The Electrical Properties of Saturated Crustal Rocks: Measurement and Implications. Paul Glover University Montpellier II
|
|
|
- Felicia Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Electrical Properties of Saturated Crustal Rocks: Measurement and Implications Paul Glover University Montpellier II 1
2 Structure Basics Ignoring the difficult mathematics Past Experiments Benchtop Multisalinity Confining Pressure Deformation Developments in Montpellier Application to the Pyrennees 2
3 Basic Theory 3
4 Causes in Rocks Matrix Fluid Surface Melt Rock Forming Minerals Minor Minerals Electrolyte Double Layer Molten Rock Hydrated Amphiboles & Clay Minerals Electronic Metal Oxides & Sulphides, & Graphite Electronic Natural Brines Ionic +ve ions on mineral surfaces Ionic ions in melt Ionic 4
5 Fundamentals of Measurement Electrical properties are incredibly sensitive to changes in the rock microstructure Therefore, ideally suited as a probe In-phase and out-of-phase components Vary with frequency (Impedance Spectroscopy) Can vary with AC amplitude (AC Voltammetry) 5
6 Related Measured Variables Measured In-phase impedance, Z Out of phase impedance, Z In-phase admittance, Y Out of phase admittance, Y Scaled real permittivity, e Scaled imaginary permittivity, e Length, L Diameter, D Permeability, k Porosity, f Electrical properties of fluids Specific In-phase resistivity, ρ Out of phase resistivity, ρ In-phase conductivity, σ Out of phase conductivity, σ Real permittivity, ε Imaginary permittivity, ε Real realtive permittivity, K Imag. relative permittivity, K Phase angle, θ Electrical properties of fluids 6
7 Basic Equations I * Z = Z' + i Z " * " * 1 Y ' i Y where Y * Z Y = + = σ ρ * " * 1 = σ ' + i σ where σ = and σ = * ρ * " * 1 = ρ' + i ρ where ρ = and ρ = * σ * * Y L A Z * * L A 7
8 8 Basic Equations II ω σ ε ε ε ε i where i * * " * ' = + = = + = ε ε * * " * ' K where K i K K 2 " ' tan 1 π σ σ θ = σ e μ = n *
9 Argand Plot - ρ 1 Hz Response 1 MHz Functions: ρ Bode Plot Debye ρ ρ ρ ρ ρ o = iωτ - ρ 1 Hz log (Frequency) 1 MHz 9
10 Argand Plot - ρ 1 Hz Response Functions: 1 MHz α ρ Bode Plot Cole & Cole ρ ρ = ρ + ρ o 1 + i ρ ( ) ( 1 ωτ α ) - ρ 1 Hz log (Frequency) 1 MHz 10
11 Rocks Basic Constant Frequency Archie s Law (Archie, 1942) m eff = σ f χ f hence σ τ = ( ) 1 m χ Simple mixing laws to account for only the conductivity of the fluid saturating the pores of the rocks Modified Archie s Law (Glover et al., 2000) (log (1 χ ) log (1 χ )) σ eff = σ mat (1 χ f ) m f f + σ f χ m f 11
12 1 Conventional: m=1.0 Archie s Law Old & New Effective Conductivity (S/m) Conventional: m=1.5 Conventional: m=2.0 Conventional: m=2.5 Modified: m=1.0 Modified: m=1.5 Modified: m=2.0 Modified: m= Volume Fraction of Phase B 12
13 Rocks Added Constant Frequency Bussian (1983) 1 σ eff = σ f + m F 1 F ( ( ) σ ) s Complex theory containing surface conduction BUT still no frequency dependence Revil & Glover (1998) σ f σ = Fξ + ξ ξ + ξ 4, for Fξ ξ F ( ) ( ), 13
14 Fluid Flow in Rocks There exists: An undisturbed central zone of laminar flow, and A surface boundary layer of turbulent flow, and Zero flow at the rock surface 14
15 Electrical Conduction in Rocks There exists: A -ve charged rock surface, and A layer of +ve adsorbed ions, and A net ve diffuse layer [thickness f(salinity)] and Net neutral bulk fluid 15
16 Electrical Conduction in Rocks Boundary of moveable fluids is in diffuse layer Flow separates ve charges to the right and +ve charges are left behind this generates a potential difference called the STREAMING POTENTIAL 16
17 Challenges 17
18 Electrical Properties in Geosciences Theory of bulk and surface conduction in saturated rocks Generalisation to multi-frequency space Improvement of interpretation and analysis of MT data Electrical precursor signals associated with earthquakes Electrical signals associated with volcanic activity Fluid flow mapping in the crust using remote electrical tomography Improved borehole and remote tools for the oil and water industries Characterisation of sites for nuclear waste storage 18
19 Some Progress 19
20 MultiSalinity Experiments (CoCw) 10 Prepare a range of solutions of different salinities Measure the conductivities of each of the solutions Saturate the rock with solution 1 Measure the conductivity of the rock Replace with solution 2 Measure the conductivity of the rock again, and so on Conductivity of Rock (S/m) Clean SST (Berea) Clayey SST (Darley Dale) Conductivity of Solution (S/m) 20
21 Confining Pressure Saturated rocks confined in a hysrostatic oil pressure vessel 4 electrode Pt-blacked Pt system used 0 to 50 and 25 to 400 MPa ranges (2 vessels) Frequency sweeps carried out Rock containing low salinity fluids Size of dispersion curve inflates as pore structure collapses with pressure Shape of dispersion curve does not change 21
22 The Bode Plots 1600 In Phase Resistivity ( ohm.m ) MPa 10 MPa 20 MPa 30 MPa 40 MPa 50 MPa 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 Frequency (Hz) Out of Phase Resistivity ( ohm.m ) MPa 10 MPa 20 MPa 30 MPa 40 MPa 50 MPa 0 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 Frequency (Hz) 22
23 The Argand Plot Out of Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) MPa 10 MPa 20 MPa 30 MPa 40 MPa 50 MPa Confining Pressure Increasing In Phase Resitivity (ohm.m) 23
24 Uniaxial Deformation Saturated rocks confined in a load frame 4 electrode Pt-blacked Pt system used No confining pressure, 0 to 1.5% strain at /s Electrical properties measured at 1000 Hz Rock containing low salinity fluids Shape of conductivity measurements indicate that they mirror two sets of microcracks closing and opening 24
25 See 1 slide 25
26 Triaxial Deformation I Saturated rocks confined in a hydrostatic oil pressure vessel and load frame 4 electrode Pt-blacked Pt system used 50 MPa confining pressure, 0 to 2% strain at /s Electrical properties measured at 1000 Hz and frequency sweeps Rock containing low salinity fluids 26
27 Triaxial Deformation II Size of dispersion curve changes with deformation Initially bigger as cracks close Then smaller as new cracks form and link Shape is similar indicating that the dispersion mechanism is not changing Single frequency measurements indicate that the conductivity is a direction sensitive crack damage parameter This has been used to successfully reconstruct the measured stress-strain curve 27
28 See 4 slides 28
29 Developments at the Université Montpellier II 29
30 The New Measurement Cell Voltage Connexion 2 Fluid Inlet Current Connexion 2 Polyolefin Sleeving PTFE End-piece Sample Perspex Pressure Vessel Perspex Spacers Perspex End Closure BNC Coaxial Connectors Voltage Connexion 1 Fluid Outlet Current Connexion 1 Confining Pressure Inlet Current Electrode Blacked Pt Gauze Filter Paper Voltage Electrode Blacked Pt Gauze Pt100 Sensor Porous Disc SMA Gold-Plated Coaxial Connectors Temperature Lead-through Swagelock Fittings (Drilled-out) 30
31 The Cell Fully Assembled 31
32 The Cell in its Retaining Box Non-conducting materials 4 or 2 electrodes Pt-blacked Pt Gauze Heat-shrink sleeving with silicone 50 Ω miniature coaxial leads with SMC connectors 32
33 P Fluid resur e Solartr Impe dance on129 4 Tempe raturec ontrol er Loger Inte rface 5 0TerΩ minatio ns Fans (x2) S tirers Re servoirs Solartr F RA on1260 Plex iglas Cabine Heater PreTrans ducersure Transdu Pres ure cer ReturnT Pump 1 Reservo (Syrin Pump 2ge) Mea sureme ntcel (Perista ltic) Pt10 1 0BarGa CP resure onfining Schematic Diagram of the Rig Rig in temperatures controlled enclosure Heater, fans and special control box Measurements made from 10 μhz to 32 MHz Solartron 1260 FRA Logging of fluid pressures, with back pressure 33
34 The Assembled Rig Entire fluid process in temperature controlled environment All measurements logged to PC Shielded, low electrical noise apparatus 34
35 Dummy Test Measurements 10 μhz to 32 MHz Noise-free measurements Single dispersion curve for 501 nf element In Phase Impedance (Ω) = log10 (1/2πRC) = 3.18 khz Out of Phase Impedance (Ω) log10 (Frequency (Hz)) 35
36 New Fluid Change Experiments Single Frequency 200 Hz Changing Fluids from Distilled Water to 1 M NaCl Porosity = 0.12 NaCl (M) m Distilled In Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) Distilled Water to 0.01 M NaCl 0.01 M NaCl to 0.1 M NaCl 0.1 M NaCl to 1 M NaCl Time (s) 36
37 New CoCw Measurements 1.E+00 1.E-01 Effective Conductivity (S/m) 1.E-02 1.E-03 1.E-04 1.E-05 Gres de Fontainebleau Gres de Clashach 1.E-06 1.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 Fluid Conductivity (S/m) 37
38 New Electro-Kinetic Measurements Gres de Fontainebleau 0 0 Zeta Potential (mv) Streaming Potential (mv) Pressure Difference (MPa)
39 New Impedance Measurements Gres de Fontainebleau Bode Diagram Argand Diagram No Flow 200 ml/hr 39
40 Spectroscopy of Carrara Marble Flow causes charge separation that takes 2 days to relax Now known to be ARTIFACT In Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) 150 Initial No Flow 130 Flow Stopped 0.5 hrs Flow Stopped 1.33 hrs 110 Flow Stopped 4.23 hrs Flow Stopped hrs Flow Stopped hrs E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 1.E+07 Out of Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) Initial No Flow Flow Stopped 0.5 hrs Flow Stopped 1.33 hrs Flow Stopped 4.23 hrs Flow Stopped hrs Flow Stopped hrs Out of Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) Initial No Flow Flow Stopped 0.5 hrs Flow Stopped 1.33 hrs Flow Stopped 4.23 hrs Flow Stopped hrs Flow Stopped hrs Frequency (Hz) In Phase Resistivity (ohm.m) 5 1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 1.E+07 Frequency (Hz) 40
41 Crustal Conductivity Modelling 41
42 Location of the Study 42
43 Questions What are the mechanisms of the conductivities in the crust and mantle? What is the mechanism of the high conductivities in the slab? If the slab high conductivities are caused by partial melting, what is the partial melt fraction and what is the melt connectivity? Why is there no surface volcanism in the Pyrenees? 43
44 Fluid Salinity & Conductivity Lab. Rock Conductivities Elevation Model Structure Pressure Predicted Conductivitiesor Melt Fractions Parallel Layer Thermal Properties Gravity Seismic Structure Lithology Density Rock Conductivity Prescribed Melt Fraction Melt Conductivity Waff/HS Upper Bound Random Areas Modified Archie s Law HS Lower Bound Lab. Melt Conductivities Temperature Perp. Layer MT Conductivity For Comparison 44
45 Mixing Models 6 mixing Models have been used: Parallel model (arithmetic mean) Hashin-Shtrikman upper bound Waff s model Random model (geometric mean) Modified Archie s law Hashin-Shtrikman lower bound Perpendicular model (harmonic mean) Well Connected Melt Moderately Connected Melt Badly Connected Melt 45
46 Effective Conductivity MT Observed Conductivities 46
47 Effective Conductivity Hashin- Shtrikman Upper Bound/Waff s Model 47
48 Effective Conductivity Hashin- Shtrikman Lower Bound 48
49 All Effective Conductivity Models 49
50 Melt Fraction Hashin- Shtrikman Upper Bound/Waff s Model 50
51 Melt Fraction Hashin- Shtrikman Lower Bound 51
52 Summary I A two-dimensional conductivity model for the Pyrenees has been constructed A good match to the conductivities observed by MT is possible Aqueous fluids alone can explain the conductivity in most of the profile Aqueous fluids cannot explain the conductivity of the subducting slab 52
53 Summary II Partial melting is likely to be the cause of the very high slab conductivities A partial melt fraction of at least 4.7% is necessary This is consistent with geochemical melting models The melt must be well connected The absence of surface volcanism is partly due to its compressive tectonic regime, and volcanism is likely in the Pyrenees if the area becomes extensive 53
PERMITTIVITY VARIATIONS ON MARBLE BEAMS SUBJECTED TO VARIOUS LOADING LEVELS
 The 1 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing»Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering«September 1-3, 29, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 431-436
The 1 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing»Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering«September 1-3, 29, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 431-436
Hydrological geophysical relationships
 International PhD Course in HYDROGEOPHYSICS Hydrological geophysical relationships Andrew Binley Lancaster University Overview In the course we will concentrate on electrical, electromagnetic and radar
International PhD Course in HYDROGEOPHYSICS Hydrological geophysical relationships Andrew Binley Lancaster University Overview In the course we will concentrate on electrical, electromagnetic and radar
MODELLING THE STRESS-STRAIN BEHAVIOUR OF SATURATED ROCKS UNDERGOING TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION USING COMPLEX ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY MEASUREMENTS
 MODELLING THE STRESS-STRAIN BEHAVIOUR OF SATURATED ROCKS UNDERGOING TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION USING COMPLEX ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY MEASUREMENTS R W. J. GLOVER 1, J. B. GOMEZ 2, R G. MEREDITH 2, S. A. BOON
MODELLING THE STRESS-STRAIN BEHAVIOUR OF SATURATED ROCKS UNDERGOING TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION USING COMPLEX ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY MEASUREMENTS R W. J. GLOVER 1, J. B. GOMEZ 2, R G. MEREDITH 2, S. A. BOON
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System
 Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System Combined Resonant Column (RC) & Torsional Cyclic Shear (TCS) Test apparatus to determinate with saturated soil : Shear Modulus Damping Modulus versus Shear
Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System Combined Resonant Column (RC) & Torsional Cyclic Shear (TCS) Test apparatus to determinate with saturated soil : Shear Modulus Damping Modulus versus Shear
Anisotropic permeabilities evolution of reservoir rocks under pressure:
 Extended reserves Clean refining Fuel-efficient vehicles Diversified fuels Controlled CO 2 Anisotropic permeabilities evolution : New experimental and numerical approaches (1) Dautriat J. 1-2*, Gland N.
Extended reserves Clean refining Fuel-efficient vehicles Diversified fuels Controlled CO 2 Anisotropic permeabilities evolution : New experimental and numerical approaches (1) Dautriat J. 1-2*, Gland N.
(name) Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant. Final Exam
 10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
Dielectric Properties of Oil Shale
 Dielectric Properties of Oil Shale Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 26th Oil Shale Symposium, Golden CO, October 16-18, 26 Jeffery Roberts. Jerry Sweeney. Philip Harben. Steve Carlson UCRL-ABS-222487
Dielectric Properties of Oil Shale Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 26th Oil Shale Symposium, Golden CO, October 16-18, 26 Jeffery Roberts. Jerry Sweeney. Philip Harben. Steve Carlson UCRL-ABS-222487
Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics
 Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics (Source: Matthew Becker, California State University) Site Characterization Definition: quantitative description of the hydraulic, geologic, and chemical properties
Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics (Source: Matthew Becker, California State University) Site Characterization Definition: quantitative description of the hydraulic, geologic, and chemical properties
Electrical Surveying (part A)
 Electrical Surveying (part A) Dr. Laurent Marescot Course given at the University of Fribourg (2009) Contact: laurent@tomoquest.com www.tomoquest.com 1 Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method
Electrical Surveying (part A) Dr. Laurent Marescot Course given at the University of Fribourg (2009) Contact: laurent@tomoquest.com www.tomoquest.com 1 Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method
Tectonics. Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting GNH7/GG09/GEOL4002 EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
 Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
1. Resistivity of rocks
 RESISTIVITY 1) Resistivity of rocks 2) General principles of resistivity surveying 3) Field procedures, interpretation and examples 4) Summary and conclusions INDUCED POLARIZATION 1) General principles
RESISTIVITY 1) Resistivity of rocks 2) General principles of resistivity surveying 3) Field procedures, interpretation and examples 4) Summary and conclusions INDUCED POLARIZATION 1) General principles
INVESTIGATION ON THE EFFECT OF STRESS ON CEMENTATION FACTOR OF IRANIAN CARBONATE OIL RESERVOIR ROCKS
 SCA4-41 1/7 INVESTIGATION ON THE EFFECT OF STRESS ON CEMENTATION FACTOR OF IRANIAN CARBONATE OIL RESERVOIR ROCKS R. Behin, RIPI, NIOC This paper was prepared for presentation at the International Symposium
SCA4-41 1/7 INVESTIGATION ON THE EFFECT OF STRESS ON CEMENTATION FACTOR OF IRANIAN CARBONATE OIL RESERVOIR ROCKS R. Behin, RIPI, NIOC This paper was prepared for presentation at the International Symposium
Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with high salinity NaCl brine
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L21306, doi:10.1029/2009gl040549, 2009 Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with high salinity NaCl brine M. Z. Jaafar,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L21306, doi:10.1029/2009gl040549, 2009 Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with high salinity NaCl brine M. Z. Jaafar,
Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization
 Observation Scale Wavelength 10 0 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 12 10 16 10 18 10 20 Frequency (Hz) Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization Elastic, Mechanical, Petrophysical
Observation Scale Wavelength 10 0 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 12 10 16 10 18 10 20 Frequency (Hz) Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization Elastic, Mechanical, Petrophysical
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT. 6.1 Introduction. 6.2 Overburden Pressures
 6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
RESEARCH PROPOSAL. Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q. Yi Shen
 RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
Rock Mechanics Laboratory Tests for Petroleum Applications. Rob Marsden Reservoir Geomechanics Advisor Gatwick
 Rock Mechanics Laboratory Tests for Petroleum Applications Rob Marsden Reservoir Geomechanics Advisor Gatwick Summary A wide range of well established and proven laboratory tests are available for petroleum
Rock Mechanics Laboratory Tests for Petroleum Applications Rob Marsden Reservoir Geomechanics Advisor Gatwick Summary A wide range of well established and proven laboratory tests are available for petroleum
Effect of Dielectric Permittivity Distribution in Invaded Zone on Induction Log Data
 Effect of Dielectric Permittivity Distribution in Invaded Zone on Induction Log Data Igor Yeltsov 1,2,3, Timofey Eltsov 1,2,3, Aleksandr Makarov 4, and Marina Nikitenko 1,4 1 Institute of Petroleum Geology
Effect of Dielectric Permittivity Distribution in Invaded Zone on Induction Log Data Igor Yeltsov 1,2,3, Timofey Eltsov 1,2,3, Aleksandr Makarov 4, and Marina Nikitenko 1,4 1 Institute of Petroleum Geology
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP)
 Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLARY PRESSURE AND RESISTIVITY INDEX
 SCA2005-4 /2 ELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLAY PESSUE AND ESISTIVITY INDEX Kewen Li *, Stanford University and Yangtz University and Wade Williams, Core Lab, Inc. * Corresponding author This paper was prepared
SCA2005-4 /2 ELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLAY PESSUE AND ESISTIVITY INDEX Kewen Li *, Stanford University and Yangtz University and Wade Williams, Core Lab, Inc. * Corresponding author This paper was prepared
Dielectric Analysis of Insulation Liquids
 using Liquid Test Fixture 16451A from Keysight By Britta Pfeiffer 2018 by OMICRON Lab V1.0 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support. Page 2
using Liquid Test Fixture 16451A from Keysight By Britta Pfeiffer 2018 by OMICRON Lab V1.0 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support. Page 2
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration
 The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
Chapter 4 Influences of Compositional, Structural and Environmental Factors on. Soil EM Properties
 Chapter 4 Influences of Compositional, Structural and Environmental Factors on Soil EM Properties 4. 1 Introduction The measured soil electromagnetic properties can be affected by a large number of factors
Chapter 4 Influences of Compositional, Structural and Environmental Factors on Soil EM Properties 4. 1 Introduction The measured soil electromagnetic properties can be affected by a large number of factors
Crack-initiation and fracture propagation in reservoir rocks
 Crack-initiation and fracture propagation in reservoir rocks Srutarshi Pradhan Fracture & Flow meeting, January 2013, IMSc, Chennai, India 1 Dynamics of fracture Crack-growth in nano-materials onset of
Crack-initiation and fracture propagation in reservoir rocks Srutarshi Pradhan Fracture & Flow meeting, January 2013, IMSc, Chennai, India 1 Dynamics of fracture Crack-growth in nano-materials onset of
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics
 Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Crosswell tomography imaging of the permeability structure within a sandstone oil field.
 Crosswell tomography imaging of the permeability structure within a sandstone oil field. Tokuo Yamamoto (1), and Junichi Sakakibara (2) (1) University of Miami and Yamamoto Engineering Corporation, (2)
Crosswell tomography imaging of the permeability structure within a sandstone oil field. Tokuo Yamamoto (1), and Junichi Sakakibara (2) (1) University of Miami and Yamamoto Engineering Corporation, (2)
SRC software. Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties
 SRC software Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties Outline About SRC software. Introduction to rock modelling. Rock modelling program structure. Examples
SRC software Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties Outline About SRC software. Introduction to rock modelling. Rock modelling program structure. Examples
4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration
 Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Estimating Permeability from Acoustic Velocity and Formation Resistivity Factor
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 582-587 and Formation Resistivity Factor Majid Nabi-Bidhendi Institute of Geophysics, University of Tehran, P.O. Box 14155-6466,
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 582-587 and Formation Resistivity Factor Majid Nabi-Bidhendi Institute of Geophysics, University of Tehran, P.O. Box 14155-6466,
Reservoir Rock Properties COPYRIGHT. Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study
 Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay
 Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay Financial support of the EU: SELFRAC scientific project DIGA network Cécile Coll (GeomaC, Liège) Jacques
Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay Financial support of the EU: SELFRAC scientific project DIGA network Cécile Coll (GeomaC, Liège) Jacques
Critical Borehole Orientations Rock Mechanics Aspects
 Critical Borehole Orientations Rock Mechanics Aspects By R. BRAUN* Abstract This article discusses rock mechanics aspects of the relationship between borehole stability and borehole orientation. Two kinds
Critical Borehole Orientations Rock Mechanics Aspects By R. BRAUN* Abstract This article discusses rock mechanics aspects of the relationship between borehole stability and borehole orientation. Two kinds
Geoelectricity. ieso 2010
 Geoelectricity ieso 2010 1 RESISTIVITY SURVEY AT VENETO VILLA GRITTI AT THE TOWN OF TREVISO (VENETO REGION) The survey was carried out to verify the underground presence of the fondations of a rustic building.
Geoelectricity ieso 2010 1 RESISTIVITY SURVEY AT VENETO VILLA GRITTI AT THE TOWN OF TREVISO (VENETO REGION) The survey was carried out to verify the underground presence of the fondations of a rustic building.
VI. Porous Media. Lecture 34: Transport in Porous Media
 VI. Porous Media Lecture 34: Transport in Porous Media 4/29/20 (corrected 5/4/2 MZB) Notes by MIT Student. Conduction In the previous lecture, we considered conduction of electricity (or heat conduction
VI. Porous Media Lecture 34: Transport in Porous Media 4/29/20 (corrected 5/4/2 MZB) Notes by MIT Student. Conduction In the previous lecture, we considered conduction of electricity (or heat conduction
Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua
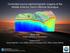 Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua Kerry Key Scripps Institution of Oceanography Collaborators: Samer Naif (SIO, now LDEO), Steven Constable (SIO),
Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua Kerry Key Scripps Institution of Oceanography Collaborators: Samer Naif (SIO, now LDEO), Steven Constable (SIO),
Sections Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas
 Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Capacity fade studies of Lithium Ion cells
 Capacity fade studies of Lithium Ion cells by Branko N. Popov, P.Ramadass, Bala S. Haran, Ralph E. White Center for Electrochemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of South
Capacity fade studies of Lithium Ion cells by Branko N. Popov, P.Ramadass, Bala S. Haran, Ralph E. White Center for Electrochemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of South
ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF INTACT AND FRACTURED GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ROCKS
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 2001 SGP-TR-168 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF INTACT AND FRACTURED
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 2001 SGP-TR-168 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF INTACT AND FRACTURED
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luong, D. T. (2014). Electrokinetics in porous media General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luong, D. T. (2014). Electrokinetics in porous media General
DEVEX 2016 Masterclass Pt:2 Continuous core data = Less Uncertainty? Craig Lindsay Core Specialist Services Limited
 DEVEX 2016 Masterclass Pt:2 Continuous core data = Less Uncertainty? Craig Lindsay Core Specialist Services Limited Themes for discussion: Sampling frequency Impact of heterogeneity Value of continuous
DEVEX 2016 Masterclass Pt:2 Continuous core data = Less Uncertainty? Craig Lindsay Core Specialist Services Limited Themes for discussion: Sampling frequency Impact of heterogeneity Value of continuous
Pore radius distribution and fractal dimension derived from spectral induced polarization
 Pore radius distribution and fractal dimension derived from spectral induced polarization Zeyu Zhang 1 & Andreas Weller 2 1) Southwest Petroleum University, China & Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung
Pore radius distribution and fractal dimension derived from spectral induced polarization Zeyu Zhang 1 & Andreas Weller 2 1) Southwest Petroleum University, China & Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung
Functionalization of reduced graphene oxides by redox-active ionic liquids for energy storage
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Functionalization of reduced graphene oxides by redox-active ionic liquids for energy storage Sung Dae Cho, a Jin Kyu Im, b Han-Ki Kim, c Hoon Sik
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Functionalization of reduced graphene oxides by redox-active ionic liquids for energy storage Sung Dae Cho, a Jin Kyu Im, b Han-Ki Kim, c Hoon Sik
*To whom correspondence should be addressed. This file includes text and figures divided into four supplementary items:
 Supplementary Materials for: Porosity evolution at the brittle-ductile transition in the continental crust: Implications for deep hydro-geothermal circulation. Violay M., Heap M.J., Acosta M., and Madonna
Supplementary Materials for: Porosity evolution at the brittle-ductile transition in the continental crust: Implications for deep hydro-geothermal circulation. Violay M., Heap M.J., Acosta M., and Madonna
First Field Test of NAPL Detection with High Resolution Borehole Seismic Imaging
 1 First Field Test of NAPL Detection with High Resolution Borehole Seismic Imaging Jil T. Geller, John E. Peterson, Kenneth H. Williams, Jonathan B. Ajo!Franklin*, and Ernest L. Majer Earth Sciences Division,
1 First Field Test of NAPL Detection with High Resolution Borehole Seismic Imaging Jil T. Geller, John E. Peterson, Kenneth H. Williams, Jonathan B. Ajo!Franklin*, and Ernest L. Majer Earth Sciences Division,
PETROPHYSICAL STUDIES OF SANDSTONES UNDER TRUE-TRIAXIAL STRESS CONDITIONS
 PETROPHYSICAL STUDIES OF SANDSTONES UNDER TRUE-TRIAXIAL STRESS CONDITIONS M.S. King, S.Al-Harthy * and X.D. Jing **, Centre for Petroleum Studies, Royal School of Mines Imperial College of Science, Technology
PETROPHYSICAL STUDIES OF SANDSTONES UNDER TRUE-TRIAXIAL STRESS CONDITIONS M.S. King, S.Al-Harthy * and X.D. Jing **, Centre for Petroleum Studies, Royal School of Mines Imperial College of Science, Technology
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood
 Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Mohr Coulomb failure criterion with Mohr circle of stress 2 ' 2 ' ' ' 3 ' 1 ' 3 ' 1 Cot Sin c ' ' 2
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Mohr Coulomb failure criterion with Mohr circle of stress 2 ' 2 ' ' ' 3 ' 1 ' 3 ' 1 Cot Sin c ' ' 2
Seismic wave attenuation at low frequencies: measurements and mechanisms
 Seismic wave attenuation at low frequencies: measurements and mechanisms Nicola Tisato*, Claudio Madonna, Erik H. Saenger (ETH Zurich & Spectraseis) nicola.tisato@erdw.ethz.ch Why The study of fluid saturation
Seismic wave attenuation at low frequencies: measurements and mechanisms Nicola Tisato*, Claudio Madonna, Erik H. Saenger (ETH Zurich & Spectraseis) nicola.tisato@erdw.ethz.ch Why The study of fluid saturation
Geology 228/378 Applied & Environmental Geophysics Lecture 8. Induced Polarization (IP) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
 Geology 228/378 Applied & Environmental Geophysics Lecture 8 Induced Polarization (IP) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Induced Polarization (IP) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) 1. Time domain
Geology 228/378 Applied & Environmental Geophysics Lecture 8 Induced Polarization (IP) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Induced Polarization (IP) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) 1. Time domain
PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES
 Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
Module 5: Failure Criteria of Rock and Rock masses. Contents Hydrostatic compression Deviatoric compression
 FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION
 LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION Jack Dvorkin Stanford University and Rock Solid Images April 25, 2005 SUMMARY In a viscoelastic sample, the causality principle links the attenuation of
LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION Jack Dvorkin Stanford University and Rock Solid Images April 25, 2005 SUMMARY In a viscoelastic sample, the causality principle links the attenuation of
Scaling Analysis of Energy Storage by Porous Electrodes
 Scaling Analysis of Energy Storage by Porous Electrodes Martin Z. Bazant May 14, 2012 1 Theoretical Capacity The maximum theoretical capacity occurs as E i 0, E p 0 E a 1, where E i, E p, and E a are the
Scaling Analysis of Energy Storage by Porous Electrodes Martin Z. Bazant May 14, 2012 1 Theoretical Capacity The maximum theoretical capacity occurs as E i 0, E p 0 E a 1, where E i, E p, and E a are the
Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks
 Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks Philip Meredith Mineral, Ice & Rock Physics Laboratory Department of Earth Sciences University College London Euroconference, Erice, September
Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks Philip Meredith Mineral, Ice & Rock Physics Laboratory Department of Earth Sciences University College London Euroconference, Erice, September
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY
 ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
Fracturing in saturated rocks undergoing triaxial deformation using complex electrical conductivity measurements: experimental study
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 5621 (2000) 201^213 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Fracturing in saturated rocks undergoing triaxial deformation using complex electrical conductivity measurements: experimental
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 5621 (2000) 201^213 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Fracturing in saturated rocks undergoing triaxial deformation using complex electrical conductivity measurements: experimental
P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response
 P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response Tiewei He* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada tieweihe@phys.ualberta.ca and Douglas Schmitt University
P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response Tiewei He* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada tieweihe@phys.ualberta.ca and Douglas Schmitt University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary information: Our 1080 km x 360 km model setup includes a 7 km thick oceanic crust adjacent to a 60 km thick, 250 km wide orogenic crust. Both the oceanic and the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary information: Our 1080 km x 360 km model setup includes a 7 km thick oceanic crust adjacent to a 60 km thick, 250 km wide orogenic crust. Both the oceanic and the
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
 Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with natural and artificial brines at high salinity
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007593, 2010 Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with natural and artificial brines at high salinity
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007593, 2010 Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with natural and artificial brines at high salinity
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK
 THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
Coupled seismoelectric wave propagation in porous media. Mehran Gharibi Robert R. Stewart Laurence R. Bentley
 Coupled seismoelectric wave propagation in porous media Mehran Gharibi Robert R. Stewart Laurence R. Bentley a Introduction Seismic waves induce electric and magnetic fields. Conversion of acoustic energy
Coupled seismoelectric wave propagation in porous media Mehran Gharibi Robert R. Stewart Laurence R. Bentley a Introduction Seismic waves induce electric and magnetic fields. Conversion of acoustic energy
Effect of Gas Hydrate Saturation on Hydraulic Conductivity of Marine Sediments
 Effect of Gas Hydrate Saturation on Hydraulic Conductivity of Marine Sediments *Chul-Whan Kang 1), Ah-Ram Kim 2), Hak-Sung Kim 3), Gye-Chun Cho 4) and Joo-Yong Lee 5) 1), 2), 3), 4) Department of Civil
Effect of Gas Hydrate Saturation on Hydraulic Conductivity of Marine Sediments *Chul-Whan Kang 1), Ah-Ram Kim 2), Hak-Sung Kim 3), Gye-Chun Cho 4) and Joo-Yong Lee 5) 1), 2), 3), 4) Department of Civil
VMS-GeoMil. Background
 Background When using a drilling rig for cone penetration testing, a mechanical clamp can be mounted to the drilling head (by means of a special transition piece). The depth than can be achieved depends
Background When using a drilling rig for cone penetration testing, a mechanical clamp can be mounted to the drilling head (by means of a special transition piece). The depth than can be achieved depends
Global geophysics and wave propagation
 Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
Dynamic analysis. 1. Force and stress
 Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells
 Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
Layer Composition Thickness State of Matter
 Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
GG 454 March 19, EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26)
 GG 454 March 19, 2002 1 EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26) I Main Topics A Driving and resisting stresses at the base of an inclined block B Factor of safety C Effective stress D Mohr-Coulomb
GG 454 March 19, 2002 1 EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26) I Main Topics A Driving and resisting stresses at the base of an inclined block B Factor of safety C Effective stress D Mohr-Coulomb
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Part 7. Nonlinearity
 Part 7 Nonlinearity Linear System Superposition, Convolution re ( ) re ( ) = r 1 1 = r re ( 1 + e) = r1 + r e excitation r = r() e response In the time domain: t rt () = et () ht () = e( τ) ht ( τ) dτ
Part 7 Nonlinearity Linear System Superposition, Convolution re ( ) re ( ) = r 1 1 = r re ( 1 + e) = r1 + r e excitation r = r() e response In the time domain: t rt () = et () ht () = e( τ) ht ( τ) dτ
A study on the Variation of Streaming Potential Coefficient with Physical Parameters of Rocks
 VNU Journal o Science: Mathematics Physics, Vol. 33, No. 1 (2017) 60-68 A study on the Variation o Streaming Potential Coeicient with Physical Parameters o Rocks Luong Duy Thanh 1,*, Rudol Sprik 2 1 Thuy
VNU Journal o Science: Mathematics Physics, Vol. 33, No. 1 (2017) 60-68 A study on the Variation o Streaming Potential Coeicient with Physical Parameters o Rocks Luong Duy Thanh 1,*, Rudol Sprik 2 1 Thuy
Fracture of andesite in the brittle and brittleductile transition regimes
 Fracture of andesite in the brittle and brittleductile transition regimes R. Smith 1,*, P.R. Sammonds 1, C.R.J. Kilburn 1, H. Tuffen 2,1 1. Department of Earth Sciences, UCL, Gower Street, London, WC1E
Fracture of andesite in the brittle and brittleductile transition regimes R. Smith 1,*, P.R. Sammonds 1, C.R.J. Kilburn 1, H. Tuffen 2,1 1. Department of Earth Sciences, UCL, Gower Street, London, WC1E
A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials
 A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials Chloé Arson ALERT PhD Prize PhD Advisor : Behrouz Gatmiri Paris-Est University, U.R. Navier, geotechnical group (CERMES) This research
A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials Chloé Arson ALERT PhD Prize PhD Advisor : Behrouz Gatmiri Paris-Est University, U.R. Navier, geotechnical group (CERMES) This research
EIS of Organic Coatings and Paints
 EIS of Organic Coatings and Paints Introduction All My Impedance Spectra Look the Same! "I m an experienced polymer chemist. I m trying to use Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) to predict the
EIS of Organic Coatings and Paints Introduction All My Impedance Spectra Look the Same! "I m an experienced polymer chemist. I m trying to use Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) to predict the
Electroseismics for CO 2 storage and hydrocarbon reservoirs. Fabio I. Zyserman
 Electroseismics for CO 2 storage and hydrocarbon reservoirs Fabio I. Zyserman EOST, March 12th, 213 Electroseismics: field experiments Thompson et al, 27 Electroseismic response in gas and oil reservoirs
Electroseismics for CO 2 storage and hydrocarbon reservoirs Fabio I. Zyserman EOST, March 12th, 213 Electroseismics: field experiments Thompson et al, 27 Electroseismic response in gas and oil reservoirs
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background
 The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
Well Logging. Salam Al Rbeawi 2011
 Well Logging Salam Al Rbeawi 2011 Well Logging: Is a technique used for formation evaluation to determine the size of the reservoir and the amount of oil and gas in place. The following parameters can
Well Logging Salam Al Rbeawi 2011 Well Logging: Is a technique used for formation evaluation to determine the size of the reservoir and the amount of oil and gas in place. The following parameters can
Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
 Newly formed rock from rising magma rises above sea floor and forms mountain ranges known as midocean ridges. Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
Newly formed rock from rising magma rises above sea floor and forms mountain ranges known as midocean ridges. Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082
 Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082 Introduction K T : relative dielectric constant of the material ε o : relative permittivity of free space (8.854*10-12 F/m) h: distance between electrodes (m - material
Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082 Introduction K T : relative dielectric constant of the material ε o : relative permittivity of free space (8.854*10-12 F/m) h: distance between electrodes (m - material
Modelling of viscoelastic properties of a curing adhesive
 Computational Methods and Experiments in Materials Characterisation III 241 Modelling of viscoelastic properties of a curing adhesive J. de Vreugd 1, K. M. B. Jansen 1, L. J. Ernst 1 & J. A. C. M. Pijnenburg
Computational Methods and Experiments in Materials Characterisation III 241 Modelling of viscoelastic properties of a curing adhesive J. de Vreugd 1, K. M. B. Jansen 1, L. J. Ernst 1 & J. A. C. M. Pijnenburg
TIME DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY (TDR) IN MEASURING WATER CONTENTS AND HYDRATE SATURATIONS IN MARINE SEDIMENTS
 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2011), Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom, July 17-21, 2011. TIME DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY (TDR) IN MEASURING WATER CONTENTS AND HYDRATE
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2011), Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom, July 17-21, 2011. TIME DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY (TDR) IN MEASURING WATER CONTENTS AND HYDRATE
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT
 PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT Charles G. Sammis and Ronald L. Biegel University of Southern California Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No. FA8718-04-C-0012 ABSTRACT
PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT Charles G. Sammis and Ronald L. Biegel University of Southern California Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No. FA8718-04-C-0012 ABSTRACT
Electrical Methods. Resistivity Surveying
 Electrical Methods Resistivity Surveying Geologic Resistivity 1101 Resistivity surveying investigates variations of electrical resistance, by causing an electrical current to flow through the subsurface
Electrical Methods Resistivity Surveying Geologic Resistivity 1101 Resistivity surveying investigates variations of electrical resistance, by causing an electrical current to flow through the subsurface
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER
 VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications
 Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications Lecture Note 7 May 19, 2014 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Electrochemical
Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications Lecture Note 7 May 19, 2014 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Electrochemical
Land seismic sources
 Seismic Sources HOW TO GENERATE SEISMIC WAVES? Exploration seismology mostly artificial sources à active technique Natural sources can also be used (e.g. earthquakes) usually for tectonic studies (passive
Seismic Sources HOW TO GENERATE SEISMIC WAVES? Exploration seismology mostly artificial sources à active technique Natural sources can also be used (e.g. earthquakes) usually for tectonic studies (passive
Structural Engineering Research Group (SERG) April 10, 2013 Dielectric Modeling of Hydrated Cement Paste Panels
 Structural Engineering Research Group (SERG) April 10, 2013 Dielectric Modeling of Hydrated Cement Paste Panels Hao Liu Advisor: Dr. Tzu-Yang Yu Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
Structural Engineering Research Group (SERG) April 10, 2013 Dielectric Modeling of Hydrated Cement Paste Panels Hao Liu Advisor: Dr. Tzu-Yang Yu Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
Introduction. Electrical surveying. Resistivity method Induced polarization method (IP) Self-potential (SP) method
 Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method Induced polarization method (IP) Self-potential (SP) method Higher frequency methods (electromagnetic surveys): Electromagnetic induction methods Ground
Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method Induced polarization method (IP) Self-potential (SP) method Higher frequency methods (electromagnetic surveys): Electromagnetic induction methods Ground
Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa.
 2053-11 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Seismic monitoring on volcanoes in a multi-disciplinary context Jürgen
2053-11 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Seismic monitoring on volcanoes in a multi-disciplinary context Jürgen
Announcements. Manganese nodule distribution
 Announcements Lithospheric plates not as brittle as previously thought ESCI 322 Meet in Env. Studies Bldg Rm 60 at 1 PM on Tuesday One week (Thursday): Quiz on Booth 1994 and discussion. (Lots of odd terms
Announcements Lithospheric plates not as brittle as previously thought ESCI 322 Meet in Env. Studies Bldg Rm 60 at 1 PM on Tuesday One week (Thursday): Quiz on Booth 1994 and discussion. (Lots of odd terms
ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF ANDESITE AND HYDROTHERMAL BRECCIA FROM THE AWIBENGKOK GEOTHERMAL FIELD, INDONESIA
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 24-26, 2000 SGP-TR-165 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF ANDESITE AND HYDROTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 24-26, 2000 SGP-TR-165 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENTS OF ANDESITE AND HYDROTHERMAL
Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
 Transp Porous Med (2018) 124:31 56 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1036-z Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
Transp Porous Med (2018) 124:31 56 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1036-z Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
e - Galvanic Cell 1. Voltage Sources 1.1 Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell
 Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE
 181 ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE Sukhyoun Kim, Graham Heinson & John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Adelaide, SA, 5005 ABSTRACT
181 ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE Sukhyoun Kim, Graham Heinson & John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Adelaide, SA, 5005 ABSTRACT
Rheology and the Lithosphere
 Rheology and the Lithosphere Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/8/2017 16:51 We Discuss Rheology and the Lithosphere What is rheology?
Rheology and the Lithosphere Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/8/2017 16:51 We Discuss Rheology and the Lithosphere What is rheology?
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
