x c (t)e st dt, s C Continuous-ime Fourier ransform (CF): ote that:
Stability. X(s) Y(s) = (s + 2) 2 (s 2) System has 2 poles: points where Y(s) -> at s = +2 and s = -2. Y(s) 8X(s) G 1 G 2
 Stability 8X(s) X(s) Y(s) = (s 2) 2 (s 2) System has 2 poles: points where Y(s) -> at s = 2 and s = -2 If all poles are in region where s < 0, system is stable in Fourier language s = jω G 0 - x3 x7 Y(s)
Stability 8X(s) X(s) Y(s) = (s 2) 2 (s 2) System has 2 poles: points where Y(s) -> at s = 2 and s = -2 If all poles are in region where s < 0, system is stable in Fourier language s = jω G 0 - x3 x7 Y(s)
4 The Continuous Time Fourier Transform
 96 4 The Continuous Time ourier Transform ourier (or frequency domain) analysis turns out to be a tool of even greater usefulness Extension of ourier series representation to aperiodic signals oundation
96 4 The Continuous Time ourier Transform ourier (or frequency domain) analysis turns out to be a tool of even greater usefulness Extension of ourier series representation to aperiodic signals oundation
Fourier Transform for Continuous Functions
 Fourier Transform for Continuous Functions Central goal: representing a signal by a set of orthogonal bases that are corresponding to frequencies or spectrum. Fourier series allows to find the spectrum
Fourier Transform for Continuous Functions Central goal: representing a signal by a set of orthogonal bases that are corresponding to frequencies or spectrum. Fourier series allows to find the spectrum
Continuous Time Signal Analysis: the Fourier Transform. Lathi Chapter 4
 Continuous Time Signal Analysis: the Fourier Transform Lathi Chapter 4 Topics Aperiodic signal representation by the Fourier integral (CTFT) Continuous-time Fourier transform Transforms of some useful
Continuous Time Signal Analysis: the Fourier Transform Lathi Chapter 4 Topics Aperiodic signal representation by the Fourier integral (CTFT) Continuous-time Fourier transform Transforms of some useful
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
Ch 4: The Continuous-Time Fourier Transform
 Ch 4: The Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Fourier Transform of x(t) Inverse Fourier Transform jt X ( j) x ( t ) e dt jt x ( t ) X ( j) e d 2 Ghulam Muhammad, King Saud University Continuous-time aperiodic
Ch 4: The Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Fourier Transform of x(t) Inverse Fourier Transform jt X ( j) x ( t ) e dt jt x ( t ) X ( j) e d 2 Ghulam Muhammad, King Saud University Continuous-time aperiodic
LINEAR SYSTEMS. J. Elder PSYC 6256 Principles of Neural Coding
 LINEAR SYSTEMS Linear Systems 2 Neural coding and cognitive neuroscience in general concerns input-output relationships. Inputs Light intensity Pre-synaptic action potentials Number of items in display
LINEAR SYSTEMS Linear Systems 2 Neural coding and cognitive neuroscience in general concerns input-output relationships. Inputs Light intensity Pre-synaptic action potentials Number of items in display
Mathematical Foundations of Signal Processing
 Mathematical Foundations of Signal Processing Module 4: Continuous-Time Systems and Signals Benjamín Béjar Haro Mihailo Kolundžija Reza Parhizkar Adam Scholefield October 24, 2016 Continuous Time Signals
Mathematical Foundations of Signal Processing Module 4: Continuous-Time Systems and Signals Benjamín Béjar Haro Mihailo Kolundžija Reza Parhizkar Adam Scholefield October 24, 2016 Continuous Time Signals
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
Homework 7 Solution EE235, Spring Find the Fourier transform of the following signals using tables: te t u(t) h(t) = sin(2πt)e t u(t) (2)
 Homework 7 Solution EE35, Spring. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals using tables: (a) te t u(t) h(t) H(jω) te t u(t) ( + jω) (b) sin(πt)e t u(t) h(t) sin(πt)e t u(t) () h(t) ( ejπt e
Homework 7 Solution EE35, Spring. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals using tables: (a) te t u(t) h(t) H(jω) te t u(t) ( + jω) (b) sin(πt)e t u(t) h(t) sin(πt)e t u(t) () h(t) ( ejπt e
EE Homework 13 - Solutions
 EE3054 - Homework 3 - Solutions. (a) The Laplace transform of e t u(t) is s+. The pole of the Laplace transform is at which lies in the left half plane. Hence, the Fourier transform is simply the Laplace
EE3054 - Homework 3 - Solutions. (a) The Laplace transform of e t u(t) is s+. The pole of the Laplace transform is at which lies in the left half plane. Hence, the Fourier transform is simply the Laplace
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 10 Fourier Transform
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 10 Fourier ransform What We Did Last ime Reflection of mechanical waves Similar to reflection of electromagnetic waves Mechanical impedance is defined by For transverse/longitudinal
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 10 Fourier ransform What We Did Last ime Reflection of mechanical waves Similar to reflection of electromagnetic waves Mechanical impedance is defined by For transverse/longitudinal
The Discrete-Time Fourier
 Chapter 3 The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 3-1-1 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Definition The CTFT of
Chapter 3 The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 3-1-1 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Definition The CTFT of
EE 3054: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal.
 EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to HT 2011 For hints and answers visit dwm/courses/2tf
 Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis
 IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis Handout 5: Sampling Theory S Godsill Signal Processing and Communications Group, Engineering Department, Cambridge, UK Lent 2015 1 / 85 Sampling and Aliasing All of
IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis Handout 5: Sampling Theory S Godsill Signal Processing and Communications Group, Engineering Department, Cambridge, UK Lent 2015 1 / 85 Sampling and Aliasing All of
Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited
 Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018 Frame # 1 Slide # 1 A. Antoniou
Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018 Frame # 1 Slide # 1 A. Antoniou
Line Spectra and their Applications
 In [ ]: cd matlab pwd Line Spectra and their Applications Scope and Background Reading This session concludes our introduction to Fourier Series. Last time (http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/cpjobling/eg-47-
In [ ]: cd matlab pwd Line Spectra and their Applications Scope and Background Reading This session concludes our introduction to Fourier Series. Last time (http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/cpjobling/eg-47-
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II
 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
Now identified: Noise sources Amplifier components and basic design How to achieve best signal to noise?
 Signal processing Now identified: Noise sources Amplifier components and basic design How to achieve best signal to noise? Possible constraints power consumption ability to provide power & extract heat,
Signal processing Now identified: Noise sources Amplifier components and basic design How to achieve best signal to noise? Possible constraints power consumption ability to provide power & extract heat,
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4
 Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
Wavenumber-Frequency Space
 Wavenumber-Frequency Space ECE 6279: Spatial Array Processing Spring 2011 Lecture 3 Prof. Aaron D. Lanterman School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology AL: 404-385-2548
Wavenumber-Frequency Space ECE 6279: Spatial Array Processing Spring 2011 Lecture 3 Prof. Aaron D. Lanterman School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology AL: 404-385-2548
Spectral Analysis of Random Processes
 Spectral Analysis of Random Processes Spectral Analysis of Random Processes Generally, all properties of a random process should be defined by averaging over the ensemble of realizations. Generally, all
Spectral Analysis of Random Processes Spectral Analysis of Random Processes Generally, all properties of a random process should be defined by averaging over the ensemble of realizations. Generally, all
Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) 1 Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) The DTFT is the Fourier transform of choice for analyzing infinite-length signals and systems Useful for conceptual, pencil-and-paper
Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) 1 Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) The DTFT is the Fourier transform of choice for analyzing infinite-length signals and systems Useful for conceptual, pencil-and-paper
A system that is both linear and time-invariant is called linear time-invariant (LTI).
 The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE111 Signal Processing & Systems Analysis Lecture Notes: Time, Frequency & Transform Domains February 28, 2012 Signals & Systems Signals are mapped
The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE111 Signal Processing & Systems Analysis Lecture Notes: Time, Frequency & Transform Domains February 28, 2012 Signals & Systems Signals are mapped
Ver 3808 E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms (2014) E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms. Problem Sheet 1 (Lecture 1)
 Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Fourier Series and Integrals
 Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Continuous-Time Fourier Transform
 Signals and Systems Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Chang-Su Kim continuous time discrete time periodic (series) CTFS DTFS aperiodic (transform) CTFT DTFT Lowpass Filtering Blurring or Smoothing Original
Signals and Systems Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Chang-Su Kim continuous time discrete time periodic (series) CTFS DTFS aperiodic (transform) CTFT DTFT Lowpass Filtering Blurring or Smoothing Original
ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING CHAPTER 3 : LINEAR SYSTEM RESPONSE (GENERAL CASE)
 3. Linear System Response (general case) 3. INTRODUCTION In chapter 2, we determined that : a) If the system is linear (or operate in a linear domain) b) If the input signal can be assumed as periodic
3. Linear System Response (general case) 3. INTRODUCTION In chapter 2, we determined that : a) If the system is linear (or operate in a linear domain) b) If the input signal can be assumed as periodic
1.1 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS USED IN SIGNAL PROCESSING. δ(t) = for t = 0, = 0 for t 0. δ(t)dt = 1. (1.1)
 SIGNAL THEORY AND ANALYSIS A signal, in general, refers to an electrical waveform whose amplitude varies with time. Signals can be fully described in either the time or frequency domain. This chapter discusses
SIGNAL THEORY AND ANALYSIS A signal, in general, refers to an electrical waveform whose amplitude varies with time. Signals can be fully described in either the time or frequency domain. This chapter discusses
Homework 6 EE235, Spring 2011
 Homework 6 EE235, Spring 211 1. Fourier Series. Determine w and the non-zero Fourier series coefficients for the following functions: (a 2 cos(3πt + sin(1πt + π 3 w π e j3πt + e j3πt + 1 j2 [ej(1πt+ π
Homework 6 EE235, Spring 211 1. Fourier Series. Determine w and the non-zero Fourier series coefficients for the following functions: (a 2 cos(3πt + sin(1πt + π 3 w π e j3πt + e j3πt + 1 j2 [ej(1πt+ π
The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002.
 The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 505.460 Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002 Final exam Name: You are allowed to use: 1. Table 3.1 (page 206) & Table
The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 505.460 Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002 Final exam Name: You are allowed to use: 1. Table 3.1 (page 206) & Table
The Continuous-time Fourier
 The Continuous-time Fourier Transform Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline Representation of Aperiodic signals:
The Continuous-time Fourier Transform Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline Representation of Aperiodic signals:
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 11 Dispersion
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 11 Dispersion What We Did Last Time Defined Fourier transform f (t) = F(ω)e iωt dω F(ω) = 1 2π f(t) and F(w) represent a function in time and frequency domains Analyzed
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 11 Dispersion What We Did Last Time Defined Fourier transform f (t) = F(ω)e iωt dω F(ω) = 1 2π f(t) and F(w) represent a function in time and frequency domains Analyzed
2 Frequency-Domain Analysis
 2 requency-domain Analysis Electrical engineers live in the two worlds, so to speak, of time and frequency. requency-domain analysis is an extremely valuable tool to the communications engineer, more so
2 requency-domain Analysis Electrical engineers live in the two worlds, so to speak, of time and frequency. requency-domain analysis is an extremely valuable tool to the communications engineer, more so
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series
 Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Lecture 7 ELE 301: Signals and Systems
 Lecture 7 ELE 30: Signals and Systems Prof. Paul Cuff Princeton University Fall 20-2 Cuff (Lecture 7) ELE 30: Signals and Systems Fall 20-2 / 22 Introduction to Fourier Transforms Fourier transform as
Lecture 7 ELE 30: Signals and Systems Prof. Paul Cuff Princeton University Fall 20-2 Cuff (Lecture 7) ELE 30: Signals and Systems Fall 20-2 / 22 Introduction to Fourier Transforms Fourier transform as
Poularikas A. D. Fourier Transform The Handbook of Formulas and Tables for Signal Processing. Ed. Alexander D. Poularikas Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC,
 Poularikas A. D. Fourier Transform The Handbook of Formulas and Tables for Signal Processing. Ed. Alexander D. Poularikas Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 999 3 Fourier Transform 3. One-Dimensional Fourier Transform
Poularikas A. D. Fourier Transform The Handbook of Formulas and Tables for Signal Processing. Ed. Alexander D. Poularikas Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 999 3 Fourier Transform 3. One-Dimensional Fourier Transform
MEDE2500 Tutorial Nov-7
 (updated 2016-Nov-4,7:40pm) MEDE2500 (2016-2017) Tutorial 3 MEDE2500 Tutorial 3 2016-Nov-7 Content 1. The Dirac Delta Function, singularity functions, even and odd functions 2. The sampling process and
(updated 2016-Nov-4,7:40pm) MEDE2500 (2016-2017) Tutorial 3 MEDE2500 Tutorial 3 2016-Nov-7 Content 1. The Dirac Delta Function, singularity functions, even and odd functions 2. The sampling process and
7. Find the Fourier transform of f (t)=2 cos(2π t)[u (t) u(t 1)]. 8. (a) Show that a periodic signal with exponential Fourier series f (t)= δ (ω nω 0
![7. Find the Fourier transform of f (t)=2 cos(2π t)[u (t) u(t 1)]. 8. (a) Show that a periodic signal with exponential Fourier series f (t)= δ (ω nω 0 7. Find the Fourier transform of f (t)=2 cos(2π t)[u (t) u(t 1)]. 8. (a) Show that a periodic signal with exponential Fourier series f (t)= δ (ω nω 0](/thumbs/96/126850209.jpg) Fourier Transform Problems 1. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals: a) f 1 (t )=e 3 t sin(10 t)u (t) b) f 1 (t )=e 4 t cos(10 t)u (t) 2. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals:
Fourier Transform Problems 1. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals: a) f 1 (t )=e 3 t sin(10 t)u (t) b) f 1 (t )=e 4 t cos(10 t)u (t) 2. Find the Fourier transform of the following signals:
Review: Continuous Fourier Transform
 Review: Continuous Fourier Transform Review: convolution x t h t = x τ h(t τ)dτ Convolution in time domain Derivation Convolution Property Interchange the order of integrals Let Convolution Property By
Review: Continuous Fourier Transform Review: convolution x t h t = x τ h(t τ)dτ Convolution in time domain Derivation Convolution Property Interchange the order of integrals Let Convolution Property By
Sinc Functions. Continuous-Time Rectangular Pulse
 Sinc Functions The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE114 Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes: Sinc Functions and Sampling Theory October 7, 2011 A rectangular pulse in time/frequency
Sinc Functions The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE114 Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes: Sinc Functions and Sampling Theory October 7, 2011 A rectangular pulse in time/frequency
Assignment 4 Solutions Continuous-Time Fourier Transform
 Assignment 4 Solutions Continuous-Time Fourier Transform ECE 3 Signals and Systems II Version 1.01 Spring 006 1. Properties of complex numbers. Let c 1 α 1 + jβ 1 and c α + jβ be two complex numbers. a.
Assignment 4 Solutions Continuous-Time Fourier Transform ECE 3 Signals and Systems II Version 1.01 Spring 006 1. Properties of complex numbers. Let c 1 α 1 + jβ 1 and c α + jβ be two complex numbers. a.
Signals and Systems: Part 2
 Signals and Systems: Part 2 The Fourier transform in 2πf Some important Fourier transforms Some important Fourier transform theorems Convolution and Modulation Ideal filters Fourier transform definitions
Signals and Systems: Part 2 The Fourier transform in 2πf Some important Fourier transforms Some important Fourier transform theorems Convolution and Modulation Ideal filters Fourier transform definitions
Frequency Domain Representations of Sampled and Wrapped Signals
 Frequency Domain Representations of Sampled and Wrapped Signals Peter Kabal Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering McGill University Montreal, Canada v1.5 March 2011 c 2011 Peter Kabal 2011/03/11
Frequency Domain Representations of Sampled and Wrapped Signals Peter Kabal Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering McGill University Montreal, Canada v1.5 March 2011 c 2011 Peter Kabal 2011/03/11
26. The Fourier Transform in optics
 26. The Fourier Transform in optics What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic waves The spectrum of a light wave Fourier transform of an exponential The Dirac delta function The Fourier transform of e
26. The Fourier Transform in optics What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic waves The spectrum of a light wave Fourier transform of an exponential The Dirac delta function The Fourier transform of e
Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results
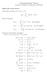 Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Lecture 34. Fourier Transforms
 Lecture 34 Fourier Transforms In this section, we introduce the Fourier transform, a method of analyzing the frequency content of functions that are no longer τ-periodic, but which are defined over the
Lecture 34 Fourier Transforms In this section, we introduce the Fourier transform, a method of analyzing the frequency content of functions that are no longer τ-periodic, but which are defined over the
Definition of Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Definition of Discrete-Time ourier Transform (DTT) {x[n]} = X(e jω ) + n= {X(e jω )} = x[n] x[n]e jωn Why use the above awkward notation for the transform? X(e jω )e jωn dω Answer: It is consistent with
Definition of Discrete-Time ourier Transform (DTT) {x[n]} = X(e jω ) + n= {X(e jω )} = x[n] x[n]e jωn Why use the above awkward notation for the transform? X(e jω )e jωn dω Answer: It is consistent with
Introduction to Fourier Transforms. Lecture 7 ELE 301: Signals and Systems. Fourier Series. Rect Example
 Introduction to Fourier ransforms Lecture 7 ELE 3: Signals and Systems Fourier transform as a limit of the Fourier series Inverse Fourier transform: he Fourier integral theorem Prof. Paul Cuff Princeton
Introduction to Fourier ransforms Lecture 7 ELE 3: Signals and Systems Fourier transform as a limit of the Fourier series Inverse Fourier transform: he Fourier integral theorem Prof. Paul Cuff Princeton
Fourier series. Complex Fourier series. Positive and negative frequencies. Fourier series demonstration. Notes. Notes. Notes.
 Fourier series Fourier series of a periodic function f (t) with period T and corresponding angular frequency ω /T : f (t) a 0 + (a n cos(nωt) + b n sin(nωt)), n1 Fourier series is a linear sum of cosine
Fourier series Fourier series of a periodic function f (t) with period T and corresponding angular frequency ω /T : f (t) a 0 + (a n cos(nωt) + b n sin(nωt)), n1 Fourier series is a linear sum of cosine
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems
 Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes
 RANDOM'PROCESSES'AND'TIME'SERIES'ANALYSIS.'PART'II:'RANDOM'PROCESSES' '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''Problem'Sheets' Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes 1. Give
RANDOM'PROCESSES'AND'TIME'SERIES'ANALYSIS.'PART'II:'RANDOM'PROCESSES' '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''Problem'Sheets' Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes 1. Give
1 Signals and systems
 978--52-5688-4 - Introduction to Orthogonal Transforms: With Applications in Data Processing and Analysis Signals and systems In the first two chapters we will consider some basic concepts and ideas as
978--52-5688-4 - Introduction to Orthogonal Transforms: With Applications in Data Processing and Analysis Signals and systems In the first two chapters we will consider some basic concepts and ideas as
Signals. Time-domain & Frequency-domain representations. Signals & Noises YCJ
 Signals Deterministic signals & Stochastic (random) signals Continuous time signals & Discrete Time signals Analog signals & Digital signals Energy signals & Power signals Periodic signals & Non-periodic
Signals Deterministic signals & Stochastic (random) signals Continuous time signals & Discrete Time signals Analog signals & Digital signals Energy signals & Power signals Periodic signals & Non-periodic
d n 1 f dt n 1 + K+ a 0f = C cos(ωt + φ)
 Tutorial TUTOR: THE PHASOR TRANSFORM All voltages currents in linear circuits with sinusoidal sources are described by constant-coefficient linear differential equations of the form (1) a n d n f dt n
Tutorial TUTOR: THE PHASOR TRANSFORM All voltages currents in linear circuits with sinusoidal sources are described by constant-coefficient linear differential equations of the form (1) a n d n f dt n
ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 5 Fourier Transform
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 5 Fourier Transform Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Introduction Fourier Transform Properties of Fourier
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 5 Fourier Transform Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Introduction Fourier Transform Properties of Fourier
Once again a practical exposition, not fully mathematically rigorous Definition F(s) =
 Laplace transforms Once again a practical exposition, not fully mathematically rigorous Definition F(s) = 0 f(t).e -st.dt NB lower limit of integral = 0 unilateral LT more rigorously F(s) = 0 f(t).e -st.dt
Laplace transforms Once again a practical exposition, not fully mathematically rigorous Definition F(s) = 0 f(t).e -st.dt NB lower limit of integral = 0 unilateral LT more rigorously F(s) = 0 f(t).e -st.dt
ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, Name:
 ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, 205 Name:. The quiz is closed book, except for one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes. 2. Turn off
ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, 205 Name:. The quiz is closed book, except for one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes. 2. Turn off
The structure of laser pulses
 1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
Fourier Series. Spectral Analysis of Periodic Signals
 Fourier Series. Spectral Analysis of Periodic Signals he response of continuous-time linear invariant systems to the complex exponential with unitary magnitude response of a continuous-time LI system at
Fourier Series. Spectral Analysis of Periodic Signals he response of continuous-time linear invariant systems to the complex exponential with unitary magnitude response of a continuous-time LI system at
Review of Discrete-Time System
 Review of Discrete-Time System Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Acknowledgment: ENEE630 slides were based on class notes developed by Profs. K.J. Ray Liu and Min Wu.
Review of Discrete-Time System Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Acknowledgment: ENEE630 slides were based on class notes developed by Profs. K.J. Ray Liu and Min Wu.
e iωt dt and explained why δ(ω) = 0 for ω 0 but δ(0) =. A crucial property of the delta function, however, is that
 Phys 531 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 14, 1/11). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so you ll want to refer
Phys 531 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 14, 1/11). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so you ll want to refer
Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is
![Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is](/thumbs/89/98498368.jpg) Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section 5. 3 The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is X ( e jω) = n= x[n]e jωn x[n] can be reconstructed from its
Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section 5. 3 The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is X ( e jω) = n= x[n]e jωn x[n] can be reconstructed from its
Functions of a Complex Variable (S1) Lecture 11. VII. Integral Transforms. Integral transforms from application of complex calculus
 Functions of a Complex Variable (S1) Lecture 11 VII. Integral Transforms An introduction to Fourier and Laplace transformations Integral transforms from application of complex calculus Properties of Fourier
Functions of a Complex Variable (S1) Lecture 11 VII. Integral Transforms An introduction to Fourier and Laplace transformations Integral transforms from application of complex calculus Properties of Fourier
Summary of Fourier Transform Properties
 Summary of Fourier ransform Properties Frank R. Kschischang he Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of oronto January 7, 207 Definition and Some echnicalities
Summary of Fourier ransform Properties Frank R. Kschischang he Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of oronto January 7, 207 Definition and Some echnicalities
Fourier Series. Fourier Transform
 Math Methods I Lia Vas Fourier Series. Fourier ransform Fourier Series. Recall that a function differentiable any number of times at x = a can be represented as a power series n= a n (x a) n where the
Math Methods I Lia Vas Fourier Series. Fourier ransform Fourier Series. Recall that a function differentiable any number of times at x = a can be represented as a power series n= a n (x a) n where the
ENGIN 211, Engineering Math. Laplace Transforms
 ENGIN 211, Engineering Math Laplace Transforms 1 Why Laplace Transform? Laplace transform converts a function in the time domain to its frequency domain. It is a powerful, systematic method in solving
ENGIN 211, Engineering Math Laplace Transforms 1 Why Laplace Transform? Laplace transform converts a function in the time domain to its frequency domain. It is a powerful, systematic method in solving
Notes 07 largely plagiarized by %khc
 Notes 07 largely plagiarized by %khc Warning This set of notes covers the Fourier transform. However, i probably won t talk about everything here in section; instead i will highlight important properties
Notes 07 largely plagiarized by %khc Warning This set of notes covers the Fourier transform. However, i probably won t talk about everything here in section; instead i will highlight important properties
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C1 HANDOUT 6. Dr Anil Kokaram Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept.
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6. Dr Anil Kokaram Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. anil.kokaram@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ sigmedia FOURIER ANALYSIS Have seen how the behaviour of systems
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6. Dr Anil Kokaram Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. anil.kokaram@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ sigmedia FOURIER ANALYSIS Have seen how the behaviour of systems
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.011: Introduction to Communication, Control and Signal Processing QUIZ 1, March 16, 2010 ANSWER BOOKLET
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.011: Introduction to Communication, Control and Signal Processing QUIZ 1, March 16, 2010 ANSWER BOOKLET
pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system or elsewhere, power supply fluctuations ground currents
 Noise What is NOISE? A definition: Any unwanted signal obscuring signal to be observed two main origins EXTRINSIC NOISE examples... pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system
Noise What is NOISE? A definition: Any unwanted signal obscuring signal to be observed two main origins EXTRINSIC NOISE examples... pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system
ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS. Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I 1/52
 1/52 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I Linear Time Invariant Systems A general LTI system may be described by the linear constant coefficient differential equation: a n d n
1/52 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I Linear Time Invariant Systems A general LTI system may be described by the linear constant coefficient differential equation: a n d n
LECTURE 12 Sections Introduction to the Fourier series of periodic signals
 Signals and Systems I Wednesday, February 11, 29 LECURE 12 Sections 3.1-3.3 Introduction to the Fourier series of periodic signals Chapter 3: Fourier Series of periodic signals 3. Introduction 3.1 Historical
Signals and Systems I Wednesday, February 11, 29 LECURE 12 Sections 3.1-3.3 Introduction to the Fourier series of periodic signals Chapter 3: Fourier Series of periodic signals 3. Introduction 3.1 Historical
Representation of Signals and Systems. Lecturer: David Shiung
 Representation of Signals and Systems Lecturer: David Shiung 1 Abstract (1/2) Fourier analysis Properties of the Fourier transform Dirac delta function Fourier transform of periodic signals Fourier-transform
Representation of Signals and Systems Lecturer: David Shiung 1 Abstract (1/2) Fourier analysis Properties of the Fourier transform Dirac delta function Fourier transform of periodic signals Fourier-transform
Ver Chap Lecture 15- ECE 240a. Q-Switching. Mode Locking. ECE 240a Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture Q-Switch Discussion
 ing Ver Chap. 9.3 Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 1 ing ing (Cavity Dumping) 1 Turn-off cavity - prevent lasing 2 Pump lots of energy into upper state - use pulsed pump 3 Turn cavity back on - all the energy
ing Ver Chap. 9.3 Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 1 ing ing (Cavity Dumping) 1 Turn-off cavity - prevent lasing 2 Pump lots of energy into upper state - use pulsed pump 3 Turn cavity back on - all the energy
Fourier Series Example
 Fourier Series Example Let us compute the Fourier series for the function on the interval [ π,π]. f(x) = x f is an odd function, so the a n are zero, and thus the Fourier series will be of the form f(x)
Fourier Series Example Let us compute the Fourier series for the function on the interval [ π,π]. f(x) = x f is an odd function, so the a n are zero, and thus the Fourier series will be of the form f(x)
6 The Fourier transform
 6 The Fourier transform In this presentation we assume that the reader is already familiar with the Fourier transform. This means that we will not make a complete overview of its properties and applications.
6 The Fourier transform In this presentation we assume that the reader is already familiar with the Fourier transform. This means that we will not make a complete overview of its properties and applications.
EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10
 EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10 Class Contents Signals and Systems Continuous-Time and Discrete-Time Time-Domain and Frequency Domain (all these dimensions are tightly coupled) SIGNALS SYSTEMS
EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10 Class Contents Signals and Systems Continuous-Time and Discrete-Time Time-Domain and Frequency Domain (all these dimensions are tightly coupled) SIGNALS SYSTEMS
Lecture 4: Fourier Transforms.
 1 Definition. Lecture 4: Fourier Transforms. We now come to Fourier transforms, which we give in the form of a definition. First we define the spaces L 1 () and L 2 (). Definition 1.1 The space L 1 ()
1 Definition. Lecture 4: Fourier Transforms. We now come to Fourier transforms, which we give in the form of a definition. First we define the spaces L 1 () and L 2 (). Definition 1.1 The space L 1 ()
Fundamentals of the Discrete Fourier Transform
 Seminar presentation at the Politecnico di Milano, Como, November 12, 2012 Fundamentals of the Discrete Fourier Transform Michael G. Sideris sideris@ucalgary.ca Department of Geomatics Engineering University
Seminar presentation at the Politecnico di Milano, Como, November 12, 2012 Fundamentals of the Discrete Fourier Transform Michael G. Sideris sideris@ucalgary.ca Department of Geomatics Engineering University
Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis
 D1 APPENDIX D Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis Consider a network with input x(t) and output y(t) as shown in Figure D-1. If an input x 1 (t) produces an output y 1 (t), and an input x
D1 APPENDIX D Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis Consider a network with input x(t) and output y(t) as shown in Figure D-1. If an input x 1 (t) produces an output y 1 (t), and an input x
