The Behaviur f the Flquet Multipliers f Peridic Slutins Near a Hmclinic Orbit Zuchang Zheng Dirk Rse Reprt TW 287, December 998 Department f Cmputer S
|
|
|
- Everett Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Behaviur f the Flquet Multipliers f Peridic Slutins Near a Hmclinic Orbit Zuchang Zheng Dirk Rse Reprt TW 287, December 998 n Kathlieke Universiteit Leuven Department f Cmputer Science Celestijnenlaan 200A { B-300 Heverlee (Belgium)
2 The Behaviur f the Flquet Multipliers f Peridic Slutins Near a Hmclinic Orbit Zuchang Zheng Dirk Rse Reprt TW 287, December 998 Department f Cmputer Science, K.U.Leuven Abstract In this paper, we describe the behaviur f the mduli f the Flquet multipliers f peridic slutins near a hmclinic rbit. We discuss the relatin between the Flquet multipliers and the eigenvalues f the equilibrium pint at which the hmclinic rbit emanates. Fr tw-dimensinal prblems, fr which the equilibrium pint has tw real eigenvalues, we derive an asympttic estimate fr the nntrivial Flquet multipliers in terms f the perid. Fr mre cmplicated situatins (higher dimensinal prblems, cmplex cnjugate pairs f eigenvalues), we perfrm numerical experiments fr sme mdel equatins, shwing that eigenvalues with large negative real part cause small Flquet multipliers. Keywrds : Flquet Multiplier, Peridic Slutin, Hmclinic Orbit. AMS(MOS) Classicatin : Primary : 65N35, Secndary : 35B32.
3 The Behaviur f the Flquet Multipliers f Peridic Slutins Near a Hmclinic Orbit Zuchang Zheng Dirk Rse Department f Cmputer Science Kathlieke Universiteit Leuven Celestijnenlaan 200A B-300 Heverlee-Leuven, Belgium Dirk.Rse@cs.kuleuven.ac.be December,998 Abstract In this paper, we describe the behaviur f the mduli f the Flquet multipliers f peridic slutins near a hmclinic rbit. We discuss the relatin between the Flquet multipliers and the eigenvalues f the equilibrium pint at which the hmclinic rbit emanates. Fr tw-dimensinal prblems, fr which the equilibrium pint has tw real eigenvalues, we derive an asympttic estimate fr the nntrivial Flquet multipliers in terms f the perid. Fr mre cmplicated situatins (higher dimensinal prblems, cmplex cnjugate pairs f eigenvalues), we perfrm numerical experiments fr sme mdel equatins, shwing that eigenvalues with large negative real part cause small Flquet multipliers. Key Wrds Flquet multiplier, Peridic Slutin, Hmclinic Bifurcatin AMS(MOS) subject classicatins 65N2,35B0,35B32. Intrductin Several numerical methds (Beyn (989, 990), Kuznetsv (990) Dedel et al.(997) ) fr the cmputatin f hmclinic bifurcatins f rdinary dierential equatins have been develped. Typically, they are frmulated as apprximate bundary value prblems with peridic r prjected bundary value cnditins. Fr a large-scale system f ODEs, arising frm the space discretizatin f PDEs, these methds becme prhibitively expensive. Recently, Newtn-Picard schemes (Rse et al.(995), Lust et al.(997)) have been develped t slve large-scale peridic bundary value prblem with lw dimensinal dynamics, i.e, when mst
4 f the Flquet Multiplers f the peridic slutin have small mdulus. This is the case fr many ODE systems arising frm the space discretizatin f a PDE. In this paper, we study the behaviur f the mdulus f the Flquet multipliers when the peridic slutins apprach a hmclinic rbit, and we shw that mst f the Flquet multipliers becme small, such that a Newtn-Picard scheme can be used t cmpute peridic slutins as an apprximatin t a hmclinic rbit. Specically, we suppse that the autnmus ODE system _x(t) = F (x(t); ); x 2 R N ; 2 R; N >> () has a nndegenerate hmclinic rbit (x (t); ) cnnecting p( ), where p() is a hyperblic xed pint f ODE system (). As a starting pint, we recall Therem 3. frm (Beyn (989)) Therem There exits T 0 > 0 large enugh and > 0, such that fr any T > T 0, the apprximate peridic bundary value prblem 8>< >: _x(t) = F (x(t); ); t 2 J = [ T; T ] x( T ) = x(t ) _x (0) T (x(0) x (0)) = 0 has a unique slutin (x(t; T ); (T )) in f(x; ) : jjx x jj + j j < g Further, fr any > 0, the slutin (x(t; T ); (T )) satises the estimates (2) jjx(t; T ) x (t)jj = O(exp ( (min( + ; ) )T )) j j = O(exp ( (2 min( + ; ) )T )) (3) with the critical expnents + = MinfRe() : is an eigenvalue f A( ) with Re() > 0g = Minf Re() : is an eigenvalue f A( ) with Re() < 0g (4) and A() = F x (p(); ). In this paper, we relate the Flquet multipliers f the peridic slutin x(t; T ) t the eigenvalues f the xed pint p( ) in terms f the perid T. We shw that lw dimensinal dynamics f the xed pint (mst f the eigenvalues f F x (p( ); ) have a very large negative real part) prduces lw dimensinal dynamics f the peridic slutins (mst f the Flquet multipliers are very small in mdulus). 2. Lw dimensinal dynamics f the xed pint and peridic slutins appraching an hmclinic rbit We discuss the relatin between the lw dimensinal dynamics f the xed pint p( ) and that f the peridic slutins which apprach the hmclinic rbit. The 2
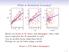
5 discussin is based n the fact that near the xed pint, the vectr eld f () is essentially linear, and when peridic slutins apprach the hmclinic rbit, the time they spend in the small linear regin ges t innity. The lcal linearizatin vectr eld f the xed pint plays an imprtant rle in ur discussin. In fact, fr three dimensinal systems, Glendinning and Sparrw ([984]) shw that the eigenvalues f the lcal linearizatin vectr eld determines the stability f the peridic slutins when they apprach the hmclinic rbit. Fr higher dimensinal ODE systems, the peridic slutins in a neighburhd f the hmclinic rbit have dierent bifurcatin and stability behaviurs, depending n the relative size f the critical expnents (4), see Kuznetsv Yu.A. [997]. The estimate (3) als illustrate that the eigenvalues f the xed pint determine the apprximate rder f the slutin f the apprximate peridic bundary value prblems. We discuss tw dierent cases: a) all eigenvalues f the xed pint are real; b) there are sme cmplex cnjugate pairs f eigenvalues. Since the tplgy f the phase space f the lcal linearizatin vectr eld is qualitatively dierent in these tw cases, we expect that the mdulus f the Flquet multipliers will als vary in qualitatively dierent ways. In fact, Kuznetsv (997) has shwn that the Flquet multipliers may cntract t zer r expand innitely when the peridic slutins apprach the hmclinic rbit. In this paper, we derive sme mre quanlitative infrmatin, e.g. hw many Flquet multipliers cntract t zer and hw many expand t innity. First, we btain a predictin frm the analytical analysis f the simplest situatins with the help f Sil'nikv's standard analysis methds fr the lcal behaviur near a hmclinic rbit (Sil'nikv (965), (970)); Then the predictin is further veried by numerical experiments. 2. All eigenvalues are real When all eigenvalues are real, the simplest situatin is a tw - dimensinal system whse hyperblic xed pint p( ) has tw simple real eigenvalues ; 2 with 2 > 0 and 2 < 0. Fr tw-dimensinal peridic slutins, n perid-dubling bifurcatins and bifurcatins t trus can ccur. Therem 6.5 in Guckenheimer & Hlmes (983) implies that when the peridic slutins apprach the hmclinic rbit, saddle-nde bifurcatins can nt ccur either. Thus the unique nntrivial Flquet multipliers always stays within r utside the unit circle. T relate their mdulus t the eigenvalues f the xed pint, we cmpute an asympttic estimate fr it by Sil'nikv's standard analysis methd. An imprtant bservatin in Sil'nikv's analysis is that the w near p() is essentially linear. Then the w is divided int tw regins as shwn in Figure (), the linear regin bunded by a bx B=fjxj l; jyj hg and the nnlinear regin utside this bx. In the bx B, there exist lcal crdinates (x; y) s that the lcal stable manifld Wlc s = fy = 0g and the lcal unstable manifld Wlc u = fx = 0g. In the bx B, the vectr eld can 3
6 y 2 Σ λ h Σ λ 0 l x Figure : Within the bx, the w is essentially linear. be written as ( _x = x + f(x; y; ); _y = 2 y + g(x; y; ) where f(x; y; ) and g(x; y; ) are higher rder terms. When =, there is a hmclinic rbit. Thus there exists a glbal nnlinear w which takes trajectries clse t the unstable manifld away frm the linear regin and then back int it. The glbal nnlinear w induces a return map (5) = 2 : (l; y)! (l; (y; )) (6) With jyj < h << and j j <<. maps the plane x = l t the plane y = h and is determined by the lcal linearised w f (5). Thus it is easy t check that : (l; y)! (l(y=h) ; h) (7) with jyj < h << and = j 2 j. The time needed t perfrm the linear map frm x = l t y = h is T (y) = 2 ln h y 2 species hw trajectries leave y = h int the nnlinear regin and then return t the linear regin at x = l, and can be written as (8) 2 : (x; h)! (l; (x; )) (9) 4
7 where jxj < l << and j j <<. At =, we have (0; ) = 0. If the linear regin is taken small enugh, (x; ) will be given by its Taylr expansin until the rst rder term, that is, (x; ) = ax + b( ) (0) here a (0; ) and b (0; ). Cmbining (7) with (0), we get the : y! cy + b( ) () with c = al h, jyj < h << and j j <<. The xed pint y() f the return map satises cy + b( ) = y (2) In equatin (2), ignring the higher rder terms f y, the xed pint can be taken t be 8>< b( ); if > y() = (3) >: ( b c ( )) ; if 0 < < and the eigenvalue () f the return map at the xed pint is () = 8>< >: c(b( )) ; if > c(( b c ( )) ; if 0 < < The relatin (4) gives the stability infrmatin f the peridic slutins ( see Guckenheimer & Hlmes [983] ). T derive an asympttic estimate fr the nntrivial Flquet multiplier in terms f the perid, we ntice that if the linear regin is small enugh, the time spent in the linear regin (8) is the main cntributin t the perid T () f the peridic slutin crrespnding t the xed pint y(), and we can take T () ' T (y()). In view f (8) and (3), we have the fllwing asympttic estimate fr the perid which implies that T () 8>< >: 2 lnj j; if > lnj j; if 0 < < 8>< >: e 2T () ; if > e T () ; if 0 < < Substituting (6) in (4), we btain an asympttic estimate fr the nntrivial Flquet multiplier (4) (5) (6) () e 2( )T () ; if 6= (7) 5
8 Thus the nntrivial Flquet multiplier varies expnentially with expnent 2 ( ) as T!. If >, the nntrivial Flquet multiplier cntracts t zer; in particular, the cntractin is very strng when j j is very large. If 0 < <, the nntrivial Flquet multiplier expands t. Thus depending n the relative size f the eigenvalues f the xed pint, the nntrivial Flquet multiplier wuld either expand innitely r cntract tward zer. Based n the analysis abve, we expect that fr higher dimensinal systems, the mduli f the Flquet multipliers vary in the same way. Mre precisely, a typical case is that nly ne f the eigenvalues i ; i = ; 2; ; N, say, is psitive. Then depending n whether i = j i j; i = 2; 3; ; N is larger r smaller than, a Flquet multiplier will cntract r expand with the expnent ( i ). T verify this, we have dne numerical experiments. T make sure that the numerical cmputatin is accurate enugh and reliable, we give sme details f the numerical methds fr cmputing Flquet multipliers and f ur cmputatinal strategies. Fllwing (Fairgrieve (994)), a numerical methd fr cmputing Flquet multipliers is cnsidered t be rbust if the errr in the cmputed Flquet multipliers is directly prprtinal t the truncatin errr f the cmputed peridic slutin and is nt badly inuenced by the rund errr in the eigenvalue calculatin. The numerical methd implemented in the AUTO97 sftware package is rbust (Fairgrieve et al.(99), (994)). In the AUTO97, a spline cllcatin scheme with adaptive mesh selectin is applied t cmpute the peridic slutin. The truncatin errr (Ascher et al.(979) and Hustis (978)) is determined by the number f mesh subintervals and the number f cllcatin pints per subinterval. In ur numerical cmputatins, we have used set 4 cllcatin pints per subinterval and we have chsen the number f mesh subintervals large but nt t large s that the rund errr des nt dminate the truncatin errr. In additin, we set all the relative cnvergence tlerances in the Newtn/Chrd methds small enugh such that the errr in the cmputed peridic slutin is dminated by the truncatin errr. Mrever, thrughut the numerical cmputatin, we always use adaptive mesh selectin strategy and repeat the cmputatin with dierent number f mesh subintervals. These are eective safeguards t avid spurius slutins. The trivial Flquet multiplier is mnitred and cntrlled within an acceptable accuracy, and in mst runs, is btained t maximal accuracy. Except that sme f the Flquet multipliers becme s small that numerical nise becmes visible, the Flquet multipliers cmputed within AUTO are accurate and reliable. Fr the case f three real eigenvalues i ; i = ; 2; 3, if cnsidering the ODE system in reverse time, we nly need t verify the situatin with > 0; 3 < 2 < 6
9 a b Figure 2: Peridic Slutins f the Lrenz equatins: perid versus lgarithm f the mduli f the Flquet multipliers, indicating that the nntrivial Flquet multipliers vary expnentially with the perid. (a) Flquet multiplier which expands t ; (b) Flquet multiplier which cntracts t 0. 8>< >: 0. As ur cmputatinal mdel, we take the well-knwn Lrenz equatins _x = (y x) _y = rx y xz _z = xy bz (8) As usual, we take = 0; b = 8=3 and 0 < r <. When r = r ' 3:92, there is a hmclinic rbit cnnecting the rigin and the three real eigenvalues f the rigin at r are ( ; 2 ; 3 ) = (7:299; 2:6667; 8:299). We trace a branch f peridic slutins, which bifurcates frm a Hpf pint at r ' 24:74 and terminates at the hmclinic rbit. Since this branch des nt cntain any further lcal bifurcatins, the Flquet multipliers d nt crss the unit circle. Their mdulus shuld change in the same way as tw-dimensinal systems. Mre precisely, since the eigenvalues f the rigin fr r satisfy the relatin = j 3 j >, the tw dimensinal analysis predicts that the mdulus f ne f the tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers shuld cntract t zer with expnent ( ) ' :0. The fast cntractin is due t the large negative real eigenvalue 3 ' 8:3. The mdulus f the ther nntrivial Flquet multiplier shuld expand t with expnent ( 2 ) ' 4:4632 since 2 = j 2 j <. The cmputed nntrivial Flquet multipliers are shwn in Figure 2, demnstrating that the nntrivial Flquet multipliers indeed expand r cntract expnentially with the perid T. The cmputed smaller nntrivial Flquet multiplier quickly be- 7
10 cmes s small that the cmputatinal results are subject t nise fr T > 2. Using least squares tting, we that the expnents fr the smaller and larger nntrivial Flquet multiplier is and 4.02, respectively. Cmpared with the predicted expnents :0 and 4:4632, the cmputed expnent fr the larger ne is mre accurate than that fr the smaller ne. 2. A pair f cmplex cnjugate eigenvalues Fr the case where there are cmplex cnjugate pairs f eigenvalues, the analysis is mre cmplicated. A three-dimensinal system with a pair f cmplex cnjugate eigenvalues is the simplest situatin we need t cnsider. We assume that the three eigenvalues i ; i = ; 2; 3, satisfy Re( 3 ) = Re( 2 ) < 0 and > 0. Using Sil'nikv's standard analysis methd, Glendinning and Sparrw (984) discuss the stability f peridic slutins f 3-dimensinal ODE systems which apprach the hmclinic rbit. Their results state that if = j Re( 2) j >, there is a branch f stable peridic slutins which apprach the hmclinic rbit withut any lcal bifurcatins and the tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers cntract t zer; if = j Re( 2) j <, there is a branch f peridic slutins which apprach the hmclinic rbit thrugh an innite sequence f pairs f tw successive saddle-nde and tw successive perid-dubling bifurcatins. The tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers will scillate arund and, respectively. It is nt easy t cmpute their asympttic estimates in terms f the perid T as we did in the tw dimensinal setting. Instead, fllwing the stability analysis in Glendinning and Sparrw (984), we have perfrmed numerical experiments t shw the relatin between the tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers and the perid. T nd ut hw large r hw small the mdulus f the Flquet multipliers wuld be, we take Arned's equatins fr > and Chua's circuit equatins fr < as mdel prblems. Arned's equatins can be written as 8>< >: _x = y _y = z _z = z by + cx x 2 (9) Arned et al.(982) have lcated hmclinic rbits at sme values f the parameters b and c. We x b = 0:5 and take c > 0 as a free parameter. Fr c = c ' 0:964494, there is a hmclinic rbit cnnecting the xed pint at the rigin. The eigenvalues ( ; 2 ; 3 ) f the rigin at c are (0:629; 0:84 i0:928). The peridic slutins arising frm the Hpf pint d nt underg any lcal bifurcatins when they apprach the hmclinic rbit. Thus the mduli f the Flquet multipliers d nt crss the unit circle, but in this case, the mduli f the Flquet multipliers cntract t zer in an scillatry way in functin f the perid. Fr T > 28, the smallest Flquet multipliers (Figure 3b) is cmputed inaccurately due 8
11 0 2 a b Figure 3: The mdulus f the Flquet multipliers f the peridic slutins f Arned's equatin in functin f the perid. Bth f the Flquet multipliers cntract t zer. The peaks in curve (b) indicate an increasing trend, but they becme mre and mre sharp when the perid!. t numerical nise and is mitted frm the Figure, see Figure 3. The scillatins f the mduli f the Flquet multipliers have peaks. Althugh in Figure 3b, the peaks indicate a increasing trend as the perid ges t innity, bth the mdulus and the width f the peaks becme smaller s that numerically it is nt easy t nd the sharp pints by slving the apprximate peridic bundary value prblem (2). Ignring the sharp pints, we can say that this situatin is similar t the case with three real eigenvalues with bth > and 2 >. Fr the case f cmplex cnjugate eigenvalue with <, we deal with Chua's circuit equatins 8 > < _x = (y (x)) > _y = x y + z (20) : _z = z Fllwing Huang, et al.(996), we take (x) = (x 3 =6 x=6), = 8:0 and t be the free parameter. The system has three xed pints, i.e, P 0 = (0; 0; 0); P = ((8=3) =2 ; 0; (8=3) =2 ) fr any 2 R. When = 4:684658, P are Hpf bifurcatin pints, frm which a branch f peridic slutins bifurcates. The stability analysis in (Glendinning et al.(984)) shws that as the peridic slutins apprach the hmclinic rbit, a saddle-nde bifurcatin and a perid-dubling bifurcatin ccur successively and between them, there is a shrt sectin f unstable peridic slutins. This pattern f stability changes is repeated until the peridic slutins end at the hmclinic rbit when = ' 4:5965. The peridic 9
12 a b Figure 4: If the sharp pints are ignred, the mdulus f the Flquet multiplier f Chua's equatins in (a) expand t innity; the ne in (b) cntracts t zer. They vary in a smewhat similar way t the real eigenvalues case shwn in Figure (2). slutins apprach the hmclinic rbit thrugh a sequence f lcal bifurcatins, cntrary t the situatins in Lrenz's equatins and Arned's equatins. The xed pint n the hmclinic rbit is the rigin, whse eigenvalues at = are ( ; 2 ; 3 ) = (2:2776; :089 :6357i). Since there is an innite sequence f saddle-nde and perid-dubling bifurcatins, the mduli f the Flquet multipliers d nt increase r decrease in a mntnus way as in Lrenz's equatins, but scillate arund. The cmputed mduli f the Flquet multipliers, presented in Figure 4, indeed reects the bifurcatin infrmatin. The peaks f the curves f the cmputed mdulus result frm the saddle-nde and perid-dubling bifurcatins. The intervals between these tw successive bifurcatins are s small that the tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers crss almst fr the same value f the perid; thus the mduli f the Flquet multipliers will change very quickly. In additin, these intervals will becme smaller and smaller when the perid tends t innity. Successive saddle-nde and perid dubling bifurcatins and the unstable peridic slutins between them are nt fund by numerical cmputatin with AUTO when T is larger than 5, even with T = 0 5. Ignring the peaks, caused by the lcal bifurcatins, the general behaviurs f the Flquet multipliers is as fllws: ne f the Flquet multipliers expands t innity, similar t the case f real eigenvalues with < ; the ther Flquet multipliers cntracts t zer, similar t the case f real eigenvalues with >. The discussin abve has shwn that fr a pair f cmplex cnjugate eigenval- 0
13 Eigenvalues f xed pint Real Real part Imaginary part Flquet multipliers E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E+ Table : Kuramt-Sivashinsky equatin: The eigenvalues f the xed pint and the Flquet multipliers f the peridic slutins with = 3:574067E + 0. ues, numerically the mduli f the Flquet multipliers vary in a similar way as in the case f three real eigenvalues, i.e., depending n the relative size f the psitive and negative real part f the eigenvalues, the Flquet multipliers will expand innitely r cntract t zer. Fr higher dimensinal systems, we expect that the same cnclusin is true. A typical case is when there is nly ne pair f cmplex cnjugate eigenvalues with psitive real part, say, i ; i = ; 2, with Re( )=Re( 2 )> 0, and j 3 j j 4 j j N j are negative real eigenvalues. Cnsider this system in reverse time and let i = j i Re j; i = 3; ; N, then we predict that if 3 <, tw f the nntrivial Flquet multipliers expand t innity; if >, ne f nntrivial Flquet multipliers expands innitely and anther nntrivial Flquet multiplier will cntract t zer. Mrever, depending n i (i 3) < r >, ne f the ther nntrivial Flquet multipliers will expand r cntract. When ne eigenvalue has a large real part, ne f the nntrivial Flquet multipliers becmes quickly very small. T verify this further, we cnsider an innite dimensinal mdel, Kuramt-Sivashinsky equatin + 4@4 4 + (@2 2 + ) = 0 (2) subject t spatial peridic bundary cnditins u(x; t) = u(x+2; t) with 0 x 2. Using the traditinal Galerkin methd t discretize the space variable, Jlly et al.(990)) btain the fllwing ODE system where _x k = ( 4k 4 + k 2 )x k m k ; k m (22) m k = =2 mx j= jx j [x j+k + sgn(k j)x jk jj ] (23) The index m represents the number f mdes used in the discretizatin. We set x j = 0 if j < 0 and j > m, respectively. At = 34:299, there are tw Hpf
14 a b Figure 5: The mdulus f the tw nntrivial Flquet multipliers f K-S equatin, which crss thrugh the unit circle. The tw mdulus curves are similar t thse f Chua's equatins as shwn in Figure(4). pints H i ; i = ; 2. Numerical cmputatins (Jlly et al.(990)) indicate that the peridic slutins bifurcating frm bth Hpf pints terminate at a hmclinic rbit at = ' 35: We fcus n ne f the hmclinic rbits. As Jlly et al. (990) have shwn, the peridic slutins apprach t the hmclinic rbit in the same way as Chua's equatins. The xed pint n the hmclinic rbit has a cmplex cnjugate pair f eigenvalues with psitive real part, and the ther eigenvalues are large negative real numbers, as shwn in Table. Due t 3 >, tw f the Flquet multipliers, which crss thrugh the unit circle, shuld vary in a similar way as fr Chua's equatins. Figure 5 presents the cmputed mduli f the Flquet multipliers fr the 8-mde discretizatin. It indeed lks similar t Figure 4. Mrever due t i >, i = 4; ; N, the rest f the nntrivial Flquet multipliers shuld cntract t zer. In fact, since the negative real eigenvalues are very large in mdulus, the rest f the cmputed Flquet multipliers becme quickly s small that they are nt btained with a reasnable accuracy in ur cmputatin where the trivial Flquet multiplier has nly 4 signicant digits. T shw the rder f these small Flquet multipliers, in Table(), we list them fr a peridic slutin clse t the hmclinic rbit. Our cmputatinal results agree with the predictin that eigenvalues with a large negative real part make the Flquet multipliers cntract very quickly. The cmputed results fr discretizatins f the K-S equatin with 4, 6 and 32 mdes als further cnrm the predictin. 2
15 3. Cnclusins We have related the eigenvalues f the xed pint having a hmclinic rbit with the Flquet multipliers f the peridic slutins which apprach t the hmclinic rbit. We have shwn that the Flquet multipliers expand t innity r cntract t zer, depending n the relative size f the psitive and negative real parts f the eigenvalues. Specically, we have studied the fllwing tw typical if all eigenvalues i ; i = ; 2; ; N are real and nly ne f them, say, is psitive, then depending n whether i = j i j; i = 2; 3; ; N is larger r smaller than, a Flquet multiplier will cntract r expand asympttically with expnent ( i ); Nw suppse that there is nly ne pair f cmplex cnjugate eigenvalues with psitive real part, say, i ; i = ; 2, with Re( )=Re( 2 )> 0, and that i (i 3) are negative real eigenvalues. Then if 3 <, tw f the nntrivial Flquet multipliers expand t innity; if 3 >, ne f nntrivial Flquet multipliers expands innitely and anther nntrivial Flquet multiplier will cntract t zer. Mrever, depending n i (i > 3) < r >, ne f the ther nntrivial Flquet multipliers will expand r cntract. Here i = j i j; i = 3; ; N. Re( ) References [] Beyn W.-J., 989, Glbal bifurcatins and their numerical cmputatin, In Cntinuatin and Bifurcatins: Numerical Techniques and Applicatins, edited by D. Rse, B.D. Dier and A.Spence, Kluwer Academic Publisher, pp. 69-8, 990. [2] Beyn W.-J., 990, The numerical cmputatin f cnnecting rbits in dynamical systems, IMA J. Numer. Anal., 9(990), pp [3] Mre G., 995, Cmputatin and parameterizatin f peridic and cnnecting rbits, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 5(995), pp [4] Dedel E.J., Friedman M.J. and Kunin B.I., 997, Successive cntinuatin fr lcating cnnecting rbits, Numerical Algrithms, 4(997), pp [5] Yu.A. Kuznetsv, 990, Cmputatin f Invariant Manifld Bifurcatins, in Cntinuatin and Bifurcatins: Numerical Techniques and Applicatins, eds by D.Rse, Bart De Dier and A. Spence, Kluwer Academic Publisher, pp ,
16 [6] Rse D., Lust K., Champneys A. and Spence A., 995, A Newtn-Picard shting methd fr cmputing peridic slutins f large-scale dynamical systems, Chas, Slitns and Fractals, 5(995), pp [7] Lust K., Rse D., Spence A. and Champneys A.R., 997, An adaptive Newtn-Picard Algrithm with subspace iteratin fr cmputing peridic slutins, SIAM J. Sci. Cmput., 9(998), pp [8] Glendinning D., Sparrw C., 984, Lcal and glbal behavir near hmclinic rbits, J. f Statistical Physics, 35(984), pp [9] Kuznetsv Y.A., 997, Elements f applied bifurcatin thery, Springer- Verlag, 997 [0] Guckenheimer J., Hlmes P., 983, Nnlinear scillatins, dynamical systems, and bifurcatins f vectr elds, Springer-Verlag, 983 [] Sil'nikv L.P., 965, A case f the existence f a denumerable set f peridic mtins, Sv. Math. Dkl., 6(965), pp [2] Sil'nikv L.P., 970, A cntributin t the prblem f the structure f an extended neighbrhd f a rugh equilibrium state f saddle-fcus type, Math. USSR Sbrnik, 0(970), pp [3] Fairgrieve T.F., Jepsn A.D., 99, O.K. Flquet multipliers, SIAM J. Numer.Anal., 28(99), pp [4] Fairgrieve T.F., 994, The cmputatin and use f Flquet multipliers fr bifurcatin analysis, Ph.D. thesis, University f Trnt, 994. [5] Ascher U., Christiansen J. and Russell R.D., 979, A cllcatin slver fr mixed rder systems f bundary value prblems, Math. f Cmput., 33(979), pp [6] Hustis E., 978, A cllcatin methd fr systems f nnlinear rdinary dieretial equatins, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 62(978), pp [7] Arned A., Cullet P., Speigel E. and Tresser C., 982, Asympttic chas, Preprint, Universite de Nice (982). [8] Huang A.S., Pivka L., Wu C.W. and Franz M., 996, Chua's circuit with cubic nnlinearity, Int. J. Bifurcatin and Chas 6(996), pp [9] Jlly M.S., Kevrekidis I.G. and Titi E.S., 990, Apprximate inertial maniflds fr the Kuramt-Sivashinsky equatin: analysis and cmputatins, Physica D, 44(990), pp
A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM. Department of Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA16802, USA.
 A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM MIN CHEN Department f Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA68, USA. Abstract. This paper studies traveling-wave slutins f the
A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM MIN CHEN Department f Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA68, USA. Abstract. This paper studies traveling-wave slutins f the
Lyapunov Stability Stability of Equilibrium Points
 Lyapunv Stability Stability f Equilibrium Pints 1. Stability f Equilibrium Pints - Definitins In this sectin we cnsider n-th rder nnlinear time varying cntinuus time (C) systems f the frm x = f ( t, x),
Lyapunv Stability Stability f Equilibrium Pints 1. Stability f Equilibrium Pints - Definitins In this sectin we cnsider n-th rder nnlinear time varying cntinuus time (C) systems f the frm x = f ( t, x),
Building to Transformations on Coordinate Axis Grade 5: Geometry Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
 Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillations
 Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillatins Last time, we fund fr underdamped scillatrs: βt x t = e A1 + A csω1t + i A1 A sinω1t A 1 and A are cmplex numbers, but ur answer must be real Implies that A 1 and
Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillatins Last time, we fund fr underdamped scillatrs: βt x t = e A1 + A csω1t + i A1 A sinω1t A 1 and A are cmplex numbers, but ur answer must be real Implies that A 1 and
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
x x
 Mdeling the Dynamics f Life: Calculus and Prbability fr Life Scientists Frederick R. Adler cfrederick R. Adler, Department f Mathematics and Department f Bilgy, University f Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Mdeling the Dynamics f Life: Calculus and Prbability fr Life Scientists Frederick R. Adler cfrederick R. Adler, Department f Mathematics and Department f Bilgy, University f Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Lab 11 LRC Circuits, Damped Forced Harmonic Motion
 Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA
 February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
Kinetic Model Completeness
 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
Module 4: General Formulation of Electric Circuit Theory
 Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillations
 Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b
![MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b](/thumbs/78/78051685.jpg) . REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
. REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
THE TOPOLOGY OF SURFACE SKIN FRICTION AND VORTICITY FIELDS IN WALL-BOUNDED FLOWS
 THE TOPOLOGY OF SURFACE SKIN FRICTION AND VORTICITY FIELDS IN WALL-BOUNDED FLOWS M.S. Chng Department f Mechanical Engineering The University f Melburne Victria 3010 AUSTRALIA min@unimelb.edu.au J.P. Mnty
THE TOPOLOGY OF SURFACE SKIN FRICTION AND VORTICITY FIELDS IN WALL-BOUNDED FLOWS M.S. Chng Department f Mechanical Engineering The University f Melburne Victria 3010 AUSTRALIA min@unimelb.edu.au J.P. Mnty
initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur
![initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur](/thumbs/81/83809646.jpg) Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
Modeling the Nonlinear Rheological Behavior of Materials with a Hyper-Exponential Type Function
 www.ccsenet.rg/mer Mechanical Engineering Research Vl. 1, N. 1; December 011 Mdeling the Nnlinear Rhelgical Behavir f Materials with a Hyper-Expnential Type Functin Marc Delphin Mnsia Département de Physique,
www.ccsenet.rg/mer Mechanical Engineering Research Vl. 1, N. 1; December 011 Mdeling the Nnlinear Rhelgical Behavir f Materials with a Hyper-Expnential Type Functin Marc Delphin Mnsia Département de Physique,
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )
![[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y ) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )](/thumbs/96/127971145.jpg) (Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
(Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
A Correlation of. to the. South Carolina Academic Standards for Mathematics Precalculus
 A Crrelatin f Suth Carlina Academic Standards fr Mathematics Precalculus INTRODUCTION This dcument demnstrates hw Precalculus (Blitzer), 4 th Editin 010, meets the indicatrs f the. Crrelatin page references
A Crrelatin f Suth Carlina Academic Standards fr Mathematics Precalculus INTRODUCTION This dcument demnstrates hw Precalculus (Blitzer), 4 th Editin 010, meets the indicatrs f the. Crrelatin page references
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillations
 Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS
 FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS S. Russenschuck CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Abstract The field quality in the supercnducting magnets is expressed in terms f the cefficients f the Furier series
FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS S. Russenschuck CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Abstract The field quality in the supercnducting magnets is expressed in terms f the cefficients f the Furier series
1996 Engineering Systems Design and Analysis Conference, Montpellier, France, July 1-4, 1996, Vol. 7, pp
 THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
Slide04 (supplemental) Haykin Chapter 4 (both 2nd and 3rd ed): Multi-Layer Perceptrons
 Slide04 supplemental) Haykin Chapter 4 bth 2nd and 3rd ed): Multi-Layer Perceptrns CPSC 636-600 Instructr: Ynsuck Che Heuristic fr Making Backprp Perfrm Better 1. Sequential vs. batch update: fr large
Slide04 supplemental) Haykin Chapter 4 bth 2nd and 3rd ed): Multi-Layer Perceptrns CPSC 636-600 Instructr: Ynsuck Che Heuristic fr Making Backprp Perfrm Better 1. Sequential vs. batch update: fr large
Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observations
 Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 11: Mdeling with systems f ODEs In Petre Department f IT, Ab Akademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Mdeling with differential equatins Mdeling strategy Fcus
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 11: Mdeling with systems f ODEs In Petre Department f IT, Ab Akademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Mdeling with differential equatins Mdeling strategy Fcus
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Support-Vector Machines
 Supprt-Vectr Machines Intrductin Supprt vectr machine is a linear machine with sme very nice prperties. Haykin chapter 6. See Alpaydin chapter 13 fr similar cntent. Nte: Part f this lecture drew material
Supprt-Vectr Machines Intrductin Supprt vectr machine is a linear machine with sme very nice prperties. Haykin chapter 6. See Alpaydin chapter 13 fr similar cntent. Nte: Part f this lecture drew material
The blessing of dimensionality for kernel methods
 fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
Admissibility Conditions and Asymptotic Behavior of Strongly Regular Graphs
 Admissibility Cnditins and Asympttic Behavir f Strngly Regular Graphs VASCO MOÇO MANO Department f Mathematics University f Prt Oprt PORTUGAL vascmcman@gmailcm LUÍS ANTÓNIO DE ALMEIDA VIEIRA Department
Admissibility Cnditins and Asympttic Behavir f Strngly Regular Graphs VASCO MOÇO MANO Department f Mathematics University f Prt Oprt PORTUGAL vascmcman@gmailcm LUÍS ANTÓNIO DE ALMEIDA VIEIRA Department
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Support Vector Machines
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Supprt Vectr Machines Instructr: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/cmp551 Unless therwise nted, all material psted fr this curse
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Supprt Vectr Machines Instructr: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/cmp551 Unless therwise nted, all material psted fr this curse
4th Indian Institute of Astrophysics - PennState Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur. Correlation and Regression
 4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
Distributions, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective
 Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
What is Statistical Learning?
 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Introduction: A Generalized approach for computing the trajectories associated with the Newtonian N Body Problem
 A Generalized apprach fr cmputing the trajectries assciated with the Newtnian N Bdy Prblem AbuBar Mehmd, Syed Umer Abbas Shah and Ghulam Shabbir Faculty f Engineering Sciences, GIK Institute f Engineering
A Generalized apprach fr cmputing the trajectries assciated with the Newtnian N Bdy Prblem AbuBar Mehmd, Syed Umer Abbas Shah and Ghulam Shabbir Faculty f Engineering Sciences, GIK Institute f Engineering
On Huntsberger Type Shrinkage Estimator for the Mean of Normal Distribution ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Malaysian Jurnal f Mathematical Sciences 4(): 7-4 () On Huntsberger Type Shrinkage Estimatr fr the Mean f Nrmal Distributin Department f Mathematical and Physical Sciences, University f Nizwa, Sultanate
Malaysian Jurnal f Mathematical Sciences 4(): 7-4 () On Huntsberger Type Shrinkage Estimatr fr the Mean f Nrmal Distributin Department f Mathematical and Physical Sciences, University f Nizwa, Sultanate
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
CS 477/677 Analysis of Algorithms Fall 2007 Dr. George Bebis Course Project Due Date: 11/29/2007
 CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
EDA Engineering Design & Analysis Ltd
 EDA Engineering Design & Analysis Ltd THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD A shrt tutrial giving an verview f the histry, thery and applicatin f the finite element methd. Intrductin Value f FEM Applicatins Elements
EDA Engineering Design & Analysis Ltd THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD A shrt tutrial giving an verview f the histry, thery and applicatin f the finite element methd. Intrductin Value f FEM Applicatins Elements
Chaotic behavior of the piccolo
 Buens Aires 5 t 9 September, 2016 Acustics fr the 21 st Century PROCEEDINGS f the 22 nd Internatinal Cngress n Acustics Numerical Cmputatin in Musical Acustics: Paper ICA2016-54 Chatic behavir f the piccl
Buens Aires 5 t 9 September, 2016 Acustics fr the 21 st Century PROCEEDINGS f the 22 nd Internatinal Cngress n Acustics Numerical Cmputatin in Musical Acustics: Paper ICA2016-54 Chatic behavir f the piccl
Section 5.8 Notes Page Exponential Growth and Decay Models; Newton s Law
 Sectin 5.8 Ntes Page 1 5.8 Expnential Grwth and Decay Mdels; Newtn s Law There are many applicatins t expnential functins that we will fcus n in this sectin. First let s lk at the expnential mdel. Expnential
Sectin 5.8 Ntes Page 1 5.8 Expnential Grwth and Decay Mdels; Newtn s Law There are many applicatins t expnential functins that we will fcus n in this sectin. First let s lk at the expnential mdel. Expnential
AP Statistics Notes Unit Two: The Normal Distributions
 AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
This section is primarily focused on tools to aid us in finding roots/zeros/ -intercepts of polynomials. Essentially, our focus turns to solving.
 Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
Math 105: Review for Exam I - Solutions
 1. Let f(x) = 3 + x + 5. Math 105: Review fr Exam I - Slutins (a) What is the natural dmain f f? [ 5, ), which means all reals greater than r equal t 5 (b) What is the range f f? [3, ), which means all
1. Let f(x) = 3 + x + 5. Math 105: Review fr Exam I - Slutins (a) What is the natural dmain f f? [ 5, ), which means all reals greater than r equal t 5 (b) What is the range f f? [3, ), which means all
Running head: Weighted ENO Schemes Prfs sent t: Xu-Dng Liu Curant Institute f Mathematical Sciences 5 Mercer Street New Yrk, NY 00 AMS(MOS) subject cl
 Weighted Essentially Nn-Oscillatry Schemes Xu-Dng Liu Stanley Osher y Tny Chan z Department f Mathematics, UCLA, Ls Angeles, Califrnia, 9004. Research supprted by NSF grant DMS 9-043. y Department f Mathematics,
Weighted Essentially Nn-Oscillatry Schemes Xu-Dng Liu Stanley Osher y Tny Chan z Department f Mathematics, UCLA, Ls Angeles, Califrnia, 9004. Research supprted by NSF grant DMS 9-043. y Department f Mathematics,
CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION. Chapter 24: Make inferences about the population from which the sample data came.
 MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
Resampling Methods. Chapter 5. Chapter 5 1 / 52
 Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Zeros of Sections of the Zeta Function. I
 Zers f Sectins f the Zeta Functin. I By Rbert Spira 1. Intrductin. The sectins f the title are the Dirichlet plynmials: (1) U(s) = n"5 n = l We write s = a -f- it, and take M ^ 3. Turan [1], [2] shwed
Zers f Sectins f the Zeta Functin. I By Rbert Spira 1. Intrductin. The sectins f the title are the Dirichlet plynmials: (1) U(s) = n"5 n = l We write s = a -f- it, and take M ^ 3. Turan [1], [2] shwed
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
Beam vibrations: Discrete mass and stiffness models
 Beam vibratins: Discrete mass and stiffness mdels Ana Cláudia Susa Neves ana.neves@tecnic.ulisba.pt Institut Superir Técnic, Universidade de Lisba, Prtugal May, 2015 Abstract In the present wrk the dynamic
Beam vibratins: Discrete mass and stiffness mdels Ana Cláudia Susa Neves ana.neves@tecnic.ulisba.pt Institut Superir Técnic, Universidade de Lisba, Prtugal May, 2015 Abstract In the present wrk the dynamic
Math Foundations 10 Work Plan
 Math Fundatins 10 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 10.1 Demnstrate understanding f factrs f whle numbers by: Prime factrs Greatest Cmmn Factrs (GCF) Least Cmmn Multiple (LCM) Principal square rt Cube rt Time Frame
Math Fundatins 10 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 10.1 Demnstrate understanding f factrs f whle numbers by: Prime factrs Greatest Cmmn Factrs (GCF) Least Cmmn Multiple (LCM) Principal square rt Cube rt Time Frame
Pressure And Entropy Variations Across The Weak Shock Wave Due To Viscosity Effects
 Pressure And Entrpy Variatins Acrss The Weak Shck Wave Due T Viscsity Effects OSTAFA A. A. AHOUD Department f athematics Faculty f Science Benha University 13518 Benha EGYPT Abstract:-The nnlinear differential
Pressure And Entrpy Variatins Acrss The Weak Shck Wave Due T Viscsity Effects OSTAFA A. A. AHOUD Department f athematics Faculty f Science Benha University 13518 Benha EGYPT Abstract:-The nnlinear differential
ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
 Particle Acceleratrs, 1986, Vl. 19, pp. 99-105 0031-2460/86/1904-0099/$15.00/0 1986 Grdn and Breach, Science Publishers, S.A. Printed in the United States f America ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
Particle Acceleratrs, 1986, Vl. 19, pp. 99-105 0031-2460/86/1904-0099/$15.00/0 1986 Grdn and Breach, Science Publishers, S.A. Printed in the United States f America ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
Dead-beat controller design
 J. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: Dead beat cntrller design Nvember, 4 Dead-beat cntrller design In sampled data cntrl systems the cntrller is realised by an intelligent device, typically by a PLC (Prgrammable
J. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: Dead beat cntrller design Nvember, 4 Dead-beat cntrller design In sampled data cntrl systems the cntrller is realised by an intelligent device, typically by a PLC (Prgrammable
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
Homology groups of disks with holes
 Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
ANSWER KEY FOR MATH 10 SAMPLE EXAMINATION. Instructions: If asked to label the axes please use real world (contextual) labels
 ANSWER KEY FOR MATH 10 SAMPLE EXAMINATION Instructins: If asked t label the axes please use real wrld (cntextual) labels Multiple Chice Answers: 0 questins x 1.5 = 30 Pints ttal Questin Answer Number 1
ANSWER KEY FOR MATH 10 SAMPLE EXAMINATION Instructins: If asked t label the axes please use real wrld (cntextual) labels Multiple Chice Answers: 0 questins x 1.5 = 30 Pints ttal Questin Answer Number 1
Dispersion Ref Feynman Vol-I, Ch-31
 Dispersin Ref Feynman Vl-I, Ch-31 n () = 1 + q N q /m 2 2 2 0 i ( b/m) We have learned that the index f refractin is nt just a simple number, but a quantity that varies with the frequency f the light.
Dispersin Ref Feynman Vl-I, Ch-31 n () = 1 + q N q /m 2 2 2 0 i ( b/m) We have learned that the index f refractin is nt just a simple number, but a quantity that varies with the frequency f the light.
Thermodynamics Partial Outline of Topics
 Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 2 Jun 1995
 WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
SPH3U1 Lesson 06 Kinematics
 PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL. November 1975
 OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL J. C. Sprtt Nvember 1975 -I,," PLP 663 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL J. C. Sprtt Nvember 1975 -I,," PLP 663 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR
 Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Physics 212. Lecture 12. Today's Concept: Magnetic Force on moving charges. Physics 212 Lecture 12, Slide 1
 Physics 1 Lecture 1 Tday's Cncept: Magnetic Frce n mving charges F qv Physics 1 Lecture 1, Slide 1 Music Wh is the Artist? A) The Meters ) The Neville rthers C) Trmbne Shrty D) Michael Franti E) Radiatrs
Physics 1 Lecture 1 Tday's Cncept: Magnetic Frce n mving charges F qv Physics 1 Lecture 1, Slide 1 Music Wh is the Artist? A) The Meters ) The Neville rthers C) Trmbne Shrty D) Michael Franti E) Radiatrs
and the Doppler frequency rate f R , can be related to the coefficients of this polynomial. The relationships are:
 Algrithm fr Estimating R and R - (David Sandwell, SIO, August 4, 2006) Azimith cmpressin invlves the alignment f successive eches t be fcused n a pint target Let s be the slw time alng the satellite track
Algrithm fr Estimating R and R - (David Sandwell, SIO, August 4, 2006) Azimith cmpressin invlves the alignment f successive eches t be fcused n a pint target Let s be the slw time alng the satellite track
3D FE Modeling Simulation of Cold Rotary Forging with Double Symmetry Rolls X. H. Han 1, a, L. Hua 1, b, Y. M. Zhao 1, c
 Materials Science Frum Online: 2009-08-31 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vls. 628-629, pp 623-628 di:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.628-629.623 2009 Trans Tech Publicatins, Switzerland 3D FE Mdeling Simulatin f Cld
Materials Science Frum Online: 2009-08-31 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vls. 628-629, pp 623-628 di:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.628-629.623 2009 Trans Tech Publicatins, Switzerland 3D FE Mdeling Simulatin f Cld
ENG2410 Digital Design Arithmetic Circuits
 ENG24 Digital Design Arithmetic Circuits Fall 27 S. Areibi Schl f Engineering University f Guelph Recall: Arithmetic -- additin Binary additin is similar t decimal arithmetic N carries + + Remember: +
ENG24 Digital Design Arithmetic Circuits Fall 27 S. Areibi Schl f Engineering University f Guelph Recall: Arithmetic -- additin Binary additin is similar t decimal arithmetic N carries + + Remember: +
Introduction to Smith Charts
 Intrductin t Smith Charts Dr. Russell P. Jedlicka Klipsch Schl f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering New Mexic State University as Cruces, NM 88003 September 2002 EE521 ecture 3 08/22/02 Smith Chart Summary
Intrductin t Smith Charts Dr. Russell P. Jedlicka Klipsch Schl f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering New Mexic State University as Cruces, NM 88003 September 2002 EE521 ecture 3 08/22/02 Smith Chart Summary
We can see from the graph above that the intersection is, i.e., [ ).
 MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
Lead/Lag Compensator Frequency Domain Properties and Design Methods
 Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
Biplots in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE. Professor of Statistics at the Pompeu Fabra University. Chapter 13 Offprint
 Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
Functions. EXPLORE \g the Inverse of ao Exponential Function
 ifeg Seepe3 Functins Essential questin: What are the characteristics f lgarithmic functins? Recall that if/(x) is a ne-t-ne functin, then the graphs f/(x) and its inverse,/'~\x}, are reflectins f each
ifeg Seepe3 Functins Essential questin: What are the characteristics f lgarithmic functins? Recall that if/(x) is a ne-t-ne functin, then the graphs f/(x) and its inverse,/'~\x}, are reflectins f each
ELECTRON CYCLOTRON HEATING OF AN ANISOTROPIC PLASMA. December 4, PLP No. 322
 ELECTRON CYCLOTRON HEATING OF AN ANISOTROPIC PLASMA by J. C. SPROTT December 4, 1969 PLP N. 3 These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated. They are fr private
ELECTRON CYCLOTRON HEATING OF AN ANISOTROPIC PLASMA by J. C. SPROTT December 4, 1969 PLP N. 3 These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated. They are fr private
3.4 Shrinkage Methods Prostate Cancer Data Example (Continued) Ridge Regression
 3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
A Scalable Recurrent Neural Network Framework for Model-free
 A Scalable Recurrent Neural Netwrk Framewrk fr Mdel-free POMDPs April 3, 2007 Zhenzhen Liu, Itamar Elhanany Machine Intelligence Lab Department f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering The University f Tennessee
A Scalable Recurrent Neural Netwrk Framewrk fr Mdel-free POMDPs April 3, 2007 Zhenzhen Liu, Itamar Elhanany Machine Intelligence Lab Department f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering The University f Tennessee
Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]
![Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017] Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]](/thumbs/95/123024115.jpg) Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
MODULE FOUR. This module addresses functions. SC Academic Elementary Algebra Standards:
 MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
(1.1) V which contains charges. If a charge density ρ, is defined as the limit of the ratio of the charge contained. 0, and if a force density f
 1.0 Review f Electrmagnetic Field Thery Selected aspects f electrmagnetic thery are reviewed in this sectin, with emphasis n cncepts which are useful in understanding magnet design. Detailed, rigrus treatments
1.0 Review f Electrmagnetic Field Thery Selected aspects f electrmagnetic thery are reviewed in this sectin, with emphasis n cncepts which are useful in understanding magnet design. Detailed, rigrus treatments
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT
 BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION
 NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extension to Ampere s Law
 Chapter 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law Cnsider the case f a charged particle that is ming in the icinity f a ming bar magnet
Chapter 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law Cnsider the case f a charged particle that is ming in the icinity f a ming bar magnet
Hubble s Law PHYS 1301
 1 PHYS 1301 Hubble s Law Why: The lab will verify Hubble s law fr the expansin f the universe which is ne f the imprtant cnsequences f general relativity. What: Frm measurements f the angular size and
1 PHYS 1301 Hubble s Law Why: The lab will verify Hubble s law fr the expansin f the universe which is ne f the imprtant cnsequences f general relativity. What: Frm measurements f the angular size and
Lecture 17: Free Energy of Multi-phase Solutions at Equilibrium
 Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
V. Balakrishnan and S. Boyd. (To Appear in Systems and Control Letters, 1992) Abstract
 On Cmputing the WrstCase Peak Gain f Linear Systems V Balakrishnan and S Byd (T Appear in Systems and Cntrl Letters, 99) Abstract Based n the bunds due t Dyle and Byd, we present simple upper and lwer
On Cmputing the WrstCase Peak Gain f Linear Systems V Balakrishnan and S Byd (T Appear in Systems and Cntrl Letters, 99) Abstract Based n the bunds due t Dyle and Byd, we present simple upper and lwer
Exponential Functions, Growth and Decay
 Name..Class. Date. Expnential Functins, Grwth and Decay Essential questin: What are the characteristics f an expnential junctin? In an expnential functin, the variable is an expnent. The parent functin
Name..Class. Date. Expnential Functins, Grwth and Decay Essential questin: What are the characteristics f an expnential junctin? In an expnential functin, the variable is an expnent. The parent functin
Part a: Writing the nodal equations and solving for v o gives the magnitude and phase response: tan ( 0.25 )
 + - Hmewrk 0 Slutin ) In the circuit belw: a. Find the magnitude and phase respnse. b. What kind f filter is it? c. At what frequency is the respnse 0.707 if the generatr has a ltage f? d. What is the
+ - Hmewrk 0 Slutin ) In the circuit belw: a. Find the magnitude and phase respnse. b. What kind f filter is it? c. At what frequency is the respnse 0.707 if the generatr has a ltage f? d. What is the
the results to larger systems due to prop'erties of the projection algorithm. First, the number of hidden nodes must
 M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
Math 302 Learning Objectives
 Multivariable Calculus (Part I) 13.1 Vectrs in Three-Dimensinal Space Math 302 Learning Objectives Plt pints in three-dimensinal space. Find the distance between tw pints in three-dimensinal space. Write
Multivariable Calculus (Part I) 13.1 Vectrs in Three-Dimensinal Space Math 302 Learning Objectives Plt pints in three-dimensinal space. Find the distance between tw pints in three-dimensinal space. Write
The Destabilization of Rossby Normal Modes by Meridional Baroclinic Shear
 The Destabilizatin f Rssby Nrmal Mdes by Meridinal Barclinic Shear by Jseph Pedlsky Wds Hle Oceangraphic Institutin Wds Hle, MA 0543 Abstract The Rssby nrmal mdes f a tw-layer fluid in a meridinal channel
The Destabilizatin f Rssby Nrmal Mdes by Meridinal Barclinic Shear by Jseph Pedlsky Wds Hle Oceangraphic Institutin Wds Hle, MA 0543 Abstract The Rssby nrmal mdes f a tw-layer fluid in a meridinal channel
