Chapter 2 Lecture 7 Longitudinal stick fixed static stability and control 4 Topics
|
|
|
- Dennis Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter 2 Lecture 7 Longitudinal stick ixed static stability and control 4 Topics Revised expression or mcgt mαt in stick-ixed case 2.5 ontributions o uselage to mcg and mα ontribution o body to mα based on slender body theory orrection to moment contribution o uselage or ineness ratio orrection to moment contribution o uselage or non-circular cross-section orrection to moment contribution o uselage or uselage camber ontribution o nacelle to mα Revised expression or mcgt Substituting or Lt in Eq.(2.37) gives: mcgt = -VHη Lαt[it - ε 0+α(1- )+ δ e+ tabδ tab] = mot - V H η Lαt [α(1- )+ δ e+ tab δ tab] (2.47) where, = / ; tab = / δ α δ α Lt Lt Lt Lt e t (2.48) and mot = - V H η Lαt (i t - ε 0 ) (2.49) mαt in stick-ixed case It may be pointed out that the pilot moves the elevator through the orward and backward movements o the control stick. Further, depending on the values o chosen light speed and altitude, the pilot adjusts the positions o the elevator to make mcg equal to zero. In small airplanes, like the general aviation airplanes, the pilot continues to hold the stick and maintain the elevator delection. In this background the analysis o the static stability o an airplane where the control Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 1
2 delection remains same even ater disturbance is called static stability stickixed. Hence, to obtain an expression or in stick-ixed case it is assumed that the mαt elevator delection (δ e ) and the tab delection (δ t ) remain unchanged ater the disturbance. Accordingly when Eq.(2.47) is dierentiated with respect to α,the derivatives o δ e and δ t are zero i.e., in this case, (dδ e /) = (dδ t /) = 0 and the ollowing result is obtained: ( mαt ) stick ixed = - VH η Lαt(1- ) Remarks: i) mαt is negative. To illustrate this, consider typical values as: η = 0.9, V H = 0.5, Lαt = 4.0 per radian and / = 0.4. Then, mαt = -0.5 x 0.9 x 4 x (1-0.4) = /radian. ii) V H depends on (S t /S) and (l t / c ). Hence, the contribution o tail to stability ( mαt ) can be increased in magnitude by increasing (S t /S) or (l t /c ) i.e. by increasing the area o the horizontal tail or by shiting the tail backwards. iii) m0 is the value o mcg when α is zero. It ( m0 ) is the sum o terms like (2.50) mow, mot etc. This value ( m0 ) can be adjusted by changing m0t. In this context we observe rom Eq.(2.49) that: m0t = - VH η Lαt(it - ε 0) This suggests that by choosing a suitable value o i t, the value o mo can be adjusted. This would permit trim, with zero elevator delection, at a chosen value o lit coeicient (see Fig.2.6 and example 2.5). The chosen value o L or this purpose is invariably the value o L during cruise. This serves as criterion or selecting tail setting. iv) In the beginning o this section a reason or examination o the stick-ixed stability was given by considering the case o general aviation airplane. However, the analysis o stick-ixed stability is carried out or all airplanes and the level o ( mαt ) stick-ixed decides the elevator delection required in steady light and in manoeuvres (see subsections and 4.2). Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 2
3 2.5 ontributions o uselage to mcg and mα Fuselage and nacelle are classiied as bodies. The steps or estimating the contributions o a body to mcg and mα are based on the descriptions in chapter 2, o Re.1.1, chapter 5 o Re.1.7 and chapter 3 o Re In this approach, the contribution o the body to mα is estimated based on the slender body theory and subsequently applying corrections or the eects o (a) inite ineness ratio, (b) non-circular cross section, (c) uselage camber and (d) downwash due to wing ontribution o body to mα based on slender body theory The potential low past and an axisymmetric slender body was studied by Munk in 1924 (see Re.1.1, chapter 2 or bibliographic details). He showed that a body at an angle o attack has a pressure distribution as shown in Fig.2.18 and produces no net orce, but a moment. He showed that the rate o change o moment with angle o attack α, in radians, is given by: dm 1 = 2q volume o body ;q = ρv 2 Alternatively when α is in degrees, 2 dm Volume o body q = 28.7 (2.51) Fig.2.18 Streamlines and potential low pressure distribution on an axisymmetric body; the negative and positive signs indicate respectively that the local pressure is lower or higher than the ree stream pressure Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 3
4 Remark: In a viscous low, the pressure distribution about the body changes and it experiences lit and drag orrection to moment contribution o uselage or ineness ratio Generally the uselage has a inite length. For such a uselage Multhopp in 1942 (see Re.1.1, chapter 2 or bibliographic details) suggested the ollowing correction to Eq.(2.51). dm (k2-k 1) = q x volume o body 28.7 (2.52) Where, (k 2 -k 1 ) is a actor which depends on the ineness ratio (l /d e ) o the body; l is the length o the body and d e is the equivalent diameter deined as: (π/4)d e 2 = max. cross sectional area o uselage. Figure 2.19 presents variation o (k 2 -k 1 ) with ineness ratio Fig.2.19 orrection to moment contribution o uselage or ineness ratio (Adapted rom Re.2.2, section ) orrection to moment contribution o uselage or non-circular cross section For a uselage o non-circular cross-section, Eq.(2.52) is modiied as: l l dm (k2-k 1)q π 2 (k2-k 1)q = w dx = w 2 dx (2.53) 0 0 Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 4
5 where, w is the local width o the uselage. Hence, the contribution o uselage to mα can be expressed as : dm mα = (2.54) 1ρV 2 Sc orrection to moment contribution due to uselage or uselage camber and downwash due to wing In an airplane, the low past a uselage is aected by the upwash-downwash ield o the wing (Fig.2.12). Further, the midpoints o the uselage cross sections may not lie in a straight line. In such a case the uselage is said to have a camber (Fig.2.20). A uselage with camber would produce a pitching moment coeicient ( mo ) even when FRL is at zero angle o attack. Fig.2.20 Fuselage with camber For a uselage with camber, mcg is expressed as: mcg = m0 + mαα (2.55) with k -k = w (α +i )Δx and (2.56) 36.5Sc l m0 0L x=0 Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 5
6 k -k mα = w Δx 36.5Sc l x=0 (2.57) where, (a) w is the average width over a length Δx o uselage (Fig.2.21) (b) i is the incidence angle o uselage camber line with respect to FRL. It is taken negative when there is nosedrop or at upsweep (Fig.2.20). (c ) α 0L is the zero lit angle o wing relative to FRL i.e. α 0L = α 0Lw + i w and (d) / is the derivative with α o the local value o upwash / downwash along the uselage. Fig.2.21 Division o uselage or calculation o m0 Though / along the uselage can be calculated rom an approach like the liting line theory, the ollowing emprical procedure is generally regarded adequate or evaluating mα. a) The uselage is divided into segments as shown in Fig.(2.22). b) The local value o, / ahead o the wing is denoted by u /. It is estimated rom Fig.(2.23). For the segment immediately ahead o the wing (section 5 in Fig.2.22) the value o u / varies rapidly and is estimated rom the curve b in Fig.2.23 (see example 2.4). For other segments ahead o wing, the curve a in the same igure is used to estimate u /. (c) For the portion o the uselage covered by the wing root (length c indicated in Fig.2.22) / is taken as zero. Actually, the contribution o this portion is taken to be zero as, this portion is accounted or under the wing area. Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 6
7 Fig.2.22 Division o uselage or calculation o mα Fig.2.23 Upwash ield ahead o wing (Adapted rom Re.2.2, section ) Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 7
8 (d) For the portion o the uselage behind the wing (segments 6 to 11 in Fig.2.22), / is assumed to vary linearly rom 0 to {1- (/) tail } where (/) tail is the value o (/) at a.c. o tail. Hence, x i = [1- ( ) tail] lt (2.58) The procedure is illustrated in example 2.4 or a low speed airplane and in Appendix or a jet airplane Remarks: i) In Re.2.2, the quantity / o Eq.(2.57) is written as (1+ / ) and values o / therein are accordingly lower by one as compared to those in Fig ii) The values in Fig.2.23 are or a LαWB o /deg. LαWB is the slope o lit curve o the wing-body combination which is roughly equal to LαW when the aspect ratio o the wing is greater than ive. For other values o LαW multiply the values o / by a actor o ( LαW /0.0785). Note that LαW is in deg -1. See also example ontribution o nacelle to mα The contribution o nacelle to mα can be calculated in a manner similar to that or the uselage. Generally it is neglected. Dept. o Aerospace Engg., IIT Madras 8
Chapter 2 Lecture 9 Longitudinal stick fixed static stability and control 6 Topics
 hapter Leture 9 Longitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 6 Topis Eample.4 Eample.4 Referene.4 desribes the stability and ontrol data for ten airplanes. This inludes a general aviation airplane
hapter Leture 9 Longitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 6 Topis Eample.4 Eample.4 Referene.4 desribes the stability and ontrol data for ten airplanes. This inludes a general aviation airplane
Chapter 2 Lecture 8 Longitudinal stick fixed static stability and control 5 Topics
 Flight dynamis II Stability and ontrol hapter 2 Leture 8 Longitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 5 Topis 2.6 ontributions of power plant to mg and mα 2.6.1 Diret ontributions of powerplant to
Flight dynamis II Stability and ontrol hapter 2 Leture 8 Longitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 5 Topis 2.6 ontributions of power plant to mg and mα 2.6.1 Diret ontributions of powerplant to
Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture- 05 Stability: Tail Contribution and Static Margin (Refer Slide Time: 00:15)
Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture- 05 Stability: Tail Contribution and Static Margin (Refer Slide Time: 00:15)
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required,
 Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur
 Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur Problems Stability Tail Contribution Completed We were trying to understand whatever
Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur Problems Stability Tail Contribution Completed We were trying to understand whatever
Chapter 1 Lecture 2. Introduction 2. Topics. Chapter-1
 Chapter 1 Lecture 2 Introduction 2 Topics 1.4 Equilibrium of airplane 1.5 Number of equations of motion for airplane in flight 1.5.1 Degrees of freedom 1.5.2 Degrees of freedom for a rigid airplane 1.6
Chapter 1 Lecture 2 Introduction 2 Topics 1.4 Equilibrium of airplane 1.5 Number of equations of motion for airplane in flight 1.5.1 Degrees of freedom 1.5.2 Degrees of freedom for a rigid airplane 1.6
AE Stability and Control of Aerospace Vehicles
 AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
Flight Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege
 Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
and K becoming functions of Mach number i.e.: (3.49)
 Chapter 3 Lecture 11 Drag polar 6 Topics 3.3.4 Parabolic drag polar at high speeds 3.3.5 Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes 3.3.6 Variations of C Do and K for
Chapter 3 Lecture 11 Drag polar 6 Topics 3.3.4 Parabolic drag polar at high speeds 3.3.5 Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes 3.3.6 Variations of C Do and K for
Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 2
 Chapter 6 Lecture Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide Topics 6.5 Maximum rate of climb and imum angle of climb 6.5. Parameters influencing (R/C) of a jet airplane 6.5. Parameters influencing
Chapter 6 Lecture Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide Topics 6.5 Maximum rate of climb and imum angle of climb 6.5. Parameters influencing (R/C) of a jet airplane 6.5. Parameters influencing
Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics
 David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40)
 APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
Mechanics of Flight. Warren F. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY
 Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
Chapter 8 Performance analysis IV Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 27) Keywords: Topics 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Accelerated level flight
 Chapter 8 Performance analysis I Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 7) Keywords: Accelerated level flight; accelerated climb; energy height. Topics 8.1 Introduction 8. Accelerated level flight
Chapter 8 Performance analysis I Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 7) Keywords: Accelerated level flight; accelerated climb; energy height. Topics 8.1 Introduction 8. Accelerated level flight
Chapter 5 Lecture 19. Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3. Topics. Chapter-5
 Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Chapter 3 Lecture 8. Drag polar 3. Topics. Chapter-3
 Chapter 3 ecture 8 Drag polar 3 Topics 3.2.7 Boundary layer separation, adverse pressure gradient and favourable pressure gradient 3.2.8 Boundary layer transition 3.2.9 Turbulent boundary layer over a
Chapter 3 ecture 8 Drag polar 3 Topics 3.2.7 Boundary layer separation, adverse pressure gradient and favourable pressure gradient 3.2.8 Boundary layer transition 3.2.9 Turbulent boundary layer over a
A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
 A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN ROBBIE BUNGE 1. Introduction The longitudinal dynamics of fixed-wing aircraft are a case in which classical
A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN ROBBIE BUNGE 1. Introduction The longitudinal dynamics of fixed-wing aircraft are a case in which classical
/ m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6]
![/ m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6] / m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6]](/thumbs/91/105418625.jpg) Code No: R05322101 Set No. 1 1. (a) Explain the following terms with examples i. Stability ii. Equilibrium. (b) Comment upon the requirements of stability of a i. Military fighter aircraft ii. Commercial
Code No: R05322101 Set No. 1 1. (a) Explain the following terms with examples i. Stability ii. Equilibrium. (b) Comment upon the requirements of stability of a i. Military fighter aircraft ii. Commercial
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters 2 Lecture 20 Topics
 Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight. Questions
 Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight Questions Q. If only the elevator size of a given aircraft is decreased; keeping horizontal tail area unchanged; then the aircraft
Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight Questions Q. If only the elevator size of a given aircraft is decreased; keeping horizontal tail area unchanged; then the aircraft
Chapter 3 Lecture 14 Longitudinal stick free static stability and control 3 Topics
 Chaptr 3 Lctur 14 Longitudinal stick fr static stability and control 3 Topics 3.4.4 Rquirmnt for propr stick forc variation 3.4.5 Fl of th stability lvl by th pilot Exampl 3.3 3.5 Dtrmination of stick-fr
Chaptr 3 Lctur 14 Longitudinal stick fr static stability and control 3 Topics 3.4.4 Rquirmnt for propr stick forc variation 3.4.5 Fl of th stability lvl by th pilot Exampl 3.3 3.5 Dtrmination of stick-fr
Extended longitudinal stability theory at low Re - Application to sailplane models
 Extended longitudinal stability theory at low Re - Application to sailplane models matthieu.scherrer@free.fr November 26 C L C m C m W X α NP W X V NP W Lift coefficient Pitching moment coefficient Pitching
Extended longitudinal stability theory at low Re - Application to sailplane models matthieu.scherrer@free.fr November 26 C L C m C m W X α NP W X V NP W Lift coefficient Pitching moment coefficient Pitching
Spacecraft and Aircraft Dynamics
 Spacecraft and Aircraft Dynamics Matthew M. Peet Illinois Institute of Technology Lecture 4: Contributions to Longitudinal Stability Aircraft Dynamics Lecture 4 In this lecture, we will discuss Airfoils:
Spacecraft and Aircraft Dynamics Matthew M. Peet Illinois Institute of Technology Lecture 4: Contributions to Longitudinal Stability Aircraft Dynamics Lecture 4 In this lecture, we will discuss Airfoils:
9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram Flight limitations Operating envelop 9.4.
 Chapter 9 Lecture 31 Performance analysis V Manoeuvres 4 Topics 9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram 9.4.1 Flight limitations 9.4.2 Operating envelop 9.4.3 V-n
Chapter 9 Lecture 31 Performance analysis V Manoeuvres 4 Topics 9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram 9.4.1 Flight limitations 9.4.2 Operating envelop 9.4.3 V-n
Aircraft Design I Tail loads
 Horizontal tail loads Aircraft Design I Tail loads What is the source of loads? How to compute it? What cases should be taken under consideration? Tail small wing but strongly deflected Linearized pressure
Horizontal tail loads Aircraft Design I Tail loads What is the source of loads? How to compute it? What cases should be taken under consideration? Tail small wing but strongly deflected Linearized pressure
Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3
 Chapter 6 Lecture 3 Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3 Topics 6.6. Climb hydrograph 6.7. Absolute ceiling and service ceiling 6.8 Time to climb 6.9 Steady descent 6.0 Glide 6.0.
Chapter 6 Lecture 3 Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3 Topics 6.6. Climb hydrograph 6.7. Absolute ceiling and service ceiling 6.8 Time to climb 6.9 Steady descent 6.0 Glide 6.0.
ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics of 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Effects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool)
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT D: Applied Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics o 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Eects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool) AE301 Aerodynamics I : List o Subjects
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT D: Applied Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics o 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Eects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool) AE301 Aerodynamics I : List o Subjects
Solving Partial Differential Equations Numerically. Miklós Bergou with: Gary Miller, David Cardoze, Todd Phillips, Mark Olah
 Solving Partial Dierential Equations Numerically Miklós Bergou with: Gary Miller, David Cardoze, Todd Phillips, Mark Olah Overview What are partial dierential equations? How do we solve them? (Example)
Solving Partial Dierential Equations Numerically Miklós Bergou with: Gary Miller, David Cardoze, Todd Phillips, Mark Olah Overview What are partial dierential equations? How do we solve them? (Example)
April 15, 2011 Sample Quiz and Exam Questions D. A. Caughey Page 1 of 9
 April 15, 2011 Sample Quiz Exam Questions D. A. Caughey Page 1 of 9 These pages include virtually all Quiz, Midterm, Final Examination questions I have used in M&AE 5070 over the years. Note that some
April 15, 2011 Sample Quiz Exam Questions D. A. Caughey Page 1 of 9 These pages include virtually all Quiz, Midterm, Final Examination questions I have used in M&AE 5070 over the years. Note that some
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005
 University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3)
 Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3) Keywords : Importance of stability and control analysis ; brief historical background ; basic concepts static stability, dynamic stability, longitudinal, lateral
Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3) Keywords : Importance of stability and control analysis ; brief historical background ; basic concepts static stability, dynamic stability, longitudinal, lateral
Chapter 2 Lecture 5 Longitudinal stick fixed static stability and control 2 Topics
 hapter 2 eture 5 ongitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 2 Topis 2.2 mg and mα as sum of the ontributions of various omponent 2.3 ontributions of ing to mg and mα 2.3.1 orretion to mα for effets
hapter 2 eture 5 ongitudinal stik fied stati stability and ontrol 2 Topis 2.2 mg and mα as sum of the ontributions of various omponent 2.3 ontributions of ing to mg and mα 2.3.1 orretion to mα for effets
Introduction to Flight Dynamics
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Flight Dynamics Flight dynamics deals principally with the response of aerospace vehicles to perturbations in their flight environments and to control inputs. In order to understand
Chapter 1 Introduction to Flight Dynamics Flight dynamics deals principally with the response of aerospace vehicles to perturbations in their flight environments and to control inputs. In order to understand
A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system
 ANZIAM J. 47 (EMAC2005) pp.c615 C632, 2007 C615 A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system C. K. H. Chin R. L. May (Received 2 November 2005; revised 31 January 2007) Abstract We integrate together
ANZIAM J. 47 (EMAC2005) pp.c615 C632, 2007 C615 A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system C. K. H. Chin R. L. May (Received 2 November 2005; revised 31 January 2007) Abstract We integrate together
Airfoils and Wings. Eugene M. Cliff
 Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
Chapter 8 Dynamic stability analysis II Longitudinal motion (Lectures 28 to 32)
 Chapter 8 Dynamic stability analysis II Longitudinal motion (Lectures 28 to 32) Keywords : Stability quartic or characteristic equation for longitudinal motion and its solution ; roots of characteristic
Chapter 8 Dynamic stability analysis II Longitudinal motion (Lectures 28 to 32) Keywords : Stability quartic or characteristic equation for longitudinal motion and its solution ; roots of characteristic
Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate?
 water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
PRINCIPLES OF FLIGHT
 1 Considering a positive cambered aerofoil, the pitching moment when Cl=0 is: A infinite B positive (nose-up). C negative (nose-down). D equal to zero. 2 The angle between the aeroplane longitudinal axis
1 Considering a positive cambered aerofoil, the pitching moment when Cl=0 is: A infinite B positive (nose-up). C negative (nose-down). D equal to zero. 2 The angle between the aeroplane longitudinal axis
The Ascent Trajectory Optimization of Two-Stage-To-Orbit Aerospace Plane Based on Pseudospectral Method
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 00 (014) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia APISAT014, 014 Asia-Paciic International Symposium on Aerospace Technology,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 00 (014) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia APISAT014, 014 Asia-Paciic International Symposium on Aerospace Technology,
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum
 DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
Design, Analysis and Research Corporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight Controls Part I
 Design, Analysis and Research Corporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight Controls Part I Copyright 00 by Dr. Jan Roskam Year of Print, 00 (Errata Revised August
Design, Analysis and Research Corporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight Controls Part I Copyright 00 by Dr. Jan Roskam Year of Print, 00 (Errata Revised August
Consider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution:
 Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Controlling the Heat Flux Distribution by Changing the Thickness of Heated Wall
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 2(7)7270-7275, 2012 2012, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal o Basic and Applied Scientiic Research www.textroad.com Controlling the Heat Flux Distribution by Changing
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 2(7)7270-7275, 2012 2012, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal o Basic and Applied Scientiic Research www.textroad.com Controlling the Heat Flux Distribution by Changing
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows
 Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Alternative Expressions for the Velocity Vector Velocity restricted to the vertical plane. Longitudinal Equations of Motion
 Linearized Longitudinal Equations of Motion Robert Stengel, Aircraft Flig Dynamics MAE 33, 008 Separate solutions for nominal and perturbation flig paths Assume that nominal path is steady and in the vertical
Linearized Longitudinal Equations of Motion Robert Stengel, Aircraft Flig Dynamics MAE 33, 008 Separate solutions for nominal and perturbation flig paths Assume that nominal path is steady and in the vertical
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
High Speed Aerodynamics. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow
 39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
Thin airfoil theory. Chapter Compressible potential flow The full potential equation
 hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
SPC Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30
 SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
Modelling the dynamics of an unmanned aircraft using a graphical simulation tool
 Modelling the dynamics of an unmanned aircraft using a graphical simulation tool Sara Jansson Ahmed Department of Aeronautical and Vehicle Engineering KTH - Royal Institute of Technology SE 100 44 Stockholm,
Modelling the dynamics of an unmanned aircraft using a graphical simulation tool Sara Jansson Ahmed Department of Aeronautical and Vehicle Engineering KTH - Royal Institute of Technology SE 100 44 Stockholm,
Introduction to Aeronautics
 Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
Lecture 18. Waves and Sound
 Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Flight Dynamics, Simulation, and Control
 Flight Dynamics, Simulation, and Control For Rigid and Flexible Aircraft Ranjan Vepa CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an
Flight Dynamics, Simulation, and Control For Rigid and Flexible Aircraft Ranjan Vepa CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an
Objectives. By the time the student is finished with this section of the workbook, he/she should be able
 FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions......8 Absolute Value Functions.....48 Translations o Functions..57 Radical Functions...61 Eponential Functions...7 Logarithmic Functions......8 Cubic Functions......91 Piece-Wise
FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions......8 Absolute Value Functions.....48 Translations o Functions..57 Radical Functions...61 Eponential Functions...7 Logarithmic Functions......8 Cubic Functions......91 Piece-Wise
Flight Dynamics and Control
 Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Reference material Lecture Notes Flight Dynamics Principles, M.V. Cook, Arnold, 1997 Fundamentals of Airplane Flight
Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Reference material Lecture Notes Flight Dynamics Principles, M.V. Cook, Arnold, 1997 Fundamentals of Airplane Flight
Constrained Optimal Control I
 Optimal Control, Guidance and Estimation Lecture 34 Constrained Optimal Control I Pro. Radhakant Padhi Dept. o Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute o Science - Bangalore opics Motivation Brie Summary
Optimal Control, Guidance and Estimation Lecture 34 Constrained Optimal Control I Pro. Radhakant Padhi Dept. o Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute o Science - Bangalore opics Motivation Brie Summary
Chapter 4 The Equations of Motion
 Chapter 4 The Equations of Motion Flight Mechanics and Control AEM 4303 Bérénice Mettler University of Minnesota Feb. 20-27, 2013 (v. 2/26/13) Bérénice Mettler (University of Minnesota) Chapter 4 The Equations
Chapter 4 The Equations of Motion Flight Mechanics and Control AEM 4303 Bérénice Mettler University of Minnesota Feb. 20-27, 2013 (v. 2/26/13) Bérénice Mettler (University of Minnesota) Chapter 4 The Equations
Chapter 3 (Lectures 12, 13 and 14) Longitudinal stick free static stability and control
 Fligh dynamics II Sabiliy and conrol haper 3 (Lecures 1, 13 and 14) Longiudinal sick free saic sabiliy and conrol Keywords : inge momen and is variaion wih ail angle, elevaor deflecion and ab deflecion
Fligh dynamics II Sabiliy and conrol haper 3 (Lecures 1, 13 and 14) Longiudinal sick free saic sabiliy and conrol Keywords : inge momen and is variaion wih ail angle, elevaor deflecion and ab deflecion
FLIGHT DYNAMICS. Robert F. Stengel. Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford
 FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.)
 1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
Flight Vehicle Terminology
 Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Pitch Control of Flight System using Dynamic Inversion and PID Controller
 Pitch Control of Flight System using Dynamic Inversion and PID Controller Jisha Shaji Dept. of Electrical &Electronics Engineering Mar Baselios College of Engineering & Technology Thiruvananthapuram, India
Pitch Control of Flight System using Dynamic Inversion and PID Controller Jisha Shaji Dept. of Electrical &Electronics Engineering Mar Baselios College of Engineering & Technology Thiruvananthapuram, India
OE4625 Dredge Pumps and Slurry Transport. Vaclav Matousek October 13, 2004
 OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008
 Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008 Standards o Length, Mass, and Time ( - length quantities) - mass - time Derived Quantities: Examples Dimensional Analysis useul to check equations and to
Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008 Standards o Length, Mass, and Time ( - length quantities) - mass - time Derived Quantities: Examples Dimensional Analysis useul to check equations and to
Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December Anna University.
 Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December 006. Anna University. Time: 3 hours Answer ALL questions Part A- (10 x = 0 marks) Maximum:
Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December 006. Anna University. Time: 3 hours Answer ALL questions Part A- (10 x = 0 marks) Maximum:
Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow of A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium
 Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow o A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium Mostaa A.A.Mahmoud Department o Mathematics, Faculty o Science, Benha University (358), Egypt Abstract The
Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow o A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium Mostaa A.A.Mahmoud Department o Mathematics, Faculty o Science, Benha University (358), Egypt Abstract The
Giovanni Tarantino, Dipartimento di Fisica e Tecnologie Relative, Università di Palermo (Italia)
 THE INTERACTIVE PHYSICS FLIGHT SIMULATOR Giovanni Tarantino, Dipartimento di Fisica e Tecnologie Relative, Università di Palermo (Italia) Abstract This paper describes a modelling approach to the dynamics
THE INTERACTIVE PHYSICS FLIGHT SIMULATOR Giovanni Tarantino, Dipartimento di Fisica e Tecnologie Relative, Università di Palermo (Italia) Abstract This paper describes a modelling approach to the dynamics
ν δ - 1 -
 ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS. Convective heat transfer analysis of nanofluid flowing inside a
 Chapter 4 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS Convective heat transer analysis o nanoluid lowing inside a straight tube o circular cross-section under laminar and turbulent conditions
Chapter 4 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS Convective heat transer analysis o nanoluid lowing inside a straight tube o circular cross-section under laminar and turbulent conditions
16.333: Lecture # 7. Approximate Longitudinal Dynamics Models
 16.333: Lecture # 7 Approxiate Longitudinal Dynaics Models A couple ore stability derivatives Given ode shapes found identify sipler odels that capture the ain responses Fall 24 16.333 6 1 More Stability
16.333: Lecture # 7 Approxiate Longitudinal Dynaics Models A couple ore stability derivatives Given ode shapes found identify sipler odels that capture the ain responses Fall 24 16.333 6 1 More Stability
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments
 Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Aircraft & spacecraft loads Translating loads to stresses Faculty of Aerospace Engineering 29-11-2011 Delft University of Technology
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Aircraft & spacecraft loads Translating loads to stresses Faculty of Aerospace Engineering 29-11-2011 Delft University of Technology
Beam Bending Stresses and Shear Stress
 Beam Bending Stresses and Shear Stress Notation: A = name or area Aweb = area o the web o a wide lange section b = width o a rectangle = total width o material at a horizontal section c = largest distance
Beam Bending Stresses and Shear Stress Notation: A = name or area Aweb = area o the web o a wide lange section b = width o a rectangle = total width o material at a horizontal section c = largest distance
The polar for uncambered and cambered airfoils. The angel of attack α
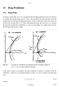 13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
Dynamics and Control Preliminary Examination Topics
 Dynamics and Control Preliminary Examination Topics 1. Particle and Rigid Body Dynamics Meirovitch, Leonard; Methods of Analytical Dynamics, McGraw-Hill, Inc New York, NY, 1970 Chapters 1-5 2. Atmospheric
Dynamics and Control Preliminary Examination Topics 1. Particle and Rigid Body Dynamics Meirovitch, Leonard; Methods of Analytical Dynamics, McGraw-Hill, Inc New York, NY, 1970 Chapters 1-5 2. Atmospheric
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW QUICK REFERENCE. Important Terms
 Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: , p-issn: X.Volume12,Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan.-Feb.2016)PP
 IOSR Journal o Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn:78-578, p-issn: 39-765X.Volume,Issue Ver. III (Jan.-Feb.6)PP 88- www.iosrjournals.org Eect o Chemical Reaction on MHD Boundary Layer Flow o Williamson Nanoluid
IOSR Journal o Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn:78-578, p-issn: 39-765X.Volume,Issue Ver. III (Jan.-Feb.6)PP 88- www.iosrjournals.org Eect o Chemical Reaction on MHD Boundary Layer Flow o Williamson Nanoluid
Asymptote. 2 Problems 2 Methods
 Asymptote Problems Methods Problems Assume we have the ollowing transer unction which has a zero at =, a pole at = and a pole at =. We are going to look at two problems: problem is where >> and problem
Asymptote Problems Methods Problems Assume we have the ollowing transer unction which has a zero at =, a pole at = and a pole at =. We are going to look at two problems: problem is where >> and problem
Design, Analysis and Research Corporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight Controls Part I
 Design, Analysis and Research orporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight ontrols Part I opyright 995 by Dr. Jan Roskam Year of Print, 995 (Errata Revised August 7,
Design, Analysis and Research orporation (DARcorporation) ERRATA: Airplane Flight Dynamics and Automatic Flight ontrols Part I opyright 995 by Dr. Jan Roskam Year of Print, 995 (Errata Revised August 7,
( 1) ( 2) ( 1) nan integer, since the potential is no longer simple harmonic.
 . Anharmonic Oscillators Michael Fowler Landau (para 8) considers a simple harmonic oscillator with added small potential energy terms mα + mβ. We ll simpliy slightly by dropping the term, to give an equation
. Anharmonic Oscillators Michael Fowler Landau (para 8) considers a simple harmonic oscillator with added small potential energy terms mα + mβ. We ll simpliy slightly by dropping the term, to give an equation
Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines.
 Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
A REPORT ON PERFORMANCE OF ANNULAR FINS HAVING VARYING THICKNESS
 VOL., NO. 8, APRIL 6 ISSN 89-668 ARPN Journal o Engineering and Applied Sciences 6-6 Asian Research Publishing Networ (ARPN). All rights reserved. A REPORT ON PERFORMANCE OF ANNULAR FINS HAVING VARYING
VOL., NO. 8, APRIL 6 ISSN 89-668 ARPN Journal o Engineering and Applied Sciences 6-6 Asian Research Publishing Networ (ARPN). All rights reserved. A REPORT ON PERFORMANCE OF ANNULAR FINS HAVING VARYING
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s
 One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diffusion
 Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Inverse Theory: What It Is and What It Does
 Geosciences 567: CHAPTER (RR/GZ) CHAPTER : INTRODUCTION Inverse Theory: What It Is and What It Does Inverse theory, at least as I choose to deine it, is the ine art o estimating model parameters rom data
Geosciences 567: CHAPTER (RR/GZ) CHAPTER : INTRODUCTION Inverse Theory: What It Is and What It Does Inverse theory, at least as I choose to deine it, is the ine art o estimating model parameters rom data
ESTIMATION OF PITCHING MOMENT OF A HYBRID LIFTING FUSELAGE - DISGUISED AS HULL OF AN AIRSHIP
 2006-2016 Asian Research Publishing Netork (ARPN). All rights reserved..arpnjournals.com ESTIMATION OF PITCHING MOMENT OF A HYBRID LIFTING FUSELAGE - DISGUISED AS HULL OF AN AIRSHIP Anar Ul Haque 1, Waqar
2006-2016 Asian Research Publishing Netork (ARPN). All rights reserved..arpnjournals.com ESTIMATION OF PITCHING MOMENT OF A HYBRID LIFTING FUSELAGE - DISGUISED AS HULL OF AN AIRSHIP Anar Ul Haque 1, Waqar
Chapter 3 Weight estimation - 2 Lecture 7 Topics
 Chater-3 Chater 3 eight estimation - 2 ecture 7 Toics 3.5 Estimation o uel raction ( / 0 ) 3.5.1 Mission roile 3.5.2 eight ractions or various segments o mission 3.5.3 Fuel raction or warm u, taxing and
Chater-3 Chater 3 eight estimation - 2 ecture 7 Toics 3.5 Estimation o uel raction ( / 0 ) 3.5.1 Mission roile 3.5.2 eight ractions or various segments o mission 3.5.3 Fuel raction or warm u, taxing and
Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics
 Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics 4.12 Introductory remarks on choice of engine 4.13 Engines considered for airplane applications 4.14 Piston engine-propeller
Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics 4.12 Introductory remarks on choice of engine 4.13 Engines considered for airplane applications 4.14 Piston engine-propeller
Lecture-4. Flow Past Immersed Bodies
 Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag
 Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
Localizer Hold Autopilot
 Localizer Hold Autopilot Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Localizer hold autopilot is one of the important
Localizer Hold Autopilot Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Localizer hold autopilot is one of the important
Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. Increasing and Decreasing Functions. Video
 SECTION and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 79 Section and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is increasing or decreasing Appl
SECTION and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 79 Section and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is increasing or decreasing Appl
AN ENHANCED CORRECTION FACTOR TECHNIQUE FOR AERODYNAMIC INFLUENCE COEFFICIENT METHODS
 AN ENHANCED CORRECTION ACTOR TECHNIQUE OR AERODYNAMIC INLUENCE COEICIENT METHODS Ioan Jadic, Dayton Hartley and Jagannath Giri Raytheon Aircraft Company, Wichita, Kansas 67-85 Phone: 36-676-436 E-mail:
AN ENHANCED CORRECTION ACTOR TECHNIQUE OR AERODYNAMIC INLUENCE COEICIENT METHODS Ioan Jadic, Dayton Hartley and Jagannath Giri Raytheon Aircraft Company, Wichita, Kansas 67-85 Phone: 36-676-436 E-mail:
HYDROMAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID
 Rita Choudhury et al. / International Journal o Engineering Science and Technology (IJEST) HYDROAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID RITA CHOUDHURY Department
Rita Choudhury et al. / International Journal o Engineering Science and Technology (IJEST) HYDROAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID RITA CHOUDHURY Department
Heat-fluid Coupling Simulation of Wet Friction Clutch
 3rd International Conerence on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2015) Heat-luid Coupling Simulation o Wet Friction Clutch Tengjiao Lin 1,a *, Qing Wang 1, b, Quancheng Peng 1,c and Yan Xie
3rd International Conerence on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2015) Heat-luid Coupling Simulation o Wet Friction Clutch Tengjiao Lin 1,a *, Qing Wang 1, b, Quancheng Peng 1,c and Yan Xie
