SRT Division and the Pentium FDIV Bug (draft lecture notes, CSCI P415)
|
|
|
- Percival Miles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SRT Division and the Pentium FDIV Bug (draft lecture notes, CSCI P4) Steven D. Johnson September 0, 000 Abstract This talk explains the widely publicized design error in a 994 issue of the Intel Corp. Pentium microprocessor. I present the SRT division algorithm on which the hardware is based. Then I show where the error occurs, and why it wasn t caught in verification. Finally, I speculation about whether the source of the but was a design error or a process error. For a sequence, {q i } [n] of digits, let [Q] m denote m k=0 q k 0 k We abuse notation above by interpreting digit q k as a number, and will omit the subscript m unless the context demands it. Here is an algorithm for long division. Dividend P and divisor D have been normalized to be less than 0. The partial values {p i } [n] are there only for discussion purposes. { P, D < 0} p 0, d, i := P, D, 0; while i < n do {inv inv} b choose q i {0... 9} such that... {p i q i d < d} p i+, i = 0(p i q i d), i + e { P [Q] d < d } 0 n Hence, on termination P/D [Q] n D < D 0 n
2 To put this in the usual way, the remainder (difference between computed an actual quotients) is smaller than D. Note that Thus, the loop invariants are, p = 0(p q d) = 0(0(p q d) q d) = 0(0(0(p 0 q 0 d) q d) q d) = 0 p 0 ( 0 q 0 d 0 q d 0 q 0 d ) = 0 P 0 k q k d d k=0 = 0 P [Q] d inv p i = 0 i P [Q] i d inv p i < 0 i D None of the arguments above are affected by the actual value of the radix (base). 0 can be replaced by any b and the program is still correct. In computer division the radix is a power of two; in the Pentium series, the radix is 4.
3 R 8 ) R 8 )
4 R - {00-97 R- = 40 R- ) 4 = 40 R+8} = =
5 The examples illustrate that by maintaining two partial quotients, one of positive quotient digits and the other of negative ones, we can sometimes recover from an invalid guess for the next digit. It is important to understand that this refinement is not error correcting. If the selected digit is too remote from the correct one, there is no chance of recovering. Within those limits, however, we can perform nonrestoring long division: making a guess based on the leading digits of the dividend and divisor, which is close enough to be corrected. Hence, we do not have to backtrack if the guess is wrong. SRT hardware exploits this in two ways. The first is the nonrestoring quality, just described. In radix 4, this would mean a choice of quotient digits from the set {,,, 0,,, }. However, the actual selection set used in hardware is {,, 0,, }. This reduces the multiplications to shifts. We always avoid selecting ± as a quotient digit. The geometric sum, i + = 8 Recall from (probably) your first homework assignment in mathematical induction that a + ar + ar + + ar n = a(i rn+ ) r In the algorithm, we need to keep p k+ within the range [ 8 d, 8 d]. To summarize, our division algorithm now looks like { P, D < } p 0, d, i := P, D, 0; while i < n do {inv inv} b choose q i {... + } such that... { 4(p i q i d) 8 d} p i+, i = 4(p i q i d), i + { e P [Q] d < d } 4 n where [Q] m = m k=0 q k 4 k inv p i = 4 i P [Q] d inv p i < 4 i D To maintain p i within range, each quotient digit must map the interval [ 8 d, 8 d]
6 into the interval [ d, d]. This is how we arrive at the staggered selections: Overlapping ranges permit a choice of two possible quotient digits. At any point along this interval, if the wrong digit a digit other than the one/two possibilities is selected, the algorithm cannot recover. Now, just like people doing long division, the algorithm must guess the next quotient digit, based on the most significant digits of the dividend and divisor. This guessing is represented by a two dimensional look-up table, indexed by the 7 leading bits of p + i, including the sign bit, and the five leading bits of d. Edleman cites Coe and Tang as stating that table entries may be determined by the following thresholds. In this table, we take P to be 8p k 8 and D to be 6d 6. q P min P max 8 D 4 4 D 8 4 D 4 D 0 8 D 8 + D D D 4 D D 6
7 -8/D -/D -4/D -/D -/D /D /D 4/D /D 8/D D P 4 The lookup table is a discrete version of this table, with boundaries lying within the overlapping regions (inexact rendering!): -8/D -/D -4/D -/D -/D /D /D 4/D /D 8/D D P 4 There were five errors in the lookup table, all along the boundary between the region and the thought-to-be-inaccessible region above it. Actually, an adjustment must be made in the table to account for the fact that P is represented in carry-save form. That is, the value of P is maintained 7
8 in two registers, S and C under the invariant that P = S + C. To add D and P, the actual computation performs S, C := (S C D), shiftleft((s C) (C D) (D S)) bitwise in parallel. Subtraction is similar; D is complemented bit-wise, giving D, and the is compensated by shifting a into the vacated 0-bit of C. In this way, carry propagation is eliminated until a single final addition is performed to recover P. The carry-save representation weakens the bounds on the digit selection regions. It can be shown that this may be compensated by lowering all upper bounds by 8. It would appear that this lowering exposed the five errors in the Pentium s lookup table. -8/D -/D -4/D -/D -/D /D /D 4/D /D 8/D D P 4 There remains a question of why the bug wasn t discovered in testing. Here are some relevant points: The lookup table is not symmetric. Random dividends and divisors do not result in random table accesses. In fact table access is far from uniform (!?). In fact, the algorithm accesses a bad entry to produce a bad p k+ only if p k indexes the table just below it. Note that since D never changes, the algorithm is always operating on a single column of the table. Theorem (Coe, Tang [Edelman]). a flawed table entry can only be reached if the divisor has the form d = d d d d 4 d d... and.d d d d 4 addresses one of the buggy columns 8
9 [Edelman] the error is bounded by e- when dividing two numbers in the standard interval [, ); and, no matter what happens the first eight quotient digits will be correct. References. Pratt. Anatomy of the Pentium Bug.. Edelman, Mathematics of the Pentium division bug.. Sharangpani and Barton. Statistical analysis of floating point flaw in the Pentium processor (994) 4. Clarke, German, and Zhao. Verifying the SRT division algorithm using theorem proving techniques.. Ruess, Shankar, and Srivas. Modular verification of SRT division. 6. Miner. Chapter six of Hardware Verification using Coinductive Assertions (PhD dissertation) 9
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 27 - misc2
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 27 - misc2 May 1, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec27-misc2 Page 1 Outline Linear Feedback Shift Registers Theory and practice Simple hardware division algorithms
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 27 - misc2 May 1, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec27-misc2 Page 1 Outline Linear Feedback Shift Registers Theory and practice Simple hardware division algorithms
Graduate Institute of Electronics Engineering, NTU Basic Division Scheme
 Basic Division Scheme 台灣大學電子所吳安宇博士 2002 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Shift/subtract division algorithm. Programmed division. Restoring hardware dividers. Nonstoring and signed division. Radix-2 SRT divisioin.
Basic Division Scheme 台灣大學電子所吳安宇博士 2002 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Shift/subtract division algorithm. Programmed division. Restoring hardware dividers. Nonstoring and signed division. Radix-2 SRT divisioin.
Lecture 11. Advanced Dividers
 Lecture 11 Advanced Dividers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 15 Variation in Dividers 15.3, Combinational and Array Dividers Chapter 16, Division
Lecture 11 Advanced Dividers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 15 Variation in Dividers 15.3, Combinational and Array Dividers Chapter 16, Division
Verifying the SRT Division Algorithm Using Theorem Proving Techniques
 Verifying the SRT Division Algorithm Using Theorem Proving Techniques E. M. Clarke* S.M. German** X. Zhao* Abstract. We verify the correctness of an SRT division circuit similar to the one in the Intcl
Verifying the SRT Division Algorithm Using Theorem Proving Techniques E. M. Clarke* S.M. German** X. Zhao* Abstract. We verify the correctness of an SRT division circuit similar to the one in the Intcl
EDULABZ INTERNATIONAL NUMBER SYSTEM
 NUMBER SYSTEM 1. Find the product of the place value of 8 and the face value of 7 in the number 7801. Ans. Place value of 8 in 7801 = 800, Face value of 7 in 7801 = 7 Required product = 800 7 = 00. How
NUMBER SYSTEM 1. Find the product of the place value of 8 and the face value of 7 in the number 7801. Ans. Place value of 8 in 7801 = 800, Face value of 7 in 7801 = 7 Required product = 800 7 = 00. How
Divisibility of Natural Numbers
 10-19-2009 Divisibility of Natural Numbers We now return to our discussion of the natural numbers. We have built up much of the mathematical foundation for the natural numbers (N = 1, 2, 3,...). We used
10-19-2009 Divisibility of Natural Numbers We now return to our discussion of the natural numbers. We have built up much of the mathematical foundation for the natural numbers (N = 1, 2, 3,...). We used
Some Facts from Number Theory
 Computer Science 52 Some Facts from Number Theory Fall Semester, 2014 These notes are adapted from a document that was prepared for a different course several years ago. They may be helpful as a summary
Computer Science 52 Some Facts from Number Theory Fall Semester, 2014 These notes are adapted from a document that was prepared for a different course several years ago. They may be helpful as a summary
( 3) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
 81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN. 2 s-complement Representation
 4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 203 Lecture #3: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division 2 s-complement Representation RECALL
4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 203 Lecture #3: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division 2 s-complement Representation RECALL
Notes on arithmetic. 1. Representation in base B
 Notes on arithmetic The Babylonians that is to say, the people that inhabited what is now southern Iraq for reasons not entirely clear to us, ued base 60 in scientific calculation. This offers us an excuse
Notes on arithmetic The Babylonians that is to say, the people that inhabited what is now southern Iraq for reasons not entirely clear to us, ued base 60 in scientific calculation. This offers us an excuse
C241 Homework Assignment 7
 C24 Homework Assignment 7. Prove that for all whole numbers n, n i 2 = n(n + (2n + The proof is by induction on k with hypothesis H(k i 2 = k(k + (2k + base case: To prove H(, i 2 = = = 2 3 = ( + (2 +
C24 Homework Assignment 7. Prove that for all whole numbers n, n i 2 = n(n + (2n + The proof is by induction on k with hypothesis H(k i 2 = k(k + (2k + base case: To prove H(, i 2 = = = 2 3 = ( + (2 +
Part I, Number Systems. CS131 Mathematics for Computer Scientists II Note 1 INTEGERS
 CS131 Part I, Number Systems CS131 Mathematics for Computer Scientists II Note 1 INTEGERS The set of all integers will be denoted by Z. So Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. The decimal number system uses the
CS131 Part I, Number Systems CS131 Mathematics for Computer Scientists II Note 1 INTEGERS The set of all integers will be denoted by Z. So Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. The decimal number system uses the
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic
 Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
The Euclidean Algorithm and Multiplicative Inverses
 1 The Euclidean Algorithm and Multiplicative Inverses Lecture notes for Access 2009 The Euclidean Algorithm is a set of instructions for finding the greatest common divisor of any two positive integers.
1 The Euclidean Algorithm and Multiplicative Inverses Lecture notes for Access 2009 The Euclidean Algorithm is a set of instructions for finding the greatest common divisor of any two positive integers.
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 9 September 30, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 9 1/47 Fast Exponentiation Algorithms Number Theory Needed for RSA Elementary Number Theory
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 9 September 30, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 9 1/47 Fast Exponentiation Algorithms Number Theory Needed for RSA Elementary Number Theory
DIVISION BY DIGIT RECURRENCE
 DIVISION BY DIGIT RECURRENCE 1 SEVERAL DIVISION METHODS: DIGIT-RECURRENCE METHOD studied in this chapter MULTIPLICATIVE METHOD (Chapter 7) VARIOUS APPROXIMATION METHODS (power series expansion), SPECIAL
DIVISION BY DIGIT RECURRENCE 1 SEVERAL DIVISION METHODS: DIGIT-RECURRENCE METHOD studied in this chapter MULTIPLICATIVE METHOD (Chapter 7) VARIOUS APPROXIMATION METHODS (power series expansion), SPECIAL
Chapter 5: Solutions to Exercises
 1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac and Tomás Lang Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, an imprint of Elsevier Science, c 2004 Updated: September 9, 2003 Chapter 5: Solutions to Selected Exercises With contributions
1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac and Tomás Lang Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, an imprint of Elsevier Science, c 2004 Updated: September 9, 2003 Chapter 5: Solutions to Selected Exercises With contributions
Long division for integers
 Feasting on Leftovers January 2011 Summary notes on decimal representation of rational numbers Long division for integers Contents 1. Terminology 2. Description of division algorithm for integers (optional
Feasting on Leftovers January 2011 Summary notes on decimal representation of rational numbers Long division for integers Contents 1. Terminology 2. Description of division algorithm for integers (optional
CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)...
 Table of Contents CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)... 20 7.0 ANCHOR PROBLEM: ZOOMING IN ON THE NUMBER LINE... 24 SECTION 7.1: REPRESENT NUMBERS GEOMETRICALLY... 26 7.1a Class Activity:
Table of Contents CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)... 20 7.0 ANCHOR PROBLEM: ZOOMING IN ON THE NUMBER LINE... 24 SECTION 7.1: REPRESENT NUMBERS GEOMETRICALLY... 26 7.1a Class Activity:
The goal differs from prime factorization. Prime factorization would initialize all divisors to be prime numbers instead of integers*
 Quantum Algorithm Processor For Finding Exact Divisors Professor J R Burger Summary Wiring diagrams are given for a quantum algorithm processor in CMOS to compute, in parallel, all divisors of an n-bit
Quantum Algorithm Processor For Finding Exact Divisors Professor J R Burger Summary Wiring diagrams are given for a quantum algorithm processor in CMOS to compute, in parallel, all divisors of an n-bit
NUMBERS AND CODES CHAPTER Numbers
 CHAPTER 2 NUMBERS AND CODES 2.1 Numbers When a number such as 101 is given, it is impossible to determine its numerical value. Some may say it is five. Others may say it is one hundred and one. Could it
CHAPTER 2 NUMBERS AND CODES 2.1 Numbers When a number such as 101 is given, it is impossible to determine its numerical value. Some may say it is five. Others may say it is one hundred and one. Could it
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) 4-bit LFSR
 Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Dividing Polynomials
 3-3 3-3 Dividing Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Divide using long division. 1. 161 7 2. 12.18 2.1 23 5.8 Divide. 3. 4. 6x + 15y 3 7a 2 ab a 2x + 5y 7a b Objective
3-3 3-3 Dividing Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Divide using long division. 1. 161 7 2. 12.18 2.1 23 5.8 Divide. 3. 4. 6x + 15y 3 7a 2 ab a 2x + 5y 7a b Objective
CHAPTER 2 NUMBER SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 2 NUMBER SYSTEMS The Decimal Number System : We begin our study of the number systems with the familiar decimal number system. The decimal system contains ten unique symbol 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
CHAPTER 2 NUMBER SYSTEMS The Decimal Number System : We begin our study of the number systems with the familiar decimal number system. The decimal system contains ten unique symbol 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
Downloaded from
 Question 1: Exercise 2.1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) Page 1 of 24 (iv) (v) (v) Page
Question 1: Exercise 2.1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) Page 1 of 24 (iv) (v) (v) Page
The minimal polynomial
 The minimal polynomial Michael H Mertens October 22, 2015 Introduction In these short notes we explain some of the important features of the minimal polynomial of a square matrix A and recall some basic
The minimal polynomial Michael H Mertens October 22, 2015 Introduction In these short notes we explain some of the important features of the minimal polynomial of a square matrix A and recall some basic
9. Datapath Design. Jacob Abraham. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017
 9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements. Tajana Simunic Rosing
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations
 Australian Computer Science Communications, Vol.22, No.4, 2, pp.9 6, IEEE Comp. Society Press Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations Wanming Chu and Yamin Li Computer Architecture
Australian Computer Science Communications, Vol.22, No.4, 2, pp.9 6, IEEE Comp. Society Press Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations Wanming Chu and Yamin Li Computer Architecture
A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. XX, NO. X, MONTH 2007 1 A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations James A. Muir Abstract We present a simple algorithm
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. XX, NO. X, MONTH 2007 1 A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations James A. Muir Abstract We present a simple algorithm
Top Down Design. Gunnar Gotshalks 03-1
 Top Down Design 03-1 Top Down Description Top down is also known as step wise refinement and functional decomposition Given an operation, there are only the following three choices for refinement» Sequence
Top Down Design 03-1 Top Down Description Top down is also known as step wise refinement and functional decomposition Given an operation, there are only the following three choices for refinement» Sequence
Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives
 Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department Univ. of California at Los Angeles California Robert McIlhenny
Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department Univ. of California at Los Angeles California Robert McIlhenny
A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations
 A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations James A. Muir School of Computer Science Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada http://www.scs.carleton.ca/ jamuir 23 October
A Simple Left-to-Right Algorithm for Minimal Weight Signed Radix-r Representations James A. Muir School of Computer Science Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada http://www.scs.carleton.ca/ jamuir 23 October
Faster arithmetic for number-theoretic transforms
 University of New South Wales 7th October 2011, Macquarie University Plan for talk 1. Review number-theoretic transform (NTT) 2. Discuss typical butterfly algorithm 3. Improvements to butterfly algorithm
University of New South Wales 7th October 2011, Macquarie University Plan for talk 1. Review number-theoretic transform (NTT) 2. Discuss typical butterfly algorithm 3. Improvements to butterfly algorithm
MATH Dr. Halimah Alshehri Dr. Halimah Alshehri
 MATH 1101 haalshehri@ksu.edu.sa 1 Introduction To Number Systems First Section: Binary System Second Section: Octal Number System Third Section: Hexadecimal System 2 Binary System 3 Binary System The binary
MATH 1101 haalshehri@ksu.edu.sa 1 Introduction To Number Systems First Section: Binary System Second Section: Octal Number System Third Section: Hexadecimal System 2 Binary System 3 Binary System The binary
NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS & COMPUTING 6th Edition
 NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS & COMPUTING 6th Edition Ward Cheney/David Kincaid c UT Austin Engage Learning: Thomson-Brooks/Cole www.engage.com www.ma.utexas.edu/cna/nmc6 September 1, 2011 2011 1 / 42 1.1 Mathematical
NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS & COMPUTING 6th Edition Ward Cheney/David Kincaid c UT Austin Engage Learning: Thomson-Brooks/Cole www.engage.com www.ma.utexas.edu/cna/nmc6 September 1, 2011 2011 1 / 42 1.1 Mathematical
How fast can we add (or subtract) two numbers n and m?
 Addition and Subtraction How fast do we add (or subtract) two numbers n and m? How fast can we add (or subtract) two numbers n and m? Definition. Let A(d) denote the maximal number of steps required to
Addition and Subtraction How fast do we add (or subtract) two numbers n and m? How fast can we add (or subtract) two numbers n and m? Definition. Let A(d) denote the maximal number of steps required to
3.3 Dividing Polynomials. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
Svoboda-Tung Division With No Compensation
 Svoboda-Tung Division With No Compensation Luis MONTALVO (IEEE Student Member), Alain GUYOT Integrated Systems Design Group, TIMA/INPG 46, Av. Félix Viallet, 38031 Grenoble Cedex, France. E-mail: montalvo@archi.imag.fr
Svoboda-Tung Division With No Compensation Luis MONTALVO (IEEE Student Member), Alain GUYOT Integrated Systems Design Group, TIMA/INPG 46, Av. Félix Viallet, 38031 Grenoble Cedex, France. E-mail: montalvo@archi.imag.fr
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen
 L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
Solutions to Tutorial 4 (Week 5)
 The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 4 (Week 5) MATH2069/2969: Discrete Mathematics and Graph Theory Semester 1, 2018 1. Prove by induction that, for all
The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 4 (Week 5) MATH2069/2969: Discrete Mathematics and Graph Theory Semester 1, 2018 1. Prove by induction that, for all
Computer Architecture 10. Residue Number Systems
 Computer Architecture 10 Residue Number Systems Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 A Puzzle What number has the reminders 2, 3 and 2 when divided by the numbers 7, 5 and 3? x mod 7 = 2 x mod 5 =
Computer Architecture 10 Residue Number Systems Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 A Puzzle What number has the reminders 2, 3 and 2 when divided by the numbers 7, 5 and 3? x mod 7 = 2 x mod 5 =
An Informal introduction to Formal Verification
 An Informal introduction to Formal Verification Osman Hasan National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, Pakistan O. Hasan Formal Verification 2 Agenda q Formal Verification Methods,
An Informal introduction to Formal Verification Osman Hasan National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, Pakistan O. Hasan Formal Verification 2 Agenda q Formal Verification Methods,
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
Chapter 1: Solutions to Exercises
 1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac and Tomás Lang Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, an imprint of Elsevier, c 2004 Exercise 1.1 (a) 1. 9 bits since 2 8 297 2 9 2. 3 radix-8 digits since 8 2 297 8 3 3. 3
1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac and Tomás Lang Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, an imprint of Elsevier, c 2004 Exercise 1.1 (a) 1. 9 bits since 2 8 297 2 9 2. 3 radix-8 digits since 8 2 297 8 3 3. 3
Mathematical Induction
 Mathematical Induction Representation of integers Mathematical Induction Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.1 5.3 1 Representations of Integers Let b be a positive integer greater than 1. Then if n is a positive
Mathematical Induction Representation of integers Mathematical Induction Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.1 5.3 1 Representations of Integers Let b be a positive integer greater than 1. Then if n is a positive
COMPUTERS ORGANIZATION 2ND YEAR COMPUTE SCIENCE MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING UNIT 3 - ARITMETHIC-LOGIC UNIT JOSÉ GARCÍA RODRÍGUEZ JOSÉ ANTONIO SERRA PÉREZ
 OMUTERS ORGANIZATION 2ND YEAR OMUTE SIENE MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING UNIT 3 - ARITMETHI-LOGI UNIT JOSÉ GARÍA RODRÍGUEZ JOSÉ ANTONIO SERRA ÉREZ Tema 3. La Unidad entral de roceso. A.L.U. Arithmetic Logic Unit
OMUTERS ORGANIZATION 2ND YEAR OMUTE SIENE MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING UNIT 3 - ARITMETHI-LOGI UNIT JOSÉ GARÍA RODRÍGUEZ JOSÉ ANTONIO SERRA ÉREZ Tema 3. La Unidad entral de roceso. A.L.U. Arithmetic Logic Unit
, a 1. , a 2. ,..., a n
 CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
Lecture 6: Introducing Complexity
 COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 6: Introducing Complexity Ian Pratt-Hartmann Room KB2.38: email: ipratt@cs.man.ac.uk 2015 16 You need this book: Make sure you use the up-to-date
COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 6: Introducing Complexity Ian Pratt-Hartmann Room KB2.38: email: ipratt@cs.man.ac.uk 2015 16 You need this book: Make sure you use the up-to-date
New Minimal Weight Representations for Left-to-Right Window Methods
 New Minimal Weight Representations for Left-to-Right Window Methods James A. Muir 1 and Douglas R. Stinson 2 1 Department of Combinatorics and Optimization 2 School of Computer Science University of Waterloo
New Minimal Weight Representations for Left-to-Right Window Methods James A. Muir 1 and Douglas R. Stinson 2 1 Department of Combinatorics and Optimization 2 School of Computer Science University of Waterloo
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen
 L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
A number that can be written as, where p and q are integers and q Number.
 RATIONAL NUMBERS 1.1 Definition of Rational Numbers: What are rational numbers? A number that can be written as, where p and q are integers and q Number. 0, is known as Rational Example:, 12, -18 etc.
RATIONAL NUMBERS 1.1 Definition of Rational Numbers: What are rational numbers? A number that can be written as, where p and q are integers and q Number. 0, is known as Rational Example:, 12, -18 etc.
6.5 Dividing Polynomials
 Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
A HIGH-SPEED PROCESSOR FOR RECTANGULAR-TO-POLAR CONVERSION WITH APPLICATIONS IN DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS *
 Copyright IEEE 999: Published in the Proceedings of Globecom 999, Rio de Janeiro, Dec 5-9, 999 A HIGH-SPEED PROCESSOR FOR RECTAGULAR-TO-POLAR COVERSIO WITH APPLICATIOS I DIGITAL COMMUICATIOS * Dengwei
Copyright IEEE 999: Published in the Proceedings of Globecom 999, Rio de Janeiro, Dec 5-9, 999 A HIGH-SPEED PROCESSOR FOR RECTAGULAR-TO-POLAR COVERSIO WITH APPLICATIOS I DIGITAL COMMUICATIOS * Dengwei
Logical Abduction and its Applications in Program Verification. Isil Dillig MSR Cambridge
 Logical Abduction and its Applications in Program Verification? Isil Dillig MSR Cambridge What is Abduction? Abduction: Opposite of deduction 2 / 21 What is Abduction? Abduction: Opposite of deduction
Logical Abduction and its Applications in Program Verification? Isil Dillig MSR Cambridge What is Abduction? Abduction: Opposite of deduction 2 / 21 What is Abduction? Abduction: Opposite of deduction
Modular numbers and Error Correcting Codes. Introduction. Modular Arithmetic.
 Modular numbers and Error Correcting Codes Introduction Modular Arithmetic Finite fields n-space over a finite field Error correcting codes Exercises Introduction. Data transmission is not normally perfect;
Modular numbers and Error Correcting Codes Introduction Modular Arithmetic Finite fields n-space over a finite field Error correcting codes Exercises Introduction. Data transmission is not normally perfect;
Warm-Up. Use long division to divide 5 into
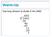 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
ALU (3) - Division Algorithms
 HUMBOLDT-UNIVERSITÄT ZU BERLIN INSTITUT FÜR INFORMATIK Lecture 12 ALU (3) - Division Algorithms Sommersemester 2002 Leitung: Prof. Dr. Miroslaw Malek www.informatik.hu-berlin.de/rok/ca CA - XII - ALU(3)
HUMBOLDT-UNIVERSITÄT ZU BERLIN INSTITUT FÜR INFORMATIK Lecture 12 ALU (3) - Division Algorithms Sommersemester 2002 Leitung: Prof. Dr. Miroslaw Malek www.informatik.hu-berlin.de/rok/ca CA - XII - ALU(3)
History & Binary Representation
 History & Binary Representation C. R. da Cunha 1 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, RS 91501-970, Brazil. August 30, 2017 Abstract In this lesson we will review the history
History & Binary Representation C. R. da Cunha 1 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, RS 91501-970, Brazil. August 30, 2017 Abstract In this lesson we will review the history
Integers and Division
 Integers and Division Notations Z: set of integers N : set of natural numbers R: set of real numbers Z + : set of positive integers Some elements of number theory are needed in: Data structures, Random
Integers and Division Notations Z: set of integers N : set of natural numbers R: set of real numbers Z + : set of positive integers Some elements of number theory are needed in: Data structures, Random
Lecture 8. Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8 Sequential Multipliers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 9, Basic Multiplication Scheme Chapter 10, High-Radix Multipliers Chapter
Lecture 8 Sequential Multipliers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 9, Basic Multiplication Scheme Chapter 10, High-Radix Multipliers Chapter
CS 124 Math Review Section January 29, 2018
 CS 124 Math Review Section CS 124 is more math intensive than most of the introductory courses in the department. You re going to need to be able to do two things: 1. Perform some clever calculations to
CS 124 Math Review Section CS 124 is more math intensive than most of the introductory courses in the department. You re going to need to be able to do two things: 1. Perform some clever calculations to
8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic
 8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic 8.1 Primes and Factors Over two millennia ago already, people all over the world were considering the properties of numbers. One of the simplest concepts is prime numbers.
8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic 8.1 Primes and Factors Over two millennia ago already, people all over the world were considering the properties of numbers. One of the simplest concepts is prime numbers.
2 Arithmetic. 2.1 Greatest common divisors. This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}.
 2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
CSCI 255. S i g n e d N u m s / S h i f t i n g / A r i t h m e t i c O p s.
 Ying.Yang 1.-1 CSCI 255 http://cs.furman.edu In mathematics, negative integers exists -> forced to do it binary In a binary string, the MSB is sacrificed as the signed bit 0 => Positive Value 1 => Negative
Ying.Yang 1.-1 CSCI 255 http://cs.furman.edu In mathematics, negative integers exists -> forced to do it binary In a binary string, the MSB is sacrificed as the signed bit 0 => Positive Value 1 => Negative
Numbers and Arithmetic
 Numbers and Arithmetic See: P&H Chapter 2.4 2.6, 3.2, C.5 C.6 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Building a Processor memory inst register file alu
Numbers and Arithmetic See: P&H Chapter 2.4 2.6, 3.2, C.5 C.6 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Building a Processor memory inst register file alu
CSE 241 Digital Systems Spring 2013
 CSE 241 Digital Systems Spring 2013 Instructor: Prof. Kui Ren Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture slides modified from many online resources and used solely for the educational purpose.
CSE 241 Digital Systems Spring 2013 Instructor: Prof. Kui Ren Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture slides modified from many online resources and used solely for the educational purpose.
Conversions between Decimal and Binary
 Conversions between Decimal and Binary Binary to Decimal Technique - use the definition of a number in a positional number system with base 2 - evaluate the definition formula ( the formula ) using decimal
Conversions between Decimal and Binary Binary to Decimal Technique - use the definition of a number in a positional number system with base 2 - evaluate the definition formula ( the formula ) using decimal
Handout 2 Gaussian elimination: Special cases
 06-21254 Mathematical Techniques for Computer Science The University of Birmingham Autumn Semester 2017 School of Computer Science c Achim Jung September 28, 2017 Handout 2 Gaussian elimination: Special
06-21254 Mathematical Techniques for Computer Science The University of Birmingham Autumn Semester 2017 School of Computer Science c Achim Jung September 28, 2017 Handout 2 Gaussian elimination: Special
Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures. July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20
 Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures J. Villalba E. Antelo J.D. Bruguera E.L. Zapata July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20 Published in: J. of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for
Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures J. Villalba E. Antelo J.D. Bruguera E.L. Zapata July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20 Published in: J. of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for
Proof: If (a, a, b) is a Pythagorean triple, 2a 2 = b 2 b / a = 2, which is impossible.
 CS103 Handout 07 Fall 2013 October 2, 2013 Guide to Proofs Thanks to Michael Kim for writing some of the proofs used in this handout. What makes a proof a good proof? It's hard to answer this question
CS103 Handout 07 Fall 2013 October 2, 2013 Guide to Proofs Thanks to Michael Kim for writing some of the proofs used in this handout. What makes a proof a good proof? It's hard to answer this question
SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION
 2.25 SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION PART A: LONG DIVISION Ancient Example with Integers 2 4 9 8 1 In general: dividend, f divisor, d We can say: 9 4 = 2 + 1 4 By multiplying both sides
2.25 SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION PART A: LONG DIVISION Ancient Example with Integers 2 4 9 8 1 In general: dividend, f divisor, d We can say: 9 4 = 2 + 1 4 By multiplying both sides
Lecture 12 : Recurrences DRAFT
 CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics 3/1/2011 Lecture 12 : Recurrences Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Dalibor Zelený DRAFT Last few classes we talked about program correctness. We
CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics 3/1/2011 Lecture 12 : Recurrences Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Dalibor Zelený DRAFT Last few classes we talked about program correctness. We
Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic. Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography
 Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak (kak@purdue.edu) January 26, 2017
Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak (kak@purdue.edu) January 26, 2017
3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices
 3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices 3.4 The integers and division This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers
3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices 3.4 The integers and division This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers
This is a recursive algorithm. The procedure is guaranteed to terminate, since the second argument decreases each time.
 8 Modular Arithmetic We introduce an operator mod. Let d be a positive integer. For c a nonnegative integer, the value c mod d is the remainder when c is divided by d. For example, c mod d = 0 if and only
8 Modular Arithmetic We introduce an operator mod. Let d be a positive integer. For c a nonnegative integer, the value c mod d is the remainder when c is divided by d. For example, c mod d = 0 if and only
Mat Week 8. Week 8. gcd() Mat Bases. Integers & Computers. Linear Combos. Week 8. Induction Proofs. Fall 2013
 Fall 2013 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Section 3.7, 4.1, & 5.2 Assignments: Sections 3.6, 3.7, 4.1 Proof Worksheets Attendance: Strongly Encouraged Overview 3.6 Integers and Algorithms 3.7
Fall 2013 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Section 3.7, 4.1, & 5.2 Assignments: Sections 3.6, 3.7, 4.1 Proof Worksheets Attendance: Strongly Encouraged Overview 3.6 Integers and Algorithms 3.7
Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1
 Residue Number Systems 1 Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1 7.1 Arithmetic in a modulus system The great speed of arithmetic in Residue Number Systems (RNS) comes from a simple theorem from number theory:
Residue Number Systems 1 Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1 7.1 Arithmetic in a modulus system The great speed of arithmetic in Residue Number Systems (RNS) comes from a simple theorem from number theory:
Student Responsibilities Week 8. Mat Section 3.6 Integers and Algorithms. Algorithm to Find gcd()
 Student Responsibilities Week 8 Mat 2345 Week 8 Reading: Textbook, Section 3.7, 4.1, & 5.2 Assignments: Sections 3.6, 3.7, 4.1 Induction Proof Worksheets Attendance: Strongly Encouraged Fall 2013 Week
Student Responsibilities Week 8 Mat 2345 Week 8 Reading: Textbook, Section 3.7, 4.1, & 5.2 Assignments: Sections 3.6, 3.7, 4.1 Induction Proof Worksheets Attendance: Strongly Encouraged Fall 2013 Week
Numbers & Arithmetic. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See: P&H Chapter , 3.2, C.5 C.
 Numbers & Arithmetic Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See: P&H Chapter 2.4-2.6, 3.2, C.5 C.6 Example: Big Picture Computer System Organization and Programming
Numbers & Arithmetic Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See: P&H Chapter 2.4-2.6, 3.2, C.5 C.6 Example: Big Picture Computer System Organization and Programming
QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING?
 QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING? WILLIAM Y. SIT Department of Mathematics, The City College of The City University of New York, New York, NY 10031, USA E-mail: wyscc@cunyvm.cuny.edu This is a talk on how to program
QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING? WILLIAM Y. SIT Department of Mathematics, The City College of The City University of New York, New York, NY 10031, USA E-mail: wyscc@cunyvm.cuny.edu This is a talk on how to program
4.5 Rational functions.
 4.5 Rational functions. We have studied graphs of polynomials and we understand the graphical significance of the zeros of the polynomial and their multiplicities. Now we are ready to etend these eplorations
4.5 Rational functions. We have studied graphs of polynomials and we understand the graphical significance of the zeros of the polynomial and their multiplicities. Now we are ready to etend these eplorations
MA 1B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET 3 SOLUTIONS. Solution. (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4
 MA B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET SOLUTIONS (Reading) ( pts)[ch, Problem (d), (e)] Solution (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4 i= x iv i = b, where v i is the ith column of A, and 4 A = 8
MA B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET SOLUTIONS (Reading) ( pts)[ch, Problem (d), (e)] Solution (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4 i= x iv i = b, where v i is the ith column of A, and 4 A = 8
Introduction to Number Theory. The study of the integers
 Introduction to Number Theory The study of the integers of Integers, The set of integers = {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}. In this lecture, if nothing is said about a variable, it is an integer. Def. We
Introduction to Number Theory The study of the integers of Integers, The set of integers = {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}. In this lecture, if nothing is said about a variable, it is an integer. Def. We
CHAPTER 6. Prime Numbers. Definition and Fundamental Results
 CHAPTER 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results 6.1. Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and the only positive divisors of p are 1 and p. If n
CHAPTER 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results 6.1. Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and the only positive divisors of p are 1 and p. If n
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane.
 Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 3 Lecture 3 3.1 General remarks March 4, 2018 This
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 3 Lecture 3 3.1 General remarks March 4, 2018 This
Long and Synthetic Division of Polynomials
 Long and Synthetic Division of Polynomials Long and synthetic division are two ways to divide one polynomial (the dividend) by another polynomial (the divisor). These methods are useful when both polynomials
Long and Synthetic Division of Polynomials Long and synthetic division are two ways to divide one polynomial (the dividend) by another polynomial (the divisor). These methods are useful when both polynomials
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences
 Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 1 b. 0.2 1. 2 3.2 3 c. 20 16 2 20 2. Determine which of the epressions are polynomials. For each polynomial,
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 1 b. 0.2 1. 2 3.2 3 c. 20 16 2 20 2. Determine which of the epressions are polynomials. For each polynomial,
Algorithms CMSC Basic algorithms in Number Theory: Euclid s algorithm and multiplicative inverse
 Algorithms CMSC-27200 Basic algorithms in Number Theory: Euclid s algorithm and multiplicative inverse Instructor: László Babai Last updated 02-14-2015. Z denotes the set of integers. All variables in
Algorithms CMSC-27200 Basic algorithms in Number Theory: Euclid s algorithm and multiplicative inverse Instructor: László Babai Last updated 02-14-2015. Z denotes the set of integers. All variables in
This Unit: Arithmetic. CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design. Pre-Class Exercise. Readings
 This Unit: Arithmetic CI 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 3: Arithmetic Based on slides by Prof. Amir Roth & Prof. Milo Martin App App App ystem software Mem CPU I/O A little review Binary + 2s
This Unit: Arithmetic CI 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 3: Arithmetic Based on slides by Prof. Amir Roth & Prof. Milo Martin App App App ystem software Mem CPU I/O A little review Binary + 2s
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 8
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 8 Polynomials Polynomials constitute a rich class of functions which are both easy to describe and widely applicable in
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 8 Polynomials Polynomials constitute a rich class of functions which are both easy to describe and widely applicable in
Answers (1) A) 36 = - - = Now, we can divide the numbers as shown below. For example : 4 = 2, 2 4 = -2, -2-4 = -2, 2-4 = 2.
 Answers (1) A) 36 We can divide the two numbers by using the following steps : 1. Firstly, we will divide the mathematical signs of the numbers. We place a negative sign before the negative numbers and
Answers (1) A) 36 We can divide the two numbers by using the following steps : 1. Firstly, we will divide the mathematical signs of the numbers. We place a negative sign before the negative numbers and
Simple Iteration, cont d
 Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Simple Iteration, cont d In general, nonlinear equations cannot be solved in a finite sequence
Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Simple Iteration, cont d In general, nonlinear equations cannot be solved in a finite sequence
Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively
 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE 6.1 Fundamental Results Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively D (p) = { p 1 1 p}. Otherwise
6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE 6.1 Fundamental Results Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively D (p) = { p 1 1 p}. Otherwise
CHAPTER 1 NUMBER SYSTEMS. 1.1 Introduction
 N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
Appendix: Synthetic Division
 Appendix: Synthetic Division AP Learning Objectives In this section, we will learn how to: 1. Divide polynomials using synthetic division. Synthetic division is a short form of long division with polynomials.
Appendix: Synthetic Division AP Learning Objectives In this section, we will learn how to: 1. Divide polynomials using synthetic division. Synthetic division is a short form of long division with polynomials.
Checkpoint Questions Due Monday, October 1 at 2:15 PM Remaining Questions Due Friday, October 5 at 2:15 PM
 CS103 Handout 03 Fall 2012 September 28, 2012 Problem Set 1 This first problem set is designed to help you gain a familiarity with set theory and basic proof techniques. By the time you're done, you should
CS103 Handout 03 Fall 2012 September 28, 2012 Problem Set 1 This first problem set is designed to help you gain a familiarity with set theory and basic proof techniques. By the time you're done, you should
The Impossibility of Certain Types of Carmichael Numbers
 The Impossibility of Certain Types of Carmichael Numbers Thomas Wright Abstract This paper proves that if a Carmichael number is composed of primes p i, then the LCM of the p i 1 s can never be of the
The Impossibility of Certain Types of Carmichael Numbers Thomas Wright Abstract This paper proves that if a Carmichael number is composed of primes p i, then the LCM of the p i 1 s can never be of the
Lecture 7 Feb 4, 14. Sections 1.7 and 1.8 Some problems from Sec 1.8
 Lecture 7 Feb 4, 14 Sections 1.7 and 1.8 Some problems from Sec 1.8 Section Summary Proof by Cases Existence Proofs Constructive Nonconstructive Disproof by Counterexample Nonexistence Proofs Uniqueness
Lecture 7 Feb 4, 14 Sections 1.7 and 1.8 Some problems from Sec 1.8 Section Summary Proof by Cases Existence Proofs Constructive Nonconstructive Disproof by Counterexample Nonexistence Proofs Uniqueness
Binary Multipliers. Reading: Study Chapter 3. The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding
 Binary Multipliers The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 4 4 8 2 6
Binary Multipliers The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 4 4 8 2 6
