Hybrid pixel detectors for photon science at synchrotrons and FELs
|
|
|
- Carmella Cook
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Gemma Tinti on behalf of the SLS Detector Group Hybrid pixel detectors for photon science at synchrotrons and FELs RD51 meeting 10 June 2015
2 Outline Synchrotrons (SwissLightSource as example) and typical experiments FELs (Swiss-FEL as example) Requirements for detectors Development of hybrid pixel detectors at PSI Outlook on upgrades of machines and requirements for future detectors 2
3 The Swiss Light Source 288 m circumference Xrays 3 ev 45 kev Single Photon Counting (SPC) Synchrotron source: Huge number of weak photon bunches (a bunch every 2 ns) Bunch length is 20 ps Photons impinge on the detector with a semi-continuous time distribution t 100ns 3
4 SLS beamlines kev Tot flux ~ ph/s 6-20keV Tot flux ~ ph/s ev Tot flux ~ ph/s 4-19 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s Coherent flux ~ ph/s Fluxes are given on the focal spot ev Tot flux ~ ph/s/cm ev Tot flux ~ ph/s/cm ev ev ev Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s ev Tot flux ~ ph/s 5-38 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s ev Tot flux ~ kev 12 ph/s Tot flux ~ ph/s 8-45 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s 4
5 MYTHEN PILATUS SLS beamlines and detectors PILATUS 6-20keV Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s ev Tot flux ~ ph/s (MCP+CCD) PEEM 4-19 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s Coherent flux ~ ph/s PILATUS EIGER ev Tot flux ~ ph/s/cm ev Tot flux ~ ph/s/cm 2 (MCP+CCD ) E spectrometer P + Photomultiplier P+ CCD ev APD APD ev Si drift Si diode PILATUS ev Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s kev EIGER Tot flux ~ ph/s kev Tot flux ~ ph/s PILATUS 5-20 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s APD / CCD ev Tot flux ~ ph/s 5-38 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s ev Tot flux ~ ph/s PILATUS 8-45 kev Tot flux ~ ph/s MYTHEN scintillator (1-10 um) + optics+ high speed CMOS CCD (20 um pix) 5
6 Diffraction experiments at synchrotrons Typical experimental setup: Typical applications: Coherent Diffractive Imaging (CDI) Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) Scanning SAXS Protein Crystallography X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) PILATUS 2M! EIGER 500k! PILATUS 6M! 6
7 Protein Crystallography O(10 um) extraction 7
8 more than 900 protein structures solved at PXI beamline at SLS ~2/3 using Pilatus II 6M compiled by Sandro Waltersperger Oct
9 Ptychography Coherent imaging Diffraction pattern Coherent X-rays FZP Achieves imaging resolution of ~10 nm OSA Object The object (EIGER chip) is raster scanned by an out of focus beam Can be combined with CT for 3D imaging Diffraction patterns at overlapping positions on the object are recorded The information in the overlap is used to recover the dp phase Object: Both the attenuation and phase shift in Eiger readout chip the object can be reconstructed 9
10 Large area, high resolution Ptychography Optics Express, Vol. 22, Issue 12, pp (2014) csaxs beamline 5 um 45 nm resolution Large area: 500 um x 290 um Zoom in on a pixel 10
11 Light expected to users in 2016 SwissFEL: New generation X-ray free electron laser Xrays kev (7 to 1 Å) 100 Hz repetition rate in two bunch charge modes (10 and 200 pc) 1.8 to 21 fs pulse lengths Pulse energies between 10 and 200 µj photons/pulse SwissFEL Higher brilliance than synchrotron and faster dynamics Swiss Light Source FEL: Fewer intense bunches All photons in the bunch coming at once High number of particles/channel per bunch t 100fs 11
12 Requirements for X-ray detectors at synchrotrons and FELs Energy range: 2-40 kev SLS and SwissFEL), up to 150 kev (ESRF/Spring 8) Single photon sensitivity: noise << signal ~ O(100 e - ) Sufficient angular coverage: large area (40 x 40 cm 2 ) Spatial resolution: millions of pixels (75 x 75 um 2 ) High frame rates: Tens of khz Ability to gate or synchronization to experimental machines Synchrotrons: High count rate capability: count rates 1 MHz/pixel FELs: High dynamic range: kev photons/pixel/pulse 12
13 Swiss Light Source Detectors Microstrips 50 um Single Photon Counting MYTHEN Pixels 25 µm Pixels 75 µm EIGER Pixels ~200 µm PILATUS (DECTRIS) Charge Integrating GOTTHARD MÖNCH JUNGFRAU AGIPD 13
14 Hybrid pixel detectors wirebonds sensor X-ray +Vbias Si Sensor chip bump bonds E Indium bump (~18 um) Readout chip EIGER 75 um 25 um 75 um A module: many (8) chips 1 sensor 25 um 14
15 Sensor: Si and high Z materials Absorption of the X-rays in sensor: mainly photoelectric effect (<40 kev), pointlike The energy is converted into electric charge About 3.6 ev to generate an e-h pair in silicon Signal is 1000 e - for 3.6 kev photons Study of high Z materials (CdTe, GaAs) to extend the quantum efficiency at higher energies Standard silicon sensors: 300um thick, 2um backplane 300 um Al+backplane 15
16 Single photon counting detectors X-ray Si Sensor E +V bias Indium bump (~18 um) Readout chip Counter Advantages: Large dynamic range of counter Background rejection Ideal Signal to Noise Ratio Gating of the counter at high rates Amplification+ shaping v th Comparison to a threshold Counting Number of photons Disadvantages: Pile-up for high photon intensities Minimum pixel size due to charge sharing between pixels Minimum detectable energy 16
17 EIGER systems 75 x 75 um2 pixel size 500k module Multi-module detectors First 500k in PSI 1.5 M Tradeoff between frame rate and counter dynamic range 9M Pixel array Size Frame 4b Frame 8b Frame 12b Data 100Hz1 Module 512 x x77 mm2 23 khz 12 khz 8kHz 419 Mb/s 1.5M 512 x x238 mm2 23 khz 12kHz 8kHz 1.26 Gb/s 9M 3072 x x238 mm2 23 khz 12 khz 8kHz 7.55 Gb/s 1) 8 bit Almost dead time free detector High frame rate independent on size Data rate grows with size 17
18 Threshold calibration and noise Monochromatic X-rays E I Adj. Gain Global Threshold V cmp The preamplifier gain in EIGER is user configurable to scan a different range of photon energies The threshold setting can be calibrated into photon energy Threshold is calibrated to be uniform in the detector and its dispersion is negligible (20 e - ) in respect to noise Noise decreases with higher pre-amp gain As the noise at high gain is ~100 e -, we see photons >3 kev 18
19 Monochromatic X-rays E PILE UP Rate correction as a function of energy I Adj. Gain Paralizable counter model: One can correct for inefficiencies Threshold V cmp counter Low Medium Simulated High t (50 ns/div) For the same energy, lower gain optimizes for rate capabilities MHz/pixel 19
20 The future: charge integrating detectors for FELs Swiss-FEL will deliver photons/pulse in ~hundreds of fs Photon counters cannot be used Development of charge integrating detectors with charge information For the detector the main challenges are: Single photon resolution Dynamic range of 10 4 photons In exposure dynamic gain switching is the solution V out Gain switching threshold Gain 0 Gain 2 Gain 1 (high) (low) (medium) input charge 20
21 JUNGFRAU at SwissFEL Top view. Cut through ESA chamber. 9 JUNGFRAU modules (4.5 Mpixel). Single module. 32 JUNGFRAU modules (16 Mpixel). Readout board. Detector infrastructure: Power, cooling, data, controls. 21
22 JUNGFRAU Measurements from Jungfrau 0.2 prototype Integrated charge Single photon sensitivity ~30 ɣ ~700 ɣ J.H. Jungmann-Smith et al, JINST 9, P12013 Detector returns the charge info (ADC) and the gain used Automatic gain switching: White visible light illumination Increasing integration time Covers dynamic range of > 4 orders of magnitude! gain stage 0 (high) gain stage 1 (medium) gain stage 2 (low) Calibration of the integrated charge vs number of photons needs to be studied and applied Noise < Poisson statistical limit Targeted frame rate of 2 khz: Count rate of 20 MHz/pixel Factor 20 better than EIGER! Use at synchrotrons is under study! 22
23 Noise of JUNGFRAU 27 e- JUNGFRA U 1.0 JUNGFRA U eprototype to test low noise & energydispersive detection. Chip to be SwissFEL. JUNGFRAU 0.4 JUNGFRAU 1.0 RMS Noise [e-] RMS Noise [ev] < 100 < 210 5σ RMS Noise [ev] < 500 < 1050 SwissFEL will provide Xrays with energy as low as 2 kev Extend the use of hybrid pixel detectors to lower photon energies 23
24 Small pixels: the MÖNCH detector 25 x 25 um2 pixel size Active area: 4x4 mm2 160 x160 pixels Smallest pixel size of hybrid pix detectors: bump bonding yield is >99.9% Low noise detector 30 e- noise RMS : minimum photon energy 500 ev! Plan larger systems as a low energy detector High spatial resolution: algorithm to exploit the charge shared between more pixels allow for 1um spatial resolution Active area 1x1 cm2 400 x 400 pixels Frame rate foreseen up to 6 khz counts MÖNCH 03 prototype Noise peak of MÖNCH 500 ev Goal 2 x 3 cm2 chip noise [ev] 24
25 Perspective for the future accelerators FELs are getting into operation now and plans to upgrade many synchrotrons to diffraction limited light sources: Upgrade at synchrotrons: FELs SwissFEL 3 rd generation synchrotrons Riccardo Bartolini (Oxford University) 4 th low emittance rings workshop, 2014 A factor lower horizontal emittance MAX IV (2015), SIRIUS (2016), ESRF-2 (2019), SLSII (>2021?) etc 25
26 Perspective for the future detectors Applications like ptychography and protein crystallography are hungry for brightness and coherence High flux ptychography due to increased coherent flux-> higher rate capabilities ( MHz/pixel) needed for the detector. Protein crystallography beamlines will increase the flux O(10-100) by using a multilayer monochromator instead of Si monocrometor to allow higher flux PX -> higher rate capabilities needed for the detector. Study of dynamics -> deadtime free detector operation at very fast frame rates ( khz) Angular coverage and a good spatial resolution (when increasing the detector distance from the sample) will be needed -> large area detectors (49 Mpixels ~ 60 x 60 cm 2 ). The coherent flux increase at some synchrotrons will be at higher photon energies -> high quantum efficiency up to 30/40 kev Spatial resolution is improved by smaller pixel sizes with interpolation of the charge shared between pixels ->replacement of CCDs with pixel detectors Development towards low energies (~0.5 kev) will be favored ->replacement of CCDs 26
27 Swiss Light Source Detector Group AGIPD Group leader GOTTHARD & JUNGFRAU Electronics MÖNCH Mechanics Software MYTHEN & MÖNCH AGIPD & GOTTHARD EIGER MÖNCH AGIPD MÖNCH & EIGER JUNGFRAU Firmware Back: Sebastian Cartier, Dominic Greiffenberg, Lukas Schädler, Bernd Schmitt, Aldo Mozzanica, Christian Ruder, Dhanya Maliakal Front: Anna Bergamaschi, Xintian Shi, Gemma Tinti, Marco Ramilli, Davide Mezza, Roberto Dinapoli, Julia Smith, Martin Brückner 10/06/
28 More Information. 28
29 The European XFEL challenge & AGIPD 600 µs 100 ms 100 ms 99.4 ms 200 x 200 um 2 pixel size 220 ns FEL process X-ray photons <100 fs bunches/s with 4.5 MHz repetition rate Single photon sensitivity Dynamic range >10 4 Low noise High radiation tolerance (100 MGy) 5 MHz frame rate: Storage of 352 images on pixel cells and readout in the idle time 29
30 Study of performance of EIGER as a PEEM detector Photo emission microscope from ELMITEC Feasibility studies Source UV lamp/ synchrotron beam Vacuum achieved: 5x10-9 mbar Ongoing efforts to reach mbar Single chip: active area 1.92 x1.92 cm2 Round board is vacuum barrier 20 kev typically 30
31 PEEM with EIGER H. Marchetto FoV=25 µm, 10 sec, 5 avg FoV=50 µm, 5 sec, 200 avg Graphene/SiC Pb/Si(111) 31
32 PilatusII6M at the Protein Crystallography Station No of Modules Detector Size [mm] 60, 12 x x 448 Format Pixel size Dynamic range/pixel Count rate/pixel Readout time Frame rate pixels 172 x 172 µm 2 20bits ~ 1-3 MHz 3.5 ms 12.5 Hz made continuous shutter-less operation possible at PX Sold and further developed By Dectris 10/06/2015
33 Small pixels: the MOENCH detector
34 Hybrid SLS detectors MYTHEN EIGER GOTTHARD JUNGFRAU MÖNCH AGIPD 1D/2D Strip Pixel Strip Pixel Pixel Pixel Working Mechanism Photon Counting Photon Counting Charge Integrating Charge Integrating Charge Integrating Charge Integrating Strip/Pixel size [µm] Maximum frame rate [khz] 1 (4 bit) 23 (4 bit) 40 2 (14 bit) 6 (not final) 4500 Minimum Energy [kev] 5 <3.5 < <6 Applications Powder diffraction, energydispersive spectrometers, beam position. Ptychography, coherent imaging, protein FLASH, main energydispersive detector for EUXFEL. Spectroscopic applications, high count rate applications at XFELs & synchrotrons. (Biological) imaging & tomography, RIXS, spectroscopy, Laue diffraction. Development for the EUXFEL. Status Project At beam lines. Moving to beam line. At beam lines. Prototype. Experimental /Prototype. Moving to beam line. 34
Special SLS Symposium on Detectors
 Special SLS Symposium on Detectors Tuesday, December 12, 2017 9:30 to 12:15, WBGB/019 09:30 - What are hybrid pixel detectors? - An introduction with focus on single photon counting detectors Erik Fröjdh
Special SLS Symposium on Detectors Tuesday, December 12, 2017 9:30 to 12:15, WBGB/019 09:30 - What are hybrid pixel detectors? - An introduction with focus on single photon counting detectors Erik Fröjdh
SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation
 SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation Tuesday, December 7, 2010 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 The optics layout of the PEARL beamline P. Oberta, U. Flechsig and M. Muntwiler 10:30 Instrumentation for
SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation Tuesday, December 7, 2010 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 The optics layout of the PEARL beamline P. Oberta, U. Flechsig and M. Muntwiler 10:30 Instrumentation for
Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements
 Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements Julian Becker University of Hamburg Detector Laboratory new data 1. Heating estimations 2. Confined breakdown 3. Range switching in adjacent pixels
Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements Julian Becker University of Hamburg Detector Laboratory new data 1. Heating estimations 2. Confined breakdown 3. Range switching in adjacent pixels
The MID instrument.
 The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements
 Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements Julian Becker University of Hamburg Detector Laboratory 1. Si-type influence on charge collection time 2. Measurements on charge collection time 3.
Impact of high photon densities on AGIPD requirements Julian Becker University of Hamburg Detector Laboratory 1. Si-type influence on charge collection time 2. Measurements on charge collection time 3.
Research with Synchrotron Radiation. Part I
 Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
TIMEPIX3 First measurements and characterization of a hybrid pixel detector working in event driven mode
 TIMEPIX3 First measurements and characterization of a hybrid pixel detector working in event driven mode Erik Fröjdh 1,2, Michael Campbell 2, Massimiliano de Gaspari 2, Szymon Kulis 2, Xavier Llopart 2,
TIMEPIX3 First measurements and characterization of a hybrid pixel detector working in event driven mode Erik Fröjdh 1,2, Michael Campbell 2, Massimiliano de Gaspari 2, Szymon Kulis 2, Xavier Llopart 2,
Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument
 Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument WP-85 A. De Fanis, T. Mazza, H. Zhang, M. Meyer European XFEL GmbH TDR_2012: http://www.xfel.eu/documents/technical_documents XFEL Users Meeting 2014, January
Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument WP-85 A. De Fanis, T. Mazza, H. Zhang, M. Meyer European XFEL GmbH TDR_2012: http://www.xfel.eu/documents/technical_documents XFEL Users Meeting 2014, January
Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements
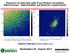 Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements Quasi-static speckles from colloidal suspension near random compact packing volume fraction Speckles
Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements Quasi-static speckles from colloidal suspension near random compact packing volume fraction Speckles
Imaging & Microscopy
 Coherent X-ray X Imaging & Microscopy => Opportunities Using a Diffraction-Limited Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Synchrotron Source Q. Shen D. Bilderback, K.D. Finkelstein, E. Fontes, & S. Gruner Cornell
Coherent X-ray X Imaging & Microscopy => Opportunities Using a Diffraction-Limited Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Synchrotron Source Q. Shen D. Bilderback, K.D. Finkelstein, E. Fontes, & S. Gruner Cornell
Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources. Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010
 Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/aboutssrl/documents/future-x-rays-09.pdf special acknowledgment to John Corlett,
Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/aboutssrl/documents/future-x-rays-09.pdf special acknowledgment to John Corlett,
Wolter Imaging On Z. Chris Bourdon, Manager Z Imaging and Spectroscopy Julia Vogel, LLNL; Ming Wu, SNL ICF Diagnostics Workshop, October 5 th 2015
 Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Wolter Imaging On Z Chris Bourdon, Manager Z Imaging and Spectroscopy Julia Vogel, LLNL; Ming Wu, SNL ICF
Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Wolter Imaging On Z Chris Bourdon, Manager Z Imaging and Spectroscopy Julia Vogel, LLNL; Ming Wu, SNL ICF
FLASH overview. Nikola Stojanovic. PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg,
 FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design
 UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic. Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center
 Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center Light and Its Wavelength, Sizes of Material Virus Mosquito Protein Bacteria Atom
Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center Light and Its Wavelength, Sizes of Material Virus Mosquito Protein Bacteria Atom
USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB. ERL as a X-ray Light Source
 USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB ERL as a X-ray Light Source Contents Introduction Light sources landscape General motivation
USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB ERL as a X-ray Light Source Contents Introduction Light sources landscape General motivation
AGIPD AGIPD Meeting: November 2015
 AGIPD AGIPD Meeting: November 2015 A. Allahgholi 2, L.Bianco 2, A. Delfs 2, R. Dinapoli 1, P. Goettlicher 2, M. Gronewald 4, H. Graafsma 2,5, D. Greiffenberg 1, B.H. Henrich 1, H. Hirsemann 2, S. Jack
AGIPD AGIPD Meeting: November 2015 A. Allahgholi 2, L.Bianco 2, A. Delfs 2, R. Dinapoli 1, P. Goettlicher 2, M. Gronewald 4, H. Graafsma 2,5, D. Greiffenberg 1, B.H. Henrich 1, H. Hirsemann 2, S. Jack
Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy
 Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy Taka Tanaka (SLAC/KIPAC) 9/19/2007 SLAC Advanced Instrumentation Seminar Outline Introduction CdTe Diode
Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy Taka Tanaka (SLAC/KIPAC) 9/19/2007 SLAC Advanced Instrumentation Seminar Outline Introduction CdTe Diode
Hybrid X-ray Area Detectors for High-Flux Applications
 Hybrid X-ray Area Detectors for High-Flux Applications Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Ithaca, NY 14853 smg26@cornell.edu 1 Basic Hybrid Pixel Array Detector
Hybrid X-ray Area Detectors for High-Flux Applications Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Ithaca, NY 14853 smg26@cornell.edu 1 Basic Hybrid Pixel Array Detector
Development of a Radiation Hard CMOS Monolithic Pixel Sensor
 Development of a Radiation Hard CMOS Monolithic Pixel Sensor M. Battaglia 1,2, D. Bisello 3, D. Contarato 2, P. Denes 2, D. Doering 2, P. Giubilato 2,3, T.S. Kim 2, Z. Lee 2, S. Mattiazzo 3, V. Radmilovic
Development of a Radiation Hard CMOS Monolithic Pixel Sensor M. Battaglia 1,2, D. Bisello 3, D. Contarato 2, P. Denes 2, D. Doering 2, P. Giubilato 2,3, T.S. Kim 2, Z. Lee 2, S. Mattiazzo 3, V. Radmilovic
SLS Symposium on Towards XFEL
 SLS Symposium on Towards XFEL Tuesday, November 6, 2012 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 Ultrafast dynamics of magneto-structural phase transitions S. O. Mariager, A. Caviezel, P. Beaud, S. L. Johnson, S.
SLS Symposium on Towards XFEL Tuesday, November 6, 2012 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 Ultrafast dynamics of magneto-structural phase transitions S. O. Mariager, A. Caviezel, P. Beaud, S. L. Johnson, S.
Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA
 Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA Alfred M. Sehone Lumkile Msebi Oleg Lishyk Stanislav Stanishevski Yuliya Brechko Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear reactions, JINR,
Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA Alfred M. Sehone Lumkile Msebi Oleg Lishyk Stanislav Stanishevski Yuliya Brechko Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear reactions, JINR,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE*
 SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI
 Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Short Pulse, Low charge Operation of the LCLS. Josef Frisch for the LCLS Commissioning Team
 Short Pulse, Low charge Operation of the LCLS Josef Frisch for the LCLS Commissioning Team 1 Normal LCLS Parameters First Lasing in April 10, 2009 Beam to AMO experiment August 18 2009. Expect first user
Short Pulse, Low charge Operation of the LCLS Josef Frisch for the LCLS Commissioning Team 1 Normal LCLS Parameters First Lasing in April 10, 2009 Beam to AMO experiment August 18 2009. Expect first user
Development of a table top TW laser accelerator for medical imaging isotope production
 Development of a table top TW laser accelerator for medical imaging isotope production R U I Z, A L E X A N D R O 1 ; L E R A, R O B E R T O 1 ; T O R R E S - P E I R Ó, S A LVA D O R 1 ; B E L L I D O,
Development of a table top TW laser accelerator for medical imaging isotope production R U I Z, A L E X A N D R O 1 ; L E R A, R O B E R T O 1 ; T O R R E S - P E I R Ó, S A LVA D O R 1 ; B E L L I D O,
MEASUREMENT OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION AND DETECTION EFFICIENCY OF X-RAY STREAK CAMERA BY SINGLE PHOTON IMAGES
 Proceedings of IBIC212, Tsukuba, Japan MEASUREMENT OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION AND DETECTION EFFICIENCY OF X-RAY STREAK CAMERA BY SINGLE PHOTON IMAGES A. Mochihashi, M. Masaki, S. Takano, K. Tamura, H. Ohkuma,
Proceedings of IBIC212, Tsukuba, Japan MEASUREMENT OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION AND DETECTION EFFICIENCY OF X-RAY STREAK CAMERA BY SINGLE PHOTON IMAGES A. Mochihashi, M. Masaki, S. Takano, K. Tamura, H. Ohkuma,
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL
 Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Detecting high energy photons. Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples)
 Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
Time resolved transverse and longitudinal phase space measurements at the high brightness photo injector PITZ
 Time resolved transverse and longitudinal phase space measurements at the high brightness photo injector PITZ 1. Motivation 2. Transverse deflecting structure 3. Longitudinal phase space tomography 4.
Time resolved transverse and longitudinal phase space measurements at the high brightness photo injector PITZ 1. Motivation 2. Transverse deflecting structure 3. Longitudinal phase space tomography 4.
Two-electron photo-excited atomic processes near inner-shell threshold studied by RIXS spectroscopy
 Two-electron photo-excited atomic processes near inner-shell threshold studied by RIXS spectroscopy Matjaž Kavčič J. Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia K. Bučar F. Gasser M. Kavčič A. Mihelič M. Štuhec
Two-electron photo-excited atomic processes near inner-shell threshold studied by RIXS spectroscopy Matjaž Kavčič J. Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia K. Bučar F. Gasser M. Kavčič A. Mihelič M. Štuhec
Future Light Sources March 5-9, 2012 Low- alpha mode at SOLEIL 1
 Introduction: bunch length measurements Reminder of optics Non- linear dynamics Low- alpha operation On the user side: THz and X- ray short bunch science CSR measurement and modeling Future Light Sources
Introduction: bunch length measurements Reminder of optics Non- linear dynamics Low- alpha operation On the user side: THz and X- ray short bunch science CSR measurement and modeling Future Light Sources
Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch
 Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch Normally z el >> N u 1 Chaotic light Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron /=1/N u Temporal phase space area z ~(/
Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch Normally z el >> N u 1 Chaotic light Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron /=1/N u Temporal phase space area z ~(/
Problem Solving. radians. 180 radians Stars & Elementary Astrophysics: Introduction Press F1 for Help 41. f s. picture. equation.
 Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal
 SwissFEL Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen 1 2 C. Vicario 1, R. Clemens 1 and C. P. Hauri 1,2 THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal 10/16/12 Workshop on High Field THz science
SwissFEL Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen 1 2 C. Vicario 1, R. Clemens 1 and C. P. Hauri 1,2 THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal 10/16/12 Workshop on High Field THz science
X- & γ-ray Instrumentation
 X- & γ-ray Instrumentation Used nuclear physics detectors Proportional Counters Scintillators The Dark Ages Simple collimators HEAO A1 & A2: 2 x 8 degree field of view Confusion limit is about 200 sources
X- & γ-ray Instrumentation Used nuclear physics detectors Proportional Counters Scintillators The Dark Ages Simple collimators HEAO A1 & A2: 2 x 8 degree field of view Confusion limit is about 200 sources
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2
 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
Development and characterization of 3D semiconductor X-rays detectors for medical imaging
 Development and characterization of 3D semiconductor X-rays detectors for medical imaging Marie-Laure Avenel, Eric Gros d Aillon CEA-LETI, DETectors Laboratory marie-laure.avenel@cea.fr Outlines Problematic
Development and characterization of 3D semiconductor X-rays detectors for medical imaging Marie-Laure Avenel, Eric Gros d Aillon CEA-LETI, DETectors Laboratory marie-laure.avenel@cea.fr Outlines Problematic
X-ray Free-electron Lasers
 X-ray Free-electron Lasers Ultra-fast Dynamic Imaging of Matter II Ischia, Italy, 4/30-5/3/ 2009 Claudio Pellegrini UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy Outline 1. Present status of X-ray free-electron
X-ray Free-electron Lasers Ultra-fast Dynamic Imaging of Matter II Ischia, Italy, 4/30-5/3/ 2009 Claudio Pellegrini UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy Outline 1. Present status of X-ray free-electron
Development of Soft X-rayX using Laser Compton Scattering
 26 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop on Nanometre-Size Colliding Beams September 2-6, 2002 at Lausanne Development of Soft X-rayX Source using Laser Compton Scattering R. Kuroda*, S. Kashiwagi*,
26 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop on Nanometre-Size Colliding Beams September 2-6, 2002 at Lausanne Development of Soft X-rayX Source using Laser Compton Scattering R. Kuroda*, S. Kashiwagi*,
Gas Based Detectors for FEL Photon Diagnostics.
 Gas Based Detectors for FEL Photon Diagnostics. Kai Tiedtke Satellite Workshop on Photon Beam Diagnostics, 29 Jan. 2015 Outline. Intensity and Beam Position Monitor (GMD) @ FLASH Gas-Monitor-Detector for
Gas Based Detectors for FEL Photon Diagnostics. Kai Tiedtke Satellite Workshop on Photon Beam Diagnostics, 29 Jan. 2015 Outline. Intensity and Beam Position Monitor (GMD) @ FLASH Gas-Monitor-Detector for
A Straight Forward Path (Roadmap) to EUV High Brightness LPP Source
 Introduction and Outline A Straight Forward Path (Roadmap) to EUV High Brightness LPP Source Rainer Lebert, AIXUV Target Features of High Brightness EUV Source LPP Concept to reach Specification Target
Introduction and Outline A Straight Forward Path (Roadmap) to EUV High Brightness LPP Source Rainer Lebert, AIXUV Target Features of High Brightness EUV Source LPP Concept to reach Specification Target
CCD OPERATION. The BBD was an analog delay line, made up of capacitors such that an analog signal was moving along one step at each clock cycle.
 CCDS Lesson 4 CCD OPERATION The predecessor of the CCD was a device called the BUCKET BRIGADE DEVICE developed at the Phillips Research Labs The BBD was an analog delay line, made up of capacitors such
CCDS Lesson 4 CCD OPERATION The predecessor of the CCD was a device called the BUCKET BRIGADE DEVICE developed at the Phillips Research Labs The BBD was an analog delay line, made up of capacitors such
Status Report on the Survey and Alignment efforts at DESY
 Status Report on the Survey and Alignment efforts at DESY Johannes J. Prenting Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, MEA2 IWAA 2008 KEK Japan Major New Projects @ DESY - : European X-ray Free Electron
Status Report on the Survey and Alignment efforts at DESY Johannes J. Prenting Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, MEA2 IWAA 2008 KEK Japan Major New Projects @ DESY - : European X-ray Free Electron
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection
 Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR)
 Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of SASE FEL Simulations of CTR Summary Issues for Discussion Mini-Workshop on THz Option at PITZ DESY, Zeuthen
Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of SASE FEL Simulations of CTR Summary Issues for Discussion Mini-Workshop on THz Option at PITZ DESY, Zeuthen
FLASH/DESY, Hamburg. Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team -
 First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors. Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH
 Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Part A Principles of Semiconductor Detectors 1. Basic Principles 2. Typical Applications 3. Planar Technology 4. Read-out
Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Part A Principles of Semiconductor Detectors 1. Basic Principles 2. Typical Applications 3. Planar Technology 4. Read-out
Synchrotron XRPD. Fabia Gozzo. Excelsus Structural Solutions sprl, Brussels, Belgium Excelsus Structural Solutions (Swiss) AG, Switzerland
 Synchrotron XRPD Fabia Gozzo Excelsus Structural Solutions sprl, Brussels, Belgium Excelsus Structural Solutions (Swiss) AG, Switzerland Outlook I. LoD and LoQ II. SR-XRPD: is a synchrotron source enough
Synchrotron XRPD Fabia Gozzo Excelsus Structural Solutions sprl, Brussels, Belgium Excelsus Structural Solutions (Swiss) AG, Switzerland Outlook I. LoD and LoQ II. SR-XRPD: is a synchrotron source enough
X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources
 X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources Christian Gutt Department of Physics, University ofsiegen, Germany gutt@physik.uni-siegen.de Outline How to measure dynamics
X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources Christian Gutt Department of Physics, University ofsiegen, Germany gutt@physik.uni-siegen.de Outline How to measure dynamics
Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources
 XDL Workshop 6 @ Cornell Univ. Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources Yuya Shinohara Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
XDL Workshop 6 @ Cornell Univ. Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources Yuya Shinohara Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals
 The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals Summary Information for Submitting Proposals We encourage scientists from all over the world to submit applications for beam time proposal to utilize
The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals Summary Information for Submitting Proposals We encourage scientists from all over the world to submit applications for beam time proposal to utilize
Status Report: Charge Cloud Explosion
 Status Report: Charge Cloud Explosion J. Becker, D. Eckstein, R. Klanner, G. Steinbrück University of Hamburg Detector laboratory 1. Introduction and Motivation. Set-up available for measurement 3. Measurements
Status Report: Charge Cloud Explosion J. Becker, D. Eckstein, R. Klanner, G. Steinbrück University of Hamburg Detector laboratory 1. Introduction and Motivation. Set-up available for measurement 3. Measurements
Vertical Polarization Option for LCLS-II. Abstract
 SLAC National Accelerator Lab LCLS-II TN-5-8 March 5 Vertical Polarization Option for LCLS-II G. Marcus, T. Raubenheimer SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 95 G. Penn LBNL, Berkeley, CA 97 Abstract Vertically polarized
SLAC National Accelerator Lab LCLS-II TN-5-8 March 5 Vertical Polarization Option for LCLS-II G. Marcus, T. Raubenheimer SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 95 G. Penn LBNL, Berkeley, CA 97 Abstract Vertically polarized
Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors
 Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors Henrik Loos 48 th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on Future Light Sources SLAC 2010 1 1 Henrik Loos LCLS Injector Injector Diagnostics Characterize
Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors Henrik Loos 48 th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on Future Light Sources SLAC 2010 1 1 Henrik Loos LCLS Injector Injector Diagnostics Characterize
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH
 Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
ThomX Machine Advisory Committee. (LAL Orsay, March ) Ring Beam Dynamics
 ThomX Machine Advisory Committee (LAL Orsay, March 20-21 2017) Ring Beam Dynamics A. Loulergue, M. Biagini, C. Bruni, I. Chaikovska I. Debrot, N. Delerue, A. Gamelin, H. Guler, J. Zang Programme Investissements
ThomX Machine Advisory Committee (LAL Orsay, March 20-21 2017) Ring Beam Dynamics A. Loulergue, M. Biagini, C. Bruni, I. Chaikovska I. Debrot, N. Delerue, A. Gamelin, H. Guler, J. Zang Programme Investissements
JRA3: Technology development for high-time-resolution astronomy
 JRA3: Technology development for high-time-resolution astronomy ( HTRA: ~ 10 ms -- 1μs ) Objectives: - To develop the most promising technologies for HTRA - Assess relative strengths/areas of application
JRA3: Technology development for high-time-resolution astronomy ( HTRA: ~ 10 ms -- 1μs ) Objectives: - To develop the most promising technologies for HTRA - Assess relative strengths/areas of application
Peter Fischer, ziti, Universität Heidelberg. Silicon Detectors & Readout Electronics
 Silicon Detectors and Readout Electronics Peter Fischer, ziti, Universität Heidelberg 1 Content of the Lecture (sorted by subject) Introduction: Applications of silicon detectors Requirements, measured
Silicon Detectors and Readout Electronics Peter Fischer, ziti, Universität Heidelberg 1 Content of the Lecture (sorted by subject) Introduction: Applications of silicon detectors Requirements, measured
VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab.
 VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab. Yuri Saveliev on behalf of VELA and CLARA teams STFC, ASTeC, Cockcroft Institute Daresbury Lab., UK Outline VELA (Versatile Electron
VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab. Yuri Saveliev on behalf of VELA and CLARA teams STFC, ASTeC, Cockcroft Institute Daresbury Lab., UK Outline VELA (Versatile Electron
Generation and characterization of ultra-short electron and x-ray x pulses
 Generation and characterization of ultra-short electron and x-ray x pulses Zhirong Huang (SLAC) Compact XFEL workshop July 19-20, 2010, Shanghai, China Ultra-bright Promise of XFELs Ultra-fast LCLS Methods
Generation and characterization of ultra-short electron and x-ray x pulses Zhirong Huang (SLAC) Compact XFEL workshop July 19-20, 2010, Shanghai, China Ultra-bright Promise of XFELs Ultra-fast LCLS Methods
High Energy Upgrade: LCLS-II-HE High Repetition Rate Soft X-rays Hard X-rays
 High Energy Upgrade: LCLS-II-HE High Repetition Rate Soft X-rays Hard X-rays Electronic & nuclear coupling Emergent properties Materials heterogeneity lattice spin charge orbital LCLS-II-HE provides: Ultrafast
High Energy Upgrade: LCLS-II-HE High Repetition Rate Soft X-rays Hard X-rays Electronic & nuclear coupling Emergent properties Materials heterogeneity lattice spin charge orbital LCLS-II-HE provides: Ultrafast
Synchrotron Radiation Representation in Phase Space
 Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Synchrotron Radiation Representation in Phase Space Ivan Bazarov and Andrew Gasbarro phase space of coherent (left) and incoherent (right)
Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Synchrotron Radiation Representation in Phase Space Ivan Bazarov and Andrew Gasbarro phase space of coherent (left) and incoherent (right)
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen
 Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Paul Scherrer Institut Pavle Juranić, R. Ischebeck, L. Patthey, V. Schlott, C. David, C. P. Hauri, I. Gorgisyan Single Shot Spectrometer and Pulse and Arrival Time
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Paul Scherrer Institut Pavle Juranić, R. Ischebeck, L. Patthey, V. Schlott, C. David, C. P. Hauri, I. Gorgisyan Single Shot Spectrometer and Pulse and Arrival Time
Detection: from the Dark Ages to the X-ray Detectors for future SR and FEL Photon Sources
 Detection: from the Dark Ages to the X-ray Detectors for future SR and FEL Photon Sources Michael Krisch Head of Instrumentation Services and Development Division European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
Detection: from the Dark Ages to the X-ray Detectors for future SR and FEL Photon Sources Michael Krisch Head of Instrumentation Services and Development Division European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation
 SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
New opportunities with X-ray Laser Sources
 WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN Luc Patthey :: SwissFEL Photonics :: Paul Scherrer Institut New opportunities with X-ray Laser Sources Symposium on OLAC 2018: NTB Campus, Buchs: 12.04.18 X-ray and
WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN Luc Patthey :: SwissFEL Photonics :: Paul Scherrer Institut New opportunities with X-ray Laser Sources Symposium on OLAC 2018: NTB Campus, Buchs: 12.04.18 X-ray and
SCSS Prototype Accelerator -- Its outline and achieved beam performance --
 SCSS Prototype Accelerator -- Its outline and achieved beam performance -- Hitoshi TANAKA RIKEN, XFEL Project Office 1 Content 1. Light Quality; SPring-8 v.s. XFEL 2. What are the critical issues? 3. Mission
SCSS Prototype Accelerator -- Its outline and achieved beam performance -- Hitoshi TANAKA RIKEN, XFEL Project Office 1 Content 1. Light Quality; SPring-8 v.s. XFEL 2. What are the critical issues? 3. Mission
The Hermes Recoil Silicon Detector
 The Hermes Recoil Silicon Detector Introduction Detector design considerations Silicon detector overview TIGRE microstrip sensors Readout electronics Test beam results Vertex 2002 J. Stewart DESY Zeuthen
The Hermes Recoil Silicon Detector Introduction Detector design considerations Silicon detector overview TIGRE microstrip sensors Readout electronics Test beam results Vertex 2002 J. Stewart DESY Zeuthen
Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation
 Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation Frederico Alves Lima Centro Nacional de Pesquisa em Energia e Materiais - CNPEM Laboratório Nacional de Luz Síncrotron - LNLS International School on Laser-Beam Interactions
Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation Frederico Alves Lima Centro Nacional de Pesquisa em Energia e Materiais - CNPEM Laboratório Nacional de Luz Síncrotron - LNLS International School on Laser-Beam Interactions
How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging
 How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging Stanford University EE Computer Systems Colloquium February 23 rd, 2011 EE380 Peter
How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging Stanford University EE Computer Systems Colloquium February 23 rd, 2011 EE380 Peter
Energy calibration of the threshold of Medipix for ATLAS
 Energy calibration of the threshold of Medipix for ATLAS Céline Lebel Université de Montréal lebel@lps.umontreal.ca presenting for the Institut of Experimental and Applied Physics of the Czech Technical
Energy calibration of the threshold of Medipix for ATLAS Céline Lebel Université de Montréal lebel@lps.umontreal.ca presenting for the Institut of Experimental and Applied Physics of the Czech Technical
Atmospheric Extinction
 Atmospheric Extinction Calibrating stellar photometry requires correction for loss of light passing through the atmosphere. Atmospheric Rayleigh and aerosol scattering preferentially redirects blue light
Atmospheric Extinction Calibrating stellar photometry requires correction for loss of light passing through the atmosphere. Atmospheric Rayleigh and aerosol scattering preferentially redirects blue light
The intense, pulsed positron source EPOS at the Research Centre Dresden-Rossendorf
 The intense, pulsed positron source EPOS at the Research Centre Dresden-Rossendorf The EPOS Team and R. Krause-Rehberg Martin-Luther University, Halle-Wittenberg, Dept. of Physics, 06099 Halle / Germany
The intense, pulsed positron source EPOS at the Research Centre Dresden-Rossendorf The EPOS Team and R. Krause-Rehberg Martin-Luther University, Halle-Wittenberg, Dept. of Physics, 06099 Halle / Germany
Probing and Driving Molecular Dynamics with Femtosecond Pulses
 Miroslav Kloz Probing and Driving Molecular Dynamics with Femtosecond Pulses (wavelengths above 200 nm, energies below mj) Why femtosecond lasers in biology? Scales of size and time are closely rerated!
Miroslav Kloz Probing and Driving Molecular Dynamics with Femtosecond Pulses (wavelengths above 200 nm, energies below mj) Why femtosecond lasers in biology? Scales of size and time are closely rerated!
Principles of Neutron Imaging
 Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Manuel Morgano Neutron Imaging & Activation Group, Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland Principles of Neutron Imaging PSI, 8. Oktober 2015 1. Absorption-based imaging
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Manuel Morgano Neutron Imaging & Activation Group, Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland Principles of Neutron Imaging PSI, 8. Oktober 2015 1. Absorption-based imaging
Detection of X-Rays. Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics
 Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS. Coherence Properties. J. B. Hastings. Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
 Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
Study of Solder Ball Bump Bonded Hybrid Silicon Pixel Detectors at DESY
 Study of Solder Ball Bump Bonded Hybrid Silicon Pixel Detectors at DESY S. Arab, S. Choudhury, G. Dolinska, K. Hansen, I. Korol, H. Perrey, D. Pitzl, S. Spannagel ( DESY Hamburg ) E. Garutti, M. Hoffmann,
Study of Solder Ball Bump Bonded Hybrid Silicon Pixel Detectors at DESY S. Arab, S. Choudhury, G. Dolinska, K. Hansen, I. Korol, H. Perrey, D. Pitzl, S. Spannagel ( DESY Hamburg ) E. Garutti, M. Hoffmann,
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ
 Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
Electron Crystallography for Structure Solution Latest Results from the PSI Electron Diffraction Group
 WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN Dr. Tim Grüne :: Paul Scherrer Institut :: tim.gruene@psi.ch Electron Crystallography for Structure Solution Latest Results from the PSI Electron Diffraction Group
WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN Dr. Tim Grüne :: Paul Scherrer Institut :: tim.gruene@psi.ch Electron Crystallography for Structure Solution Latest Results from the PSI Electron Diffraction Group
Introduction to XAFS. Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology. Revised 4/11/97
 Introduction to XAFS Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology Revised 4/11/97 2 tutorial.nb Outline Overview of Tutorial 1: Overview of XAFS 2: Basic Experimental design
Introduction to XAFS Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology Revised 4/11/97 2 tutorial.nb Outline Overview of Tutorial 1: Overview of XAFS 2: Basic Experimental design
Single Photon detectors
 Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
= 6 (1/ nm) So what is probability of finding electron tunneled into a barrier 3 ev high?
 STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
Neutron Instruments I & II. Ken Andersen ESS Instruments Division
 Neutron Instruments I & II ESS Instruments Division Neutron Instruments I & II Overview of source characteristics Bragg s Law Elastic scattering: diffractometers Continuous sources Pulsed sources Inelastic
Neutron Instruments I & II ESS Instruments Division Neutron Instruments I & II Overview of source characteristics Bragg s Law Elastic scattering: diffractometers Continuous sources Pulsed sources Inelastic
PoS(TIPP2014)033. Upgrade of MEG Liquid Xenon Calorimeter. Ryu SAWADA. ICEPP, the University of Tokyo
 ICEPP, the University of Tokyo E-mail: sawada@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp The MEG experiment yielded the most stringent upper limit on the branching ratio of the flavorviolating muon decay µ + e + γ. A major
ICEPP, the University of Tokyo E-mail: sawada@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp The MEG experiment yielded the most stringent upper limit on the branching ratio of the flavorviolating muon decay µ + e + γ. A major
An Overview of the Activities of ICS Sources in China
 An Overview of the Activities of ICS Sources in China Chuanxiang Tang *, Yingchao Du, Wenhui Huang * tang.xuh@tsinghua.edu.cn Department of Engineering physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
An Overview of the Activities of ICS Sources in China Chuanxiang Tang *, Yingchao Du, Wenhui Huang * tang.xuh@tsinghua.edu.cn Department of Engineering physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Part V Undulators for Free Electron Lasers
 Part V Undulators for Free Electron Lasers Pascal ELLEAUME European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble V, 1/22, P. Elleaume, CAS, Brunnen July 2-9, 2003. Oscillator-type Free Electron Laser V, 2/22,
Part V Undulators for Free Electron Lasers Pascal ELLEAUME European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble V, 1/22, P. Elleaume, CAS, Brunnen July 2-9, 2003. Oscillator-type Free Electron Laser V, 2/22,
First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL
 First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov ICFA workshop, Arcidosso, Italy, 22.09.2017 Outline Harmonic lasing Harmonic lasing self-seeded (HLSS) FEL Experiments
First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov ICFA workshop, Arcidosso, Italy, 22.09.2017 Outline Harmonic lasing Harmonic lasing self-seeded (HLSS) FEL Experiments
Imaging with entangled photons
 Imaging with entangled photons L. Gasparini 1, M. Perenzoni 1, H. Xu 1, L. Parmesan 1, M. Moreno Garcia 1, D. Stoppa 4, B. Bessire 2, M. Unternährer 2, A. Stefanov 2, V.Mitev 3 and D.L. Boiko 3 1 Fondazione
Imaging with entangled photons L. Gasparini 1, M. Perenzoni 1, H. Xu 1, L. Parmesan 1, M. Moreno Garcia 1, D. Stoppa 4, B. Bessire 2, M. Unternährer 2, A. Stefanov 2, V.Mitev 3 and D.L. Boiko 3 1 Fondazione
Development of Radiation Hard Si Detectors
 Development of Radiation Hard Si Detectors Dr. Ajay K. Srivastava On behalf of Detector Laboratory of the Institute for Experimental Physics University of Hamburg, D-22761, Germany. Ajay K. Srivastava
Development of Radiation Hard Si Detectors Dr. Ajay K. Srivastava On behalf of Detector Laboratory of the Institute for Experimental Physics University of Hamburg, D-22761, Germany. Ajay K. Srivastava
Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR)
 Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE
 Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
Detector R&D in KAPAC
 Detector R&D in KAPAC Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Outline Compton Camera SOI detector Scintillator Polarimeter Cherenkov Camera
Detector R&D in KAPAC Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Outline Compton Camera SOI detector Scintillator Polarimeter Cherenkov Camera
Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films
 A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films Phil Willmott, Christian Schlepütz tz,, Roger Herger, Oliver Bunk, and Bruce Patterson Beamline X04SA Materials
A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films Phil Willmott, Christian Schlepütz tz,, Roger Herger, Oliver Bunk, and Bruce Patterson Beamline X04SA Materials
New Concept of EPOS Progress of the Mono-energetic Positron Beam (MePS) Gamma-induced Positron Spectroscopy (GiPS)
 Progress of the EPOS Project: Gamma Induced Positron Spectroscopy (GiPS) R. Krause-Rehberg 1,*,W.Anwand 2,G.Brauer 2, M. Butterling 1,T.Cowan 2,M. Jungmann 1, A. Krille 1, R. Schwengner 2, A. Wagner 2
Progress of the EPOS Project: Gamma Induced Positron Spectroscopy (GiPS) R. Krause-Rehberg 1,*,W.Anwand 2,G.Brauer 2, M. Butterling 1,T.Cowan 2,M. Jungmann 1, A. Krille 1, R. Schwengner 2, A. Wagner 2
Module of Silicon Photomultipliers as a single photon detector of Cherenkov photons
 Module of Silicon Photomultipliers as a single photon detector of Cherenkov photons R. Pestotnik a, H. Chagani a, R. Dolenec a, S. Korpar a,b, P. Križan a,c, A. Stanovnik a,c a J. Stefan Institute, b University
Module of Silicon Photomultipliers as a single photon detector of Cherenkov photons R. Pestotnik a, H. Chagani a, R. Dolenec a, S. Korpar a,b, P. Križan a,c, A. Stanovnik a,c a J. Stefan Institute, b University
Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression
 Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression S. Bettoni M. Aiba, B. Beutner, M. Pedrozzi, E. Prat, S. Reiche, T. Schietinger Outline. Introduction. Experimental studies a. Measurement procedure
Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression S. Bettoni M. Aiba, B. Beutner, M. Pedrozzi, E. Prat, S. Reiche, T. Schietinger Outline. Introduction. Experimental studies a. Measurement procedure
