Applications of Coherent X-Rays at the LCLS
|
|
|
- Ethel Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applications of Coherent X-Rays at the LCLS Gerhard Grübel Notke-Strasse Hamburg Germany SLAC, October 17,
2 LCLS and coherence based techniques Imaging techniques (CDI, FTH) X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) Recent developments and results Conclusions SLAC, October 17,
3 LCLS Characteristics LCLS radiation (0.8-8 kev) ultrashort pulse duration 100 fs extreme pulse intensities ph coherent radiation Coherence based Imaging techniques Coherent Diffraction Imaging (CDI) Fourier Transform Holography (FTH) X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) SLAC, October 17,
4 Coherence Coherence based based Imaging Imaging techniques techniques Phase retrieval algorithm lensless, resolution limited hard x-rays: shorter lengthscales, bulksensitivity and compatibility with extreme conditions obey over-sampling condition or use reference beam (FTH) Short pulse: snapshots (pump-probe) overcome damage limits SLAC, October 17,
5 X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) dynamics on short lengthscales in the time domain reciprocal space technique hard x-rays: shorter lengthscales, bulk-sensitivity and compatibility with extreme conditions (coherent) flux limited (τ >μs) S(Q,t) dynamic structure factor Short pulse: ns-fs timescale SLAC, October 17,
6 LCLS and coherence based techniques Imaging techniques (CDI, FTH) X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) Recent developments and results Conclusions SLAC, October 17,
7 Coherent Diffraction Imaging (CDI) Reconstruction (phasing) of a speckle pattern: oversampling technique gold dots on SiN membrane λ=17å coherent beam at X1A reconstruction (0.1 μm diameter, 80 nm thick) (NSLS), ph/s 10μm pinhole oversampling technique 24 μm x 24 μm pixel CCD Miao, Charalambous, Kirz, Sayre, Nature, 400, July 1999 SLAC, October 17,
8 Single Molecule Diffraction An approach to three-dimensional structures of biomolecules by using singlemolecule diffraction images: A simulation 3-D structure (2.5 Å resolution) of rubisco molecule. (106 kda) Top view of a section (kz=0) of 3-D scattering pattern from 10 6 single molecules (of known relative orientation) each exposed by a single 10 fs XFEL pulse (λ=1.5å, 0.1μm beamsize) containing photons. Reconstructed 3-D pattern (from D projections). Phasing by oversampling technique. J. Miao, K.O. Hodgson and D. Sayre, PNAS, 98, 6641 (2001) SLAC, October 17,
9 Beam Sample Interaction SLAC, October 17,
10 Deformation fields inside nanocrystals I.K. Robinson, I.A. Vartaniants, G.J. Williams, M.A. Pfeifer, J.A. Pitney, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, (2001) M.A. Pfeifer, G.J. Williams, I.K. Vartaniants, R. Harder and I.K. Robinson, Nature 442, 63 (2006) CDI of (about 750 nm) Pb nanocrystals on Si substrate illuminated with 1.38Å coherent x-rays and CCD tuned to the Pb (111) reflection (with 2 images separated by a 0.01 deg. rotation of the sample shown below). Density of crystals is regarded as a complex function with the real part being the electron density and the imaginary part representing the projection of the local deformation of the crystal onto the Q vector of the Bragg peak being measured. Reconstructed electron density revealing (111) facets. Reconstructed imaginary part revealing (in the center) a phase-shift corresponding to about 1.1/2π (111) lattice spacings or about 0.5Å SLAC, October 17,
11 Fourier Transform Holography Random magnetic (stripe) domains in a [Co(4)Pt(7)] 50 ML sample, illuminated together with a reference aperature (1.5 µm) at the Co LIII edge absorption edge with a 778 ev (1.59 nm) 20 µm coherent soft x-ray beam. S. Eisebitt, J. Lüning, W.F. Schlotter, M. Lörgen, O. Hellwig, W.Eberhardt and J. Stöhr, NATURE, 432, 885 (2004) SLAC, October 17,
12 Femtosecond Imaging Model structure in 20 nm SiN membrane Speckle pattern recorded with a single (25 fs) pulse Reconstructed image Incident FEL pulse: 25 fs, 32 nm, 4x10 14 W cm -2 (10 12 ph/pulse) H. Chapman et al., Nature Physics, 2,839 (2006) SLAC, October 17,
13 High-Resolution Scanning X-ray Diffraction Miroscopy P. Thibault, M. Dierolf, A. Menzel, O. Bunk, C, David, F. Pfeiffer, Science, vol 321, 381 (2008) Measure multiple (overlapping) diffraction patterns (as suggested e.g. by Rodenburg et al. and known as ptychography) to provide overdetermination in the data followed by a reconstruction algorithm(s): Difference map (Elser), Ptychography (Rodenburg et al.,.), Wigner Deconvolution (Rodenburg, Chapman,..) 201x201 diffraction pattern (6.8 kev), 300 nm beam ( 100 nm steps with 300 nm beam), 50 ms exposure from a 30 μm diameter Fresnel zone plate with 70 nm outer zone width. SLAC, October 17,
14 Hard X-Ray Holographic Diffraction Imaging L.M. Stadler, C. Gutt, T. Autenrieth, O. Leupold, S. Rehbein,Y. Chuskin and G. Grübel; Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, (2008) Combine FTH and CDI: Au nanostructure (letter P ) 200 nm structure width; 220 nm height and 5 x 175 nm Au reference dots on 50 nm Si 3 N 4 illuminated with 8 kev (10x10 μm 2 ) beam. Use Fourier Transform Hologram as input for the CDI hybrid-input algorithm. Find resolution of about 25 nm and retrieve height of object: 235 nm +/- 10% SLAC, October 17,
15 Ultrafast single-shot diffraction imaging of nanoscale dynamics Ultrafast single-shot diffraction imaging of nanoscale dynamics A. Barty et al., nature photonics 2, 415 (2008) Pump-probe experiment on nano-patterned (FIPetched) Si 3 N 4 membrane (Ir-coated) pumped with Nd:YLF 523 nm, 12.5 ps long 25 μj pulses and probed with 10 fs 13.5 nm 20 μm FLASH pulses. Correlation functions indicate sample disintegration with a speed of about m/s SLAC, October 17,
16 Summary: Imaging Techniques Summary enormous progress since the 1999 paper impressive progress in solving the inversion problem better understanding of the damage problem much progress towards biological systems (particle injection systems, molecular orientation,..) new methods emerge (ptychography, combination CDI+FTH, FTH+URA,..) considerable single shot experience (XUV) ultimately achievable resolution for small systems still under discussion FEL light in the hard X-ray regime is missing SLAC, October 17,
17 LCLS and coherence based techniques Imaging techniques (CDI, FTH) X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) Recent developments and results Conclusions SLAC, October 17,
18 X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) first (X-ray) speckle in 1991 (X25) Diffuse (001) peak of Cu 3 Au M. Sutton, S.G.J. Mochrie, T. Greytak, S.E. Nagler, L.E. Berman, G.A. Held and G.B. Stephenson, Nature 352, 608 (1991) XPCS critical dynamics in Fe 3 Al (1995) 1st g 2 (t) function: colloidal gold (1995) multitude soft matter studies (colloids, polymers...) non-equilibrium dynamics (1998) surface dynamics (2001) heterogeneous dynamics,.. cdw, magnetism,... SLAC, October 17,
19 X-Ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) g 2 (Q,t) = <I(Q,t) I(Q,t+τ)> <I(Q,t)> 2 g 2 (Q,t) = 1 + f(q) f(q,t) 2 f(q,t): intermediate scattering function f(q,t) = exp [(-Γ t) ß ] single Q (point detector): fast 2-D multi-q (CCD detector): slow ß > 1,=1,<1 SLAC, October 17,
20 Dynamics of complex fluids A. Robert J.Appl.Cryst.40,s34(2007) silica (R=2610Å) in glycerol; T= 259 K; η=56 Pas f(q,t) = exp (-Γt) Γ(Q) = D(Q) Q 2 D(Q) D 0 =k B T/6πηR H SLAC, October 17,
21 Dynamics of complex fluids Mochrie, Mayes, Sandy, Sutton, Brauer, Stephenson, Abernathy, Grübel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1275 (1997) PS-PI (R=23.7 nm) micelles in PS matrix at T 293 K (top) and 393 K (bottom) The most likely density fluctuations decay the slowest (degennes narrowing) SLAC, October 17,
22 Non-equilibrium Dynamics Malik, Sandy, Lurio, Stephenson, Mochrie, McNulty, Sutton, PRL 81, 5832 (1998) Phase separating Glass (Na 2 O) 0.07 (B 2 O 3 ) 0.22 (SiO 2 ) 0.71 T=1033K quench (B 2 O 3 )-rich (SiO 2 )-rich 943K<T<963K SLAC, October 17,
23 Two time correlation function <I(t 1 ) I(t 2 )> - <I(t 1 )> <I(t 1 )> C(q,t 1,t 2 ) = [<I 2 (t 1 )> - <I(t 1 )> 2 ] 1/2 [<I 2 (t 2 )> - <I(t 1 )> 2 ] 1/2 Fluctuations τ = τ ( q,t ) Δt = t 1 -t 2 t = (t 1 +t 2 )/2 Two time correlation function τ (q,t) = [t max (q)-t o ] { a [t-t o ] / [t max (q)-t o ] } (1-n) x τ(q,t) ~ 1/q t 2/3 ^ a = 0.72(2) (1-n) = 0.65(4) = 1 ⅓ SLAC, October 17,
24 Surface dynamics Seydel, Madsen, Tolan, Grübel, Press, Phys. Rev. B 63, (2001) Glassforming liquid: glycerol Γ(Q) = c Q c = γ(t)/2η(t)} SLAC, October 17,
25 Particle Dynamics in Polymer-Metal Nanocomposite Thin Films S. Narayanan, D.R. Lee, A. Hagman, X. Li and J. Wang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, (2007) Entangled polymer [120, 65 kg/mol]: Relaxation time ~ q R -1 (-0.9) drift mechanism ß > 1 Less entangled polymer [30 kg/mol]: aging, jamming Relaxation time ~ q -1.6 R particles move faster, governed by ß< 1 hydrodynamic interactions Au nanoparticles (0.9nm) on polystyrene (PS; R G =5-10nm) on Pd (Cr) Si substrate. R AU < R G probe individuality of polymer. Increase intensity by wave-guiding effects SLAC, October 17,
26 Antiferromagnetic domain fluctuations Shpyrko, Isaacs, Logan, Feng, Aeppli, Jaramillo, Kim, Rosenbaum, Zschack, Sprung, Narayanan, Sandy, Nature, 447, 68 (2007) Chromium supports a SDW (including domain walls). The SDW is accompanied by a CDW. Autocorrelation function of the [200] Bragg peak and the CDW superlattice peaks [2-2δ,0,0]. Slow component indicative of thermally activated domain wall dynamics at high T and T independent switching (tunneling) at low T. SLAC, October 17,
27 Summary: Imaging Techniques Summary steady progress since the 1991 paper many applications from many different fields (soft matter, hard matter, surfaces and interfaces) indicating that XPCS has achieved quite some maturity accessible dynamics mostly slow (τ > μs) and at moderate Q limited by fast 2-d detectors but ultimately by coherent flux fast (ns-fs) and(or) large Q dynamics only at a FEL source need XCS beamline asap SLAC, October 17,
28 SR based XPCS data 2-D surface 1-D SLAC, October 17,
29 Summary: Imaging Techniques Questions: How to do (fast) dynamics experiments at a 120 Hz machine? Is there enough intensity to (single-shot) image e.g. a magnetic system? Can two subsequently recorded (speckle) pattern be compared? SLAC, October 17,
30 XPCS at LCLS: movie mode Movie mode allows access to slow dynamics: f << 1/ΔT = 120 Hz SLAC, October 17,
31 Delay-Line Mode Delay Line: 1ps <Δt <10ns (1ns 300 mm) Delay-Line mode allows access to fast (fs-ns) dynamics SLAC, October 17,
32 X-ray delay-line E=8.388 kev 8 x Si(511) Tuning range: 0 ΔT 2.83 ns available via DESY-SLAC MoU talk Roseker SLAC, October 17,
33 Summary: Imaging Techniques Questions: How to do (fast) dynamics experiments at a 120 Hz machine? Is there enough intensity to (single-shot) image e.g. a magnetic system? Can two subsequently recorded (speckle) pattern be compared? SLAC, October 17,
34 Prototype experiments at Flash FLASH the Free Electron Laser Facility Hamburg operating from 50 nm to 6.5 nm SLAC, October 17,
35 Photon parameters at FLASH: Magnetism? FLASH operates for λ > 6.5 nm wavelength average energy per pulse photons per pulse 778 ev Co L III edge fundamental 7.97nm ~ 12 µj 4.8 * rd harmonic 2.66nm ~ 72 nj 1.0 * th harmonic 1.59nm ~ 3.5 nj 2.8 * 10 7 pulse duration 10 fs at 8.0 nm 1 fs at 1.6 nm SLAC, October 17,
36 Sample CoPd multilayer, CoPt multilayer Hitachi (Hellwig), UHH (Oepen) 150 nm SiN membrane, 20 nm Pd base, 50 repeats of Co(1.2nm)/Pd(0.8nm), capped with 1.2 nm Pd providing out of plane magnetic moments Actors C. Gutt 1, L.M. Stadler 1, S. Streit-Nierobisch 1, C. Günther 2, R. Könnecke 2, B. Pfau 2, S. Eisebitt 2, A.P. Mancuso 1, J. Gulden 1, B. Reime 1, E. Weckert 1, J. Feldhaus 1, I.A. Vartaniants 1, F. Staier 3, A. Rosenhahn 3, R. Barth 3, M. Grunze 3,M. Martins 4, O. Hellwig 5, H. Stillrich 6, D. Stickler 6, R. Frömter 6, H.P. Oepen 6, T. Nisius 7, T. Wilhein 7, K. Honkavaara 1, B. Faatz 1, R. Treusch 1, S. Schreiber 1, E. Saldin 1, E. Schneidmiller 1, M. Yurkov 1 and G. Grübel 1 1 DESY, Hamburg, Germany 2 BESSY, Berlin, Germany 3 Physikalische Chemie, Universität Heidelberg, Germany 4 Experimentelle Physik, Universität Hamburg, Germany 5 Angewandte Physik, Universität Hamburg, Germany 6 FH Koblenz, Remagen Germany PRL (submitted) SLAC, October 17,
37 Experimental Setup Setup PG 2 Beamline monochromator 200 lines per mm dispersive element : temporal broadening of pulse ca fs (ray-tracing) but transmission only 10-4 at 800 ev Instrument: M. Martins, M. Wellhöfer, J.T. Hoeft, W. Wurth, J. Feldhaus, and R. Follath, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, (2006) SLAC, October 17,
38 783.5 ev (off resoanance) SLAC, October 17,
39 778.1 ev (resonant Co L-edge) q max =0.033 nm s exposure (21 pulses x 5 Hz) Frame contains 6.7 x 10 4 photons Need x 10 5 for single shot (get 10 4 from beamline transmission and 10 4 from fundamental = x10 8 ) SLAC, October 17,
40 Scattering close to the Co M edge Single bunch mode; 5 bunches/s E<59.9 ev (fundamental) CoPt 23.5 nm (off resonance) 20 fs (single shot) 5 μj (5x10 11 ph/pulse) SLAC, October 17,
41 Resonant Scattering at the Co M edge Single bunch mode; 5 bunches/s E=59.9 ev (fundamental) CoPt 20.7 nm (on resonance) 20 fs (single shot) 5 μj (5x10 11 ph/pulse) SLAC, October 17,
42 Resonant Scattering at the Co M edge Single bunch mode; 5 bunches/s 1-st bunch 2-nd bunch CoPt 20.7 nm (on resonance) 20 fs (single shot) 5 μj (5x10 11 ph/pulse) SLAC, October 17,
43 Single bunch mode; 5 bunches/s FEL pulse energy [µj] CoPt 20.7 nm (on resonance) 20 fs (single shot) 5 μj (5x10 11 ph/pulse) SLAC, October 17,
44 Magnetic speckle pattern from two consecutive single shots low pulse energy XPCS is feasible!! SLAC, October 17,
45 Summary There is a route towards doing fast XPCS at a FEL machine. (delay-line mode) A prototype X-ray delay-line is tested and ready for use. Standard (movie mode) XPCS is straight forward. There is a series of very interesting experiments that are ready to go. XCS beamline in 2011/2012 comes too late. The inversion problem seems to be under control. Good understanding of the damage problem Much progress toward biological systems (particle injection systems, molecular orientation,..) Considerable single shot experience (XUV) Hard FEL X-rays are missing Detectors remain an issue. Information on the dynamics of a system can also be obtained by Imaging. The choice (XPCS vs. Imaging) depends on the problem. XPCS is less demanding since the inversion problem does not exist. SLAC, October 17,
46 Layout Thank you for your attention SLAC, October 17,
A facility for Femtosecond Soft X-Ray Imaging on the Nanoscale
 A facility for Femtosecond Soft X-Ray Imaging on the Nanoscale Jan Lüning Outline Scientific motivation: Random magnetization processes Technique: Lensless imaging by Fourier Transform holography Feasibility:
A facility for Femtosecond Soft X-Ray Imaging on the Nanoscale Jan Lüning Outline Scientific motivation: Random magnetization processes Technique: Lensless imaging by Fourier Transform holography Feasibility:
Ultrafast XPCS. Gerhard Grübel
 . Ultrafast XPCS Gerhard Grübel W.Roseker, S. Lee, F. Lehmkühler, I. Steinke, H. Schulte-Schrepping, M. Walther, G.B. Stephenson, P. Fuoss, M. Sikorski, and A. Robert DESY Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron,
. Ultrafast XPCS Gerhard Grübel W.Roseker, S. Lee, F. Lehmkühler, I. Steinke, H. Schulte-Schrepping, M. Walther, G.B. Stephenson, P. Fuoss, M. Sikorski, and A. Robert DESY Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Demonstration of Feasibility of X-Ray Free Electron Laser Studies of Dynamics of Nanoparticles in Entangled Polymer Melts
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Demonstration of Feasibility of X-Ray Free Electron Laser Studies of Dynamics of Nanoparticles in Entangled Polymer Melts Jerome Carnis 1, Wonsuk Cha 1, James Wingert 2, Jinback
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Demonstration of Feasibility of X-Ray Free Electron Laser Studies of Dynamics of Nanoparticles in Entangled Polymer Melts Jerome Carnis 1, Wonsuk Cha 1, James Wingert 2, Jinback
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung
 . Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 10 Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2014 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Location: Hörs AP, Physik, Jungiusstrasse
. Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 10 Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2014 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Location: Hörs AP, Physik, Jungiusstrasse
Delay-Line Imaging and XPCS
 . Delay-Line Imaging and XPCS Gerhard Grübel W.Roseker, F. Lehmkühler, L. MüIler, S. Schleitzer, M. Berntsen, H. Schulte-Schrepping, M. Walther DESY Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron, Notkestr. 85, 22607
. Delay-Line Imaging and XPCS Gerhard Grübel W.Roseker, F. Lehmkühler, L. MüIler, S. Schleitzer, M. Berntsen, H. Schulte-Schrepping, M. Walther DESY Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron, Notkestr. 85, 22607
Coherent X-ray Scattering and X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy
 Coherent X-ray Scattering and X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy Laurence Lurio Department of Physics Northern Illinois University http://www.niu.edu/~llurio/coherence/ Outline Theory of X-ray Photon
Coherent X-ray Scattering and X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy Laurence Lurio Department of Physics Northern Illinois University http://www.niu.edu/~llurio/coherence/ Outline Theory of X-ray Photon
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik I. Coherence based techniques II. Christian Gutt DESY, Hamburg
 Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik I Coherence based techniques II Christian Gutt DESY Hamburg christian.gutt@desy.de 8. January 009 Outline 18.1. 008 Introduction to Coherence 8.01. 009 Structure determination
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik I Coherence based techniques II Christian Gutt DESY Hamburg christian.gutt@desy.de 8. January 009 Outline 18.1. 008 Introduction to Coherence 8.01. 009 Structure determination
X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Joachim Stöhr Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory
 X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Joachim Stöhr Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory X-Rays have come a long way Application to Magnetic Systems 1 µm 1895 1993 2003 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/stohr/index.htm
X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Joachim Stöhr Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory X-Rays have come a long way Application to Magnetic Systems 1 µm 1895 1993 2003 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/stohr/index.htm
X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources
 X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources Christian Gutt Department of Physics, University ofsiegen, Germany gutt@physik.uni-siegen.de Outline How to measure dynamics
X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS) at Synchrotron and FEL sources Christian Gutt Department of Physics, University ofsiegen, Germany gutt@physik.uni-siegen.de Outline How to measure dynamics
The MID instrument.
 The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
Phase imaging of magnetic nanostructures using resonant soft x-ray holography
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 440 007 Phase imaging of magnetic nanostructures using resonant soft x-ray holography A. Scherz,, * W. F. Schlotter,, K. Chen,, R. Rick,, J. Stöhr, J. Lüning, I. McNulty, 3,4 Ch.
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 440 007 Phase imaging of magnetic nanostructures using resonant soft x-ray holography A. Scherz,, * W. F. Schlotter,, K. Chen,, R. Rick,, J. Stöhr, J. Lüning, I. McNulty, 3,4 Ch.
Toward a single mode Free Electron Laser for coherent hard X-ray experiments
 SLAC-PUB-15661 Toward a single mode Free Electron Laser for coherent hard X-ray experiments Sooheyong Lee 1,2,, Zhirong Huang 1, Yuantao Ding 1, Paul Emma 1, Wojciech Roseker 2, Gerhard Grübel 2 and Aymeric
SLAC-PUB-15661 Toward a single mode Free Electron Laser for coherent hard X-ray experiments Sooheyong Lee 1,2,, Zhirong Huang 1, Yuantao Ding 1, Paul Emma 1, Wojciech Roseker 2, Gerhard Grübel 2 and Aymeric
Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Henry.Chapman@desy.de Isaac Newton Opticks 1704 Newton was the first
Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Henry.Chapman@desy.de Isaac Newton Opticks 1704 Newton was the first
Ultrafast Structural Dynamics in Solids Klaus Sokolowski-Tinten
 Ultrafast Structural Dynamics in Solids Klaus Sokolowski-Tinten Institut für Experimentelle Physik STI Round-Table Meeting, Hamburg, 22. - 24. Juni 2004 Outline motivation: why short pulses and the XFEL
Ultrafast Structural Dynamics in Solids Klaus Sokolowski-Tinten Institut für Experimentelle Physik STI Round-Table Meeting, Hamburg, 22. - 24. Juni 2004 Outline motivation: why short pulses and the XFEL
Imaging & Microscopy
 Coherent X-ray X Imaging & Microscopy => Opportunities Using a Diffraction-Limited Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Synchrotron Source Q. Shen D. Bilderback, K.D. Finkelstein, E. Fontes, & S. Gruner Cornell
Coherent X-ray X Imaging & Microscopy => Opportunities Using a Diffraction-Limited Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Synchrotron Source Q. Shen D. Bilderback, K.D. Finkelstein, E. Fontes, & S. Gruner Cornell
Coherence measurements and coherent diffractive imaging at FLASH
 Coherence measurements and coherent diffractive imaging at FLASH * I A Vartanyants, A P Mancuso, A Singer, O M Yefanov, J Gulden To cite this version: * I A Vartanyants, A P Mancuso, A Singer, O M Yefanov,
Coherence measurements and coherent diffractive imaging at FLASH * I A Vartanyants, A P Mancuso, A Singer, O M Yefanov, J Gulden To cite this version: * I A Vartanyants, A P Mancuso, A Singer, O M Yefanov,
Colloidal samples investigated using coherent x-ray scattering methods. Michael Sprung DESY Hamburg,
 Colloidal samples investigated using coherent x-ray scattering methods Michael Sprung DESY Hamburg, 09.11.014 Acknowledgements Coherence beamline A. Schavkan, A. Ricci, A. Zozulya, F. Westermeier, S. Bondarenko,
Colloidal samples investigated using coherent x-ray scattering methods Michael Sprung DESY Hamburg, 09.11.014 Acknowledgements Coherence beamline A. Schavkan, A. Ricci, A. Zozulya, F. Westermeier, S. Bondarenko,
FLASH overview. Nikola Stojanovic. PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg,
 FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
Brightness and Coherence of Synchrotron Radiation and Free Electron Lasers. Zhirong Huang SLAC, Stanford University May 13, 2013
 Brightness and Coherence of Synchrotron Radiation and Free Electron Lasers Zhirong Huang SLAC, Stanford University May 13, 2013 Introduction GE synchrotron (1946) opened a new era of accelerator-based
Brightness and Coherence of Synchrotron Radiation and Free Electron Lasers Zhirong Huang SLAC, Stanford University May 13, 2013 Introduction GE synchrotron (1946) opened a new era of accelerator-based
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2
 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
XPCS and Shear Flow. Wesley Burghardt Department of Chemical & Biological Engineering Northwestern University
 XPCS and Shear Flow Wesley Burghardt Department of Chemical & Biological Engineering Northwestern University Outline Background: XPCS & rheology XPCS during shear Unidirectional shear flow Oscillatory
XPCS and Shear Flow Wesley Burghardt Department of Chemical & Biological Engineering Northwestern University Outline Background: XPCS & rheology XPCS during shear Unidirectional shear flow Oscillatory
Trends in X-ray Synchrotron Radiation Research
 Trends in X-ray Synchrotron Radiation Research Storage rings Energy Recovery Linacs (ERL) Free Electron Lasers Jochen R. Schneider DESY Development of the brilliance of X-ray sources Since the discovery
Trends in X-ray Synchrotron Radiation Research Storage rings Energy Recovery Linacs (ERL) Free Electron Lasers Jochen R. Schneider DESY Development of the brilliance of X-ray sources Since the discovery
Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL
 Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov FEL seminar, DESY Hamburg June 21, 2016 In a planar undulator (K ~ 1 or K >1) the odd harmonics can be radiated on-axis (widely used in SR
Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov FEL seminar, DESY Hamburg June 21, 2016 In a planar undulator (K ~ 1 or K >1) the odd harmonics can be radiated on-axis (widely used in SR
Making Functional Surfaces and Thin Films: Where are the Atoms?
 Making Functional Surfaces and Thin Films: Where are the Atoms? K. Ludwig, A. DeMasi, J. Davis and G. Erdem Department of Physics Materials Science and Engineering Program Why x-rays? λ ~10-10 m ~ distance
Making Functional Surfaces and Thin Films: Where are the Atoms? K. Ludwig, A. DeMasi, J. Davis and G. Erdem Department of Physics Materials Science and Engineering Program Why x-rays? λ ~10-10 m ~ distance
X-ray Intensity Fluctuation Spectroscopy. Mark Sutton McGill University
 X-ray Intensity Fluctuation Spectroscopy Mark Sutton McGill University McGill University Collaborators J-F. Pelletier K. Laaziri K. Hassani A. Fluerasu E. Dufresne G. Brown M. Grant Yale/MIT S. Mochrie
X-ray Intensity Fluctuation Spectroscopy Mark Sutton McGill University McGill University Collaborators J-F. Pelletier K. Laaziri K. Hassani A. Fluerasu E. Dufresne G. Brown M. Grant Yale/MIT S. Mochrie
Inline Spectrometer as Permanent Optics at the X-ray Correlation Spectroscopy Instrument to Support Seeding Operation
 Inline Spectrometer as Permanent Optics at the X-ray Correlation Spectroscopy Instrument to Support Seeding Operation Amber L. Gray Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI)
Inline Spectrometer as Permanent Optics at the X-ray Correlation Spectroscopy Instrument to Support Seeding Operation Amber L. Gray Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI)
How can x-ray intensity fluctuation spectroscopy push the frontiers of Materials Science. Mark Sutton McGill University
 How can x-ray intensity fluctuation spectroscopy push the frontiers of Materials Science Mark Sutton McGill University Coherent diffraction (001) Cu 3 Au peak Sutton et al., The Observation of Speckle
How can x-ray intensity fluctuation spectroscopy push the frontiers of Materials Science Mark Sutton McGill University Coherent diffraction (001) Cu 3 Au peak Sutton et al., The Observation of Speckle
Coherent X-ray Diffraction on Quantum Dots
 Coherent X-ray Diffraction on Quantum Dots Ivan Vartaniants HASYLAB, DESY, Hamburg, Germany Or Coming Back to Crystallography Participants of the Project University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA
Coherent X-ray Diffraction on Quantum Dots Ivan Vartaniants HASYLAB, DESY, Hamburg, Germany Or Coming Back to Crystallography Participants of the Project University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA
Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements
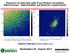 Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements Quasi-static speckles from colloidal suspension near random compact packing volume fraction Speckles
Dynamics of materials with X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy - Opportunities and detector requirements Quasi-static speckles from colloidal suspension near random compact packing volume fraction Speckles
Ultrafast Optical Demagnetization manipulates Nanoscale Spin Structure in Domain Walls: Supplementary Information
 Ultrafast Optical Demagnetization manipulates Nanoscale Spin Structure in Domain Walls: Supplementary Information B. Pfau 1, S. Schaffert 1, L. Müller, C. Gutt, A. Al-Shemmary, F. Büttner 1,3,4,5, R. Delaunay
Ultrafast Optical Demagnetization manipulates Nanoscale Spin Structure in Domain Walls: Supplementary Information B. Pfau 1, S. Schaffert 1, L. Müller, C. Gutt, A. Al-Shemmary, F. Büttner 1,3,4,5, R. Delaunay
First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL
 First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov ICFA workshop, Arcidosso, Italy, 22.09.2017 Outline Harmonic lasing Harmonic lasing self-seeded (HLSS) FEL Experiments
First operation of a Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov ICFA workshop, Arcidosso, Italy, 22.09.2017 Outline Harmonic lasing Harmonic lasing self-seeded (HLSS) FEL Experiments
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008
 Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
FLASH/DESY, Hamburg. Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team -
 First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
X-ray crystallography has a record of extraordinary achievement
 FOCUS REVIEW ARTICLE PUBLISHED ONLINE: 30 NOVEMBER 2010 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2010.240 Coherent lensless X-ray imaging Henry N. Chapman 1 and Keith A. Nugent 2 * Very high resolution X-ray imaging has been
FOCUS REVIEW ARTICLE PUBLISHED ONLINE: 30 NOVEMBER 2010 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2010.240 Coherent lensless X-ray imaging Henry N. Chapman 1 and Keith A. Nugent 2 * Very high resolution X-ray imaging has been
Spectroscopy with Free Electron Lasers. David Bernstein SASS Talk January 28 th, 2009
 Spectroscopy with Free Electron Lasers David Bernstein SASS Talk January 28 th, 2009 Overview Who am I?! What is FLASH?! The promise of Free Electron Lasers (FELs) The Trouble with Spectroscopy Sample
Spectroscopy with Free Electron Lasers David Bernstein SASS Talk January 28 th, 2009 Overview Who am I?! What is FLASH?! The promise of Free Electron Lasers (FELs) The Trouble with Spectroscopy Sample
Status and Perspectives for XPCS New Possibilities for XPCS at the ERL?
 Status and Perspectives for XPCS New Possibilities for XPCS at the ERL? Towards The Ultimate XPCS Beamline Is (focusing) optics useful? Can beam induced sample damage be avoided? Which detector could we
Status and Perspectives for XPCS New Possibilities for XPCS at the ERL? Towards The Ultimate XPCS Beamline Is (focusing) optics useful? Can beam induced sample damage be avoided? Which detector could we
Time-resolved Diffuse Scattering: phonon spectoscopy with ultrafast x rays
 Time-resolved Diffuse Scattering: phonon spectoscopy with ultrafast x rays David A. Reis PULSE Institute, Departments of Photon Science and Applied Physics, Stanford University SLAC National Accelerator
Time-resolved Diffuse Scattering: phonon spectoscopy with ultrafast x rays David A. Reis PULSE Institute, Departments of Photon Science and Applied Physics, Stanford University SLAC National Accelerator
Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation
 SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
The BESSY - FEL Collaboration
 The BESSY - FEL Collaboration Planning the Revolution for Research with soft X-Rays Photon Energy Range : 20 ev up to 1 kev λ/λ 10-2 to 10-4 Peak Power: 1mJ in 200 fs >> 5 GW Time Structure: 200 fs (
The BESSY - FEL Collaboration Planning the Revolution for Research with soft X-Rays Photon Energy Range : 20 ev up to 1 kev λ/λ 10-2 to 10-4 Peak Power: 1mJ in 200 fs >> 5 GW Time Structure: 200 fs (
Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources. Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010
 Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/aboutssrl/documents/future-x-rays-09.pdf special acknowledgment to John Corlett,
Performance Metrics of Future Light Sources Robert Hettel, SLAC ICFA FLS 2010 March 1, 2010 http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/aboutssrl/documents/future-x-rays-09.pdf special acknowledgment to John Corlett,
The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design
 UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
Elimination of X-Ray Diffraction through Stimulated X-Ray Transmission
 SLAC-R-169 Elimination of X-Ray Diffraction through Stimulated X-Ray Transmission B. Wu, 1 T. Wang, C. E. Graves, 1 D. Zhu, 3 W. F. Schlotter, 3 J. Turner, 3 O. Hellwig, Z. Chen, 5 H. A. Dürr, 3 A. Scherz,
SLAC-R-169 Elimination of X-Ray Diffraction through Stimulated X-Ray Transmission B. Wu, 1 T. Wang, C. E. Graves, 1 D. Zhu, 3 W. F. Schlotter, 3 J. Turner, 3 O. Hellwig, Z. Chen, 5 H. A. Dürr, 3 A. Scherz,
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science
 The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
Ultrafast nanoscience with ELI ALPS
 Ultrafast nanoscience with ELI ALPS Péter Dombi Wigner Research Centre for Physics, Budapest & Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics, Garching Overview ultrafast (femtosecond/attosecond) dynamicsin metal
Ultrafast nanoscience with ELI ALPS Péter Dombi Wigner Research Centre for Physics, Budapest & Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics, Garching Overview ultrafast (femtosecond/attosecond) dynamicsin metal
Supporting Information for: Transformation in VO 2 Thin Films by
 Supporting Information for: Imaging Nanometer Phase Coexistence at Defects During the Insulator-Metal Phase Transformation in VO 2 Thin Films by Resonant Soft X-Ray Holography Luciana Vidas,, Christian
Supporting Information for: Imaging Nanometer Phase Coexistence at Defects During the Insulator-Metal Phase Transformation in VO 2 Thin Films by Resonant Soft X-Ray Holography Luciana Vidas,, Christian
Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources
 XDL Workshop 6 @ Cornell Univ. Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources Yuya Shinohara Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
XDL Workshop 6 @ Cornell Univ. Hierarchical Dynamics of Soft Matters & Prospects of Japanese Future Light Sources Yuya Shinohara Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
Solid-State Dynamics and Education
 Chapter 6 Solid-State Dynamics and Education (http://www.eduphys.ethz.ch/) Head Prof. Dr. Andreas Vaterlaus Academic Staff Dr. Yves Acremann Andreas Fognini Dr. Christian Helm Dr. Thomas Michlmayr Martin
Chapter 6 Solid-State Dynamics and Education (http://www.eduphys.ethz.ch/) Head Prof. Dr. Andreas Vaterlaus Academic Staff Dr. Yves Acremann Andreas Fognini Dr. Christian Helm Dr. Thomas Michlmayr Martin
Polarization control experiences in single pass seeded FELs. Carlo Spezzani on behalf of
 Polarization control experiences in single pass seeded FELs Carlo Spezzani on behalf of the FERMI team & the storage ring FEL group Outline Introduction Storage Ring FEL test facility characterization
Polarization control experiences in single pass seeded FELs Carlo Spezzani on behalf of the FERMI team & the storage ring FEL group Outline Introduction Storage Ring FEL test facility characterization
Disordered Materials: Glass physics
 Disordered Materials: Glass physics > 2.7. Introduction, liquids, glasses > 4.7. Scattering off disordered matter: static, elastic and dynamics structure factors > 9.7. Static structures: X-ray scattering,
Disordered Materials: Glass physics > 2.7. Introduction, liquids, glasses > 4.7. Scattering off disordered matter: static, elastic and dynamics structure factors > 9.7. Static structures: X-ray scattering,
AMO physics with LCLS
 AMO physics with LCLS Phil Bucksbaum Director, Stanford PULSE Center SLAC Strong fields for x-rays LCLS experimental program Experimental capabilities End-station layout PULSE Ultrafast X-ray Summer June
AMO physics with LCLS Phil Bucksbaum Director, Stanford PULSE Center SLAC Strong fields for x-rays LCLS experimental program Experimental capabilities End-station layout PULSE Ultrafast X-ray Summer June
General theory of diffraction
 General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
Magnetization dynamics and fs pulsed X-ray sources
 HERCULES SPECIALIZED COURSE: Neutrons and Synchrotron Radiation for Magnetism (HSC18) Magnetization dynamics and fs pulsed X-ray sources Jan Lüning Laboratoire de Chimie Physique Matière et Rayonnement
HERCULES SPECIALIZED COURSE: Neutrons and Synchrotron Radiation for Magnetism (HSC18) Magnetization dynamics and fs pulsed X-ray sources Jan Lüning Laboratoire de Chimie Physique Matière et Rayonnement
Diamond Update: Surface and Interface Beamlines
 Diamond Update: Surface and Interface Beamlines I. K. Robinson University College London Diamond Light Source Argonne SIS group pizza lunch 21 April 2009 Outline Coherent X-ray Diffraction Imaging of small
Diamond Update: Surface and Interface Beamlines I. K. Robinson University College London Diamond Light Source Argonne SIS group pizza lunch 21 April 2009 Outline Coherent X-ray Diffraction Imaging of small
Fundamentals of X ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy
 Fundamentals of X ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy Asst. Prof. Oleg Shpyrko University i of California i San Diego website: oleg.ucsd.edu X-ray Revolution (Future is Bright!) incandescent light sources
Fundamentals of X ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy Asst. Prof. Oleg Shpyrko University i of California i San Diego website: oleg.ucsd.edu X-ray Revolution (Future is Bright!) incandescent light sources
The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals
 The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals Summary Information for Submitting Proposals We encourage scientists from all over the world to submit applications for beam time proposal to utilize
The Second Half Year 2017 PAL-XFEL Call for Proposals Summary Information for Submitting Proposals We encourage scientists from all over the world to submit applications for beam time proposal to utilize
Short Wavelength Regenerative Amplifier FELs (RAFELs)
 Short Wavelength Regenerative Amplifier FELs (RAFELs) Neil Thompson, David Dunning ASTeC, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington UK Brian McNeil Strathclyde University, Glasgow, UK Jaap Karssenberg & Peter van
Short Wavelength Regenerative Amplifier FELs (RAFELs) Neil Thompson, David Dunning ASTeC, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington UK Brian McNeil Strathclyde University, Glasgow, UK Jaap Karssenberg & Peter van
Hidden Symmetry in Disordered Matter
 MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUTE FOR METALS RESEARCH Department LDMM Hidden Symmetry in Disordered Matter P. Wochner T. Demmer V. Bugaev A. Díaz Ortiz H. Dosch C. Gutt T. Autenrieth A. Duri G. Grübel DESY F. Zontone
MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUTE FOR METALS RESEARCH Department LDMM Hidden Symmetry in Disordered Matter P. Wochner T. Demmer V. Bugaev A. Díaz Ortiz H. Dosch C. Gutt T. Autenrieth A. Duri G. Grübel DESY F. Zontone
Scientific Instrument MID
 XFEL.EU TR-2011-008 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN REPORT Scientific Instrument MID January 2012, Web Version A. Madsen for Scientific Instrument MID (WP83) at the European XFEL European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser Facility
XFEL.EU TR-2011-008 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN REPORT Scientific Instrument MID January 2012, Web Version A. Madsen for Scientific Instrument MID (WP83) at the European XFEL European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser Facility
4 FEL Physics. Technical Synopsis
 4 FEL Physics Technical Synopsis This chapter presents an introduction to the Free Electron Laser (FEL) physics and the general requirements on the electron beam parameters in order to support FEL lasing
4 FEL Physics Technical Synopsis This chapter presents an introduction to the Free Electron Laser (FEL) physics and the general requirements on the electron beam parameters in order to support FEL lasing
Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling
 Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David
Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David
Photon science at FLASH during the last user campaign 2008/9
 Photon science at FLASH during the last user campaign 2008/9 S. Düsterer FLASH-Seminar 13. October 2009 Summary of FLASH operation Wavelength range (fundamental): 6.8-47 nm Spectral width (FWHM): 0.5-1
Photon science at FLASH during the last user campaign 2008/9 S. Düsterer FLASH-Seminar 13. October 2009 Summary of FLASH operation Wavelength range (fundamental): 6.8-47 nm Spectral width (FWHM): 0.5-1
THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal
 SwissFEL Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen 1 2 C. Vicario 1, R. Clemens 1 and C. P. Hauri 1,2 THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal 10/16/12 Workshop on High Field THz science
SwissFEL Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen 1 2 C. Vicario 1, R. Clemens 1 and C. P. Hauri 1,2 THz field strength larger than MV/cm generated in organic crystal 10/16/12 Workshop on High Field THz science
Self-Assembled Iron Oxide Thin Films at the Liquid-Air Interface
 Self-Assembled Iron Oxide Thin Films at the Liquid-Air Interface Leandra Boucheron Candidacy Exam September 4, 2013 Introduction Outline Techniques and Results Grazing Incidence Diffraction (GID) X-Ray
Self-Assembled Iron Oxide Thin Films at the Liquid-Air Interface Leandra Boucheron Candidacy Exam September 4, 2013 Introduction Outline Techniques and Results Grazing Incidence Diffraction (GID) X-Ray
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations
 Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES).
 S1 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES). The combined SAXS/XANES measurements were carried out at the µspot beamline at BESSY II (Berlin, Germany). The beamline
S1 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES). The combined SAXS/XANES measurements were carried out at the µspot beamline at BESSY II (Berlin, Germany). The beamline
Design of an x-ray split- and delay-unit for the European XFEL
 Invited Paper Design of an x-ray split- and delay-unit for the European XFEL Sebastian Roling 1*, Liubov Samoylova 3, Björn Siemer 1, Harald Sinn 3, Frank Siewert 2, Frank Wahlert 1, Michael Wöstmann 1
Invited Paper Design of an x-ray split- and delay-unit for the European XFEL Sebastian Roling 1*, Liubov Samoylova 3, Björn Siemer 1, Harald Sinn 3, Frank Siewert 2, Frank Wahlert 1, Michael Wöstmann 1
Coherent X-ray diffraction for Condensed matter physics
 Coherent X-ray diffraction for Condensed matter physics Sylvain RAVY CRISTAL beamline Synchrotron SOLEIL Saint Aubin 91192 Gif-sur-Yvette France Collaborations David Le Bolloc h, (lab. physique des solides,
Coherent X-ray diffraction for Condensed matter physics Sylvain RAVY CRISTAL beamline Synchrotron SOLEIL Saint Aubin 91192 Gif-sur-Yvette France Collaborations David Le Bolloc h, (lab. physique des solides,
Set-up for ultrafast time-resolved x-ray diffraction using a femtosecond laser-plasma kev x-ray-source
 Set-up for ultrafast time-resolved x-ray diffraction using a femtosecond laser-plasma kev x-ray-source C. Blome, K. Sokolowski-Tinten *, C. Dietrich, A. Tarasevitch, D. von der Linde Inst. for Laser- and
Set-up for ultrafast time-resolved x-ray diffraction using a femtosecond laser-plasma kev x-ray-source C. Blome, K. Sokolowski-Tinten *, C. Dietrich, A. Tarasevitch, D. von der Linde Inst. for Laser- and
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS. Coherence Properties. J. B. Hastings. Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
 Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
Coherence properties of the radiation from SASE FEL
 CERN Accelerator School: Free Electron Lasers and Energy Recovery Linacs (FELs and ERLs), 31 May 10 June, 2016 Coherence properties of the radiation from SASE FEL M.V. Yurkov DESY, Hamburg I. Start-up
CERN Accelerator School: Free Electron Lasers and Energy Recovery Linacs (FELs and ERLs), 31 May 10 June, 2016 Coherence properties of the radiation from SASE FEL M.V. Yurkov DESY, Hamburg I. Start-up
ULTRAFAST COHERENT DIFFRACTION IMAGING WITH X-RAY FREE- ELECTRON LASERS*
 ULTRAFAST COHERENT DIFFRACTION IMAGING WITH X-RAY FREE- ELECTRON LASERS* H. N. Chapman #, S. Bajt, A. Barty, W.H. Benner, M.J. Bogan, M. Frank, S.P. Hau-Riege, R.A. London, S. Marchesini, E. Spiller, A.
ULTRAFAST COHERENT DIFFRACTION IMAGING WITH X-RAY FREE- ELECTRON LASERS* H. N. Chapman #, S. Bajt, A. Barty, W.H. Benner, M.J. Bogan, M. Frank, S.P. Hau-Riege, R.A. London, S. Marchesini, E. Spiller, A.
Flexible control of femtosecond pulse duration and separation using an emittance-spoiling foil in x-ray free-electron lasers
 SLAC PUB 16312 June 2015 Flexible control of femtosecond pulse duration and separation using an emittance-spoiling foil in x-ray free-electron lasers Y. Ding 1, C. Behrens 2, R. Coffee 1, F.-J. Decker
SLAC PUB 16312 June 2015 Flexible control of femtosecond pulse duration and separation using an emittance-spoiling foil in x-ray free-electron lasers Y. Ding 1, C. Behrens 2, R. Coffee 1, F.-J. Decker
Two-Stage Chirped-Beam SASE-FEL for High Power Femtosecond X-Ray Pulse Generation
 Two-Stage Chirped-Beam SASE-FEL for High ower Femtosecond X-Ray ulse Generation C. Schroeder*, J. Arthur^,. Emma^, S. Reiche*, and C. ellegrini* ^ Stanford Linear Accelerator Center * UCLA 12-10-2001 LCLS-TAC
Two-Stage Chirped-Beam SASE-FEL for High ower Femtosecond X-Ray ulse Generation C. Schroeder*, J. Arthur^,. Emma^, S. Reiche*, and C. ellegrini* ^ Stanford Linear Accelerator Center * UCLA 12-10-2001 LCLS-TAC
Time-resolved X-Ray Holography
 Time-resolved X-Ray Holography Max Born Institute, Berlin Technical University Berlin Holography Dennis Gábor 1900 1979 (1921-24 @ TUB) Nobel Prize Physics. Holography and 3D information G.-J. Lay / Wikipedia
Time-resolved X-Ray Holography Max Born Institute, Berlin Technical University Berlin Holography Dennis Gábor 1900 1979 (1921-24 @ TUB) Nobel Prize Physics. Holography and 3D information G.-J. Lay / Wikipedia
DIFFRACTION UNDER LASER IRRADIATION. ANF RECIPROCS C. Mariette
 DIFFRACTION UNDER LASER IRRADIATION ANF RECIPROCS- 2018 C. Mariette Okhoshi et al., Nat. Chem.(2010) Calculated DOS of photo-switchable Ti 3 O 5 Photochromism Conductivity Insulating Metal This also
DIFFRACTION UNDER LASER IRRADIATION ANF RECIPROCS- 2018 C. Mariette Okhoshi et al., Nat. Chem.(2010) Calculated DOS of photo-switchable Ti 3 O 5 Photochromism Conductivity Insulating Metal This also
Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers. Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL PSAS 2008
 Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL Hamburg @ PSAS 2008 People involved in this work MPI-K S. W. E. (ASG) J. R. Crespo L. U. G. Brenner
Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL Hamburg @ PSAS 2008 People involved in this work MPI-K S. W. E. (ASG) J. R. Crespo L. U. G. Brenner
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Attosecond Science. Jon Marangos, Director Extreme Light Consortium, Imperial College London
 Attosecond Science Jon Marangos, Director Extreme Light Consortium, Imperial College London Electron Orbit in Bohr Model T orbit 150 as for H ground state Electron Motion In most matter electrons are in
Attosecond Science Jon Marangos, Director Extreme Light Consortium, Imperial College London Electron Orbit in Bohr Model T orbit 150 as for H ground state Electron Motion In most matter electrons are in
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices
 Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
Generating intense attosecond x-ray pulses using ultraviolet-laser-induced microbunching in electron beams. Abstract
 Febrary 2009 SLAC-PUB-13533 Generating intense attosecond x-ray pulses using ultraviolet-laser-induced microbunching in electron beams D. Xiang, Z. Huang and G. Stupakov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory,
Febrary 2009 SLAC-PUB-13533 Generating intense attosecond x-ray pulses using ultraviolet-laser-induced microbunching in electron beams D. Xiang, Z. Huang and G. Stupakov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory,
Overview of x-ray techniques
 Overview of x-ray techniques Makina YABASHI SPring-8/JASRI ICFA Future Light Sources Subpanel Miniworkshop on XFEL Short Bunch Measurement and Timing Stanford Linear Accelerator Center July, 26 2004 1
Overview of x-ray techniques Makina YABASHI SPring-8/JASRI ICFA Future Light Sources Subpanel Miniworkshop on XFEL Short Bunch Measurement and Timing Stanford Linear Accelerator Center July, 26 2004 1
XRD endstation: condensed matter systems
 XRD endstation: condensed matter systems Justine Schlappa SCS Instrument Beamline Scientist Hamburg, January 24, 2017 2 Outline Motivation Baseline XRD setup R&D setup Two-color operation and split&delay
XRD endstation: condensed matter systems Justine Schlappa SCS Instrument Beamline Scientist Hamburg, January 24, 2017 2 Outline Motivation Baseline XRD setup R&D setup Two-color operation and split&delay
X-Ray Spectroscopy at LCLS
 LCLS proposal preparation workshop for experiments at XPP, June 21, 2008, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA ħω ħω e - X-Ray Spectroscopy at LCLS Uwe Bergmann SSRL Stanford Linear Accelerator Center bergmann@slac.stanford.edu
LCLS proposal preparation workshop for experiments at XPP, June 21, 2008, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA ħω ħω e - X-Ray Spectroscopy at LCLS Uwe Bergmann SSRL Stanford Linear Accelerator Center bergmann@slac.stanford.edu
Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics
 Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics Richard Haight IBM TJ Watson Research Center PO Box 218 Yorktown Hts., NY 10598 Collaborators Al Wagner Pete Longo Daeyoung
Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics Richard Haight IBM TJ Watson Research Center PO Box 218 Yorktown Hts., NY 10598 Collaborators Al Wagner Pete Longo Daeyoung
Spectroscopies for Unoccupied States = Electrons
 Spectroscopies for Unoccupied States = Electrons Photoemission 1 Hole Inverse Photoemission 1 Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy 1 Electron/Hole Emission 1 Hole Absorption Will be discussed with core levels
Spectroscopies for Unoccupied States = Electrons Photoemission 1 Hole Inverse Photoemission 1 Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy 1 Electron/Hole Emission 1 Hole Absorption Will be discussed with core levels
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
X-Rays From Laser Plasmas
 X-Rays From Laser Plasmas Generation and Applications I. C. E. TURCU CLRC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK and J. B. DANCE JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents
X-Rays From Laser Plasmas Generation and Applications I. C. E. TURCU CLRC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK and J. B. DANCE JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents
Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch
 Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch Normally z el >> N u 1 Chaotic light Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron /=1/N u Temporal phase space area z ~(/
Undulator radiation from electrons randomly distributed in a bunch Normally z el >> N u 1 Chaotic light Spectral property is the same as that of a single electron /=1/N u Temporal phase space area z ~(/
SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation
 SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation Tuesday, December 7, 2010 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 The optics layout of the PEARL beamline P. Oberta, U. Flechsig and M. Muntwiler 10:30 Instrumentation for
SLS Symposium on X-Ray Instrumentation Tuesday, December 7, 2010 10:00 to 12:15, WBGB/019 10:00 The optics layout of the PEARL beamline P. Oberta, U. Flechsig and M. Muntwiler 10:30 Instrumentation for
Research with Synchrotron Radiation. Part I
 Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals. JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu
 New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu Why new algorithms? New research questions New experimental techniques Better insight
New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu Why new algorithms? New research questions New experimental techniques Better insight
Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
Transverse Coherence Properties of the LCLS X-ray Beam
 LCLS-TN-06-13 Transverse Coherence Properties of the LCLS X-ray Beam S. Reiche, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA October 31, 2006 Abstract Self-amplifying spontaneous radiation free-electron lasers, such
LCLS-TN-06-13 Transverse Coherence Properties of the LCLS X-ray Beam S. Reiche, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA October 31, 2006 Abstract Self-amplifying spontaneous radiation free-electron lasers, such
Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
The European X-ray Free- Electron Laser Facility in Hamburg
 The European X-ray Free- Electron Laser Facility in Hamburg Massimo Altarelli European X-ray Free-Electron Laser Facility 22607 Hamburg, Germany massimo.altarelli@xfel.eu Some Third Generation Synchrotrons
The European X-ray Free- Electron Laser Facility in Hamburg Massimo Altarelli European X-ray Free-Electron Laser Facility 22607 Hamburg, Germany massimo.altarelli@xfel.eu Some Third Generation Synchrotrons
Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion
 Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion C. Wimmer a, U. Fantz a,b and the NNBI-Team a a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM
Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion C. Wimmer a, U. Fantz a,b and the NNBI-Team a a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques
 Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2)
 Photosensitization of nanostructured TiO 2 electrodes with CdSe quntum dots: effects of microstructure in substrates Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2) Department of Applied Physics and Chemistry 1), and
Photosensitization of nanostructured TiO 2 electrodes with CdSe quntum dots: effects of microstructure in substrates Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2) Department of Applied Physics and Chemistry 1), and
Transient lattice dynamics in fs-laser-excited semiconductors probed by ultrafast x-ray diffraction
 Transient lattice dynamics in fs-laser-excited semiconductors probed by ultrafast x-ray diffraction K. Sokolowski-Tinten, M. Horn von Hoegen, D. von der Linde Inst. for Laser- and Plasmaphysics, University
Transient lattice dynamics in fs-laser-excited semiconductors probed by ultrafast x-ray diffraction K. Sokolowski-Tinten, M. Horn von Hoegen, D. von der Linde Inst. for Laser- and Plasmaphysics, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
