Compressor 1. Evaporator. Condenser. Expansion valve. CHE 323, October 8, Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Tutorial problem 5.
|
|
|
- Willis Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHE 33, October 8, 014. Cemical Engineering Termodynamics. Tutorial problem 5. In a simple compression refrigeration process, an adiabatic reversible compressor is used to compress propane, used as a refrigerant. Te compressed gas delivered by te compressor is fed to a condenser tat produces saturated liquid at 40 C. Te expansion valve produces a mixture of vapour and liquid at -30 C witin te evaporator. Te evaporator produces a saturated vapour at -30 C tat is fed to te compressor. Te refrigeration unit is designed as a capacity of tons (4000 BTU/r or 7.4kW, QL = 7.4 kw). Determine te molar flow rate of propane, te power of te compressor, te CO of te refrigerator, te duty of te condenser, te total entropy of te system, and te total entropy of te process, considering tat eat is removed from an environment at -10 C, and tat te eat of te condenser is released to te surroundings at 30 C. Find below a simplified diagram of te compression refrigeration cycle: 4 Compressor 1 Evaporator 3 Condenser Expansion valve To calculate tis cycle, assume tat wen te fluid is in vapour pase, it beaves as an ideal gas. Te following are te properties of te fluid. C3H8 MW= 44g/mol Tc = 369.8K c = 4.49 Ma ω=0.15 Cp gas = 68 J/mol-K (assume to be constant) sat, ka = exp( /(t C+50.4)) ΔHvap /(R*Tc) = 7*(1-Tr) *ω*(1-Tr) To calculate your entalpies and entropies use te condition of stream (saturated liquid at 40 C) as reference, in oter words, make = 0 J/mol, s = 0 J/mol-K
2 Solution: Basic approac to follow: Wat data is given? Wic are te assumptions? Make drawings and process diagrams. Wat is appening? Wic are te equations required? And Units? Start solving te easiest first Items tat ave te more information available IMORTANT: Read ALL te text twice, not just look for te numbers in between te letters. - Wat data is given? Fluid: ropane. Formulas and values for properties given. Cp, Hvap, sat, MW, Tc, etc. Compressor: Adiabatic + Reversible Isentropic Condenser: Outlet is 40C Evaporator: Outlet is -30C Valve: Expands fluid instantly. Tis case is from Sat.Liq to Liq.Vap.Mix. System designed for: QL= tonref = 7.4kW Surroundings: Hig: TH= 30C ; Low: TL=-10C - Wic are te assumptions? No pressure drops in Evaporator nor Condenser, terefore: = 1 ; 4 = 3. But 1 > 4. Valve: is Adiabatic and no Work, ten: 3 = (proved troug te energy balance) Vapour ase ONLY: Assume Ideal Gas. Valid for Sat.Vap and Super Heated Vapour ONLY. Reference State: Stream 40C). Take = 0 and s = 0.
3 - Drawings and Diagrams: TL Evaporator QL Compressor Expansion valve WC QH TH Condenser 1 4 QH 40 C C 4 QL WC - Basic Equations required: - Energy Balance (See Inside of Front Cover of your Book) Write te equation for eac equipment - Entropy Cange for System and Surroundings - Isentropic Relations for Ideal Gases - Units: Remember work in Kelvins and te conversions of bar to ka, m 3 to liters, etc. Start Solving: - Easiest calculations first: We can identify te two levels of pressure of te refrigeration cycle by calculating te vapour pressures at 40 C (te condenser produces saturated liquid), and at -30 C (te evaporator produces saturated vapour). C = 1== exp( /(0+50.4)) = ka. C = 3=4= exp( /( )) = ka. Now we start writing te Energy Balance equations for eac equipment and see wat we know for eac one (Careful wit sign conventions) - Compressor: WC = -n*(1 4) Units: W [J/s] WC (+) since is consumed ; n [mol/s] ; [J/mol] Now we need n, 1 and 4 (wait, still oter equations to write ) From assumptions: Compressor is Isentropic and Streams 1 and 4 are vapours, terefore, we can take tem as Ideal Gases.
4 Since te compression process is adiabatic reversible, ten te process is isentropic. ΔS41 = Cp*dT/T R*ln(1/4) = 0 T4 =-30 C = 43K. Use te equation above to find T1. ΔS41 =68*ln(T1/43) *ln(1366.9/166.7) = 0 Ten T1 = 43*exp(8.314*ln(1366.9/166.7)/68) K = K (~ 41. C) 0 ln Tis is te derivation of one of te isentropic relationsips for Ideal Gases To find 1, we need to add te terms necessary from te reference point (), see diagram: C 41. C To find 1, ten 1= +ΔHvap@40 C (to saturated vapour@40 C) + Cpgas*(41.-40)(to supereated vapour@ 41. C) Hvap Cp* T From given Correlation for HVap: ΔHvap@40 C =8.314*369.8*(7*(1-313/369.8)^ *0.15*(1-313/369.8)^0.456) J/mol ΔHvap@40 C =1376 J/mol Finally 1 = *( ) J/mol = J/mol To calculate 4, we follow a similar approac, we can calculate te entalpy of te saturated vapour at 40 C, and ten reduce te pressure to ka and 40 C, ten reduce te temperature to -30 C. Note: for an Ideal Gas, te entalpy does not depend on pressure. Remember, =u+v => = u+rt, were u is only a function of temperature. Finally: C 1-30 C Hvap 4 Cp* T ressure Effect 4= + ΔHvap@40 C (to saturated vapour@40 C) + 0 (effect of cange of pressure to 166.7ka)+ Cp gas*(-30 C-40 C) 4= *(-30-40) J/mol = 8516 J/mol We still need n and te oter entalpies, so we continue to write te equations for te following equipments. - Condenser: QH = n*(-1) Units: Q [J/s] QH (-) since is rejected to surroundings
5 We ave already 1= J/mol and =0 (Reference). Still need n for te refrigerant - Valve: Because te expansion valve is isentalpic, 3==0 J/mol. - Evaporator: QL = n*(4-3) Units: Q [J/s] QL (+) since is taken from surroundings At tis point, we know QL (given), 3 and 4 (calculated above). Applying te first law for open systems around te evaporator, neglecting canges in kinetic and potential energy, and at steady state: H4- H3 = QL since no work in te evaporator. nrefrigerant*(4-3) = QL = 7.4 kw. Ten, nrefrigerant = 7.4*10^3 J/s/(8516-0)J/mol = mol/s Now, since we got te value for n and we already ave all te entalpies, we can go back to energy balances for te oter equipments and solve for te missing variables, WC, QH. Compressor: Applying te first law for open systems around te compressor, neglecting canges in kinetic and potential energy, and at steady state: H1- H4 = W since te compressor is adiabatic. nrefrigerant*(1-4) = WC = mol/s *( )J/mol = 419 W = 4.kW (Consumed) Condenser: Applying te first law for open systems around te condenser, neglecting canges in kinetic and potential energy, and at steady state: H- H1 = QH since no work in te condenser. mrefrigerant*(-1) = QH =0.869 mol/s *( )J/mol = W = -11.6kW We can calculate te CO of te process = QL/ W = 7.44kW/4.kW = 1.76 Compare tis number to te CO for te Carnot cycle in between te same TH and TL See tat CO < COCarnot.
6 Entropy of te system: For simplicity, we calculate only te entropy canges for eac process, and for te entire system we get: ΔSsystem= ΔS41 + ΔS1 + ΔS3 + ΔS34 were: ΔSi-o= nrefrigerant*(si-so) NOTE: Te use of SGen term explained in Aurelio s tutorial will NOT be evaluated ere for simplicity. But first, we need to calculate all te entropies of eac stream. Reference => s = 0 J/mol-K saturated liquid at 40 C ( = ka) Remember te definition of Entropy: % &' ()* For determining s1 we follow a similar approac as we did for 1. We can approximate te entropy cange due to te pase cange to Hvap/Tsat, assuming tat te pat is reversible and pressure is constant. 1 1 Te contribution of te vapour eating section can be calculated troug te expression for Ideal Gas: Hvap/T Temp+ress cange Ten: s1 = s + ΔHvap@40 C/313K (to 40 C) + Cp*ln(314.3/313) (to 1366ka & 314.3K) Finally, s1 = /313+68*ln(314.3/313) J/mol-K = 4.7 J/mol-K Since te compressor is isentropic, ten s1=s4 = 4.7 J/mol-K We can calculate te entropy s3 starting from s4 (saturated vapour at -30 C) and considering 4 and 3 (evaporation at -30 C), we can approximate s3 as in te diagram 1 40 C 1 Hvap@40C/T s3 = s4 +(3-4)/(73-30)K = 4.7 J/mol-K + (0-8516)J/mol/43K = 7.65 J/mol-K C 4 (3-4)/T4
7 Finally, it is possible to calculate te entropy cange for eac equipment: Entropy of te compressor ΔS41= 0 W/K (te compressor is adiabatic+reversible = isentropic) Entropy of te condenser ΔS1= nrefrigerant*(s-s1) = mol/s*(0-4.7)j/mol-k = W/K Entropy of te expansion valve ΔS3= nrefrigerant*(s3-s) = mol/s*(7.65-0)j/mol-k = 6.65 W/K Entropy of te evaporator ΔS34= nrefrigerant*(s4-s3) = mol/s*( )j/mol-k = W/K ΔSsystem= ΔS41 + ΔS1 + ΔS3 + ΔS34 = W/K = 0 W/K Tis makes sense because being a cycle, ten te cange in entropy around te cycle sould be zero (remember, entropy is a state function and if you return to te point of origin of te cycle, ten te cange of entropy sould be zero). - Entropy of te surroundings = + QH /Toutside air - QL /Trefrigerated In tis case te term + QH is because tis eat is absorbed by te outside air, and - QL is eat released from te refrigerated environment. ΔSsurroundings = +11.6kW/(30+73)K kw/(-10+73)k =0.010 kw/k = +10 W/K Ten, ΔStotal = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings = W/K = +10 W/K Because te total entropy of te system is positive, ten te process complies wit te second law of termodynamic ( ΔStotal 0), and is feasible.
= T. (kj/k) (kj/k) 0 (kj/k) int rev. Chapter 6 SUMMARY
 Capter 6 SUMMARY e second la of termodynamics leads to te definition of a ne property called entropy ic is a quantitative measure of microscopic disorder for a system. e definition of entropy is based
Capter 6 SUMMARY e second la of termodynamics leads to te definition of a ne property called entropy ic is a quantitative measure of microscopic disorder for a system. e definition of entropy is based
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
Chapters 19 & 20 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Section A 01. (12 M) (s 2 s 3 ) = 313 s 2 = s 1, h 3 = h 4 (s 1 s 3 ) = kj/kgk. = kj/kgk. 313 (s 3 s 4f ) = ln
 0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page 1. Note: You can expect other types of questions on the test than the ones presented here!
 Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page Note: You can expect oter types of questions on te test tan te ones presented ere! Questions Example. Find te vertex of te quadratic f(x) = 4x 2 x. Example 2.
Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page Note: You can expect oter types of questions on te test tan te ones presented ere! Questions Example. Find te vertex of te quadratic f(x) = 4x 2 x. Example 2.
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muhammad Rashid Usman
 Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muammad Rasid Usman Institute of Cemical Engineering and Tecnology University of te Punjab, Laore. Figure taken from: ttp://eatexcanger-design.com/20/0/06/eat-excangers-6/
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muammad Rasid Usman Institute of Cemical Engineering and Tecnology University of te Punjab, Laore. Figure taken from: ttp://eatexcanger-design.com/20/0/06/eat-excangers-6/
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF A LIMIT
 LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
ENGR Thermodynamics
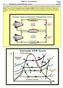 ENGR 224 - hermodynamics #1 - Diagram for a Cascade VCR Cycle (21 ts) Baratuci Final 13-Jun-11 On a full sheet of paper, construct a complete Diagram for the cascade cascade vapor-compression refrigeration
ENGR 224 - hermodynamics #1 - Diagram for a Cascade VCR Cycle (21 ts) Baratuci Final 13-Jun-11 On a full sheet of paper, construct a complete Diagram for the cascade cascade vapor-compression refrigeration
Previous lecture. Today lecture
 Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
(b) The heat transfer can be determined from an energy balance on the system
 8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
Carnot Factor of a Vapour Power Cycle with Regenerative Extraction
 Journal of Modern Pysics, 2017, 8, 1795-1808 ttp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp ISSN Online: 2153-120X ISSN Print: 2153-1196 arnot Factor of a Vapour Power ycle wit Regenerative Extraction Duparquet Alain
Journal of Modern Pysics, 2017, 8, 1795-1808 ttp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp ISSN Online: 2153-120X ISSN Print: 2153-1196 arnot Factor of a Vapour Power ycle wit Regenerative Extraction Duparquet Alain
Lecture 10: Carnot theorem
 ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
Chapter 4. Entropy and the Second Law. Soong Ho Um Sungkyunkwan University Chemical Engineering
 Chapter 4. Entropy and the Second Law Soong Ho Um Sungkyunkwan University Chemical Engineering 1 st Law to 2 nd Law The first law, discussed in the previous chapter, expresses a fundamental principle,
Chapter 4. Entropy and the Second Law Soong Ho Um Sungkyunkwan University Chemical Engineering 1 st Law to 2 nd Law The first law, discussed in the previous chapter, expresses a fundamental principle,
the first derivative with respect to time is obtained by carefully applying the chain rule ( surf init ) T Tinit
 .005 ermal Fluids Engineering I Fall`08 roblem Set 8 Solutions roblem ( ( a e -D eat equation is α t x d erfc( u du π x, 4αt te first derivative wit respect to time is obtained by carefully applying te
.005 ermal Fluids Engineering I Fall`08 roblem Set 8 Solutions roblem ( ( a e -D eat equation is α t x d erfc( u du π x, 4αt te first derivative wit respect to time is obtained by carefully applying te
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Physics 207 Lecture 23
 ysics 07 Lecture ysics 07, Lecture 8, Dec. Agenda:. Finis, Start. Ideal gas at te molecular level, Internal Energy Molar Specific Heat ( = m c = n ) Ideal Molar Heat apacity (and U int = + W) onstant :
ysics 07 Lecture ysics 07, Lecture 8, Dec. Agenda:. Finis, Start. Ideal gas at te molecular level, Internal Energy Molar Specific Heat ( = m c = n ) Ideal Molar Heat apacity (and U int = + W) onstant :
Answer Key THERMODYNAMICS TEST (a) 33. (d) 17. (c) 1. (a) 25. (a) 2. (b) 10. (d) 34. (b) 26. (c) 18. (d) 11. (c) 3. (d) 35. (c) 4. (d) 19.
 HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
Preface. Here are a couple of warnings to my students who may be here to get a copy of what happened on a day that you missed.
 Preface Here are my online notes for my course tat I teac ere at Lamar University. Despite te fact tat tese are my class notes, tey sould be accessible to anyone wanting to learn or needing a refreser
Preface Here are my online notes for my course tat I teac ere at Lamar University. Despite te fact tat tese are my class notes, tey sould be accessible to anyone wanting to learn or needing a refreser
General Physics I. New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, The 2nd Law, Entropy and Information. Prof. WAN, Xin
 General Pysics I New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, e 2nd Law, Entropy and Information Prof. AN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn ttp://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Carnot s Engine Efficiency of a Carnot Engine isotermal
General Pysics I New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, e 2nd Law, Entropy and Information Prof. AN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn ttp://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Carnot s Engine Efficiency of a Carnot Engine isotermal
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
Logarithmic functions
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter 5: Derivatives of transcendental functions Section Derivatives of Logaritmic functions Wat ou need to know alread: Definition of derivative and all basic
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter 5: Derivatives of transcendental functions Section Derivatives of Logaritmic functions Wat ou need to know alread: Definition of derivative and all basic
4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics
 4:5 Equilibrium Thermodynamics Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and Water Chapter 3. The Entropy Balance By J.R. Elliott, Jr. Unit I. Energy and Entropy Chapter 3. The Entropy Balance Introduction to Entropy
4:5 Equilibrium Thermodynamics Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and Water Chapter 3. The Entropy Balance By J.R. Elliott, Jr. Unit I. Energy and Entropy Chapter 3. The Entropy Balance Introduction to Entropy
II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Numerical Differentiation
 Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
A = h w (1) Error Analysis Physics 141
 Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
The Verlet Algorithm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 Cemistry 380.37 Fall 2015 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 9, 2015 Te Verlet Algoritm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Equations of motion For a many-body system consisting of N particles, Newton's classical
Cemistry 380.37 Fall 2015 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 9, 2015 Te Verlet Algoritm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Equations of motion For a many-body system consisting of N particles, Newton's classical
MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 2016 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 2016
 MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 206 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 206 Full Name: Student #: Last First Indicate wic Tutorial Section you attend by filling in te appropriate circle: Tut 0
MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 206 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 206 Full Name: Student #: Last First Indicate wic Tutorial Section you attend by filling in te appropriate circle: Tut 0
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
DYNAMIC MODELING OF ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC) SYSTEM FOR FAULT DIAGNOSIS AND CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
 DYNAMIC MODELING OF ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC SYSTEM FOR FAULT DIAGNOSIS AND CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN Sungjin Coi and Susan Krumdieck University of Canterbury, Private Bag 48, Cristcurc 84 New Zealand sungjin.coi@pg.canterbury.ac.nz
DYNAMIC MODELING OF ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC SYSTEM FOR FAULT DIAGNOSIS AND CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN Sungjin Coi and Susan Krumdieck University of Canterbury, Private Bag 48, Cristcurc 84 New Zealand sungjin.coi@pg.canterbury.ac.nz
8-4 P 2. = 12 kw. AIR T = const. Therefore, Q &
 8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
1 The concept of limits (p.217 p.229, p.242 p.249, p.255 p.256) 1.1 Limits Consider the function determined by the formula 3. x since at this point
 MA00 Capter 6 Calculus and Basic Linear Algebra I Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Te concept of its (p.7 p.9, p.4 p.49, p.55 p.56). Limits Consider te function determined by te formula f Note
MA00 Capter 6 Calculus and Basic Linear Algebra I Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Te concept of its (p.7 p.9, p.4 p.49, p.55 p.56). Limits Consider te function determined by te formula f Note
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Homework 1. Problem 1 Browse the 331 website to answer: When you should use data symbols on a graph. (Hint check out lab reports...
 Homework 1 Problem 1 Browse te 331 website to answer: Wen you sould use data symbols on a grap. (Hint ceck out lab reports...) Solution 1 Use data symbols to sow data points unless tere is so muc data
Homework 1 Problem 1 Browse te 331 website to answer: Wen you sould use data symbols on a grap. (Hint ceck out lab reports...) Solution 1 Use data symbols to sow data points unless tere is so muc data
Differential Calculus (The basics) Prepared by Mr. C. Hull
 Differential Calculus Te basics) A : Limits In tis work on limits, we will deal only wit functions i.e. tose relationsips in wic an input variable ) defines a unique output variable y). Wen we work wit
Differential Calculus Te basics) A : Limits In tis work on limits, we will deal only wit functions i.e. tose relationsips in wic an input variable ) defines a unique output variable y). Wen we work wit
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria
 Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
5.1 We will begin this section with the definition of a rational expression. We
 Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Section 2.7 Derivatives and Rates of Change Part II Section 2.8 The Derivative as a Function. at the point a, to be. = at time t = a is
 Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Phase space in classical physics
 Pase space in classical pysics Quantum mecanically, we can actually COU te number of microstates consistent wit a given macrostate, specified (for example) by te total energy. In general, eac microstate
Pase space in classical pysics Quantum mecanically, we can actually COU te number of microstates consistent wit a given macrostate, specified (for example) by te total energy. In general, eac microstate
Thermodynamics Lecture Series
 Termodynamics Lecture Series Ideal Ranke Cycle Te Practical Cycle Applied Sciences Education Researc Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@otmail.com ttp://www5.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj1.tml
Termodynamics Lecture Series Ideal Ranke Cycle Te Practical Cycle Applied Sciences Education Researc Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@otmail.com ttp://www5.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj1.tml
MTH-112 Quiz 1 Name: # :
 MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Problem Set 4: Whither, thou turbid wave SOLUTIONS
 PH 253 / LeClair Spring 2013 Problem Set 4: Witer, tou turbid wave SOLUTIONS Question zero is probably were te name of te problem set came from: Witer, tou turbid wave? It is from a Longfellow poem, Te
PH 253 / LeClair Spring 2013 Problem Set 4: Witer, tou turbid wave SOLUTIONS Question zero is probably were te name of te problem set came from: Witer, tou turbid wave? It is from a Longfellow poem, Te
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
Availability and Irreversibility
 Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
DEFINITION OF A DERIVATIVE
 DEFINITION OF A DERIVATIVE Section 2.1 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2017 viet.dang@umbleisd.net 2.1: Definition of a Derivative 1 DEFINITION A. Te derivative of a function allows you to find te SLOPE OF THE
DEFINITION OF A DERIVATIVE Section 2.1 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2017 viet.dang@umbleisd.net 2.1: Definition of a Derivative 1 DEFINITION A. Te derivative of a function allows you to find te SLOPE OF THE
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 26, 27, 37, 44, 46, 52, 58
 PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
1. Which one of the following expressions is not equal to all the others? 1 C. 1 D. 25x. 2. Simplify this expression as much as possible.
 004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
Exam 1 Review Solutions
 Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
The Laws of Thermodynamics
 1 Te Laws of Termodynamics CLICKER QUESTIONS Question J.01 Description: Relating termodynamic processes to PV curves: isobar. Question A quantity of ideal gas undergoes a termodynamic process. Wic curve
1 Te Laws of Termodynamics CLICKER QUESTIONS Question J.01 Description: Relating termodynamic processes to PV curves: isobar. Question A quantity of ideal gas undergoes a termodynamic process. Wic curve
2.8 The Derivative as a Function
 .8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
.8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
Introduction to Derivatives
 Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
2.3 Product and Quotient Rules
 .3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
.3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, :30 p.m. to 7:30 p.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS. Andrew S. Rosen
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Andrew S. Rosen SYMBOL DICTIONARY 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Symbol Dictionary... 3 1. Measured Thermodynamic Properties and Other Basic Concepts... 5 1.1 Preliminary Concepts
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Andrew S. Rosen SYMBOL DICTIONARY 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Symbol Dictionary... 3 1. Measured Thermodynamic Properties and Other Basic Concepts... 5 1.1 Preliminary Concepts
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Heat Transfer/Heat Exchanger
 Heat ransfer/heat Excanger How is te eat transfer? Mecanism of Convection Applications. Mean fluid Velocity and Boundary and teir effect on te rate of eat transfer. Fundamental equation of eat transfer
Heat ransfer/heat Excanger How is te eat transfer? Mecanism of Convection Applications. Mean fluid Velocity and Boundary and teir effect on te rate of eat transfer. Fundamental equation of eat transfer
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
We name Functions f (x) or g(x) etc.
 Section 2 1B: Function Notation Bot of te equations y 2x +1 and y 3x 2 are functions. It is common to ave two or more functions in terms of x in te same problem. If I ask you wat is te value for y if x
Section 2 1B: Function Notation Bot of te equations y 2x +1 and y 3x 2 are functions. It is common to ave two or more functions in terms of x in te same problem. If I ask you wat is te value for y if x
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION. James T. Smith San Francisco State University. In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example,
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION James T Smit San Francisco State University In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example, f( x) = x + x f ( x) = x x Tis tecnique requires your knowing
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION James T Smit San Francisco State University In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example, f( x) = x + x f ( x) = x x Tis tecnique requires your knowing
Simulation and verification of a plate heat exchanger with a built-in tap water accumulator
 Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
(Refer Slide Time: 00:00:43 min) Welcome back in the last few lectures we discussed compression refrigeration systems.
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Solution for the Homework 4
 Solution for te Homework 4 Problem 6.5: In tis section we computed te single-particle translational partition function, tr, by summing over all definite-energy wavefunctions. An alternative approac, owever,
Solution for te Homework 4 Problem 6.5: In tis section we computed te single-particle translational partition function, tr, by summing over all definite-energy wavefunctions. An alternative approac, owever,
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 3 Thermoelectric Coolers
 3- Capter 3 ermoelectric Coolers Contents Capter 3 ermoelectric Coolers... 3- Contents... 3-3. deal Equations... 3-3. Maximum Parameters... 3-7 3.3 Normalized Parameters... 3-8 Example 3. ermoelectric
3- Capter 3 ermoelectric Coolers Contents Capter 3 ermoelectric Coolers... 3- Contents... 3-3. deal Equations... 3-3. Maximum Parameters... 3-7 3.3 Normalized Parameters... 3-8 Example 3. ermoelectric
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION
 LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
Calculus I Homework: The Derivative as a Function Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: Te Derivative as a Function Page 1 Example (2.9.16) Make a careful sketc of te grap of f(x) = sin x and below it sketc te grap of f (x). Try to guess te formula of f (x) from its grap.
Calculus I Homework: Te Derivative as a Function Page 1 Example (2.9.16) Make a careful sketc of te grap of f(x) = sin x and below it sketc te grap of f (x). Try to guess te formula of f (x) from its grap.
MAT 145. Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points
 MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
The total error in numerical differentiation
 AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
1 1. Rationalize the denominator and fully simplify the radical expression 3 3. Solution: = 1 = 3 3 = 2
 MTH - Spring 04 Exam Review (Solutions) Exam : February 5t 6:00-7:0 Tis exam review contains questions similar to tose you sould expect to see on Exam. Te questions included in tis review, owever, are
MTH - Spring 04 Exam Review (Solutions) Exam : February 5t 6:00-7:0 Tis exam review contains questions similar to tose you sould expect to see on Exam. Te questions included in tis review, owever, are
1. State whether the function is an exponential growth or exponential decay, and describe its end behaviour using limits.
 Questions 1. State weter te function is an exponential growt or exponential decay, and describe its end beaviour using its. (a) f(x) = 3 2x (b) f(x) = 0.5 x (c) f(x) = e (d) f(x) = ( ) x 1 4 2. Matc te
Questions 1. State weter te function is an exponential growt or exponential decay, and describe its end beaviour using its. (a) f(x) = 3 2x (b) f(x) = 0.5 x (c) f(x) = e (d) f(x) = ( ) x 1 4 2. Matc te
f a h f a h h lim lim
 Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 20 June 2005
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
1 Power is transferred through a machine as shown. power input P I machine. power output P O. power loss P L. What is the efficiency of the machine?
 1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
Announcements. Exam 4 - Review of important concepts
 Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
QUIZZES RIEPJCPIγPJEJJJY
 Che 3021 Thermodynamics I QUIZZES RIEPJCPIγPJEJJJY QUIZ 1. Find Molecular Weights: 1 1 CO 2 2 NaCl 3 Aspirin C 9 H 8 O 4 CO2 = NaCl = C9H8O4 = PIgPJC Quiz 1. Temperature conversion 1 Convert 94 o F, to
Che 3021 Thermodynamics I QUIZZES RIEPJCPIγPJEJJJY QUIZ 1. Find Molecular Weights: 1 1 CO 2 2 NaCl 3 Aspirin C 9 H 8 O 4 CO2 = NaCl = C9H8O4 = PIgPJC Quiz 1. Temperature conversion 1 Convert 94 o F, to
Phys102 First Major-182 Zero Version Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday, February 14, 2019 Page: 1
 Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
Lesson 6: The Derivative
 Lesson 6: Te Derivative Def. A difference quotient for a function as te form f(x + ) f(x) (x + ) x f(x + x) f(x) (x + x) x f(a + ) f(a) (a + ) a Notice tat a difference quotient always as te form of cange
Lesson 6: Te Derivative Def. A difference quotient for a function as te form f(x + ) f(x) (x + ) x f(x + x) f(x) (x + x) x f(a + ) f(a) (a + ) a Notice tat a difference quotient always as te form of cange
Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
 MATH 111 07 (Kunkle), Eam 1 100 pts, 75 minutes No notes, books, electronic devices, or outside materials of an kind. Read eac problem carefull and simplif our answers. Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
MATH 111 07 (Kunkle), Eam 1 100 pts, 75 minutes No notes, books, electronic devices, or outside materials of an kind. Read eac problem carefull and simplif our answers. Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
NUCLEAR THERMAL-HYDRAULIC FUNDAMENTALS
 NUCLEAR THERMAL-HYDRAULIC FUNDAMENTALS Dr. J. Micael Doster Departent of Nuclear Engineering Nort Carolina State University Raleig, NC Copyrigted POER CYCLES Te analysis of Terodynaic Cycles is based alost
NUCLEAR THERMAL-HYDRAULIC FUNDAMENTALS Dr. J. Micael Doster Departent of Nuclear Engineering Nort Carolina State University Raleig, NC Copyrigted POER CYCLES Te analysis of Terodynaic Cycles is based alost
MVT and Rolle s Theorem
 AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area
 7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area Introduction finding te area under te grap of a nonnegative, continuous function f In tis section a formula is obtained for finding te area of te region bounded between
7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area Introduction finding te area under te grap of a nonnegative, continuous function f In tis section a formula is obtained for finding te area of te region bounded between
