Generalized Gumbel distribution of current fluctuations in purple membrane monolayers. Abstract
|
|
|
- Shanon Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generalized Gumbel distribution of current fluctuations in purple membrane monolayers E. Alfinito arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Aug 2012 Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Innovazione, Università del Salento, via Monteroni, I Lecce-Italy (EU) and CNISM - Consorzio Nazionale Interuniversitario per le Scienze Fisiche della Materia, via della Vasca Navale, 84, Roma-Italy (EU) L. Reggiani Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica Ennio De Giorgi, Università del Salento, via Monteroni, I Lecce-Italy (EU) and CNISM - Consorzio Nazionale Interuniversitario per le Scienze Fisiche della Materia, via della Vasca Navale, 84, Roma-Italy (EU) (Dated: August 2, 2012) Abstract We investigate the nature of a class of probability density functions, say G(a), with a the shape parameter, which generalizes the Gumbel distribution. These functions appear in a model of charge transport, when applied to a metal-insulator-metal structure, where the insulator is constituted by a monolayer of bacteriorhodopsin. Current shows a sharp increase above about 3 V, interpreted as the cross-over between direct and injection sequential-tunneling regimes. In particular, we show that, changing the bias value, the probability density function changes its look from bimodal to unimodal. Actually, the bimodal distributions can be resolved in at least a couple of G(a) functions with different values of the shape parameter. PACS numbers: Ng Distribution theory and Monte Carlo studies Rr General statistical methods a Fluctuation phenomena, random processes, noise, and Brownian motion eleonora.alfinito@unisalento.it lino.reggiani@unisalento.it 1
2 There is a widespread evidence that fluctuations of macroscopic observables exhibiting extreme events [1 3] can be described by means of the generalized Gumbel distribution G(a), with a the shape parameter: G(a) = θ(a)aa Γ(a) exp{ a[θ(a)(z +ν(a))+e θ(a)(z+ν(a)) ]} (1) where the function ν(a) is defined in terms of the Gamma function Γ(a) and its derivatives ν(a) = 1 θ(a) (ln(a) ψ(a)) Γ(a), ψ(a) and θ 2 (a) indicating, respectively, the Gamma, digamma and trigamma function. In the definition given in (1), G(a) is a normalized distribution function with zero mean and unitary variance. This distribution is quite intriguing, since it crosses the perimeter of the extreme value statistics, describing physical phenomena of very different nature [1, 4 6]. Among its main features, here we recall that the well-known Bramwell-Holdsworth-Pintor (BHP) distribution [7], found relevant for the description of critical behaviors in magnetic, fluidodynamics [7] and percolative systems [8] is practically coincident with the distribution G(π/2) [1, 5, 6]. Furthermore, for a = 1 this distribution, also called scaled Gumbel distribution, is used to describe the fluctuations of the conditional galaxy density [9]. Finally, for a the G(a) recovers the Gaussian distribution. Therefore, this distribution has a unifying character since it describes, on respect the value of a, the statistics of events from critical to non-critical conditions. The shape parameter a can take all the positive real numbers [5]. The commonly accepted interpretation of integer valued G(a) is the straightforward generalization of the Gumbel distribution, i.e. it describes the distribution of the a-th largest value of a set of independent and identically distributed (iid) variables[1, 6]. Not so easy the interpretation of non-integer valued G(a): in this case distributions are related to long, but finite, range correlations which do not allow for a single variable to be dominant [5]. In other words, when a is not integer, G(a) describes a finite-size system with correlations at all the scale lengths. As a rough distinction, we can say that integer a values correspond to the establishment of ordering in the relevant variables, and non integer a values correspond to a loss of ordering, a more democratic situation in which variance is large and the weight of events far from the mean is large. 2
3 In this letter we investigate the fluctuations around the steady state of the current flowing through a monolayer of bacteriorhodopsin (br)[10], an integral membrane protein sensitive to the light, as function of the applied voltage. By making use of an atomic force microscope (AFM) technique, in a large range of applied bias (up to about 8 V), it was experimentally observed [11] that the current exhibits a sharp transition between a near linear (Ohmic) regime and a superlinear one (roughly as V 8 increase of current at a threshold voltage of about 3 V). This behavior resembles a phase transition where the two different charge transport behaviors can be associated with a direct tunneling (DT) and an injection (or Fowler Nordheim) tunneling (FN) regime, respectively. This result was quantitatively reproduced within a microscopic model based on an impedance network protein analogous (INPA) [12]. Figure 1 reports the current voltage (I-V) characteristic, as obtained by the experiments [11](see continuous curve) and the theoretical model (see the full circles) when the AFM tip just touches the protein monolayer at about 4.6 nm from the bottom metal-contact. The transport model uses a stochastic approach to select the tunneling mechanism (DT or FN) based on the probability reported in the inset of Fig. 1. By construction, the numerical approach allows for the simultaneous calculation of the current and its fluctuations around the steady state. Accordingly, with respect to the steady value, the calculated current evolution is found to exhibit spikes that resemble extreme events, whose number increases with the bias value, until it becomes difficult to establish what is extreme and what normal [13]. The calculated variance of current fluctuations corresponding to the I-V characteristic of Fig. (1), shows a a rather abrupt increase in concomitance with the cross-over region, at about 3 V. The giant increase, for about five orders in the magnitude of current variance, is associated with the opening of low resistance paths between contacts: they originate by the establishing of the FN regime which replaces the low voltage DT regime [13]. In the following we briefly survey the theoretical approach. The INPA model aims to predict the static and dynamical electrical responses of a protein in vitro, i.e. directly contacted or sandwiched with functionalized contacts to an external bias. In particular, the single protein is described by means of an irregular impedance network, with ideal contacts [12]. The aminoacids constituting the tertiary structure of the protein are taken as the nodes of the network and the interaction between aminoacids as the links of the network. For a given applied voltage the network is solved within Kirchhoff rules by associating 3
4 I(nA) 10 0 Trasmission probability V C DT 1 ev i,j / Φ V G FN 10 4 circles : simulation line : experiment V(Volt) FIG. 1: Experimental and calculated data for the I-V characteristics of Ref.[11]. In the inset, the transmission probability as given by DT (dashed line) and the interpolation of DT and FN (continuous line) for the typical parameters: m e the free electron mass, l i,j = 5.5 Å, Φ=219 mev. The critical, V C, and Ginzburg V G, voltages are indicated. an impedance to each link. The transfer of electrons between a couple of nodes, selected according to an interaction radius, is ruled by two different probabilities: [ Pi,j D = exp 2l ] i,j 2m e (Φ 1 2 ev i,j), ev i,j < Φ, (2) for the DT regime and [ ( ) Pij FN 2li,j 2me Φ = exp ev i,j ] Φ 2, ev i,j Φ, (3) for the FN regime. Here V i,j is the local potential drop between the couple of i,j aminoacids and m e is the electron effective mass, here taken the same of the bare value. A smooth variation of the aminoacid resistivity is introduced to take into account the superlinear current response: ρ(v) = ρ MAX ev < Φ ρ MAX ( Φ ev )+ρ min(1 Φ ev ) ev Φ where ρ MAX = Ω Å is the resistivity value which should be used to fit the I-V characteristic at the lowest voltages, ρ min = Ω Å plays the role of an extremely low series resistance, limiting the current at the highest voltages, and Φ = 219 mev is the value 4 (4)
5 V 0.5V 1.0V 2.0V 5.0V 9.0V 10 0 frequency ln(i) FIG. 2: Histograms of current fluctuations, V=0.1-9V. of the energy barrier separating two nodes, here taken to be the same for all the couples of nodes [12]. The electrical model well reproduces the measured I-V characteristic of br. On the other hand, since the two tunneling regimes are stochastically chosen according to their probability, the model provides also the instantaneous current fluctuations. To estimate the probability density functions (PDFs) of current fluctuations, we follow this procedure. In a first step, we collect the histograms of ln(i) for different bias values in the range from 0.1 to 9 V. As reported in Fig. 2, in all the bias range the histograms strongly deviate from a symmetric Gaussian-like shape. Furthermore, at intermediate and high bias, i.e. near to the transition and beyond, they exhibit a nearly unimodal shape, while at bias lower than 1 V, the shape becomes bimodal. In a second step, we look for a fitting function of these histograms. For bias values larger than 1 V, the function: H(a) = A 0 exp { aa 1 (x+m) ae } A 1(x+m) (5) where A 0,A 1,a,m are the curve parameters, gives a good approximation of calculated data. To reduce the histogram to a standard PDF, the above parameters should be adjusted. In doing so, we guess that the final PDF is the generalized Gumbel distribution (1) with the same value of a; the standardization of histograms is performed by reshuffling the independent variable as follows: x = σz + b, and the new expression of the test function 5
6 becomes: H (z) = A 0 exp { a(a 1 σ)(z + bσ + mσ } ) ae A 1σ(z+ bσ +mσ ) (6) which is proportional to G(a), when assuming: σ = θ ( a, b = ν a m ) σ. A 1 σ In particular, λh (z) = G(a) and the frequency normalization is λ(a) = σ aa Γ(a) The parameters < x >, σ, λ are an a-generalization of the usual mean value (location parameter) and the scale parameter[14]. Intheregionofbiasvalues1 5V thisproceduregivesasinglepdf,the scaledgumbel G(1) [9] as shown in Fig. 3. A 1 A λφ (ln(i) <ln(i)>)/σ FIG. 3: Normalized distributions, V=1 V (triangles), 2 V (empty squares), 5 V(diamonds). The continuous curve is G(1). In a third step, we analyze the bimodal histograms. Following the suggestions of [7, 15], the bimodal shape is interpreted as the effect of the superposition of different curves. In the present case we succeed in resolving two prevailing contributions: the H(2)-histogram and a H(0.6)-histogram. By using the standardization technique shown above, both H(2) and H(0.6) can be traced back to the G(2) and G(0.6) distributions, respectively. The comparison between the Hs and Gs curves is shown in Figs. 4 and 5, for bias V=0.1 V. Notice that the curve on G(2) could be also resolved in at least two different parts, thus signaling that the G(2) is a superposition of other PDFs. 6
7 10 1 H(2) Frequency H(0.6) lni FIG. 4: Histograms at V=0.1 V. Continuous line refers to the fitting function H(2), dashed line refers to the fitting function H(0.6), circles are the calculated data. In the last step we observe that far from the transition, the G(1) smooths down to a different unimodal distribution. Figure 6 reports the calculated data and the fit with two different PDFs. The G(0.7) gives the best fit G(2.0) G(0.6) 10 1 λ Φ (x <x>)/σ FIG. 5: PDFs with V=0.1 V. Continuous line refers to the fitting function G(2), dashed line refers to the fitting function G(0.6), symbols are the calculated data when rescaled (see text). The most relevant result of the present investigation stems in solving the, apparently, substantial difference between the bimodal PDFs, evidenced before the transition, and the unimodal PDFs, emerging at the transition and beyond. Bimodal distributions have been previously investigated as mixture of universal unimodal distributions [15], but to our knowledge, a continuous transformation from bimodal to unimodal behaviour has not been 7
8 10 0 G(0.7) 10 1 λφ G(0.6) (x <x>)/σ FIG. 6: PDFs of current fluctuations for V=9 V. Data have been compared with both the PDF G(0.7) and G(0.6). To better resolve the differences among the distributions, the G(0.6) curve and the relative data are shifted of 0.1 on the vertical axis. observed. A further contribution to this topic is the observation that the PDF: G(a) = θ(a)aa Γ(a) exp{ aw aew } (7) is equivalent, in the sense of distribution, to the Gamma distribution of shape parameter a and life-time 1/λ: This can be seen by using the change of variables: f(t) = 1 Γ(a) λa t a 1 e λt. (8) ae θ(a)w = λt and requiring the normalization [16]. The Gamma distributions is well known in economics and granular materials [18] and is usually interpreted as the distribution of a sum of a (if a is integer) iid exponentially distributed variables characterized by the same life-time. In other words, the sum of different Gamma functions with the same life-time is still a Gamma function with a shape parameter equal to the sum of the single parameters [17]. Otherwise, for iid with different life times, the variable sum (convolution) can be expressed by means of Gamma and Beta distribution functions [17] Therefore, we make the following conjecture: the G(2) PDF we found in the low bias region, takes into account two different kinds of current, one due to the maximal resistivity (DT regime) and the other one due to the minimal resistivity (FN regime) [13]. 8
9 The observed not-perfect convolution in a single G(2) could be due to the (very) different life times of the events. The G(1) PDF signals the existence of a single dominant current regime, due to the superposition of all the possible resistivities values (ρ(v), ρ MAX, ρ min ) (FN). This perfect superposition is announced by the G(0.6) PDF which detaches by the G(2) at low bias. The shape parameter lower than 1 signals the not-complete superposition. In addition, above the transition, the minimal resistivity becomes more and more dominant and this drains the G(1) distribution producing a PDF with a shape parameter lower than 1, G(0.7). The presence of G(1) in a wide bias range suggests a further interpretation of the phenomenon: the strengthening of the system configuration. It happens that the phase transition between the two tunneling regimes is not abrupt but covers the bias value region 1 5 V. In this region, at the microscopic level, the links can choose among the resistivity values ρ MAX, ρ min and ρ(v) because both the DT and the FN regimes coexist. In different contexts, [19], the complete realization of the phase transition is associated with a temperature, called Ginzburg temperature, above which the ordering of the system is completed (in some cases with the formation of topological defects). By analogy, we can call the voltage value below which the transition is finalized (V=5 V), the Ginzburg voltage, V G, and the voltage value at which the transition starts (V C =1 V), the critical voltage V C (see Fig. 1) [13] In conclusion, the main results presented in this letter are the following: 1. The probability density functions of current fluctuations show both unimodal and bimodal shapes. 2. The bimodal PDFs can be decomposed into at least two unimodal functions. 3. All the PDFs can be drawn back to the parametric G(a) distribution function(1). 4. The shape parameter a is a function of the applied bias. As final remark, we observe that what found on current fluctuations is a model prediction, since no measurements have been performed so far. The proposed model finely describe the I-V characteristics, and the interpretation of the PDF of fluctuations is in line with the theoretical mechanism of current transport leaving the experimental test as a future challenge. 9
10 Acknowledgments This research is supported by the European Commission under the Bioelectronic Olfactory Neuron Device (BOND) project within the grant agreement number [1] A. Noullez and J.-F. Pinton, Eur.Phys. J.B. 28, (2002) [2] A. Cohen, Y. Roth and B. Shapiro, Phys. Rev. B 38, (1988); [3] S.T. Bramwell, T. Fennell, P.C.W. Holdsworth, and B. Portelli, Europhys. Lett. 57, (2002) [4] T. Antal, M. Droz, G. Györgyi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, (2001) [5] E. Bertin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, (2005) [6] S. Joubaud, A. Petrosyan, et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 2008 (180601) [7] S.T. Bramwell, Nature Physics 5, 443 (2009); S.T. Bramwell, P.C.W. Holdsworth and J.-F. Pintor, Nature 396, 552 (1998); S.T. Bramwell, K. Christensen, J.-Y. Fortin,et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3744 (2000). [8] C. Pennetta, E. Alfinito, L. Reggiani and S. Ruffo, Physica A 340, 380 (2004) [9] T. Antal, F. Sylos Labini, N.L. Vasilyev and Y. V. Baryshev, Eur. Phys. J. 88, (2009) [10] D. Oesterhelt, Angew. Chemie 88, 16 (1976) [11] I. Casuso, L. Fumagalli, J. Samitier, et al., Phys. Rev. E 76, (2007) [12] E. Alfinito, J. -F. Millithaler, L. Reggiani, Phys. Rev. E 83, (2011); E. Alfinito and L. Reggiani, Europhys. Lett. 85, 2009 (86002) [13] E. Alfinito, J.-F. Millithaler, and L. Reggiani, preprint arxiv: [14] The Γ(a) function and its derivatives have been calculated by using the Wolfram Web Resouce: [15] D. Jaskiernak, P.N.J. Lane, A. Robinson, A. Lucieer, Remote Sens. of Environment 115, 573 (2011) L. Rajaram and C.R. Tsokos, Stoch. Analysis and Applications 24, 1061 (2006) [16] D. Dufresne, Electronic J. Probabilities 15, 2010 (2163) [17] M. Akkouchi, Soochow J. Mathematics 2, 205 (2005) [18] T. Aste and T. Di Matteo, Phys. Rev. E 77, (2008) [19] T. W. B. Kibble, in: Topological Defects and the non-equilibrium Dynamics... by Y. B. Bunkov 10
11 and H. Godfrin (Eds), NATO Science Series, 549, 7 (1999); E. Alfinito and G. Vitiello, Phys. Rev. B 65, (2002). 11
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 31 Oct 2001
 Monte Carlo simulation of electromigration phenomena in metallic lines C. Pennetta, L. Reggiani and E. Alfinito arxiv:cond-mat/0110647v1 31 Oct 2001 INFM - National Nanotechnology Laboratory, Dipartimento
Monte Carlo simulation of electromigration phenomena in metallic lines C. Pennetta, L. Reggiani and E. Alfinito arxiv:cond-mat/0110647v1 31 Oct 2001 INFM - National Nanotechnology Laboratory, Dipartimento
Generalised extreme value statistics and sum of correlated variables.
 and sum of correlated variables. Laboratoire Charles Coulomb CNRS & Université Montpellier 2 P.C.W. Holdsworth, É. Bertin (ENS Lyon), J.-Y. Fortin (LPS Nancy), S.T. Bramwell, S.T. Banks (UCL London). University
and sum of correlated variables. Laboratoire Charles Coulomb CNRS & Université Montpellier 2 P.C.W. Holdsworth, É. Bertin (ENS Lyon), J.-Y. Fortin (LPS Nancy), S.T. Bramwell, S.T. Banks (UCL London). University
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013135 TITLE: Current Instability and Shot Noise in Nanometric Semiconductor Hetero structures DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013135 TITLE: Current Instability and Shot Noise in Nanometric Semiconductor Hetero structures DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
A variational approach to Ising spin glasses in finite dimensions
 . Phys. A: Math. Gen. 31 1998) 4127 4140. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-447098)89176-2 A variational approach to Ising spin glasses in finite dimensions R Baviera, M Pasquini and M Serva Dipartimento di
. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 31 1998) 4127 4140. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-447098)89176-2 A variational approach to Ising spin glasses in finite dimensions R Baviera, M Pasquini and M Serva Dipartimento di
Fluctuations near a critical point
 Bari 3-5 September 2008 Fluctuations near a critical point S. Ciliberto, S. Joubaud, B. Persier, A. Petrossyan Laboratoire de Physique, ENS de Lyon - UMR5672 CNRS Fluctuations near a critical point Motivations
Bari 3-5 September 2008 Fluctuations near a critical point S. Ciliberto, S. Joubaud, B. Persier, A. Petrossyan Laboratoire de Physique, ENS de Lyon - UMR5672 CNRS Fluctuations near a critical point Motivations
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 18 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 18 Jul 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 18 Jul 2008](/thumbs/82/86968635.jpg) Negro and Danube are mirror rivers arxiv:0807.2988v1 [physics.data-an] 18 Jul 2008 R. Gonçalves a, A. A. Pinto b a Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto R. Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-465, Porto,
Negro and Danube are mirror rivers arxiv:0807.2988v1 [physics.data-an] 18 Jul 2008 R. Gonçalves a, A. A. Pinto b a Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto R. Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-465, Porto,
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 80 1 JUNE 1998 NUMBER 22 Field-Induced Stabilization of Activation Processes N. G. Stocks* and R. Mannella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Pisa, and Istituto Nazionale
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 80 1 JUNE 1998 NUMBER 22 Field-Induced Stabilization of Activation Processes N. G. Stocks* and R. Mannella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Pisa, and Istituto Nazionale
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Aug 2014 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Aug 2014](/thumbs/74/70452476.jpg) Hyperuniformity of critical absorbing states Daniel Hexner and Dov Levine, Department of Physics, Technion, Haifa, Israel Initiative for the Theoretical Sciences - CUNY Graduate Center 65 Fifth Avenue,
Hyperuniformity of critical absorbing states Daniel Hexner and Dov Levine, Department of Physics, Technion, Haifa, Israel Initiative for the Theoretical Sciences - CUNY Graduate Center 65 Fifth Avenue,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/86/93817801.jpg) CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
Invaded cluster dynamics for frustrated models
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1998 Invaded cluster dynamics for frustrated models Giancarlo Franzese, 1, * Vittorio Cataudella, 1, * and Antonio Coniglio 1,2, * 1 INFM, Unità di Napoli,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1998 Invaded cluster dynamics for frustrated models Giancarlo Franzese, 1, * Vittorio Cataudella, 1, * and Antonio Coniglio 1,2, * 1 INFM, Unità di Napoli,
Random sequential adsorption and diffusion of dimers and k-mers on a square lattice
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 114, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 2001 Random sequential adsorption and diffusion of dimers and k-mers on a square lattice C. Fusco and P. Gallo Dipartimento di Fisica and Istituto
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 114, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 2001 Random sequential adsorption and diffusion of dimers and k-mers on a square lattice C. Fusco and P. Gallo Dipartimento di Fisica and Istituto
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI. INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY
 CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram
 Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1878 I. Experimental setup OPA, DFG Ti:Sa Oscillator, Amplifier PD U DC U Analyzer HV Energy analyzer MCP PS CCD Polarizer UHV Figure S1: Experimental setup used in mid infrared photoemission
doi:1.138/nature1878 I. Experimental setup OPA, DFG Ti:Sa Oscillator, Amplifier PD U DC U Analyzer HV Energy analyzer MCP PS CCD Polarizer UHV Figure S1: Experimental setup used in mid infrared photoemission
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999](/thumbs/95/123482736.jpg) BARI-TH 347/99 arxiv:cond-mat/9907149v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 PHASE ORDERING IN CHAOTIC MAP LATTICES WITH CONSERVED DYNAMICS Leonardo Angelini, Mario Pellicoro, and Sebastiano Stramaglia Dipartimento
BARI-TH 347/99 arxiv:cond-mat/9907149v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 PHASE ORDERING IN CHAOTIC MAP LATTICES WITH CONSERVED DYNAMICS Leonardo Angelini, Mario Pellicoro, and Sebastiano Stramaglia Dipartimento
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems
 Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c](/thumbs/89/100796430.jpg) Wealth Dynamics on Complex Networks arxiv:cond-mat/0402466v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Siena, Via Roma 56, 53100
Wealth Dynamics on Complex Networks arxiv:cond-mat/0402466v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Siena, Via Roma 56, 53100
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001](/thumbs/73/68736391.jpg) Autocorrelation functions in 3D Fully Frustrated Systems arxiv:cond-mat/0107509v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001 G. Franzese a, A. Fierro a, A. De Candia a and A. Coniglio a,b Dipartimento di Scienze
Autocorrelation functions in 3D Fully Frustrated Systems arxiv:cond-mat/0107509v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001 G. Franzese a, A. Fierro a, A. De Candia a and A. Coniglio a,b Dipartimento di Scienze
Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps. Abstract
 Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps Jorge A. Revelli 1 Alejandro D. Sánchez 2, and Horacio S. Wio 1 1) Grupo de Física Estadística Centro Atómico Bariloche
Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps Jorge A. Revelli 1 Alejandro D. Sánchez 2, and Horacio S. Wio 1 1) Grupo de Física Estadística Centro Atómico Bariloche
Hysteretic Transitions in the Kuramoto Model with Inertia
 Rostock 4 p. Hysteretic Transitions in the uramoto Model with Inertia A. Torcini, S. Olmi, A. Navas, S. Boccaletti http://neuro.fi.isc.cnr.it/ Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi - CNR - Firenze, Italy Istituto
Rostock 4 p. Hysteretic Transitions in the uramoto Model with Inertia A. Torcini, S. Olmi, A. Navas, S. Boccaletti http://neuro.fi.isc.cnr.it/ Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi - CNR - Firenze, Italy Istituto
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014
![Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014 Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014](/thumbs/73/69324282.jpg) Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 1.138/NPHYS491 Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2 Contents SI-1. Characterizations of monolayer WTe2 devices SI-2. Magnetoresistance and temperature
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 1.138/NPHYS491 Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2 Contents SI-1. Characterizations of monolayer WTe2 devices SI-2. Magnetoresistance and temperature
Nanoscale electrical conductivity of the purple membrane monolayer
 Nanoscale electrical conductivity of the purple membrane monolayer I. Casuso, 1 L. Fumagalli, 1 J. Samitier, 1 E. Padrós, 2 L. Reggiani, 3 V. Akimov, 3 and G. Gomila 1 1 Deptartment Electrònica, Universitat
Nanoscale electrical conductivity of the purple membrane monolayer I. Casuso, 1 L. Fumagalli, 1 J. Samitier, 1 E. Padrós, 2 L. Reggiani, 3 V. Akimov, 3 and G. Gomila 1 1 Deptartment Electrònica, Universitat
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model
 Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Use of dynamical coupling for improved quantum state transfer
 Use of dynamical coupling for improved quantum state transfer A. O. Lyakhov and C. Bruder Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Basel, Klingelbergstr. 82, 45 Basel, Switzerland We propose
Use of dynamical coupling for improved quantum state transfer A. O. Lyakhov and C. Bruder Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Basel, Klingelbergstr. 82, 45 Basel, Switzerland We propose
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999
![Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999](/thumbs/71/65846802.jpg) Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Supplementary Figure 1 Change of the Tunnelling Transmission Coefficient from the Bulk to the Surface as a result of dopant ionization Colour-map of
 Supplementary Figure 1 Change of the Tunnelling Transmission Coefficient from the Bulk to the Surface as a result of dopant ionization Colour-map of change of the tunnelling transmission coefficient through
Supplementary Figure 1 Change of the Tunnelling Transmission Coefficient from the Bulk to the Surface as a result of dopant ionization Colour-map of change of the tunnelling transmission coefficient through
arxiv:physics/ v1 31 Aug 2006
 Detrending Moving Average variance: a derivation of the scaling law Sergio Arianos and Anna Carbone Dipartimento di Fisica, Politecnico di Torino, arxiv:physics/060833 v 3 Aug 2006 Corso Duca degli Abruzzi
Detrending Moving Average variance: a derivation of the scaling law Sergio Arianos and Anna Carbone Dipartimento di Fisica, Politecnico di Torino, arxiv:physics/060833 v 3 Aug 2006 Corso Duca degli Abruzzi
!"#$%&'()*"+,-./*($-"#+"0+'*"12%3+ (#3+4"#&'*"12%3+5'6+6)17-$%1$/)%8*
 Università di Pisa!"$%&'()*"+,-./*($-"+"0+'*"12%3+ (3+4"&'*"12%3+5'6+6)17-$%1$/)%8* $%&'()*% I(8,4-(J1&-%9(0&/1/&14(,9155K0&6%4J,L(%&1MN51--4%&(',)0&6%4J,-(',)O151'%J2&(',L(%&() P&(Q14=(-R9(:(=, +$%,-..'/*0*'%
Università di Pisa!"$%&'()*"+,-./*($-"+"0+'*"12%3+ (3+4"&'*"12%3+5'6+6)17-$%1$/)%8* $%&'()*% I(8,4-(J1&-%9(0&/1/&14(,9155K0&6%4J,L(%&1MN51--4%&(',)0&6%4J,-(',)O151'%J2&(',L(%&() P&(Q14=(-R9(:(=, +$%,-..'/*0*'%
Frequency Influence on the Hot-Electron Noise Reduction in GaAs Operating under Periodic Signals
 Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium UFPS, Vilnius, Lithuania 2007 Frequency Influence on the Hot-Electron Noise Reduction in GaAs Operating under
Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium UFPS, Vilnius, Lithuania 2007 Frequency Influence on the Hot-Electron Noise Reduction in GaAs Operating under
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 15 Feb 2002
 Resistance and Resistance Fluctuations in Random Resistor Networks Under Biased Percolation C. Pennetta 1, L. Reggiani 1, Gy. Trefán 2 and E. Alfinito 1 1 INFM - National Nanotechnology Laboratory, Dipartimento
Resistance and Resistance Fluctuations in Random Resistor Networks Under Biased Percolation C. Pennetta 1, L. Reggiani 1, Gy. Trefán 2 and E. Alfinito 1 1 INFM - National Nanotechnology Laboratory, Dipartimento
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010](/thumbs/94/118952645.jpg) arxiv:1005.0565v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 Critical Slowing Down along the Dynamic Phase Boundary in Ising meanfield dynamics Muktish Acharyya Department of Physics, Presidency College 86/1 College
arxiv:1005.0565v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 Critical Slowing Down along the Dynamic Phase Boundary in Ising meanfield dynamics Muktish Acharyya Department of Physics, Presidency College 86/1 College
Phase transitions in the Potts spin-glass model
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1998 Phase transitions in the Potts spin-glass model Giancarlo Franzese 1 and Antonio Coniglio 1,2 1 Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1998 Phase transitions in the Potts spin-glass model Giancarlo Franzese 1 and Antonio Coniglio 1,2 1 Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli,
Supporting information for. Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in. monolayer molybdenum disulfide
 Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
From time series to superstatistics
 From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
Approximate Bayesian Computation
 Approximate Bayesian Computation Michael Gutmann https://sites.google.com/site/michaelgutmann University of Helsinki and Aalto University 1st December 2015 Content Two parts: 1. The basics of approximate
Approximate Bayesian Computation Michael Gutmann https://sites.google.com/site/michaelgutmann University of Helsinki and Aalto University 1st December 2015 Content Two parts: 1. The basics of approximate
Spontaneous recovery in dynamical networks
 Spontaneous recovery in dynamical networks A) Model: Additional Technical Details and Discussion Here we provide a more extensive discussion of the technical details of the model. The model is based on
Spontaneous recovery in dynamical networks A) Model: Additional Technical Details and Discussion Here we provide a more extensive discussion of the technical details of the model. The model is based on
Lee Yang zeros and the Ising model on the Sierpinski gasket
 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 32 (999) 57 527. Printed in the UK PII: S35-447(99)2539- Lee Yang zeros and the Ising model on the Sierpinski gasket Raffaella Burioni, Davide Cassi and Luca Donetti Istituto Nazionale
J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 32 (999) 57 527. Printed in the UK PII: S35-447(99)2539- Lee Yang zeros and the Ising model on the Sierpinski gasket Raffaella Burioni, Davide Cassi and Luca Donetti Istituto Nazionale
single-electron electron tunneling (SET)
 single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Nov 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Nov 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Nov 2004](/thumbs/80/82235863.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/411654v2 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Nov 24 ork probability distribution in single molecule experiments Alberto Imparato ( ) and Luca Peliti ( ) Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche and Unità INFM, Università
arxiv:cond-mat/411654v2 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Nov 24 ork probability distribution in single molecule experiments Alberto Imparato ( ) and Luca Peliti ( ) Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche and Unità INFM, Università
What is possible to do with noisy quantum computers?
 What is possible to do with noisy quantum computers? Decoherence, inaccuracy and errors in Quantum Information Processing Sara Felloni and Giuliano Strini sara.felloni@disco.unimib.it Dipartimento di Informatica
What is possible to do with noisy quantum computers? Decoherence, inaccuracy and errors in Quantum Information Processing Sara Felloni and Giuliano Strini sara.felloni@disco.unimib.it Dipartimento di Informatica
New experimental evidence for the role of long- range potential fluctuations in the mechanism of 1/f noise in a-si:h
 New experimental evidence for the role of long- range potential fluctuations in the mechanism of 1/f noise in a-si:h J.P.R. Bakker 1, P.J.S. van Capel 1, B.V. Fine 2,3, and J.I. Dijkhuis 1 1 Debye Institute
New experimental evidence for the role of long- range potential fluctuations in the mechanism of 1/f noise in a-si:h J.P.R. Bakker 1, P.J.S. van Capel 1, B.V. Fine 2,3, and J.I. Dijkhuis 1 1 Debye Institute
Current noise in quantum well infrared photodetectors: eœect of electron Coulomb interaction
 PHILOSOPHICAL MAGAZINE B, 000, VOL. 80, NO. 4, 775± 780 Current noise in quantum well infrared photodetectors: eœect of electron Coulomb interaction A. CARBONE{ and P. MAZZETTI Dipartimento di Fisica,
PHILOSOPHICAL MAGAZINE B, 000, VOL. 80, NO. 4, 775± 780 Current noise in quantum well infrared photodetectors: eœect of electron Coulomb interaction A. CARBONE{ and P. MAZZETTI Dipartimento di Fisica,
Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 061102 (2004) Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point D. Ryvkine, M. I. Dykman, and B. Golding Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 061102 (2004) Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point D. Ryvkine, M. I. Dykman, and B. Golding Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Nov 2000
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Nov 2000 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Nov 2000](/thumbs/93/112312086.jpg) Common Origin of Quantum Regression and Quantum Fluctuation Dissipation Theorems arxiv:cond-mat/0011420v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Nov 2000 P. Shiktorov, E. Starikov, V. Gružinskis Semiconductor Physics
Common Origin of Quantum Regression and Quantum Fluctuation Dissipation Theorems arxiv:cond-mat/0011420v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Nov 2000 P. Shiktorov, E. Starikov, V. Gružinskis Semiconductor Physics
Superstatistics and temperature fluctuations. F. Sattin 1. Padova, Italy
 Superstatistics and temperature fluctuations F Sattin 1 Padova, Italy Abstract Superstatistics [C Beck and EGD Cohen, Physica A 322, 267 (2003)] is a formalism aimed at describing statistical properties
Superstatistics and temperature fluctuations F Sattin 1 Padova, Italy Abstract Superstatistics [C Beck and EGD Cohen, Physica A 322, 267 (2003)] is a formalism aimed at describing statistical properties
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 5 Nov 2004
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 5 Nov 2004 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 5 Nov 2004](/thumbs/72/67704246.jpg) Ion Resonance Instability in the ELTRAP electron plasma G. Bettega, 1 F. Cavaliere, 2 M. Cavenago, 3 A. Illiberi, 1 R. Pozzoli, 1 and M. Romé 1 1 INFM Milano Università, INFN Sezione di Milano, Dipartimento
Ion Resonance Instability in the ELTRAP electron plasma G. Bettega, 1 F. Cavaliere, 2 M. Cavenago, 3 A. Illiberi, 1 R. Pozzoli, 1 and M. Romé 1 1 INFM Milano Università, INFN Sezione di Milano, Dipartimento
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 Nov 2007
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 Nov 2007 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 Nov 2007](/thumbs/72/66543126.jpg) Work and heat probability distribution of an optically driven Brownian particle: Theory and experiments arxiv:77.439v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 Nov 27 A. Imparato, 1 L. Peliti, 2, 3, 4 G. Pesce, 2,5 G.
Work and heat probability distribution of an optically driven Brownian particle: Theory and experiments arxiv:77.439v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 Nov 27 A. Imparato, 1 L. Peliti, 2, 3, 4 G. Pesce, 2,5 G.
arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 14 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 14 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 14 Nov 2014](/thumbs/94/118501710.jpg) Variation of the critical percolation threshold in the Achlioptas processes Paraskevas Giazitzidis, 1 Isak Avramov, 2 and Panos Argyrakis 1 1 Department of Physics, University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki,
Variation of the critical percolation threshold in the Achlioptas processes Paraskevas Giazitzidis, 1 Isak Avramov, 2 and Panos Argyrakis 1 1 Department of Physics, University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki,
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers
 Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010](/thumbs/81/83040079.jpg) Chaos in Sandpile Models Saman Moghimi-Araghi and Ali Mollabashi Physics department, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 55-96, Tehran, Iran We have investigated the weak chaos exponent to see if
Chaos in Sandpile Models Saman Moghimi-Araghi and Ali Mollabashi Physics department, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 55-96, Tehran, Iran We have investigated the weak chaos exponent to see if
Emissione di luce in campo prossimo da atomi artificiali
 Università degli Studi di Messina Dipartimento di Fisica della Materia Italye Tecnologie Fisiche Avanzate Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Switzerland Institute of Theoretical Physics Emissione
Università degli Studi di Messina Dipartimento di Fisica della Materia Italye Tecnologie Fisiche Avanzate Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Switzerland Institute of Theoretical Physics Emissione
On the Onsager-Yang-Value of the Spontaneous Magnetization
 On the Onsager-Yang-Value of the Spontaneous Magnetization G. Benettin, G. Gallavotti*, G. Jona-Lasinio, A. L. Stella Istituto di Fisica del Universita, Padova, Italy Received November 10, 1972 Abstract:
On the Onsager-Yang-Value of the Spontaneous Magnetization G. Benettin, G. Gallavotti*, G. Jona-Lasinio, A. L. Stella Istituto di Fisica del Universita, Padova, Italy Received November 10, 1972 Abstract:
Performance Evaluation of Generalized Polynomial Chaos
 Performance Evaluation of Generalized Polynomial Chaos Dongbin Xiu, Didier Lucor, C.-H. Su, and George Em Karniadakis 1 Division of Applied Mathematics, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912, USA, gk@dam.brown.edu
Performance Evaluation of Generalized Polynomial Chaos Dongbin Xiu, Didier Lucor, C.-H. Su, and George Em Karniadakis 1 Division of Applied Mathematics, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912, USA, gk@dam.brown.edu
Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment
 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University of London 1 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University
Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University of London 1 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 21 Sep 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 21 Sep 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 21 Sep 1998](/thumbs/81/84419124.jpg) Critical Currents of Josephson-Coupled Wire Arrays J. Kent Harbaugh and D. Stroud (March 7, 217) arxiv:cond-mat/989279v1 cond-mat.supr-con 21 Sep 1998 We calculate the current-voltage characteristics and
Critical Currents of Josephson-Coupled Wire Arrays J. Kent Harbaugh and D. Stroud (March 7, 217) arxiv:cond-mat/989279v1 cond-mat.supr-con 21 Sep 1998 We calculate the current-voltage characteristics and
CMS Note Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS NOTE 2001/023 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment CMS Note Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland May 18, 2001 Investigations of operating scenarios
Available on CMS information server CMS NOTE 2001/023 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment CMS Note Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland May 18, 2001 Investigations of operating scenarios
Charge-transport and tunneling in single-walled carbon nanotube bundles
 Charge-transport and tunneling in single-walled carbon nanotube bundles M. Salvato a,b, M. Cirillo a, M. Lucci a, S. Orlanducci c, I. Ottaviani a, M. L. Terranova c, and F. Toschi c a) Dipartimento di
Charge-transport and tunneling in single-walled carbon nanotube bundles M. Salvato a,b, M. Cirillo a, M. Lucci a, S. Orlanducci c, I. Ottaviani a, M. L. Terranova c, and F. Toschi c a) Dipartimento di
On the Asymptotic Convergence. of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans. Research School Of Chemistry
 1 On the Asymptotic Convergence of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans Research School Of Chemistry Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia
1 On the Asymptotic Convergence of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans Research School Of Chemistry Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia
Is the peculiar behavior of 1/f noise. inhomogeneities?
 Is the peculiar behavior of 1/f noise in graphene the result of the interplay between band-structure and inhomogeneities? B. Pellegrini, P. Marconcini, M. Macucci, G. Fiori, and G. Basso Dipartimento di
Is the peculiar behavior of 1/f noise in graphene the result of the interplay between band-structure and inhomogeneities? B. Pellegrini, P. Marconcini, M. Macucci, G. Fiori, and G. Basso Dipartimento di
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Jan 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Jan 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Jan 1999](/thumbs/74/69993481.jpg) Hall potentiometer in the ballistic regime arxiv:cond-mat/9901135v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Jan 1999 B. J. Baelus and F. M. Peeters a) Departement Natuurkunde, Universiteit Antwerpen (UIA), Universiteitsplein
Hall potentiometer in the ballistic regime arxiv:cond-mat/9901135v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Jan 1999 B. J. Baelus and F. M. Peeters a) Departement Natuurkunde, Universiteit Antwerpen (UIA), Universiteitsplein
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Nov 2011
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Nov 2011 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Nov 2011](/thumbs/81/83818451.jpg) Discontinuous percolation transitions in real physical systems Y.S. Cho and B. Kahng Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University, Seoul 5-747, Korea (Dated: June 26, 28) arxiv:5.982v2
Discontinuous percolation transitions in real physical systems Y.S. Cho and B. Kahng Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University, Seoul 5-747, Korea (Dated: June 26, 28) arxiv:5.982v2
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References. File name: Peer Review File Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References File name: Peer Review File Description: Supplementary Figure Electron micrographs and ballistic transport
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References File name: Peer Review File Description: Supplementary Figure Electron micrographs and ballistic transport
SIMULATED TEMPERING: A NEW MONTECARLO SCHEME
 arxiv:hep-lat/9205018v1 22 May 1992 SIMULATED TEMPERING: A NEW MONTECARLO SCHEME Enzo MARINARI (a),(b) and Giorgio PARISI (c) Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Via della Ricerca Scientifica,
arxiv:hep-lat/9205018v1 22 May 1992 SIMULATED TEMPERING: A NEW MONTECARLO SCHEME Enzo MARINARI (a),(b) and Giorgio PARISI (c) Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Via della Ricerca Scientifica,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 29 Dec 1996
 Chaotic enhancement of hydrogen atoms excitation in magnetic and microwave fields Giuliano Benenti, Giulio Casati Università di Milano, sede di Como, Via Lucini 3, 22100 Como, Italy arxiv:cond-mat/9612238v1
Chaotic enhancement of hydrogen atoms excitation in magnetic and microwave fields Giuliano Benenti, Giulio Casati Università di Milano, sede di Como, Via Lucini 3, 22100 Como, Italy arxiv:cond-mat/9612238v1
Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space Supplementary Note : Total PDF The total (snap-shot) PDF is obtained
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space Supplementary Note : Total PDF The total (snap-shot) PDF is obtained
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006](/thumbs/91/104898931.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/678v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Dec 6 Abstract Electronic structure of the Au/benzene-,-dithiol/Au transport interface: Effects of chemical bonding U. Schwingenschlögl, C. Schuster Institut für
arxiv:cond-mat/678v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Dec 6 Abstract Electronic structure of the Au/benzene-,-dithiol/Au transport interface: Effects of chemical bonding U. Schwingenschlögl, C. Schuster Institut für
THE 2D ANALOGUE OF THE REISSNER-NORDSTROM SOLUTION. S. Monni and M. Cadoni ABSTRACT
 INFNCA-TH9618 September 1996 THE 2D ANALOGUE OF THE REISSNER-NORDSTROM SOLUTION S. Monni and M. Cadoni Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Cagliari, Via Ospedale 72, I-09100 Cagliari, Italy.
INFNCA-TH9618 September 1996 THE 2D ANALOGUE OF THE REISSNER-NORDSTROM SOLUTION S. Monni and M. Cadoni Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Cagliari, Via Ospedale 72, I-09100 Cagliari, Italy.
arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 29 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 29 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 29 Sep 2017](/thumbs/75/71889227.jpg) Radiation enhancement and temperature in the collapse regime of gravitational scattering arxiv:1709.10375v1 [hep-th] 29 Sep 2017 (Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Firenze and INFN Sezione di Firenze)
Radiation enhancement and temperature in the collapse regime of gravitational scattering arxiv:1709.10375v1 [hep-th] 29 Sep 2017 (Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Firenze and INFN Sezione di Firenze)
A measure of data collapse for scaling
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS A: MATHEMATICAL AND GENERAL J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 34 (21) 6375 638 PII: S35-447(1)25737- A measure of data collapse for scaling Somendra M Bhattacharjee
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS A: MATHEMATICAL AND GENERAL J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 34 (21) 6375 638 PII: S35-447(1)25737- A measure of data collapse for scaling Somendra M Bhattacharjee
Electron counting with quantum dots
 Electron counting with quantum dots Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics Zürich with S. Gustavsson I. Shorubalko R. Leturcq T. Ihn A. C. Gossard Time-resolved charge detection Single photon detection Time-resolved
Electron counting with quantum dots Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics Zürich with S. Gustavsson I. Shorubalko R. Leturcq T. Ihn A. C. Gossard Time-resolved charge detection Single photon detection Time-resolved
D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul 2, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3
 D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3 1 Istituto di Struttura della Materia C.N.R., 00016 Roma, Italy Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, M5S 3H6, Canada 3 Dipartimento
D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3 1 Istituto di Struttura della Materia C.N.R., 00016 Roma, Italy Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, M5S 3H6, Canada 3 Dipartimento
When do diffusion-limited trajectories become memoryless?
 When do diffusion-limited trajectories become memoryless? Maciej Dobrzyński CWI (Center for Mathematics and Computer Science) Kruislaan 413, 1098 SJ Amsterdam, The Netherlands Abstract Stochastic description
When do diffusion-limited trajectories become memoryless? Maciej Dobrzyński CWI (Center for Mathematics and Computer Science) Kruislaan 413, 1098 SJ Amsterdam, The Netherlands Abstract Stochastic description
Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean Field model and Kuramoto model
 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on News, Expectations and Trends in Statistical Physics (NEXT-ΣΦ 2005) 13-18 August 2005, Kolymbari, Crete, Greece Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on News, Expectations and Trends in Statistical Physics (NEXT-ΣΦ 2005) 13-18 August 2005, Kolymbari, Crete, Greece Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean
Numerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks
 umerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks Zhenhua Wu, 1 Cecilia Lagorio, 2 Lidia A. Braunstein, 1,2 Reuven Cohen, 3 Shlomo Havlin, 3 and H. Eugene Stanley
umerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks Zhenhua Wu, 1 Cecilia Lagorio, 2 Lidia A. Braunstein, 1,2 Reuven Cohen, 3 Shlomo Havlin, 3 and H. Eugene Stanley
NON-UNIVERSALITY OF THE NAZAROV-SODIN CONSTANT
 NON-UNIVERSALITY OF THE NAZAROV-SODIN CONSTANT Abstract. We prove that the Nazarov-Sodin constant, which up to a natural scaling gives the leading order growth for the expected number of nodal components
NON-UNIVERSALITY OF THE NAZAROV-SODIN CONSTANT Abstract. We prove that the Nazarov-Sodin constant, which up to a natural scaling gives the leading order growth for the expected number of nodal components
Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions
 75 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 26 Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions Wellington Gomes Dantas and Jürgen F. Stilck Instituto de Física, Universidade
75 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 26 Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions Wellington Gomes Dantas and Jürgen F. Stilck Instituto de Física, Universidade
ON ELECTRON FIELD EMISSION FROM NANOCARBONS
 ON ELECTRON FIELD EMISSION FROM NANOCARBONS Igor S. Altman, Peter V. Pikhitsa, Mansoo Choi National CRI Center for Nano Particle Control, Institute of Advanced Machinery and Design, School of Mechanical
ON ELECTRON FIELD EMISSION FROM NANOCARBONS Igor S. Altman, Peter V. Pikhitsa, Mansoo Choi National CRI Center for Nano Particle Control, Institute of Advanced Machinery and Design, School of Mechanical
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 9 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 9 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 9 May 2015](/thumbs/80/82534602.jpg) Scaling properties of generalized two-dimensional Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equations V. Juknevičius Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy, Vilnius University, A. Goštauto 2, LT-008 Vilnius, Lithuania
Scaling properties of generalized two-dimensional Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equations V. Juknevičius Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy, Vilnius University, A. Goštauto 2, LT-008 Vilnius, Lithuania
Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models
 arxiv:cond-mat/0210545 v1 24 Oct 2002 Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models L. Bussolari, P. Contucci, M. Degli Esposti, C. Giardinà Dipartimento di Matematica dell Università di Bologna,
arxiv:cond-mat/0210545 v1 24 Oct 2002 Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models L. Bussolari, P. Contucci, M. Degli Esposti, C. Giardinà Dipartimento di Matematica dell Università di Bologna,
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010](/thumbs/85/91333090.jpg) Thresholds for epidemic spreading in networks Claudio Castellano 1 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 2 1 Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi (CNR-ISC), UOS Sapienza and Dip. di Fisica, Sapienza Università di Roma,
Thresholds for epidemic spreading in networks Claudio Castellano 1 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 2 1 Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi (CNR-ISC), UOS Sapienza and Dip. di Fisica, Sapienza Università di Roma,
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 3: Systematics, nuisance parameters
 Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 3: Systematics, nuisance parameters http://benasque.org/2018tae/cgi-bin/talks/allprint.pl TAE 2018 Centro de ciencias Pedro Pascual Benasque, Spain 3-15
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 3: Systematics, nuisance parameters http://benasque.org/2018tae/cgi-bin/talks/allprint.pl TAE 2018 Centro de ciencias Pedro Pascual Benasque, Spain 3-15
Fast Numerical Methods for Stochastic Computations
 Fast AreviewbyDongbinXiu May 16 th,2013 Outline Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 4 5 Example: Burgers Equation Let us consider the Burger s equation: u t + uu x = νu xx, x [ 1, 1] u( 1) =1 u(1) = 1 Example:
Fast AreviewbyDongbinXiu May 16 th,2013 Outline Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 4 5 Example: Burgers Equation Let us consider the Burger s equation: u t + uu x = νu xx, x [ 1, 1] u( 1) =1 u(1) = 1 Example:
2 Title: "Ultrathin flexible electronic device based on tunneling effect: a flexible ferroelectric tunnel
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 208 Supplementary information 2 Title: "Ultrathin flexible electronic device
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 208 Supplementary information 2 Title: "Ultrathin flexible electronic device
Emergence of resonances in neural systems: the interplay between adaptive threshold and short-term synaptic plasticity
 Emergence of resonances in neural systems: the interplay between adaptive threshold and short-term synaptic plasticity Jorge F. Mejias 1,2 and Joaquín J. Torres 2 1 Department of Physics and Center for
Emergence of resonances in neural systems: the interplay between adaptive threshold and short-term synaptic plasticity Jorge F. Mejias 1,2 and Joaquín J. Torres 2 1 Department of Physics and Center for
arxiv:nucl-th/ v2 26 Feb 2002
 NEGAIVE SPECIFIC HEA IN OU-OF-EQUILIBRIUM NONEXENSIVE SYSEMS A. Rapisarda and V. Latora Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Università di Catania and INFN Sezione di Catania, Corso Italia 57, I-95129
NEGAIVE SPECIFIC HEA IN OU-OF-EQUILIBRIUM NONEXENSIVE SYSEMS A. Rapisarda and V. Latora Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Università di Catania and INFN Sezione di Catania, Corso Italia 57, I-95129
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Mar 2012](/thumbs/73/68169064.jpg) arxiv:119.658v2 cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Mar 212 Fluctuation theorems in presence of information gain and feedback Sourabh Lahiri 1, Shubhashis Rana 2 and A. M. Jayannavar 3 Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
arxiv:119.658v2 cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Mar 212 Fluctuation theorems in presence of information gain and feedback Sourabh Lahiri 1, Shubhashis Rana 2 and A. M. Jayannavar 3 Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
NON-GAUSSIANITY AND PURITY IN FINITE DIMENSION
 International Journal of Quantum Information Vol. 7, Supplement (9) 97 13 c World Scientific Publishing Company NON-GAUSSIANITY AND PURITY IN FINITE DIMENSION MARCO G. GENONI, and MATTEO G. A. PARIS,,
International Journal of Quantum Information Vol. 7, Supplement (9) 97 13 c World Scientific Publishing Company NON-GAUSSIANITY AND PURITY IN FINITE DIMENSION MARCO G. GENONI, and MATTEO G. A. PARIS,,
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
Application of density estimation methods to quantal analysis
 Application of density estimation methods to quantal analysis Koichi Yoshioka Tokyo Medical and Dental University Summary There has been controversy for the quantal nature of neurotransmission of mammalian
Application of density estimation methods to quantal analysis Koichi Yoshioka Tokyo Medical and Dental University Summary There has been controversy for the quantal nature of neurotransmission of mammalian
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) (b) (a) Supplementary Figure 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
A Reflexive toy-model for financial market
 A Reflexive toy-model for financial market An alternative route towards intermittency. Luigi Palatella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università del Salento via Arnesano, I-73100 Lecce, Italy SM&FT 2011 - The
A Reflexive toy-model for financial market An alternative route towards intermittency. Luigi Palatella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università del Salento via Arnesano, I-73100 Lecce, Italy SM&FT 2011 - The
NON LINEAR PULSE EVOLUTION IN SEEDED AND CASCADED FELS
 NON LINEAR PULSE EVOLUTION IN SEEDED AND CASCADED FELS L. Giannessi, S. Spampinati, ENEA C.R., Frascati, Italy P. Musumeci, INFN & Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma La Sapienza, Roma, Italy Abstract
NON LINEAR PULSE EVOLUTION IN SEEDED AND CASCADED FELS L. Giannessi, S. Spampinati, ENEA C.R., Frascati, Italy P. Musumeci, INFN & Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma La Sapienza, Roma, Italy Abstract
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 20 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 20 Mar 2014 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 20 Mar 2014](/thumbs/91/105879098.jpg) EFFECTIVE DEPHASING FOR A QUBIT INTERACTING WITH A TRANSVERSE CLASSICAL FIELD CLAUDIA BENEDETTI Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano, I-20133 Milano, Italy claudia.benedetti@unimi.it
EFFECTIVE DEPHASING FOR A QUBIT INTERACTING WITH A TRANSVERSE CLASSICAL FIELD CLAUDIA BENEDETTI Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano, I-20133 Milano, Italy claudia.benedetti@unimi.it
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
An exact representation of the fermion dynamics in terms of Poisson processes and its connection with Monte Carlo algorithms
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 November 1999 Europhys. Lett., 48 (3), pp. 243-249 (1999) An exact representation of the fermion dynamics in terms of Poisson processes and its connection with Monte Carlo algorithms
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 November 1999 Europhys. Lett., 48 (3), pp. 243-249 (1999) An exact representation of the fermion dynamics in terms of Poisson processes and its connection with Monte Carlo algorithms
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling
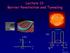 Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Tutorial on Approximate Bayesian Computation
 Tutorial on Approximate Bayesian Computation Michael Gutmann https://sites.google.com/site/michaelgutmann University of Helsinki Aalto University Helsinki Institute for Information Technology 16 May 2016
Tutorial on Approximate Bayesian Computation Michael Gutmann https://sites.google.com/site/michaelgutmann University of Helsinki Aalto University Helsinki Institute for Information Technology 16 May 2016
