Thermodynamics. AP Physics B
|
|
|
- Chloe Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thermodynamics AP Physics B
2 Important Distinctions Thermodynamics study of processes in which energy is transferred as heat and work. There is a difference between heat and work: Heat is energy transferred due to a difference in temperature. Work is energy transferred that is unrelated to a difference in temperature. Open System where mass and energy are exchanged between objects and the environment. Closed System where mass does not enter or leave the system, but energy is exchanged with the environment. Isolated System closed system in which no energy is exchanged with the environment.
3 Work done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then applies a force on the piston wall pushing it a specific displacement. Thus it can be said that a gas can do WORK.
4 Work done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then applies a force on the piston wall pushing it a specific displacement. Thus it can be said that a gas can do WORK. where W is work done by the gas
5 Work is the AREA of a P vs. V graph by Here is how it would be written for W = work done on the gas: W = PΔV on ΔV = + = Work is done BY the gas (gas loses E) ΔV = = Work is done ON the gas (environment loses E) So the overall value of W on is (+) when work is done ON the gas.
6 Work is the AREA of a P vs. V graph Here is how it would be written for W = work done on the gas: W = PΔV on ΔV = + = Work is done BY the gas ΔV = = Work is done ON the gas W by = positive W on = negative When ΔV is positive, since energy is expelled BY the gas.
7 Work is the AREA of a P vs. V graph Here is how it would be written for W = work done on the gas: W = PΔV on ΔV = + = Work is done BY the gas ΔV = = Work is done ON the gas W by = positive W on = negative When ΔV is positive, since energy is expelled BY the gas. The negative sign in the equation for WORK is often misunderstood. Since work done BY a gas has a positive volume change we must understand that the gas itself is USING UP ENERGY or in other words, it is losing energy, thus the negative sign. When work is done ON a gas the change in volume is negative. This cancels out the negative sign in the equation. This makes sense, as some EXTERNAL agent is ADDING energy to the gas.
8 Internal Energy (ΔU) and Heat Energy (Q) All of the energy inside a system is called INTERNAL ENERGY, ΔU. When you add HEAT, (Q), you are adding energy and the internal energy INCREASES. Both are measured in Joules. But when you add heat, there is usually an increase in temperature associated with the change.
9 First Law of Thermodynamics The internal energy of a system tends to increase when HEAT is added and work is done ON the system. ΔU = Q +W ΔU = Q Add +W on or ΔU = Q Add W by The bottom line is that if you ADD heat and transfer work TO the gas, the internal energy must obviously go up, as you have MORE than what you started with.
10 Thermo in Chemistry Class vs. Physics Class In chemistry we look at the changes in chemical processes (like chemical reactions), but in physics we look at the changes in the physical processes. Physics reveals the underlying laws of thermodynamics, while chemistry likely applies the principles to particular chemical reactions under study. Chemical engineers (physicists) apply the laws of thermodynamics to large scale apparatuses that produce end products. Chemists focus on variables such as enthalpy (H) and Gibbs Free Energy (G), while physicists focus on variables such as heat supplied/removed (Q) and work done (W) by an expanding gas sample.
11 Difference between ΔH and Q Enthalpy is defined as H = U + PV or ΔH = ΔU + Δ(PV) ΔH = Q + W + Δ(PV) IF pressure is constant ΔH = Q + W + PΔV but since W = - PΔV, ΔH = Q But this is if and ONLY IF pressure is constant!
12 Another Difference Between ΔH and Q There is an important fundamental difference between enthalpy and heat. Lets say you are studying a process that takes your system from P 1, V 1 and T 1 to P 2, V 2 and T 2. Now, there are many different paths one can take between the two thermodynamic states. Along each of these paths, the values of Q and W will differ. However, no matter what path you take, ΔH for the transformation will always be the same because ΔH depends only on the initial and final states of the transformation. For example, an adiabatic path has Q = 0, whereas a nonadiabatic path between the same two states would have Q 0. State functions include: U, P, V, H, and S Non-state (path dependent) functions include: Q, W
13 Example Sketch a PV diagram and find the work done by the gas during the following stages. (a) A gas is expanded from a volume of 1.0 L to 3.0 L at a constant pressure of 3.0 atm. W BY = PΔV = ( ) = 600 J (b) The gas is then cooled at a constant volume until the pressure falls to 2.0 atm W = PΔV = 0,.since ΔV = 0
14 Example continued c) The gas is then compressed at a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from a volume of 3.0 L to 1.0 L. W ON = PΔV = ( ) = = -400 J d) The gas is then heated until its pressure increases from 2.0 atm to 3.0 atm at a constant volume.
15 Example continued What is the NET WORK? 600 J J = 200 J Rule of thumb: If the system rotates CW, the NET work by the gas is positive. NET work is the area inside the shape. If the system rotates CCW, the NET work done by the gas is negative (because work is done on the gas).
16 Example A series of thermodynamic processes is shown in the pv-diagram. In process ab 150 J of heat is added to the system, and in process bd, 600J of heat is added. Fill in the chart J 840 J 990 J J - _
17 Special Cases with the First Law Isothermal Process thermodynamic process in which the temperature of the system remains constant. Occurs often when heat reservoirs are present. Adiabatic Process thermodynamic process in which no heat is exchanged between the system and its environment. Occurs rapidly or when well insulated. Isobaric Process thermodynamic process in which the pressure of the system remains constant. Isochoric Process thermodynamic process in which the volume of the system remains constant. P P P P ΔT = 0; ΔU = 0, so W = -Q V Q = 0, so ΔU = W V W = -PΔV V ΔV = 0; W = 0, so ΔU = Q V
18 Thermodynamic Processes - Isothermal To keep the temperature constant both the pressure and volume change to compensate. (Volume goes up, pressure goes down) BOYLES LAW
19 Thermodynamic Processes - Isobaric Heat is added to the gas which increases the Internal Energy (U) Work is done by the gas as it changes in volume. The path of an isobaric process is a horizontal line called an isobar. U = Q - W can be used since the WORK is POSITIVE in this case
20 Thermodynamic Processes - Isovolumetric
21 Thermodynamic Processes - Adiabatic ADIABATIC- (GREEKadiabatos : "impassable") In other words, NO HEAT can leave or enter the system.
22 In Summary
23 Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat will not flow spontaneously from a colder body to a warmer body AND heat energy cannot be transformed completely into mechanical work. In other words: 1) Heat always flows from a hot body to a cold body 2) Nothing is 100% efficient
24 Engines Heat flows from a HOT reservoir to a COLD reservoir Q H = remove from, absorbs = hot Q C = exhausts to, expels = cold
25 Engine Efficiency In order to determine the thermal efficiency of an engine you have to look at how much ENERGY you get OUT based on how much you energy you take IN. In other words:
26 Is there an IDEAL engine model? Our goal is to figure out just how efficient such a heat engine can be: what s the most work we can possibly get for a given amount of fuel? The efficiency question was first posed and solved by Sadi Carnot in 1820, not long after steam engines had become efficient enough to begin replacing water wheels, at that time the main power sources for industry. Not surprisingly, perhaps, Carnot visualized the heat engine as a kind of water wheel in which heat (the fluid ) dropped from a high temperature to a low temperature, losing potential energy which the engine turned into work done, just like a water wheel.
27 Carnot Efficiency Carnot believed that there was an absolute zero of temperature, to which fluid would give up all its heat energy. Therefore, if it falls only half-way to absolute zero from its beginning temperature, it will give up half its heat, and an engine taking in heat at T and shedding it at ½T will be utilizing half the possible heat, and be 50% efficient. Picture a water wheel that takes in water at the top of a waterfall, but lets it out halfway down. So, the efficiency of an ideal engine operating between two temperatures will be equal to the fraction of the temperature drop towards absolute zero that the heat undergoes.
28 Carnot Efficiency Carnot temperatures must be expressed in KELVIN!!!!!! The Carnot model has 4 parts An Isothermal Expansion An Adiabatic Expansion An Isothermal Compression An Adiabatic Compression The PV diagram, in a way, shows us that the ratio of the heats are symbolic to the ratio of the 2 temperatures
29 Example A particular engine has a power output of 5000 W and an efficiency of 25%. If the engine expels 8000 J of heat in each cycle, find (a) the heat absorbed in each cycle and (b) the time for each cycle 10,667 J 2667 J 0.53 s
30 Example The efficiency of a Carnot engine is 30%. The engine absorbs 800 J of heat per cycle from a hot temperature reservoir at 500 K. Determine (a) the heat expelled per cycle and (b) the temperature of the cold reservoir 240 J 560 J 350 K
Thermodynamics. AP Physics B
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B ork done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then
Thermodynamics AP Physics B ork done by a gas Suppose you had a piston filled with a specific amount of gas. As you add heat, the temperature rises and thus the volume of the gas expands. The gas then
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 16 Thermodynamics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes
 Name APPH7_Notes3key Page 1 of 6 AP Physics Date Notes: Thermodynamics 12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy
Name APPH7_Notes3key Page 1 of 6 AP Physics Date Notes: Thermodynamics 12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy
Thermodynamics: The Laws
 Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
CH 15. Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
The laws of Thermodynamics. Work in thermodynamic processes
 The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
Physics 150. Thermodynamics. Chapter 15
 Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
Physics 115. Specific heats revisited Entropy. General Physics II. Session 13
 Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
First law: examples 1) isobaric process
 P A P question B P C v In which case is the work done on the gas largest? The area under the curves in cases B and C is largest (i.e. the absolute amount of work is largest). In case C, the volume becomes
P A P question B P C v In which case is the work done on the gas largest? The area under the curves in cases B and C is largest (i.e. the absolute amount of work is largest). In case C, the volume becomes
Physics 202 Homework 5
 Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
THERMODYNAMICS. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Isotherm
 12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
NOTE: Only CHANGE in internal energy matters
 The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
Physics 1501 Lecture 37
 Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Chapter 19. First Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05
 Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05 Heat and Work Work during volume change Work in Thermodynamics Work can be done on a deformable system, such as a gas Consider a cylinder
Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05 Heat and Work Work during volume change Work in Thermodynamics Work can be done on a deformable system, such as a gas Consider a cylinder
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
THERMODYNAMICS b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
 THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes
 The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Beginning with the Industrial Revolution, humans have harnessed power through the use of the first law of thermodynamics,
The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Beginning with the Industrial Revolution, humans have harnessed power through the use of the first law of thermodynamics,
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Lecture 26. Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators.
 ecture 26 Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators. The Second aw of Thermodynamics Introduction The absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is
ecture 26 Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators. The Second aw of Thermodynamics Introduction The absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is
Carnot Cycle - Chemistry LibreTexts
 CARNOT CYCLE The Carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of incidental wasteful processes
CARNOT CYCLE The Carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of incidental wasteful processes
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle. Irreversible Processes. Reversible Processes. Carnot Cycle
 Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Introduction to Thermodynamics And Applications. Physics 420 Patrick Lawrence
 Introduction to Thermodynamics And Applications Physics 420 Patrick Lawrence Topics Confusion about Heat, Internal Energy and Temperature Methods of heat transfer The Ideal Gas Law Compression Applications
Introduction to Thermodynamics And Applications Physics 420 Patrick Lawrence Topics Confusion about Heat, Internal Energy and Temperature Methods of heat transfer The Ideal Gas Law Compression Applications
Process Nature of Process
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion of Solids
 Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
THERMODINAMICS. Tóth Mónika
 THERMODINAMICS Tóth Mónika 2014 monika.a.toth@aok.pte.hu Temperature Temperature: is related to the average energy of the motion of the particles of an object or system. Different temperature scales. Thermometer
THERMODINAMICS Tóth Mónika 2014 monika.a.toth@aok.pte.hu Temperature Temperature: is related to the average energy of the motion of the particles of an object or system. Different temperature scales. Thermometer
CHAPTER 15 The Laws of Thermodynamics. Units
 CHAPTER 15 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes and the First Law Human Metabolism and the First Law The Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction Heat
CHAPTER 15 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes and the First Law Human Metabolism and the First Law The Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction Heat
Thermodynamics: The First Law and Heat Transfer
 Thermodynamics: The First Law and Heat Transfer From Warmup I would love to work problems in class. I think a synthesis problem might be useful. I try to make the best use of our very limited class time.
Thermodynamics: The First Law and Heat Transfer From Warmup I would love to work problems in class. I think a synthesis problem might be useful. I try to make the best use of our very limited class time.
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 6, Chapter 19: 7, 12, 19, 30, 37, 44, 53, 61, 69
 PYS 0 Practice problem set 6, hapter 9: 7,, 9, 0, 7, 44,, 6, 69 9.7. Solve: (a) he heat extracted from the cold reservoir is calculated as follows: (b) he heat exhausted to the hot reservoir is K 4.0 00
PYS 0 Practice problem set 6, hapter 9: 7,, 9, 0, 7, 44,, 6, 69 9.7. Solve: (a) he heat extracted from the cold reservoir is calculated as follows: (b) he heat exhausted to the hot reservoir is K 4.0 00
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 26, 27, 37, 44, 46, 52, 58
 PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
Physics 2101 Section 3 April 23th: Chap. 18 Ann n ce n e t nnt : Quiz #8 Today Exam #4, A Exam #4, p A ril 28
 Physics 2101 Section 3 April 23 th : Chap. 18 Announcements: n nt Quiz #8 Today Exam #4, April 28 th (Ch. 13.6-18.8) 18.8) Final Exam: May 11 th (Tuesday), 7:30 AM Make up Final: May 15 th (Saturday) 7:30
Physics 2101 Section 3 April 23 th : Chap. 18 Announcements: n nt Quiz #8 Today Exam #4, April 28 th (Ch. 13.6-18.8) 18.8) Final Exam: May 11 th (Tuesday), 7:30 AM Make up Final: May 15 th (Saturday) 7:30
Laws of Thermodynamics
 Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts
 236 7 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 7 CHAPTER First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts CONTENTS THERMODYNAMIC TERMS SYSTEM, BOUNDARY, SURROUNDINGS HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS TYPES OF THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
236 7 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 7 CHAPTER First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts CONTENTS THERMODYNAMIC TERMS SYSTEM, BOUNDARY, SURROUNDINGS HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS TYPES OF THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, Physics 121. April 24, Course Information
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
ΔU = Q W. Tue Dec 1. Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM WALTER 145. Thermodynamics 1st Law. 2 nd Law. Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H. Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK expansion?
 ...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics E int = Q + W other state variables E int is a state variable, so only depends on condition (P, V, T, ) of system. Therefore, E int only depends on initial and final states
First Law of Thermodynamics E int = Q + W other state variables E int is a state variable, so only depends on condition (P, V, T, ) of system. Therefore, E int only depends on initial and final states
Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
Another way of stating the Second Law then is: the universe is constantly getting more disorderly! Viewed that way, we can see the Second Law all
 Another way of stating the Second Law then is: the universe is constantly getting more disorderly! Viewed that way, we can see the Second Law all about us. We have to work hard to straighten a room, but
Another way of stating the Second Law then is: the universe is constantly getting more disorderly! Viewed that way, we can see the Second Law all about us. We have to work hard to straighten a room, but
Tuesday April 18 Topics for this Lecture: Thermodynamics Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas Law Laws of Thermodynamics PV diagrams & state transitions
 Tuesday April 18 Topics for this Lecture: Thermodynamics Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas Law Laws of Thermodynamics PV diagrams & state transitions Assignment 14 due Friday Pre-class due 15min before class The
Tuesday April 18 Topics for this Lecture: Thermodynamics Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas Law Laws of Thermodynamics PV diagrams & state transitions Assignment 14 due Friday Pre-class due 15min before class The
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state X along the path XYZX as shown in the PV-diagram.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines
 Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
Second Law of Thermodynamics -
 Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
2/18/2019. Ideal-Gas Processes. Thermodynamics systems. Thermodynamics systems
 Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems
 Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
S15--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch13_14_15 PRACTICE
 Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
6.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 6.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics Physics Tool box Thermodynamic System - any collection of objects that is convenient to regard as a unit, and may have the potential to exchange energy with its surroundings.
6.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics Physics Tool box Thermodynamic System - any collection of objects that is convenient to regard as a unit, and may have the potential to exchange energy with its surroundings.
Downloaded from
 Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
People s Physics book 3e
 The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
The area under the graph in a PV diagram is equal in magnitude to
 a volume V and exerts a uniform pressure P on the cylinder walls and the piston. The gas is compressed slowly enough so the system remains essentially in thermodynamic equilibrium at all times. As the
a volume V and exerts a uniform pressure P on the cylinder walls and the piston. The gas is compressed slowly enough so the system remains essentially in thermodynamic equilibrium at all times. As the
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
10. Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka)
 10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
11/29/2017 IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES. UNIT 2 Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory
 11/9/017 AP PHYSICS UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory CHAPTER 13 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES The U G of the water-earth system at the
11/9/017 AP PHYSICS UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory CHAPTER 13 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES The U G of the water-earth system at the
ATMO 551a Fall The Carnot Cycle
 What is a arnot ycle and Why do we care The arnot ycle arnot was a French engineer who was trying to understand how to extract usable mechanical work from a heat engine, that is an engine where a gas or
What is a arnot ycle and Why do we care The arnot ycle arnot was a French engineer who was trying to understand how to extract usable mechanical work from a heat engine, that is an engine where a gas or
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
Phys 22: Homework 10 Solutions W A = 5W B Q IN QIN B QOUT A = 2Q OUT 2 QOUT B QIN B A = 3Q IN = QIN B QOUT. e A = W A e B W B A Q IN.
 HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Reversible Processes. Furthermore, there must be no friction (i.e. mechanical energy loss) or turbulence i.e. it must be infinitely slow.
 Reversible Processes A reversible thermodynamic process is one in which the universe (i.e. the system and its surroundings) can be returned to their initial conditions. Because heat only flows spontaneously
Reversible Processes A reversible thermodynamic process is one in which the universe (i.e. the system and its surroundings) can be returned to their initial conditions. Because heat only flows spontaneously
Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes
 Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes Last time we started discussing cyclic heat engines these are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work We found that in general, heat engines
Lecture 10: Heat Engines and Reversible Processes Last time we started discussing cyclic heat engines these are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work We found that in general, heat engines
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3
![Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3 Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3](/thumbs/75/71840722.jpg) Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
Heat What is heat? Work = 2. PdV 1
 eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
Boundary. Surroundings
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Topics: Chapter Goal: Conservation of Energy Work in Ideal-Gas Processes
 Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
DAY 28. Summary of Primary Topics Covered. The 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics
 DAY 28 Summary of Primary Topics Covered The 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics The 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics says this - - Heat energy naturally flows from hotter objects to colder objects. We know this happens,
DAY 28 Summary of Primary Topics Covered The 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics The 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics says this - - Heat energy naturally flows from hotter objects to colder objects. We know this happens,
Temperature and Thermometers. Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated.
 Heat Energy Temperature and Thermometers Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated. Thermometers are instruments designed to measure temperature. In order
Heat Energy Temperature and Thermometers Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated. Thermometers are instruments designed to measure temperature. In order
Entropy and the Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics
 CHAPTER 5 Entropy and the Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics Key Points Entropy, S, is a state function that predicts the direction of natural, or spontaneous, change. Entropy increases for a spontaneous
CHAPTER 5 Entropy and the Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics Key Points Entropy, S, is a state function that predicts the direction of natural, or spontaneous, change. Entropy increases for a spontaneous
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Irreversible Processes
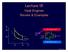 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Exam 1 Solutions 100 points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
