Drops sliding down an incline: Singular corners.
|
|
|
- Beverly Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Drops sliding down an incline: Singular corners. Laurent Limat Laboratoire Matière et Systèmes Complexes, MSC, Paris Diderot University with: -Jean-Marc Flesselles, Thomas Podgorski (initial experiments) -Adrian Daerr, Nolwenn Le Grand Bruno Andreotti, Emmanuelle Rio, Ivo Peters (3D visualization + PIV+optics) - Jacco Snoeijer, Howard Stone, Jens Eggers (corner models)
2 Partial wetting What happens on a tilted plate?
3 V Hysteresis: drop can remain pinned...! ("cos#) ~ $g V 2/3 or begins to slide U -viscous effects -> shape changes? -wetting dynamics with 3D aspects ->? -Inclined, curved contact line possibly developing a singular point
4 3D Sliding drops: -Bikerman, JCS 1950, Furmidge, JCS Dussan (and Chow), JFM 1983, Kim, Lee + Kang, JCIS > onset of motion -> calculations for rounded drops yield condition -> sliding velocities of oval drops related to viscous dissipation -Podgorski, Flesselles, LL, PRL Le Grand, Daerr, LL, JFM Rio, Daerr, Andreotti, LL, PRL > Singularity at drop rear -> 3D structure of interface -> flow structure, contact angle distribution -Stone + LL, Europhys. Lett > similarity solution of hydrodynamics -Snoeijer, Le Grand, Rio, LL, Phys. Fl > flow structure, rounded corners -Snoeijer, Le Grand, LL, Stone, Eggers, Phys. Fl > opening angle selection, pearling transition Other model: Cummins, Ben Amar, Pomeau, Phys. Fl > model based on Laplace +directional Young condition Numerical simulations: -Schwartz et al., Physica D, Thiele et al --Gaskell et al. (Leeds)
5 Ca=&U/! sin%~1/ca Silicon oil drops on fluoropolymers
6 Cohen Nagel Courrech-du-Pont Eggers Daerr, Le Grand, LL, 2005 Singularities at interfaces (Rutland and Jameson!71) Quéré, Lorenceau
7 U air liquid Analogy with Landau-Levich Blake, Ruschak (Nature 1979) Snoeijer, Delon, Andreotti, Fermigier PRL 2006
8 Interpretation: # d =F(Ca) --> 0 (or a critical value) # # a # r! d 0 U! U e Ca=&U/! U n = U sin "! d >0 " U U! U e ; U n " U e! d U < U e # d =F(Ca sin%)! 0 => sin! = Ca c Ca Blake, Ruschak(Nature 1979)
9 Other point of view: Drops avoid wetting by tilting contact lines plate withdrawn from bath Ca sin! U>U C! Blake and Ruschak!79 Ca normal velocity: maximum speed=u c //Mach cone => sin% ~ 1/Ca
10 Outline: Experiment - Observations 3D structure and flow in sliding drops 3D geometry of sliding drops flow structure - autosimilarity Matching with contact lines opening angle selection pearling transition Curvature at the tip curved contact lines divergence of curvature U>U c U n =U>U c U n =Usinf =U c
11 Pipette EXPERIMENT Syringe VideoCamera Miror Bécher a FAST CAM ' iiyama Tilted glass plate + 3M fluoropolymers A. Daerr, N. Le Grand, LL, J. Fl. Mech. (2005)
12
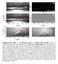
13 sliding silicon oil drops... increasing Ca="U0/# Podgorski, Flesselles Limat, PRL!01 Le Grand, Daerr, Limat JFM!05 Side views rounded corner cusp conical singularity pearling U0 Stone, LL, Europhys. "04 Glass plate + fluoropolymer coating Partial wetting: contact angle 45º
14 80 # d =# c # d = 0 1 sin(") # d adv # d rcd # d ( ) # c advancing receding rounded drops corners cusps! ( ) pearling drops 0,8 0,6 0,4 0,2 % ,002 0,004 0,006 0,008 Ca? Non-zero // De Gennes // Raphaël, Golestanian ( -Sin% ~1/Ca, but - non-zero critical angle # c -Conical interface : #, ( non-zero Daerr, Le Grand, LL, J.Fl. Mech. 2005
15 Voïnov-Cox model 80 sin(") 0,8 # d ( ) adv 60 0,6 40 0,4 # d ( ) rcd 20 0,2! ( ) ,002 0,004 0,006 0,008 rounded drops corners Ca cusps pearling drops 1 - Mass conservation: Uh = h 3 3" # (h xx) x - To be completed with : # = # e for x=a and a matching with an outer solution for x -> ) 9Log(b/a)=130 9Log(b/a)=130 3 Ca h 2 = h xxx macroscopic microscopic " 3 (b) = " 3 (a) ± 9CaLog( b a) # e (equilibrium angle) everything is singular for h=0
16 ! =104 cp 1! =1040 cp 1 80 Rounded drops sin$ 0,8 80 " a sin$ 0,8 60 " a 40 " r 0,6 Rounded corners " a, " r, # ( ) sin$ Corners Cusp 0,4 60 Rounded drop " a, " r, # ( ) sin$ Rounded corner 40 Corner " r 0,6 0,4 20 # 0,2 20 # Cusp 0, ,001 0,002 0,003 0,004 0,005 0,006 0,007 Ca ,002 0,004 0,006 0,008 0,01 Ca Same with two other viscosities.
17 U Front and rear curvatures Ca=&U/!
18 Structure of the singularity h(x,y)? U(x,y)=<v(x,y,z)> /z? U(x,y) r U (x, y) = " h 2 3# $P Flow driven by capillary pressure! Stone + LL, Europhys 04 Snoeijer et al., Phys. Fluids 05
19 corner model r U (x, y) = h 2 3" #($h) + steady state solutions: y h( x - U 0 t, y) x 3Ca "h "x = #. h 3 #($h) [ ] Ca="U 0 / #
20 corner geometry 3Ca "h "x = #. h 3 #($h) [ ] y equation allows similarity solutions: 1/3 h(x,y) = Ca x H(y/x) x Note: Ca has disappeared
21 corner geometry y 3Ca "h "x = #. h 3 #($h) [ ] equations allow similarity solutions: x 1/3 h(x,y) = Ca x H(y/x) 1-parameter family: H b.c: H = H = 0 (symmetry) H0 H (continuity) Note: Ca has disappeared y/x
22 corner geometry y % ( x 1/3 h(x,y) = Ca x H(y/x) H tan( H0 = tan $/ Ca 1/3 tan% Infinite number of solutions, irrespectively of Ca (we will need later an extra-condition) y/x
23 relation ( and % % % ( H0 = tan $ / Ca 1/3 (no adjustable parameters) dashed: (tan$) 3 35 = 16 Ca ( tan!) 2
24 velocity field h(x,y) U(x,y)=U 0 F(y/x) F deduced from H PIV experiment: tracers Rio, Andreotti, Daerr
25 velocity field Theory: velocity self-similar U = U(y/x) 52 µm 312 µm # flow direction * " Snoeijer et al. Phys Fluids!05
26 velocity field Theory: velocity self-similar U = U(y/x) components 52 mm Ur 312 mm Uf % Snoeijer et al. Phys. Fluids!05
27 But. - Selection of %? - Prediction of pearling instability? How to manage with the singularity at contact line?
28 Classical argument: # # d =F(Ca) --> 0 or a critical value # r! d 0 U! U e Ca=&U/! U n = U sin "! d >0 " U U! U e ; U n " U e! d U < U e Blake, Ruschak(Nature 1979) Podgorski et al (PRL 2000) # d =F(Ca sin%)! 0 => sin! = Ca c Ca
29 Low % paradox: f! W pressure gradients become weaker... velocity + 0! + 0 implies drop speed + 0 maximum speed!! Breakdown of 1/Ca law Ca %~1/Ca %
30 %-selection : mixing contact line and bulk flow 70 rounded drop corner cusp pearling drop 1 tan 3 (!(35/16)Ca tan 2 % and: 60 50! a Cox-Voïnov 0,8! a,! r, " ( ) 40 30! r (! r =! c ) sin# 0,6 0,4 sin# 20! c #! 2 (/sin% and: " 3 = " 3 e # 9(Casin$)Log( b a) 10 Similarity solution 0 0 0,002 0,004 0,006 0,008 0,01 Ca Ca " = e sin# $ & 9Log(b/a) + %& 70 ' ) ( sin2# ) 2 () 0,2 0
31 Snoeijer, Eggers Ca=&U/! d dx = " d dx small - Lubrication + parabolic approx. Ca[ HY " H # Y # ] $ " H & 3 Y% H ) ( + ' Y 2 * X Flowing down Left behind Viscous capillary flux - Directional Cox-Voïnov law: " 3 # (2 H Y )3 # " e 3 $ 9Ca(%Y X )Log(b /a) Consistency: Ca, Log(b/a) ~Ca/,~1 Ca sin%
32 About directional Cox-Voïnov law E. Rio, A. Daerr, B. Andreotti, LL, Phys Rev Lett 2004
33 Lubrification: < r u >= " h 2 3# $P P " #$%h Singular at contact line " /"x # >> " /"x // Mass conservation: u - >>u // <u - >=u c-line u c-line -> local 2D situation
34 Ca=&U/! d dx = " d dx small - Lubrication + parabolic approx. Ca[ HY " H # Y # ] $ " H & 3 Y% H ) ( + ' Y 2 * X Flowing down Left behind Viscous capillary flux - Directional Cox-Voïnov law: " 3 # (2 H Y )3 # " e 3 $ 9Ca(%Y X )Log(b /a) Consistency: Ca, Log(b/a) ~Ca/,~1 Ca sin%
35 For, = 1/[Ln(b/a)] 1/2 small there exist corner solutions (H~Y~X) with: 3Ca "# $ 6(% /") 3 e (% /") 2 3Ca/(,# r3 ) %!25 unstable stable %/, Oval drops -> Log(b/a)~10,~0.3
36 3Ca/(,# r3 ) %/,
37 - beyond maximum speed: rivulet solutions Y! U - rivulet width Y! vs U f W
38 Curvature at the tip... Le Grand et al. JFM!05 1/R (1/mm) Problem: U 0 sin% = U c => U 0 >U c!! Ca Idea: U c =f(r) => U 0 sin% = U c (R=)) et U 0 =U c (R) -Critical speed Ca(1/R)?=> calc. for «large» R -> Snoeijer et al. Phys. Fl Other question: R(Ca)? Scaling laws for tip equilibrium
39 An open issue: divergence of 1/R Ivo Peters Adrian Daerr 1/R~Aexp(B Ca) Similar to Lorenceau
40 Difficult to understand: F cap ~ L# 2! ~F visc ~L & (U/#) Log(R/a) L -> 1/R ~(1/a) exp(# 3 /Ca) To get 1/R ~(1/a) exp(ca/# 3 ) One would need F visc ~L & (U/#) / Log(R/a).
41 Discussion drops have singular shapes to avoid wetting inclined: reduces normal speed curved: additional capillary forces Rio et al. PRL!05 3D structure governed by similarity solutions. Matching with contact line (where the flow is perpendicular) selects opening angle. Matching becomes impossible above a critical Capillary number -> pearling Behavior of 1/R at the tip remains to be Understood
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
Cornered drops and rivulets
 Cornered drops and rivulets PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 042104 2007 J. H. Snoeijer School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, United Kingdom; Laboratoire MSC, UMR 7057 of
Cornered drops and rivulets PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 042104 2007 J. H. Snoeijer School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, United Kingdom; Laboratoire MSC, UMR 7057 of
Cornered drops and rivulets
 Cornered drops and rivulets J. H. Snoeijer 1,2, N. Le Grand-Piteira 2, L. Limat 2, H.A. Stone 3, and J. Eggers 1 1 School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, United
Cornered drops and rivulets J. H. Snoeijer 1,2, N. Le Grand-Piteira 2, L. Limat 2, H.A. Stone 3, and J. Eggers 1 1 School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TW, United
On the Landau-Levich Transition
 10116 Langmuir 2007, 23, 10116-10122 On the Landau-Levich Transition Maniya Maleki Institute for AdVanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS), Zanjan 45195, P.O. Box 45195-1159, Iran Etienne Reyssat and
10116 Langmuir 2007, 23, 10116-10122 On the Landau-Levich Transition Maniya Maleki Institute for AdVanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS), Zanjan 45195, P.O. Box 45195-1159, Iran Etienne Reyssat and
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena. Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS Outline 1. Creeping flow: hydrodynamics at low Reynolds numbers (2 hrs) 2. Thin films and lubrication flows (3 hrs + problem session
Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS Outline 1. Creeping flow: hydrodynamics at low Reynolds numbers (2 hrs) 2. Thin films and lubrication flows (3 hrs + problem session
Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part 1: A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation
 Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part : A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation By JACCO H. SNOEIJER, BRUNO ANDREOTTI, GILES DELON AND MARC FERMIGIER
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part : A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation By JACCO H. SNOEIJER, BRUNO ANDREOTTI, GILES DELON AND MARC FERMIGIER
Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 1. A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation
 J. Fluid Mech. (7), vol. 579, pp. 63 83. c 7 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s117516 Printed in the United Kingdom 63 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 1. A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation
J. Fluid Mech. (7), vol. 579, pp. 63 83. c 7 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s117516 Printed in the United Kingdom 63 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 1. A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation
Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena. Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS Outline 1. Creeping flow: hydrodynamics at low Reynolds numbers (2 hrs) 2. Thin films and lubrication flows (3 hrs + problem session
Hydrodynamics of wetting phenomena Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS Outline 1. Creeping flow: hydrodynamics at low Reynolds numbers (2 hrs) 2. Thin films and lubrication flows (3 hrs + problem session
Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part 2: Experiments
 Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part 2: Experiments By GILES DELON 1, MARC FERMIGIER 1, JACCO H. SNOEIJER 1,2 AND BRUNO ANDREOTTI 1 1 Physique
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line Part 2: Experiments By GILES DELON 1, MARC FERMIGIER 1, JACCO H. SNOEIJER 1,2 AND BRUNO ANDREOTTI 1 1 Physique
Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 2. Experiments
 J. Fluid Mech. (28), vol. 64, pp. 55 75. c 28 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s221128979 Printed in the United Kingdom 55 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 2. Experiments GILES DELON 1,
J. Fluid Mech. (28), vol. 64, pp. 55 75. c 28 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s221128979 Printed in the United Kingdom 55 Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 2. Experiments GILES DELON 1,
Characteristic lengths at moving contact lines for a perfectly wetting fluid: the influence of speed on the dynamic contact angle
 Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Characteristic lengths at moving contact lines for a perfectly wetting fluid: the influence of speed on the dynamic contact angle By Jens Eggers
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Characteristic lengths at moving contact lines for a perfectly wetting fluid: the influence of speed on the dynamic contact angle By Jens Eggers
Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films
 Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films Lou Kondic Department of Mathematical Sciences Center for Applied Mathematics and Statistics New Jersey Institute of Technology Presented at Annual Meeting
Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films Lou Kondic Department of Mathematical Sciences Center for Applied Mathematics and Statistics New Jersey Institute of Technology Presented at Annual Meeting
Depinning of 2d and 3d droplets blocked by a hydrophobic defect
 Depinning of 2d and 3d droplets blocked by a hydrophobic defect P. Beltrame 1, P. Hänggi 1, E. Knobloch 2, and U. Thiele 3 1 Institut für Physik, Universität Augsburg, D-86135 Augsburg, Germany 2 Department
Depinning of 2d and 3d droplets blocked by a hydrophobic defect P. Beltrame 1, P. Hänggi 1, E. Knobloch 2, and U. Thiele 3 1 Institut für Physik, Universität Augsburg, D-86135 Augsburg, Germany 2 Department
PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 5, Supp, Pages 85 92 c 2008 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES K. M. HAY AND
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 5, Supp, Pages 85 92 c 2008 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES K. M. HAY AND
Transitions in viscous withdrawal
 Transitions in viscous withdrawal Wendy W. Zhang Physics & James Franck Institute University of Chicago Minisymposium: Tip-streaming & flow/ehd flow focusing APS-DFD Meeting San Antonio, TX November 2008
Transitions in viscous withdrawal Wendy W. Zhang Physics & James Franck Institute University of Chicago Minisymposium: Tip-streaming & flow/ehd flow focusing APS-DFD Meeting San Antonio, TX November 2008
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Thickness and Shape of Films Driven by a Marangoni Flow
 Langmuir 1996, 12, 5875-5880 5875 Thickness and Shape of Films Driven by a Marangoni Flow X. Fanton, A. M. Cazabat,* and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, Collège de France, 11
Langmuir 1996, 12, 5875-5880 5875 Thickness and Shape of Films Driven by a Marangoni Flow X. Fanton, A. M. Cazabat,* and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, Collège de France, 11
Deformation of a droplet adhering to a solid surface in shear flow: onset of interfacial sliding
 J. Fluid Mech. (27), vol. 58, pp. 451 466. c 27 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s2211275721 Printed in the United Kingdom 451 Deformation of a droplet adhering to a solid surface in shear flow: onset
J. Fluid Mech. (27), vol. 58, pp. 451 466. c 27 Cambridge University Press doi:1.117/s2211275721 Printed in the United Kingdom 451 Deformation of a droplet adhering to a solid surface in shear flow: onset
Wetting contact angle
 Wetting contact angle Minh Do-Quang www.flow.kth.se Outline Statics; capillarity and wetting Dynamics; models describing dynamic wetting Hydrodynamics (Tanner-Cox-Voinov law) Molecular kinetics theory
Wetting contact angle Minh Do-Quang www.flow.kth.se Outline Statics; capillarity and wetting Dynamics; models describing dynamic wetting Hydrodynamics (Tanner-Cox-Voinov law) Molecular kinetics theory
Solvability condition for the moving contact line
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 78, 564 28 Solvability condition for the moving contact line L. M. Pismen 1 and Jens Eggers 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Minerva Center for Nonlinear Physics of Complex
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 78, 564 28 Solvability condition for the moving contact line L. M. Pismen 1 and Jens Eggers 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Minerva Center for Nonlinear Physics of Complex
+ S/y. The wetted portion of the surface is then delimited by a certain contact line L (here a
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 21 (4), pp. 483-488 (1993) 1 February 1993 Contact Line Elasticity of a Completely Wetting Liquid Rising on a Wall. E. RAPHAEL(*)( ) and J. F. JoA"Y(**) (*) Institute
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 21 (4), pp. 483-488 (1993) 1 February 1993 Contact Line Elasticity of a Completely Wetting Liquid Rising on a Wall. E. RAPHAEL(*)( ) and J. F. JoA"Y(**) (*) Institute
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114088847.jpg) This draft was prepared using the LaTeX style file belonging to the Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1 arxiv:1901.03548v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Jan 2019 Directional spreading of a viscous droplet on a conical
This draft was prepared using the LaTeX style file belonging to the Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1 arxiv:1901.03548v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Jan 2019 Directional spreading of a viscous droplet on a conical
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media
 Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
the moving contact line
 Molecular hydrodynamics of the moving contact line Tiezheng Qian Mathematics Department Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in collaboration with Ping Sheng (Physics Dept, HKUST) Xiao-Ping Wang
Molecular hydrodynamics of the moving contact line Tiezheng Qian Mathematics Department Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in collaboration with Ping Sheng (Physics Dept, HKUST) Xiao-Ping Wang
characterize antiadhesive surfaces
 Capillary bridge formation and breakage: a test to characterize antiadhesive surfaces TITLE RUNNING HEAD: Capillary bridge for antiadhesive surfaces. Laurianne Vagharchakian 1, Frédéric Restagno 2, Liliane
Capillary bridge formation and breakage: a test to characterize antiadhesive surfaces TITLE RUNNING HEAD: Capillary bridge for antiadhesive surfaces. Laurianne Vagharchakian 1, Frédéric Restagno 2, Liliane
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles. Abstract
 Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
Vibration of submillimeter-size supported droplets
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 73, 041602 2006 Vibration of submillimeter-size supported droplets Franck Celestini* and Richard Kofman Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, UMR 6622, CNRS, Université de
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 73, 041602 2006 Vibration of submillimeter-size supported droplets Franck Celestini* and Richard Kofman Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, UMR 6622, CNRS, Université de
Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena
 ? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell
 On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
Gravity and Inertia Effects in Plate Coating
 JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE 203, 278 285 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CS985444 Gravity and Inertia Effects in Plate Coating Alain de Ryck* and David Quéré,1 *École des Mines d Albi-Carmaux, route de
JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE 203, 278 285 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CS985444 Gravity and Inertia Effects in Plate Coating Alain de Ryck* and David Quéré,1 *École des Mines d Albi-Carmaux, route de
drops in motion Frieder Mugele the physics of electrowetting and its applications Physics of Complex Fluids University of Twente
 drops in motion the physics of electrowetting and its applications Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids niversity of Twente 1 electrowetting: the switch on the wettability voltage outline q q q q q
drops in motion the physics of electrowetting and its applications Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids niversity of Twente 1 electrowetting: the switch on the wettability voltage outline q q q q q
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Mar 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Mar 2013](/thumbs/73/68837875.jpg) Hydrodynamics of air entrainment by moving contact lines T.S. Chan 1, S. Srivastava 2,5, A. Marchand 3, B. Andreotti 3, L. Biferale 4, F. Toschi 2,5,6 and J.H. Snoeijer 1 1 Physics of Fluids Group, Faculty
Hydrodynamics of air entrainment by moving contact lines T.S. Chan 1, S. Srivastava 2,5, A. Marchand 3, B. Andreotti 3, L. Biferale 4, F. Toschi 2,5,6 and J.H. Snoeijer 1 1 Physics of Fluids Group, Faculty
Thin Film Breakup and Rivulet Evolution Modeling
 Thin Film Breakup and Rivulet Evolution Modeling Nicola Suzzi, Giulio Croce 2, Paola D Agaro 3 DIEG - Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica, Gestionale e Meccanica - Universitá di Udine - Via delle Scienze
Thin Film Breakup and Rivulet Evolution Modeling Nicola Suzzi, Giulio Croce 2, Paola D Agaro 3 DIEG - Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica, Gestionale e Meccanica - Universitá di Udine - Via delle Scienze
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013](/thumbs/73/68817731.jpg) Supporting Information: Short and long time drop dynamics on lubricated substrates Andreas Carlson1,3,4,, Pilnam Kim2,4, Gustav Amberg3, and Howard A. Stone4, arxiv:1309.6339v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct
Supporting Information: Short and long time drop dynamics on lubricated substrates Andreas Carlson1,3,4,, Pilnam Kim2,4, Gustav Amberg3, and Howard A. Stone4, arxiv:1309.6339v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct
Dip coating in the presence of a substrate-liquid interaction potential
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 17, 102105 2005 Dip coating in the presence of a substrate-liquid interaction potential R. Krechetnikov a and G. M. Homsy Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California,
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 17, 102105 2005 Dip coating in the presence of a substrate-liquid interaction potential R. Krechetnikov a and G. M. Homsy Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California,
On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability
 On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability L. Pauchard, F. Varela LÓpez*, M. Rosen*, C. Allain, P. Perrot** and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405
On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability L. Pauchard, F. Varela LÓpez*, M. Rosen*, C. Allain, P. Perrot** and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405
1. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work
 . Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
Kinetic Slip Condition, van der Waals Forces, and Dynamic. Contact Angle. Abstract
 Kinetic Slip Condition, van der Waals Forces, and Dynamic Contact Angle Len M. Pismen and Boris Y. Rubinstein Department of Chemical Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 3000, Israel.
Kinetic Slip Condition, van der Waals Forces, and Dynamic Contact Angle Len M. Pismen and Boris Y. Rubinstein Department of Chemical Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 3000, Israel.
Gravitational effects on the deformation of a droplet adhering to a horizontal solid surface in shear flow
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 122105 2007 Gravitational effects on the deformation of a droplet adhering to a horizontal solid surface in shear flow P. Dimitrakopoulos Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 122105 2007 Gravitational effects on the deformation of a droplet adhering to a horizontal solid surface in shear flow P. Dimitrakopoulos Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Wetting kinetics in forced spreading
 Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Research & Creative Works 2016 Wetting kinetics in forced spreading Amer Mohammad Al-Shareef Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/doctoral_dissertations
Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Research & Creative Works 2016 Wetting kinetics in forced spreading Amer Mohammad Al-Shareef Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/doctoral_dissertations
On the distinguished limits of the Navier slip model of the moving contact line problem
 J. Fluid Mech. (015), vol. 77, pp. 107 16. c Cambridge University Press 015 doi:10.1017/jfm.015.173 107 On the distinguished limits of the Navier slip model of the moving contact line problem Weiqing Ren
J. Fluid Mech. (015), vol. 77, pp. 107 16. c Cambridge University Press 015 doi:10.1017/jfm.015.173 107 On the distinguished limits of the Navier slip model of the moving contact line problem Weiqing Ren
The growth of leading-edge distortions on a viscous sheet
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1999 The growth of leading-edge distortions on a viscous sheet L. M. Hocking Department of Mathematics, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1999 The growth of leading-edge distortions on a viscous sheet L. M. Hocking Department of Mathematics, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E
Microfluidic crystals: Impossible order
 Microfluidic crystals: Impossible order Tsevi Beatus, Roy Bar-Ziv, T. T. Weizmann Institute International Symposium on Non-Equilibrium Soft Matter Kyoto 2008 1 Outline Micro-fluidic droplets: micron sized
Microfluidic crystals: Impossible order Tsevi Beatus, Roy Bar-Ziv, T. T. Weizmann Institute International Symposium on Non-Equilibrium Soft Matter Kyoto 2008 1 Outline Micro-fluidic droplets: micron sized
Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow
 OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
Thin flow over a sphere
 1 University of Waterloo, Faculty of Mathematics, Waterloo, Canada 2 Ryerson University, Department of Mathematics, Toronto, Canada IMA8 2016, June 12-16, Bad Honnef, Germany Problem description Related
1 University of Waterloo, Faculty of Mathematics, Waterloo, Canada 2 Ryerson University, Department of Mathematics, Toronto, Canada IMA8 2016, June 12-16, Bad Honnef, Germany Problem description Related
Candidates must show on each answer book the type of calculator used. Only calculators permitted under UEA Regulations may be used.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen
 Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
DETERMINATION OF THE DYNAMIC CONTACT ANGLE TROUGH THE MENISCUS PROFILE * Stanimir Iliev, Nina Pesheva
 МАТЕМАТИКА И МАТЕМАТИЧЕСКО ОБРАЗОВАНИЕ, 2011 MATHEMATICS AND EDUCATION IN MATHEMATICS, 2011 Proceedings of the Fortieth Jubilee Spring Conference of the Union of Bulgarian Mathematicians Borovetz, April
МАТЕМАТИКА И МАТЕМАТИЧЕСКО ОБРАЗОВАНИЕ, 2011 MATHEMATICS AND EDUCATION IN MATHEMATICS, 2011 Proceedings of the Fortieth Jubilee Spring Conference of the Union of Bulgarian Mathematicians Borovetz, April
Driven large contact angle droplets on chemically heterogeneous substrates
 October 2012 EPL, 100 (2012) 16002 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/100/16002 www.epljournal.org Driven large contact angle droplets on chemically heterogeneous substrates D. Herde 1,U.Thiele 2,S.Herminghaus 1 and
October 2012 EPL, 100 (2012) 16002 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/100/16002 www.epljournal.org Driven large contact angle droplets on chemically heterogeneous substrates D. Herde 1,U.Thiele 2,S.Herminghaus 1 and
Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane
 Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Pinto
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Pinto
The effects of gravity on the capillary instability in tubes
 J. Fluid Mech. (2006), vol. 556, pp. 217 226. c 2006 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112006009505 Printed in the United Kingdom 217 The effects of gravity on the capillary instability in tubes
J. Fluid Mech. (2006), vol. 556, pp. 217 226. c 2006 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112006009505 Printed in the United Kingdom 217 The effects of gravity on the capillary instability in tubes
Contact angle hysteresis: a review of fundamentals and applications
 Contact angle hysteresis: a review of fundamentals and applications The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Contact angle hysteresis: a review of fundamentals and applications The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Critical fields and intermediate state
 621 Lecture 6.3 Critical fields and intermediate state Magnetic fields exert pressure on a superconductor: expelling the flux from the sample makes it denser in the space outside, which costs magnetic
621 Lecture 6.3 Critical fields and intermediate state Magnetic fields exert pressure on a superconductor: expelling the flux from the sample makes it denser in the space outside, which costs magnetic
Surfactant effect on the motion of long bubbles in horizontal capillary tubes
 Surfactant effect on the motion of long bubbles in horizontal capillary tubes Prabir Daripa 1, and G. Paşa 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX-77843 2 Institute of
Surfactant effect on the motion of long bubbles in horizontal capillary tubes Prabir Daripa 1, and G. Paşa 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX-77843 2 Institute of
Influence of the Flow Direction on the Mass Transport of Vapors Through Membranes Consisting of Several Layers
 Influence of the Flow Direction on the Mass Transport of Vapors Through Membranes Consisting of Several Layers Thomas Loimer 1,a and Petr Uchytil 2,b 1 Institute of Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer, Vienna
Influence of the Flow Direction on the Mass Transport of Vapors Through Membranes Consisting of Several Layers Thomas Loimer 1,a and Petr Uchytil 2,b 1 Institute of Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer, Vienna
Faceted drops on heterogeneous surfaces
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 239 245 (2001) Faceted drops on heterogeneous surfaces T. Cubaud and M. Fermigier Laboratoire PMMH, CNRS UMR 7636, ESPCI 10 rue Vauquelin,
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 239 245 (2001) Faceted drops on heterogeneous surfaces T. Cubaud and M. Fermigier Laboratoire PMMH, CNRS UMR 7636, ESPCI 10 rue Vauquelin,
A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic. of thin partially wetting films
 A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic of thin partially wetting films J. LALLEMENT a, P. VILLEDIEU a, P. TRONTIN a, C. LAURENT a a. Onera - The French Aerospace Lab Toulouse) - ONERA - F-31055
A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic of thin partially wetting films J. LALLEMENT a, P. VILLEDIEU a, P. TRONTIN a, C. LAURENT a a. Onera - The French Aerospace Lab Toulouse) - ONERA - F-31055
J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France Paris Cedex 05, France
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 Mar 2015](/thumbs/72/66529196.jpg) Rayleigh-Taylor instability under an inclined plane P.-T. Brun,1, 2, a) Adam Damiano,1 Pierre Rieu,1 Gioele Balestra,1 and Franc ois Gallaire1 1) Laboratory of Fluid Mechanics and Instabilities, EPFL,
Rayleigh-Taylor instability under an inclined plane P.-T. Brun,1, 2, a) Adam Damiano,1 Pierre Rieu,1 Gioele Balestra,1 and Franc ois Gallaire1 1) Laboratory of Fluid Mechanics and Instabilities, EPFL,
Nearly-zero contact angle hysteresis on lubricated surfaces. Dan Daniel, IMRE, A*STAR
 Nearly-zero contact angle hysteresis on lubricated surfaces Dan Daniel, IMRE, A*STAR 2011 1 mm Oleoplaning droplets on lubricated surfaces lubricant film lubricant film 2011 Lubricated repels blood and
Nearly-zero contact angle hysteresis on lubricated surfaces Dan Daniel, IMRE, A*STAR 2011 1 mm Oleoplaning droplets on lubricated surfaces lubricant film lubricant film 2011 Lubricated repels blood and
Numerical analysis of tips in viscous flow
 Numerical analysis of tips in viscous flow J. Eggers and S. Courrech du Pont Abstract. When a bubble (or drop) is placed in a strong viscous flow (e.g. a shear flow), it develops very sharp tips at its
Numerical analysis of tips in viscous flow J. Eggers and S. Courrech du Pont Abstract. When a bubble (or drop) is placed in a strong viscous flow (e.g. a shear flow), it develops very sharp tips at its
DLVO interaction between the spheres
 DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops
 J. Fluid Mech. (00), vol. 45, pp. 4 40. c 00 Cambridge University Press DOI: 0.07/S000000708 Printed in the United Kingdom 4 Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops By L. M A H A D E V A N, M. A D
J. Fluid Mech. (00), vol. 45, pp. 4 40. c 00 Cambridge University Press DOI: 0.07/S000000708 Printed in the United Kingdom 4 Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops By L. M A H A D E V A N, M. A D
The Flow of Thin Liquid Layers on Circular Cylinders
 The Flow of Thin Liquid Layers on Circular Cylinders Leonard W. Schwartz and Thomas A. Cender Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716 ISCST-20180917PM-A-CF4 Presented
The Flow of Thin Liquid Layers on Circular Cylinders Leonard W. Schwartz and Thomas A. Cender Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716 ISCST-20180917PM-A-CF4 Presented
Liquid interfaces in viscous straining flows: numerical studies of the selective withdrawal transition
 J. Fluid Mech. (2008), vol. 613, pp. 171 203. c 2008 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112008001900 Printed in the United Kingdom 171 Liquid interfaces in viscous straining flows: numerical studies
J. Fluid Mech. (2008), vol. 613, pp. 171 203. c 2008 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112008001900 Printed in the United Kingdom 171 Liquid interfaces in viscous straining flows: numerical studies
INFLUENCE OF THE SURFACE FORCES ON THE APPARENT CONTACT ANGLE AT PARTIAL WETTING AND IN THE PRESENCE OF HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER
 Proceedings of the 2 nd European Conference on Microfluidics - Microfluidics 21 - Toulouse, December 8-1, 21 µflu1-212 INFLUENCE OF THE SURFACE FORCES ON THE APPARENT CONTACT ANGLE AT PARTIAL WETTING AND
Proceedings of the 2 nd European Conference on Microfluidics - Microfluidics 21 - Toulouse, December 8-1, 21 µflu1-212 INFLUENCE OF THE SURFACE FORCES ON THE APPARENT CONTACT ANGLE AT PARTIAL WETTING AND
Frieder Mugele. Physics of Complex Fluids. University of Twente. Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT
 coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
14 8 Freezing droplets
 8 Freezing droplets Task Place a water droplet on a plate cooled down to around -20 C. As it freezes, the shape of the droplet may become cone-like with a sharp top. Investigate this effect. 2 Equipment
8 Freezing droplets Task Place a water droplet on a plate cooled down to around -20 C. As it freezes, the shape of the droplet may become cone-like with a sharp top. Investigate this effect. 2 Equipment
Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion
 Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion 24 mars 2017 1 When can we neglect diffusion? When the Peclet number is not very small we cannot ignore the convection term in the transport equation.
Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion 24 mars 2017 1 When can we neglect diffusion? When the Peclet number is not very small we cannot ignore the convection term in the transport equation.
Contact-line dynamics and damping for oscillating free surface flows
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 3 MARCH 2004 Contact-line dynamics and damping for oscillating free surface flows Lei Jiang a) RA3-254, Logic Technology Development, Intel Corporation, 2501 NW 229th
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 3 MARCH 2004 Contact-line dynamics and damping for oscillating free surface flows Lei Jiang a) RA3-254, Logic Technology Development, Intel Corporation, 2501 NW 229th
Capillary rise of a wetting fluid in a semi-circular groove
 68.45Gd L etalement The J. Phys. France 50 (1989) 485491 15 FÉVRIER 1989, 485 Classification Physics Abstracts 47.15 68.10Gw Capillary rise of a wetting fluid in a semicircular groove Elie Raphael Laboratoire
68.45Gd L etalement The J. Phys. France 50 (1989) 485491 15 FÉVRIER 1989, 485 Classification Physics Abstracts 47.15 68.10Gw Capillary rise of a wetting fluid in a semicircular groove Elie Raphael Laboratoire
On a slender dry patch in a liquid film draining under gravity down an inclined plane
 Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics (21), vol. 12, pp. 233 252. c 21 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 233 On a slender dry patch in a liquid film draining under gravity down an inclined
Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics (21), vol. 12, pp. 233 252. c 21 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 233 On a slender dry patch in a liquid film draining under gravity down an inclined
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 26 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 26 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 26 Jan 2016](/thumbs/73/68299281.jpg) Relaxation of nonspherical sessile drops towards equilibrium Vadim S. Nikolayev and Daniel A. Beysens ESEME, Service des Basses Températures, CEA-Grenoble (France) (Dated: January 27, 2016) arxiv:1601.06957v1
Relaxation of nonspherical sessile drops towards equilibrium Vadim S. Nikolayev and Daniel A. Beysens ESEME, Service des Basses Températures, CEA-Grenoble (France) (Dated: January 27, 2016) arxiv:1601.06957v1
Course 1 : basic concepts. Pierre Simon de Laplace (1814), in his book Essai Philosophique sur les Probabilités (Philosophical Essay on Probability):
 Course 1 : basic concepts Pierre Simon de Laplace (1814), in his book Essai Philosophique sur les Probabilités (Philosophical Essay on Probability): We must consider the present state of Universe as the
Course 1 : basic concepts Pierre Simon de Laplace (1814), in his book Essai Philosophique sur les Probabilités (Philosophical Essay on Probability): We must consider the present state of Universe as the
ISCST shall not be responsible for statements or opinions contained in papers or printed in its publications.
 Modeling of Drop Motion on Solid Surfaces with Wettability Gradients J. B. McLaughlin, Sp. S. Saravanan, N. Moumen, and R. S. Subramanian Department of Chemical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam,
Modeling of Drop Motion on Solid Surfaces with Wettability Gradients J. B. McLaughlin, Sp. S. Saravanan, N. Moumen, and R. S. Subramanian Department of Chemical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam,
FLUID MECHANICS. Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies
 FLUID MECHANICS Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies CHAP 9. FLOW OVER IMMERSED BODIES CONTENTS 9.1 General External Flow Characteristics 9.3 Drag 9.4 Lift 9.1 General External Flow Characteristics 9.1.1
FLUID MECHANICS Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies CHAP 9. FLOW OVER IMMERSED BODIES CONTENTS 9.1 General External Flow Characteristics 9.3 Drag 9.4 Lift 9.1 General External Flow Characteristics 9.1.1
7 The Navier-Stokes Equations
 18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
The Microscopic and Macroscopic Structure of the Precursor Layer in Spreading Viscous Drops
 The Microscopic and Macroscopic Structure of the Precursor Layer in Spreading Viscous Drops H. Pirouz Kavehpour a), Ben Ovryn b), Gareth H. McKinley a) a) Hatsopoulos Microfluids Laboratory, Department
The Microscopic and Macroscopic Structure of the Precursor Layer in Spreading Viscous Drops H. Pirouz Kavehpour a), Ben Ovryn b), Gareth H. McKinley a) a) Hatsopoulos Microfluids Laboratory, Department
Uniform Electric Fields
 Uniform Electric Fields The figure shows an electric field that is the same in strength and direction at every point in a region of space. This is called a uniform electric field. The easiest way to produce
Uniform Electric Fields The figure shows an electric field that is the same in strength and direction at every point in a region of space. This is called a uniform electric field. The easiest way to produce
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 24 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 24 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 24 Sep 2014](/thumbs/89/98676990.jpg) Theory and experiments on the ice-water front propagation in droplets freezing on a subzero surface. Michael Nauenberg Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 arxiv:1409.7052v1
Theory and experiments on the ice-water front propagation in droplets freezing on a subzero surface. Michael Nauenberg Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 arxiv:1409.7052v1
Front and back instability of a liquid film on a slightly inclined plate
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2003 Front and back instability of a liquid film on a slightly inclined plate Uwe Thiele and Edgar Knobloch Department of Physics, University of California,
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2003 Front and back instability of a liquid film on a slightly inclined plate Uwe Thiele and Edgar Knobloch Department of Physics, University of California,
An energy balance approach to modeling the hydrodynamically driven spreading of a liquid drop
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 182 (2001) 109 122 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa An energy balance approach to modeling the hydrodynamically driven spreading of a liquid
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 182 (2001) 109 122 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa An energy balance approach to modeling the hydrodynamically driven spreading of a liquid
Mastering the Coating Thickness Obtained Using Liquids with a Yield-Stress
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 57, 2017 Guest Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Laura Piazza, Serafim Bakalis Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-48-8;
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 57, 2017 Guest Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Laura Piazza, Serafim Bakalis Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-48-8;
PF BC. When is it Energetically Favourable for a Rivulet of Perfectly Wetting Fluid to Split?
 PF 05-0109-BC When is it Energetically Favourable for a Rivulet of Perfectly Wetting Fluid to Split? S. K. Wilson 1 and B. R. Duffy 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Strathclyde, Livingstone Tower,
PF 05-0109-BC When is it Energetically Favourable for a Rivulet of Perfectly Wetting Fluid to Split? S. K. Wilson 1 and B. R. Duffy 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Strathclyde, Livingstone Tower,
Molecular Hydrodynamics of the Moving Contact Line in Two-phase Immiscible Flows
 COMMUNICATIONS IN COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 1-52 Commun. Comput. Phys. February 26 Molecular Hydrodynamics of the Moving Contact Line in Two-phase Immiscible Flows Tiezheng Qian 1,, Xiao-Ping
COMMUNICATIONS IN COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 1-52 Commun. Comput. Phys. February 26 Molecular Hydrodynamics of the Moving Contact Line in Two-phase Immiscible Flows Tiezheng Qian 1,, Xiao-Ping
Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection
 Slide 1 Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection scaling, heat transport and structures E. Calzavarini and F. Toschi, D. Lohse, R. Tripiccione, C. R. Doering, J. D. Gibbon, A. Tanabe Euromech Colloquium
Slide 1 Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection scaling, heat transport and structures E. Calzavarini and F. Toschi, D. Lohse, R. Tripiccione, C. R. Doering, J. D. Gibbon, A. Tanabe Euromech Colloquium
On the displacement of three-dimensional fluid droplets adhering to a plane wall in viscous pressure-driven flows
 J. Fluid Mech. (2001), vol. 435, pp. 327 350. Printed in the United Kingdom c 2001 Cambridge University Press 327 On the displacement of three-dimensional fluid droplets adhering to a plane wall in viscous
J. Fluid Mech. (2001), vol. 435, pp. 327 350. Printed in the United Kingdom c 2001 Cambridge University Press 327 On the displacement of three-dimensional fluid droplets adhering to a plane wall in viscous
2 Navier-Stokes Equations
 1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
Instabilities in the flow of thin films on heterogeneous surfaces
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 9 SEPTEMBER 2004 Instabilities in the flow of thin films on heterogeneous surfaces Lou Kondic a) Department of Mathematical Sciences & Center for Applied Mathematics
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 9 SEPTEMBER 2004 Instabilities in the flow of thin films on heterogeneous surfaces Lou Kondic a) Department of Mathematical Sciences & Center for Applied Mathematics
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Two Hundred Years of Capillarity Research
 Two Hundred Years of Capillarity Research Two centuries after seminal work by Pierre-Simon Laplace and Thomas Young, capillarity s modern applications arise in fields ranging from biology and oceanography
Two Hundred Years of Capillarity Research Two centuries after seminal work by Pierre-Simon Laplace and Thomas Young, capillarity s modern applications arise in fields ranging from biology and oceanography
Contents. Microfluidics - Jens Ducrée Physics: Laminar and Turbulent Flow 1
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane
 Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González, and Lou Kondic Citation: Phys. Fluids 24, 3214 (212); doi: 1.163/1.368582 View online: http://dx.doi.org/1.163/1.368582
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González, and Lou Kondic Citation: Phys. Fluids 24, 3214 (212); doi: 1.163/1.368582 View online: http://dx.doi.org/1.163/1.368582
Maximal deformation of an impacting drop
 J. Fluid Mech. (24), vol. 57, pp. 99 28. c 24 Cambridge University Press DOI:.7/S222494 Printed in the United Kingdom 99 Maximal deformation of an impacting drop By CHRISTOPHE CLANET, CÉDRIC BÉGUIN, DENIS
J. Fluid Mech. (24), vol. 57, pp. 99 28. c 24 Cambridge University Press DOI:.7/S222494 Printed in the United Kingdom 99 Maximal deformation of an impacting drop By CHRISTOPHE CLANET, CÉDRIC BÉGUIN, DENIS
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES. Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles
 CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
Boundary Conditions for the Moving Contact Line Problem. Abstract
 Boundary Conditions for the Moving Contact Line Problem Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 10012, USA Weinan E Department of Mathematics and PACM,
Boundary Conditions for the Moving Contact Line Problem Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 10012, USA Weinan E Department of Mathematics and PACM,
