Modeling & Control of Hybrid Systems. Chapter 7 Model Checking and Timed Automata
|
|
|
- Eunice Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeling & Control of Hybrid Systems Chapter 7 Model Checking and Timed Automata Overview 1. Introduction 2. Transition systems 3. Bisimulation 4. Timed automata hs check.1
2 1. Introduction Model checking = process of automatically analyzing properties of systems by exploring their state space Finite state systems properties can be investigated by systematically exploring states E.g., check whether particular set of states will be reached Not possible for hybrid systems since number of states is infinite However, for some hybrid systems one can find equivalent finite state system by partitioning state space into finite number of sets such that any two states in set exhibit similar behavior analyze hybrid system by working with sets of partition Generation and analysis of finite partition can be carried out by computer hs check.2
3 2. Transition systems Transition system T =(S,δ,S 0,S F ) consists of set of states S (finite or infinite) transition relation δ : S P(S) set of initial states S 0 S set of final states S F S Trajectory of transition system is (in)finite sequence of states {s i } N i=0 such that s 0 S 0 s i+1 δ(s i ) for all i hs check.3
4 Example of finite state transition system q 0 q 1 q 2 States: S={q 0,...,q 6 }; q 3 q 4 q 5 q 6 Transition relation: δ(q 0 )={q 0,q 1,q 2 }, δ(q 1 )={q 0,q 3,q 4 }, δ(q 2 )= {q 0,q 5,q 6 }, δ(q 3 )=δ(q 4 )=δ(q 5 )=δ(q 6 )= Initial states: S 0 ={q 0 } Final states: S F ={q 3,q 6 } (indicated by double circles) hs check.4
5 Transition system of hybrid automaton Hybrid automaton can be transformed into transition system by abstracting away time Consider hybrid automaton H =(Q,X,Init, f,inv,e,g,r) and final set of states F Q X Define S=Q X, i.e., s=(q,x) S 0 =Init S F = F transition relation δ consists of two parts: discrete transition relation δ e for each edge e=(q,q ) E: { {q δ e ( ˆq, ˆx)= } R(e, ˆx) if ˆq=q and ˆx G(e) if ˆq q or ˆx G(e) hs check.5
6 Transition system of hybrid automaton (cont.) continuous transition relation δ C : δ C ( ˆq, ˆx)={( ˆq, ˆx ) ˆq = ˆq and t f 0, x(t f )= ˆx t [0,t f ],x(t) Inv( ˆq)} where x( ) is solution of ẋ= f(ˆq,x) with x(0)= ˆx Overall transition relation is then δ(s)=δ C (s) e E δ e (s) transition from s to s is possible if either discrete transition e E of hybrid system brings s to s, or s can flow continuously to s after some time hs check.6
7 Transition system of hybrid automaton (cont.) Time has been abstracted away: we do not care how long it takes to get from s to s, we only care whether it is possible to get there eventually transition system captures sequence of events that hybrid system may experience, but not timing of these events hs check.7
8 Reachability Transition system is reachable if there exists trajectory such that s i S F for some i hs check.8
9 3. Bisimulation Turn infinite state system into finite state system by grouping together states that have similar behavior partition Yields so-called quotient transition system finite number of states can be analyzed more easily Problem: for most partitions properties of quotient transition system do not allow to draw any useful conclusions about properties of original system However, special type of partition for which quotient system ˆT is equivalent to original transition system T: bisimulation hs check.9
10 Important property If partition {S i } i I is bisimulation of transition system T and ˆT is quotient transition system, then S F is reachable by T if and only if corresponding final state Ŝ F in ˆT is reachable by ˆT For finite state systems computational efficiency Study reachability in quotient system instead of original system (quotient system usually much smaller than original) For infinite state systems: Even if original transition system has infinite number of states, sometimes bisimulation consisting of finite number of sets answer reachability questions for infinite state system by studying equivalent finite state system hs check.10
11 Bisimulation algorithm For timed automata we can always find finite bisimulation Bisimulation algorithm (see lecture notes): For finite state systems bisimulation algorithm will always terminate Problem: it may be more work to find bisimulation than to investigate reachability of the original system For infinite state systems: sometimes, algorithm may never terminate (reason: not all infinite state transition systems have finite bisimulations) hs check.11
12 Bisimulation algorithm (continued) For timed automata: bisimulation algorithm terminates in finite number of steps Disadvantage: total number of states in the quotient transition system grows very quickly (exponentially) as number of timers n increases hs check.12
13 4. Timed automata Timed automata involve simple continuous dynamics: all differential equations of form ẋ=1, all invariants, guards, etc. involve comparison of real-valued states with constants (e.g., x=1, x<2, x 0, etc.) Timed automata are limited for modeling physical systems However, very well suited for encoding timing constraints such as event A must take place at least 2 seconds after event B and not more than 5 seconds before event C Applications: multimedia, Internet, audio protocol verification hs check.13
14 4.1 Example of timed automaton x 1 = x 2 = 0 q 1 x 2 > 2 x 1 := 3 x 2 := 0 q 2 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 2 3 x 1 := 0 x 1 > 4 x 1 5 hs check.14
15 Timed automata (cont.) For timed automaton of example: all constants are non-negative integers can be generalized Given any timed automaton whose definition involves rational and/or negative constants, we can define an equivalent timed automaton whose definition involves only non-negative integers Done by scaling and shifting (adding appropriate integer) some of states Transformation into transition systems transition system corresponding to timed automaton always has finite bisimulation Standard bisimulation for timed automata is region graph hs check.15
16 x 2 Region graph x 1 = x 2 = x 1 q 1 x 2 > 2 x 1 := 3 x 2 := 0 q 2 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 2 3 x 1 := 0 x 1 > 4 x 1 5 hs check.16
17 x 1 = x 2 = 0 Construction of region graph ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 2 > 2 x 1 := 3 x 2 := 0 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 2 3 x 1 := 0 x 1 > 4 x 1 5 Assume w.l.o.g. that all constants are non-negative integers Let C i be largest constant with which x i is compared in initial sets, guards, invariants and resets In example: C 1 = 5 and C 2 = 3 If all we know about timed automaton is these bounds C i, then x i could be compared with any integer M {0,1...,C i } in some guard, reset or initial condition set Hence, discrete transitions of timed automaton may be able to distinguish states with x i < M from states with x i = M and from states with x i > M (e.g., discrete transition may be possible from state with x i < M but not from state with x i > M) hs check.17
18 x 1 = x 2 = 0 Construction of region graph (cont.) Add sets to candidate bisimulation: ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 2 3 x 2 > 2 x 1 := 0 x 1 := 3 x 2 := 0 x 1 > 4 ẋ 1 = 1 ẋ 2 = 1 x 1 5 for x 1 : x 1 (0,1),x 1 (1,2),x 1 (2,3),x 1 (3,4),x 1 (4,5),x 1 (5, ) x 1 = 0,x 1 = 1,x 1 = 2,x 1 = 3,x 1 = 4,x 1 = 5 for x 2 : x 2 (0,1),x 2 (1,2),x 2 (2,3),x 2 (3, ) x 2 = 0,x 2 = 1,x 2 = 2,x 2 = 3 Products of all sets: {x R 2 x 1 (0,1) x 2 (0,1)} {x R 2 x 1 (0,1) x 2 = 1} {x R 2 x 1 = 1 x 2 (0,1)} {x R 2 x 1 = 1 x 2 = 1} {x R 2 x 1 (1,2) x 2 (3, )}, etc. define all sets in R 2 that discrete dynamics can distinguish open squares, open horizontal and vertical line segments, integer points, and open, unbounded rectangles hs check.18
19 x 2 Construction of region graph (cont.) 2 Since ẋ 1 = ẋ 2 = 1, continuous states move diagonally up along 45 lines by allowing time to flow timed automaton may distinguish points below diagonal of each square, points above diagonal, and points on the diagonal E.g., points above diagonal of square {x R 2 x 1 (0,1) x 2 (0,1)} will leave square through line {x R 2 x 1 (0,1) x 2 = 1} Points below diagonal leave square through line {x R 2 x 1 = 1 x 2 (0,1)} Points on diagonal leave square through point (1,1) 2 x 1 hs check.19
20 Construction of region graph (cont.) x 2 Split each open square in three: two open triangles and open diagonal line segment is enough to generate bisimulation: Theorem: The region graph is finite bisimulation of timed automaton Disadvantage: total number of regions in the region graph grows very quickly (exponentially) as n increases x 1 hs check.20
21 5. Summary Verification of hybrid systems hard problem Transition systems Bisimulation & reachability turn infinite state system into finite state system by grouping together states that have similar behavior Timed automata finite bisimulation hs check.21
Discrete abstractions of hybrid systems for verification
 Discrete abstractions of hybrid systems for verification George J. Pappas Departments of ESE and CIS University of Pennsylvania pappasg@ee.upenn.edu http://www.seas.upenn.edu/~pappasg DISC Summer School
Discrete abstractions of hybrid systems for verification George J. Pappas Departments of ESE and CIS University of Pennsylvania pappasg@ee.upenn.edu http://www.seas.upenn.edu/~pappasg DISC Summer School
Lecture 6: Reachability Analysis of Timed and Hybrid Automata
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Lecture 6: Reachability Analysis of Timed and Hybrid Automata Sayan Mitra Special Classes of Hybrid Automata Timed Automata ß Rectangular Initialized HA Rectangular
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Lecture 6: Reachability Analysis of Timed and Hybrid Automata Sayan Mitra Special Classes of Hybrid Automata Timed Automata ß Rectangular Initialized HA Rectangular
Recent results on Timed Systems
 Recent results on Timed Systems Time Petri Nets and Timed Automata Béatrice Bérard LAMSADE Université Paris-Dauphine & CNRS berard@lamsade.dauphine.fr Based on joint work with F. Cassez, S. Haddad, D.
Recent results on Timed Systems Time Petri Nets and Timed Automata Béatrice Bérard LAMSADE Université Paris-Dauphine & CNRS berard@lamsade.dauphine.fr Based on joint work with F. Cassez, S. Haddad, D.
Automata-theoretic analysis of hybrid systems
 Automata-theoretic analysis of hybrid systems Madhavan Mukund SPIC Mathematical Institute 92, G N Chetty Road Chennai 600 017, India Email: madhavan@smi.ernet.in URL: http://www.smi.ernet.in/~madhavan
Automata-theoretic analysis of hybrid systems Madhavan Mukund SPIC Mathematical Institute 92, G N Chetty Road Chennai 600 017, India Email: madhavan@smi.ernet.in URL: http://www.smi.ernet.in/~madhavan
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Algorithmic analysis for linear hybrid systems Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University SS 2015 Ábrahám - Hybrid Systems
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Algorithmic analysis for linear hybrid systems Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University SS 2015 Ábrahám - Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems and computer science a short tutorial
 Hybrid systems and computer science a short tutorial Eugene Asarin Université Paris 7 - LIAFA SFM 04 - RT, Bertinoro p. 1/4 Introductory equations Hybrid Systems = Discrete+Continuous SFM 04 - RT, Bertinoro
Hybrid systems and computer science a short tutorial Eugene Asarin Université Paris 7 - LIAFA SFM 04 - RT, Bertinoro p. 1/4 Introductory equations Hybrid Systems = Discrete+Continuous SFM 04 - RT, Bertinoro
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems 5. Linear hybrid automata I Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 06 October
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems 5. Linear hybrid automata I Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 06 October
 Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Linear hybrid automata I Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 06 October 2017
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Linear hybrid automata I Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 06 October 2017
CEGAR:Counterexample-Guided Abstraction Refinement
 CEGAR: Counterexample-guided Abstraction Refinement Sayan Mitra ECE/CS 584: Embedded System Verification November 13, 2012 Outline Finite State Systems: Abstraction Refinement CEGAR Validation Refinment
CEGAR: Counterexample-guided Abstraction Refinement Sayan Mitra ECE/CS 584: Embedded System Verification November 13, 2012 Outline Finite State Systems: Abstraction Refinement CEGAR Validation Refinment
Timed Automata. Semantics, Algorithms and Tools. Zhou Huaiyang
 Timed Automata Semantics, Algorithms and Tools Zhou Huaiyang Agenda } Introduction } Timed Automata } Formal Syntax } Operational Semantics } Verification Problems } Symbolic Semantics & Verification }
Timed Automata Semantics, Algorithms and Tools Zhou Huaiyang Agenda } Introduction } Timed Automata } Formal Syntax } Operational Semantics } Verification Problems } Symbolic Semantics & Verification }
EE291E Lecture Notes 3 Autonomous Hybrid Automata
 EE9E Lecture Notes 3 Autonomous Hybrid Automata Claire J. Tomlin January, 8 The lecture notes for this course are based on the first draft of a research monograph: Hybrid Systems. The monograph is copyright
EE9E Lecture Notes 3 Autonomous Hybrid Automata Claire J. Tomlin January, 8 The lecture notes for this course are based on the first draft of a research monograph: Hybrid Systems. The monograph is copyright
models, languages, dynamics Eugene Asarin PIMS/EQINOCS Workshop on Automata Theory and Symbolic Dynamics LIAFA - University Paris Diderot and CNRS
 models, s, LIAFA - University Paris Diderot and CNRS PIMS/EQINOCS Workshop on Automata Theory and Symbolic Dynamics Context A model for verification of real-time systems Invented by Alur and Dill in early
models, s, LIAFA - University Paris Diderot and CNRS PIMS/EQINOCS Workshop on Automata Theory and Symbolic Dynamics Context A model for verification of real-time systems Invented by Alur and Dill in early
The algorithmic analysis of hybrid system
 The algorithmic analysis of hybrid system Authors: R.Alur, C. Courcoubetis etc. Course teacher: Prof. Ugo Buy Xin Li, Huiyong Xiao Nov. 13, 2002 Summary What s a hybrid system? Definition of Hybrid Automaton
The algorithmic analysis of hybrid system Authors: R.Alur, C. Courcoubetis etc. Course teacher: Prof. Ugo Buy Xin Li, Huiyong Xiao Nov. 13, 2002 Summary What s a hybrid system? Definition of Hybrid Automaton
Student s Name Course Name Mathematics Grade 7. General Outcome: Develop number sense. Strand: Number. R D C Changed Outcome/achievement indicator
 Strand: Number Specific Outcomes It is expected that students will: 1. Determine and explain why a number is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 or 10, and why a number cannot be divided by 0. [C, R] 2. Demonstrate
Strand: Number Specific Outcomes It is expected that students will: 1. Determine and explain why a number is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 or 10, and why a number cannot be divided by 0. [C, R] 2. Demonstrate
A Decidable Class of Planar Linear Hybrid Systems
 A Decidable Class of Planar Linear Hybrid Systems Pavithra Prabhakar, Vladimeros Vladimerou, Mahesh Viswanathan, and Geir E. Dullerud University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Abstract. The paper shows
A Decidable Class of Planar Linear Hybrid Systems Pavithra Prabhakar, Vladimeros Vladimerou, Mahesh Viswanathan, and Geir E. Dullerud University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Abstract. The paper shows
Hybrid Automata. Lecturer: Tiziano Villa 1. Università di Verona
 Hybrid Automata Lecturer: Tiziano Villa 1 1 Dipartimento d Informatica Università di Verona tiziano.villa@univr.it Thanks to Carla Piazza, Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica, Università di Udine
Hybrid Automata Lecturer: Tiziano Villa 1 1 Dipartimento d Informatica Università di Verona tiziano.villa@univr.it Thanks to Carla Piazza, Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica, Università di Udine
for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization
 Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Stavros Tripakis UC Berkeley EECS 144/244 Fall 2013 Copyright 2013, E. A. Lee, J. Roydhowdhury, S. A. Seshia, S. Tripakis All rights
Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Stavros Tripakis UC Berkeley EECS 144/244 Fall 2013 Copyright 2013, E. A. Lee, J. Roydhowdhury, S. A. Seshia, S. Tripakis All rights
Algorithmic Verification of Stability of Hybrid Systems
 Algorithmic Verification of Stability of Hybrid Systems Pavithra Prabhakar Kansas State University University of Kansas February 24, 2017 1 Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Systems in which software "cyber"
Algorithmic Verification of Stability of Hybrid Systems Pavithra Prabhakar Kansas State University University of Kansas February 24, 2017 1 Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Systems in which software "cyber"
Limits at Infinity. Horizontal Asymptotes. Definition (Limits at Infinity) Horizontal Asymptotes
 Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Hybrid Systems Course Lyapunov stability
 Hybrid Systems Course Lyapunov stability OUTLINE Focus: stability of an equilibrium point continuous systems decribed by ordinary differential equations (brief review) hybrid automata OUTLINE Focus: stability
Hybrid Systems Course Lyapunov stability OUTLINE Focus: stability of an equilibrium point continuous systems decribed by ordinary differential equations (brief review) hybrid automata OUTLINE Focus: stability
Timed Automata. Chapter Clocks and clock constraints Clock variables and clock constraints
 Chapter 10 Timed Automata In the previous chapter, we have discussed a temporal logic where time was a discrete entities. A time unit was one application of the transition relation of an LTS. We could
Chapter 10 Timed Automata In the previous chapter, we have discussed a temporal logic where time was a discrete entities. A time unit was one application of the transition relation of an LTS. We could
Hybrid Systems - Lecture n. 3 Lyapunov stability
 OUTLINE Focus: stability of equilibrium point Hybrid Systems - Lecture n. 3 Lyapunov stability Maria Prandini DEI - Politecnico di Milano E-mail: prandini@elet.polimi.it continuous systems decribed by
OUTLINE Focus: stability of equilibrium point Hybrid Systems - Lecture n. 3 Lyapunov stability Maria Prandini DEI - Politecnico di Milano E-mail: prandini@elet.polimi.it continuous systems decribed by
Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems
 Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems James Worrell Department of Computer Science, Oxford University (Joint work with Ventsislav Chonev and Joël Ouaknine) CONCUR September 2nd
Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems James Worrell Department of Computer Science, Oxford University (Joint work with Ventsislav Chonev and Joël Ouaknine) CONCUR September 2nd
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION
 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
A Hybrid Control Model of Fractone-Dependent Morphogenesis
 A Hybrid Control Model of Fractone-Dependent Morphogenesis University of Hawaii at Manoa May 28, 2015 Many thanks go to: Dr. Monique Chyba Dr. Frederic Mercier Committee Members: Dr. George Wilkens, Dr.
A Hybrid Control Model of Fractone-Dependent Morphogenesis University of Hawaii at Manoa May 28, 2015 Many thanks go to: Dr. Monique Chyba Dr. Frederic Mercier Committee Members: Dr. George Wilkens, Dr.
Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems
 Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems James Worrell Department of Computer Science, Oxford University (Joint work with Ventsislav Chonev and Joël Ouaknine) FICS 2015 September 12th,
Reachability Problems for Continuous Linear Dynamical Systems James Worrell Department of Computer Science, Oxford University (Joint work with Ventsislav Chonev and Joël Ouaknine) FICS 2015 September 12th,
Notes on State Minimization
 U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 1 Professor Luca Trevisan 2/3/2015 Notes on State Minimization These notes present a technique to prove a lower bound on the number of
U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 1 Professor Luca Trevisan 2/3/2015 Notes on State Minimization These notes present a technique to prove a lower bound on the number of
Numerical Methods. Exponential and Logarithmic functions. Jaesung Lee
 Numerical Methods Exponential and Logarithmic functions Jaesung Lee Exponential Function Exponential Function Introduction We consider how the expression is defined when is a positive number and is irrational.
Numerical Methods Exponential and Logarithmic functions Jaesung Lee Exponential Function Exponential Function Introduction We consider how the expression is defined when is a positive number and is irrational.
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic
 Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 4, 2013 Outline 1 Showing The PP
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 4, 2013 Outline 1 Showing The PP
Automatic Generation of Polynomial Invariants for System Verification
 Automatic Generation of Polynomial Invariants for System Verification Enric Rodríguez-Carbonell Technical University of Catalonia Talk at EPFL Nov. 2006 p.1/60 Plan of the Talk Introduction Need for program
Automatic Generation of Polynomial Invariants for System Verification Enric Rodríguez-Carbonell Technical University of Catalonia Talk at EPFL Nov. 2006 p.1/60 Plan of the Talk Introduction Need for program
APPROXIMATE SIMULATION RELATIONS FOR HYBRID SYSTEMS 1. Antoine Girard A. Agung Julius George J. Pappas
 APPROXIMATE SIMULATION RELATIONS FOR HYBRID SYSTEMS 1 Antoine Girard A. Agung Julius George J. Pappas Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 1914 {agirard,agung,pappasg}@seas.upenn.edu
APPROXIMATE SIMULATION RELATIONS FOR HYBRID SYSTEMS 1 Antoine Girard A. Agung Julius George J. Pappas Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 1914 {agirard,agung,pappasg}@seas.upenn.edu
CDS 270 (Fall 09) - Lecture Notes for Assignment 8.
 CDS 270 (Fall 09) - Lecture Notes for Assignment 8. ecause this part of the course has no slides or textbook, we will provide lecture supplements that include, hopefully, enough discussion to complete
CDS 270 (Fall 09) - Lecture Notes for Assignment 8. ecause this part of the course has no slides or textbook, we will provide lecture supplements that include, hopefully, enough discussion to complete
Symbolic Reachability Analysis of Lazy Linear Hybrid Automata. Susmit Jha, Bryan Brady and Sanjit A. Seshia
 Symbolic Reachability Analysis of Lazy Linear Hybrid Automata Susmit Jha, Bryan Brady and Sanjit A. Seshia Traditional Hybrid Automata Traditional Hybrid Automata do not model delay and finite precision
Symbolic Reachability Analysis of Lazy Linear Hybrid Automata Susmit Jha, Bryan Brady and Sanjit A. Seshia Traditional Hybrid Automata Traditional Hybrid Automata do not model delay and finite precision
Models for Efficient Timed Verification
 Models for Efficient Timed Verification François Laroussinie LSV / ENS de Cachan CNRS UMR 8643 Monterey Workshop - Composition of embedded systems Model checking System Properties Formalizing step? ϕ Model
Models for Efficient Timed Verification François Laroussinie LSV / ENS de Cachan CNRS UMR 8643 Monterey Workshop - Composition of embedded systems Model checking System Properties Formalizing step? ϕ Model
What we have done so far
 What we have done so far DFAs and regular languages NFAs and their equivalence to DFAs Regular expressions. Regular expressions capture exactly regular languages: Construct a NFA from a regular expression.
What we have done so far DFAs and regular languages NFAs and their equivalence to DFAs Regular expressions. Regular expressions capture exactly regular languages: Construct a NFA from a regular expression.
Analysis of a Boost Converter Circuit Using Linear Hybrid Automata
 Analysis of a Boost Converter Circuit Using Linear Hybrid Automata Ulrich Kühne LSV ENS de Cachan, 94235 Cachan Cedex, France, kuehne@lsv.ens-cachan.fr 1 Introduction Boost converter circuits are an important
Analysis of a Boost Converter Circuit Using Linear Hybrid Automata Ulrich Kühne LSV ENS de Cachan, 94235 Cachan Cedex, France, kuehne@lsv.ens-cachan.fr 1 Introduction Boost converter circuits are an important
EECS 144/244: Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization
 EECS 144/244: Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Discrete Systems Lecture: Automata, State machines, Circuits Stavros Tripakis University of California, Berkeley Stavros
EECS 144/244: Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Discrete Systems Lecture: Automata, State machines, Circuits Stavros Tripakis University of California, Berkeley Stavros
An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling
 CS620, IIT BOMBAY An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling Ashutosh Trivedi Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Bombay CS620: New Trends in IT: Modeling and Verification of Cyber-Physical
CS620, IIT BOMBAY An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling Ashutosh Trivedi Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Bombay CS620: New Trends in IT: Modeling and Verification of Cyber-Physical
On simulations and bisimulations of general flow systems
 On simulations and bisimulations of general flow systems Jen Davoren Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering The University of Melbourne, AUSTRALIA and Paulo Tabuada Department of Electrical
On simulations and bisimulations of general flow systems Jen Davoren Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering The University of Melbourne, AUSTRALIA and Paulo Tabuada Department of Electrical
ONR MURI AIRFOILS: Animal Inspired Robust Flight with Outer and Inner Loop Strategies. Calin Belta
 ONR MURI AIRFOILS: Animal Inspired Robust Flight with Outer and Inner Loop Strategies Provable safety for animal inspired agile flight Calin Belta Hybrid and Networked Systems (HyNeSs) Lab Department of
ONR MURI AIRFOILS: Animal Inspired Robust Flight with Outer and Inner Loop Strategies Provable safety for animal inspired agile flight Calin Belta Hybrid and Networked Systems (HyNeSs) Lab Department of
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic
 Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 4, 2013 Outline Showing The PP Trajectories
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories are periodic James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 4, 2013 Outline Showing The PP Trajectories
On Reachability for Hybrid Automata over Bounded Time
 On Reachability for Hybrid Automata over Bounded Time Thomas Brihaye, Laurent Doyen 2, Gilles Geeraerts 3, Joël Ouaknine 4, Jean-François Raskin 3, and James Worrell 4 Université de Mons, Belgium 2 LSV,
On Reachability for Hybrid Automata over Bounded Time Thomas Brihaye, Laurent Doyen 2, Gilles Geeraerts 3, Joël Ouaknine 4, Jean-François Raskin 3, and James Worrell 4 Université de Mons, Belgium 2 LSV,
The State Explosion Problem
 The State Explosion Problem Martin Kot August 16, 2003 1 Introduction One from main approaches to checking correctness of a concurrent system are state space methods. They are suitable for automatic analysis
The State Explosion Problem Martin Kot August 16, 2003 1 Introduction One from main approaches to checking correctness of a concurrent system are state space methods. They are suitable for automatic analysis
More on Regular Languages and Non-Regular Languages
 More on Regular Languages and Non-Regular Languages CSCE A35 Decision Properties of Regular Languages Given a (representation, e.g., RE, FA, of a) regular language L, what can we tell about L? Since there
More on Regular Languages and Non-Regular Languages CSCE A35 Decision Properties of Regular Languages Given a (representation, e.g., RE, FA, of a) regular language L, what can we tell about L? Since there
Abstractions of hybrid systems: formal languages to describe dynamical behaviour
 Abstractions of hybrid systems: formal languages to describe dynamical behaviour Rebekah Carter, Eva M. Navarro-López School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester, M13
Abstractions of hybrid systems: formal languages to describe dynamical behaviour Rebekah Carter, Eva M. Navarro-López School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester, M13
Control of Sampled Switched Systems using Invariance Analysis
 1st French Singaporean Workshop on Formal Methods and Applications Control of Sampled Switched Systems using Invariance Analysis Laurent Fribourg LSV - ENS Cachan & CNRS Laurent Fribourg Lsv - ENS Cachan
1st French Singaporean Workshop on Formal Methods and Applications Control of Sampled Switched Systems using Invariance Analysis Laurent Fribourg LSV - ENS Cachan & CNRS Laurent Fribourg Lsv - ENS Cachan
On o-minimal hybrid systems
 "!$#&%('*)+#-,(.0/0!2143(5768'(9(:=*?*?*@BADCFE GIH JLKNMPOQHOQMIRS TVUXWZY[O]\ ^_Ù ^_abcmd^ V%e3B:`,efLgh5i)j%&,lkl!nmh%(5i)+fo6Q)p,('q)p#e%&,r9-sm"t$uB5])+#v/w) x*) y257!m%(5]) fz6o3[1(%e!ch573[!lfz6{.!25
"!$#&%('*)+#-,(.0/0!2143(5768'(9(:=*?*?*@BADCFE GIH JLKNMPOQHOQMIRS TVUXWZY[O]\ ^_Ù ^_abcmd^ V%e3B:`,efLgh5i)j%&,lkl!nmh%(5i)+fo6Q)p,('q)p#e%&,r9-sm"t$uB5])+#v/w) x*) y257!m%(5]) fz6o3[1(%e!ch573[!lfz6{.!25
In this section you will learn the following : 40.1Double integrals
 Module 14 : Double Integrals, Applilcations to Areas and Volumes Change of variables Lecture 40 : Double integrals over rectangular domains [Section 40.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the
Module 14 : Double Integrals, Applilcations to Areas and Volumes Change of variables Lecture 40 : Double integrals over rectangular domains [Section 40.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the
Bounded Model Checking with SAT/SMT. Edmund M. Clarke School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 1/39
 Bounded Model Checking with SAT/SMT Edmund M. Clarke School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 1/39 Recap: Symbolic Model Checking with BDDs Method used by most industrial strength model checkers:
Bounded Model Checking with SAT/SMT Edmund M. Clarke School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 1/39 Recap: Symbolic Model Checking with BDDs Method used by most industrial strength model checkers:
540 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 4, APRIL Algorithmic Analysis of Nonlinear Hybrid Systems
 540 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 4, APRIL 1998 Algorithmic Analysis of Nonlinear Hybrid Systems Thomas A. Henzinger, Pei-Hsin Ho, Howard Wong-Toi Abstract Hybrid systems are digital
540 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 4, APRIL 1998 Algorithmic Analysis of Nonlinear Hybrid Systems Thomas A. Henzinger, Pei-Hsin Ho, Howard Wong-Toi Abstract Hybrid systems are digital
Date: Math 7 Final Exam Review Name:
 Specific Outcome Achievement Indicators Chapter Got it?? the Solve a given problem involving the addition of two or more decimal numbers. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals
Specific Outcome Achievement Indicators Chapter Got it?? the Solve a given problem involving the addition of two or more decimal numbers. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Linear hybrid automata II: Approximation of reachable state sets Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University SS 2015 Ábrahám
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems Linear hybrid automata II: Approximation of reachable state sets Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University SS 2015 Ábrahám
Symbolic Real Time Model Checking. Kim G Larsen
 Smbolic Real Time Model Checking Kim G Larsen Overview Timed Automata Decidabilit Results The UPPAAL Verification Engine Datastructures for zones Liveness Checking Algorithm Abstraction and Compositionalit
Smbolic Real Time Model Checking Kim G Larsen Overview Timed Automata Decidabilit Results The UPPAAL Verification Engine Datastructures for zones Liveness Checking Algorithm Abstraction and Compositionalit
Pushdown timed automata:a binary reachability characterization and safety verication
 Theoretical Computer Science 302 (2003) 93 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Pushdown timed automata:a binary reachability characterization and safety verication Zhe Dang School of Electrical Engineering
Theoretical Computer Science 302 (2003) 93 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Pushdown timed automata:a binary reachability characterization and safety verication Zhe Dang School of Electrical Engineering
Embedded Systems 5. Synchronous Composition. Lee/Seshia Section 6.2
 Embedded Systems 5-1 - Synchronous Composition Lee/Seshia Section 6.2 Important semantic model for concurrent composition Here: composition of actors Foundation of Statecharts, Simulink, synchronous programming
Embedded Systems 5-1 - Synchronous Composition Lee/Seshia Section 6.2 Important semantic model for concurrent composition Here: composition of actors Foundation of Statecharts, Simulink, synchronous programming
Software Verification
 Software Verification Grégoire Sutre LaBRI, University of Bordeaux, CNRS, France Summer School on Verification Technology, Systems & Applications September 2008 Grégoire Sutre Software Verification VTSA
Software Verification Grégoire Sutre LaBRI, University of Bordeaux, CNRS, France Summer School on Verification Technology, Systems & Applications September 2008 Grégoire Sutre Software Verification VTSA
Representing Arithmetic Constraints with Finite Automata: An Overview
 Representing Arithmetic Constraints with Finite Automata: An Overview Bernard Boigelot Pierre Wolper Université de Liège Motivation Linear numerical constraints are a very common and useful formalism (our
Representing Arithmetic Constraints with Finite Automata: An Overview Bernard Boigelot Pierre Wolper Université de Liège Motivation Linear numerical constraints are a very common and useful formalism (our
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems 7. Linear hybrid automata II Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 6 October
Modeling and Analysis of Hybrid Systems 7. Linear hybrid automata II Prof. Dr. Erika Ábrahám Informatik 2 - LuFG Theory of Hybrid Systems RWTH Aachen University Szeged, Hungary, 27 September - 6 October
A Partial List of Topics: Math Spring 2009
 A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
Stepping stones for Number systems. 1) Concept of a number line : Marking using sticks on the floor. (1 stick length = 1 unit)
 Quality for Equality Stepping stones for Number systems 1) Concept of a number line : Marking using sticks on the floor. (1 stick length = 1 unit) 2) Counting numbers: 1,2,3,... Natural numbers Represent
Quality for Equality Stepping stones for Number systems 1) Concept of a number line : Marking using sticks on the floor. (1 stick length = 1 unit) 2) Counting numbers: 1,2,3,... Natural numbers Represent
Unbounded, Fully Symbolic Model Checking of Timed Automata using Boolean Methods
 Unbounded, Fully Symbolic Model Checking of Timed Automata using Boolean Methods Sanjit A. Seshia and Randal E. Bryant Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Verifying Timed Embedded Systems
Unbounded, Fully Symbolic Model Checking of Timed Automata using Boolean Methods Sanjit A. Seshia and Randal E. Bryant Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Verifying Timed Embedded Systems
More on Finite Automata and Regular Languages. (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall / 41
 More on Finite Automata and Regular Languages (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall 2016 1 / 41 Pumping Lemma is not a Sufficient Condition Example 1 We know L = {b m c m m > 0} is not regular. Let us consider
More on Finite Automata and Regular Languages (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall 2016 1 / 41 Pumping Lemma is not a Sufficient Condition Example 1 We know L = {b m c m m > 0} is not regular. Let us consider
Q 1. Richland School District Two 8th Grade Mathematics Pacing Guide. Last Edit: 1/17/17
 Overview of Units Pacing Guide Standards and Indicators Suggested Days Q 1 1-2 Unit 1: Geometry and Measurement: Transformations in the Plane Congruence: - Translations - Reflections - Rotations - Congruent
Overview of Units Pacing Guide Standards and Indicators Suggested Days Q 1 1-2 Unit 1: Geometry and Measurement: Transformations in the Plane Congruence: - Translations - Reflections - Rotations - Congruent
Timed Automata VINO 2011
 Timed Automata VINO 2011 VeriDis Group - LORIA July 18, 2011 Content 1 Introduction 2 Timed Automata 3 Networks of timed automata Motivation Formalism for modeling and verification of real-time systems.
Timed Automata VINO 2011 VeriDis Group - LORIA July 18, 2011 Content 1 Introduction 2 Timed Automata 3 Networks of timed automata Motivation Formalism for modeling and verification of real-time systems.
Formal Verification Techniques. Riccardo Sisto, Politecnico di Torino
 Formal Verification Techniques Riccardo Sisto, Politecnico di Torino State exploration State Exploration and Theorem Proving Exhaustive exploration => result is certain (correctness or noncorrectness proof)
Formal Verification Techniques Riccardo Sisto, Politecnico di Torino State exploration State Exploration and Theorem Proving Exhaustive exploration => result is certain (correctness or noncorrectness proof)
Integration. Tuesday, December 3, 13
 4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling
 CS620, IIT BOMBAY An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling Ashutosh Trivedi Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Bombay CS620: New Trends in IT: Modeling and Verification of Cyber-Physical
CS620, IIT BOMBAY An Introduction to Hybrid Systems Modeling Ashutosh Trivedi Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Bombay CS620: New Trends in IT: Modeling and Verification of Cyber-Physical
University of California. Berkeley, CA fzhangjun johans lygeros Abstract
 Dynamical Systems Revisited: Hybrid Systems with Zeno Executions Jun Zhang, Karl Henrik Johansson y, John Lygeros, and Shankar Sastry Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University
Dynamical Systems Revisited: Hybrid Systems with Zeno Executions Jun Zhang, Karl Henrik Johansson y, John Lygeros, and Shankar Sastry Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University
Overview. Discrete Event Systems Verification of Finite Automata. What can finite automata be used for? What can finite automata be used for?
 Computer Engineering and Networks Overview Discrete Event Systems Verification of Finite Automata Lothar Thiele Introduction Binary Decision Diagrams Representation of Boolean Functions Comparing two circuits
Computer Engineering and Networks Overview Discrete Event Systems Verification of Finite Automata Lothar Thiele Introduction Binary Decision Diagrams Representation of Boolean Functions Comparing two circuits
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules Derivative constant function if c is any real number, then Example: The Power Rule: If n is a positive integer, then Example: Extended Power Rule: If r is any real number,
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules Derivative constant function if c is any real number, then Example: The Power Rule: If n is a positive integer, then Example: Extended Power Rule: If r is any real number,
Dynamical Systems Revisited: Hybrid Systems with Zeno Executions
 Dynamical Systems Revisited: Hybrid Systems with Zeno Executions Jun Zhang, Karl Henrik Johansson, John Lygeros, and Shankar Sastry Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University
Dynamical Systems Revisited: Hybrid Systems with Zeno Executions Jun Zhang, Karl Henrik Johansson, John Lygeros, and Shankar Sastry Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University
Chapter Two: Finite Automata
 Chapter Two: Finite Automata In theoretical computer science, automata theory is the study of abstract machines (or more appropriately, abstract 'mathematical' machines or systems) and the computational
Chapter Two: Finite Automata In theoretical computer science, automata theory is the study of abstract machines (or more appropriately, abstract 'mathematical' machines or systems) and the computational
Automata-based Verification - III
 COMP30172: Advanced Algorithms Automata-based Verification - III Howard Barringer Room KB2.20: email: howard.barringer@manchester.ac.uk March 2009 Third Topic Infinite Word Automata Motivation Büchi Automata
COMP30172: Advanced Algorithms Automata-based Verification - III Howard Barringer Room KB2.20: email: howard.barringer@manchester.ac.uk March 2009 Third Topic Infinite Word Automata Motivation Büchi Automata
EQ: What are limits, and how do we find them? Finite limits as x ± Horizontal Asymptote. Example Horizontal Asymptote
 Finite limits as x ± The symbol for infinity ( ) does not represent a real number. We use to describe the behavior of a function when the values in its domain or range outgrow all finite bounds. For example,
Finite limits as x ± The symbol for infinity ( ) does not represent a real number. We use to describe the behavior of a function when the values in its domain or range outgrow all finite bounds. For example,
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Bid Category
 A Correlation of Pearson to the for Mathematics Bid Category 12-020-20 for Mathematics for Mathematics Ratios and Proportional Relationships 7.RP Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve
A Correlation of Pearson to the for Mathematics Bid Category 12-020-20 for Mathematics for Mathematics Ratios and Proportional Relationships 7.RP Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve
MCPS Algebra 2 and Precalculus Standards, Categories, and Indicators*
 Content Standard 1.0 (HS) Patterns, Algebra and Functions Students will algebraically represent, model, analyze, and solve mathematical and real-world problems involving functional patterns and relationships.
Content Standard 1.0 (HS) Patterns, Algebra and Functions Students will algebraically represent, model, analyze, and solve mathematical and real-world problems involving functional patterns and relationships.
Nonlinear Real Arithmetic and δ-satisfiability. Paolo Zuliani
 Nonlinear Real Arithmetic and δ-satisfiability Paolo Zuliani School of Computing Science Newcastle University, UK (Slides courtesy of Sicun Gao, UCSD) 1 / 27 Introduction We use hybrid systems for modelling
Nonlinear Real Arithmetic and δ-satisfiability Paolo Zuliani School of Computing Science Newcastle University, UK (Slides courtesy of Sicun Gao, UCSD) 1 / 27 Introduction We use hybrid systems for modelling
Büchi Automata and their closure properties. - Ajith S and Ankit Kumar
 Büchi Automata and their closure properties - Ajith S and Ankit Kumar Motivation Conventional programs accept input, compute, output result, then terminate Reactive program : not expected to terminate
Büchi Automata and their closure properties - Ajith S and Ankit Kumar Motivation Conventional programs accept input, compute, output result, then terminate Reactive program : not expected to terminate
Verification of analog and mixed-signal circuits using hybrid systems techniques
 FMCAD, November 2004, Austin Verification of analog and mixed-signal circuits using hybrid systems techniques Thao Dang, Alexandre Donze, Oded Maler VERIMAG Grenoble, France Plan 1. Introduction 2. Verification
FMCAD, November 2004, Austin Verification of analog and mixed-signal circuits using hybrid systems techniques Thao Dang, Alexandre Donze, Oded Maler VERIMAG Grenoble, France Plan 1. Introduction 2. Verification
Hybrid Systems Modeling, Analysis and Control
 Hybrid Systems Modeling, Analysis and Control Radu Grosu Vienna University of Technology Lecture 6 Continuous AND Discrete Systems Control Theory Continuous systems approximation, stability control, robustness
Hybrid Systems Modeling, Analysis and Control Radu Grosu Vienna University of Technology Lecture 6 Continuous AND Discrete Systems Control Theory Continuous systems approximation, stability control, robustness
An Efficient State Space Generation for the Analysis of Real-Time Systems
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science May 2000 An Efficient State Space Generation for the Analysis of Real-Time Systems Inhye
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science May 2000 An Efficient State Space Generation for the Analysis of Real-Time Systems Inhye
Copyright 2012 UC Regents and ALEKS Corporation. ALEKS is a registered trademark of ALEKS Corporation. P. 1/6
 Course Name: MTH099 Fall 2012 Prov Course Code: ADPNR-EADAW ALEKS Course: Beginning and Intermediate Algebra Combined Instructor: Lynd Course Dates: Begin: 08/23/2012 End: 01/20/2013 Course Content: 210
Course Name: MTH099 Fall 2012 Prov Course Code: ADPNR-EADAW ALEKS Course: Beginning and Intermediate Algebra Combined Instructor: Lynd Course Dates: Begin: 08/23/2012 End: 01/20/2013 Course Content: 210
Complexity Issues in Automated Addition of Time-Bounded Liveness Properties 1
 Complexity Issues in Automated Addition of Time-Bounded Liveness Properties 1 Borzoo Bonakdarpour and Sandeep S. Kulkarni Software Engineering and Network Systems Laboratory, Department of Computer Science
Complexity Issues in Automated Addition of Time-Bounded Liveness Properties 1 Borzoo Bonakdarpour and Sandeep S. Kulkarni Software Engineering and Network Systems Laboratory, Department of Computer Science
CISC 4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 1 Regular Languages. Section 1.1: Finite Automata. What is a computer? Finite automata
 CISC 4090: Theory of Computation Chapter Regular Languages Xiaolan Zhang, adapted from slides by Prof. Werschulz Section.: Finite Automata Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences
CISC 4090: Theory of Computation Chapter Regular Languages Xiaolan Zhang, adapted from slides by Prof. Werschulz Section.: Finite Automata Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences
Georgios E. Fainekos, Savvas G. Loizou and George J. Pappas. GRASP Lab Departments of CIS, MEAM and ESE University of Pennsylvania
 Georgios E. Fainekos, Savvas G. Loizou and George J. Pappas CDC 2006 Math free Presentation! Lab Departments of CIS, MEAM and ESE University of Pennsylvania Motivation Motion Planning 60 50 40 π 0 π 4
Georgios E. Fainekos, Savvas G. Loizou and George J. Pappas CDC 2006 Math free Presentation! Lab Departments of CIS, MEAM and ESE University of Pennsylvania Motivation Motion Planning 60 50 40 π 0 π 4
Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period:
 Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period: Chapter 1 1. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. j 44 [1] 2. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. 24 j [2] 3. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period: Chapter 1 1. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. j 44 [1] 2. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. 24 j [2] 3. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
MATH Spring 2010 Topics per Section
 MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
y2 + 4y - 5 c a + b 27 i C) ) (16, ) B) (16 3 3, )
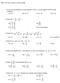 MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
On decision problems for timed automata
 On decision problems for timed automata Olivier Finkel Equipe de Logique Mathématique, U.F.R. de Mathématiques, Université Paris 7 2 Place Jussieu 75251 Paris cedex 05, France. finkel@logique.jussieu.fr
On decision problems for timed automata Olivier Finkel Equipe de Logique Mathématique, U.F.R. de Mathématiques, Université Paris 7 2 Place Jussieu 75251 Paris cedex 05, France. finkel@logique.jussieu.fr
Classes and conversions
 Classes and conversions Regular expressions Syntax: r = ε a r r r + r r Semantics: The language L r of a regular expression r is inductively defined as follows: L =, L ε = {ε}, L a = a L r r = L r L r
Classes and conversions Regular expressions Syntax: r = ε a r r r + r r Semantics: The language L r of a regular expression r is inductively defined as follows: L =, L ε = {ε}, L a = a L r r = L r L r
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment
 Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Liveness in L/U-Parametric Timed Automata
 Liveness in L/U-Parametric Timed Automata Étienne André and Didier Lime [AL17] Université Paris 13, LIPN and École Centrale de Nantes, LS2N Highlights, 14 September 2017, London, England Étienne André
Liveness in L/U-Parametric Timed Automata Étienne André and Didier Lime [AL17] Université Paris 13, LIPN and École Centrale de Nantes, LS2N Highlights, 14 September 2017, London, England Étienne André
Reachability Analysis of Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems using Zonotopes May 7, / 56
 Reachability Analysis of Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems using Zonotopes Matthias Althoff Carnegie Mellon Univ. May 7, 2010 Reachability Analysis of Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems using Zonotopes May 7, 2010
Reachability Analysis of Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems using Zonotopes Matthias Althoff Carnegie Mellon Univ. May 7, 2010 Reachability Analysis of Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems using Zonotopes May 7, 2010
Hybrid Automata and ɛ-analysis on a Neural Oscillator
 Hybrid Automata and ɛ-analysis on a Neural Oscillator A. Casagrande 1 T. Dreossi 2 C. Piazza 2 1 DMG, University of Trieste, Italy 2 DIMI, University of Udine, Italy Intuitively... Motivations: Reachability
Hybrid Automata and ɛ-analysis on a Neural Oscillator A. Casagrande 1 T. Dreossi 2 C. Piazza 2 1 DMG, University of Trieste, Italy 2 DIMI, University of Udine, Italy Intuitively... Motivations: Reachability
Recognizing Safety and Liveness by Alpern and Schneider
 Recognizing Safety and Liveness by Alpern and Schneider Calvin Deutschbein 17 Jan 2017 1 Intro 1.1 Safety What is safety? Bad things do not happen For example, consider the following safe program in C:
Recognizing Safety and Liveness by Alpern and Schneider Calvin Deutschbein 17 Jan 2017 1 Intro 1.1 Safety What is safety? Bad things do not happen For example, consider the following safe program in C:
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems. Lecture #1 Hybrid systems are everywhere: Examples
 Hybrid Control and Switched Systems Lecture #1 Hybrid systems are everywhere: Examples João P. Hespanha University of California at Santa Barbara Summary Examples of hybrid systems 1. Bouncing ball 2.
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems Lecture #1 Hybrid systems are everywhere: Examples João P. Hespanha University of California at Santa Barbara Summary Examples of hybrid systems 1. Bouncing ball 2.
Lecture Notes on Emptiness Checking, LTL Büchi Automata
 15-414: Bug Catching: Automated Program Verification Lecture Notes on Emptiness Checking, LTL Büchi Automata Matt Fredrikson André Platzer Carnegie Mellon University Lecture 18 1 Introduction We ve seen
15-414: Bug Catching: Automated Program Verification Lecture Notes on Emptiness Checking, LTL Büchi Automata Matt Fredrikson André Platzer Carnegie Mellon University Lecture 18 1 Introduction We ve seen
MA 180 Lecture. Chapter 0. College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra
 0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
Natural Numbers: Also called the counting numbers The set of natural numbers is represented by the symbol,.
 Name Period Date: Topic: Real Numbers and Their Graphs Standard: 9-12.A.1.3 Objective: Essential Question: What is the significance of a point on a number line? Determine the relative position on the number
Name Period Date: Topic: Real Numbers and Their Graphs Standard: 9-12.A.1.3 Objective: Essential Question: What is the significance of a point on a number line? Determine the relative position on the number
Rational Numbers and Exponents
 Rational and Exponents Math 7 Topic 4 Math 7 Topic 5 Math 8 - Topic 1 4-2: Adding Integers 4-3: Adding Rational 4-4: Subtracting Integers 4-5: Subtracting Rational 4-6: Distance on a Number Line 5-1: Multiplying
Rational and Exponents Math 7 Topic 4 Math 7 Topic 5 Math 8 - Topic 1 4-2: Adding Integers 4-3: Adding Rational 4-4: Subtracting Integers 4-5: Subtracting Rational 4-6: Distance on a Number Line 5-1: Multiplying
