CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 5
|
|
|
- Marjory Booth
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 5 1. Brief historical sketch of heat engine ( using heat to produce work ) Newcomen Engine - atmospheric engine built by Thomas Newcomen, primarily used to pump water out of coal mines ( ~1712 ), - check out animation ) - Remarks: a. Work is actually done by the atmosphere, after cylinder approached vacuum. b. Valves were automated using tappets and weights that depend on the position of the pump. CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 1 c. One Newcomen engine known as Fairbottom Bobs was purchased, dismantled and then reassembled in H. Ford Museum in Dearborn, MI. Fig. 1. Newcomen Engine. 1 1 Illustration from D.S.L. Cardwell, From Watt to Clausius, Heinemann Educational Books, Ltd., 1971,p.16 CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 2
2 James Watt s 2-Cylinder Solution (~1763) - Came across the problem when fixing a model Newcomen engine for a class in Glasgow University: the reduced scale made the engine very inefficient. - Had to use latent heat calculation as well as phase-diagram of steam - Research results: i) For engine economy, the engine needs to be hot all the time ii) For maximum power, the steam pressure at saturation point needs to be lower (i.e. at lower temperature) so that the atmosphere can push more effectively. - Problem: a cylinder can not be simultaneously hot and cold. - Solution: use two separate cylinders - Also used low-pressure steam to help push piston down. (see Fig. 2) - Watt, and business partner Matthew Boulton, dominated the engine industry (with several improved designs) for several years. - A Watt-Boulton rotative engine is also housed in Henry Ford Museum. CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 3 Fig.2. James Watt s two-cylinder engine. 2 2 Illustration from D.S.L. Cardwell, From Watt to Clausius, Heinemann Educational Books, Ltd., 1971,p.49 CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 4
3 Carnot Cycle - proposed by Sadi Carnot in 1824, inspired by heat engines, specially Watt s steam engine. - Inspired by Watt s 2-cylinder engine, concluded that to generate power, one must have a cold body reservoir as well as a hot body reservoir (isothermal paths). For maximum power, the paths should be reversible, and outside the heating and cooling sub-paths, no heat exchange between gas and surrounding (adiabatic paths). - The cycle is idealized but it represents the most efficient heat engine. CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 5 Fig. 3. Carnot s Cycle. 3 3 Illustration from D.S.L. Cardwell, From Watt to Clausius, Heinemann Educational Books, Ltd., 1971,p.194. CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 6
4 2. The Carnot Cycles ( assume an ideal gas with constant c p ) a) To produce work using hot and cold reservoir (Carnot engine) - Isothermal expansion (1 2), adiabatic expansion (2 3), isothermal compression (3 4), adiabatic compression (4 1) Fig. 4. Carnot engine cycle. - Sample given conditions/data: T H (= T 1 ), T C (= T 4 ), v 1, v 3 and c p. - Can compute for pressure and molar volume at all points. i) P 1 = RT H /v 1, P 3 = RT C /v 3 ii) P 2 = P 3 (T H /T C ) k/(k 1), P 4 = P 1 (T C /T H ) k/(k 1) Note: P 1 /P 2 = P 4 /P 3 for the cycle CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 7 iii) v 2 = RT H /P 2, v 4 = RT C /P 4 (or v 2 = v 1 (P 1 /P 2 ), v 4 = v 3 (P 3 /P 4 )) Note: v 2 /v 1 = v 3 /v 4 - Can also find u, q in and w by of each sub-path. i) u 1 2 = 0, q in,1 2 = RT H ln(v 2 /v 1 ) = w by,1 2 u 3 4 = 0, q in,3 4 = RT C ln(v 4 /v 3 ) = w by,3 4 ii) q in,2 3 = 0, w by,2 3 = u 2 3 = c v (T H T C ) q in,4 1 = 0, w by,4 1 = u 4 1 = c v (T C T H ) - Net work done by gas: w by,net = RT H ln(v 2 /v 1 ) + RT C ln(v 3 /v 4 ) +c v (T H T C ) + c v (T C T H ) = R(T H T C ) ln(v 2 /v 1 ) [ because v 2 /v 1 = v 3 /v 4 ] - Efficiency : η = w by,net /q in,1 2 η = R(T H T C ) ln(v 2 /v 1 ) RT H ln(v 2 /v 1 ) = T H T C T H CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 8
5 also known as Carnot efficiency : the ideal maximum work that can be obtained from an engine Note: it only depends on the temperatures of the hot and cold reservoirs does not depend on the working fluid (i.e. not dependent on any particular constant value of c p ; as long as the ideal gas behavior is a good approximation) b) To extract (pump) heat from a cold reservoir to a hot reservoir (Carnot refrigerator) Fig. 5. Carnot refrigeration cycle. CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 9 - Similar calculations, except (1,2,3,4) is replaced by (d,c,b,a), and paths are in reversed directions. Thus, i) u a b = 0, q in,a b = RT C ln(v b /v a ) = w by,b a u c d = 0, q in,c d = RT H ln(v d /v c ) = w by,c d ii) q in,b c = 0, w by,b c = u b c = c v (T C T H ) - Net work done on gas: q in,d a = 0, w by,d a = u d a = c v (T H T C ) w on,net = RT C ln(v a /v b ) + RT H ln(v c /v d ) +c v (T H T C ) + c v (T C T H ) = R(T H T C ) ln(v a /v b ) [ because v d /v c = v b /v a ] - Coefficient of performance (COP) COP = q in,a b w on,net = T C T H T C Q: Can we have η > 1? Can we have COP > 1? CM3230 Lecture 5 Page 10
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
October 18, 2011 Carnot cycle - 1
 Carnot Cycle In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (The book is now free online You should try it out) To construct an engine, Carnot noted, at
Carnot Cycle In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (The book is now free online You should try it out) To construct an engine, Carnot noted, at
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H. Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK expansion?
 ...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
Lecture 9. Heat engines. Pre-reading: 20.2
 Lecture 9 Heat engines Pre-reading: 20.2 Review Second law when all systems taking part in a process are included, the entropy remains constant or increases. No process is possible in which the total entropy
Lecture 9 Heat engines Pre-reading: 20.2 Review Second law when all systems taking part in a process are included, the entropy remains constant or increases. No process is possible in which the total entropy
Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
CARNOT CYCLE = T = S ( U,V )
 hermodynamics CANO CYCE Do not trouble students with history In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (he book is now free online You should try it
hermodynamics CANO CYCE Do not trouble students with history In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (he book is now free online You should try it
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
The Physics of Energy
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Corso di Laurea in FISICA II Introduction to thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni The Physics of Energy Use
Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Corso di Laurea in FISICA II Introduction to thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni The Physics of Energy Use
Thermodynamics. AP Physics B
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B ork done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then
Thermodynamics AP Physics B ork done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Thermodynamics. AP Physics B
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B Important Distinctions Thermodynamics study of processes in which energy is transferred as heat and work. There is a difference between heat and work: Heat is energy transferred
Thermodynamics AP Physics B Important Distinctions Thermodynamics study of processes in which energy is transferred as heat and work. There is a difference between heat and work: Heat is energy transferred
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Carnot Cycle - Chemistry LibreTexts
 CARNOT CYCLE The Carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of incidental wasteful processes
CARNOT CYCLE The Carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of incidental wasteful processes
Lecture 26. Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators.
 ecture 26 Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators. The Second aw of Thermodynamics Introduction The absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is
ecture 26 Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators. The Second aw of Thermodynamics Introduction The absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is
Heat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle. Irreversible Processes. Reversible Processes. Carnot Cycle
 Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Physics 202 Homework 5
 Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Not so black. Black Hole Thermodynamics. Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish.
 Not so black Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish. Black Hole Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of thermodynamics requires that black holes are round *. First law of thermodynamics requires
Not so black Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish. Black Hole Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of thermodynamics requires that black holes are round *. First law of thermodynamics requires
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines
 Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics. Charanjeet Singh Bansrao. Abstract
 Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics Charanjeet Singh Bansrao bansraos@yahoo.co.in Abstract We know that internal energy of an ideal gas is a state function and it solely
Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics Charanjeet Singh Bansrao bansraos@yahoo.co.in Abstract We know that internal energy of an ideal gas is a state function and it solely
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0)
 Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
V. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. V. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 P V. he Second aw of hermodynamics E. he Carnot Cycle. he reversible heat engine (a piston cylinder device) that operates on a cycle between heat reservoirs at and, as shown below on a P-v diagram, is
P V. he Second aw of hermodynamics E. he Carnot Cycle. he reversible heat engine (a piston cylinder device) that operates on a cycle between heat reservoirs at and, as shown below on a P-v diagram, is
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes
 Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes Last time we started discussing cyclic heat engines these are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work We found that in general, heat engines
Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes Last time we started discussing cyclic heat engines these are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work We found that in general, heat engines
SOLUTION: Consider the system to be the refrigerator (shown in the following schematic), which operates over a cycle in normal operation.
 Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 452 Summer Quarter 2014
 Lecture 0 7/6/ ERD: 5. DeVoe:.3.,.3.3 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 5 Summer Quarter 0 A. Work and the Second Law of Thermodynamics: Efficiency of eat Engines One of the most
Lecture 0 7/6/ ERD: 5. DeVoe:.3.,.3.3 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 5 Summer Quarter 0 A. Work and the Second Law of Thermodynamics: Efficiency of eat Engines One of the most
Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Lecture 26, Dec. 1 Goals: Chapter 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators. Recognize some practical applications
Lecture 26, Dec. 1 Goals: Chapter 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators. Recognize some practical applications
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ]
![w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ] w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ]](/thumbs/85/91320285.jpg) Chemistry 433 Lecture 9 Entropy and the Second Law NC State University Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions One might be tempted based on the results of thermochemistry to predict that all exothermic reactions
Chemistry 433 Lecture 9 Entropy and the Second Law NC State University Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions One might be tempted based on the results of thermochemistry to predict that all exothermic reactions
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Physics 1501 Lecture 37
 Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy
 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Addison Ault, Department of Chemistry, Cornell College, Mt. Vernon IA. The Carnot cycle is usually described in terms of classical
 1 The Carnot Cycle: from Classical Thermo to Stat Thermo Addison Ault, Department of Chemistry, Cornell College, Mt. Vernon IA The Carnot cycle is usually described in terms of classical thermodynamics,
1 The Carnot Cycle: from Classical Thermo to Stat Thermo Addison Ault, Department of Chemistry, Cornell College, Mt. Vernon IA The Carnot cycle is usually described in terms of classical thermodynamics,
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
Heat engines and the second law of thermodynamics
 Heat engines and the second law of thermodynamics Thermodynamic cycles A thermodynamic cycle is a series of processes which change the volume, temperature and pressure of a gas, but which at the end return
Heat engines and the second law of thermodynamics Thermodynamic cycles A thermodynamic cycle is a series of processes which change the volume, temperature and pressure of a gas, but which at the end return
Thermodynamics Lecture Series
 Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
The Laws of Thermodynamics
 MME 231: Lecture 06 he Laws of hermodynamics he Second Law of hermodynamics. A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUE, Dhaka oday s opics Relation between entropy transfer and heat Entropy change
MME 231: Lecture 06 he Laws of hermodynamics he Second Law of hermodynamics. A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUE, Dhaka oday s opics Relation between entropy transfer and heat Entropy change
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Thermodynamics of Materials
 Thermodynamics of Materials 2nd Lecture 2008. 3. 5 (Wed.) Temperature Scale After thermometers were invented, different thermometers used different temperature scales. Standardization was necessary. Invent
Thermodynamics of Materials 2nd Lecture 2008. 3. 5 (Wed.) Temperature Scale After thermometers were invented, different thermometers used different temperature scales. Standardization was necessary. Invent
The need for something else: Entropy
 Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Physics 121, April 29, The Second Law of Thermodynamics.
 Physics 121, April 29, 2008. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. http://www.horizons.uc.edu/masterjuly1998/oncampus.htm Physics 121. April 29, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: The Second
Physics 121, April 29, 2008. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. http://www.horizons.uc.edu/masterjuly1998/oncampus.htm Physics 121. April 29, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: The Second
Examples. Fire Piston (demo) Example (Comparison of processes)
 Examples Fire Piston (demo) Fire Piston istory http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fire_piston Example 19.68 (Comparison of processes) Fire piston calculations http://complex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262/soln/fire_piston.pdf
Examples Fire Piston (demo) Fire Piston istory http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fire_piston Example 19.68 (Comparison of processes) Fire piston calculations http://complex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262/soln/fire_piston.pdf
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Applied Thermodynamics. Gas Power Cycles
 Applied Thermodynamics Gas Power Cycles By: Mohd Yusof Taib Faculty of Mechanical Engineering myusof@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims To identify and recognized ideal thermodynamics cycle. To analyze
Applied Thermodynamics Gas Power Cycles By: Mohd Yusof Taib Faculty of Mechanical Engineering myusof@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims To identify and recognized ideal thermodynamics cycle. To analyze
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
T s change via collisions at boundary (not mechanical interaction)
 Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Second Law of Thermodynamics -
 Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Physics 207 Lecture 27. Lecture 26. Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators
 Goals: Lecture 26 Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators Reading assignment for Wednesday: Chapter 20. Physics 207: Lecture 27, Pg 1 Entropy A
Goals: Lecture 26 Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators Reading assignment for Wednesday: Chapter 20. Physics 207: Lecture 27, Pg 1 Entropy A
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Existing Resources: Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics background and interests:
 Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
THERMODYNAMICS. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Isotherm
 12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
Irreversible Processes
 Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 16, 2013
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
Photon steam engines. Work can be extracted from a single heat bath at the boundary between classical and quantum thermodynamics
 Photon steam engines Work can be extracted from a single heat bath at the boundary between classical and quantum thermodynamics A quantum Carnot engine. Hot atoms flow from a heat bath at temperature T
Photon steam engines Work can be extracted from a single heat bath at the boundary between classical and quantum thermodynamics A quantum Carnot engine. Hot atoms flow from a heat bath at temperature T
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 115. Specific heats revisited Entropy. General Physics II. Session 13
 Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1
 Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Heat What is heat? Work = 2. PdV 1
 eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
Irreversible Processes
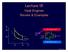 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
MC 405 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy
 Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, Physics 121. April 24, Course Information
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 2007
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 007 5.9 Energy Environment and Society (a Project Based First Year Subject supported by the d'arbeloff Program) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 007 5.9 Energy Environment and Society (a Project Based First Year Subject supported by the d'arbeloff Program) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Notes Set 4c: Heat engines and the Carnot cycle
 ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
