SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 8: State Variable Feedback Control Systems
|
|
|
- Leona Miles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 8: Sae Variable Feedback Conrol Syses INTRODUCTION Sae variable descripions for dynaical syses describe he evoluion of he sae vecor, as a funcion of he sae and he inpu. There ay be an oupu equaion as well, bu we shall no be concerned wih i in his discussion. For coninuous ie syses he sae equaion is a differenial equaion of he for f, u. In his equaion, he sae and he conrol inpu u are vecors. Therefore he funcion f, u is also vecor valued. If one akes he inpu a funcion of he sae, u g hen he syse is a sae variable feedback syse. The funcion g is called a conrol law. We shall sudy wo eaples of sae variable conrol syses in his lab. I is generally he case ha he differenial equaions are non-linear. Therefore hey are very difficul o sudy, alhough hey are no paricularly difficul o siulae nuerically using soehing like MATLAB. One analyical design ool which can be used in he viciniy of a vecor is a linearizaion of he syse. This is an approiaion which is valid only for sall disances fro. Provided ha f,, or is a res poin, hen he linearized syse is 3 z Az + Bu, where z is he deviaion of he sae vecor fro he noinal poin. The arices A and B are copued fro he funcion f, u as follows: 5 A i, j fi j, u and 6 B i, j fi u j., u The righ hand side of equaion 3 conains he linear ers in a Taylor series approiaion of he righ hand side of equaion. Using he linearizaion, one can apply several well-known design ehods for linear syses o obain a conrol sraegy. Once ipleened however, he syse will perfor well only in he region for which he linear approiaion is good. We will ge a ase of his in he second proble o be sudied in his lab. Page of 8
2 TIME OPTIMAL CONTROL OF A LINEAR SYSTEM BUSHAW S PROBLEM u Figure One A echanical syse aced upon by a force u. Consider a rigid body of ass aced upon by a single force. If he syse is consrained o ove in one diension only hen Newon s law of oion is F a. For sipliciy, se he ass o, and call he force u. Then he differenial equaion describing he oion is u. This syse is he uliae in sipliciy, bu i can ake for an ineresing conrol proble. In sae variable for, i has diension wo. If we define he sae vecor o be 7, hen he siple equaion u becoes 8 + u, which is in he for A + Bu. One can ake a feedback syse ou of his by aking he conrol inpu u o be a funcion of he sae vecor. We shall ake his proble ore pracical by consraining he inpu: Conrol inpu consrain: u, for each. This consrain is realisic in any siuaions. For our proble, i liis he acceleraion o a os. A ypical proble involving a bounded inpu is he ie opial conrol proble. The goal is o drive he syse fro any iniial sae o a specified arge in iniu ie. The soluion o his proble is usually bang-bang, which is a colorful way of saying ha he conrol u is alos always or -. In oher words he inpu is always on he boundary of he consrained se of allowable inpus. A feedback conrol law has he for 9 u g,. If we respec he consrain, his funcion canno be linear. Thus he feedback syse will be nonlinear, and will be described by he differenial equaion g, +. Page of 8
3 Figure Two conains phase plane porrais of he nonlinear syse described by equaion, wih differen conrol laws. These are u aiu acceleraion u aiu deceleraion, if v, linear wih sauraion u γ whereγ v v, if v, if v u sign + bang-bang conrol. u is always eiher full on or full off u u - Linear, wih clipping bang-bang conrol Figure Two Trajecories of he syse u wih four choices for u. Page 3 of 8
4 Eaine he -file doublin., or double inegraor, found on he web page, and ake noe of how he differenial equaions are nuerically inegraed, using MATLAB: becoes + d + d or +d*. u becoes + d + u d or +d*u. funcion doublina,b,g % doublina,b,g % run he double inegraor. % a and b are vecors of diension % g is a sring describing he conrol funcion % ug, L;T;dT/L;d*[:L-];epsilon.; zeros,l;vzeros,l; :,a;a;a; k; while k<lsuabs[;]-b>epsilon; uevalg; +d*;+d*u; :,k[;]; vku; kk+; end % We have no shown several lines which draw graphs u -sign*+*abs u phase plane elapsed ie Figure Three A siulaion of he syse, using he bang-bang conrol law. The equaions are, u, which is apparen fro he graph. Page of 8
5 This ool nuerically inegraes he differenial equaions and produces he graphs shown in Figure Three. The conrol law is passed as a sring, and herefore you can run he syse for any law ha you can wrie an epression for. The paraeers a and b are colun vecors of diension, wih a he iniial sae and b a arge sae. The siulaion will erinae if he rajecory ges close o b, or if he ie ges o, whichever happens firs. Here is an eaple:»g -sign*+*abs ;»doublin[-;],[;],g.938 The final ie is prined. In his eaple i is jus shor of seconds. See Figure Three. Assignen:. Copue he soluions o he differenial equaion 7 for arbirary iniial condiions, when u. In oher words find forulas for and when a and a.. Design a conrol law u g, which akes he syse o he poin, in iniu 3 ie. The conrol us no violae he consrain ha u, and should work for any choice of iniial condiions. Use he ool doublin. o es your conrol law g. For eaple,»doublinrandn,,[-3;],g eercises he syse wih a rando iniial sae. For your repor, include wo randoized sars, and he specific case»doublin[;],[-3;],g Also repor your conrol law g, and he design philosophy you used o ge i. THE CART AND THE PENDULUM The broo balancing or invered pendulu syse shown in Figure Four has been a popular eaple for any years. The proble is o keep he ball in he air. Noe ha he applied force is raher indirec. We can only ove he car horizonally and hereby influence he pendulu indirecly. This proble is very close o he one ha gave he early builders of rockes headaches. A rocke us be guided fro he base by swiveling he rocke nozzles. If you have seen ovies of early rocke launches, you will have seen rockes ha had o be desroyed because hey wen off course. In his lab we will siulae he dynaics of his syse using he MATLAB differenial equaion solver ode3. We will siulae he oion wih zero applied force, and hen aep o sabilize he syse, abou is unsable zero sae posiion, by linearizing and hen using a linear conrol law. You will sudy his sabilizaion proble, and ge soe daa on is liiaions. The syse is governed by a pair of coupled, second order nonlinear differenial equaions. In order o use he equaion solver we shall pu he in sae variable for. Ne, we will linearize he sae variable equaions abou he unsable res poin where he car and pendulu are a res wih he pendulu sraigh up:. For he resuling linear sae variable equaion, we can ge a sabilizing linear feedback conrol law. Page 5 of 8
6 Page 6 of 8 rigid pendulu of lengh L and ass ball of ass u pendulu angle, easured counerclockwise fro verical car posiion car of ass Conrol Force Figure Four The Car and he Pendulu wih apologies o Edgar Allen Poe Here are all he equaions: Equaions of oion of he car and pendulu sin sin cos sin cos g u Definiion of Sae vecor for he car and pendulu 3 Non-linear Sae Variable Equaions for he car and pendulu 3 + sin sin cos cos g u
7 Linearized Sae Variable Equaions abou he zero sae A + Bu, where Linear feedback conrol law A g + g, and B. 5 u G, where G [g g g 3 g ]. Linearized Feedback syse 6 A + BG. The MATLAB differenial equaion solver ode3 ay be used o copue soluions o he nonlinear equaions. Use he help faciliy o see how ode3 are used. To ake he graph shown in Figure Five, use he following coands: [,y]ode3 car,,,[;pi/6;;]; subplo,,,plo,y:,;ile subplo,,,plo,y:,;ile \hea.5 6 hea Figure Five Car posiion and pendulu angle as a funcion of ie, when he conrol force is zero, for iniial condiions, bu π / 6. This is he siuaion depiced in Figure Four. Page 7 of 8
8 The sring car idenifies he -file car. locaed on he webpage, which conains he equaions. funcion docar, % docar, % Nonlinear equaions of oion for he Car and % pendulu syse, for use by he MATLAB ode solver ode3 g;m;u; %conrol force for free oion % u[ ]*; % a linear feedback law ccos;ssin; do[3:;inv[m+ -c;-c ]*[u-^*s;g-3**s]]; Visualize he oion of he car and pendulu as he curves in Figure Five depic i. The pendulu falls o he lef and coes up again o an angle opposie he saring angle. I coes o res oenarily and hen reverses iself. Meanwhile he car is rocking back and forh in a periodic oion. The horizonal coponen of oenu is zero for his se of iniial condiions, and wih no force applied. Therefore he car does no have any aggregae horizonal oion. Noice ha here is a choice of conrol inpus in he -file car.. You can acivae he linear feedback law by reoving he coen characer. Wih a lile era effor, one can even produce a priiive ovie of he oion of he car. The -file covie., found on he webpage under -files for Lab 8, assebles several fraes based on he soluion o he differenial equaion, o ake a ovie. Assignen:»[,y]ode3 car,[ 3],[;pi/8;;]; % solve he diff. eqn.»figure,plo,y:,[ ] % This plos and hea»figure % resize he window. Make i sall!»covie_deo % his uses he array y copued by ode3»oviem,3 % M is he ovie produced by covie 3. Using he definiions in equaions 5 and 6, copue he arices A and B of he linearizaion of he syse abou he zero sae. Your resuls should agree wih equaion.. In MATLAB coand ode, creae he arices A and B of he linearized equaion, using he values and g. Then consruc he by ari G[.6,-53.6,5., -9.]. Using he MATLAB eig funcion o coue eigenvalues, copue he eigenvalues of he open-loop syse, eiga, and he eigenvalues of he closed-loop syse, eiga+b*g. Wha do you conclude abou he behavior of he wo syses in he viciniy of he zero sae? 5. Now siulae he car and pendulu syse using ode3 in a anner siilar o he eaple above, ecep ha he -file car. should be edied o acivaed he linear feedback conrol law. Use he sae iniial condiions as in he eaple, bu wih a greaer ie lii. Plo he resuling and hea. Then ry o ake a ovie. Now vary he iniial condiions [ hea ]. Making several runs, wih a shor ie duraion, ry o characerize he region abou he poin, in he,, plane for which he linear conrol syse can balance he broo. Choose several pairs and hen ake arks on he plane of he for + if he pendulu is balanced and - if i isn. Page 8 of 8
Introduction to Numerical Analysis. In this lesson you will be taken through a pair of techniques that will be used to solve the equations of.
 Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Thus the force is proportional but opposite to the displacement away from equilibrium.
 Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
Lecture 23 Damped Motion
 Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
M x t = K x F t x t = A x M 1 F t. M x t = K x cos t G 0. x t = A x cos t F 0
 Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
Homework 2 Solutions
 Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
Practice Problems - Week #4 Higher-Order DEs, Applications Solutions
 Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Viscous Damping Summary Sheet No Damping Case: Damped behaviour depends on the relative size of ω o and b/2m 3 Cases: 1.
 Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
(1) (2) Differentiation of (1) and then substitution of (3) leads to. Therefore, we will simply consider the second-order linear system given by (4)
 Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Higher Order Difference Schemes for Heat Equation
 Available a p://pvau.edu/aa Appl. Appl. Ma. ISSN: 9-966 Vol., Issue (Deceber 009), pp. 6 7 (Previously, Vol., No. ) Applicaions and Applied Maeaics: An Inernaional Journal (AAM) Higer Order Difference
Available a p://pvau.edu/aa Appl. Appl. Ma. ISSN: 9-966 Vol., Issue (Deceber 009), pp. 6 7 (Previously, Vol., No. ) Applicaions and Applied Maeaics: An Inernaional Journal (AAM) Higer Order Difference
Application of Homotopy Analysis Method for Solving various types of Problems of Partial Differential Equations
 Applicaion of Hooopy Analysis Mehod for olving various ypes of Probles of Parial Differenial Equaions V.P.Gohil, Dr. G. A. anabha,assisan Professor, Deparen of Maheaics, Governen Engineering College, Bhavnagar,
Applicaion of Hooopy Analysis Mehod for olving various ypes of Probles of Parial Differenial Equaions V.P.Gohil, Dr. G. A. anabha,assisan Professor, Deparen of Maheaics, Governen Engineering College, Bhavnagar,
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
x y θ = 31.8 = 48.0 N. a 3.00 m/s
 4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
Week 1 Lecture 2 Problems 2, 5. What if something oscillates with no obvious spring? What is ω? (problem set problem)
 Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Math Wednesday March 3, , 4.3: First order systems of Differential Equations Why you should expect existence and uniqueness for the IVP
 Mah 2280 Wednesda March 3, 200 4., 4.3: Firs order ssems of Differenial Equaions Wh ou should epec eisence and uniqueness for he IVP Eample: Consider he iniial value problem relaed o page 4 of his eserda
Mah 2280 Wednesda March 3, 200 4., 4.3: Firs order ssems of Differenial Equaions Wh ou should epec eisence and uniqueness for he IVP Eample: Consider he iniial value problem relaed o page 4 of his eserda
2.7. Some common engineering functions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
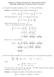 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Conservation of Momentum. The purpose of this experiment is to verify the conservation of momentum in two dimensions.
 Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION
 Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems. Lecture #3 What can go wrong? Trajectories of hybrid systems
 Hybrid Conrol and Swiched Sysems Lecure #3 Wha can go wrong? Trajecories of hybrid sysems João P. Hespanha Universiy of California a Sana Barbara Summary 1. Trajecories of hybrid sysems: Soluion o a hybrid
Hybrid Conrol and Swiched Sysems Lecure #3 Wha can go wrong? Trajecories of hybrid sysems João P. Hespanha Universiy of California a Sana Barbara Summary 1. Trajecories of hybrid sysems: Soluion o a hybrid
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY
 INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform. Joseph Fourier, our hero. Lord Kelvin on Fourier s theorem. What do we want from the Fourier Transform?
 ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
Math 2142 Exam 1 Review Problems. x 2 + f (0) 3! for the 3rd Taylor polynomial at x = 0. To calculate the various quantities:
 Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
Math Week 14 April 16-20: sections first order systems of linear differential equations; 7.4 mass-spring systems.
 Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
!!"#"$%&#'()!"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./0)1-*23)
 "#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
"#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
RC, RL and RLC circuits
 Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
HOMEWORK # 2: MATH 211, SPRING Note: This is the last solution set where I will describe the MATLAB I used to make my pictures.
 HOMEWORK # 2: MATH 2, SPRING 25 TJ HITCHMAN Noe: This is he las soluion se where I will describe he MATLAB I used o make my picures.. Exercises from he ex.. Chaper 2.. Problem 6. We are o show ha y() =
HOMEWORK # 2: MATH 2, SPRING 25 TJ HITCHMAN Noe: This is he las soluion se where I will describe he MATLAB I used o make my picures.. Exercises from he ex.. Chaper 2.. Problem 6. We are o show ha y() =
Y 0.4Y 0.45Y Y to a proper ARMA specification.
 HG Jan 04 ECON 50 Exercises II - 0 Feb 04 (wih answers Exercise. Read secion 8 in lecure noes 3 (LN3 on he common facor problem in ARMA-processes. Consider he following process Y 0.4Y 0.45Y 0.5 ( where
HG Jan 04 ECON 50 Exercises II - 0 Feb 04 (wih answers Exercise. Read secion 8 in lecure noes 3 (LN3 on he common facor problem in ARMA-processes. Consider he following process Y 0.4Y 0.45Y 0.5 ( where
Let us start with a two dimensional case. We consider a vector ( x,
 Roaion marices We consider now roaion marices in wo and hree dimensions. We sar wih wo dimensions since wo dimensions are easier han hree o undersand, and one dimension is a lile oo simple. However, our
Roaion marices We consider now roaion marices in wo and hree dimensions. We sar wih wo dimensions since wo dimensions are easier han hree o undersand, and one dimension is a lile oo simple. However, our
15. Vector Valued Functions
 1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Let us consider equation (6.16) once again. We have, can be found by the following equation
 41 Le us consider equaion (6.16) once again. We hae, dp d Therefore, d p d Here dp is he change in oenu caused by he force in he ie ineral d. Change in oenu caused by he force for a ie ineral 1, can be
41 Le us consider equaion (6.16) once again. We hae, dp d Therefore, d p d Here dp is he change in oenu caused by he force in he ie ineral d. Change in oenu caused by he force for a ie ineral 1, can be
4.5 Constant Acceleration
 4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
Chapter 3 Boundary Value Problem
 Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Physics 240: Worksheet 16 Name
 Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Constant Acceleration
 Objecive Consan Acceleraion To deermine he acceleraion of objecs moving along a sraigh line wih consan acceleraion. Inroducion The posiion y of a paricle moving along a sraigh line wih a consan acceleraion
Objecive Consan Acceleraion To deermine he acceleraion of objecs moving along a sraigh line wih consan acceleraion. Inroducion The posiion y of a paricle moving along a sraigh line wih a consan acceleraion
Echocardiography Project and Finite Fourier Series
 Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
MOMENTUM CONSERVATION LAW
 1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Exam #2 PHYSICS 211 Monday July 6 th, 2009 Please write down your name also on the back page of this exam
 Exa #2 PHYSICS 211 Monday July 6 h, 29 NME Please wrie down your nae also on he back pae of his exa 1. The fiure ives how he force varies as a funcion of he posiion. Such force is acin on a paricle, which
Exa #2 PHYSICS 211 Monday July 6 h, 29 NME Please wrie down your nae also on he back pae of his exa 1. The fiure ives how he force varies as a funcion of he posiion. Such force is acin on a paricle, which
1 Widrow-Hoff Algorithm
 COS 511: heoreical Machine Learning Lecurer: Rob Schapire Lecure # 18 Scribe: Shaoqing Yang April 10, 014 1 Widrow-Hoff Algorih Firs le s review he Widrow-Hoff algorih ha was covered fro las lecure: Algorih
COS 511: heoreical Machine Learning Lecurer: Rob Schapire Lecure # 18 Scribe: Shaoqing Yang April 10, 014 1 Widrow-Hoff Algorih Firs le s review he Widrow-Hoff algorih ha was covered fro las lecure: Algorih
dp dt For the time interval t, approximately, we can write,
 PHYSICS OCUS 58 So far we hae deal only wih syses in which he oal ass of he syse, sys, reained consan wih ie. Now, we will consider syses in which ass eners or leaes he syse while we are obsering i. The
PHYSICS OCUS 58 So far we hae deal only wih syses in which he oal ass of he syse, sys, reained consan wih ie. Now, we will consider syses in which ass eners or leaes he syse while we are obsering i. The
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Sections 2.2 & 2.3 Limit of a Function and Limit Laws
 Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #4
 PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
Problem set 2 for the course on. Markov chains and mixing times
 J. Seif T. Hirscher Soluions o Proble se for he course on Markov chains and ixing ies February 7, 04 Exercise 7 (Reversible chains). (i) Assue ha we have a Markov chain wih ransiion arix P, such ha here
J. Seif T. Hirscher Soluions o Proble se for he course on Markov chains and ixing ies February 7, 04 Exercise 7 (Reversible chains). (i) Assue ha we have a Markov chain wih ransiion arix P, such ha here
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
AP Calculus BC Chapter 10 Part 1 AP Exam Problems
 AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
Math 4600: Homework 11 Solutions
 Mah 46: Homework Soluions Gregory Handy [.] One of he well-known phenomenological (capuring he phenomena, bu no necessarily he mechanisms) models of cancer is represened by Gomperz equaion dn d = bn ln(n/k)
Mah 46: Homework Soluions Gregory Handy [.] One of he well-known phenomenological (capuring he phenomena, bu no necessarily he mechanisms) models of cancer is represened by Gomperz equaion dn d = bn ln(n/k)
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
= ( ) ) or a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization (T = R
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
TP A.14 The effects of cut angle, speed, and spin on object ball throw
 echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
Lecture 20: Riccati Equations and Least Squares Feedback Control
 34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
The equation to any straight line can be expressed in the form:
 Sring Graphs Par 1 Answers 1 TI-Nspire Invesigaion Suden min Aims Deermine a series of equaions of sraigh lines o form a paern similar o ha formed by he cables on he Jerusalem Chords Bridge. Deermine he
Sring Graphs Par 1 Answers 1 TI-Nspire Invesigaion Suden min Aims Deermine a series of equaions of sraigh lines o form a paern similar o ha formed by he cables on he Jerusalem Chords Bridge. Deermine he
Math Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1
 Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1 1. Problem 1. (+20 ps) (a) (+10 ps) i. +5 ps graph for x of he rain vs. ime. The graph needs o be parabolic and concave upward. ii. +3 ps graph for x of he person
Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1 1. Problem 1. (+20 ps) (a) (+10 ps) i. +5 ps graph for x of he rain vs. ime. The graph needs o be parabolic and concave upward. ii. +3 ps graph for x of he person
x i v x t a dx dt t x
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
k 1 k 2 x (1) x 2 = k 1 x 1 = k 2 k 1 +k 2 x (2) x k series x (3) k 2 x 2 = k 1 k 2 = k 1+k 2 = 1 k k 2 k series
 Final Review A Puzzle... Consider wo massless springs wih spring consans k 1 and k and he same equilibrium lengh. 1. If hese springs ac on a mass m in parallel, hey would be equivalen o a single spring
Final Review A Puzzle... Consider wo massless springs wih spring consans k 1 and k and he same equilibrium lengh. 1. If hese springs ac on a mass m in parallel, hey would be equivalen o a single spring
( ) a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization ( T = R + These look like, respectively:
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
Section 14 Forces in Circular Motion
 Secion 14 orces in Circular Moion Ouline 1 Unifor Circular Moion Non-unifor Circular Moion Phsics 04A Class Noes Wh do objecs do wha he do? The answer we have been invesigaing is forces If forces can eplain
Secion 14 orces in Circular Moion Ouline 1 Unifor Circular Moion Non-unifor Circular Moion Phsics 04A Class Noes Wh do objecs do wha he do? The answer we have been invesigaing is forces If forces can eplain
2.1: What is physics? Ch02: Motion along a straight line. 2.2: Motion. 2.3: Position, Displacement, Distance
 Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration
 rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
BEng (Hons) Telecommunications. Examinations for / Semester 2
 BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
y = (y 1)*(y 3) t
 MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
Homework 2: Kinematics and Dynamics of Particles Due Friday Feb 8, 2019
 EN4: Dynamics and Vibraions Homework : Kinemaics and Dynamics of Paricles Due Friday Feb 8, 19 School of Engineering Brown Universiy 1. Sraigh Line Moion wih consan acceleraion. Virgin Hyperloop One is
EN4: Dynamics and Vibraions Homework : Kinemaics and Dynamics of Paricles Due Friday Feb 8, 19 School of Engineering Brown Universiy 1. Sraigh Line Moion wih consan acceleraion. Virgin Hyperloop One is
LAB # 2 - Equilibrium (static)
 AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
A. Using Newton s second law in one dimension, F net. , write down the differential equation that governs the motion of the block.
 Simple SIMPLE harmonic HARMONIC moion MOTION I. Differenial equaion of moion A block is conneced o a spring, one end of which is aached o a wall. (Neglec he mass of he spring, and assume he surface is
Simple SIMPLE harmonic HARMONIC moion MOTION I. Differenial equaion of moion A block is conneced o a spring, one end of which is aached o a wall. (Neglec he mass of he spring, and assume he surface is
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
EXERCISES FOR SECTION 1.5
 1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
The average rate of change between two points on a function is d t
 SM Dae: Secion: Objecive: The average rae of change beween wo poins on a funcion is d. For example, if he funcion ( ) represens he disance in miles ha a car has raveled afer hours, hen finding he slope
SM Dae: Secion: Objecive: The average rae of change beween wo poins on a funcion is d. For example, if he funcion ( ) represens he disance in miles ha a car has raveled afer hours, hen finding he slope
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuits
 Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
Chapter 7: Solving Trig Equations
 Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
TIME DELAY BASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OBSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM
 TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
Phys 221 Fall Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Physics 221 Fall 2008 Homework #2 Solutions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sept 9, 2008
 Physics 221 Fall 28 Homework #2 Soluions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sep 9, 28 2.1 A paricle moving along he x-axis moves direcly from posiion x =. m a ime =. s o posiion x = 1. m by ime = 1. s, and hen moves direcly
Physics 221 Fall 28 Homework #2 Soluions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sep 9, 28 2.1 A paricle moving along he x-axis moves direcly from posiion x =. m a ime =. s o posiion x = 1. m by ime = 1. s, and hen moves direcly
Robotics I. April 11, The kinematics of a 3R spatial robot is specified by the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters in Tab. 1.
 Roboics I April 11, 017 Exercise 1 he kinemaics of a 3R spaial robo is specified by he Denavi-Harenberg parameers in ab 1 i α i d i a i θ i 1 π/ L 1 0 1 0 0 L 3 0 0 L 3 3 able 1: able of DH parameers of
Roboics I April 11, 017 Exercise 1 he kinemaics of a 3R spaial robo is specified by he Denavi-Harenberg parameers in ab 1 i α i d i a i θ i 1 π/ L 1 0 1 0 0 L 3 0 0 L 3 3 able 1: able of DH parameers of
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read sections 25.4 & 25.5, the introduction to chapter 26 and sections 26.1 to 26.2 & 26.4.
 PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
IMPLICIT AND INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREMS PAUL SCHRIMPF 1 OCTOBER 25, 2013
 IMPLICI AND INVERSE FUNCION HEOREMS PAUL SCHRIMPF 1 OCOBER 25, 213 UNIVERSIY OF BRIISH COLUMBIA ECONOMICS 526 We have exensively sudied how o solve sysems of linear equaions. We know how o check wheher
IMPLICI AND INVERSE FUNCION HEOREMS PAUL SCHRIMPF 1 OCOBER 25, 213 UNIVERSIY OF BRIISH COLUMBIA ECONOMICS 526 We have exensively sudied how o solve sysems of linear equaions. We know how o check wheher
Solutions from Chapter 9.1 and 9.2
 Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Wave Mechanics. January 16, 2017
 Wave Mechanics January 6, 7 The ie-dependen Schrödinger equaion We have seen how he ie-dependen Schrodinger equaion, Ψ + Ψ i Ψ follows as a non-relaivisic version of he Klein-Gordon equaion. In wave echanics,
Wave Mechanics January 6, 7 The ie-dependen Schrödinger equaion We have seen how he ie-dependen Schrodinger equaion, Ψ + Ψ i Ψ follows as a non-relaivisic version of he Klein-Gordon equaion. In wave echanics,
Suggested Practice Problems (set #2) for the Physics Placement Test
 Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Test points. Provide the best answer to the following questions and problems. Watch your sig figs.
 Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Review - Quiz # 1. 1 g(y) dy = f(x) dx. y x. = u, so that y = xu and dy. dx (Sometimes you may want to use the substitution x y
 Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1. Kinematics I: Position and Velocity
 1. Kinemaics I: Posiion and Velociy Inroducion The purpose of his eperimen is o undersand and describe moion. We describe he moion of an objec by specifying is posiion, velociy, and acceleraion. In his
1. Kinemaics I: Posiion and Velociy Inroducion The purpose of his eperimen is o undersand and describe moion. We describe he moion of an objec by specifying is posiion, velociy, and acceleraion. In his
