Ver Chap Lecture 15- ECE 240a. Q-Switching. Mode Locking. ECE 240a Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture Q-Switch Discussion
|
|
|
- Chester Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ing Ver Chap. 9.3 Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 1
2 ing ing (Cavity Dumping) 1 Turn-off cavity - prevent lasing 2 Pump lots of energy into upper state - use pulsed pump 3 Turn cavity back on - all the energy in the upper state depleted in a few round trips 1 If single-(round-trip) pass gain is 5 then after 10 round-trips AC response Step Response Gain switching d l g Gain medium l s Shutter (Q-switch) Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 2
3 Geometry Lecture 15 ing Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 3
4 Analysis ing Total gain in one round trip Total loss G = Exp[2 N(t)σl g }{{} ] line integrated gain = e 2g(t) e 2g th. = Πj R j Π i T i }{{}} e 2αsls {{} mirrror and transmission losss scattering loss The loss term defines the threshold gain g th Photon lifetime (from before) τ p = = τ RT 1 S τ RT 1 e 2g th Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 4
5 Rate of Net Photon Gain ing Define N p as the net change in the photon number during one round trip. Rate of change is dn p(t) dt = = = ( ) L G 1 N p(t) τ RT ( e 2(g(t) g th ) ) 1 N p(t) τ RT ( e 2(g(t) g th ) ) 1 Np(t) 1 e 2g th τ p Assume net increase per round-trip is small and expand e x 1 + x where dn p(t) dt = Np(t) τ p ( ) n(t) 1 n th n(t). = (N 2 (t) N 1 (t)) Al g is the total number of excited states (atoms) in the cavity that interact with the mode cross-sectional area A. Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 5
6 ing If ratio n(t) n th If ratio n(t) n th > 1, then there is a net gain in the photon number N p(t) < 1, then the net photon number decreases. Now for every photon that is added, there is a decrease in the upper state and an increase in the lower state. Therefore, the rate of change of the total number of excited states n(t) that can interact is given by or n(t) dt = }{{} 2 n(t) N p(t) n th τ p lose on upper/gain on lower dn(t) dt = 2 n(t) n th N p(t) τ p Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 6
7 Governing Equations ing In order to solve, normalize the time by the photon lifetime so that T = t/τ p. The two governing equations become dn p(t ) dt = N p(t ) ( ) n(t ) 1 n th dn(t ) dt = 2 n(t ) n th N p(t) These are a set of nonlinear coupled first order equations. Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 7
8 ing Occurs when all of the modes add in phase. Look at spectrum Spectrum may be written as S(ω ω 0 ) = g 1 (ω ω 0 ) L(ω ω 0 l f) l= For simplicity assume g 1 (ω) is a gaussian g 1 (f) = e ω2 /2σ 2 and L(ω) is a Lorentzian of the form L(ω) = 1 ω 2 + B 2 Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 8
9 Plot of Spectrum ing S(f f0) f f 0 Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 9
10 Rewrite Spectrum ing Now re-write l= L(ω ω 0 l f) as a convolution of the Lorentzian and an impulse train so that l= L(ω ω 0 l f) = L(ω ω 0 ) S(ω ω 0 ) = g 1 (ω ω 0 ) L(ω ω 0 ) l= l= δ(ω l ω) δ(ω l ω) Now take the Fourier transform to determine the ( { }) F T 1 {L(ω ω 0 )} F T 1 δ(ω ω 0 i ω) Γ(τ) = F T 1 {g 1 (ω ω 0 )} i= Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 10
11 Time Response ing First term is the Fourier transform gaussian which is a gaussian F T 1 {g 1 (ω ω 0 )} = σe 2π2 σ 2 τ 2 The second term is the transform Lorentzian which is a double-sided exponential F T 1 {L(ω ω 0 )} = B exp [ τ ] Final term is the transform n impulse train which is another impulse train δ(ω i ω) 1 δ(t i ω ω ) i= i= Put it all together 2Bπ 3/2 [ Γ(τ) = Bπ exp 2π i ] [ ( exp 2π 2 σ 2 τ i ) 2 ] ν ν ν i= Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 11
12 Plot ing Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 12
13 Time Response as Sum of Phasors ing Write the field in time as a sum of complex amplitudes (phasors) e(t) = (N 1)/2 (N 1)/2 E n(t) exp [j(ω 0 + nω c)t + φ n(t)] where N is total number of modes mplitude E n and phase φ n Now sum assuming equal amplitudes ( similar to cavity studied before) [ ] e(t) = E 0 e jω0t sin(nωct/2) sin(ω ct/2) Intensity is given by the square [ ] 2 I(t) = e(t) 2 = E2 0 sin(nωct/2) 2η 0 η 0 sin(ω ct/2) Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 13
14 ing Peak is N 2 times the intensity in one mode Therefore if we assume each mode contributes equally then P peak = N P ave Now if the modes have unequal contributions, estimate the relationship between the peak and the average power using equal area argument P peak t pulse = P aveτ RT or t pulse = τrt N where N is the number of modes that are phase-locked Now N can be estimated by linewidth of gain profile so that or N = ν (c/2d) = ντrt t pulse τrt N 1 ν Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 14
15 ing Active mode locking - force the phase relationship by use modulator allows the mode-locking homogeneously broadened medium Passive mode locking - use a saturable absorber that only passes a high amplitude field. Lasers - Fall 2017 Lecture 15 15
Pulsed Lasers Revised: 2/12/14 15: , Henry Zmuda Set 5a Pulsed Lasers
 Pulsed Lasers Revised: 2/12/14 15:27 2014, Henry Zmuda Set 5a Pulsed Lasers 1 Laser Dynamics Puled Lasers More efficient pulsing schemes are based on turning the laser itself on and off by means of an
Pulsed Lasers Revised: 2/12/14 15:27 2014, Henry Zmuda Set 5a Pulsed Lasers 1 Laser Dynamics Puled Lasers More efficient pulsing schemes are based on turning the laser itself on and off by means of an
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses II
 The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses II The phase condition Trains of pulses the Shah function Laser modes and mode locking 1 There are 3 conditions for steady-state laser operation. Amplitude condition
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses II The phase condition Trains of pulses the Shah function Laser modes and mode locking 1 There are 3 conditions for steady-state laser operation. Amplitude condition
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II
 27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
Photon Physics. Week 4 26/02/2013
 Photon Physics Week 4 6//13 1 Classical atom-field interaction Lorentz oscillator: Classical electron oscillator with frequency ω and damping constant γ Eqn of motion: Final result: Classical atom-field
Photon Physics Week 4 6//13 1 Classical atom-field interaction Lorentz oscillator: Classical electron oscillator with frequency ω and damping constant γ Eqn of motion: Final result: Classical atom-field
Frequency- and Time-Domain Spectroscopy
 Frequency- and Time-Domain Spectroscopy We just showed that you could characterize a system by taking an absorption spectrum. We select a frequency component using a grating or prism, irradiate the sample,
Frequency- and Time-Domain Spectroscopy We just showed that you could characterize a system by taking an absorption spectrum. We select a frequency component using a grating or prism, irradiate the sample,
S. Blair February 15,
 S Blair February 15, 2012 66 32 Laser Diodes A semiconductor laser diode is basically an LED structure with mirrors for optical feedback This feedback causes photons to retrace their path back through
S Blair February 15, 2012 66 32 Laser Diodes A semiconductor laser diode is basically an LED structure with mirrors for optical feedback This feedback causes photons to retrace their path back through
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses
 The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The importance of bandwidth More than just a light bulb Two, three, and four levels rate equations Gain and saturation But first: the progress has been amazing!
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The importance of bandwidth More than just a light bulb Two, three, and four levels rate equations Gain and saturation But first: the progress has been amazing!
ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS. Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I 1/52
 1/52 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I Linear Time Invariant Systems A general LTI system may be described by the linear constant coefficient differential equation: a n d n
1/52 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 2 Laplace Transform I Linear Time Invariant Systems A general LTI system may be described by the linear constant coefficient differential equation: a n d n
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics. Chapter 5. The Laser Amplifier
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 5. The Laser Amplifier 1 The laser amplifier 5.1 Amplifier Gain 5.2 Amplifier Bandwidth 5.3 Amplifier Phase-Shift 5.4 Amplifier Power source and rate equations
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 5. The Laser Amplifier 1 The laser amplifier 5.1 Amplifier Gain 5.2 Amplifier Bandwidth 5.3 Amplifier Phase-Shift 5.4 Amplifier Power source and rate equations
LASERS. Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion)
 L- LASERS Representative applications: Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion) Oscillators: Blasting: Energy States: Hydrogen atom Frequency/distance reference, local oscillators,
L- LASERS Representative applications: Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion) Oscillators: Blasting: Energy States: Hydrogen atom Frequency/distance reference, local oscillators,
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS Theory of the Laser Oscillation
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS407 6. Theory of the Laser Oscillation 1 I. Laser oscillator: Overview Laser is an optical oscillator. Resonant optical amplifier whose output is fed back into its input
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS407 6. Theory of the Laser Oscillation 1 I. Laser oscillator: Overview Laser is an optical oscillator. Resonant optical amplifier whose output is fed back into its input
γ c = rl = lt R ~ e (g l)t/t R Intensität 0 e γ c t Zeit, ns
 There is however one main difference in this chapter compared to many other chapters. All loss and gain coefficients are given for the intensity and not the amplitude and are therefore a factor of 2 larger!
There is however one main difference in this chapter compared to many other chapters. All loss and gain coefficients are given for the intensity and not the amplitude and are therefore a factor of 2 larger!
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9
 Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
EE 3054: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal.
 EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
The structure of laser pulses
 1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
Signal and systems. Linear Systems. Luigi Palopoli. Signal and systems p. 1/5
 Signal and systems p. 1/5 Signal and systems Linear Systems Luigi Palopoli palopoli@dit.unitn.it Wrap-Up Signal and systems p. 2/5 Signal and systems p. 3/5 Fourier Series We have see that is a signal
Signal and systems p. 1/5 Signal and systems Linear Systems Luigi Palopoli palopoli@dit.unitn.it Wrap-Up Signal and systems p. 2/5 Signal and systems p. 3/5 Fourier Series We have see that is a signal
Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 2
 Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 06... Changhee Lee School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Seoul National Univ. chlee7@snu.ac.kr /9 9. Stimulated emission and thermal radiation The
Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 06... Changhee Lee School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Seoul National Univ. chlee7@snu.ac.kr /9 9. Stimulated emission and thermal radiation The
Lecture 9. PMTs and Laser Noise. Lecture 9. Photon Counting. Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs) Laser Phase Noise. Relative Intensity
 s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers. Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 2015
 MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 05 Note: some problems are taken or adapted from Fundamentals of Photonics, in which case the corresponding number is
MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 05 Note: some problems are taken or adapted from Fundamentals of Photonics, in which case the corresponding number is
Photon Physics. Week 5 5/03/2013
 Photon Physics Week 5 5/3/213 1 Rate equations including pumping dn 2 = R 2 N * σ 21 ( ω L ω ) I L N 2 R 2 2 dn 1 = R 1 + N * σ 21 ( ω L ω ) I L N 1 + N 2 A 21 ss solution: dn 2 = dn 1 = N 2 = R 2 N *
Photon Physics Week 5 5/3/213 1 Rate equations including pumping dn 2 = R 2 N * σ 21 ( ω L ω ) I L N 2 R 2 2 dn 1 = R 1 + N * σ 21 ( ω L ω ) I L N 1 + N 2 A 21 ss solution: dn 2 = dn 1 = N 2 = R 2 N *
Lecture 10. Lidar Effective Cross-Section vs. Convolution
 Lecture 10. Lidar Effective Cross-Section vs. Convolution q Introduction q Convolution in Lineshape Determination -- Voigt Lineshape (Lorentzian Gaussian) q Effective Cross Section for Single Isotope --
Lecture 10. Lidar Effective Cross-Section vs. Convolution q Introduction q Convolution in Lineshape Determination -- Voigt Lineshape (Lorentzian Gaussian) q Effective Cross Section for Single Isotope --
All-Optical Delay with Large Dynamic Range Using Atomic Dispersion
 All-Optical Delay with Large Dynamic Range Using Atomic Dispersion M. R. Vanner, R. J. McLean, P. Hannaford and A. M. Akulshin Centre for Atom Optics and Ultrafast Spectroscopy February 2008 Motivation
All-Optical Delay with Large Dynamic Range Using Atomic Dispersion M. R. Vanner, R. J. McLean, P. Hannaford and A. M. Akulshin Centre for Atom Optics and Ultrafast Spectroscopy February 2008 Motivation
LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 2
 By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
Computer Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the Solid State Diode Pumped Nd 3+ :YAG Laser with Intracavity Saturable Absorber
 Copyright 2009 by YASHKIR CONSULTING LTD Computer Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the Solid State Diode Pumped Nd 3+ :YAG Laser with Intracavity Saturable Absorber Yuri Yashkir 1 Introduction The
Copyright 2009 by YASHKIR CONSULTING LTD Computer Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the Solid State Diode Pumped Nd 3+ :YAG Laser with Intracavity Saturable Absorber Yuri Yashkir 1 Introduction The
LIST OF TOPICS BASIC LASER PHYSICS. Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii
 ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
Paper B2: Radiation and Matter - Basic Laser Physics
 Paper B2: Radiation and Matter - Basic Laser Physics Dr Simon Hooker Michaelmas Term 2006 ii Contents 1 The Interaction of Radiation and Matter 1 1.1 Introduction.............................. 1 1.2 Radiation...............................
Paper B2: Radiation and Matter - Basic Laser Physics Dr Simon Hooker Michaelmas Term 2006 ii Contents 1 The Interaction of Radiation and Matter 1 1.1 Introduction.............................. 1 1.2 Radiation...............................
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II
 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results
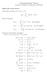 Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Last Lecture. Overview and Introduction. 1. Basic optics and spectroscopy. 2. Lasers. 3. Ultrafast lasers and nonlinear optics
 Last Lecture Overview and Introduction 1. Basic optics and spectroscopy. Lasers 3. Ultrafast lasers and nonlinear optics 4. Time-resolved spectroscopy techniques Jigang Wang, Feb, 009 Today 1. Spectroscopy
Last Lecture Overview and Introduction 1. Basic optics and spectroscopy. Lasers 3. Ultrafast lasers and nonlinear optics 4. Time-resolved spectroscopy techniques Jigang Wang, Feb, 009 Today 1. Spectroscopy
Signals & Systems. Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform. Alp Ertürk
 Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Quantum Electronics/Laser Physics Chapter 4 Line Shapes and Line Widths
 Quantum Electronics/Laser Physics Chapter 4 Line Shapes and Line Widths 4.1 The Natural Line Shape 4.2 Collisional Broadening 4.3 Doppler Broadening 4.4 Einstein Treatment of Stimulated Processes Width
Quantum Electronics/Laser Physics Chapter 4 Line Shapes and Line Widths 4.1 The Natural Line Shape 4.2 Collisional Broadening 4.3 Doppler Broadening 4.4 Einstein Treatment of Stimulated Processes Width
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19
 OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19 1. (a) Suppose you want to use a lens focus a Gaussian laser beam of wavelength λ in order to obtain a beam waist radius w
OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19 1. (a) Suppose you want to use a lens focus a Gaussian laser beam of wavelength λ in order to obtain a beam waist radius w
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
Laplace Transform Part 1: Introduction (I&N Chap 13)
 Laplace Transform Part 1: Introduction (I&N Chap 13) Definition of the L.T. L.T. of Singularity Functions L.T. Pairs Properties of the L.T. Inverse L.T. Convolution IVT(initial value theorem) & FVT (final
Laplace Transform Part 1: Introduction (I&N Chap 13) Definition of the L.T. L.T. of Singularity Functions L.T. Pairs Properties of the L.T. Inverse L.T. Convolution IVT(initial value theorem) & FVT (final
ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, Name:
 ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, 205 Name:. The quiz is closed book, except for one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes. 2. Turn off
ECE 3084 QUIZ 2 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY APRIL 2, 205 Name:. The quiz is closed book, except for one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes. 2. Turn off
EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10
 EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10 Class Contents Signals and Systems Continuous-Time and Discrete-Time Time-Domain and Frequency Domain (all these dimensions are tightly coupled) SIGNALS SYSTEMS
EE 224 Signals and Systems I Review 1/10 Class Contents Signals and Systems Continuous-Time and Discrete-Time Time-Domain and Frequency Domain (all these dimensions are tightly coupled) SIGNALS SYSTEMS
Homework 4. May An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt
 Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers
 ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers Dr. Lukas Chrostowski Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia January, 2013 Module Learning Objectives: Understand the importance of
ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers Dr. Lukas Chrostowski Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia January, 2013 Module Learning Objectives: Understand the importance of
MEDE2500 Tutorial Nov-7
 (updated 2016-Nov-4,7:40pm) MEDE2500 (2016-2017) Tutorial 3 MEDE2500 Tutorial 3 2016-Nov-7 Content 1. The Dirac Delta Function, singularity functions, even and odd functions 2. The sampling process and
(updated 2016-Nov-4,7:40pm) MEDE2500 (2016-2017) Tutorial 3 MEDE2500 Tutorial 3 2016-Nov-7 Content 1. The Dirac Delta Function, singularity functions, even and odd functions 2. The sampling process and
Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes
 RANDOM'PROCESSES'AND'TIME'SERIES'ANALYSIS.'PART'II:'RANDOM'PROCESSES' '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''Problem'Sheets' Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes 1. Give
RANDOM'PROCESSES'AND'TIME'SERIES'ANALYSIS.'PART'II:'RANDOM'PROCESSES' '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''Problem'Sheets' Problem Sheet 1 Examples of Random Processes 1. Give
Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers
 Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers In any atom or solid, the state of the electrons can change by: 1) Stimulated absorption - in the presence of a light wave, a photon is absorbed, the electron is
Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers In any atom or solid, the state of the electrons can change by: 1) Stimulated absorption - in the presence of a light wave, a photon is absorbed, the electron is
Paper Review. Special Topics in Optical Engineering II (15/1) Minkyu Kim. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985
 Paper Review IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985 Contents Semiconductor laser review High speed semiconductor laser Parasitic elements limitations Intermodulation products Intensity noise Large
Paper Review IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985 Contents Semiconductor laser review High speed semiconductor laser Parasitic elements limitations Intermodulation products Intensity noise Large
Spectral Broadening Mechanisms
 Spectral Broadening Mechanisms Lorentzian broadening (Homogeneous) Gaussian broadening (Inhomogeneous, Inertial) Doppler broadening (special case for gas phase) The Fourier Transform NC State University
Spectral Broadening Mechanisms Lorentzian broadening (Homogeneous) Gaussian broadening (Inhomogeneous, Inertial) Doppler broadening (special case for gas phase) The Fourier Transform NC State University
OPTI 511, Spring 2016 Problem Set 9 Prof. R. J. Jones
 OPTI 5, Spring 206 Problem Set 9 Prof. R. J. Jones Due Friday, April 29. Absorption and thermal distributions in a 2-level system Consider a collection of identical two-level atoms in thermal equilibrium.
OPTI 5, Spring 206 Problem Set 9 Prof. R. J. Jones Due Friday, April 29. Absorption and thermal distributions in a 2-level system Consider a collection of identical two-level atoms in thermal equilibrium.
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems
 Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
In Situ Imaging of Cold Atomic Gases
 In Situ Imaging of Cold Atomic Gases J. D. Crossno Abstract: In general, the complex atomic susceptibility, that dictates both the amplitude and phase modulation imparted by an atom on a probing monochromatic
In Situ Imaging of Cold Atomic Gases J. D. Crossno Abstract: In general, the complex atomic susceptibility, that dictates both the amplitude and phase modulation imparted by an atom on a probing monochromatic
Lecture 7: Laplace Transform and Its Applications Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto
 Dr-Ing Sudchai Boonto Department of Control System and Instrumentation Engineering King Mongkut s Unniversity of Technology Thonburi Thailand Outline Motivation The Laplace Transform The Laplace Transform
Dr-Ing Sudchai Boonto Department of Control System and Instrumentation Engineering King Mongkut s Unniversity of Technology Thonburi Thailand Outline Motivation The Laplace Transform The Laplace Transform
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to HT 2011 For hints and answers visit dwm/courses/2tf
 Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Figure 3.1 Effect on frequency spectrum of increasing period T 0. Consider the amplitude spectrum of a periodic waveform as shown in Figure 3.2.
 3. Fourier ransorm From Fourier Series to Fourier ransorm [, 2] In communication systems, we oten deal with non-periodic signals. An extension o the time-requency relationship to a non-periodic signal
3. Fourier ransorm From Fourier Series to Fourier ransorm [, 2] In communication systems, we oten deal with non-periodic signals. An extension o the time-requency relationship to a non-periodic signal
1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses
 1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses 1.1 We first perform the Fourier transform directly on the Gaussian electric field: E(ω) = F[E(t)] = A 0 e 4 ln ( t T FWHM ) e i(ω 0t+ϕ CE ) e iωt
1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses 1.1 We first perform the Fourier transform directly on the Gaussian electric field: E(ω) = F[E(t)] = A 0 e 4 ln ( t T FWHM ) e i(ω 0t+ϕ CE ) e iωt
Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017
 Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017 Monday/Wednesday 2:00-3:20 p.m. Beckman Laser Institute Library, MSTB 214 (lab) Teaching Assistants (Office hours: Every Tuesday at 2pm outside of the
Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017 Monday/Wednesday 2:00-3:20 p.m. Beckman Laser Institute Library, MSTB 214 (lab) Teaching Assistants (Office hours: Every Tuesday at 2pm outside of the
Review of Fourier Transform
 Review of Fourier Transform Fourier series works for periodic signals only. What s about aperiodic signals? This is very large & important class of signals Aperiodic signal can be considered as periodic
Review of Fourier Transform Fourier series works for periodic signals only. What s about aperiodic signals? This is very large & important class of signals Aperiodic signal can be considered as periodic
EE 472 Solutions to some chapter 4 problems
 EE 472 Solutions to some chapter 4 problems 4.4. Erbium doped fiber amplifier An EDFA is pumped at 1480 nm. N1 and N2 are the concentrations of Er 3+ at the levels E 1 and E 2 respectively as shown in
EE 472 Solutions to some chapter 4 problems 4.4. Erbium doped fiber amplifier An EDFA is pumped at 1480 nm. N1 and N2 are the concentrations of Er 3+ at the levels E 1 and E 2 respectively as shown in
Experimental characterization of Cr4+:YAG passively Q-switched Cr:Nd:GSGG lasers and comparison with a simple rate equation model
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Optical Science and Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 7-21-2008 Experimental characterization of Cr4+:YAG passively Q-switched Cr:Nd:GSGG lasers and comparison
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Optical Science and Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 7-21-2008 Experimental characterization of Cr4+:YAG passively Q-switched Cr:Nd:GSGG lasers and comparison
Core Concepts Review. Orthogonality of Complex Sinusoids Consider two (possibly non-harmonic) complex sinusoids
 Overview of Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Topics Definition Compare & contrast with Laplace transform Conditions for existence Relationship to LTI systems Examples Ideal lowpass filters Relationship
Overview of Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Topics Definition Compare & contrast with Laplace transform Conditions for existence Relationship to LTI systems Examples Ideal lowpass filters Relationship
Nonlinear Optics (NLO)
 Nonlinear Optics (NLO) (Manual in Progress) Most of the experiments performed during this course are perfectly described by the principles of linear optics. This assumes that interacting optical beams
Nonlinear Optics (NLO) (Manual in Progress) Most of the experiments performed during this course are perfectly described by the principles of linear optics. This assumes that interacting optical beams
Cavity decay rate in presence of a Slow-Light medium
 Cavity decay rate in presence of a Slow-Light medium Laboratoire Aimé Cotton, Orsay, France Thomas Lauprêtre Fabienne Goldfarb Fabien Bretenaker School of Physical Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University,
Cavity decay rate in presence of a Slow-Light medium Laboratoire Aimé Cotton, Orsay, France Thomas Lauprêtre Fabienne Goldfarb Fabien Bretenaker School of Physical Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University,
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4
 Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations
 3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations NMR is a technique which is well suited to study dynamic processes, such as the rates of chemical reactions. The time window which can be investigated in
3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations NMR is a technique which is well suited to study dynamic processes, such as the rates of chemical reactions. The time window which can be investigated in
Figure 5.1: Theodore Maiman constructed the first operational laser. Wikipedia). 5.1 Emission and absorption of electromagnetic radiation
 5 Laser The word laser is an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was demonstrated by Theodore Maiman in 1960. Figure 5.1: Theodore Maiman constructed the
5 Laser The word laser is an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was demonstrated by Theodore Maiman in 1960. Figure 5.1: Theodore Maiman constructed the
The effective factors on threshold conditions in laser diode Passive Q-Switching
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (4)4079-4084, 0 0, TextRoad Publication ISSN 090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The effective factors on threshold conditions in laser
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (4)4079-4084, 0 0, TextRoad Publication ISSN 090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The effective factors on threshold conditions in laser
MODERN OPTICS. P47 Optics: Unit 9
 MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems
 Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
6.003: Signals and Systems. CT Fourier Transform
 6.003: Signals and Systems CT Fourier Transform April 8, 200 CT Fourier Transform Representing signals by their frequency content. X(jω)= x(t)e jωt dt ( analysis equation) x(t)= X(jω)e jωt dω ( synthesis
6.003: Signals and Systems CT Fourier Transform April 8, 200 CT Fourier Transform Representing signals by their frequency content. X(jω)= x(t)e jωt dt ( analysis equation) x(t)= X(jω)e jωt dω ( synthesis
Ultrafast Laser Physics
 Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 7: Active modelocking Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Mode locking by forcing
Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 7: Active modelocking Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Mode locking by forcing
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Let x(t) be a CT periodic signal with period T, i.e., xt ( + T) = xt ( ), t R Example: the rectangular
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Let x(t) be a CT periodic signal with period T, i.e., xt ( + T) = xt ( ), t R Example: the rectangular
Signals and Systems. Lecture 14 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON
 Signals and Systems Lecture 14 DR TAIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) I SIGAL PROCESSIG IMPERIAL COLLEGE LODO Introduction. Time sampling theorem resume. We wish to perform spectral analysis using
Signals and Systems Lecture 14 DR TAIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) I SIGAL PROCESSIG IMPERIAL COLLEGE LODO Introduction. Time sampling theorem resume. We wish to perform spectral analysis using
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
A few Experimental methods for optical spectroscopy Classical methods Modern methods. Remember class #1 Generating fast LASER pulses
 A few Experimental methods for optical spectroscopy Classical methods Modern methods Shorter class Remember class #1 Generating fast LASER pulses, 2017 Uwe Burghaus, Fargo, ND, USA W. Demtröder, Laser
A few Experimental methods for optical spectroscopy Classical methods Modern methods Shorter class Remember class #1 Generating fast LASER pulses, 2017 Uwe Burghaus, Fargo, ND, USA W. Demtröder, Laser
Today: general condition for threshold operation physics of atomic, vibrational, rotational gain media intro to the Lorentz model
 Today: general condition for threshold operation physics of atomic, vibrational, rotational gain media intro to the Lorentz model Laser operation Simplified energy conversion processes in a laser medium:
Today: general condition for threshold operation physics of atomic, vibrational, rotational gain media intro to the Lorentz model Laser operation Simplified energy conversion processes in a laser medium:
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II
 27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
27. The Fourier Transform in optics, II Parseval s Theorem The Shift theorem Convolutions and the Convolution Theorem Autocorrelations and the Autocorrelation Theorem The Shah Function in optics The Fourier
Source-Free RC Circuit
 First Order Circuits Source-Free RC Circuit Initial charge on capacitor q = Cv(0) so that voltage at time 0 is v(0). What is v(t)? Prof Carruthers (ECE @ BU) EK307 Notes Summer 2018 150 / 264 First Order
First Order Circuits Source-Free RC Circuit Initial charge on capacitor q = Cv(0) so that voltage at time 0 is v(0). What is v(t)? Prof Carruthers (ECE @ BU) EK307 Notes Summer 2018 150 / 264 First Order
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials
 Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3.2 The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
B 2 P 2, which implies that g B should be
 Enhanced Summary of G.P. Agrawal Nonlinear Fiber Optics (3rd ed) Chapter 9 on SBS Stimulated Brillouin scattering is a nonlinear three-wave interaction between a forward-going laser pump beam P, a forward-going
Enhanced Summary of G.P. Agrawal Nonlinear Fiber Optics (3rd ed) Chapter 9 on SBS Stimulated Brillouin scattering is a nonlinear three-wave interaction between a forward-going laser pump beam P, a forward-going
Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4.1
 Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4. A large class of aperiodic CT signals can be represented by the CT Fourier transform (CTFT). The (CT) Fourier transform (or spectrum)
Fourier transform representation of CT aperiodic signals Section 4. A large class of aperiodic CT signals can be represented by the CT Fourier transform (CTFT). The (CT) Fourier transform (or spectrum)
Lecture #6 Chemical Exchange
 Lecture #6 Chemical Exchange Topics Introduction Effects on longitudinal magnetization Effects on transverse magnetization Examples Handouts and Reading assignments Kowalewski, Chapter 13 Levitt, sections
Lecture #6 Chemical Exchange Topics Introduction Effects on longitudinal magnetization Effects on transverse magnetization Examples Handouts and Reading assignments Kowalewski, Chapter 13 Levitt, sections
Optical beams and resonators
 Optical beams and resonators Introduction on transverse modes in optical resonators Laser Physics course SK341X, 2015 Anne-Lise Viotti Lasers, A. E. Siegman, 1986. Contents Introduction Optical resonators
Optical beams and resonators Introduction on transverse modes in optical resonators Laser Physics course SK341X, 2015 Anne-Lise Viotti Lasers, A. E. Siegman, 1986. Contents Introduction Optical resonators
6.003: Signals and Systems. CT Fourier Transform
 6.003: Signals and Systems CT Fourier Transform April 8, 200 CT Fourier Transform Representing signals by their frequency content. X(jω)= x(t)e jωt dt ( analysis equation) x(t)= 2π X(jω)e jωt dω ( synthesis
6.003: Signals and Systems CT Fourier Transform April 8, 200 CT Fourier Transform Representing signals by their frequency content. X(jω)= x(t)e jωt dt ( analysis equation) x(t)= 2π X(jω)e jωt dω ( synthesis
Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique
 Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique Doppler effects in absorption/backscatter coefficient Integration technique for temperature Searchlight integration lidar Rayleigh integration temperature
Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique Doppler effects in absorption/backscatter coefficient Integration technique for temperature Searchlight integration lidar Rayleigh integration temperature
Lecture 15. Temperature Lidar (4) Doppler Techniques
 Lecture 15. Temperature Lidar (4) Doppler Techniques q Doppler effects in absorption and backscatter coefficient vs. cross-section q Doppler Technique to Measure Temperature and Wind Ø Doppler Shift and
Lecture 15. Temperature Lidar (4) Doppler Techniques q Doppler effects in absorption and backscatter coefficient vs. cross-section q Doppler Technique to Measure Temperature and Wind Ø Doppler Shift and
Ver 3808 E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms (2014) E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms. Problem Sheet 1 (Lecture 1)
 Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Implementation and evaluation of data analysis strategies for time-resolved optical spectroscopy
 Supporting information Implementation and evaluation of data analysis strategies for time-resolved optical spectroscopy Chavdar Slavov, Helvi Hartmann, Josef Wachtveitl Institute of Physical and Theoretical
Supporting information Implementation and evaluation of data analysis strategies for time-resolved optical spectroscopy Chavdar Slavov, Helvi Hartmann, Josef Wachtveitl Institute of Physical and Theoretical
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete
 MI OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 8 For information about citing these materials or our erms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSES INSIUE
MI OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 8 For information about citing these materials or our erms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSES INSIUE
ECE 301 Fall 2011 Division 1 Homework 10 Solutions. { 1, for 0.5 t 0.5 x(t) = 0, for 0.5 < t 1
 ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Let x be a periodic continuous-time signal with period, such that {, for.5 t.5 x(t) =, for.5
ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Let x be a periodic continuous-time signal with period, such that {, for.5 t.5 x(t) =, for.5
Series FOURIER SERIES. Graham S McDonald. A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis
 Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is
![Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is](/thumbs/89/98498368.jpg) Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section 5. 3 The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is X ( e jω) = n= x[n]e jωn x[n] can be reconstructed from its
Discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) representation of DT aperiodic signals Section 5. 3 The (DT) Fourier transform (or spectrum) of x[n] is X ( e jω) = n= x[n]e jωn x[n] can be reconstructed from its
Lecture 8 Con,nuous- Wave Laser*
 Lecture 8 Con,nuous- Wave Laser* Min Yan Op,cs and Photonics, KTH 24/04/15 1 * Some figures and texts belong to: O. Svelto, Principles of Lasers, 5th Ed., Springer. Reading Principles of Lasers (5th Ed.):
Lecture 8 Con,nuous- Wave Laser* Min Yan Op,cs and Photonics, KTH 24/04/15 1 * Some figures and texts belong to: O. Svelto, Principles of Lasers, 5th Ed., Springer. Reading Principles of Lasers (5th Ed.):
Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited
 Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018 Frame # 1 Slide # 1 A. Antoniou
Chapter 6 THE SAMPLING PROCESS 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Fourier Transform Revisited Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018 Frame # 1 Slide # 1 A. Antoniou
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez
 F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Monday and Wednesday, 5:30-6:45 pm P&A Room 184. Textbook: Many good ones (see webpage) Lectures follow order
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Monday and Wednesday, 5:30-6:45 pm P&A Room 184. Textbook: Many good ones (see webpage) Lectures follow order
Control and Manipulation of the Kerr-lens Mode-locking Dynamics in Lasers
 Control and Manipulation of the Kerr-lens Mode-locking Dynamics in Lasers Shai Yefet Department of Physics Ph.D. Thesis Submitted to the Senate of Bar-Ilan University Ramat Gan, Israel October 2013 This
Control and Manipulation of the Kerr-lens Mode-locking Dynamics in Lasers Shai Yefet Department of Physics Ph.D. Thesis Submitted to the Senate of Bar-Ilan University Ramat Gan, Israel October 2013 This
Mar Yunsu Sung. Yunsu Sung. Special Topics in Optical Engineering II(15/1)
 Mar 12 2015 Contents Two-port model Rate equation and damping Small signal response Conclusion Two Port Model I:Current V:Voltage P: Optical Power ν: Optical frequency shift Model summarize parasitic effects
Mar 12 2015 Contents Two-port model Rate equation and damping Small signal response Conclusion Two Port Model I:Current V:Voltage P: Optical Power ν: Optical frequency shift Model summarize parasitic effects
Survey on Laser Spectroscopic Techniques for Condensed Matter
 Survey on Laser Spectroscopic Techniques for Condensed Matter Coherent Radiation Sources for Small Laboratories CW: Tunability: IR Visible Linewidth: 1 Hz Power: μw 10W Pulsed: Tunabality: THz Soft X-ray
Survey on Laser Spectroscopic Techniques for Condensed Matter Coherent Radiation Sources for Small Laboratories CW: Tunability: IR Visible Linewidth: 1 Hz Power: μw 10W Pulsed: Tunabality: THz Soft X-ray
The laser oscillator. Atoms and light. Fabry-Perot interferometer. Quiz
 toms and light Introduction toms Semi-classical physics: Bohr atom Quantum-mechanics: H-atom Many-body physics: BEC, atom laser Light Optics: rays Electro-magnetic fields: Maxwell eq. s Quantized fields:
toms and light Introduction toms Semi-classical physics: Bohr atom Quantum-mechanics: H-atom Many-body physics: BEC, atom laser Light Optics: rays Electro-magnetic fields: Maxwell eq. s Quantized fields:
