Reflections and Rotations in R 3
|
|
|
- Prudence Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reflections and Rotations in R 3 P. J. Ryan May 29, 21 Rotations as Compositions of Reflections Recall that the reflection in the hyperplane H through the origin in R n is given by f(x) = x 2 ξ, x ξ (1) where ξ is a unit normal for H. Let u be a unit vector in R 3, v a unit vector orthogonal to u, and let w = u v. Then (u, v, w) is an orthonormal triple. Let T be the rotation which is the composition of refections T 1 and T 2 in planes through the origin whose unit normals are ξ and η respectively, both orthogonal to w. We may choose numbers θ and ϕ so that η = sin θ u + cos θ v ξ = sin ϕ u + cos ϕ v. If the planes are distinct, then T is not the identity rotation and the axis of T is the line through the origin with direction vector w. Using the formula (1), we have f(u) = (1 2 sin 2 ϕ) u + 2 sin ϕ cos ϕ v f(v) = 2 sin ϕ cos ϕ u + (1 2 cos 2 ϕ) v f(w) = w (2) That is, f(u) = cos 2ϕ u + sin 2ϕ v f(v) = sin 2ϕ u cos 2ϕ v f(w) = w To get the formula for the reflection involving η, just replace ϕ by θ. Then T = T 1 T 2, and we compute T (u) = cos 2(ϕ θ) u + sin 2(ϕ θ) v T (v) = sin 2(ϕ θ) u + cos 2(ϕ θ) v T (w) = w. (3) 1
2 This is a tedious verification if carried out directly. For the moment, consider the special case where u = ɛ 1, v = ɛ 2, w = ɛ 3. Then, the calculation reduces to the matrix multiplication [ ] [ ] [ ] cos 2ϕ sin 2ϕ cos 2θ sin 2θ cos 2(ϕ θ) sin 2(ϕ θ) =. sin 2ϕ cos 2ϕ sin 2θ cos 2θ sin 2(ϕ θ) cos 2(ϕ θ) From (3) we conclude that T (u), u = T (v), v = cos 2(ϕ θ). (4) and T (u), v = T (v), u. (5) Proposition 1. For all unit vectors x orthogonal to w in R 3, T (x), x = cos 2(ϕ θ). To see this, first recall that (u, v, w) is an orthonormal triple. Thus, x = x, u u + x, v v + x, w w = x, u u + x, v v (6) since x is orthogonal to w. By linearity of T, we have T (x) = x, u T (u) + x, v T (v) from which we get, using (5) to eliminate the cross terms, T (x), x = x, u 2 T (u), u + x, v 2 T (v), v. Taking (4) into account and the fact that x, u 2 + x, v 2 = x 2 = 1, we have verified the proposition. This justifies the idea that T is a rotation by 2(ϕ θ) about its axis. In general, for any unit orthogonal vectors u and v, and any number α, the transformation T (u) = cos α u + sin α v T (v) = sin α u + cos α v T (w) = w (7) is called a rotation by α. As long as T is not the identity, the axis of the rotation will be the line through the origin with direction vector u v. 2
3 Counter-Clockwise and Clockwise Rotations Although the notions of clockwise and counterclockwise rotations are not defined in any absolute sense in R 3, we give the following definition: Definition 2. Let T be the rotation described in (7). If ω is any positive multiple of u v, then T is said to be counter-clockwise with respect to ω and clockwise with respect to ω. This means that a counter-clockwise rotation by π is also a clockwise rotation by π. It also means that a counter-clockwise rotation by α is also a clockwise rotation by 2π α. In order to test if a given rotation is counter-clockwise, we now derive a more general criterion. Proposition 3. Let T be a rotation by α, where < α π, counter-clockwise with respect to ω. Then x T (x), ω for all x orthogonal to ω. Proof. From (7) we compute u T (u) = sin α w u T (v) = cos α w v T (u) = cos α w v T (v) = sin α w Note that u T (u), w = v T (v), w = sin α. Now let x be a unit vector orthogonal to w. We can write (6) in the form (8) x = cos β u + sin β v for some suitable number β. Then, x T (x) = cos 2 β u T (u) + cos β sin β v T (u) + sin β cos β u T (v) + sin 2 β v T (v) = (cos 2 β + sin 2 β) sin α w = sin α w where we have used (8) to simplify the expression. This gives x T (x), ω = ω sin α as required. Thus, to determine if a given rotation is clockwise or counter-clockwise, first express it in such a way that the angle of rotation satisfies < α π. Then pick a convenient x orthogonal to the axis of rotation, and choose a particular direction vector ω for the axis. Now check the sign of x T (x), ω. Unless α = π, there are two rotations (one clockwise, one counter-clockwise) by α about a given axis. These rotations are inverses of each other. For example, in (7), we could construct the inverse by replacing α by α, then rewriting as T (u) = cos α u + sin α ( v) T ( v) = sin α u + cos α ( v) T (w) = w (9) thus maintaining < α π. This will be the clockwise rotation by α with respect to w. 3
4 Standard Matrices of Reflections and Rotations We now show how to compute the standard matrix of a reflection or rotation in R 3. In particular, we derive the matrices of counter-clockwise rotations by α about the coordinate axes. Let A be the standard matrix of the reflection defined in formula (1). Then the equations (2) give cos 2ϕ sin 2ϕ AP = P sin 2ϕ cos 2ϕ. (1) Note that P is an orthogonal matrix, since its columns are an orthonormal set. In other words, P T P = I, i.e. the inverse of P is its transpose. Thus, we may express the standard matrix of the reflection as cos 2ϕ sin 2ϕ A = P sin 2ϕ cos 2ϕ P T and hence, the standard matrix of the rotation in (3) is cos 2(ϕ θ) sin 2(ϕ θ) A = P sin 2(ϕ θ) cos 2(ϕ θ) P T Three special cases are worth mentioning. First, look at the case where w = ɛ 3, so that we can take u = ɛ 1 and v = ɛ 2. Then P is the identity and the standard matrix of the counter-clockwise rotation by α with respect to ɛ 3 is cos α sin α sin α cos α To find the standard matrix of the counter-clockwise rotation by α with respect to ɛ 1, we choose w = ɛ 1, u = ɛ 2, and v = ɛ 3. Then 1 P = 1 1 so that the standard matrix is cos α sin α 1 1 sin α cos α = cos α sin α 1 1 sin α cos α. 4
5 To find the standard matrix of the counter-clockwise rotation by α with respect to ɛ 2, we choose w = ɛ 2, u = ɛ 3, and v = ɛ 1. Then 1 P = 1 so that the standard matrix is 1 cos α sin α cos α sin α sin α cos α 1 = sin α cos α 5
5. Orthogonal matrices
 L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading
 Chapter 4 Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading The moment of a force about a point provides a measure of the
Chapter 4 Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading The moment of a force about a point provides a measure of the
4.2. ORTHOGONALITY 161
 4.2. ORTHOGONALITY 161 Definition 4.2.9 An affine space (E, E ) is a Euclidean affine space iff its underlying vector space E is a Euclidean vector space. Given any two points a, b E, we define the distance
4.2. ORTHOGONALITY 161 Definition 4.2.9 An affine space (E, E ) is a Euclidean affine space iff its underlying vector space E is a Euclidean vector space. Given any two points a, b E, we define the distance
Linear Algebra. Paul Yiu. 6D: 2-planes in R 4. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Fall 2011
 Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
Assignment 6. Using the result for the Lagrangian for a double pendulum in Problem 1.22, we get
 Assignment 6 Goldstein 6.4 Obtain the normal modes of vibration for the double pendulum shown in Figure.4, assuming equal lengths, but not equal masses. Show that when the lower mass is small compared
Assignment 6 Goldstein 6.4 Obtain the normal modes of vibration for the double pendulum shown in Figure.4, assuming equal lengths, but not equal masses. Show that when the lower mass is small compared
Answer Key for Exam #2
 Answer Key for Exam #. Use elimination on an augmented matrix: 8 6 7 7. The corresponding system is x 7x + x, x + x + x, x x which we solve for the pivot variables x, x x : x +7x x x x x x x x x x x Therefore
Answer Key for Exam #. Use elimination on an augmented matrix: 8 6 7 7. The corresponding system is x 7x + x, x + x + x, x x which we solve for the pivot variables x, x x : x +7x x x x x x x x x x x Therefore
Lecture 21 Relevant sections in text: 3.1
 Lecture 21 Relevant sections in text: 3.1 Angular momentum - introductory remarks The theory of angular momentum in quantum mechanics is important in many ways. The myriad of results of this theory, which
Lecture 21 Relevant sections in text: 3.1 Angular momentum - introductory remarks The theory of angular momentum in quantum mechanics is important in many ways. The myriad of results of this theory, which
NOTES ON LINEAR ALGEBRA CLASS HANDOUT
 NOTES ON LINEAR ALGEBRA CLASS HANDOUT ANTHONY S. MAIDA CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2 2. Basis Vectors 2 3. Linear Transformations 2 3.1. Example: Rotation Transformation 3 4. Matrix Multiplication and Function
NOTES ON LINEAR ALGEBRA CLASS HANDOUT ANTHONY S. MAIDA CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2 2. Basis Vectors 2 3. Linear Transformations 2 3.1. Example: Rotation Transformation 3 4. Matrix Multiplication and Function
Lecture 10: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11)
 Lecture 1: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11) The eigenvalue problem, Ax= λ x, occurs in many, many contexts: classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, optics 22 Eigenvectors and
Lecture 1: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11) The eigenvalue problem, Ax= λ x, occurs in many, many contexts: classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, optics 22 Eigenvectors and
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3
 Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Honors Linear Algebra, Spring Homework 8 solutions by Yifei Chen
 .. Honors Linear Algebra, Spring 7. Homework 8 solutions by Yifei Chen 8... { { W {v R 4 v α v β } v x, x, x, x 4 x x + x 4 x + x x + x 4 } Solve the linear system above, we get a basis of W is {v,,,,
.. Honors Linear Algebra, Spring 7. Homework 8 solutions by Yifei Chen 8... { { W {v R 4 v α v β } v x, x, x, x 4 x x + x 4 x + x x + x 4 } Solve the linear system above, we get a basis of W is {v,,,,
Section 7.3: SYMMETRIC MATRICES AND ORTHOGONAL DIAGONALIZATION
 Section 7.3: SYMMETRIC MATRICES AND ORTHOGONAL DIAGONALIZATION When you are done with your homework you should be able to Recognize, and apply properties of, symmetric matrices Recognize, and apply properties
Section 7.3: SYMMETRIC MATRICES AND ORTHOGONAL DIAGONALIZATION When you are done with your homework you should be able to Recognize, and apply properties of, symmetric matrices Recognize, and apply properties
Math 1180, Notes, 14 1 C. v 1 v n v 2. C A ; w n. A and w = v i w i : v w = i=1
 Math 8, 9 Notes, 4 Orthogonality We now start using the dot product a lot. v v = v v n then by Recall that if w w ; w n and w = v w = nx v i w i : Using this denition, we dene the \norm", or length, of
Math 8, 9 Notes, 4 Orthogonality We now start using the dot product a lot. v v = v v n then by Recall that if w w ; w n and w = v w = nx v i w i : Using this denition, we dene the \norm", or length, of
is Use at most six elementary row operations. (Partial
 MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
The Calculus of Vec- tors
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Newtonian Mechanics. Chapter Classical space-time
 Chapter 1 Newtonian Mechanics In these notes classical mechanics will be viewed as a mathematical model for the description of physical systems consisting of a certain (generally finite) number of particles
Chapter 1 Newtonian Mechanics In these notes classical mechanics will be viewed as a mathematical model for the description of physical systems consisting of a certain (generally finite) number of particles
1 The theoretical constructions
 Linear Transformations and Matrix Representations Samuel R Buss - Spring 003 Revision (Corrections appreciated!) These notes review the topics I lectured on while covering sections 4, 4, and 5 of the textbook
Linear Transformations and Matrix Representations Samuel R Buss - Spring 003 Revision (Corrections appreciated!) These notes review the topics I lectured on while covering sections 4, 4, and 5 of the textbook
Section 2.2: The Inverse of a Matrix
 Section 22: The Inverse of a Matrix Recall that a linear equation ax b, where a and b are scalars and a 0, has the unique solution x a 1 b, where a 1 is the reciprocal of a From this result, it is natural
Section 22: The Inverse of a Matrix Recall that a linear equation ax b, where a and b are scalars and a 0, has the unique solution x a 1 b, where a 1 is the reciprocal of a From this result, it is natural
2018 Fall 2210Q Section 013 Midterm Exam I Solution
 8 Fall Q Section 3 Midterm Exam I Solution True or False questions ( points = points) () An example of a linear combination of vectors v, v is the vector v. True. We can write v as v + v. () If two matrices
8 Fall Q Section 3 Midterm Exam I Solution True or False questions ( points = points) () An example of a linear combination of vectors v, v is the vector v. True. We can write v as v + v. () If two matrices
j=1 u 1jv 1j. 1/ 2 Lemma 1. An orthogonal set of vectors must be linearly independent.
 Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE
 REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
Distance Between Ellipses in 2D
 Distance Between Ellipses in 2D David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To
Distance Between Ellipses in 2D David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To
ISOMETRIES OF R n KEITH CONRAD
 ISOMETRIES OF R n KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction An isometry of R n is a function h: R n R n that preserves the distance between vectors: h(v) h(w) = v w for all v and w in R n, where (x 1,..., x n ) = x
ISOMETRIES OF R n KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction An isometry of R n is a function h: R n R n that preserves the distance between vectors: h(v) h(w) = v w for all v and w in R n, where (x 1,..., x n ) = x
APPLICATIONS The eigenvalues are λ = 5, 5. An orthonormal basis of eigenvectors consists of
 CHAPTER III APPLICATIONS The eigenvalues are λ =, An orthonormal basis of eigenvectors consists of, The eigenvalues are λ =, A basis of eigenvectors consists of, 4 which are not perpendicular However,
CHAPTER III APPLICATIONS The eigenvalues are λ =, An orthonormal basis of eigenvectors consists of, The eigenvalues are λ =, A basis of eigenvectors consists of, 4 which are not perpendicular However,
We could express the left side as a sum of vectors and obtain the Vector Form of a Linear System: a 12 a x n. a m2
 Week 22 Equations, Matrices and Transformations Coefficient Matrix and Vector Forms of a Linear System Suppose we have a system of m linear equations in n unknowns a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n b 1
Week 22 Equations, Matrices and Transformations Coefficient Matrix and Vector Forms of a Linear System Suppose we have a system of m linear equations in n unknowns a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n b 1
Class Meeting # 12: Kirchhoff s Formula and Minkowskian Geometry
 MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 2 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 207 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 2: Kirchhoff s Formula and Minkowskian Geometry. Kirchhoff s Formula We are now ready
MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 2 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 207 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 2: Kirchhoff s Formula and Minkowskian Geometry. Kirchhoff s Formula We are now ready
Linear Algebra March 16, 2019
 Linear Algebra March 16, 2019 2 Contents 0.1 Notation................................ 4 1 Systems of linear equations, and matrices 5 1.1 Systems of linear equations..................... 5 1.2 Augmented
Linear Algebra March 16, 2019 2 Contents 0.1 Notation................................ 4 1 Systems of linear equations, and matrices 5 1.1 Systems of linear equations..................... 5 1.2 Augmented
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB
 Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12,
 LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12, 2000 13 2 Basic concepts We will assume that the following concepts are known: Vector, column vector, row vector, transpose. Recall that x is a column vector,
LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12, 2000 13 2 Basic concepts We will assume that the following concepts are known: Vector, column vector, row vector, transpose. Recall that x is a column vector,
we have the following equation:
 1 VMTS Homework #1 due Thursday, July 6 Exercise 1 In triangle ABC, let P be 2 3 of the way from A to B, let Q be 1 3 of the way from P to C, and let the line BQ intersect AC in R How far is R along the
1 VMTS Homework #1 due Thursday, July 6 Exercise 1 In triangle ABC, let P be 2 3 of the way from A to B, let Q be 1 3 of the way from P to C, and let the line BQ intersect AC in R How far is R along the
Rigid Geometric Transformations
 Rigid Geometric Transformations Carlo Tomasi This note is a quick refresher of the geometry of rigid transformations in three-dimensional space, expressed in Cartesian coordinates. 1 Cartesian Coordinates
Rigid Geometric Transformations Carlo Tomasi This note is a quick refresher of the geometry of rigid transformations in three-dimensional space, expressed in Cartesian coordinates. 1 Cartesian Coordinates
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #2 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
Vectors. September 2, 2015
 Vectors September 2, 2015 Our basic notion of a vector is as a displacement, directed from one point of Euclidean space to another, and therefore having direction and magnitude. We will write vectors in
Vectors September 2, 2015 Our basic notion of a vector is as a displacement, directed from one point of Euclidean space to another, and therefore having direction and magnitude. We will write vectors in
Functional Analysis Review
 Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated )
 Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
2.2 Separable Equations
 2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
Math 350 Fall 2011 Notes about inner product spaces. In this notes we state and prove some important properties of inner product spaces.
 Math 350 Fall 2011 Notes about inner product spaces In this notes we state and prove some important properties of inner product spaces. First, recall the dot product on R n : if x, y R n, say x = (x 1,...,
Math 350 Fall 2011 Notes about inner product spaces In this notes we state and prove some important properties of inner product spaces. First, recall the dot product on R n : if x, y R n, say x = (x 1,...,
1 Last time: multiplying vectors matrices
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces
 Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
Upper triangular matrices and Billiard Arrays
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 493 (2016) 508 536 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Linear Algebra and its Applications www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Upper triangular matrices and Billiard Arrays
Linear Algebra and its Applications 493 (2016) 508 536 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Linear Algebra and its Applications www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Upper triangular matrices and Billiard Arrays
EXAM. Exam 1. Math 5316, Fall December 2, 2012
 EXAM Exam Math 536, Fall 22 December 2, 22 Write all of your answers on separate sheets of paper. You can keep the exam questions. This is a takehome exam, to be worked individually. You can use your notes.
EXAM Exam Math 536, Fall 22 December 2, 22 Write all of your answers on separate sheets of paper. You can keep the exam questions. This is a takehome exam, to be worked individually. You can use your notes.
Lecture 1.4: Inner products and orthogonality
 Lecture 1.4: Inner products and orthogonality Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4340, Advanced Engineering Mathematics M.
Lecture 1.4: Inner products and orthogonality Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4340, Advanced Engineering Mathematics M.
Midterm for Introduction to Numerical Analysis I, AMSC/CMSC 466, on 10/29/2015
 Midterm for Introduction to Numerical Analysis I, AMSC/CMSC 466, on 10/29/2015 The test lasts 1 hour and 15 minutes. No documents are allowed. The use of a calculator, cell phone or other equivalent electronic
Midterm for Introduction to Numerical Analysis I, AMSC/CMSC 466, on 10/29/2015 The test lasts 1 hour and 15 minutes. No documents are allowed. The use of a calculator, cell phone or other equivalent electronic
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning:
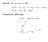 Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
10. Linear Systems of ODEs, Matrix multiplication, superposition principle (parts of sections )
 c Dr. Igor Zelenko, Fall 2017 1 10. Linear Systems of ODEs, Matrix multiplication, superposition principle (parts of sections 7.2-7.4) 1. When each of the functions F 1, F 2,..., F n in right-hand side
c Dr. Igor Zelenko, Fall 2017 1 10. Linear Systems of ODEs, Matrix multiplication, superposition principle (parts of sections 7.2-7.4) 1. When each of the functions F 1, F 2,..., F n in right-hand side
Linear Algebra II. 7 Inner product spaces. Notes 7 16th December Inner products and orthonormal bases
 MTH6140 Linear Algebra II Notes 7 16th December 2010 7 Inner product spaces Ordinary Euclidean space is a 3-dimensional vector space over R, but it is more than that: the extra geometric structure (lengths,
MTH6140 Linear Algebra II Notes 7 16th December 2010 7 Inner product spaces Ordinary Euclidean space is a 3-dimensional vector space over R, but it is more than that: the extra geometric structure (lengths,
Algebra II. Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas
 Algebra II Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas Contents 1. Quadratic forms 3 What is quadratic form? 3 Change of variables. 3 Equivalence of quadratic forms. 4 Canonical form. 4 Normal form. 7 Positive
Algebra II Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas Contents 1. Quadratic forms 3 What is quadratic form? 3 Change of variables. 3 Equivalence of quadratic forms. 4 Canonical form. 4 Normal form. 7 Positive
Week Quadratic forms. Principal axes theorem. Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 5.5, 8.2,
 Math 051 W008 Margo Kondratieva Week 10-11 Quadratic forms Principal axes theorem Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 55, 8, 83 89 Section 41 Motivation and introduction Consider
Math 051 W008 Margo Kondratieva Week 10-11 Quadratic forms Principal axes theorem Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 55, 8, 83 89 Section 41 Motivation and introduction Consider
A Primer on Three Vectors
 Michael Dine Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz September 2010 What makes E&M hard, more than anything else, is the problem that the electric and magnetic fields are vectors, and
Michael Dine Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz September 2010 What makes E&M hard, more than anything else, is the problem that the electric and magnetic fields are vectors, and
MAC Module 12 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Learning Objectives. Upon completing this module, you should be able to:
 MAC Module Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: Solve the eigenvalue problem by finding the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors
MAC Module Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: Solve the eigenvalue problem by finding the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors
MAC Module 12 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 MAC 23 Module 2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Solve the eigenvalue problem by finding the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors
MAC 23 Module 2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Solve the eigenvalue problem by finding the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors
Math 315: Linear Algebra Solutions to Assignment 7
 Math 5: Linear Algebra s to Assignment 7 # Find the eigenvalues of the following matrices. (a.) 4 0 0 0 (b.) 0 0 9 5 4. (a.) The characteristic polynomial det(λi A) = (λ )(λ )(λ ), so the eigenvalues are
Math 5: Linear Algebra s to Assignment 7 # Find the eigenvalues of the following matrices. (a.) 4 0 0 0 (b.) 0 0 9 5 4. (a.) The characteristic polynomial det(λi A) = (λ )(λ )(λ ), so the eigenvalues are
Fall TMA4145 Linear Methods. Exercise set Given the matrix 1 2
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences TMA445 Linear Methods Fall 07 Exercise set Please justify your answers! The most important part is how you arrive at an
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences TMA445 Linear Methods Fall 07 Exercise set Please justify your answers! The most important part is how you arrive at an
1 Matrices and matrix algebra
 1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
EECS 275 Matrix Computation
 EECS 275 Matrix Computation Ming-Hsuan Yang Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California at Merced Merced, CA 95344 http://faculty.ucmerced.edu/mhyang Lecture 12 1 / 18 Overview
EECS 275 Matrix Computation Ming-Hsuan Yang Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California at Merced Merced, CA 95344 http://faculty.ucmerced.edu/mhyang Lecture 12 1 / 18 Overview
Metric spaces and metrizability
 1 Motivation Metric spaces and metrizability By this point in the course, this section should not need much in the way of motivation. From the very beginning, we have talked about R n usual and how relatively
1 Motivation Metric spaces and metrizability By this point in the course, this section should not need much in the way of motivation. From the very beginning, we have talked about R n usual and how relatively
Optimization Theory. A Concise Introduction. Jiongmin Yong
 October 11, 017 16:5 ws-book9x6 Book Title Optimization Theory 017-08-Lecture Notes page 1 1 Optimization Theory A Concise Introduction Jiongmin Yong Optimization Theory 017-08-Lecture Notes page Optimization
October 11, 017 16:5 ws-book9x6 Book Title Optimization Theory 017-08-Lecture Notes page 1 1 Optimization Theory A Concise Introduction Jiongmin Yong Optimization Theory 017-08-Lecture Notes page Optimization
MOMENT OF A FORCE SCALAR FORMULATION, CROSS PRODUCT, MOMENT OF A FORCE VECTOR FORMULATION, & PRINCIPLE OF MOMENTS
 MOMENT OF A FORCE SCALAR FORMULATION, CROSS PRODUCT, MOMENT OF A FORCE VECTOR FORMULATION, & PRINCIPLE OF MOMENTS Today s Objectives : Students will be able to: a) understand and define moment, and, b)
MOMENT OF A FORCE SCALAR FORMULATION, CROSS PRODUCT, MOMENT OF A FORCE VECTOR FORMULATION, & PRINCIPLE OF MOMENTS Today s Objectives : Students will be able to: a) understand and define moment, and, b)
1 Coordinate Transformation
 1 Coordinate Transformation 1.1 HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES A position vector in a three-dimensional space (Fig. 1.1.1) may be represented (i) in vector form as r m = O m M = x m i m + y m j m + z m k m (1.1.1)
1 Coordinate Transformation 1.1 HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES A position vector in a three-dimensional space (Fig. 1.1.1) may be represented (i) in vector form as r m = O m M = x m i m + y m j m + z m k m (1.1.1)
FORMS ON INNER PRODUCT SPACES
 FORMS ON INNER PRODUCT SPACES MARIA INFUSINO PROSEMINAR ON LINEAR ALGEBRA WS2016/2017 UNIVERSITY OF KONSTANZ Abstract. This note aims to give an introduction on forms on inner product spaces and their
FORMS ON INNER PRODUCT SPACES MARIA INFUSINO PROSEMINAR ON LINEAR ALGEBRA WS2016/2017 UNIVERSITY OF KONSTANZ Abstract. This note aims to give an introduction on forms on inner product spaces and their
22m:033 Notes: 7.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
 m:33 Notes: 7. Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices Dennis Roseman University of Iowa Iowa City, IA http://www.math.uiowa.edu/ roseman May 3, Symmetric matrices Definition. A symmetric matrix is a matrix
m:33 Notes: 7. Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices Dennis Roseman University of Iowa Iowa City, IA http://www.math.uiowa.edu/ roseman May 3, Symmetric matrices Definition. A symmetric matrix is a matrix
F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N. Physics Electromagnetism: Induced Currents Science and Mathematics Education Research Group
 F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Electromagnetism: Induced Currents Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching and Learning
F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Electromagnetism: Induced Currents Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching and Learning
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY
 LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
7.4. The Inverse of a Matrix. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 The Inverse of a Matrix 7.4 Introduction In number arithmetic every number a 0has a reciprocal b written as a or such that a ba = ab =. Similarly a square matrix A may have an inverse B = A where AB =
The Inverse of a Matrix 7.4 Introduction In number arithmetic every number a 0has a reciprocal b written as a or such that a ba = ab =. Similarly a square matrix A may have an inverse B = A where AB =
Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision?
 Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision? References: -Any book on linear algebra! -[HZ] chapters 2, 4 Some of the slides in this lecture are courtesy to Prof. Octavia
Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision? References: -Any book on linear algebra! -[HZ] chapters 2, 4 Some of the slides in this lecture are courtesy to Prof. Octavia
Section x7 +
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5. Polynomial Approximations In Chapter 3 we discussed the problem of finding the affine function which best approximates a given function about some
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5. Polynomial Approximations In Chapter 3 we discussed the problem of finding the affine function which best approximates a given function about some
Math113: Linear Algebra. Beifang Chen
 Math3: Linear Algebra Beifang Chen Spring 26 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 3 Systems of Linear Equations 3 Linear Systems 3 2 Geometric Interpretation 3 3 Matrices of Linear Systems 4 4 Elementary
Math3: Linear Algebra Beifang Chen Spring 26 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 3 Systems of Linear Equations 3 Linear Systems 3 2 Geometric Interpretation 3 3 Matrices of Linear Systems 4 4 Elementary
Consistent Histories. Chapter Chain Operators and Weights
 Chapter 10 Consistent Histories 10.1 Chain Operators and Weights The previous chapter showed how the Born rule can be used to assign probabilities to a sample space of histories based upon an initial state
Chapter 10 Consistent Histories 10.1 Chain Operators and Weights The previous chapter showed how the Born rule can be used to assign probabilities to a sample space of histories based upon an initial state
Numerical Methods for Inverse Kinematics
 Numerical Methods for Inverse Kinematics Niels Joubert, UC Berkeley, CS184 2008-11-25 Inverse Kinematics is used to pose models by specifying endpoints of segments rather than individual joint angles.
Numerical Methods for Inverse Kinematics Niels Joubert, UC Berkeley, CS184 2008-11-25 Inverse Kinematics is used to pose models by specifying endpoints of segments rather than individual joint angles.
Projective Geometry. Lecture Notes W. D. GILLAM
 Projective Geometry Lecture Notes W. D. GILLAM Boǧaziçi University 2014 Contents Introduction iv 1 Transformations of the Plane 1 1.1 Linear transformations............................. 2 1.2 Isometries....................................
Projective Geometry Lecture Notes W. D. GILLAM Boǧaziçi University 2014 Contents Introduction iv 1 Transformations of the Plane 1 1.1 Linear transformations............................. 2 1.2 Isometries....................................
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1
 Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
A. Correct! These are the corresponding rectangular coordinates.
 Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 4 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 4 Jul 2013 arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 4 Jul 2013](/thumbs/87/95035090.jpg) GEOMETRY FOR SEPARABLE STATES AND CONSTRUCTION OF ENTANGLED STATES WITH POSITIVE PARTIAL TRANSPOSES KIL-CHAN HA AND SEUNG-HYEOK KYE arxiv:1307.1362v1 [quant-ph] 4 Jul 2013 Abstract. We construct faces
GEOMETRY FOR SEPARABLE STATES AND CONSTRUCTION OF ENTANGLED STATES WITH POSITIVE PARTIAL TRANSPOSES KIL-CHAN HA AND SEUNG-HYEOK KYE arxiv:1307.1362v1 [quant-ph] 4 Jul 2013 Abstract. We construct faces
Linear Regression and Its Applications
 Linear Regression and Its Applications Predrag Radivojac October 13, 2014 Given a data set D = {(x i, y i )} n the objective is to learn the relationship between features and the target. We usually start
Linear Regression and Its Applications Predrag Radivojac October 13, 2014 Given a data set D = {(x i, y i )} n the objective is to learn the relationship between features and the target. We usually start
Gravitational radiation
 Lecture 28: Gravitational radiation Gravitational radiation Reading: Ohanian and Ruffini, Gravitation and Spacetime, 2nd ed., Ch. 5. Gravitational equations in empty space The linearized field equations
Lecture 28: Gravitational radiation Gravitational radiation Reading: Ohanian and Ruffini, Gravitation and Spacetime, 2nd ed., Ch. 5. Gravitational equations in empty space The linearized field equations
Taylor and Laurent Series
 Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
An angle in the Cartesian plane is in standard position if its vertex lies at the origin and its initial arm lies on the positive x-axis.
 Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Notes on multivariable calculus
 Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
Lecture 2: Isometries of R 2
 Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Isometries of R 2 1.1 The synthetic vs. analytic approach; axiomatics We discussed briefly what an axiomatic system is: a collection of undefined terms related by axioms. Further terms
Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Isometries of R 2 1.1 The synthetic vs. analytic approach; axiomatics We discussed briefly what an axiomatic system is: a collection of undefined terms related by axioms. Further terms
:25 1. Rotations. A rotation is in general a transformation of the 3D space with the following properties:
 2011-02-17 12:25 1 1 Rotations in general Rotations A rotation is in general a transformation of the 3D space with the following properties: 1. does not change the distances between positions 2. does not
2011-02-17 12:25 1 1 Rotations in general Rotations A rotation is in general a transformation of the 3D space with the following properties: 1. does not change the distances between positions 2. does not
Least Squares Regression
 Least Squares Regression Chemical Engineering 2450 - Numerical Methods Given N data points x i, y i, i 1 N, and a function that we wish to fit to these data points, fx, we define S as the sum of the squared
Least Squares Regression Chemical Engineering 2450 - Numerical Methods Given N data points x i, y i, i 1 N, and a function that we wish to fit to these data points, fx, we define S as the sum of the squared
The double layer potential
 The double layer potential In this project, our goal is to explain how the Dirichlet problem for a linear elliptic partial differential equation can be converted into an integral equation by representing
The double layer potential In this project, our goal is to explain how the Dirichlet problem for a linear elliptic partial differential equation can be converted into an integral equation by representing
Physics 411 Lecture 7. Tensors. Lecture 7. Physics 411 Classical Mechanics II
 Physics 411 Lecture 7 Tensors Lecture 7 Physics 411 Classical Mechanics II September 12th 2007 In Electrodynamics, the implicit law governing the motion of particles is F α = m ẍ α. This is also true,
Physics 411 Lecture 7 Tensors Lecture 7 Physics 411 Classical Mechanics II September 12th 2007 In Electrodynamics, the implicit law governing the motion of particles is F α = m ẍ α. This is also true,
Extreme Values and Positive/ Negative Definite Matrix Conditions
 Extreme Values and Positive/ Negative Definite Matrix Conditions James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 8, 016 Outline 1
Extreme Values and Positive/ Negative Definite Matrix Conditions James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 8, 016 Outline 1
Rotations & reflections
 Rotations & reflections Aim lecture: We use the spectral thm for normal operators to show how any orthogonal matrix can be built up from rotations. In this lecture we work over the fields F = R & C. We
Rotations & reflections Aim lecture: We use the spectral thm for normal operators to show how any orthogonal matrix can be built up from rotations. In this lecture we work over the fields F = R & C. We
Elementary maths for GMT
 Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 1: Vectors, Representations Algebra and Linear Algebra Algebra: numbers and operations on numbers 2 + 3 = 5 3 7 = 21 Linear Algebra: tuples, triples... of numbers
Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 1: Vectors, Representations Algebra and Linear Algebra Algebra: numbers and operations on numbers 2 + 3 = 5 3 7 = 21 Linear Algebra: tuples, triples... of numbers
Homogeneous Linear Systems and Their General Solutions
 37 Homogeneous Linear Systems and Their General Solutions We are now going to restrict our attention further to the standard first-order systems of differential equations that are linear, with particular
37 Homogeneous Linear Systems and Their General Solutions We are now going to restrict our attention further to the standard first-order systems of differential equations that are linear, with particular
Rigid Geometric Transformations
 Rigid Geometric Transformations Carlo Tomasi This note is a quick refresher of the geometry of rigid transformations in three-dimensional space, expressed in Cartesian coordinates. 1 Cartesian Coordinates
Rigid Geometric Transformations Carlo Tomasi This note is a quick refresher of the geometry of rigid transformations in three-dimensional space, expressed in Cartesian coordinates. 1 Cartesian Coordinates
Topic 14 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 Row reduction and subspaces 4. Goals. Be able to put a matrix into row reduced echelon form (RREF) using elementary row operations.. Know the definitions of null and column
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 Row reduction and subspaces 4. Goals. Be able to put a matrix into row reduced echelon form (RREF) using elementary row operations.. Know the definitions of null and column
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra
 CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
2. Force Systems. 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Force
 2. Force Systems 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Force - A force is an action of one body on another. - A force is an action which tends to cause acceleration of a body (in dynamics). - A force is a vector quantity.
2. Force Systems 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Force - A force is an action of one body on another. - A force is an action which tends to cause acceleration of a body (in dynamics). - A force is a vector quantity.
Mathematics 1. Part II: Linear Algebra. Exercises and problems
 Bachelor Degree in Informatics Engineering Barcelona School of Informatics Mathematics Part II: Linear Algebra Eercises and problems February 5 Departament de Matemàtica Aplicada Universitat Politècnica
Bachelor Degree in Informatics Engineering Barcelona School of Informatics Mathematics Part II: Linear Algebra Eercises and problems February 5 Departament de Matemàtica Aplicada Universitat Politècnica
The Derivative of a Function Measuring Rates of Change of a function. Secant line. f(x) f(x 0 ) Average rate of change of with respect to over,
 The Derivative of a Function Measuring Rates of Change of a function y f(x) f(x 0 ) P Q Secant line x 0 x x Average rate of change of with respect to over, " " " " - Slope of secant line through, and,
The Derivative of a Function Measuring Rates of Change of a function y f(x) f(x 0 ) P Q Secant line x 0 x x Average rate of change of with respect to over, " " " " - Slope of secant line through, and,
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations. Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve:
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
 Jim Lambers MAT 80 Spring Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 114 in Stewart and Section 3 in Marsden and Tromba Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
Jim Lambers MAT 80 Spring Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 114 in Stewart and Section 3 in Marsden and Tromba Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
Linear Models Review
 Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Chapter 5. The multivariate normal distribution. Probability Theory. Linear transformations. The mean vector and the covariance matrix
 Probability Theory Linear transformations A transformation is said to be linear if every single function in the transformation is a linear combination. Chapter 5 The multivariate normal distribution When
Probability Theory Linear transformations A transformation is said to be linear if every single function in the transformation is a linear combination. Chapter 5 The multivariate normal distribution When
Notes on Radian Measure
 MAT 170 Pre-Calculus Notes on Radian Measure Radian Angles Terri L. Miller Spring 009 revised April 17, 009 1. Radian Measure Recall that a unit circle is the circle centered at the origin with a radius
MAT 170 Pre-Calculus Notes on Radian Measure Radian Angles Terri L. Miller Spring 009 revised April 17, 009 1. Radian Measure Recall that a unit circle is the circle centered at the origin with a radius
Practice Exam. 2x 1 + 4x 2 + 2x 3 = 4 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 = 1 2x 1 + 3x 2 + 4x 3 = 5
 Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems
 Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
