Formation and Collapse of Nonaxisymmetric Protostellar Cores in Magnetic Interstellar Clouds
|
|
|
- Spencer Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Formation and Collapse of Nonaxisymmetric Protostellar Cores in Magnetic Interstellar Clouds Glenn E. Ciolek Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy & New York Center for Studies on the Origins of Life (NSCORT) Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute 1
2 Magnetic Support of Clouds Evidence for magnetic support of molecular clouds: 2
3 Magnetic Support of Clouds Evidence for magnetic support of molecular clouds: - Polarimetry. 2
4 Magnetic Support of Clouds Hildebrand et al. (2000) 3
5 Magnetic Support of Clouds NGC 1333 IRAS 4A (Girart, Rao, & Marrone 2006) 4
6 Magnetic Support of Clouds Further evidence: 5
7 Magnetic Support of Clouds Further evidence: - Modified Chandrasekhar-Fermi method. 5
8 Magnetic Support of Clouds Further evidence: - Modified Chandrasekhar-Fermi method. - Zeeman splitting. 5
9 Magnetic Support of Clouds Further evidence: - Modified Chandrasekhar-Fermi method. - Zeeman splitting. The measured magnetic fields yield mass-to-flux ratios M Φ B ( σ n B) that are within a factor 2 below or above the critical value for gravitational collapse (Crutcher 2004). 5
10 Theoretical Models & Observations Past decade: axisymmetric models of formation and collapse of protostellar cores in magnetically supported molecular clouds were developed. 6
11 Theoretical Models & Observations Past decade: axisymmetric models of formation and collapse of protostellar cores in magnetically supported molecular clouds were developed. Ciolek & Basu (2000) applied a model to the L1544 prestellar core. 6
12 Theoretical Models & Observations Past decade: axisymmetric models of formation and collapse of protostellar cores in magnetically supported molecular clouds were developed. Ciolek & Basu (2000) applied a model to the L1544 prestellar core. - Reproduced observed density and velocity profiles (Williams et al. 1999, Caselli et al. 2002) 6
13 Theoretical Models & Observations Past decade: axisymmetric models of formation and collapse of protostellar cores in magnetically supported molecular clouds were developed. Ciolek & Basu (2000) applied a model to the L1544 prestellar core. - Reproduced observed density and velocity profiles (Williams et al. 1999, Caselli et al. 2002) - Predicted magnetic field strength, confirmed by Zeeman measurements (Crutcher & Troland 2000). 6
14 Theoretical Models & Observations Past decade: axisymmetric models of formation and collapse of protostellar cores in magnetically supported molecular clouds were developed. Ciolek & Basu (2000) applied a model to the L1544 prestellar core. - Reproduced observed density and velocity profiles (Williams et al. 1999, Caselli et al. 2002) - Predicted magnetic field strength, confirmed by Zeeman measurements (Crutcher & Troland 2000). Problem: clouds and cores usually not axisymmetric. 6
15 Theoretical Models & Observations L1544 Prestellar Core (Williams et al. 1999) 7
16 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless initial mass-to-flux ratio for a self-gravitating object: µ 0 M Φ B M Φ B 0 crit where ratio. M Φ B crit 0 17 G is the critical mass-to-flux 8
17 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless initial mass-to-flux ratio for a self-gravitating object: µ 0 M Φ B M Φ B 0 crit where ratio. M Φ B crit 0 17 G is the critical mass-to-flux µ 0 1 Subcritical, magnetically supported. 8
18 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless initial mass-to-flux ratio for a self-gravitating object: µ 0 M Φ B M Φ B 0 crit where ratio. M Φ B crit 0 17 G is the critical mass-to-flux µ 0 µ Subcritical, magnetically supported. Supercritical, gravitational collapse. 8
19 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless neutral-ion collision time: τ ni 0 neutral ion collision time gravitational contraction timescale cm n n x i 7 where x i n i n n is the degree of ionization. 9
20 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless neutral-ion collision time: τ ni 0 neutral ion collision time gravitational contraction timescale cm n n x i 7 where x i n i n n is the degree of ionization. τ ni 0 1 Ineffective neutral-ion coupling. 9
21 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless neutral-ion collision time: τ ni 0 neutral ion collision time gravitational contraction timescale cm n n x i 7 where x i n i n n is the degree of ionization. τ ni 0 τ ni Ineffective neutral-ion coupling. Some coupling of neutrals with ions & magnetic field. 9
22 Magnetic Fields & Star Formation: Fundamental Parameters Dimensionless neutral-ion collision time: τ ni 0 neutral ion collision time gravitational contraction timescale cm n n x i 7 where x i n i n n is the degree of ionization. τ ni 0 τ ni Ineffective neutral-ion coupling. Some coupling of neutrals with ions & magnetic field. For typical cloud conditions, τ ni
23 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse Model Cloud Schematic z Z(x,y) x B P ext 10
24 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse We numerically integrate the coupled nonlinear partial differential equations for the system of neutral and ion fluids, and the magnetic field in Cartesian geometry. These include: Continuity of mass. 11
25 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse We numerically integrate the coupled nonlinear partial differential equations for the system of neutral and ion fluids, and the magnetic field in Cartesian geometry. These include: Continuity of mass. Force equations of neutrals and ions. 11
26 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse We numerically integrate the coupled nonlinear partial differential equations for the system of neutral and ion fluids, and the magnetic field in Cartesian geometry. These include: Continuity of mass. Force equations of neutrals and ions. Maxwell s equations. 11
27 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse We numerically integrate the coupled nonlinear partial differential equations for the system of neutral and ion fluids, and the magnetic field in Cartesian geometry. These include: Continuity of mass. Force equations of neutrals and ions. Maxwell s equations. Poisson s equation. 11
28 Modeling Nonaxisymmetric Collapse We numerically integrate the coupled nonlinear partial differential equations for the system of neutral and ion fluids, and the magnetic field in Cartesian geometry. These include: Continuity of mass. Force equations of neutrals and ions. Maxwell s equations. Poisson s equation. Full formulation presented in Ciolek & Basu (2006). 11
29 Linearized and Fourier-Analyzed System Assume small-amplitude perturbation δ f for any physical variable f in the system of equations governing the evolution of a model cloud: δ f x y t exp i k x x k y y ωt 12
30 Linearized and Fourier-Analyzed System Assume small-amplitude perturbation δ f for any physical variable f in the system of equations governing the evolution of a model cloud: δ f x y t exp i k x x k y y ωt Resulting dispersion relation can be solved for the complex frequency ω k x ky. 12
31 Linearized and Fourier-Analyzed System Assume small-amplitude perturbation δ f for any physical variable f in the system of equations governing the evolution of a model cloud: δ f x y t exp i k x x k y y ωt Resulting dispersion relation can be solved for the complex frequency ω k x ky Gravitationally unstable modes exist if I ω The growth time for the instability is. is positive. τ g 1 I ω 12
32 Timescale for Gravitational Instability 10 3 ~ τ ni,0 = µ 0 = τ g λ 13
33 Lengthscale of Maximum Growth Rate λ g m 10 3 ~ τ ni,0 = 0.04 λ g,m µ 0 14
34 Numerical Simulations of Nonaxisymmetric Core Formation 15
35 Numerical Simulations of Nonaxisymmetric Core Formation 15
36 Numerical Simulations of Nonaxisymmetric Core Formation 15
37 Numerical Simulations of Nonaxisymmetric Core Formation 15
38 Numerical Simulations of Nonaxisymmetric Core Formation 15
39 Dynamical Infall of Protostellar Cores Basu & Ciolek (2004) 16
40 Dynamical Infall of Protostellar Cores Basu & Ciolek (2004) 16
41 Dynamical Infall of Protostellar Cores Basu & Ciolek (2004) 16
42 Summary We have developed models of protostellar core formation and nonaxisymmetric collapse in magnetic interstellar clouds. 17
43 Summary We have developed models of protostellar core formation and nonaxisymmetric collapse in magnetic interstellar clouds. From a linear analysis of the models, determined the lengthscale of maximum gravitational instability λ g m and its dependence on the parameter µ 0. λ g m has a resonance for clouds near the critical state µ
44 Summary We have developed models of protostellar core formation and nonaxisymmetric collapse in magnetic interstellar clouds. From a linear analysis of the models, determined the lengthscale of maximum gravitational instability λ g m and its dependence on the parameter µ 0. λ g m has a resonance for clouds near the critical state µ 0 1. Nonlinear simulations verify that the fundamental fragmentation scale is λ g m. 17
45 Summary We have developed models of protostellar core formation and nonaxisymmetric collapse in magnetic interstellar clouds. From a linear analysis of the models, determined the lengthscale of maximum gravitational instability λ g m and its dependence on the parameter µ 0. λ g m has a resonance for clouds near the critical state µ 0 1. Nonlinear simulations verify that the fundamental fragmentation scale is λ g m. Clouds with µ 0 2 have cores with large-scale infall velocities that are excluded by observations. 17
Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm
 Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm Shantanu Basu The University of Western Ontario Collaborators: Glenn Ciolek (RPI), Takahiro Kudoh (NAOJ), Wolf Dapp,
Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm Shantanu Basu The University of Western Ontario Collaborators: Glenn Ciolek (RPI), Takahiro Kudoh (NAOJ), Wolf Dapp,
FORMATION AND COLLAPSE OF NONAXISYMMETRIC PROTOSTELLAR CORES IN PLANAR MAGNETIC INTERSTELLAR CLOUDS: FORMULATION OF THE PROBLEM AND LINEAR ANALYSIS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 65:44Y457, 006 November 0 # 006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FORMATION AND COLLAPSE OF NONAXISYMMETRIC PROTOSTELLAR CORES IN PLANAR
The Astrophysical Journal, 65:44Y457, 006 November 0 # 006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FORMATION AND COLLAPSE OF NONAXISYMMETRIC PROTOSTELLAR CORES IN PLANAR
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores
 Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores Masahiro Machida (Kyushu University) Star Formation Process Observations have shown that Low-velocity outflows and high-velocity jets are ubiquitous
Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores Masahiro Machida (Kyushu University) Star Formation Process Observations have shown that Low-velocity outflows and high-velocity jets are ubiquitous
Magnetic Fields in the Formation of Sun-Like Stars
 Magnetic Fields in the Formation of Sun-Like Stars Josep M. Girart 1*, Ramprasad Rao 2,3, and Daniel P. Marrone 2 1 Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC- IEEC), Campus UAB Facultat de Ciències, Torre
Magnetic Fields in the Formation of Sun-Like Stars Josep M. Girart 1*, Ramprasad Rao 2,3, and Daniel P. Marrone 2 1 Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC- IEEC), Campus UAB Facultat de Ciències, Torre
SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions. Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC)
 SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC) SMA Community Day, July 11, 2011 Simultaneous process of infall and outflow"
SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC) SMA Community Day, July 11, 2011 Simultaneous process of infall and outflow"
THE ROLE OF MHD WAVES AND AMBIPOLAR DIFFUSION IN THE FORMATION OF INTERSTELLAR CLOUD CORES AND PROTOSTARS BY CHESTER ENG B.S., Columbia University, 19
 cfl Copyright by Chester Eng, 2002 THE ROLE OF MHD WAVES AND AMBIPOLAR DIFFUSION IN THE FORMATION OF INTERSTELLAR CLOUD CORES AND PROTOSTARS BY CHESTER ENG B.S., Columbia University, 1992 M.S., University
cfl Copyright by Chester Eng, 2002 THE ROLE OF MHD WAVES AND AMBIPOLAR DIFFUSION IN THE FORMATION OF INTERSTELLAR CLOUD CORES AND PROTOSTARS BY CHESTER ENG B.S., Columbia University, 1992 M.S., University
Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation
 Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
dt 2 = 0, we find that: K = 1 2 Ω (2)
 1 1. irial Theorem Last semester, we derived the irial theorem from essentially considering a series of particles which attract each other through gravitation. The result was that d = K + Ω (1) dt where
1 1. irial Theorem Last semester, we derived the irial theorem from essentially considering a series of particles which attract each other through gravitation. The result was that d = K + Ω (1) dt where
Magnetic Fields over all Scales
 Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia)
 Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia) Collaborators: Ruben Krasnopolsky (ASIAA) Sienny Shang (ASIAA) 1 Focus on magnetic effects on disk formation Investigated by many
Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia) Collaborators: Ruben Krasnopolsky (ASIAA) Sienny Shang (ASIAA) 1 Focus on magnetic effects on disk formation Investigated by many
Impact of Protostellar Outflow on Star Formation: Effects of Initial Cloud Mass
 Impact of Protostellar Outflow on Star Formation: Effects of Initial Cloud Mass Masahiro N. Machida 1 and Tomoaki Matsumoto 2 ABSTRACT Star formation efficiency controlled by the protostellar outflow in
Impact of Protostellar Outflow on Star Formation: Effects of Initial Cloud Mass Masahiro N. Machida 1 and Tomoaki Matsumoto 2 ABSTRACT Star formation efficiency controlled by the protostellar outflow in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds 1. Stability of Cloud Cores 2. Collapse and Fragmentation of Clouds 3. Applying the Virial Theorem References Myers, Physical Conditions in Molecular Clouds in
Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds 1. Stability of Cloud Cores 2. Collapse and Fragmentation of Clouds 3. Applying the Virial Theorem References Myers, Physical Conditions in Molecular Clouds in
THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS
 THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS Diego Falceta-Gonçalves, Marcelo C. de Juli & Vera Jatenco-Pereira Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e C. Atmosféricas Universidade
THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS Diego Falceta-Gonçalves, Marcelo C. de Juli & Vera Jatenco-Pereira Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e C. Atmosféricas Universidade
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
The Magnetorotational Instability
 The Magnetorotational Instability Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics March 10, 2014 These slides are based off of Balbus & Hawley (1991), Hawley
The Magnetorotational Instability Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics March 10, 2014 These slides are based off of Balbus & Hawley (1991), Hawley
Centimeter Wave Star Formation Studies in the Galaxy from Radio Sky Surveys
 Centimeter Wave Star Formation Studies in the Galaxy from Radio Sky Surveys W. J. Welch Radio Astronomy Laboratory, Depts of EECS and Astronomy University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 Tel: (510) 643-6543
Centimeter Wave Star Formation Studies in the Galaxy from Radio Sky Surveys W. J. Welch Radio Astronomy Laboratory, Depts of EECS and Astronomy University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 Tel: (510) 643-6543
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics
 Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
Testing Star Formation theories Zeeman splitting applied
 Testing Star Formation theories Zeeman splitting applied Zeeman splitting An Introduction Wikipedia Zeeman What? A particle with angular momentum essentially is like a magnet. With no external Gield, any
Testing Star Formation theories Zeeman splitting applied Zeeman splitting An Introduction Wikipedia Zeeman What? A particle with angular momentum essentially is like a magnet. With no external Gield, any
Star Formation at the Galactic Center
 PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 121:585 590, 2009 June 2009. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Star Formation at the Galactic Center
PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 121:585 590, 2009 June 2009. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Star Formation at the Galactic Center
Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized. Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative. Effect and Electron Inertia
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores
 The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores Formation of Prestellar Cores: Observations and Theory Edited by PHILIPPE ANDRE 1, SHANTANU BASU 2, and SHU-ICHIRO INUTSUKA 3 (1) Service d Astrophysique,
The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores Formation of Prestellar Cores: Observations and Theory Edited by PHILIPPE ANDRE 1, SHANTANU BASU 2, and SHU-ICHIRO INUTSUKA 3 (1) Service d Astrophysique,
c 2011 Duncan Christie
 c 2011 Duncan Christie FRAGMENTATION OF MAGNETICALLY-SUPPORTED, WEAKLY-IONIZED MOLECULAR CLOUDS BY DUNCAN CHRISTIE DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
c 2011 Duncan Christie FRAGMENTATION OF MAGNETICALLY-SUPPORTED, WEAKLY-IONIZED MOLECULAR CLOUDS BY DUNCAN CHRISTIE DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation
 Chapter 5 Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation 5.1 The road to star formation Thus far we have studied the places where stars form molecular clouds. We have discussed the ways in which
Chapter 5 Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation 5.1 The road to star formation Thus far we have studied the places where stars form molecular clouds. We have discussed the ways in which
Stellar structure and evolution. Pierre Hily-Blant April 25, IPAG
 Stellar structure and evolution Pierre Hily-Blant 2017-18 April 25, 2018 IPAG pierre.hily-blant@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr, OSUG-D/306 10 Protostars and Pre-Main-Sequence Stars 10.1. Introduction 10 Protostars
Stellar structure and evolution Pierre Hily-Blant 2017-18 April 25, 2018 IPAG pierre.hily-blant@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr, OSUG-D/306 10 Protostars and Pre-Main-Sequence Stars 10.1. Introduction 10 Protostars
Lecture 6: Protostellar Accretion
 Lecture 6: Protostellar Accretion Richard Alexander, 23rd March 2009 The angular momentum problem When we try to understand how young stars form, the obvious question to ask is how do young stars accrete
Lecture 6: Protostellar Accretion Richard Alexander, 23rd March 2009 The angular momentum problem When we try to understand how young stars form, the obvious question to ask is how do young stars accrete
Opportunities for Dust Polarization Surveys
 Opportunities for Dust Polarization Surveys C. Darren Dowell JPL/Caltech This work was performed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National
Opportunities for Dust Polarization Surveys C. Darren Dowell JPL/Caltech This work was performed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jun 2009](/thumbs/71/65532125.jpg) Star Formation at the Galactic Center Marco Fatuzzo, 1 and Fulvio Melia 2 1 Physics Department, Xavier University, Cincinnati, OH 45207 arxiv:0906.2917v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jun 2009 2 Department of Physics
Star Formation at the Galactic Center Marco Fatuzzo, 1 and Fulvio Melia 2 1 Physics Department, Xavier University, Cincinnati, OH 45207 arxiv:0906.2917v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jun 2009 2 Department of Physics
IV From cores to stars
 IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
Polarimetry with the SMA
 Polarimetry with the SMA Ramprasad Rao Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica (ASIAA) Collaborators: J. M. Girart (IEEC-CSIC), D. P. Marrone (NRAO/U. Chicago), Y. Tang (ASIAA), and a
Polarimetry with the SMA Ramprasad Rao Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica (ASIAA) Collaborators: J. M. Girart (IEEC-CSIC), D. P. Marrone (NRAO/U. Chicago), Y. Tang (ASIAA), and a
9 Fluid Instabilities
 9. Stability of a shear flow In many situations, gaseous flows can be subject to fluid instabilities in which small perturbations can rapidly flow, thereby tapping a source of free energy. An important
9. Stability of a shear flow In many situations, gaseous flows can be subject to fluid instabilities in which small perturbations can rapidly flow, thereby tapping a source of free energy. An important
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds. Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame
 Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
II- Molecular clouds
 2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
Collapse of magnetized dense cores. Is there a fragmentation crisis?
 Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations
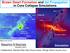 Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection
 Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Accretion Mechanisms
 Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics
 School of Physics and Astronomy ASP2062 2015 ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics Star formation II Daniel Price Key revision points 1. Star formation is a competition between gravity and pressure 2. Timescale
School of Physics and Astronomy ASP2062 2015 ASP2062 Introduction to Astrophysics Star formation II Daniel Price Key revision points 1. Star formation is a competition between gravity and pressure 2. Timescale
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona. Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015
 PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Jan 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Jan 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Jan 2008](/thumbs/93/114414741.jpg) Studies of regular and random magnetic fields in the ISM: statistics of polarization vectors and the Chandrasekhar-Fermi technique Diego Falceta-Gonçalves 1 arxiv:0801.0279v1 [astro-ph] 1 Jan 2008 Núcleo
Studies of regular and random magnetic fields in the ISM: statistics of polarization vectors and the Chandrasekhar-Fermi technique Diego Falceta-Gonçalves 1 arxiv:0801.0279v1 [astro-ph] 1 Jan 2008 Núcleo
RADIO SPECTRAL LINES. Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune
 RADIO SPECTRAL LINES Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune OUTLINE The importance of radio spectral lines. Equilibrium issues: kinetic, excitation, brightness temperatures. The equation
RADIO SPECTRAL LINES Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune OUTLINE The importance of radio spectral lines. Equilibrium issues: kinetic, excitation, brightness temperatures. The equation
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION
 MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto, Satoshi Okuzumi, Yasunori Hori
 09/19/2014 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University Department of Physics, University of Tokyo JSPS Research Fellow Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto,
09/19/2014 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University Department of Physics, University of Tokyo JSPS Research Fellow Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto,
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Collapse of Low-Mass Protostellar Cores: Part I
 Collapse of Low-Mass Protostellar Cores: Part I Isothermal Unmagnetized Solutions and Observational Diagnostics Andrea Kulier AST 541 October 9, 2012 Outline Models of Isothermal Unmagnetized Collapse
Collapse of Low-Mass Protostellar Cores: Part I Isothermal Unmagnetized Solutions and Observational Diagnostics Andrea Kulier AST 541 October 9, 2012 Outline Models of Isothermal Unmagnetized Collapse
Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds
 Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of California, San Diego ICREA - University of Barcelona (Spring 2010) Collaborators:
Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of California, San Diego ICREA - University of Barcelona (Spring 2010) Collaborators:
The Formation of Close Binary Stars
 The Formation of Binary Stars fa U Symposium, Vol. 200, 2001 H. Zinnecker and R. D. Mathieu, eds. The Formation of Close Binary Stars Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews, Physics and Astronomy, North
The Formation of Binary Stars fa U Symposium, Vol. 200, 2001 H. Zinnecker and R. D. Mathieu, eds. The Formation of Close Binary Stars Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews, Physics and Astronomy, North
formation of the cosmic large-scale structure
 formation of the cosmic large-scale structure Heraeus summer school on cosmology, Heidelberg 2013 Centre for Astronomy Fakultät für Physik und Astronomie, Universität Heidelberg August 23, 2013 outline
formation of the cosmic large-scale structure Heraeus summer school on cosmology, Heidelberg 2013 Centre for Astronomy Fakultät für Physik und Astronomie, Universität Heidelberg August 23, 2013 outline
The Formation of Star Clusters
 The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics
 Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics 12 December 2006 by JJG Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is the generalization of hydrodynamics to electrically conducting fluids. Major astrophysical applications include stellar
Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics 12 December 2006 by JJG Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is the generalization of hydrodynamics to electrically conducting fluids. Major astrophysical applications include stellar
Multifluid Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability in Weakly Ionised Astrophysical Plasmas
 Multifluid Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability in Weakly Ionised Astrophysical Plasmas Aoife Clare Jones B.A.mod. A Dissertation Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Dublin City University Supervisor:
Multifluid Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability in Weakly Ionised Astrophysical Plasmas Aoife Clare Jones B.A.mod. A Dissertation Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Dublin City University Supervisor:
Revealing Magnetic Fields in the Neutral ISM: Outlook and Goals for the Next Decade
 Revealing Magnetic Fields in the Neutral ISM: Outlook and Goals for the Next Decade Crystal L. Brogan (NRAO), Richard M. Crutcher (Illinois), C. Darren Dowell 1 (Caltech), Jessie L. Dotson (NASA/Ames),
Revealing Magnetic Fields in the Neutral ISM: Outlook and Goals for the Next Decade Crystal L. Brogan (NRAO), Richard M. Crutcher (Illinois), C. Darren Dowell 1 (Caltech), Jessie L. Dotson (NASA/Ames),
Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma. Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University
 Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University What is a Plasma? A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas consisting of positive and negative
Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University What is a Plasma? A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas consisting of positive and negative
Formation of massive stars: a review
 Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
Stellar Birth. Stellar Formation. A. Interstellar Clouds. 1b. What is the stuff. Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution. A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae)
 Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS
 Talk@INT, UW, July 5, 2006 FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS Naoki Yoshida Department of Physics Nagoya University Outline Thermal evolution of a primordial gas - Physics at high densities (cooling, chem.
Talk@INT, UW, July 5, 2006 FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS Naoki Yoshida Department of Physics Nagoya University Outline Thermal evolution of a primordial gas - Physics at high densities (cooling, chem.
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core
 (Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE GALAXY
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Doctoral Dissertations Graduate School 2008 MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE GALAXY Elizabeth Ann Mayo University of Kentucky Click here to let us know how
University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Doctoral Dissertations Graduate School 2008 MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE GALAXY Elizabeth Ann Mayo University of Kentucky Click here to let us know how
Distortion of Magnetic Fields in a Starless Core II: 3D Magnetic Field Structure of FeSt 1-457
 Distortion of Magnetic Fields in a Starless Core II: 3D Magnetic Field Structure of FeSt 1-457 arxiv:1709.04544v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Oct 2017 Ryo Kandori 1, Motohide Tamura 1,2,3, Kohji Tomisaka 2, Yasushi
Distortion of Magnetic Fields in a Starless Core II: 3D Magnetic Field Structure of FeSt 1-457 arxiv:1709.04544v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Oct 2017 Ryo Kandori 1, Motohide Tamura 1,2,3, Kohji Tomisaka 2, Yasushi
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation
 The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
Nonlinear MRI. Jeremy Goodman. CMPD/CMSO Winter School 7-12 January 2008, UCLA
 Nonlinear MRI Jeremy Goodman CMPD/CMSO Winter School 7-12 January 2008, UCLA Questions for the nonlinear regime How does the linear instability saturate? i.e., What nonlinear mode-mode interactions brake
Nonlinear MRI Jeremy Goodman CMPD/CMSO Winter School 7-12 January 2008, UCLA Questions for the nonlinear regime How does the linear instability saturate? i.e., What nonlinear mode-mode interactions brake
The Thermodynamics of Multifluid in Star Forming Regions
 The Thermodynamics of Multifluid Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence in Star Forming Regions Aaron Kinsella B.Sc. A thesis submitted for the degree of Master of Science Dublin City University Supervisor: Prof.
The Thermodynamics of Multifluid Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence in Star Forming Regions Aaron Kinsella B.Sc. A thesis submitted for the degree of Master of Science Dublin City University Supervisor: Prof.
Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?
 Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?) Yusuke Tsukamoto Kagoshima University S. Okuzumi, K. Iwasaki, M.
Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?) Yusuke Tsukamoto Kagoshima University S. Okuzumi, K. Iwasaki, M.
Sound. References: L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol. 2, Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8
 References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties. Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang
 Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
2 The incompressible Kelvin-Helmholtz instability
 Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
Interferometric Mapping of Magnetic Fields in Star-forming Regions II. NGC 2024 FIR 5
 Interferometric Mapping of Magnetic Fields in Star-forming Regions II. NGC 2024 FIR 5 Shih-Ping Lai 1, Richard M. Crutcher, José M.Girart 2, and Ramprasad Rao 3 Astronomy Department, University of Illinois,
Interferometric Mapping of Magnetic Fields in Star-forming Regions II. NGC 2024 FIR 5 Shih-Ping Lai 1, Richard M. Crutcher, José M.Girart 2, and Ramprasad Rao 3 Astronomy Department, University of Illinois,
The chemistry and thermodynamics of Pop III star formation
 The chemistry and thermodynamics of Pop III star formation Where do the first stars form Form in dark matter minihalos with mass Mhalo 5 10 5 M Redshift z = 16-20 Tvir ~ 1000 K Gas density is around 1
The chemistry and thermodynamics of Pop III star formation Where do the first stars form Form in dark matter minihalos with mass Mhalo 5 10 5 M Redshift z = 16-20 Tvir ~ 1000 K Gas density is around 1
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise
 Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Mar 2012](/thumbs/95/125374869.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2018 November 9, 2018 Bridging the gap: disk formation in the Class 0 phase with ambipolar diffusion and Ohmic dissipation Wolf B. Dapp 1,2, Shantanu Basu
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2018 November 9, 2018 Bridging the gap: disk formation in the Class 0 phase with ambipolar diffusion and Ohmic dissipation Wolf B. Dapp 1,2, Shantanu Basu
Results on the classical high-! bar-mode instability in relativistic star models for polytropic EoS with adiabatic index!=2.75.
 Results on the classical high-! bar-mode instability in relativistic star models for polytropic EoS with adiabatic index!=2.75 Luca Franci (1) in collaboration with Roberto De Pietri (1), Alessandra Feo
Results on the classical high-! bar-mode instability in relativistic star models for polytropic EoS with adiabatic index!=2.75 Luca Franci (1) in collaboration with Roberto De Pietri (1), Alessandra Feo
Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution
 MNRAS 51, 33 3353 (15) doi:1.193/mnras/stv1 Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution Bastian Körtgen and Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg
MNRAS 51, 33 3353 (15) doi:1.193/mnras/stv1 Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution Bastian Körtgen and Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg
Galaxies and Cosmology
 F. Combes P. Boisse A. Mazure A. Blanchard Galaxies and Cosmology Translated by M. Seymour With 192 Figures Springer Contents General Introduction 1 1 The Classification and Morphology of Galaxies 5 1.1
F. Combes P. Boisse A. Mazure A. Blanchard Galaxies and Cosmology Translated by M. Seymour With 192 Figures Springer Contents General Introduction 1 1 The Classification and Morphology of Galaxies 5 1.1
Some fundamentals. Statistical mechanics. The non-equilibrium ISM. = g u
 Some fundamentals Statistical mechanics We have seen that the collision timescale for gas in this room is very small relative to radiative timesscales such as spontaneous emission. The frequent collisions
Some fundamentals Statistical mechanics We have seen that the collision timescale for gas in this room is very small relative to radiative timesscales such as spontaneous emission. The frequent collisions
The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars
 Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars Daniel J. Price and Matthew R. Bate c Springer-Verlag
Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars Daniel J. Price and Matthew R. Bate c Springer-Verlag
The ideal Maxwellian plasma
 The ideal Maxwellian plasma Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada. E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Plasmas are,... The plasma state of matter may be defined as a
The ideal Maxwellian plasma Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada. E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Plasmas are,... The plasma state of matter may be defined as a
The Stellar Black Hole
 The Stellar Black Hole Kenneth Dalton e-mail: kxdalton@yahoo.com Abstract A black hole model is proposed in which a neutron star is surrounded by a neutral gas of electrons and positrons. The gas is in
The Stellar Black Hole Kenneth Dalton e-mail: kxdalton@yahoo.com Abstract A black hole model is proposed in which a neutron star is surrounded by a neutral gas of electrons and positrons. The gas is in
Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow
 Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Maths University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Appl. Maths, Leeds) N.
Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Maths University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Appl. Maths, Leeds) N.
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
Other stellar types. Open and globular clusters: chemical compositions
 Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation
 Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Introduction. Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs
 Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs Collaborators : Phil Armitage - University of Colorado Duncan Forgan- University of St Andrews Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Queen Mary, University
Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs Collaborators : Phil Armitage - University of Colorado Duncan Forgan- University of St Andrews Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Queen Mary, University
The First Stars. Simone Ferraro Princeton University. Sept 25, 2012
 The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics November, Angular momentum transport in accretion disks
 2292-13 School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics 14-25 November, 2011 Angular momentum transport in accretion disks Gianluigi Bodo Osservatorio Astronomico, Torino Italy Angular
2292-13 School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics 14-25 November, 2011 Angular momentum transport in accretion disks Gianluigi Bodo Osservatorio Astronomico, Torino Italy Angular
Typical anisotropies introduced by geometry (not everything is spherically symmetric) temperature gradients magnetic fields electrical fields
 Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores. Review of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
Gas Cloud Collisions and Stellar Cluster Formation
 Gas Cloud Collisions and Stellar Cluster Formation J. Klapp 1, G. Arreaga-Garcia 2 1 Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Nucleares, Km 36.5 Carretera México-Toluca, Ocoyoacac, 52750 Estado de México,
Gas Cloud Collisions and Stellar Cluster Formation J. Klapp 1, G. Arreaga-Garcia 2 1 Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Nucleares, Km 36.5 Carretera México-Toluca, Ocoyoacac, 52750 Estado de México,
Jin Matsumoto. Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
 Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
OH AND CN ZEEMAN OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN MOLECULAR CLOUDS
 RevMexAA (Serie de Conferencias), 36, 17 112 (29) OH AND CN ZEEMAN OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN MOLECULAR CLOUDS R. M. Crutcher 1 RESUMEN Observaciones del efecto Zeeman en OH y CN proveen información
RevMexAA (Serie de Conferencias), 36, 17 112 (29) OH AND CN ZEEMAN OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN MOLECULAR CLOUDS R. M. Crutcher 1 RESUMEN Observaciones del efecto Zeeman en OH y CN proveen información
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Shocks. Ellen Zweibel.
 Shocks Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas Shocks
Shocks Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas Shocks
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Comparing star formation models with interferometric observations of the protostar NGC 1333 IRAS 4A
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201117813 c ESO 2011 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparing star formation models with interferometric observations of the protostar NGC 1333 IRAS 4A I. Magnetohydrodynamic collapse
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201117813 c ESO 2011 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparing star formation models with interferometric observations of the protostar NGC 1333 IRAS 4A I. Magnetohydrodynamic collapse
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Formation Process of the Circumstellar Disk: Long-term Simulations in the Main Accretion Phase of Star Formation
 Formation Process of the Circumstellar Disk: Long-term Simulations in the Main Accretion Phase of Star Formation Masahiro N. Machida 1, Shu-ichiro Inutsuka 2, and Tomoaki Matsumoto 3 ABSTRACT The formation
Formation Process of the Circumstellar Disk: Long-term Simulations in the Main Accretion Phase of Star Formation Masahiro N. Machida 1, Shu-ichiro Inutsuka 2, and Tomoaki Matsumoto 3 ABSTRACT The formation
Large scale flows and coherent structure phenomena in flute turbulence
 Large scale flows and coherent structure phenomena in flute turbulence I. Sandberg 1, Zh. N. Andrushcheno, V. P. Pavleno 1 National Technical University of Athens, Association Euratom Hellenic Republic,
Large scale flows and coherent structure phenomena in flute turbulence I. Sandberg 1, Zh. N. Andrushcheno, V. P. Pavleno 1 National Technical University of Athens, Association Euratom Hellenic Republic,
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics
 Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Nov 2003
 Collapse of Magnetized Singular Isothermal Toroids: II. Rotation and Magnetic Braking Anthony Allen arxiv:astro-ph/0311377v1 17 Nov 2003 Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, PO BOX
Collapse of Magnetized Singular Isothermal Toroids: II. Rotation and Magnetic Braking Anthony Allen arxiv:astro-ph/0311377v1 17 Nov 2003 Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, PO BOX
