1 September 19, 2006
|
|
|
- Brian Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title: What s Your Angle? (2005 and 2006 Exam) Authors: SALTers Grade: 8 Description: Students investigate the effect of the angle at which light strikes a block of wood on the surface temperature of that block. Item Description WASL Evidence of Learning for the Grade Level Expectation Grade Level Expectation & Evidence of Learning Codes System of Science Properties of Systems Structure of Systems Changes in Systems Inquiry in Science Application of Science Answer & Typical A B C D *1 *2 Identify a controlled variable in an investigation. Identify the manipulated variable in an investigation. IN02b IN02c % correct 8% 14% 7% 6% 10% 21% 62% correct Identify the responding variable in an IN02d 3 6% 59% investigation correct 23% 11% Write a scientific conclusion, IN03a *4 including supporting data from an investigation, using inferential logic. SA Rubric 5 Identify the behavior of light waves PR03c when light interacts with opaque 3% 7% 87% correct substances. 2% 6 Compare models of a phenomenon to IN04a the actual phenomenon SA Rubric Identify the reason(s) for the *7 effectiveness of a solution to a AP03b 45% problem or challenge using scientific correct 17% 20% 18% concepts/principles. 8 Describe the transfers or ST02d transformations of energy within a physical system. SA Rubric 9 Identify how the position of the Sun CH07d accounts for Earth phenomena (e.g shadows). 22% 9% 7% Construct a logical plan for a IN02e 10 controlled investigation ER Rubric Point Total = MC=6pts, SA=6pts, 25% 69% 6% ER=4pts Actual Science WASL= 62 pts. 40% 40% 20% 45%MC,36%SA,19%ER Note: Points on the WASL are balanced among the Systems of Science with 33% Physical Systems, 33% Earth/Space Systems, and 33% Living Systems. *Typical pilot results. These items were not part of the 2006 Grade 8 Operational Science WASL. 62% correct Published by the Science Assessment Team of the Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction on September 9, 2006 Copyright 2006 by Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) All rights reserved. Educational institutions within the State of Washington have permission to reproduce this document. All other individuals wishing to reproduce this document must contact OSPI. 1 September 19, 2006
2 Scoring Rubric and for Item 4: Write a Conclusion Performance Description Value Points Typical Mean = 0.58 pts A 2-point response demonstrates the student understands the GLE: Explaining IN03a (2.1.3) Apply understanding of how to construct a scientific explanation using evidence and inferential logic BY writing a scientific conclusion, including supporting data from an investigation, using inferential logic. Example: The larger the angle of light striking the block the higher the temperature of the block. The smallest angle tested was 15 and the temperature increased from 26 to 36 C. The largest angle tested was 90 and the temperature increased from 28 to 56 C. The temperature was 20 warmer for the largest angle. 4 18% A 1-point response demonstrates the student has partial understanding of the GLE % A 0-point response demonstrates the student has little or no understanding of the GLE % Blank = 5% 2 September 19, 2006
3 Scoring Rubric and for Item 4: Write a Conclusion (continued) Performance Description Attributes of a Conclusion for Awarding Value Points Note: The italicized print is the part of the Example credited for the value point Conclusive statement correctly answers the investigative question (or correctly states whether the hypothesis/prediction was correct): The larger the angle of light striking the block the higher the temperature of the block. Value Points Typical Attribute Notes: 1. A vague conclusive statement (e.g. the angle of light did affect the temperature) cannot be credited, but other value points can be credited. 2. A response with an incorrect conclusive statement or no conclusive statement may not be credited any value points. 1 68% Supporting data should at least be over the entire range of the conditions investigated. Thus, the minimum reported data are the lowest and highest conditions of the manipulated variable for quantitative data (responding variable when the manipulated variable information is descriptive). Supporting Data for 15 Angle: The smallest angle tested was 15 and the temperature increased from 26 to 36 C. Supporting Data for 90 Angle: The largest angle tested was 90 and the temperature increased from 28 to 56 C. 1 38% 1 38% Explanatory language, separate from the conclusive statement, is used to connect or compare the supporting data to the conclusive statement: The temperature was 20 warmer for the largest angle. Attribute Notes: 1. This point can only be credited when at least one numeric value (or the text from a descriptive data table) for the manipulated or responding variable is included in the response. 2. A copy of the conclusive statement cannot be credited for explanatory language. However, a re-phrased credited conclusive statement can be credited. 3. Explanatory language comparing the range of the manipulated and/or responding variables may be credited (e.g. When the angle was 15º, the temperature was the lowest, 36 C). 4. If a response misquotes trend data between the highest and lowest conditions, this value point cannot be credited. 5. Transitional words (e.g. however, therefore, because, so, then, clearly, but) cannot be credited as explanatory language even when added to a conclusive statement. 6. A compound sentence as a conclusive statement may be read as two separate sentences. 1 30% Total Possible Value Points 4 3 September 19, 2006
4 Scoring Rubric for Item 4: Write a Conclusion (continued) Notes: 1. Copying the Data Table: If a response just copies the whole data table verbatim, supporting data value points may not be credited even with a correct conclusive statement and explanatory language. a) For grades 3-5, a translation of the whole data table into sentences is acceptable. b) For grades 6-8 and high school, a discussion of the whole data table may be acceptable when the data table is minimal with a very small number of data cells. 2. Supporting Data: Responses must give the precise numerical values or precise descriptive language from the data table for both the manipulated and responding variables. a) Average data (if given) rather than trial data, or data from the end of the investigation, must be included for grades 6-8 and high school. b) For grades 3-5, consistent trial data, or data before the completion of the investigation when measuring a responding variable over time can be credited. c) Rounded numerical values cannot be credited. d) Units and significant figures are not necessary for credit. e) Minor language differences in descriptive data may be acceptable as decided in range finding (e.g. not applicable). f) For grades 3-5, the manipulated variable may be implied. 3. Derived Data: Responses giving their own derived data between conditions can be credited for supporting data and explanatory language (e.g. between 15º and 90º, the temperature increased by 20 C). a) When the derived data uses the lowest and/or highest conditions, one or both supporting data points can be credited. b) Minor arithmetic errors in derived values can be acceptable as decided in range finding (e.g. none). 4 September 19, 2006
5 Performance Description Scoring Rubric and for Item 6: Modeling A 2-point response demonstrates the student understands the GLE: Modeling IN04a (2.1.4) Analyze how models represent and are used to investigate objects, events, systems, and processes BY comparing models or computer simulations of a phenomenon to the actual phenomenon Mean = 1.20 pts The response explains how the Earth-Sun Model could be changed to more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun by: Identifying one change that could be made to the model AND Explaining how that change would more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun. Examples: Identifies a change to the model Surface features like hills and valleys Larger block with more thermometers Presence of water Presence of something to represent an atmosphere (wind) Use a sphere instead of a block. Explains how the change more accurately shows how Earth is heated by the Sun The surface of Earth is uneven Light strikes the Earth at many different angles at the same time Much of Earth s surface is covered by water There is moving air above the surface of the Earth The Earth is not flat A 1-point response demonstrates the student has partial understanding of the GLE. 48% The response identifies one change that could be made to the model, but the explanation of how this change would more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun is vague or incomplete or includes a minor misconception. OR Identifies one change that could be made to the model, but the explanation is limited to the investigation and/or model. 22% A 0-point response demonstrates the student has little or no understanding of the GLE. Blank = 3% Notes: 1. Changing the manipulated variable (angles of the wooden block) cannot be credited as a change to the model. 2. The use of the term attracts light rather than the correct term absorbs light is acceptable for this item. 3. Responses that describe the shape of the Earth and/or the model Earth as circular without clarification (e.g. spherical, ball, round, curved) may not earn more than one score point. 27% 5 September 19, 2006
6 Performance Description Scoring Rubric and for Item 8: Energy Transfers in a System A 2-point response demonstrates the student understands the GLE: Energy Transfer and Transformation ST02d (1.2.2) Understand how various factors affect energy transfers and that energy can be transformed from one form of energy to another BY describing the transfers or transformations of energy within a physical system (e.g. conduction and convection of heat energy) Mean = 0.40 pts The response describes two energy transfers that occurred in the investigation by: Identifying the energy forms before and after each energy transfer AND Describing where in the system each energy transfer occurred. Examples: Forms of energy before and after transfer Electrical energy transformed into light energy Where Lamp or light bulb 8% Electrical energy transformed into heat energy Light energy transformed into heat energy Heat conduction Heat energy transferred to heat energy Heat convection Lamp or light bulb Black paper Wood block Air Black paper to the thermometer Black paper to the wooden block Lamp to the air Air to the black paper Hot air moving from the lamp to the paper A 1-point response demonstrates the student has partial understanding of the GLE. The response describes one energy transfer that occurred in the investigation by: Identifying the energy forms before and after the energy transfer AND Describing where in the system the energy transfer occurred. A 0-point response demonstrates the student has little or no understanding of the GLE. 19% 63% Blank = 9% 6 September 19, 2006
7 Item 8: Energy Transfers in a System (continued) Notes: 1. Responses may use the terms transfer and transformation interchangeably. 2. Responses may be credited as correctly describing heat energy being transferred from one object to another by identifying the two objects and the energy form (e.g. heat energy transfers from the paper to the block; heat is absorbed by the thermometer from the paper; heat came to the block from the paper, the paper s heat hit the thermometer; the paper cast its thermal energy onto the block; black paper s heat to the block) 3. Responses may be credited as correctly describing energy being transformed from one form to another by identifying one object, and identifying the energy forms before and after the transformation (e.g. electrical energy changes to light energy in the lamp). 4. Responses using heat as a verb when describing an object s temperature increasing may not be credited as identifying heat energy (e.g. light heated the paper; the wooden block warmed up the thermometer). 5. Responses may be credited as correctly identifying light energy when using terms such as: electromagnetic waves, radiant heat, radiant energy, light waves, and light beams. 6. Responses describing heat energy being transferred from the lamp to the paper may not be credited unless the response describes the carrier of the heat energy (e.g. heat was transferred from the lamp to the air). See Item Specifications for GLE PR Responses describing the lamp as a flashlight may be credited for a chemical to electrical energy transformation (e.g. in the flashlight s batteries, chemical energy was changed into electrical energy). 8. Responses describing the kinetic energy of an object in the Earth-Sun Model may not be credited because none of the objects are moving. However, a response may be credited when describing light energy transformed into kinetic energy of the molecules in the black paper. 9. Responses describing the increase in wooden block s or thermometer s potential energy as the end of the block is raised may be credited (e.g. Amy s food energy was changed into the potential energy as she raised the end of the wooden bock). 10. Responses describing energy transfers in the actual Sun-Earth system may not be credited. 7 September 19, 2006
8 Performance Description Scoring Rubric for Item 10: Plan an Investigation A 4-point response demonstrates the student understands the GLE Planning and Conducting Safe Investigations IN02e (2.1.2) Understand how to plan and conduct scientific investigations BY constructing a logical plan for a controlled or field investigation Value Points Mean = 1.50 pts 8-9 6% A 3-point response demonstrates the student partially understands the GLE % A 2-point response demonstrates the student has limited understanding of the GLE % A 1-point response demonstrates the student has very little understanding of the GLE % A 0-point response demonstrates the student has almost no understanding of the GLE. 0-1 Blank = 5% Attributes of a Controlled Investigation for Awarding Value Points 36% Investigation Attributes Prediction Prediction Reason Materials Description of Attribute The prediction portion of the hypothesis must answer the given question including the effect of the manipulated (changed) variable (angle at which sunlight strikes Earth) on the responding (dependent) variable (length of shadows case on the ground). A hypothesis must give a related reason for the prediction (e.g. because the light will be striking Earth more directly). Attribute Note: This point cannot be awarded without an attempt at a prediction. A list of the minimum materials needed to perform the procedure (e.g. lamp, protractor, meter stick, object to cast a shadow, a stand and clamp to hold this object). Attribute Notes: 1. The right amount of ingredients (e.g. x ml or y grams) needed to carry out the procedure does not need to be given in the materials list. 2. A measuring device listed as minimum may not be needed in the materials list if the list includes pre-measured amounts of a material coupled with an appropriate procedure that does not call for using the device. 3. Standard Classroom Materials do not need to be listed: paper, pencil, and safety equipment (e.g. goggles, aprons, gloves, tongs). Value Point Typical 1 55% 1 20% 1 38% 8 September 19, 2006
9 Scoring Rubric for Item 10: Plan an Investigation (continued) Investigation Attributes Attributes of a Controlled Investigation for Awarding Value Points (continued) Description of Attribute Value Point Typical Procedure The written or diagrammed procedure is evaluated as follows: up to 6 One Controlled (kept the same) Variable Manipulated (changed) Variable Responding (dependent) Variable Record Measurements Trials are Repeated Logical Steps One controlled variable must be identified or implied in the procedure or the materials list (e.g. distance of the lamp from the object, same lamp). Only one manipulated variable (angle at which sunlight strikes Earth) is identified or implied in the procedure or data table (if given). The responding variable (length of shadows) is identified or implied in the procedure or data table (if given). The procedure states or implies measurements are recorded periodically or gives a data table. Attribute Note: 1. If artificial data for the responding variable is given, no value point may be awarded. 2. The phrase take measurement cannot be used to mean record. More than one trial for all conditions is planned, or implied in a data table, to measure the responding variable. The steps of the procedure are detailed enough to repeat the procedure effectively (examples of illogical steps: no ending time indicated; states Set up as diagrammed, but diagram is inadequate; recording vague data or results). 1 50% 1 52% 1 48% 1 42% 1 16% 1 8% Total Value Points Possible 9 9 September 19, 2006
10 Scoring Rubric for Item 10: Plan an Investigation (continued) Notes: 1. If the response does not plan an appropriate procedure for the given question, the response may not earn any of the possible procedure value points. Examples: a) Repeats the procedure from the scenario b) Measures only one condition (therefore cannot establish the controlled or manipulated variables) c) Purposefully changes more than one variable simultaneously d) Writes a procedure that is too vague to possibly be appropriate e) Writes a prediction instead of a procedure 2. If the response names a bulleted attribute listed after Procedure that includes: without including that attribute in the procedure, the attribute point cannot be credited. When a bulleted attribute is named and implied in the response, both must be correct to be credited. 3. Vagueness in procedural steps shall be clarified as follows: a) Vague materials used in the procedure (e.g. add 1mL) may be credited if the vagueness is clarified in the materials list (e.g. 1mL, 2mL, and 3mL of solution). b) Measuring a vague parameter (e.g. size of plant instead of height) may be credited as a manipulated or responding variable. However, a vague parameter is difficult to repeatedly measure, so the logical steps value point cannot be credited. c) The term repeat at the end of a step refers to that step only. d) The term repeat as a separate step (or in a new paragraph) refers to the whole procedure. e) The term repeat, when qualified, cannot be credited (e.g. repeat if necessary, repeat as desired). f) A vague action that calls for the manipulated variable to be changed (e.g. increase the temperature by 5 C) without indicating how many times, gives no end to the investigation so the logical steps value point cannot be credited. g) A vague action that calls for the manipulated variable to be changed (e.g. change the temperature by 5 C) without indicating how many times, cannot be credited for more than two conditions of the manipulated variable. h) When a procedure conflicts with the labeled diagram, the procedure is too illogical to be effectively repeated. Therefore, the logical steps value point cannot be credited, but the procedure can be scored for attributes that are not in conflict. 10 September 19, 2006
Aquarium Systems PCA Scenario Map, Results, and Scoring Rubrics
 Title: Aquarium Systems (2005 and 2006 Op Exam) Authors: SALTers Grade: High School Description: Students investigate how increasing the temperature of an aquarium affects the breathing rate of goldfish
Title: Aquarium Systems (2005 and 2006 Op Exam) Authors: SALTers Grade: High School Description: Students investigate how increasing the temperature of an aquarium affects the breathing rate of goldfish
Mousetrap Car PCA Scenario Map, Results, and Scoring Rubric. Scenario Type: Application in a Physical Source: Fender Bender Physics, NSTA Press 2002
 Title: Mousetrap Car Author: Roy Beven Grade: High School Scenario Type: Application in a Physical System Source: Fender Bender Physics, NSTA Press 2002 Description: Students prepare for a Mousetrap Car
Title: Mousetrap Car Author: Roy Beven Grade: High School Scenario Type: Application in a Physical System Source: Fender Bender Physics, NSTA Press 2002 Description: Students prepare for a Mousetrap Car
Resources on this DVD & Internet relevant to the Earthquake Machine. 2. ANIMATIONS_Earthquake & Tsunami > Earthquake Machine-Blocks&Graphs
 Activity Earthquake Machine How could pulling a block of wood with a string of rubber bands have anything to do with earthquakes? There are no rubber bands in the Earth, but all solids, including the Earth
Activity Earthquake Machine How could pulling a block of wood with a string of rubber bands have anything to do with earthquakes? There are no rubber bands in the Earth, but all solids, including the Earth
Teacher Pages. Wheat Field System Scenario
 Teacher Pages Wheat Field System Scenario Copyright 2015 by Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) All rights reserved. Educational institutions within the State of Washington
Teacher Pages Wheat Field System Scenario Copyright 2015 by Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) All rights reserved. Educational institutions within the State of Washington
Answer Key Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves
 Answer Key Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves 1. Part A Based on the text and diagram, how many major bands of radiant energy are there? A Incorrect. Look at the Kinds of Radiant Energy diagram.
Answer Key Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves 1. Part A Based on the text and diagram, how many major bands of radiant energy are there? A Incorrect. Look at the Kinds of Radiant Energy diagram.
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Math Released Item Grade 8. Justify Parallel Lines VF525280
 Math Released Item 2017 Grade 8 Justify Parallel Lines VF525280 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Rubric VF525280 Rubric Score Description 3 Student response includes the following 3 elements. Reasoning
Math Released Item 2017 Grade 8 Justify Parallel Lines VF525280 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Rubric VF525280 Rubric Score Description 3 Student response includes the following 3 elements. Reasoning
Math Released Item Algebra 2. Radioactive Element Equations VH147862
 Math Released Item 2018 Algebra 2 Radioactive Element Equations VH147862 Anchor Set A1 A9 With Annotations Prompt Score Description VH147862 Rubric Part A 1 Student response includes the following element.
Math Released Item 2018 Algebra 2 Radioactive Element Equations VH147862 Anchor Set A1 A9 With Annotations Prompt Score Description VH147862 Rubric Part A 1 Student response includes the following element.
Unit Organizer: Energy in Our Life (Approximate Time: Seven weeks )
 One Stop Shop For Educators The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
One Stop Shop For Educators The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
Grade 8 Science MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide
 Grade 8 Science MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide Screen is split vertically, scene on left and questions on right Multiple questions can be on the right side of the screen which requires vertical scrolling
Grade 8 Science MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide Screen is split vertically, scene on left and questions on right Multiple questions can be on the right side of the screen which requires vertical scrolling
Arithmetic Properties w. A = lw Additive Inverse: a + (ˉa) = 0 l 1 Multiplicative Inverse: a = 1 a
 KEYSTONE REFERENCE ALGEBRA I FORMULA SHEET Formulas that you may need to solve questions on this exam are found below. You may use calculator π or the number 3.14. Arithmetic Properties w A = lw Additive
KEYSTONE REFERENCE ALGEBRA I FORMULA SHEET Formulas that you may need to solve questions on this exam are found below. You may use calculator π or the number 3.14. Arithmetic Properties w A = lw Additive
Student Sheet: Self-Assessment
 Student s Name Date Class Student Sheet: Self-Assessment Directions: Use the space provided to prepare a KWL chart. In the first column, write things you already know about energy, forces, and motion.
Student s Name Date Class Student Sheet: Self-Assessment Directions: Use the space provided to prepare a KWL chart. In the first column, write things you already know about energy, forces, and motion.
Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid
 Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid Created by: In this lesson, students investigate how stearic acid undergoes a 2014 AACT Middle School phase change from solid to liquid and back from liquid to solid. Content
Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid Created by: In this lesson, students investigate how stearic acid undergoes a 2014 AACT Middle School phase change from solid to liquid and back from liquid to solid. Content
PSSA, Grade 4 Science
 PSSA and Keystone Exams Fall 2015 Item Writing and Handscoring Training Workshops PSSA, Grade 4 Science Community Pond Handscoring Anchor Set Page 02-1 This Page Intentionally Blank Page 02-2 Page 02-3
PSSA and Keystone Exams Fall 2015 Item Writing and Handscoring Training Workshops PSSA, Grade 4 Science Community Pond Handscoring Anchor Set Page 02-1 This Page Intentionally Blank Page 02-2 Page 02-3
PSI Chemistry. Table spoons, disposable weighing dishes, scale, pencil and instruction hand out.
 Chemistry Honors Lab PSI Chemistry Names Measuring Mass As A Means Of Counting - Chemical quantities- Mole and Particles Purpose To determine the mass of given chemicals and use the data to count atoms.
Chemistry Honors Lab PSI Chemistry Names Measuring Mass As A Means Of Counting - Chemical quantities- Mole and Particles Purpose To determine the mass of given chemicals and use the data to count atoms.
Pacing Guide TEKS. Unit 1 Scientific Process Skills and Investigations
 Pacing Guide Unit Scientific Process Skills and Investigations Lab Safety/ Use of Tools Measurement Process Skills and Investigations 6.(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations
Pacing Guide Unit Scientific Process Skills and Investigations Lab Safety/ Use of Tools Measurement Process Skills and Investigations 6.(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations
Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Discover Earth Program Materials
 Lesson Summary Students will use either a computer interface or a thermometer and graph paper to learn about the different absorption properties of different albedos. Prior Knowledge & Skills Graphing
Lesson Summary Students will use either a computer interface or a thermometer and graph paper to learn about the different absorption properties of different albedos. Prior Knowledge & Skills Graphing
Student Sheet: Self-Assessment
 Student s Name Date Class Student Sheet: Self-Assessment Directions: Use the space provided to prepare a KWL chart. In the first column, write things you already know about energy, forces, and motion.
Student s Name Date Class Student Sheet: Self-Assessment Directions: Use the space provided to prepare a KWL chart. In the first column, write things you already know about energy, forces, and motion.
Name. University of Maryland Department of Physics
 Name University of Maryland Department of Physics 13. November. 2009 Instructions: Do not open this examination until the proctor tells you to begin. 1. When the proctor tells you to begin, write your
Name University of Maryland Department of Physics 13. November. 2009 Instructions: Do not open this examination until the proctor tells you to begin. 1. When the proctor tells you to begin, write your
Grade 6 Science Practice Test Answer Key
 This document contains the answer keys, rubrics, and Scoring Notes for items on the Grade 6 Science Practice Test. Additional Practice Test resources are available in the LDOE Practice Test Library. Session
This document contains the answer keys, rubrics, and Scoring Notes for items on the Grade 6 Science Practice Test. Additional Practice Test resources are available in the LDOE Practice Test Library. Session
Effective January 2008 All indicators in Standard / 11
 Scientific Inquiry 8-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design and
Scientific Inquiry 8-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design and
example can be used to refute a conjecture, it cannot be used to prove one is always true.] propositions or conjectures
![example can be used to refute a conjecture, it cannot be used to prove one is always true.] propositions or conjectures example can be used to refute a conjecture, it cannot be used to prove one is always true.] propositions or conjectures](/thumbs/91/106492203.jpg) Task Model 1 Task Expectations: The student is asked to give an example that refutes a proposition or conjecture; or DOK Level 2 The student is asked to give an example that supports a proposition or conjecture.
Task Model 1 Task Expectations: The student is asked to give an example that refutes a proposition or conjecture; or DOK Level 2 The student is asked to give an example that supports a proposition or conjecture.
Conduction, Convection, & Radiation
 Conduction, Convection, & Radiation Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural I. Introduction- What is temperature? What is heat? Ask: what is temperature? scientific measure
Conduction, Convection, & Radiation Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural I. Introduction- What is temperature? What is heat? Ask: what is temperature? scientific measure
Jell-O Rocks. Science Concept: Objectives: GLEs Addressed: Vocabulary: Materials: Most rocks are made of different substances.
 Science Concept: Most rocks are made of different substances. Objectives: The student will: describe a variety of rocks; observe and communicate about rocks; and take a photograph of a rock and describe
Science Concept: Most rocks are made of different substances. Objectives: The student will: describe a variety of rocks; observe and communicate about rocks; and take a photograph of a rock and describe
Earth & Space Science
 Earth & Space Science Grade 6 Written by Tracy Bellaire The activities in this book have two intentions: to teach concepts related to earth and space science and to provide students the opportunity to
Earth & Space Science Grade 6 Written by Tracy Bellaire The activities in this book have two intentions: to teach concepts related to earth and space science and to provide students the opportunity to
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND CLIMATE (MODIFIED FOR ADEED)
 (MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Science Concept: Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation behave differently in the atmosphere. Objectives: The student will: explain interactions between different frequencies
(MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Science Concept: Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation behave differently in the atmosphere. Objectives: The student will: explain interactions between different frequencies
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY PAPER 5: PHYSICS F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY PAPER 5: PHYSICS F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant
Free Response Questions Included in Training Module
 Free Response Questions Included in Training Module Copyright 2011 Laying the Foundation, Inc. All right reserved. The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by educators
Free Response Questions Included in Training Module Copyright 2011 Laying the Foundation, Inc. All right reserved. The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by educators
Unit 2: Vectors Student Papers
 INQUIRY PHYSICS A Modified Learning Cycle Curriculum by Granger Meador Unit 2: Vectors Student Papers inquiryphysics.org 2010 these SAMPLE NOTES, the STUDENT PAPERS, and any PRESENTATIONS for each unit
INQUIRY PHYSICS A Modified Learning Cycle Curriculum by Granger Meador Unit 2: Vectors Student Papers inquiryphysics.org 2010 these SAMPLE NOTES, the STUDENT PAPERS, and any PRESENTATIONS for each unit
Geometry Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler 2018
 Geometry Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler 2018 COPYRIGHT GEORGIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.... 1 Types of Items Included in the Sampler and Uses of
Geometry Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler 2018 COPYRIGHT GEORGIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.... 1 Types of Items Included in the Sampler and Uses of
5th Grade Science Syllabus and Classroom Expectations
 5th Grade Science Syllabus and Classroom Expectations Class Description: The organization of this class will include topics from the physical sciences, Biology, and earth Science. This year you will be
5th Grade Science Syllabus and Classroom Expectations Class Description: The organization of this class will include topics from the physical sciences, Biology, and earth Science. This year you will be
6 th Grade TEKS. Whacha-gotta-no!
 6 th Grade TEKS Whacha-gotta-no! (1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. 1(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 1(B)
6 th Grade TEKS Whacha-gotta-no! (1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. 1(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 1(B)
Name: Block: Date: Student Notes. OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter.
 Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Heat Transfer Student Notes OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter. LINK 1. Particles in
Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Heat Transfer Student Notes OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter. LINK 1. Particles in
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT High School Courses Science/Chemistry
 State Resources: Texas Education Agency STAAR Chemistry Reference Materials. Retrieved from http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/staar/science/ (look under "Specific STAAR Resources," "Science").
State Resources: Texas Education Agency STAAR Chemistry Reference Materials. Retrieved from http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/staar/science/ (look under "Specific STAAR Resources," "Science").
Student Name. Teacher
 Student Name Teacher Question: I chose this question because Research Keywords Research Topic Source: Research Summary Paragraph Hypothesis If then Variables Manipulated Variable Responding Variable Constants
Student Name Teacher Question: I chose this question because Research Keywords Research Topic Source: Research Summary Paragraph Hypothesis If then Variables Manipulated Variable Responding Variable Constants
ITEM SAMPLER RELEASED ITEMS. FOR SCIENCE Grades 4 and 6. Delaware Department of Education. May 2002
 May 2002 ITEM SAMPLER RELEASED ITEMS FOR SCIENCE Grades 4 and 6 Delaware Department of Education Document Number 95-01/02/05/05 2002 Delaware Department of Education SCIENCE Delaware Student Testing Program
May 2002 ITEM SAMPLER RELEASED ITEMS FOR SCIENCE Grades 4 and 6 Delaware Department of Education Document Number 95-01/02/05/05 2002 Delaware Department of Education SCIENCE Delaware Student Testing Program
University of Maryland Department of Physics. Spring 2009 Final Exam 20. May (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No
 University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
Reasons for the Seasons WebQuest Worksheet
 Name per Reasons for the Seasons WebQuest Worksheet Misconceptions About the Reasons for the Seasons What are misconceptions? A misconception is an incorrect idea about something. Your task is to find
Name per Reasons for the Seasons WebQuest Worksheet Misconceptions About the Reasons for the Seasons What are misconceptions? A misconception is an incorrect idea about something. Your task is to find
STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA
 1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
Name Class Date. Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A
 Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
CHM101 Lab Measurements and Conversions Grading Rubric
 CHM101 Lab Measurements and Conversions Grading Rubric Name Team Name Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Safety and proper waste
CHM101 Lab Measurements and Conversions Grading Rubric Name Team Name Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Safety and proper waste
Science: Double Award
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials AQA Level 1/2 Certificate Foundation Tier June 2015 Science: Double Award Physics Paper 2F
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials AQA Level 1/2 Certificate Foundation Tier June 2015 Science: Double Award Physics Paper 2F
Bundle at a Glance 6 th Gr. Science 2015/16. Introduction: Scientific Investigation and Reasoning Skills (3 A/B days)
 Introduction: Scientific Investigation and Reasoning Skills (3 A/B days) 6 th Gr. Process TEKS: 1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety
Introduction: Scientific Investigation and Reasoning Skills (3 A/B days) 6 th Gr. Process TEKS: 1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety
Lesson 2 Changes in State
 Lesson 2 Changes in State Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to
Lesson 2 Changes in State Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT High School Courses Science/Chemistry
 State Resources: Texas Education Agency STAAR Chemistry Reference Materials. Retrieved from http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/staar/science/ (look under "Specific STAAR Resources," "Science").
State Resources: Texas Education Agency STAAR Chemistry Reference Materials. Retrieved from http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/staar/science/ (look under "Specific STAAR Resources," "Science").
Effective January 2008 All indicators in Standard / 14
 Scientific Inquiry 7-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including the process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design
Scientific Inquiry 7-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including the process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Properties of Matter Let Me Count the Ways... 15 A Bear Eggs-pedition...25 Color Match...33 Going Nuts...39 Soup-er Floaters and Sinkers...55
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Properties of Matter Let Me Count the Ways... 15 A Bear Eggs-pedition...25 Color Match...33 Going Nuts...39 Soup-er Floaters and Sinkers...55
The effects of sodium chloride on the Boiling Point of Dihydrogen Monoxide
 The effects of sodium chloride on the Boiling Point of Dihydrogen Monoxide Background: Dissolving a solute in a liquid can change its properties. These are called Colligative Properties, which are properties
The effects of sodium chloride on the Boiling Point of Dihydrogen Monoxide Background: Dissolving a solute in a liquid can change its properties. These are called Colligative Properties, which are properties
Making Measurements. Units of Length
 Experiment #2. Measurements and Conversions. Goals 1. To measure and record length, volume and mass accurately with the correct number of significant figures 2. To convert between units using conversion
Experiment #2. Measurements and Conversions. Goals 1. To measure and record length, volume and mass accurately with the correct number of significant figures 2. To convert between units using conversion
Cut here
 LAB SAFETY MINI BOOK RUBRIC Self and Guardian Evaluation Sheet Directions: Students will make a mini book that tells a creative story which incorporates 7 important lab safety rules. Student must NOT simply
LAB SAFETY MINI BOOK RUBRIC Self and Guardian Evaluation Sheet Directions: Students will make a mini book that tells a creative story which incorporates 7 important lab safety rules. Student must NOT simply
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scienti c Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books...15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scienti c Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books...15 Earth in Space and Time The Scoop on Stars...17 Telescopes...19 Magnify the Sky...21 Star Samples...27
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scienti c Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books...15 Earth in Space and Time The Scoop on Stars...17 Telescopes...19 Magnify the Sky...21 Star Samples...27
Fall Final Exam Review: 8 th grade Independent variable: Dependent variable: Scientific Investigations:
 Name: Due Date: Class Per. Fall Final Exam Review: 8 th grade 2015 Scientific Investigations: 1. What is Qualitative data? Give an example. 2. What is Quantitative Data? Give an example. 3. Explain the
Name: Due Date: Class Per. Fall Final Exam Review: 8 th grade 2015 Scientific Investigations: 1. What is Qualitative data? Give an example. 2. What is Quantitative Data? Give an example. 3. Explain the
Math Released Item Grade 5. Expressions with Same Value 4054-M03251
 Math Released Item 2018 Grade 5 Expressions with Same Value 4054-M03251 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Score Description 4054-M03251 Rubric Part A 1 This part of the item is machine-scored. Reasoning
Math Released Item 2018 Grade 5 Expressions with Same Value 4054-M03251 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Score Description 4054-M03251 Rubric Part A 1 This part of the item is machine-scored. Reasoning
Science Enhanced Scope and Sequence Grade 6. Modeling the Atom
 Modeling the Atom Strand Topic Matter Investigating atoms, elements, molecules, and compounds Primary SOL 6.4 The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts
Modeling the Atom Strand Topic Matter Investigating atoms, elements, molecules, and compounds Primary SOL 6.4 The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts
TEKS Physics, Beginning with School Year Correlation to CPO Science Link
 TEKS Physics. (c) Knowledge and skills. (1) Scientific processes. The student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices.
TEKS Physics. (c) Knowledge and skills. (1) Scientific processes. The student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices.
S4: Modeling the Reasons for Seasonal Change
 S4: Modeling the Reasons for Seasonal Change Purpose To understand what causes the Earth s seasons, with a focus on the Earth s tilt and its spherical shape Overview Students learn how sunlight spreads
S4: Modeling the Reasons for Seasonal Change Purpose To understand what causes the Earth s seasons, with a focus on the Earth s tilt and its spherical shape Overview Students learn how sunlight spreads
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3877435969* PHYSICS 0625/23 Paper 2 Core May/June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3877435969* PHYSICS 0625/23 Paper 2 Core May/June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist > Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry. 1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist. 1.1 The Scope of Chemistry 1.2 Chemistry and You
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1.1 The Scope of Chemistry 1.2 Chemistry and You 1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist 1.4 Problem Solving in Chemistry 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1.1 The Scope of Chemistry 1.2 Chemistry and You 1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist 1.4 Problem Solving in Chemistry 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
How do you think Alexander Fleming tested his hypothesis?
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1.1 The Scope of Chemistry 1.2 Chemistry and You 1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist 1.4 Problem Solving in Chemistry 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1.1 The Scope of Chemistry 1.2 Chemistry and You 1.3 Thinking Like a Scientist 1.4 Problem Solving in Chemistry 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE PHYSICS PAPER 1F. Mark scheme. Specimen Version 1.0
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE PHYSICS PAPER F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE PHYSICS PAPER F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves. Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com
 Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Honors Chemistry 2016 Summer Assignment
 This Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment will review mathematical concepts necessary when performing mathematical calculation and laboratory experiments and focus on laboratory safety. Measurements are
This Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment will review mathematical concepts necessary when performing mathematical calculation and laboratory experiments and focus on laboratory safety. Measurements are
Batteries, Bulbs and Switches. Understanding Batteries
 Exploring Physics Electricity Magnetism -- the CD-ROM by M. Chrasekhar, R. Litherl J. Geib: Correlation of Unit Concepts with California State Science Stards Electricity Bulbs Switches Understing Batteries
Exploring Physics Electricity Magnetism -- the CD-ROM by M. Chrasekhar, R. Litherl J. Geib: Correlation of Unit Concepts with California State Science Stards Electricity Bulbs Switches Understing Batteries
EMPOWERING TEACHERS. Day 1 Read and record the details from The Earth on a large chart. LA , LA
 LA.3.1.7.5, LA.3.1.7.7 EMPOWERING TEACHERS Comprehension Instructional Routine: Compare and Contrast the Topics in Two Texts Preparation/Materials: two large texts for the teacher of The Earth and Mercury,
LA.3.1.7.5, LA.3.1.7.7 EMPOWERING TEACHERS Comprehension Instructional Routine: Compare and Contrast the Topics in Two Texts Preparation/Materials: two large texts for the teacher of The Earth and Mercury,
Science - 4th grade practice test
 Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED)
 CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Overview: Students investigate chemical reactions using given substances. Students identify chemical reactions in their daily lives. Objectives: The student
CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Overview: Students investigate chemical reactions using given substances. Students identify chemical reactions in their daily lives. Objectives: The student
Math Released Item Algebra 1. System of Inequalities VF648815
 Math Released Item 2016 Algebra 1 System of Inequalities VF648815 Prompt Rubric Task is worth a total of 3 points. VF648815 Rubric Part A Score Description 1 Student response includes the following element.
Math Released Item 2016 Algebra 1 System of Inequalities VF648815 Prompt Rubric Task is worth a total of 3 points. VF648815 Rubric Part A Score Description 1 Student response includes the following element.
Measuring the Temperature of the Sun
 Measuring the Temperature of the Sun Purpose: In this lab you will measure the solar flux, the amount of energy per unit area per unit time that reaches the Earth from the Sun. From this, you will calculate
Measuring the Temperature of the Sun Purpose: In this lab you will measure the solar flux, the amount of energy per unit area per unit time that reaches the Earth from the Sun. From this, you will calculate
Shampoo Woo, by Cindy Anderson and Matthew Dornier. Chemistry. Materials
 Louisiana Curriculum Framework Content Strand Chemistry Grade Level 9-12 Objective: The students will Perform lab investigations to determine the ph of shampoo Determine which shampoo, based on ph, is
Louisiana Curriculum Framework Content Strand Chemistry Grade Level 9-12 Objective: The students will Perform lab investigations to determine the ph of shampoo Determine which shampoo, based on ph, is
Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail
 Name: Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail Quiz Act # s 54-63 Study Guide 1.) What is the definition of energy? (page 1) The ability to do work. (anything that can cause an object to change, work or move)
Name: Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail Quiz Act # s 54-63 Study Guide 1.) What is the definition of energy? (page 1) The ability to do work. (anything that can cause an object to change, work or move)
Physics Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (PASKS) Form 3
 Physics Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (PASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
Physics Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (PASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
 PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
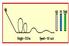 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
AP PHYSICS 1 SUMMER PREVIEW
 AP PHYSICS 1 SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to read through this summer preview, completing the practice problems, and completing TASK 1 and Task 2. It is important that you read
AP PHYSICS 1 SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to read through this summer preview, completing the practice problems, and completing TASK 1 and Task 2. It is important that you read
Mole Lab Introduction to The Mole Concept
 Mole Lab Introduction to The Mole Concept SCIENTIFIC Introduction Although technically not a laboratory experiment, this activity certainly helps to drive home the main idea behind the mole concept that
Mole Lab Introduction to The Mole Concept SCIENTIFIC Introduction Although technically not a laboratory experiment, this activity certainly helps to drive home the main idea behind the mole concept that
Page Points Score Total: 100
 Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2a 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2a 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
K-12 Environmental Education
 UCSD TIES adapted from NYSERDA Energy Smart www.schoolpowernaturally.org Solar Kit Lesson #12 Calibration Curve for a Radiation Meter TEACHER INFORMATION LEARNING OUTCOME After using measurement, students
UCSD TIES adapted from NYSERDA Energy Smart www.schoolpowernaturally.org Solar Kit Lesson #12 Calibration Curve for a Radiation Meter TEACHER INFORMATION LEARNING OUTCOME After using measurement, students
Full file at InvestigationWksht01.pdf 02_Measurement_in_Biology_Prep.pdf Exercise_02.pdf
 InvestigationWksht01.pdf 02_Measurement_in_Biology_Prep.pdf Exercise_02.pdf INVESTIGATION WORKSHEET 1 How Temperature Affects the Production of CO 2 by Yeast Name Observation: Fermentation of nutrients
InvestigationWksht01.pdf 02_Measurement_in_Biology_Prep.pdf Exercise_02.pdf INVESTIGATION WORKSHEET 1 How Temperature Affects the Production of CO 2 by Yeast Name Observation: Fermentation of nutrients
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4743961177* PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Core May/June 2009 1 hour 15 minutes
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4743961177* PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Core May/June 2009 1 hour 15 minutes
Ohio s State Tests ANSWSER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES GRADE 8 SCIENCE PART 1
 Ohio s State Tests ANSWSER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES GRADE 8 SCIENCE PART 1 Table of Contents Questions 1 4: Content Summary and Answer Key...1 Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...3 Question 1:
Ohio s State Tests ANSWSER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES GRADE 8 SCIENCE PART 1 Table of Contents Questions 1 4: Content Summary and Answer Key...1 Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...3 Question 1:
Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses
 Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter D issued under the Texas Education Code, 28.002,
Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter D issued under the Texas Education Code, 28.002,
Energy and Electromagnetism
 4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 1: Energy and Circuits Name: Big Question: What is evidence that energy is present, and what conditions allow it to flow? 1 Alignment with
4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 1: Energy and Circuits Name: Big Question: What is evidence that energy is present, and what conditions allow it to flow? 1 Alignment with
Lab 4. Friction. Goals. Introduction
 Lab 4. Friction Goals To determine whether the simple model for the frictional force presented in the text, where friction is proportional to the product of a constant coefficient of friction, µ K, and
Lab 4. Friction Goals To determine whether the simple model for the frictional force presented in the text, where friction is proportional to the product of a constant coefficient of friction, µ K, and
Using Graphene to Conduct Electricity: Guided Research. STEP-UP Lesson Plan Cisely Marshall, Teacher Booker T. Washington High School
 Using Graphene to Conduct Electricity: Guided Research STEP-UP Lesson Plan 2014 Cisely Marshall, Teacher Booker T. Washington High School Title Using Graphene to Conduct Electricity: Guided Research Problem
Using Graphene to Conduct Electricity: Guided Research STEP-UP Lesson Plan 2014 Cisely Marshall, Teacher Booker T. Washington High School Title Using Graphene to Conduct Electricity: Guided Research Problem
Angelina College Science and Mathematics Chemistry 1105 Introductory Chemistry Internet General Syllabus
 I. BASIC COURSE INFORMATION: Angelina College Science and Mathematics Chemistry 1105 Introductory Chemistry Internet General Syllabus A. Course Description: 1. Basic laboratory experiments supporting theoretical
I. BASIC COURSE INFORMATION: Angelina College Science and Mathematics Chemistry 1105 Introductory Chemistry Internet General Syllabus A. Course Description: 1. Basic laboratory experiments supporting theoretical
(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards
 Alignment of Alien Rescue with the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Alien Rescue was designed to meet the learning goals set out in the National Science Standards and TEKS. The following is
Alignment of Alien Rescue with the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Alien Rescue was designed to meet the learning goals set out in the National Science Standards and TEKS. The following is
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT Grade 3 Ciencia,Science
 State Resources: Bridging II TAKS: Module 1 Light and Optics 3 rd Grade IFD Legend Bold, italic black: Knowledge and Skills Statement (TEKS); Bold black: Student Expectation (TEKS) Bold, italic red: Student
State Resources: Bridging II TAKS: Module 1 Light and Optics 3 rd Grade IFD Legend Bold, italic black: Knowledge and Skills Statement (TEKS); Bold black: Student Expectation (TEKS) Bold, italic red: Student
Test Blueprint. Chemistry Science Standards of Learning
 Test Blueprint Chemistry 2010 Science Standards of Learning This revised test blueprint will be effective with the administration of the 2012-2013 Science Standards of Learning (SOL) tests. Notice to Reader
Test Blueprint Chemistry 2010 Science Standards of Learning This revised test blueprint will be effective with the administration of the 2012-2013 Science Standards of Learning (SOL) tests. Notice to Reader
Spring 2017 Exam 2 NAME: PIN:
 MARK BOX problem points 0 10 HAND IN PART 1 10 2 10 3-10 40=8x5 11 10 12 10 NAME: PIN: 13 10 % 100 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. (1) HAND-IN PART. Hand-in only this part. (2) NOT TO HAND-IN
MARK BOX problem points 0 10 HAND IN PART 1 10 2 10 3-10 40=8x5 11 10 12 10 NAME: PIN: 13 10 % 100 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. (1) HAND-IN PART. Hand-in only this part. (2) NOT TO HAND-IN
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT HS/Physics
 Exemplar Lesson 01: Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer State Resources: RATIONALE: This unit bundles student expectations relating to how matter reacts with changing temperature, how thermal energy is controlled
Exemplar Lesson 01: Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer State Resources: RATIONALE: This unit bundles student expectations relating to how matter reacts with changing temperature, how thermal energy is controlled
Pennsylvania. Keystone Exams. Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler
 Pennsylvania Keystone Exams Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler 2016 Keystone Algebra I Sampler Table of Contents INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I Introduction.......................................................................................
Pennsylvania Keystone Exams Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler 2016 Keystone Algebra I Sampler Table of Contents INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I Introduction.......................................................................................
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.smarteduhub.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4019966178* PHYSICS 0625/06 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2007
www.smarteduhub.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4019966178* PHYSICS 0625/06 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2007
Properties of Matter BEFORE READING BUILD BACKGROUND PREVIEW TEXT AND GRAPHICS
 READING FOCUS SKILLS: Main Idea and Details, Cause and Effect VOCABULARY: density, gas, liquid, mass, matter, mixture, solid, solubility, solution, state of matter, suspension, volume EXTENSIONS: Writing,
READING FOCUS SKILLS: Main Idea and Details, Cause and Effect VOCABULARY: density, gas, liquid, mass, matter, mixture, solid, solubility, solution, state of matter, suspension, volume EXTENSIONS: Writing,
AIMS Education Foundation
 Topic Potential and kinetic energy Key Question How does a paper model of a jumping frog illustrate the conversion of elastic potential energy to kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy? Learning
Topic Potential and kinetic energy Key Question How does a paper model of a jumping frog illustrate the conversion of elastic potential energy to kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy? Learning
Dates: January 30 March 10, 2017 Florida Standard(s): Benchmarks, descriptions, DOK levels, standards unpacked (know/do) highlighted
 Teacher(s): Amos, Littles, McGhee Grade/Subject: 8 th /Physical Science Week of: March 21-24, 2017 Unit : Atoms and the Periodic Table, Changes in Matter Dates: January 30 March 10, 2017 Florida Standard(s):
Teacher(s): Amos, Littles, McGhee Grade/Subject: 8 th /Physical Science Week of: March 21-24, 2017 Unit : Atoms and the Periodic Table, Changes in Matter Dates: January 30 March 10, 2017 Florida Standard(s):
Elizabethtown Area School District Chemistry in Your World
 Elizabethtown Area Chemistry in Your World Course Number: 319 Length of Course: 1 semester Grade Level: 11-12 Required Total Clock Hours: 120 Length of Period: 80 minutes Date Written: June 11, 2007 Periods
Elizabethtown Area Chemistry in Your World Course Number: 319 Length of Course: 1 semester Grade Level: 11-12 Required Total Clock Hours: 120 Length of Period: 80 minutes Date Written: June 11, 2007 Periods
Station 1: The Celsius Thermometer
 Station 1: The Celsius Thermometer Thermometers can be made with alcohol, or mercury. We will be using alcohol thermometers. Mercury is a dangerous substance that can be hazardous to your health if are
Station 1: The Celsius Thermometer Thermometers can be made with alcohol, or mercury. We will be using alcohol thermometers. Mercury is a dangerous substance that can be hazardous to your health if are
Science Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather
 Unit: 01 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 5 days Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
Unit: 01 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 5 days Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
