9 Fluid Instabilities
|
|
|
- Domenic Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9. Stability of a shear flow In many situations, gaseous flows can be subject to fluid instabilities in which small perturbations can rapidly flow, thereby tapping a source of free energy. An important example for this are Kelvin-Helmholtz and Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities, which we discuss in this chapter. We consider a flow in the x-direction, which in the lower half-space z < 0 has velocity U and density ρ, whereas in the upper half-space the gas streams with U 2 and has density ρ 2. In addition there can be a homogeneous gravitational field g pointing into the negative z-direction. Let us assume the flow can, at least approximately, be treated as an incompressible potential flow. Let the velocity field in the upper and lower halves be given by upper half: v 2 = Φ 2 for z > 0 (9.) lower half: v = Φ for z < 0 (9.2) The equation of motion for an incompressible gas with constant density can be written as v P + (v )v = g. (9.3) t ρ If we use the identity (v )v = v 2 /2 v, together with the assumption of a potential flow v = Φ (and hence v = 0), we can write the equation of motion as Φ P t + 2 v2 g + = 0 (9.4) ρ
2 Writing the gravitational acceleration as g = gê z, this implies Φ t + 2 v2 + gz + P = const. (9.5) ρ which is Bernoulli s theorem, a useful result that we will exploit later on. We now assume for the velocity potentials in the upper and lower half Φ = U x + φ (9.6) Φ 2 = U 2 x + φ 2 (9.7) where φ and φ 2 are infinitesimal perturbations. Note that these must fulfill 2 φ = 0 and 2 φ 2 = 0 because the density is supposed to be constant in each of the two regions. Let us further introduce a function ξ(x, t) = z that describes the z-location of the interface. The total time derivative of this equation hence describes the velocity of the interface in the z-direction. This must match the fluid velocities in the z direction of the two phases, yielding for example for the -side: This gives first Φ x x + t = Φ z. (9.8) t + ( U + φ ) = φ x x z. (9.9) The second term in brackets on the left side can be dropped to leading order. The same condition also holds for the other phase, hence we obtain the two equations: t + x U = φ z, (9.0) t + x U 2 = φ 2 z. (9.) We can now relate the perturbed interface to the unperturbed state via the Bernoulli equation. For example, for phase, we can write φ t + 2 (U + φ x )2 + gξ + P ρ = 2 U 2 + P ρ, (9.2) where the left hand side is the perturbed state, the right hand side is the unperturbed state, with the initial pressure P. An analogous equation can also be written down for phase 2, with an equal initial pressure P. In addition, the pressures P and P 2 must be equal. Equating the two pressures from the two Bernoulli equations and keeping only leading order terms leads to φ ρ t + U φ x + gξ ( φ2 = ρ 2 t + U φ 2 2 x + gξ ). (9.3) 2
3 9.2 Rayleigh-Taylor instability We now seek solutions for the three functions φ, φ 2 and ξ, fulfilling the three equations (9.0), (9.) and (9.3). To this end we make an eigenmode analysis. Consider the ansatz φ = φ (z) exp[i(kx ωt)] (9.4) which respects the symmetry of the problem. Because φ fulfills the Laplace equation, we get 2 φ z 2 = k2 φ, (9.5) which has solutions φ (z) exp(kz) and φ (z) exp( kz). However, the latter solution can be discarded because of boundary conditions, since for z we need to have an unperturbed state with φ 0. In a similar way, we can make an ansatz for φ 2 and conclude that its z-dependence can only go as φ 2 (z) exp( kz). This therefore leads to the following three equations for a single Fourier mode: φ = ˆφ exp(kz) exp[i(kx ωt)] (9.6) φ 2 = ˆφ 2 exp( kz) exp[i(kx ωt)] (9.7) ξ = ˆξ exp[i(kx ωt)] (9.8) Here ˆφ, ˆφ 2, and ˆξ are the corresponding mode amplitudes. Inserting these mode equations into the differential equations (9.0), (9.) and (9.3) yields three algebraic equations: iω ˆξ + U ik ˆξ = k ˆφ (9.9) iω ˆξ + U 2 ik ˆξ = k ˆφ 2 (9.20) ρ ( iω ˆφ + U ik ˆφ + g ˆξ) = ρ 2 ( iω ˆφ 2 + U 2 ik ˆφ 2 + g ˆξ) (9.2) Non-trivial solutions with ˆξ 0 are possible for ω 2 (ρ + ρ2) 2ωk(ρ U + ρ 2 U 2 ) + k 2 (ρ U 2 + ρ 2 U 2 2 ) + (ρ 2 ρ)kg = 0, (9.22) which is the dispersion relation. Unstable, exponentially growing mode solutions appear if there are solutions for ω with negative imaginary part. Below, we examine the dispersion relation for a few special cases. 9.2 Rayleigh-Taylor instability Let us consider the case of a fluid at rest, U = U 2 = 0. The dispersion relation simplifies to ω 2 = (ρ ρ 2 )kg ρ + ρ 2. (9.23) We see that for ρ 2 > ρ, i.e. the denser fluid lies on top, unstable solutions with ω 2 < 0 exist. This is the so-called Rayleigh-Taylor instability. It is in essence buoyancy driven and leads to the rise of lighter material in a stratified atmosphere. The free energy that is tapped here is the potential energy in the gravitational field. Also notice that for an ideal gas, arbitrary small wavelengths are unstable, and those modes will also grow fastest. 3
4 A growing Rayleigh-Taylor instability: If on the other hand we have ρ > ρ 2, then the interface is stable and will only oscillate when perturbed. 9.3 Kelvin-Helmholtz instability If we set the gravitational field to zero, g = 0, we have the situation of a pure shear flow. In this case, the solutions of the dispersion relation are given by ω /2 = k(ρ U + ρ 2 U 2 ) ρ ρ 2 ± i U U 2 (9.24) ρ + ρ 2 ρ + ρ 2 Interestingly, in an ideal gas there is an imaginary growing mode component for every U U 2 > 0! This means that a small wave-like perturbation at an interface will grow rapidly into large waves that take the form of characteristic Kelvin-Helmholtz billows. In the non-linear regime reached during the subsequent evolution of this instability the waves are rolled up, leading to the creation of vortex like structures. As the instability grows fastest for small scales (high k), with time the billows tend to get larger and larger. As the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability basically means that any sharp velocity gradient in a shear flow is unstable in a freely streaming fluid, this instability is particularly important for the creating of fluid turbulence. Under certain conditions, some modes can however be stabilized against the instability. This happens for example if we consider shearing with U U 2 in a gravitational field g > 0. Then the dispersion relation has the solutions ω = k(ρ U + ρ 2 U 2 ) ρ + ρ 2 ± k2 ρ ρ 2 (U U 2 ) 2 (ρ + ρ 2 )(ρ 2 ρ )kg ρ + ρ 2. (9.25) Stability is possible if two conditions are met. First, we need ρ > ρ 2, i.e. the lighter fluid needs to be on top (otherwise we would have in any case a Rayleigh-Taylor instability). Second, the condition (U U 2 ) 2 < (ρ + ρ 2 )(ρ + ρ 2 )g kρ ρ 2 (9.26) 4
5 9.3 Kelvin-Helmholtz instability must be fulfilled. Compared to the ordinary Kelvin-Holmholtz instability without a gravitational field, we hence see that sufficiently small wavelengths are stabilized below a threshold wavelength. The larger the shear becomes, the further this threshold moves to small scales. Characteristic Kelvin-Helmholtz billows: The Rayleigh-Taylor and Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are by no means the only fluid instabilities that can occur in an ideal gas. For example, there is also the Richtmyer-Meshov instability, which can occur when an interface is suddenly accelerated, for example due to the passage of a shock wave. In self-gravitating gases, there is the Jeans instability, which occurs when the internal gas pressure is not strong enough to prevent a positive density perturbation from growing and collapsing under its own gravitational attraction. This type of instability is particularly important in cosmic structure growth and star formation. If the gas dynamics is coupled to external sources of heat (e.g. through a radiation field), a number of further instabilities are possible. For example, a thermal instability can occur when a radiative cooling function has a negative dependence on temperature. If the temperature drops somewhere a bit more through cooling than elsewhere, the cooling rate of this cooler patch will increase such that it is cooling even faster. In this way, cool clouds can drop out of the background gas. 5
AST242 LECTURE NOTES PART 5
 AST242 LECTURE NOTES PART 5 Contents 1. Waves and instabilities 1 1.1. Sound waves compressive waves in 1D 1 2. Jeans Instability 5 3. Stratified Fluid Flows Waves or Instabilities on a Fluid Boundary
AST242 LECTURE NOTES PART 5 Contents 1. Waves and instabilities 1 1.1. Sound waves compressive waves in 1D 1 2. Jeans Instability 5 3. Stratified Fluid Flows Waves or Instabilities on a Fluid Boundary
CHAPTER 5. RUDIMENTS OF HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITY
 1 Lecture Notes on Fluid Dynamics (1.63J/.1J) by Chiang C. Mei, 00 CHAPTER 5. RUDIMENTS OF HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITY References: Drazin: Introduction to Hydrodynamic Stability Chandrasekar: Hydrodynamic
1 Lecture Notes on Fluid Dynamics (1.63J/.1J) by Chiang C. Mei, 00 CHAPTER 5. RUDIMENTS OF HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITY References: Drazin: Introduction to Hydrodynamic Stability Chandrasekar: Hydrodynamic
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities
 PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
Kelvin Helmholtz Instability
 Kelvin Helmholtz Instability A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram November 00 One of the most well known instabilities in fluid
Kelvin Helmholtz Instability A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram November 00 One of the most well known instabilities in fluid
Prototype Instabilities
 Prototype Instabilities David Randall Introduction Broadly speaking, a growing atmospheric disturbance can draw its kinetic energy from two possible sources: the kinetic and available potential energies
Prototype Instabilities David Randall Introduction Broadly speaking, a growing atmospheric disturbance can draw its kinetic energy from two possible sources: the kinetic and available potential energies
2 The incompressible Kelvin-Helmholtz instability
 Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
CHAPTER 19. Fluid Instabilities. In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities:
 CHAPTER 19 Fluid Instabilities In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities: convective instability (Schwarzschild criterion) interface instabilities (Rayleight Taylor & Kelvin-Helmholtz) gravitational
CHAPTER 19 Fluid Instabilities In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities: convective instability (Schwarzschild criterion) interface instabilities (Rayleight Taylor & Kelvin-Helmholtz) gravitational
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics
 The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation
 Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Magnetohydrodynamics Stability of a Compressible Fluid Layer Below a Vacuum Medium
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 3 (2008) 267 274 c Technical University of Lodz Magnetohydrodynamics Stability of a Compressible Fluid Layer Below a Vacuum Medium Emad E. Elmahdy Mathematics
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 3 (2008) 267 274 c Technical University of Lodz Magnetohydrodynamics Stability of a Compressible Fluid Layer Below a Vacuum Medium Emad E. Elmahdy Mathematics
Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects
 Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects Harish N Dixit and Rama Govindarajan Abstract A vortex placed at an initially straight density interface winds it
Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects Harish N Dixit and Rama Govindarajan Abstract A vortex placed at an initially straight density interface winds it
General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities
 KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities L. Brandt & J.-Ch. Loiseau KTH Mechanics, November 2015 Luca Brandt Professor at KTH Mechanics Email: luca@mech.kth.se
KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities L. Brandt & J.-Ch. Loiseau KTH Mechanics, November 2015 Luca Brandt Professor at KTH Mechanics Email: luca@mech.kth.se
7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INVISCID FLUID
 7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INISCID FLUID iscosity is a measure of the thickness of a fluid, and its resistance to shearing motions. Honey is difficult to stir because of its high viscosity, whereas water
7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INISCID FLUID iscosity is a measure of the thickness of a fluid, and its resistance to shearing motions. Honey is difficult to stir because of its high viscosity, whereas water
Convection When the radial flux of energy is carried by radiation, we derived an expression for the temperature gradient: dt dr = - 3
 Convection When the radial flux of energy is carried by radiation, we derived an expression for the temperature gradient: dt dr = - 3 4ac kr L T 3 4pr 2 Large luminosity and / or a large opacity k implies
Convection When the radial flux of energy is carried by radiation, we derived an expression for the temperature gradient: dt dr = - 3 4ac kr L T 3 4pr 2 Large luminosity and / or a large opacity k implies
Three Dimensional Models of RR Lyrae Pulsation
 Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
28. THE GRAVITATIONAL INTERCHANGE MODE, OR g-mode. We now consider the case where the magneto-fluid system is subject to a gravitational force F g
 8. THE GRAVITATIONAL INTERCHANGE MODE, OR g-mode We now consider the case where the magneto-fluid system is subject to a gravitational force F g =!g, where g is a constant gravitational acceleration vector.
8. THE GRAVITATIONAL INTERCHANGE MODE, OR g-mode We now consider the case where the magneto-fluid system is subject to a gravitational force F g =!g, where g is a constant gravitational acceleration vector.
Sound Waves Sound Waves:
 3//18 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 3//18 Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction Inference of Sound Wave equation: Sound Waves We look at small disturbances in a compressible medium (note: compressible
3//18 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 3//18 Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction Inference of Sound Wave equation: Sound Waves We look at small disturbances in a compressible medium (note: compressible
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A
 Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
Predicting Breakup Characteristics of Liquid Jets Disturbed by Practical Piezoelectric Devices
 ILASS Americas 2th Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Chicago, IL, May 27 Predicting Breakup Characteristics of Liquid Jets Disturbed by Practical Piezoelectric Devices M. Rohani,
ILASS Americas 2th Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Chicago, IL, May 27 Predicting Breakup Characteristics of Liquid Jets Disturbed by Practical Piezoelectric Devices M. Rohani,
Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized. Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative. Effect and Electron Inertia
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
Magnetohydrodynamic Waves
 Magnetohydrodynamic Waves Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 17, 2016 These slides are largely based off of 4.5 and 4.8 of The Physics of
Magnetohydrodynamic Waves Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 17, 2016 These slides are largely based off of 4.5 and 4.8 of The Physics of
The Evolution of Large-Amplitude Internal Gravity Wavepackets
 The Evolution of Large-Amplitude Internal Gravity Wavepackets Sutherland, Bruce R. and Brown, Geoffrey L. University of Alberta Environmental and Industrial Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Edmonton, Alberta,
The Evolution of Large-Amplitude Internal Gravity Wavepackets Sutherland, Bruce R. and Brown, Geoffrey L. University of Alberta Environmental and Industrial Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Edmonton, Alberta,
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics
 Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
Module 3: "Thin Film Hydrodynamics" Lecture 12: "" The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis. Some well known instabilities. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis Some well known instabilities file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture12/12_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:16 PM] Linear Stability Analysis This analysis
The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis Some well known instabilities file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture12/12_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:16 PM] Linear Stability Analysis This analysis
14. Instability of Superposed Fluids
 4. Instability of Superposed Fluids Figure 4.: Wind over water: A layer of fluid of density ρ + moving with relative velocity V over a layer of fluid of density ρ. Define interface: h(x,y,z) = z η(x,y)
4. Instability of Superposed Fluids Figure 4.: Wind over water: A layer of fluid of density ρ + moving with relative velocity V over a layer of fluid of density ρ. Define interface: h(x,y,z) = z η(x,y)
Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory
 Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory Introduction to the subject Perturbation theory of electrostatic fluctuations Landau damping - mathematics Physics of Landau damping Unmagnetized plasma waves The plasma
Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory Introduction to the subject Perturbation theory of electrostatic fluctuations Landau damping - mathematics Physics of Landau damping Unmagnetized plasma waves The plasma
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017
 Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition. Andreas Füglistaler. July 17, 2017
 Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number
 A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number H. F. Robey, S. G. Glendinning, J. A. Greenough, & S. V. Weber Lawrence Livermore National
A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number H. F. Robey, S. G. Glendinning, J. A. Greenough, & S. V. Weber Lawrence Livermore National
Solar Physics & Space Plasma Research Center (SP 2 RC) MHD Waves
 MHD Waves Robertus vfs Robertus@sheffield.ac.uk SP RC, School of Mathematics & Statistics, The (UK) What are MHD waves? How do we communicate in MHD? MHD is kind! MHD waves are propagating perturbations
MHD Waves Robertus vfs Robertus@sheffield.ac.uk SP RC, School of Mathematics & Statistics, The (UK) What are MHD waves? How do we communicate in MHD? MHD is kind! MHD waves are propagating perturbations
ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics
 School of Physics and Astronomy ASP2062 2015 ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics Star formation II Daniel Price Key revision points 1. Star formation is a competition between gravity and pressure 2. Timescale
School of Physics and Astronomy ASP2062 2015 ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics Star formation II Daniel Price Key revision points 1. Star formation is a competition between gravity and pressure 2. Timescale
Figure 11.1: A fluid jet extruded where we define the dimensionless groups
 11. Fluid Jets 11.1 The shape of a falling fluid jet Consider a circular orifice of a radius a ejecting a flux Q of fluid density ρ and kinematic viscosity ν (see Fig. 11.1). The resulting jet accelerates
11. Fluid Jets 11.1 The shape of a falling fluid jet Consider a circular orifice of a radius a ejecting a flux Q of fluid density ρ and kinematic viscosity ν (see Fig. 11.1). The resulting jet accelerates
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
Hydrodynamic Instability. Agenda. Problem definition. Heuristic approach: Intuitive solution. Mathematical approach: Linear stability theory
 Environmental Fluid Mechanics II Stratified Flow and Buoyant Mixing Hydrodynamic Instability Dong-Guan Seol INSTITUTE FOR HYDROMECHANICS National Research Center of the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu
Environmental Fluid Mechanics II Stratified Flow and Buoyant Mixing Hydrodynamic Instability Dong-Guan Seol INSTITUTE FOR HYDROMECHANICS National Research Center of the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section 1.2 and 1.3
 Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Contents. I Introduction 1. Preface. xiii
 Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Inhomogeneous Universe: Linear Perturbation Theory
 Inhomogeneous Universe: Linear Perturbation Theory We have so far discussed the evolution of a homogeneous universe. The universe we see toy is, however, highly inhomogeneous. We see structures on a wide
Inhomogeneous Universe: Linear Perturbation Theory We have so far discussed the evolution of a homogeneous universe. The universe we see toy is, however, highly inhomogeneous. We see structures on a wide
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection:
 Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
7.2.1 Seismic waves. Waves in a mass- spring system
 7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
The Rayleigh Taylor Instability Among the Stars
 The Rayleigh Taylor Instability Among the Stars Rajaram Nityananda The instability of the interface separating a denser fluid from a lighter one below it has applications to the surroundings of massive
The Rayleigh Taylor Instability Among the Stars Rajaram Nityananda The instability of the interface separating a denser fluid from a lighter one below it has applications to the surroundings of massive
Convection. If luminosity is transported by radiation, then it must obey
 Convection If luminosity is transported by radiation, then it must obey L r = 16πacr 2 T 3 3ρκ R In a steady state, the energy transported per time at radius r must be equal to the energy generation rate
Convection If luminosity is transported by radiation, then it must obey L r = 16πacr 2 T 3 3ρκ R In a steady state, the energy transported per time at radius r must be equal to the energy generation rate
Sound. References: L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol. 2, Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8
 References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution
 Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution Geoffroy Lesur DAMTP (Cambridge UK) LAOG (Grenoble) John Papaloizou Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Giant vortex in Naruto straight (Japan)
Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution Geoffroy Lesur DAMTP (Cambridge UK) LAOG (Grenoble) John Papaloizou Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Giant vortex in Naruto straight (Japan)
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research PDF-document.
 Dobra, T., Lawrie, A., & Dalziel, S. B. (2016). Nonlinear Interactions of Two Incident Internal Waves. 1-8. Paper presented at VIIIth International Symposium on Stratified Flows, San Diego, United States.
Dobra, T., Lawrie, A., & Dalziel, S. B. (2016). Nonlinear Interactions of Two Incident Internal Waves. 1-8. Paper presented at VIIIth International Symposium on Stratified Flows, San Diego, United States.
Typical anisotropies introduced by geometry (not everything is spherically symmetric) temperature gradients magnetic fields electrical fields
 Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
The Magnetorotational Instability
 The Magnetorotational Instability Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics March 10, 2014 These slides are based off of Balbus & Hawley (1991), Hawley
The Magnetorotational Instability Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics March 10, 2014 These slides are based off of Balbus & Hawley (1991), Hawley
Shear instabilities. Chapter Energetics of shear instabilities
 Chapter 7 Shear instabilities In this final Chapter, we continue our study of the stability of fluid flows by looking at another very common source of instability, shear. By definition, shear occurs whenever
Chapter 7 Shear instabilities In this final Chapter, we continue our study of the stability of fluid flows by looking at another very common source of instability, shear. By definition, shear occurs whenever
Jin Matsumoto. Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
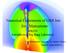 Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
INTERNAL GRAVITY WAVES
 INTERNAL GRAVITY WAVES B. R. Sutherland Departments of Physics and of Earth&Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta Contents Preface List of Tables vii xi 1 Stratified Fluids and Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
INTERNAL GRAVITY WAVES B. R. Sutherland Departments of Physics and of Earth&Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta Contents Preface List of Tables vii xi 1 Stratified Fluids and Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Figure 1. adiabatically. The change in pressure experienced by the parcel is. dp = -ρ o gξ
 6. Internal waves Consider a continuously stratified fluid with ρ o (z) the vertical density profile. z p' ξ p ρ ρ ο (z) Figure 1. Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare. At a point P raise a parcel of water by
6. Internal waves Consider a continuously stratified fluid with ρ o (z) the vertical density profile. z p' ξ p ρ ρ ο (z) Figure 1. Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare. At a point P raise a parcel of water by
Weakly Nonlinear Non-Boussinesq Internal Gravity Wavepackets
 Weakly Nonlinear Non-Boussinesq Internal Gravity Wavepackets H. V. Dosser & B. R. Sutherland Dept. of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2G7 Abstract Internal gravity wavepackets
Weakly Nonlinear Non-Boussinesq Internal Gravity Wavepackets H. V. Dosser & B. R. Sutherland Dept. of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2G7 Abstract Internal gravity wavepackets
Los Alamos National Laboratory Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 1 LA-UR
 Rayleigh-Taylor instability is generated when a heavy fluid sits above a lighter fluid in a gravitational field. The flow behavior is described in terms of bubbles of light fluid rising into the heavier
Rayleigh-Taylor instability is generated when a heavy fluid sits above a lighter fluid in a gravitational field. The flow behavior is described in terms of bubbles of light fluid rising into the heavier
6 Two-layer shallow water theory.
 6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
τ xz = τ measured close to the the surface (often at z=5m) these three scales represent inner unit or near wall normalization
 τ xz = τ measured close to the the surface (often at z=5m) these three scales represent inner unit or near wall normalization Note that w *3 /z i is used to normalized the TKE equation in case of free
τ xz = τ measured close to the the surface (often at z=5m) these three scales represent inner unit or near wall normalization Note that w *3 /z i is used to normalized the TKE equation in case of free
For example, for values of A x = 0 m /s, f 0 s, and L = 0 km, then E h = 0. and the motion may be influenced by horizontal friction if Corioli
 Lecture. Equations of Motion Scaling, Non-dimensional Numbers, Stability and Mixing We have learned how to express the forces per unit mass that cause acceleration in the ocean, except for the tidal forces
Lecture. Equations of Motion Scaling, Non-dimensional Numbers, Stability and Mixing We have learned how to express the forces per unit mass that cause acceleration in the ocean, except for the tidal forces
ChE 385M Surface Phenomena University of Texas at Austin. Marangoni-Driven Finger Formation at a Two Fluid Interface. James Stiehl
 ChE 385M Surface Phenomena University of Texas at Austin Marangoni-Driven Finger Formation at a Two Fluid Interface James Stiehl Introduction Marangoni phenomena are driven by gradients in surface tension
ChE 385M Surface Phenomena University of Texas at Austin Marangoni-Driven Finger Formation at a Two Fluid Interface James Stiehl Introduction Marangoni phenomena are driven by gradients in surface tension
Linear Analysis of Compressibility and Viscosity Effects on the MRT. Instability in Z-pinch Implosions with Sheared Axial Flows 1
 Linear Analysis of Compressibility and Viscosity Effects on the MRT Instability in Z-pinch Implosions with Sheared Axial Flows 1 Y. Zhang 1), N. Ding 1) 1) Institute of Applied Physics and Computational
Linear Analysis of Compressibility and Viscosity Effects on the MRT Instability in Z-pinch Implosions with Sheared Axial Flows 1 Y. Zhang 1), N. Ding 1) 1) Institute of Applied Physics and Computational
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method. Jue Liao
 Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
where G is Newton s gravitational constant, M is the mass internal to radius r, and Ω 0 is the
 Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components
 Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
Chapter 4. Gravity Waves in Shear. 4.1 Non-rotating shear flow
 Chapter 4 Gravity Waves in Shear 4.1 Non-rotating shear flow We now study the special case of gravity waves in a non-rotating, sheared environment. Rotation introduces additional complexities in the already
Chapter 4 Gravity Waves in Shear 4.1 Non-rotating shear flow We now study the special case of gravity waves in a non-rotating, sheared environment. Rotation introduces additional complexities in the already
ATMO/OPTI 656b Spring 09. Physical properties of the atmosphere
 The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Physical properties of the atmosphere To first order, the gas pressure at the bottom of an atmospheric column balances the downward force of gravity on the column.
The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Physical properties of the atmosphere To first order, the gas pressure at the bottom of an atmospheric column balances the downward force of gravity on the column.
10 Shallow Water Models
 10 Shallow Water Models So far, we have studied the effects due to rotation and stratification in isolation. We then looked at the effects of rotation in a barotropic model, but what about if we add stratification
10 Shallow Water Models So far, we have studied the effects due to rotation and stratification in isolation. We then looked at the effects of rotation in a barotropic model, but what about if we add stratification
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I
 Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
Intuitive Introduction To Acoustic-gravity Waves
 EP711 Supplementary Material Thursday, January 26 th, 2012 Intuitive Introduction To Acoustic-gravity Waves Jonathan B. Snively Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University 1 Contents EP711 Supplementary Material
EP711 Supplementary Material Thursday, January 26 th, 2012 Intuitive Introduction To Acoustic-gravity Waves Jonathan B. Snively Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University 1 Contents EP711 Supplementary Material
Chapter 5. Sound Waves and Vortices. 5.1 Sound waves
 Chapter 5 Sound Waves and Vortices In this chapter we explore a set of characteristic solutions to the uid equations with the goal of familiarizing the reader with typical behaviors in uid dynamics. Sound
Chapter 5 Sound Waves and Vortices In this chapter we explore a set of characteristic solutions to the uid equations with the goal of familiarizing the reader with typical behaviors in uid dynamics. Sound
PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks
 PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks Sound waves Compressions in a gas propagate as sound waves. The simplest case to consider is a gas at uniform density and at rest. Small perturbations
PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks Sound waves Compressions in a gas propagate as sound waves. The simplest case to consider is a gas at uniform density and at rest. Small perturbations
PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday, 6 May, 016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday, 6 May, 016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal
Linear stability analysis of a dual viscous layer
 1 Appendix to: A hydrodynamic instability is used to create aesthetically appealing patterns in painting Sandra Zetina 1, Francisco A. Godínez 2, Roberto Zenit 3, 1 Instituto de Investigaciones Estéticas,
1 Appendix to: A hydrodynamic instability is used to create aesthetically appealing patterns in painting Sandra Zetina 1, Francisco A. Godínez 2, Roberto Zenit 3, 1 Instituto de Investigaciones Estéticas,
Stratified Shear Flow: Instability and Wave Radiation
 Stratified Shear Flow: Instability and Wave Radiation B. R. Sutherland Dept. Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Alberta Edmonton, Canada Abstract The stability and evolution of a two-dimensional
Stratified Shear Flow: Instability and Wave Radiation B. R. Sutherland Dept. Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Alberta Edmonton, Canada Abstract The stability and evolution of a two-dimensional
SG2221 Wave Motion and Hydrodinamic Stability. MATLAB Project on 2D Poiseuille Flow Alessandro Ceci
 SG2221 Wave Motion and Hydrodinamic Stability MATLAB Project on 2D Poiseuille Flow Alessandro Ceci Base Flow 2D steady Incompressible Flow Flow driven by a constant pressure gradient Fully developed flow
SG2221 Wave Motion and Hydrodinamic Stability MATLAB Project on 2D Poiseuille Flow Alessandro Ceci Base Flow 2D steady Incompressible Flow Flow driven by a constant pressure gradient Fully developed flow
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem
 1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Fair Weather over Land
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Fair Weather over Land
Chapter 9. Barotropic Instability. 9.1 Linearized governing equations
 Chapter 9 Barotropic Instability The ossby wave is the building block of low ossby number geophysical fluid dynamics. In this chapter we learn how ossby waves can interact with each other to produce a
Chapter 9 Barotropic Instability The ossby wave is the building block of low ossby number geophysical fluid dynamics. In this chapter we learn how ossby waves can interact with each other to produce a
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 2 Turbulence Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson Turbulence Dr. DeCaria References: Air-sea Interaction: Laws and Mechanisms, Csanady An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology ( rd edition), J.R. Holton An Introduction
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson Turbulence Dr. DeCaria References: Air-sea Interaction: Laws and Mechanisms, Csanady An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology ( rd edition), J.R. Holton An Introduction
Dynamics Rotating Tank
 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Physics 221B Spring 2012 Notes 42 Scattering of Radiation by Matter
 Physics 221B Spring 2012 Notes 42 Scattering of Radiation by Matter 1. Introduction In the previous set of Notes we treated the emission and absorption of radiation by matter. In these Notes we turn to
Physics 221B Spring 2012 Notes 42 Scattering of Radiation by Matter 1. Introduction In the previous set of Notes we treated the emission and absorption of radiation by matter. In these Notes we turn to
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit
 Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
4. Complex Oscillations
 4. Complex Oscillations The most common use of complex numbers in physics is for analyzing oscillations and waves. We will illustrate this with a simple but crucially important model, the damped harmonic
4. Complex Oscillations The most common use of complex numbers in physics is for analyzing oscillations and waves. We will illustrate this with a simple but crucially important model, the damped harmonic
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Quantum fields close to black hole horizons
 Quantum fields close to black hole horizons Kinematics Accelerated scalar fields and inertial forces Photons in Rindler space vs thermal photons Interactions Static interactions of scalar, electric and
Quantum fields close to black hole horizons Kinematics Accelerated scalar fields and inertial forces Photons in Rindler space vs thermal photons Interactions Static interactions of scalar, electric and
Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion. Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009
 Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009 Outline Overview Evidence of Mixing SN 1987A Evidence in supernova remnants Basic Physics Rayleigh-Taylor
Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009 Outline Overview Evidence of Mixing SN 1987A Evidence in supernova remnants Basic Physics Rayleigh-Taylor
The Stable Boundary layer
 The Stable Boundary layer the statistically stable or stratified regime occurs when surface is cooler than the air The stable BL forms at night over land (Nocturnal Boundary Layer) or when warm air travels
The Stable Boundary layer the statistically stable or stratified regime occurs when surface is cooler than the air The stable BL forms at night over land (Nocturnal Boundary Layer) or when warm air travels
Jin Matsumoto. Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
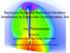 Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Geodynamics Lecture 10 The forces driving plate tectonics
 Geodynamics Lecture 10 The forces driving plate tectonics Lecturer: David Whipp! david.whipp@helsinki.fi!! 2.10.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Describe how thermal convection
Geodynamics Lecture 10 The forces driving plate tectonics Lecturer: David Whipp! david.whipp@helsinki.fi!! 2.10.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Describe how thermal convection
Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 161 Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface P. Wayne 1, D. Olmstead 1, P. Vorobieff 1, C. R. Truman 1 & S. Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 161 Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface P. Wayne 1, D. Olmstead 1, P. Vorobieff 1, C. R. Truman 1 & S. Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical
Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves
 Chapter 8 Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves We are now in a position to begin investigating more complex disturbances in a rotating, stratified environment. Most of the disturbances of interest are
Chapter 8 Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves We are now in a position to begin investigating more complex disturbances in a rotating, stratified environment. Most of the disturbances of interest are
Formation and Collapse of Nonaxisymmetric Protostellar Cores in Magnetic Interstellar Clouds
 Formation and Collapse of Nonaxisymmetric Protostellar Cores in Magnetic Interstellar Clouds Glenn E. Ciolek Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy & New York Center for Studies on the Origins
Formation and Collapse of Nonaxisymmetric Protostellar Cores in Magnetic Interstellar Clouds Glenn E. Ciolek Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy & New York Center for Studies on the Origins
2 D.D. Joseph To make things simple, consider flow in two dimensions over a body obeying the equations ρ ρ v = 0;
 Accepted for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Viscous Potential Flow By D.D. Joseph Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics, University of Minnesota, MN 55455 USA Email: joseph@aem.umn.edu (Received
Accepted for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Viscous Potential Flow By D.D. Joseph Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics, University of Minnesota, MN 55455 USA Email: joseph@aem.umn.edu (Received
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]
![Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]](/thumbs/81/83694823.jpg) Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow Introduction and formulation
 Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow. 13.1 Introduction and formulation We have concentrated our discussion on the instabilities of parallel, zonal flows. There is the largest amount of literature
Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow. 13.1 Introduction and formulation We have concentrated our discussion on the instabilities of parallel, zonal flows. There is the largest amount of literature
Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations
 Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations 9.-1 Different Flame Geometries and Single Droplet Burning Solutions for the velocities and the mixture fraction fields for some typical laminar flame configurations.
Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations 9.-1 Different Flame Geometries and Single Droplet Burning Solutions for the velocities and the mixture fraction fields for some typical laminar flame configurations.
Jin Matsumoto. Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
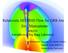 Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
IV From cores to stars
 IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies
 Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies 13.42 Lecture Notes; c A.H. Techet 1. Forces on Large Structures For discussion in this section we will be considering bodies that are quite large compared to the
Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies 13.42 Lecture Notes; c A.H. Techet 1. Forces on Large Structures For discussion in this section we will be considering bodies that are quite large compared to the
Propagation of Radio Frequency Waves Through Density Filaments
 PSFC/JA-15-13 Propagation of Radio Frequency Waves Through Density Filaments A. K. Ram and K. Hizanidis a May 015 a National Technical University of Athens (part of HELLAS) School of Electrical and Computer
PSFC/JA-15-13 Propagation of Radio Frequency Waves Through Density Filaments A. K. Ram and K. Hizanidis a May 015 a National Technical University of Athens (part of HELLAS) School of Electrical and Computer
Theory of Ship Waves (Wave-Body Interaction Theory) Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018
 Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: h(x,t) Water L
 ME9a. SOLUTIONS. Nov., 29. Due Nov. 7 PROBLEM 2 Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: y Surface Water L h(x,t x Tank The flow is assumed to be
ME9a. SOLUTIONS. Nov., 29. Due Nov. 7 PROBLEM 2 Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: y Surface Water L h(x,t x Tank The flow is assumed to be
Homogeneous Turbulence Dynamics
 Homogeneous Turbulence Dynamics PIERRE SAGAUT Universite Pierre et Marie Curie CLAUDE CAMBON Ecole Centrale de Lyon «Hf CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Abbreviations Used in This Book page xvi 1 Introduction
Homogeneous Turbulence Dynamics PIERRE SAGAUT Universite Pierre et Marie Curie CLAUDE CAMBON Ecole Centrale de Lyon «Hf CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Abbreviations Used in This Book page xvi 1 Introduction
