Decoding First-Spike Latency: A Likelihood Approach. Rick L. Jenison
|
|
|
- Alexis Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 eurocomuting (00) Decoding First-Sike Latency: A Likelihood Aroach Rick L. Jenison Deartment of Psychology University of Wisconsin Madison WI enison@wavelet.sych.wisc.edu ABSTRACT First-sike latency at the level of auditory corte aears to correlate well with sound source direction. However an unsettled issue with latency as a neural code is the aarent lack of temoral marking for the onset of the stimulus. One ossible resolution is that relative ensemble latencies could be decoded rather than absolute latencies. How an ensemble timing referent might inform a theoretical ideal observer remains largely unelored. A likelihood aroach is derived for decoding sound direction from a samle oulation of cortical neurons in cat auditory corte based on relative first-sike latencies and is evaluated using Fisher information. Key words: neural coding first-sike latency likelihood Fisher information sound localization BIO Rick Jenison is an Associate Professor in the Deartment of Psychology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. His research includes the study of neural mechanisms of mammalian sound localization with a focus on mathematical models.
2 ITRODUCTIO Latency from stimulus onset to the first evoked action otential (first-sike latency) in the auditory corte aears to correlate well with the direction of sound sources in sace [3 3 4]. Furthermore resonse latency has been shown to carry a significant roortion of the information for the hysical stimulus in addition to sike count [9 7]. An unsettled issue with resect to the use of latency as a neural code for sound direction is the aarent lack of temoral marking for the onset of the stimulus. This roblem is not secific to directional coding in the auditory system but is roblematic for decoding strategies that have been roosed in visual corte as well [7]. The obvious resolution is an internally available global time marker such as a collective oscillatory attern of activity [0]. An alternative resolution is that latencies relative to one another in an ensemble of neurons could be decoded rather than absolute latency [4 5 8]. How an ensemble timing referent might inform a theoretical ideal observer remains largely unelored. Recently we described a formal method for decoding sound location from a oulation of cortical neurons in field AI of the cat based on maimum likelihood estimation from absolute first-sike latencies []. An etension to this aroach is to relace the unknown stimulus onset by the first observed sike in an ensemble cortical oulation. Under this scenario the observer measures subsequent evoked first-sikes within the ensemble relative to the first oststimulus neural event in the ensemble. Although still based on arametric timing this aroach is related to the statistically nonarametric rank-ordered decoding described by Gautrais and Thore [6]. Using a relative referent rather than absolute imlies that all of the ensemble neural events are temorally shifted by some unknown common value relative to the hysical onset of the stimulus. In the following equations reflects the latency of the th neuron in the ensemble relative to that of the first oststimulus event evoked by one of the
3 neurons in the ensemble. Any member of the ensemble could roduce the first sike in the ensemble. By definition the neuron with the shortest absolute latency will be assigned the value of 0 (see Fig. ). is the common latency across the ensemble of neurons and hence it reflects the arameter that binds the ensemble resonses to the stimulus onset. The statistical model of the relative latency can be eressed in terms of the th recetive field model ( ) common latency and error termε as follows ( ) + ε () where the robability density of the latency noise term ε is assumed to be Gaussian with homoscedastic variance based on our rior analyses of sike latency in cortical field AI (Jenison et al. 998). The variance term actually does deend to some degree on the mean latency in our data however for uroses of this study the variance is assumed to be indeendent of the mean. The robability density function can now be written as follows: ([ + ] ( ) ) ( ) ( ) π e () The arameter is resumably not meaningful to the animal er se and its contribution to the model seems almost tautological. But is only inconsequential when the stimulus onset is known by the observer and thus is known. The observer deends on only in that it is necessary for constructing the robability density about the relative decoding of first-sike latency with resect to the first-sike in the ensemble. In this aer an aroach to deriving a likelihood function that removes this deendency on is shown thus allowing the observer to rely on only the ensemble vector of relative resonse latencies. Given that some form of this likelihood function is reresented in cortical circuitry maimization may be ossible by recursive neural rocessing [6]. 3
4 METHODS We have recently described a methodology by which cortical recetive fields that deend on the location (azimuth and elevation ) of a virtual sound source in sace (see Fig. A) can be functionally modeled []. The methods used to collect the single neuron resonses that constrain the recetive field models are described in [3] and are briefly summarized here. Barbiturate-anesthetized cats were fitted with hollow earieces sealed into the eternal ear canals through which virtual acoustic sace stimuli [5] were resented. Single neurons were recorded etracellularly in the high-frequency region of the left AI field of auditory corte. The latency of the first-sike in resonse to transient virtual acoustic sace stimuli was used as the rimary resonse variable for von Mises basis function aroimation [] (see Fig. B). The von Mises model for the recetive field is a continuous sherical function of azimuth and elevation ( ) b e{ κ ( sin sin β cos( α ) + cos cos β ) } b. (3) + The shortest latency corresonds to the best resonse of the cortical neuron and its location is defined by α and β. κ secifies the width or radius of the recetive field and the vector b contains weights whose dimensionality could etend to accommodate a linear combination of basis functions. Although we have found these basis functions to yield accurate models of satial recetive fields the analysis described here does not deend on any secific recetive field model. The latency noise within the neural ensemble is assumed to be indeendent such that the resulting likelihood function across neurons can be written as ( ) ( ) ( ) L. (4) Eanding the likelihood function and collecting the term yields 4
5 5 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) + + e e π L (5) which factors out into a second eonential term. In the statistical literature would commonly be referred to as a nuisance arameter and indeed several methods eist for removing nuisance arameters []. Under conditions where there are a small number of fied nuisance arameters maimum likelihood (ML) estimation of each nuisance arameter and backsubstitution of the estimates into the original likelihood function offers one solution. Although the nuisance arameters can be removed from the likelihood function there are still consequences when the nuisance arameters are nonorthogonal with resect to the arameters of interest. Other aroaches more Bayesian in nature include integrating out the nuisance arameters but these are not considered in this study. Deriving the ML estimator for entails taking the derivative of the log-likelihood function and setting it equal to zero ( ) 0 log L then solving for. For this articular case ( ) ( ) log + L (6) and therefore ( ) ˆ. (7)
6 Back-substituting the ML estimate ˆ for the arameter of Equation 5 yields L ( ) ( π ) e ( ( )) e ( ( )) (8) which is no longer deendent on. The second eonential term now contains the mean over the resonse latencies and the mean over recetive fields ( ) at locations and. This likelihood function is now a function of only and. This new function is commonly referred to as the rofile likelihood [4] and denoted L ( ). The rofile likelihood can now be used by the observer to obtain oint estimates of the arameters of interest and by whatever means of maimization. In the following eamles is assumed to be fied (or known) in order to simlify the analysis as well as for uroses of dislay. An ensemble of 65 modeled neurons was emloyed in the analysis. The satial distribution of the samle is shown in Fig. C with contours corresonding to the iso-intensity at 50% u from the shortest latency located at coordinates α and β (center circles). A cross-section as a function of azimuth at 0 elevation is shown in Fig. D. In this study the radius of the recetive fields were fied across the ensemble. The likelihood functions are derived from an additional 65 neurons that are a reflection of the original samle of 65 neurons about the midline in order to account for the contribution of neurons in the oosite cortical hemishere. RESULTS To investigate the imact of decoding sound direction from first-sike latency timed off the ensemble referent first-sike latencies were samled from a secific sound direction. Then the rofile likelihood function was evaluated and comared against the likelihood function without 6
7 the introduction of that is assuming the stimulus onset to be known. Fig. 3 shows the two log transformed likelihood functions for four azimuthal ( ) sound directions on the left side of the animal assuming that is fied at 0. The maimum of the log-likelihood functions would rovide the ML estimate of given the observed resonses. As can be seen both log-likelihood functions have nearly the same maimum. However the imact of introducing the binding arameter can be observed in the slight flattening of the rofile log-likelihood function near the global maimum in Fig. 3B (-95 ). The consequence of the flattening is that estimates of the maimum would be somewhat more variable. However differences near the maimum aear to be small at the other sound source directions shown in Fig. 3(A) -45 (C) -40 and (D) 0 suggesting that the degree of flattening is directionally deendent. The elanation for the flattening of the likelihood function can be found by deriving the Fisher information matri for the full likelihood (including as a arameter) and comaring it to the Fisher information for estimating and under the condition where the stimulus onset is known (ecluding as a arameter). The Fisher Information matri reflects the amount of information available for estimating each arameter from the data (neural resonses ) and is related to the curvature of the loglikelihood function near its maimum []. Again is assumed to be fied and therefore will not contribute to the information matri in this study. The full matri of course needs to be considered however the imact of is more difficult to interret with the full 3 by 3 matri. The Fisher information matri for ust two of the arameters can be defined as 7
8 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) log log log log log log E E E E J r r r r r r. (9) The cell in the uer left is the Fisher information for estimating and the cell in the lower right is the Fisher information for estimating the nuisance arameter for the rofile likelihood. The off-diagonal cells reflect the cross-information between and and will evaluate to zero if the two arameters are orthogonal. Evaluating the derivatives and eected values of each cell in Eq. 9 yields ( ) ( ) ( ) J. (0) The cells of the Fisher information matri contain the gradients of the recetive field models ( ) and the latency noise variance (assumed to be constant across the ensemble). The Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) corresonds to the diagonal of the inverse of the Fisher information matri ˆ ˆ J K and reresents the lower bound on the covariance matri of any unbiased estimator. The elanation for the flattening of the rofile likelihood is revealed by eamining the lower bound of the variance about the estimate ˆ that results from the full matri inversion of J
9 ˆ ( ) ( ). () Contrast Eq. with the variance lower bound under conditions when the stimulus onset is known ˆ ( ) () which is a simle scalar inverse of the Fisher information for estimating. The difference between Eqs. and is due to the non-zero cross-information term which due to its squaring must necessarily inflate the lower bound in Eq. with resect to Eq.. The magnitude of this inflation deends on the gradients of the sace recetive fields for a articular sound direction. To better illustrate this comarison lots of the resective CRLBs are shown for values of (azimuth). First it is interesting to note the general trend for both functions. The minimum of both CRLB functions hence the best acuity is found at 0 azimuth - a finding that arallels sychohysical eormance in most animals. Second a bum in both CRLB functions occur in the region lateral to the midline where the recetive field gradients tend toward zero that is where the first-sike latency is at its minimum. Of course this is where Fisher information declines as well. From these lots we can also infer that the greatest imact on estimation variance or error from using the ensemble first-sike as the timing referent is in this region. However the relative difference between the two CRLB functions is actually quite small for all directions suggesting that the imact of rofiling over is rather small. 9
10 DISCUSSIO In this aer we have shown how an ideal observer given the likelihood function for measured first-sike latencies timed to the first evoked sike in an ensemble of neurons can reliably estimate sound direction. When the stimulus onset is unknown the likelihood function is deendent on a common latency that must be eliminated or rofiled out in order to estimate the arameters of interest in this case and. Given our modeled ensemble based on measured sace recetive fields in the cat the imact of rofiling out the nuisance arameter is small. This suggests that decoding first-sike latency using the first evoked sike in the ensemble is a viable aroach and one that a neural system could emloy quite successfully without knowledge of when the stimulus was turned on. Furthermore the rofile likelihood is not sensitive to shifts in ensemble first-sike latencies that result from changes in sound source intensity. The ower of analyzing a secific statistical model articularly when the neural recordings are available is that the Cramer-Rao lower bound informs us as to the best eormance ossible from any unbiased estimator. So whatever neural circuit might eorm sound direction estimation it is bounded by the CRLB. Fisher information further informs us as to what asects or characteristics of the recetive fields account for the observed variations in estimation error. ACKOWLEDGEMETS This work was suorted by IH grants DC03554 and DC006. 0
11 REFERECES [] R. E. Blahut. Princiles and ractice of information theory. Addison-Wesley Reading MA 987. [] O. E. Barndof-ielson and D. R. Co. Inference and Asymtotics. Chaman and Hall London 994. [3] J. F. Brugge. R.A. Reale and J. E. Hind. The structure of satial recetive fields of neurons in rimary auditory corte of the cat. J. eurosci. 6: [4] J. J. Eggermont. Azimuth Coding in Primary Auditory Corte of the Cat. II. Relative Latency and Intersike Interval Reresentation. J. eurohysiol. 80: [5] S. Furukawa L. Xu and J. C. Middlebrooks. Coding of sound-source location by ensembles of cortical neurons J. eurosci. 0: [6] J. Gautrais and S. Thore Rate coding versus temoral order coding: a theoretical aroach. Biosystems 48: [7] T. J. Gawne T. W. Kaer and B. J. Richmond. Latency: Another otential code for feature binding in striate corte. J. eurohysiol. 76: [8] P. Heil. Auditory cortical onset resonses revisited: First-sike timing. J. eurohysiol. 77: [9] J. Heller J. A. Hertz T.W. Kaer and B. J. Richmond. Information flow and temoral coding in rimate attern vision J. Com. eurosci. : [0] J. J. Hofield Pattern recognition comutation using action otential timing for stimulus reresentation ature 376:
12 [] R. L. Jenison Models of sound location acuity with broad cortical satial recetive fields. In Central Auditory Processing and eural Modeling (ed. P. Poon and J. F. Brugge) Plenum ew York 998. [] R. L. Jenison R. A. Reale J. E. Hind and J. F. Brugge. Modeling auditory satial recetive fields with sherical aroimation functions. J. eurohysiol. 80: [3] J. C. Middlebrooks A. E. Clock L. Xu and D. M. Green. A anoramic code for sound location by cortical neurons Science 64: [4] S. Murhy and A. W. van der Vaart. On rofile likelihood J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 95: [5] A. D. Musicant J. C. K. Chan and J. E. Hind. Direction-deendent sectral roerties of cat eternal ear: ew data and cross-secies comarisons. J. Acoust. Soc. Am [6] A. Pouget K. Zhang S. Deneve and P. E. Latham P. E. Statistically efficient estimation using oulation codes. eural Comut. 0: [7] M. C. Wiener and B. J. Richmond. Using resonse models to estimate channel caacity for neuronal classification of stationary visual stimuli using temoral coding. J. eurohysiol. 8: FIGURES FIG.. Schematic for decoding first-sike latencies. The vector [... ] latencies with resect to the first evoked sike in the ensemble. r contains the FIG.. A) Virtual auditory sace surrounding the head of the cat. Each osition on the shere reresents the osition of a virtual sound source used to evoke a resonse B) Eamle of a
13 modeled cortical AI recetive field (first-sike latency) with best direction (shortest first-sike latency at 57 azimuth 5 elevation). The recetive field is modeled using a linear combination of sherical von Mises basis functions (Jenison et al. 998) and shown roected onto an equalarea ma of auditory sace C) A reresentative distribution of best directions ( α and AI recetive fields (circles) (from [3]) surrounded by iso-latency contours 50% u from the minimum latency. D) A cross-section across the samle oulation shown in Fig.. B. at 0 elevation. β ) for 65 FIG. 3. Profile likelihood L ( ) with ˆ substitution (solid line) vs. the likelihood ( ) L assuming stimulus onset to be known (dotted line) for true values of azimuth at (A) -45 (B) -95 (C) - 40 and (D) 0. The vertical lines reflect the true ositions of the four sound sources. The directions labeled -80 and 80 are actually the same direction which corresonds to the midline behind the cat s head. FIG. 4. Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (in degrees) as a function of azimuth. CRLB for the rofile likelihood L ( ) with ˆ substitution (solid line) vs. the likelihood ( ) onset to be known (dotted line). L assuming stimulus 3
14 Stimulus Onset euron #5 Resonse euron #3 Resonse euron #3 Resonse Time (ms) Figure
15 A B First-sike Latency (ms) C D FirstSike Latency (ms) Azimuth (deg) Figure Figure
16 Log-likelihood A B Log-likelihood C D Azimuth (deg) Azimuth (deg) Figure 3
17 CRLB (deg) Azimuth (deg) Figure 3 Figure 4
Combining Logistic Regression with Kriging for Mapping the Risk of Occurrence of Unexploded Ordnance (UXO)
 Combining Logistic Regression with Kriging for Maing the Risk of Occurrence of Unexloded Ordnance (UXO) H. Saito (), P. Goovaerts (), S. A. McKenna (2) Environmental and Water Resources Engineering, Deartment
Combining Logistic Regression with Kriging for Maing the Risk of Occurrence of Unexloded Ordnance (UXO) H. Saito (), P. Goovaerts (), S. A. McKenna (2) Environmental and Water Resources Engineering, Deartment
Uniform Law on the Unit Sphere of a Banach Space
 Uniform Law on the Unit Shere of a Banach Sace by Bernard Beauzamy Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Faubourg Saint Honoré 75008 Paris France Setember 008 Abstract We investigate the construction of a
Uniform Law on the Unit Shere of a Banach Sace by Bernard Beauzamy Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Faubourg Saint Honoré 75008 Paris France Setember 008 Abstract We investigate the construction of a
Optimal array pattern synthesis with desired magnitude response
 Otimal array attern synthesis with desired magnitude resonse A.M. Pasqual a, J.R. Arruda a and P. erzog b a Universidade Estadual de Caminas, Rua Mendeleiev, 00, Cidade Universitária Zeferino Vaz, 13083-970
Otimal array attern synthesis with desired magnitude resonse A.M. Pasqual a, J.R. Arruda a and P. erzog b a Universidade Estadual de Caminas, Rua Mendeleiev, 00, Cidade Universitária Zeferino Vaz, 13083-970
Estimation of Separable Representations in Psychophysical Experiments
 Estimation of Searable Reresentations in Psychohysical Exeriments Michele Bernasconi (mbernasconi@eco.uninsubria.it) Christine Choirat (cchoirat@eco.uninsubria.it) Raffaello Seri (rseri@eco.uninsubria.it)
Estimation of Searable Reresentations in Psychohysical Exeriments Michele Bernasconi (mbernasconi@eco.uninsubria.it) Christine Choirat (cchoirat@eco.uninsubria.it) Raffaello Seri (rseri@eco.uninsubria.it)
On the relationship between sound intensity and wave impedance
 Buenos Aires 5 to 9 Setember, 16 Acoustics for the 1 st Century PROCEEDINGS of the nd International Congress on Acoustics Sound Intensity and Inverse Methods in Acoustics: Paer ICA16-198 On the relationshi
Buenos Aires 5 to 9 Setember, 16 Acoustics for the 1 st Century PROCEEDINGS of the nd International Congress on Acoustics Sound Intensity and Inverse Methods in Acoustics: Paer ICA16-198 On the relationshi
1 Entropy 1. 3 Extensivity 4. 5 Convexity 5
 Contents CONEX FUNCIONS AND HERMODYNAMIC POENIALS 1 Entroy 1 2 Energy Reresentation 2 3 Etensivity 4 4 Fundamental Equations 4 5 Conveity 5 6 Legendre transforms 6 7 Reservoirs and Legendre transforms
Contents CONEX FUNCIONS AND HERMODYNAMIC POENIALS 1 Entroy 1 2 Energy Reresentation 2 3 Etensivity 4 4 Fundamental Equations 4 5 Conveity 5 6 Legendre transforms 6 7 Reservoirs and Legendre transforms
Online Learning for Sparse PCA in High Dimensions: Exact Dynamics and Phase Transitions
 Online Learning for Sarse PCA in High Dimensions: Eact Dynamics and Phase Transitions Chuang Wang and Yue M. Lu John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Alied Sciences Harvard University Abstract We study
Online Learning for Sarse PCA in High Dimensions: Eact Dynamics and Phase Transitions Chuang Wang and Yue M. Lu John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Alied Sciences Harvard University Abstract We study
On split sample and randomized confidence intervals for binomial proportions
 On slit samle and randomized confidence intervals for binomial roortions Måns Thulin Deartment of Mathematics, Usala University arxiv:1402.6536v1 [stat.me] 26 Feb 2014 Abstract Slit samle methods have
On slit samle and randomized confidence intervals for binomial roortions Måns Thulin Deartment of Mathematics, Usala University arxiv:1402.6536v1 [stat.me] 26 Feb 2014 Abstract Slit samle methods have
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORK
 Comuter Modelling and ew Technologies, 5, Vol.9, o., 3-39 Transort and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosov, LV-9, Riga, Latvia MATHEMATICAL MODELLIG OF THE WIRELESS COMMUICATIO ETWORK M. KOPEETSK Deartment
Comuter Modelling and ew Technologies, 5, Vol.9, o., 3-39 Transort and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosov, LV-9, Riga, Latvia MATHEMATICAL MODELLIG OF THE WIRELESS COMMUICATIO ETWORK M. KOPEETSK Deartment
A Comparison between Biased and Unbiased Estimators in Ordinary Least Squares Regression
 Journal of Modern Alied Statistical Methods Volume Issue Article 7 --03 A Comarison between Biased and Unbiased Estimators in Ordinary Least Squares Regression Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, Saudi
Journal of Modern Alied Statistical Methods Volume Issue Article 7 --03 A Comarison between Biased and Unbiased Estimators in Ordinary Least Squares Regression Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, Saudi
AI*IA 2003 Fusion of Multiple Pattern Classifiers PART III
 AI*IA 23 Fusion of Multile Pattern Classifiers PART III AI*IA 23 Tutorial on Fusion of Multile Pattern Classifiers by F. Roli 49 Methods for fusing multile classifiers Methods for fusing multile classifiers
AI*IA 23 Fusion of Multile Pattern Classifiers PART III AI*IA 23 Tutorial on Fusion of Multile Pattern Classifiers by F. Roli 49 Methods for fusing multile classifiers Methods for fusing multile classifiers
Radial Basis Function Networks: Algorithms
 Radial Basis Function Networks: Algorithms Introduction to Neural Networks : Lecture 13 John A. Bullinaria, 2004 1. The RBF Maing 2. The RBF Network Architecture 3. Comutational Power of RBF Networks 4.
Radial Basis Function Networks: Algorithms Introduction to Neural Networks : Lecture 13 John A. Bullinaria, 2004 1. The RBF Maing 2. The RBF Network Architecture 3. Comutational Power of RBF Networks 4.
Chapter 10. Supplemental Text Material
 Chater 1. Sulemental Tet Material S1-1. The Covariance Matri of the Regression Coefficients In Section 1-3 of the tetbook, we show that the least squares estimator of β in the linear regression model y=
Chater 1. Sulemental Tet Material S1-1. The Covariance Matri of the Regression Coefficients In Section 1-3 of the tetbook, we show that the least squares estimator of β in the linear regression model y=
Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-step monotone missing data
 Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-ste monotone missing data Masashi Hyodo, Nobumichi Shutoh 2, Takashi Seo, and Tatjana Pavlenko 3 Deartment of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo
Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-ste monotone missing data Masashi Hyodo, Nobumichi Shutoh 2, Takashi Seo, and Tatjana Pavlenko 3 Deartment of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo
MODELING THE RELIABILITY OF C4ISR SYSTEMS HARDWARE/SOFTWARE COMPONENTS USING AN IMPROVED MARKOV MODEL
 Technical Sciences and Alied Mathematics MODELING THE RELIABILITY OF CISR SYSTEMS HARDWARE/SOFTWARE COMPONENTS USING AN IMPROVED MARKOV MODEL Cezar VASILESCU Regional Deartment of Defense Resources Management
Technical Sciences and Alied Mathematics MODELING THE RELIABILITY OF CISR SYSTEMS HARDWARE/SOFTWARE COMPONENTS USING AN IMPROVED MARKOV MODEL Cezar VASILESCU Regional Deartment of Defense Resources Management
A Model for Randomly Correlated Deposition
 A Model for Randomly Correlated Deosition B. Karadjov and A. Proykova Faculty of Physics, University of Sofia, 5 J. Bourchier Blvd. Sofia-116, Bulgaria ana@hys.uni-sofia.bg Abstract: A simle, discrete,
A Model for Randomly Correlated Deosition B. Karadjov and A. Proykova Faculty of Physics, University of Sofia, 5 J. Bourchier Blvd. Sofia-116, Bulgaria ana@hys.uni-sofia.bg Abstract: A simle, discrete,
4. Score normalization technical details We now discuss the technical details of the score normalization method.
 SMT SCORING SYSTEM This document describes the scoring system for the Stanford Math Tournament We begin by giving an overview of the changes to scoring and a non-technical descrition of the scoring rules
SMT SCORING SYSTEM This document describes the scoring system for the Stanford Math Tournament We begin by giving an overview of the changes to scoring and a non-technical descrition of the scoring rules
Maximum Entropy and the Stress Distribution in Soft Disk Packings Above Jamming
 Maximum Entroy and the Stress Distribution in Soft Disk Packings Above Jamming Yegang Wu and S. Teitel Deartment of Physics and Astronomy, University of ochester, ochester, New York 467, USA (Dated: August
Maximum Entroy and the Stress Distribution in Soft Disk Packings Above Jamming Yegang Wu and S. Teitel Deartment of Physics and Astronomy, University of ochester, ochester, New York 467, USA (Dated: August
Introduction to Probability for Graphical Models
 Introduction to Probability for Grahical Models CSC 4 Kaustav Kundu Thursday January 4, 06 *Most slides based on Kevin Swersky s slides, Inmar Givoni s slides, Danny Tarlow s slides, Jaser Snoek s slides,
Introduction to Probability for Grahical Models CSC 4 Kaustav Kundu Thursday January 4, 06 *Most slides based on Kevin Swersky s slides, Inmar Givoni s slides, Danny Tarlow s slides, Jaser Snoek s slides,
Use of Transformations and the Repeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek
 Use of Transformations and the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek Introduction We describe how the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS transforms the data to rovide tests of hyotheses of interest.
Use of Transformations and the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek Introduction We describe how the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS transforms the data to rovide tests of hyotheses of interest.
arxiv: v3 [physics.data-an] 23 May 2011
![arxiv: v3 [physics.data-an] 23 May 2011 arxiv: v3 [physics.data-an] 23 May 2011](/thumbs/90/102843734.jpg) Date: October, 8 arxiv:.7v [hysics.data-an] May -values for Model Evaluation F. Beaujean, A. Caldwell, D. Kollár, K. Kröninger Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München, Germany CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
Date: October, 8 arxiv:.7v [hysics.data-an] May -values for Model Evaluation F. Beaujean, A. Caldwell, D. Kollár, K. Kröninger Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München, Germany CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
Basic statistical models
 Basic statistical models Valery Pokrovsky March 27, 2012 Part I Ising model 1 Definition and the basic roerties The Ising model (IM) was invented by Lenz. His student Ising has found the artition function
Basic statistical models Valery Pokrovsky March 27, 2012 Part I Ising model 1 Definition and the basic roerties The Ising model (IM) was invented by Lenz. His student Ising has found the artition function
Synoptic Meteorology I: The Geostrophic Approximation. 30 September, 7 October 2014
 The Equations of Motion Synotic Meteorology I: The Geostrohic Aroimation 30 Setember, 7 October 2014 In their most general form, and resented without formal derivation, the equations of motion alicable
The Equations of Motion Synotic Meteorology I: The Geostrohic Aroimation 30 Setember, 7 October 2014 In their most general form, and resented without formal derivation, the equations of motion alicable
Statics and dynamics: some elementary concepts
 1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
A PROBABILISTIC POWER ESTIMATION METHOD FOR COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS UNDER REAL GATE DELAY MODEL
 A PROBABILISTIC POWER ESTIMATION METHOD FOR COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS UNDER REAL GATE DELAY MODEL G. Theodoridis, S. Theoharis, D. Soudris*, C. Goutis VLSI Design Lab, Det. of Electrical and Comuter Eng.
A PROBABILISTIC POWER ESTIMATION METHOD FOR COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS UNDER REAL GATE DELAY MODEL G. Theodoridis, S. Theoharis, D. Soudris*, C. Goutis VLSI Design Lab, Det. of Electrical and Comuter Eng.
Period-two cycles in a feedforward layered neural network model with symmetric sequence processing
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 75, 4197 27 Period-two cycles in a feedforward layered neural network model with symmetric sequence rocessing F. L. Metz and W. K. Theumann Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 75, 4197 27 Period-two cycles in a feedforward layered neural network model with symmetric sequence rocessing F. L. Metz and W. K. Theumann Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do
Unsupervised Hyperspectral Image Analysis Using Independent Component Analysis (ICA)
 Unsuervised Hyersectral Image Analysis Using Indeendent Comonent Analysis (ICA) Shao-Shan Chiang Chein-I Chang Irving W. Ginsberg Remote Sensing Signal and Image Processing Laboratory Deartment of Comuter
Unsuervised Hyersectral Image Analysis Using Indeendent Comonent Analysis (ICA) Shao-Shan Chiang Chein-I Chang Irving W. Ginsberg Remote Sensing Signal and Image Processing Laboratory Deartment of Comuter
E-companion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse extension of the max-min newsvendor order formula
 e-comanion to Han Du and Zuluaga: Etension of Scarf s ma-min order formula ec E-comanion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse etension of the ma-min newsvendor order formula Qiaoming Han School of Mathematics
e-comanion to Han Du and Zuluaga: Etension of Scarf s ma-min order formula ec E-comanion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse etension of the ma-min newsvendor order formula Qiaoming Han School of Mathematics
System Reliability Estimation and Confidence Regions from Subsystem and Full System Tests
 009 American Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June 0-, 009 FrB4. System Reliability Estimation and Confidence Regions from Subsystem and Full System Tests James C. Sall Abstract
009 American Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June 0-, 009 FrB4. System Reliability Estimation and Confidence Regions from Subsystem and Full System Tests James C. Sall Abstract
Quick Detection of Changes in Trac Statistics: Ivy Hsu and Jean Walrand 2. Department of EECS, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720
 Quic Detection of Changes in Trac Statistics: Alication to Variable Rate Comression Ivy Hsu and Jean Walrand 2 Deartment of EECS, University of California, Bereley, CA 94720 resented at the 32nd Annual
Quic Detection of Changes in Trac Statistics: Alication to Variable Rate Comression Ivy Hsu and Jean Walrand 2 Deartment of EECS, University of California, Bereley, CA 94720 resented at the 32nd Annual
Effective conductivity in a lattice model for binary disordered media with complex distributions of grain sizes
 hys. stat. sol. b 36, 65-633 003 Effective conductivity in a lattice model for binary disordered media with comlex distributions of grain sizes R. PIASECKI Institute of Chemistry, University of Oole, Oleska
hys. stat. sol. b 36, 65-633 003 Effective conductivity in a lattice model for binary disordered media with comlex distributions of grain sizes R. PIASECKI Institute of Chemistry, University of Oole, Oleska
CHAPTER-II Control Charts for Fraction Nonconforming using m-of-m Runs Rules
 CHAPTER-II Control Charts for Fraction Nonconforming using m-of-m Runs Rules. Introduction: The is widely used in industry to monitor the number of fraction nonconforming units. A nonconforming unit is
CHAPTER-II Control Charts for Fraction Nonconforming using m-of-m Runs Rules. Introduction: The is widely used in industry to monitor the number of fraction nonconforming units. A nonconforming unit is
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 25 Sep 2002
 Energy fluctuations at the multicritical oint in two-dimensional sin glasses arxiv:cond-mat/0207694 v2 25 Se 2002 1. Introduction Hidetoshi Nishimori, Cyril Falvo and Yukiyasu Ozeki Deartment of Physics,
Energy fluctuations at the multicritical oint in two-dimensional sin glasses arxiv:cond-mat/0207694 v2 25 Se 2002 1. Introduction Hidetoshi Nishimori, Cyril Falvo and Yukiyasu Ozeki Deartment of Physics,
Discrete alpha-skew-laplace distribution
 Statistics & Oerations Research Transactions SORT 39 () January-June 25, 7-84 ISSN: 696-228 eissn: 23-883 www.idescat.cat/sort/ Statistics & Oerations Research c Institut d Estadstica de Catalunya Transactions
Statistics & Oerations Research Transactions SORT 39 () January-June 25, 7-84 ISSN: 696-228 eissn: 23-883 www.idescat.cat/sort/ Statistics & Oerations Research c Institut d Estadstica de Catalunya Transactions
Improved Capacity Bounds for the Binary Energy Harvesting Channel
 Imroved Caacity Bounds for the Binary Energy Harvesting Channel Kaya Tutuncuoglu 1, Omur Ozel 2, Aylin Yener 1, and Sennur Ulukus 2 1 Deartment of Electrical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University,
Imroved Caacity Bounds for the Binary Energy Harvesting Channel Kaya Tutuncuoglu 1, Omur Ozel 2, Aylin Yener 1, and Sennur Ulukus 2 1 Deartment of Electrical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University,
A Bound on the Error of Cross Validation Using the Approximation and Estimation Rates, with Consequences for the Training-Test Split
 A Bound on the Error of Cross Validation Using the Aroximation and Estimation Rates, with Consequences for the Training-Test Slit Michael Kearns AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 7974 mkearns@research.att.com
A Bound on the Error of Cross Validation Using the Aroximation and Estimation Rates, with Consequences for the Training-Test Slit Michael Kearns AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 7974 mkearns@research.att.com
Spectral Analysis by Stationary Time Series Modeling
 Chater 6 Sectral Analysis by Stationary Time Series Modeling Choosing a arametric model among all the existing models is by itself a difficult roblem. Generally, this is a riori information about the signal
Chater 6 Sectral Analysis by Stationary Time Series Modeling Choosing a arametric model among all the existing models is by itself a difficult roblem. Generally, this is a riori information about the signal
1 University of Edinburgh, 2 British Geological Survey, 3 China University of Petroleum
 Estimation of fluid mobility from frequency deendent azimuthal AVO a synthetic model study Yingrui Ren 1*, Xiaoyang Wu 2, Mark Chaman 1 and Xiangyang Li 2,3 1 University of Edinburgh, 2 British Geological
Estimation of fluid mobility from frequency deendent azimuthal AVO a synthetic model study Yingrui Ren 1*, Xiaoyang Wu 2, Mark Chaman 1 and Xiangyang Li 2,3 1 University of Edinburgh, 2 British Geological
A Qualitative Event-based Approach to Multiple Fault Diagnosis in Continuous Systems using Structural Model Decomposition
 A Qualitative Event-based Aroach to Multile Fault Diagnosis in Continuous Systems using Structural Model Decomosition Matthew J. Daigle a,,, Anibal Bregon b,, Xenofon Koutsoukos c, Gautam Biswas c, Belarmino
A Qualitative Event-based Aroach to Multile Fault Diagnosis in Continuous Systems using Structural Model Decomosition Matthew J. Daigle a,,, Anibal Bregon b,, Xenofon Koutsoukos c, Gautam Biswas c, Belarmino
Hotelling s Two- Sample T 2
 Chater 600 Hotelling s Two- Samle T Introduction This module calculates ower for the Hotelling s two-grou, T-squared (T) test statistic. Hotelling s T is an extension of the univariate two-samle t-test
Chater 600 Hotelling s Two- Samle T Introduction This module calculates ower for the Hotelling s two-grou, T-squared (T) test statistic. Hotelling s T is an extension of the univariate two-samle t-test
Tests for Two Proportions in a Stratified Design (Cochran/Mantel-Haenszel Test)
 Chater 225 Tests for Two Proortions in a Stratified Design (Cochran/Mantel-Haenszel Test) Introduction In a stratified design, the subects are selected from two or more strata which are formed from imortant
Chater 225 Tests for Two Proortions in a Stratified Design (Cochran/Mantel-Haenszel Test) Introduction In a stratified design, the subects are selected from two or more strata which are formed from imortant
Scaling Multiple Point Statistics for Non-Stationary Geostatistical Modeling
 Scaling Multile Point Statistics or Non-Stationary Geostatistical Modeling Julián M. Ortiz, Steven Lyster and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre or Comutational Geostatistics Deartment o Civil & Environmental Engineering
Scaling Multile Point Statistics or Non-Stationary Geostatistical Modeling Julián M. Ortiz, Steven Lyster and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre or Comutational Geostatistics Deartment o Civil & Environmental Engineering
Estimating function analysis for a class of Tweedie regression models
 Title Estimating function analysis for a class of Tweedie regression models Author Wagner Hugo Bonat Deartamento de Estatística - DEST, Laboratório de Estatística e Geoinformação - LEG, Universidade Federal
Title Estimating function analysis for a class of Tweedie regression models Author Wagner Hugo Bonat Deartamento de Estatística - DEST, Laboratório de Estatística e Geoinformação - LEG, Universidade Federal
Shadow Computing: An Energy-Aware Fault Tolerant Computing Model
 Shadow Comuting: An Energy-Aware Fault Tolerant Comuting Model Bryan Mills, Taieb Znati, Rami Melhem Deartment of Comuter Science University of Pittsburgh (bmills, znati, melhem)@cs.itt.edu Index Terms
Shadow Comuting: An Energy-Aware Fault Tolerant Comuting Model Bryan Mills, Taieb Znati, Rami Melhem Deartment of Comuter Science University of Pittsburgh (bmills, znati, melhem)@cs.itt.edu Index Terms
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 26 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 26 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 26 Oct 2012](/thumbs/93/114154382.jpg) Constraints on Yield Parameters in Extended Maximum Likelihood Fits Till Moritz Karbach a, Maximilian Schlu b a TU Dortmund, Germany, moritz.karbach@cern.ch b TU Dortmund, Germany, maximilian.schlu@cern.ch
Constraints on Yield Parameters in Extended Maximum Likelihood Fits Till Moritz Karbach a, Maximilian Schlu b a TU Dortmund, Germany, moritz.karbach@cern.ch b TU Dortmund, Germany, maximilian.schlu@cern.ch
A Solution for the Dark Matter Mystery based on Euclidean Relativity
 Long Beach 2010 PROCEEDINGS of the NPA 1 A Solution for the Dark Matter Mystery based on Euclidean Relativity Frédéric Lassiaille Arcades, Mougins 06250, FRANCE e-mail: lumimi2003@hotmail.com The study
Long Beach 2010 PROCEEDINGS of the NPA 1 A Solution for the Dark Matter Mystery based on Euclidean Relativity Frédéric Lassiaille Arcades, Mougins 06250, FRANCE e-mail: lumimi2003@hotmail.com The study
Characterizing the Behavior of a Probabilistic CMOS Switch Through Analytical Models and Its Verification Through Simulations
 Characterizing the Behavior of a Probabilistic CMOS Switch Through Analytical Models and Its Verification Through Simulations PINAR KORKMAZ, BILGE E. S. AKGUL and KRISHNA V. PALEM Georgia Institute of
Characterizing the Behavior of a Probabilistic CMOS Switch Through Analytical Models and Its Verification Through Simulations PINAR KORKMAZ, BILGE E. S. AKGUL and KRISHNA V. PALEM Georgia Institute of
Lecture 7: Linear Classification Methods
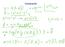 Homeork Homeork Lecture 7: Linear lassification Methods Final rojects? Grous oics Proosal eek 5 Lecture is oster session, Jacobs Hall Lobby, snacks Final reort 5 June. What is linear classification? lassification
Homeork Homeork Lecture 7: Linear lassification Methods Final rojects? Grous oics Proosal eek 5 Lecture is oster session, Jacobs Hall Lobby, snacks Final reort 5 June. What is linear classification? lassification
On Code Design for Simultaneous Energy and Information Transfer
 On Code Design for Simultaneous Energy and Information Transfer Anshoo Tandon Electrical and Comuter Engineering National University of Singaore Email: anshoo@nus.edu.sg Mehul Motani Electrical and Comuter
On Code Design for Simultaneous Energy and Information Transfer Anshoo Tandon Electrical and Comuter Engineering National University of Singaore Email: anshoo@nus.edu.sg Mehul Motani Electrical and Comuter
Linear diophantine equations for discrete tomography
 Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 10 001 59 66 59 IOS Press Linear diohantine euations for discrete tomograhy Yangbo Ye a,gewang b and Jiehua Zhu a a Deartment of Mathematics, The University of Iowa,
Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 10 001 59 66 59 IOS Press Linear diohantine euations for discrete tomograhy Yangbo Ye a,gewang b and Jiehua Zhu a a Deartment of Mathematics, The University of Iowa,
Onset Voltage of Corona Discharge in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Precipitators
 36 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, ol.4, No.1, MACH 1 Onset oltage of Corona Discharge in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Preciitators H. Ziedan 1, A. Sayed 1, A. Mizuno, and
36 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, ol.4, No.1, MACH 1 Onset oltage of Corona Discharge in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Preciitators H. Ziedan 1, A. Sayed 1, A. Mizuno, and
Empirical Bayesian EM-based Motion Segmentation
 Emirical Bayesian EM-based Motion Segmentation Nuno Vasconcelos Andrew Liman MIT Media Laboratory 0 Ames St, E5-0M, Cambridge, MA 09 fnuno,lig@media.mit.edu Abstract A recent trend in motion-based segmentation
Emirical Bayesian EM-based Motion Segmentation Nuno Vasconcelos Andrew Liman MIT Media Laboratory 0 Ames St, E5-0M, Cambridge, MA 09 fnuno,lig@media.mit.edu Abstract A recent trend in motion-based segmentation
Bayesian Spatially Varying Coefficient Models in the Presence of Collinearity
 Bayesian Satially Varying Coefficient Models in the Presence of Collinearity David C. Wheeler 1, Catherine A. Calder 1 he Ohio State University 1 Abstract he belief that relationshis between exlanatory
Bayesian Satially Varying Coefficient Models in the Presence of Collinearity David C. Wheeler 1, Catherine A. Calder 1 he Ohio State University 1 Abstract he belief that relationshis between exlanatory
+++ Modeling of Structural-dynamic Systems by UML Statecharts in AnyLogic +++ Modeling of Structural-dynamic Systems by UML Statecharts in AnyLogic
 Modeling of Structural-dynamic Systems by UML Statecharts in AnyLogic Daniel Leitner, Johannes Krof, Günther Zauner, TU Vienna, Austria, dleitner@osiris.tuwien.ac.at Yuri Karov, Yuri Senichenkov, Yuri
Modeling of Structural-dynamic Systems by UML Statecharts in AnyLogic Daniel Leitner, Johannes Krof, Günther Zauner, TU Vienna, Austria, dleitner@osiris.tuwien.ac.at Yuri Karov, Yuri Senichenkov, Yuri
The Nottingham eprints service makes this work by researchers of the University of Nottingham available open access under the following conditions.
 Harvey, David I. and Leybourne, Stehen J. and Taylor, A.M. Robert (04) On infimum Dickey Fuller unit root tests allowing for a trend break under the null. Comutational Statistics & Data Analysis, 78..
Harvey, David I. and Leybourne, Stehen J. and Taylor, A.M. Robert (04) On infimum Dickey Fuller unit root tests allowing for a trend break under the null. Comutational Statistics & Data Analysis, 78..
Short course A vademecum of statistical pattern recognition techniques with applications to image and video analysis. Agenda
 Short course A vademecum of statistical attern recognition techniques with alications to image and video analysis Lecture 6 The Kalman filter. Particle filters Massimo Piccardi University of Technology,
Short course A vademecum of statistical attern recognition techniques with alications to image and video analysis Lecture 6 The Kalman filter. Particle filters Massimo Piccardi University of Technology,
An analytical approximation method for the stabilizing solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation based on stable manifold theory
 Proceedings of the 27 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July -3, 27 ThA8.4 An analytical aroimation method for the stabilizing solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi
Proceedings of the 27 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July -3, 27 ThA8.4 An analytical aroimation method for the stabilizing solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi
Applied Fitting Theory VI. Formulas for Kinematic Fitting
 Alied Fitting heory VI Paul Avery CBX 98 37 June 9, 1998 Ar. 17, 1999 (rev.) I Introduction Formulas for Kinematic Fitting I intend for this note and the one following it to serve as mathematical references,
Alied Fitting heory VI Paul Avery CBX 98 37 June 9, 1998 Ar. 17, 1999 (rev.) I Introduction Formulas for Kinematic Fitting I intend for this note and the one following it to serve as mathematical references,
Chapter 7 Sampling and Sampling Distributions. Introduction. Selecting a Sample. Introduction. Sampling from a Finite Population
 Chater 7 and s Selecting a Samle Point Estimation Introduction to s of Proerties of Point Estimators Other Methods Introduction An element is the entity on which data are collected. A oulation is a collection
Chater 7 and s Selecting a Samle Point Estimation Introduction to s of Proerties of Point Estimators Other Methods Introduction An element is the entity on which data are collected. A oulation is a collection
REVIEW PERIOD REORDER POINT PROBABILISTIC INVENTORY SYSTEM FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH THE MIXTURE OF BACKORDERS AND LOST SALES
 T. Vasudha WARRIER, PhD Nita H. SHAH, PhD Deartment of Mathematics, Gujarat University Ahmedabad - 380009, Gujarat, INDIA E-mail : nita_sha_h@rediffmail.com REVIEW PERIOD REORDER POINT PROBABILISTIC INVENTORY
T. Vasudha WARRIER, PhD Nita H. SHAH, PhD Deartment of Mathematics, Gujarat University Ahmedabad - 380009, Gujarat, INDIA E-mail : nita_sha_h@rediffmail.com REVIEW PERIOD REORDER POINT PROBABILISTIC INVENTORY
Node-voltage method using virtual current sources technique for special cases
 Node-oltage method using irtual current sources technique for secial cases George E. Chatzarakis and Marina D. Tortoreli Electrical and Electronics Engineering Deartments, School of Pedagogical and Technological
Node-oltage method using irtual current sources technique for secial cases George E. Chatzarakis and Marina D. Tortoreli Electrical and Electronics Engineering Deartments, School of Pedagogical and Technological
SELF-SIMILAR FLOW UNDER THE ACTION OF MONOCHROMATIC RADIATION BEHIND A STRONG CYLINDRICAL SHOCK WAVE IN A NON-IDEAL GAS
 SELF-SIMILAR FLOW UNDER THE ACTION OF MONOCHROMATIC RADIATION BEHIND A STRONG CYLINDRICAL SHOCK WAVE IN A NON-IDEAL GAS *J. P. Vishwakarma and Vijay Kumar Pandey Deartment of Mathematics & Statistics,
SELF-SIMILAR FLOW UNDER THE ACTION OF MONOCHROMATIC RADIATION BEHIND A STRONG CYLINDRICAL SHOCK WAVE IN A NON-IDEAL GAS *J. P. Vishwakarma and Vijay Kumar Pandey Deartment of Mathematics & Statistics,
Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution. Chris J. Stephens. Newcastle City Council, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK
 Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution Chris J. Stehens Newcastle City Council, Newcastle uon Tyne, UK (For the Gini-Lorenz Conference, University of Siena, Italy, May 2005)
Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution Chris J. Stehens Newcastle City Council, Newcastle uon Tyne, UK (For the Gini-Lorenz Conference, University of Siena, Italy, May 2005)
Using the Divergence Information Criterion for the Determination of the Order of an Autoregressive Process
 Using the Divergence Information Criterion for the Determination of the Order of an Autoregressive Process P. Mantalos a1, K. Mattheou b, A. Karagrigoriou b a.deartment of Statistics University of Lund
Using the Divergence Information Criterion for the Determination of the Order of an Autoregressive Process P. Mantalos a1, K. Mattheou b, A. Karagrigoriou b a.deartment of Statistics University of Lund
Electronic properties of Graphene and 2-D materials. Part 2
 Electronic roerties of Grahene and -D materials z Part y The laws of Quantum Mechanics continued Time indeendent Schroedinger equation Eamles Particle in a well Harmonic oscillator Quantum Tunneling The
Electronic roerties of Grahene and -D materials z Part y The laws of Quantum Mechanics continued Time indeendent Schroedinger equation Eamles Particle in a well Harmonic oscillator Quantum Tunneling The
General Linear Model Introduction, Classes of Linear models and Estimation
 Stat 740 General Linear Model Introduction, Classes of Linear models and Estimation An aim of scientific enquiry: To describe or to discover relationshis among events (variables) in the controlled (laboratory)
Stat 740 General Linear Model Introduction, Classes of Linear models and Estimation An aim of scientific enquiry: To describe or to discover relationshis among events (variables) in the controlled (laboratory)
State Estimation with ARMarkov Models
 Deartment of Mechanical and Aerosace Engineering Technical Reort No. 3046, October 1998. Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. State Estimation with ARMarkov Models Ryoung K. Lim 1 Columbia University,
Deartment of Mechanical and Aerosace Engineering Technical Reort No. 3046, October 1998. Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. State Estimation with ARMarkov Models Ryoung K. Lim 1 Columbia University,
Paper C Exact Volume Balance Versus Exact Mass Balance in Compositional Reservoir Simulation
 Paer C Exact Volume Balance Versus Exact Mass Balance in Comositional Reservoir Simulation Submitted to Comutational Geosciences, December 2005. Exact Volume Balance Versus Exact Mass Balance in Comositional
Paer C Exact Volume Balance Versus Exact Mass Balance in Comositional Reservoir Simulation Submitted to Comutational Geosciences, December 2005. Exact Volume Balance Versus Exact Mass Balance in Comositional
substantial literature on emirical likelihood indicating that it is widely viewed as a desirable and natural aroach to statistical inference in a vari
 Condence tubes for multile quantile lots via emirical likelihood John H.J. Einmahl Eindhoven University of Technology Ian W. McKeague Florida State University May 7, 998 Abstract The nonarametric emirical
Condence tubes for multile quantile lots via emirical likelihood John H.J. Einmahl Eindhoven University of Technology Ian W. McKeague Florida State University May 7, 998 Abstract The nonarametric emirical
Partial Identification in Triangular Systems of Equations with Binary Dependent Variables
 Partial Identification in Triangular Systems of Equations with Binary Deendent Variables Azeem M. Shaikh Deartment of Economics University of Chicago amshaikh@uchicago.edu Edward J. Vytlacil Deartment
Partial Identification in Triangular Systems of Equations with Binary Deendent Variables Azeem M. Shaikh Deartment of Economics University of Chicago amshaikh@uchicago.edu Edward J. Vytlacil Deartment
Planar Transformations and Displacements
 Chater Planar Transformations and Dislacements Kinematics is concerned with the roerties of the motion of oints. These oints are on objects in the environment or on a robot maniulator. Two features that
Chater Planar Transformations and Dislacements Kinematics is concerned with the roerties of the motion of oints. These oints are on objects in the environment or on a robot maniulator. Two features that
Solved Problems. (a) (b) (c) Figure P4.1 Simple Classification Problems First we draw a line between each set of dark and light data points.
 Solved Problems Solved Problems P Solve the three simle classification roblems shown in Figure P by drawing a decision boundary Find weight and bias values that result in single-neuron ercetrons with the
Solved Problems Solved Problems P Solve the three simle classification roblems shown in Figure P by drawing a decision boundary Find weight and bias values that result in single-neuron ercetrons with the
Using a Computational Intelligence Hybrid Approach to Recognize the Faults of Variance Shifts for a Manufacturing Process
 Journal of Industrial and Intelligent Information Vol. 4, No. 2, March 26 Using a Comutational Intelligence Hybrid Aroach to Recognize the Faults of Variance hifts for a Manufacturing Process Yuehjen E.
Journal of Industrial and Intelligent Information Vol. 4, No. 2, March 26 Using a Comutational Intelligence Hybrid Aroach to Recognize the Faults of Variance hifts for a Manufacturing Process Yuehjen E.
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF BEAMS WITH MULTIPLE CONSTRAINED LAYER DAMPING PATCHES
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (998) 22(5), 78 85 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF BEAMS WITH MULTIPLE CONSTRAINED LAYER DAMPING PATCHES Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Deartment of Mechanical Engineering, The
Journal of Sound and Vibration (998) 22(5), 78 85 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF BEAMS WITH MULTIPLE CONSTRAINED LAYER DAMPING PATCHES Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Deartment of Mechanical Engineering, The
Distributed Rule-Based Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information
 istribution Statement : roved for ublic release; distribution is unlimited. istributed Rule-ased Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information June 8, 004 William J. Farrell III Lockheed Martin dvanced
istribution Statement : roved for ublic release; distribution is unlimited. istributed Rule-ased Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information June 8, 004 William J. Farrell III Lockheed Martin dvanced
Expansion in n 1 for percolation critical values on the n-cube and Z n : the first three terms
 Eansion in n for ercolation critical values on the n-cube and Z n : the first three terms Remco van der Hofstad Gordon Slade December 22, 2003 Abstract Let c (Q n ) and c (Z n ) denote the critical values
Eansion in n for ercolation critical values on the n-cube and Z n : the first three terms Remco van der Hofstad Gordon Slade December 22, 2003 Abstract Let c (Q n ) and c (Z n ) denote the critical values
Deriving Indicator Direct and Cross Variograms from a Normal Scores Variogram Model (bigaus-full) David F. Machuca Mory and Clayton V.
 Deriving ndicator Direct and Cross Variograms from a Normal Scores Variogram Model (bigaus-full) David F. Machuca Mory and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre for Comutational Geostatistics Deartment of Civil &
Deriving ndicator Direct and Cross Variograms from a Normal Scores Variogram Model (bigaus-full) David F. Machuca Mory and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre for Comutational Geostatistics Deartment of Civil &
Re-entry Protocols for Seismically Active Mines Using Statistical Analysis of Aftershock Sequences
 Re-entry Protocols for Seismically Active Mines Using Statistical Analysis of Aftershock Sequences J.A. Vallejos & S.M. McKinnon Queen s University, Kingston, ON, Canada ABSTRACT: Re-entry rotocols are
Re-entry Protocols for Seismically Active Mines Using Statistical Analysis of Aftershock Sequences J.A. Vallejos & S.M. McKinnon Queen s University, Kingston, ON, Canada ABSTRACT: Re-entry rotocols are
Principal Components Analysis and Unsupervised Hebbian Learning
 Princial Comonents Analysis and Unsuervised Hebbian Learning Robert Jacobs Deartment of Brain & Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 1467, USA August 8, 008 Reference: Much of the material
Princial Comonents Analysis and Unsuervised Hebbian Learning Robert Jacobs Deartment of Brain & Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 1467, USA August 8, 008 Reference: Much of the material
The. Consortium. Continuum Mechanics. Original notes by Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank University, London, UK Produced by the CRISP Consortium Ltd
 The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
Finite Mixture EFA in Mplus
 Finite Mixture EFA in Mlus November 16, 2007 In this document we describe the Mixture EFA model estimated in Mlus. Four tyes of deendent variables are ossible in this model: normally distributed, ordered
Finite Mixture EFA in Mlus November 16, 2007 In this document we describe the Mixture EFA model estimated in Mlus. Four tyes of deendent variables are ossible in this model: normally distributed, ordered
Research of power plant parameter based on the Principal Component Analysis method
 Research of ower lant arameter based on the Princial Comonent Analysis method Yang Yang *a, Di Zhang b a b School of Engineering, Bohai University, Liaoning Jinzhou, 3; Liaoning Datang international Jinzhou
Research of ower lant arameter based on the Princial Comonent Analysis method Yang Yang *a, Di Zhang b a b School of Engineering, Bohai University, Liaoning Jinzhou, 3; Liaoning Datang international Jinzhou
Biostat Methods STAT 5500/6500 Handout #12: Methods and Issues in (Binary Response) Logistic Regression
 Biostat Methods STAT 5500/6500 Handout #12: Methods and Issues in (Binary Resonse) Logistic Regression Recall general χ 2 test setu: Y 0 1 Trt 0 a b Trt 1 c d I. Basic logistic regression Previously (Handout
Biostat Methods STAT 5500/6500 Handout #12: Methods and Issues in (Binary Resonse) Logistic Regression Recall general χ 2 test setu: Y 0 1 Trt 0 a b Trt 1 c d I. Basic logistic regression Previously (Handout
Ecological Resemblance. Ecological Resemblance. Modes of Analysis. - Outline - Welcome to Paradise
 Ecological Resemblance - Outline - Ecological Resemblance Mode of analysis Analytical saces Association Coefficients Q-mode similarity coefficients Symmetrical binary coefficients Asymmetrical binary coefficients
Ecological Resemblance - Outline - Ecological Resemblance Mode of analysis Analytical saces Association Coefficients Q-mode similarity coefficients Symmetrical binary coefficients Asymmetrical binary coefficients
Outline. Markov Chains and Markov Models. Outline. Markov Chains. Markov Chains Definitions Huizhen Yu
 and Markov Models Huizhen Yu janey.yu@cs.helsinki.fi Det. Comuter Science, Univ. of Helsinki Some Proerties of Probabilistic Models, Sring, 200 Huizhen Yu (U.H.) and Markov Models Jan. 2 / 32 Huizhen Yu
and Markov Models Huizhen Yu janey.yu@cs.helsinki.fi Det. Comuter Science, Univ. of Helsinki Some Proerties of Probabilistic Models, Sring, 200 Huizhen Yu (U.H.) and Markov Models Jan. 2 / 32 Huizhen Yu
arxiv: v2 [stat.me] 3 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v2 [stat.me] 3 Nov 2014 arxiv: v2 [stat.me] 3 Nov 2014](/thumbs/92/109512170.jpg) onarametric Stein-tye Shrinkage Covariance Matrix Estimators in High-Dimensional Settings Anestis Touloumis Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute University of Cambridge Cambridge CB2 0RE, U.K. Anestis.Touloumis@cruk.cam.ac.uk
onarametric Stein-tye Shrinkage Covariance Matrix Estimators in High-Dimensional Settings Anestis Touloumis Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute University of Cambridge Cambridge CB2 0RE, U.K. Anestis.Touloumis@cruk.cam.ac.uk
The Noise Power Ratio - Theory and ADC Testing
 The Noise Power Ratio - Theory and ADC Testing FH Irons, KJ Riley, and DM Hummels Abstract This aer develos theory behind the noise ower ratio (NPR) testing of ADCs. A mid-riser formulation is used for
The Noise Power Ratio - Theory and ADC Testing FH Irons, KJ Riley, and DM Hummels Abstract This aer develos theory behind the noise ower ratio (NPR) testing of ADCs. A mid-riser formulation is used for
A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Supported on Elastic Foundation
 A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Suorted on Elastic Foundation Guo-ing Xia Institute of Bridge Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning Province, P. R. China
A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Suorted on Elastic Foundation Guo-ing Xia Institute of Bridge Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning Province, P. R. China
SIMULATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN LABYRINTHIC DOMAINS BY USING CELLULAR AUTOMATA
 SIMULATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN LABYRINTHIC DOMAINS BY USING CELLULAR AUTOMATA Udo Buschmann and Thorsten Rankel and Wolfgang Wiechert Deartment of Simulation University of Siegen Paul-Bonatz-Str.
SIMULATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN LABYRINTHIC DOMAINS BY USING CELLULAR AUTOMATA Udo Buschmann and Thorsten Rankel and Wolfgang Wiechert Deartment of Simulation University of Siegen Paul-Bonatz-Str.
An Improved Calibration Method for a Chopped Pyrgeometer
 96 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 17 An Imroved Calibration Method for a Choed Pyrgeometer FRIEDRICH FERGG OtoLab, Ingenieurbüro, Munich, Germany PETER WENDLING Deutsches Forschungszentrum
96 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 17 An Imroved Calibration Method for a Choed Pyrgeometer FRIEDRICH FERGG OtoLab, Ingenieurbüro, Munich, Germany PETER WENDLING Deutsches Forschungszentrum
ε(ω,k) =1 ω = ω'+kv (5) ω'= e2 n 2 < 0, where f is the particle distribution function and v p f v p = 0 then f v = 0. For a real f (v) v ω (kv T
 High High Power Power Laser Laser Programme Programme Theory Theory and Comutation and Asects of electron acoustic wave hysics in laser backscatter N J Sircombe, T D Arber Deartment of Physics, University
High High Power Power Laser Laser Programme Programme Theory Theory and Comutation and Asects of electron acoustic wave hysics in laser backscatter N J Sircombe, T D Arber Deartment of Physics, University
Introduction to Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory
 Introduction to Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory Erkki Thuneberg Deartment of hysical sciences University of Oulu 29 1. Introduction The rincial roblem of hysics is to determine how bodies behave when they
Introduction to Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory Erkki Thuneberg Deartment of hysical sciences University of Oulu 29 1. Introduction The rincial roblem of hysics is to determine how bodies behave when they
8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules
 8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules Recall the Levy-Mises flow rule, Eqn. 8.4., d ds (8.7.) The lastic multilier can be determined from the hardening rule. Given the hardening rule one can more
8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules Recall the Levy-Mises flow rule, Eqn. 8.4., d ds (8.7.) The lastic multilier can be determined from the hardening rule. Given the hardening rule one can more
Modeling and Estimation of Full-Chip Leakage Current Considering Within-Die Correlation
 6.3 Modeling and Estimation of Full-Chi Leaage Current Considering Within-Die Correlation Khaled R. eloue, Navid Azizi, Farid N. Najm Deartment of ECE, University of Toronto,Toronto, Ontario, Canada {haled,nazizi,najm}@eecg.utoronto.ca
6.3 Modeling and Estimation of Full-Chi Leaage Current Considering Within-Die Correlation Khaled R. eloue, Navid Azizi, Farid N. Najm Deartment of ECE, University of Toronto,Toronto, Ontario, Canada {haled,nazizi,najm}@eecg.utoronto.ca
Factors Effect on the Saturation Parameter S and there Influences on the Gain Behavior of Ytterbium Doped Fiber Amplifier
 Australian Journal of Basic and Alied Sciences, 5(12): 2010-2020, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Factors Effect on the Saturation Parameter S and there Influences on the Gain Behavior of Ytterbium Doed Fiber Amlifier
Australian Journal of Basic and Alied Sciences, 5(12): 2010-2020, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Factors Effect on the Saturation Parameter S and there Influences on the Gain Behavior of Ytterbium Doed Fiber Amlifier
Chapter 1 Fundamentals
 Chater Fundamentals. Overview of Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution brought in large scale automation of many tedious tasks which were earlier being erformed through manual or animal labour. Inventors
Chater Fundamentals. Overview of Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution brought in large scale automation of many tedious tasks which were earlier being erformed through manual or animal labour. Inventors
Some Unitary Space Time Codes From Sphere Packing Theory With Optimal Diversity Product of Code Size
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 5, NO., DECEMBER 4 336 Some Unitary Sace Time Codes From Shere Packing Theory With Otimal Diversity Product of Code Size Haiquan Wang, Genyuan Wang, and Xiang-Gen
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 5, NO., DECEMBER 4 336 Some Unitary Sace Time Codes From Shere Packing Theory With Otimal Diversity Product of Code Size Haiquan Wang, Genyuan Wang, and Xiang-Gen
One step ahead prediction using Fuzzy Boolean Neural Networks 1
 One ste ahead rediction using Fuzzy Boolean eural etworks 1 José A. B. Tomé IESC-ID, IST Rua Alves Redol, 9 1000 Lisboa jose.tome@inesc-id.t João Paulo Carvalho IESC-ID, IST Rua Alves Redol, 9 1000 Lisboa
One ste ahead rediction using Fuzzy Boolean eural etworks 1 José A. B. Tomé IESC-ID, IST Rua Alves Redol, 9 1000 Lisboa jose.tome@inesc-id.t João Paulo Carvalho IESC-ID, IST Rua Alves Redol, 9 1000 Lisboa
Robustness of classifiers to uniform l p and Gaussian noise Supplementary material
 Robustness of classifiers to uniform l and Gaussian noise Sulementary material Jean-Yves Franceschi Ecole Normale Suérieure de Lyon LIP UMR 5668 Omar Fawzi Ecole Normale Suérieure de Lyon LIP UMR 5668
Robustness of classifiers to uniform l and Gaussian noise Sulementary material Jean-Yves Franceschi Ecole Normale Suérieure de Lyon LIP UMR 5668 Omar Fawzi Ecole Normale Suérieure de Lyon LIP UMR 5668
Buckling of Spherical Shells Revisited. John W. Hutchinson. School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University.
 Buckling of Sherical Shells Revisited John W. Hutchinson School of Engineering and Alied Sciences, Harvard University Abstract A study is resented of the ost-buckling behavior and imerfection-sensitivity
Buckling of Sherical Shells Revisited John W. Hutchinson School of Engineering and Alied Sciences, Harvard University Abstract A study is resented of the ost-buckling behavior and imerfection-sensitivity
