t Hei I Y taxi L Y D L A teethed to get the matrix I T A Nettled Use theformula same Theorem 1) Identity transformation:
|
|
|
- Audrey Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ) Identity transformation: Use theformula Theorem to get the matrix I T A Nettled taxi t Hei I Y 2) stretch by factor of.5 horizontally, and.75 vertically: T L A teethed L Y D same
2 3) reflect across the x axis: t K TT o i 4) project onto the y axis: w Tt D A Thistles L it I too
3 5) rotate by an angle 2 (radians) about the origin: A Tk Tied I aaa fo to it okb 6) rotate by an angle about the origin: III I oh I µ lsino.ws gdy.qywgo To cosasino A Neil T I
4 7) horizontal shear with strength.4 : 8) vertical shear with strength -.3:
5 9) mystery linear transformation: ) another mystery linear transformation: A fi B f l s 3 f2, D O
6 Tues Sept.8-.9 linear transformations, and the matrix of a linear transformation. Announcements: We'll discuss today's notes first then go back to Monday examples Warm-up Exercise: So a we use the standard basis vectors I Ez In in IR to understand matrix transformations aka linear transformations express as a linear combination of 5 ej.es in IR Il cs so 35 7 E GET b What's the easiest rector to multiply the matrix I by to yield the 3rd column f Tej in 24
7 Recall, Definition: A function T which has domain equal to n and whose range lies in m is called a linear transformation if it transforms sums to sums, and scalar multiples to scalar multiples. Precisely, T : n m is linear if and only if i T u v = T u T v u, v n ii T c u = c T u c, u n. iii T J 8 whye.g apply Remark: By using the linear transformation properties (i), (ii) multiple times one can verify that linear functions transform linear combinations into linear combinations, with the same weights. For example, H Let's check step by step that if T is linear, then T c u c 2 u 2 c 3 u 3 = c T u c 2 T u 2 c 3 T u 3. why i Tlc ii quiz Tights i T cit TICE ttcgu3 i again c Thi t t ETI This ii lii with c o Thou OTH G TLE Recall as well, In n we write e = :, e 2 = :,... e n = :. We call e, e 2,... e n the standard basis for n because each x x = x 2 : x n n is easily and uniquely expressed as a linear combination of the standard basis vectors, x = x e x 2 e x n e n
8 we did these as warm up exercises Exercise Express as a linear combination of the standard basis vectors. Exercise 2 What vector should we multiply this matrix below by, so that the result is the third column of the matrix? A =
9 Yesterday we showed matrix transformations are linear This is Theorem: Every linear transformation T : n m is actually a matrix transformation, T x = A x, where the j th column of A m n, is T e j, j =, 2.,... n. In other words the matrix of T is A = T e T e... T e 22 h the converse proof: T t Tf x I xie t then x TCEI t xzt E t t intent Tie Ted Tg see.97 Hw A
10 Exercise 3 Illustrate the linear transformation theorem with the projection function T : 3 2, by writing T as a matrix transformation. T x x 2 x 3 = x x 2 formula dotproductury theorem way to 9 8 µ A filet Neil Neil Hoole p S't p A D ft 9 8
11 Exercise 4 Find a matrix formula for the linear transformation T : 2 3 which satisfies T 2 = 2 T =. And sketch the Fmapping diagram. I A filet Neil L o
12 When you learned about functions in a previous course, the following were key ideas: Definitions: The function f : X Y is one to one (sometimes called injective) if each image point of f arises from exactly one input value. In other words, f x = f x 2 x = x 2. The function f : X Y is onto (sometimes called surjective) if for each y Y there is at least one x X so that f x = y. If f : X Y is a function, then the function g : Y X is called an (the) inverse function for f if and only if g f x = x for all x X and f g y = y for all y Y. Theorem A function f : X Y has an inverse function g = f if and only f is one to one and onto. Exercise 5 For a linear function T : n m with matrix A i.e. T x = A x 5a What is the pivot condition on the matrix A that makes the linear function T one to one? 5b What is the pivot condition on the matrix A that makes the function T onto? 5c Is the transformation in Exercise 3 one to one? Is it onto? 5d Is the transformation in Exercise 4 one to one? is it onto?
Math Week 1 notes
 Math 2270-004 Week notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. Or on an amazing day we may get farther than I've predicted. We may also add or subtract some
Math 2270-004 Week notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. Or on an amazing day we may get farther than I've predicted. We may also add or subtract some
Wed Feb The vector spaces 2, 3, n. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Wed Feb 2 4-42 The vector spaces 2, 3, n Announcements: Warm-up Exercise: 4-42 The vector space m and its subspaces; concepts related to "linear combinations of vectors" Geometric interpretation of vectors
Wed Feb 2 4-42 The vector spaces 2, 3, n Announcements: Warm-up Exercise: 4-42 The vector space m and its subspaces; concepts related to "linear combinations of vectors" Geometric interpretation of vectors
Announcements Wednesday, October 04
 Announcements Wednesday, October 04 Please fill out the mid-semester survey under Quizzes on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.8, 1.9 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 1.7, 1.8, and 1.9. My office is
Announcements Wednesday, October 04 Please fill out the mid-semester survey under Quizzes on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.8, 1.9 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 1.7, 1.8, and 1.9. My office is
Math Week 1 notes
 Math 2250-004 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. Or on an amazing day we may get farther than I've predicted. We may also add or subtract some
Math 2250-004 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. Or on an amazing day we may get farther than I've predicted. We may also add or subtract some
Examples: u = is a vector in 2. is a vector in 5.
 3 Vectors and vector equations We'll carefully define vectors, algebraic operations on vectors and geometric interpretations of these operations, in terms of displacements These ideas will eventually give
3 Vectors and vector equations We'll carefully define vectors, algebraic operations on vectors and geometric interpretations of these operations, in terms of displacements These ideas will eventually give
Mon Jan Matrix and linear transformations. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Math 2270-004 Week 4 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Math 2270-004 Week 4 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Finish section 3.6 on Determinants and connections to matrix inverses. Use last week's notes. Then if we have time on Tuesday, begin:
 Math 225-4 Week 7 notes Sections 4-43 vector space concepts Tues Feb 2 Finish section 36 on Determinants and connections to matrix inverses Use last week's notes Then if we have time on Tuesday, begin
Math 225-4 Week 7 notes Sections 4-43 vector space concepts Tues Feb 2 Finish section 36 on Determinants and connections to matrix inverses Use last week's notes Then if we have time on Tuesday, begin
Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them.
 Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them. In this model, the bo temperature T = T t changes at a rate
Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them. In this model, the bo temperature T = T t changes at a rate
Unit 4 Day 8 Symmetry & Compositions
 Unit 4 Day 8 Symmetry & Compositions Warm Up Day 8 1. f ( ) 4 3. g( ) 4 a. f(-1)= a. -g()= b. f(3)= b. g(+y)= c. f(-y)= c. g(-)= 3. Write and graph an equation that has the following: -Nonremovable discontinuity
Unit 4 Day 8 Symmetry & Compositions Warm Up Day 8 1. f ( ) 4 3. g( ) 4 a. f(-1)= a. -g()= b. f(3)= b. g(+y)= c. f(-y)= c. g(-)= 3. Write and graph an equation that has the following: -Nonremovable discontinuity
for non-homogeneous linear differential equations L y = f y H
 Tues March 13: 5.4-5.5 Finish Monday's notes on 5.4, Then begin 5.5: Finding y P for non-homogeneous linear differential equations (so that you can use the general solution y = y P y = y x in this section...
Tues March 13: 5.4-5.5 Finish Monday's notes on 5.4, Then begin 5.5: Finding y P for non-homogeneous linear differential equations (so that you can use the general solution y = y P y = y x in this section...
Mon Feb Matrix algebra and matrix inverses. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Math 2270-004 Week 5 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
Math 2270-004 Week 5 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
6. The scalar multiple of u by c, denoted by c u is (also) in V. (closure under scalar multiplication)
 Definition: A subspace of a vector space V is a subset H of V which is itself a vector space with respect to the addition and scalar multiplication in V. As soon as one verifies a), b), c) below for H,
Definition: A subspace of a vector space V is a subset H of V which is itself a vector space with respect to the addition and scalar multiplication in V. As soon as one verifies a), b), c) below for H,
Announcements Wednesday, September 27
 Announcements Wednesday, September 27 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your grades on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.7 is due
Announcements Wednesday, September 27 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your grades on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.7 is due
Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them.
 Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them. In this model, the body temperature T = T t changes at a rate
Exercise 4) Newton's law of cooling is a model for how objects are heated or cooled by the temperature of an ambient medium surrounding them. In this model, the body temperature T = T t changes at a rate
Span & Linear Independence (Pop Quiz)
 Span & Linear Independence (Pop Quiz). Consider the following vectors: v = 2, v 2 = 4 5, v 3 = 3 2, v 4 = Is the set of vectors S = {v, v 2, v 3, v 4 } linearly independent? Solution: Notice that the number
Span & Linear Independence (Pop Quiz). Consider the following vectors: v = 2, v 2 = 4 5, v 3 = 3 2, v 4 = Is the set of vectors S = {v, v 2, v 3, v 4 } linearly independent? Solution: Notice that the number
Announcements Wednesday, October 25
 Announcements Wednesday, October 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. The grade breakdown is posted on Piazza. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your
Announcements Wednesday, October 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. The grade breakdown is posted on Piazza. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your
IB Math SL Year 2 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited
 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited Learning Goals: How do you apply integrals to real-world scenarios? Recall: Linear Motion When an object is moving, a ball in the air
Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited Learning Goals: How do you apply integrals to real-world scenarios? Recall: Linear Motion When an object is moving, a ball in the air
Matrix of Linear Xformations
 Matrix of Linear Xformations Theorem: If "L" is a linear transformation mapping R n into R m, there exists an mxn matrix "A" such that Lx Ax. This matrix is called the Standard Matrix for the Linear Transformation
Matrix of Linear Xformations Theorem: If "L" is a linear transformation mapping R n into R m, there exists an mxn matrix "A" such that Lx Ax. This matrix is called the Standard Matrix for the Linear Transformation
Announcements Monday, September 25
 Announcements Monday, September 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your grades on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.7 is due Friday
Announcements Monday, September 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your grades on Canvas. WeBWorK 1.7 is due Friday
Kevin James. MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices
 MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices Definition Suppose that T : R n R m is linear. We will say that T is invertible if for every b R m there is exactly one x R n so that T ( x) = b. Note If T is
MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices Definition Suppose that T : R n R m is linear. We will say that T is invertible if for every b R m there is exactly one x R n so that T ( x) = b. Note If T is
Announcements Wednesday, November 01
 Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Physics 8 Monday, October 28, 2013
 Physics 8 Monday, October 28, 2013 Turn in HW8 today. I ll make them less difficult in the future! Rotation is a hard topic. And these were hard problems. HW9 (due Friday) is 7 conceptual + 8 calculation
Physics 8 Monday, October 28, 2013 Turn in HW8 today. I ll make them less difficult in the future! Rotation is a hard topic. And these were hard problems. HW9 (due Friday) is 7 conceptual + 8 calculation
MATH Lecture 16 February 24,2017
 MATH 101 Lecture 16 February 242017 Announcements HW # due in class Monday Feb 27 : time Quiz # 3 Tuesday February 28 Sections 212.4 Read 2Section for next Multiple Choice questions today! 2.4 Library
MATH 101 Lecture 16 February 242017 Announcements HW # due in class Monday Feb 27 : time Quiz # 3 Tuesday February 28 Sections 212.4 Read 2Section for next Multiple Choice questions today! 2.4 Library
Later in this chapter, we are going to use vector functions to describe the motion of planets and other objects through space.
 10 VECTOR FUNCTIONS VECTOR FUNCTIONS Later in this chapter, we are going to use vector functions to describe the motion of planets and other objects through space. Here, we prepare the way by developing
10 VECTOR FUNCTIONS VECTOR FUNCTIONS Later in this chapter, we are going to use vector functions to describe the motion of planets and other objects through space. Here, we prepare the way by developing
Section 1.8/1.9. Linear Transformations
 Section 1.8/1.9 Linear Transformations Motivation Let A be a matrix, and consider the matrix equation b = Ax. If we vary x, we can think of this as a function of x. Many functions in real life the linear
Section 1.8/1.9 Linear Transformations Motivation Let A be a matrix, and consider the matrix equation b = Ax. If we vary x, we can think of this as a function of x. Many functions in real life the linear
Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4
 Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4 EWI / DIAM / Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller 29/04/2014 M. Möller (EWI/NA group) LA (wi1403lr) 29/04/2014 1 / 28 Review of lecture no.3 1.5 Solution Sets
Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4 EWI / DIAM / Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller 29/04/2014 M. Möller (EWI/NA group) LA (wi1403lr) 29/04/2014 1 / 28 Review of lecture no.3 1.5 Solution Sets
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis. Lecture 23
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 23 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Draw the free body diagram of a frame and its members. FRAMES b) Determine the forces acting at
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 23 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Draw the free body diagram of a frame and its members. FRAMES b) Determine the forces acting at
5.1 Second order linear differential equations, and vector space theory connections.
 Math 2250-004 Wed Mar 1 5.1 Second order linear differential equations, and vector space theory connections. Definition: A vector space is a collection of objects together with and "addition" operation
Math 2250-004 Wed Mar 1 5.1 Second order linear differential equations, and vector space theory connections. Definition: A vector space is a collection of objects together with and "addition" operation
Matrix of Linear Xformations
 Matrix of Linear Xformations Theorem: If "L" is a linear transformation mapping R n into R m, there exists an mxn matrix "A" such that Lx Ax. This matrix is called the Standard Matrix for the Linear Transformation
Matrix of Linear Xformations Theorem: If "L" is a linear transformation mapping R n into R m, there exists an mxn matrix "A" such that Lx Ax. This matrix is called the Standard Matrix for the Linear Transformation
Do you know how to find the distance between two points?
 Some notation to understand: is the line through points A and B is the ray starting at point A and extending (infinitely) through B is the line segment connecting points A and B is the length of the line
Some notation to understand: is the line through points A and B is the ray starting at point A and extending (infinitely) through B is the line segment connecting points A and B is the length of the line
Math Week 1 notes
 Math 2280-001 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Math 2280-001 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Lecture 23. ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis FRAMES S 1
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 23 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Draw the free body diagram of a frame and its members. FRAMES b) Determine the forces acting at
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 23 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Draw the free body diagram of a frame and its members. FRAMES b) Determine the forces acting at
Using the Zero Product Property to Find Horizontal Intercepts
 LESSON 11 Using the Zero Product Property to Find Horizontal Intercepts LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: exploring what happens when two factors have a product of 0. So that I can: solve equations that
LESSON 11 Using the Zero Product Property to Find Horizontal Intercepts LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: exploring what happens when two factors have a product of 0. So that I can: solve equations that
Future Self-Guides. E,.?, :0-..-.,0 Q., 5...q ',D5', 4,] 1-}., d-'.4.., _. ZoltAn Dbrnyei Introduction. u u rt 5,4) ,-,4, a. a aci,, u 4.
![Future Self-Guides. E,.?, :0-..-.,0 Q., 5...q ',D5', 4,] 1-}., d-'.4.., _. ZoltAn Dbrnyei Introduction. u u rt 5,4) ,-,4, a. a aci,, u 4. Future Self-Guides. E,.?, :0-..-.,0 Q., 5...q ',D5', 4,] 1-}., d-'.4.., _. ZoltAn Dbrnyei Introduction. u u rt 5,4) ,-,4, a. a aci,, u 4.](/thumbs/92/109036622.jpg) te SelfGi ZltAn Dbnyei Intdtin ; ) Q) 4 t? ) t _ 4 73 y S _ E _ p p 4 t t 4) 1_ ::_ J 1 `i () L VI O I4 " " 1 D 4 L e Q) 1 k) QJ 7 j ZS _Le t 1 ej!2 i1 L 77 7 G (4) 4 6 t (1 ;7 bb F) t f; n (i M Q) 7S
te SelfGi ZltAn Dbnyei Intdtin ; ) Q) 4 t? ) t _ 4 73 y S _ E _ p p 4 t t 4) 1_ ::_ J 1 `i () L VI O I4 " " 1 D 4 L e Q) 1 k) QJ 7 j ZS _Le t 1 ej!2 i1 L 77 7 G (4) 4 6 t (1 ;7 bb F) t f; n (i M Q) 7S
 Math 2250-004 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Math 2250-004 Week 1 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
is any vector v that is a sum of scalar multiples of those vectors, i.e. any v expressible as v = c 1 v n ... c n v 2 = 0 c 1 = c 2
 Math 225-4 Week 8 Finish sections 42-44 and linear combination concepts, and then begin Chapter 5 on linear differential equations, sections 5-52 Mon Feb 27 Use last Friday's notes to talk about linear
Math 225-4 Week 8 Finish sections 42-44 and linear combination concepts, and then begin Chapter 5 on linear differential equations, sections 5-52 Mon Feb 27 Use last Friday's notes to talk about linear
Announcements Wednesday, November 01
 Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Name Period. Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles. Standard: G-GPE.1. Objective:
 Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Ch. 7.6 Squares, Squaring & Parabolas
 Ch. 7.6 Squares, Squaring & Parabolas Learning Intentions: Learn about the squaring & square root function. Graph parabolas. Compare the squaring function with other functions. Relate the squaring function
Ch. 7.6 Squares, Squaring & Parabolas Learning Intentions: Learn about the squaring & square root function. Graph parabolas. Compare the squaring function with other functions. Relate the squaring function
AP Physics 1 Summer Work 2017
 AP Physics 1 Summer Work 2017 The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout the packet. All work
AP Physics 1 Summer Work 2017 The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout the packet. All work
Module 3 - Expressions & Equations Unit 5 Packet 2 - Solving Equations & Inequalities
 Name: Packet Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2018 Module 3 - Expressions & Equations Unit 5 Packet 2 - Solving Equations & Inequalities Standard 7.EE.A.1 7.EE.A.2 7.EE.B.3 7.EE.B.4 Description Apply properties
Name: Packet Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2018 Module 3 - Expressions & Equations Unit 5 Packet 2 - Solving Equations & Inequalities Standard 7.EE.A.1 7.EE.A.2 7.EE.B.3 7.EE.B.4 Description Apply properties
Tues Feb Vector spaces and subspaces. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Math 2270-004 Week 7 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
Math 2270-004 Week 7 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent
MATH 2554 (Calculus I)
 MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
Theorem 3: The solution space to the second order homogeneous linear differential equation y p x y q x y = 0 is 2-dimensional.
 Unlike in the previous example, and unlike what was true for the first order linear differential equation y p x y = q x there is not a clever integrating factor formula that will always work to find the
Unlike in the previous example, and unlike what was true for the first order linear differential equation y p x y = q x there is not a clever integrating factor formula that will always work to find the
February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018
 February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 2.2: Inverse of a Matrix Consider the scalar equation ax = b. Provided a 0, we can solve this explicity x = a 1 b where a 1 is the unique number such that
February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 2.2: Inverse of a Matrix Consider the scalar equation ax = b. Provided a 0, we can solve this explicity x = a 1 b where a 1 is the unique number such that
Section Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 13.1 Section 13.1 Goals: Graph certain plane curves. Compute limits and verify the continuity of vector functions. Multivariable Calculus 1 / 32 Section 13.1 Equation of a Line The equation of
Section 13.1 Section 13.1 Goals: Graph certain plane curves. Compute limits and verify the continuity of vector functions. Multivariable Calculus 1 / 32 Section 13.1 Equation of a Line The equation of
Exercise 2) Consider the two vectors v 1. = 1, 0, 2 T, v 2
 Exercise ) Consider the two vectors v,, T,, T 3. a) Sketch these two vectors as position vectors in 3, using the axes below. b) What geometric object is span v? Sketch a portion of this object onto your
Exercise ) Consider the two vectors v,, T,, T 3. a) Sketch these two vectors as position vectors in 3, using the axes below. b) What geometric object is span v? Sketch a portion of this object onto your
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra
 MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University February 6, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University February 6, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH
Review of Functions. Functions. Philippe B. Laval. Current Semester KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions Current Semester 1 / 12
 Review of Functions Functions Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions Current Semester 1 / 12 Introduction Students are expected to know the following concepts about functions:
Review of Functions Functions Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions Current Semester 1 / 12 Introduction Students are expected to know the following concepts about functions:
Definition. special name. 72 spans 5. Last time we proved that if Ju's is. t.vtts.tt turn. This subspace is se important that we give it
 1.7 Spanningsetsilinearndependencey 1.2 in text Last time we proved that if 72 148 Ju's is a set of vectors in R then is a subspace of R t.vtts.tt turn t tz the R This subspace is se important that we
1.7 Spanningsetsilinearndependencey 1.2 in text Last time we proved that if 72 148 Ju's is a set of vectors in R then is a subspace of R t.vtts.tt turn t tz the R This subspace is se important that we
Chapter 1.6. Perform Operations with Complex Numbers
 Chapter 1.6 Perform Operations with Complex Numbers EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1 Exercises Solve a quadratic equation Solve 2x 2 + 11 = 37. 2x 2 + 11 = 37 2x 2 = 48 Write original equation. Subtract 11 from each
Chapter 1.6 Perform Operations with Complex Numbers EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1 Exercises Solve a quadratic equation Solve 2x 2 + 11 = 37. 2x 2 + 11 = 37 2x 2 = 48 Write original equation. Subtract 11 from each
43.1 Vector Fields and their properties
 Module 15 : Vector fields, Gradient, Divergence and Curl Lecture 43 : Vector fields and their properties [Section 43.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : Concept of Vector field.
Module 15 : Vector fields, Gradient, Divergence and Curl Lecture 43 : Vector fields and their properties [Section 43.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : Concept of Vector field.
Section 4.5. Matrix Inverses
 Section 4.5 Matrix Inverses The Definition of Inverse Recall: The multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal) of a nonzero number a is the number b such that ab = 1. We define the inverse of a matrix in almost
Section 4.5 Matrix Inverses The Definition of Inverse Recall: The multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal) of a nonzero number a is the number b such that ab = 1. We define the inverse of a matrix in almost
today 3) Ford Day Registration : parts Announcements tomorrow recruitment for Ford Koch off Hall 21 HW 2 Up Presentation two 1) HW I Problems duc
 two Announcements 1) HW I Problems duc today 21 HW 2 Up Web work due Friday Rest due Tuesday parts 3) Ford Day tomorrow recruitment for Ford Koch off Hall Registration : noon Presentation : 12:15 Networking
two Announcements 1) HW I Problems duc today 21 HW 2 Up Web work due Friday Rest due Tuesday parts 3) Ford Day tomorrow recruitment for Ford Koch off Hall Registration : noon Presentation : 12:15 Networking
As you enter... (Write down the learning objective, the question and your answer.) What do you think it means for a reaction to occur spontaneously?
 Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
Mon Feb Matrix inverses, the elementary matrix approach overview of skipped section 2.5. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Math 2270-004 Week 6 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
Math 2270-004 Week 6 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a given day's notes on that day We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
Announcements Monday, November 26
 Announcements Monday, November 26 Please fill out your CIOS survey! WeBWorK 6.6, 7.1, 7.2 are due on Wednesday. No quiz on Friday! But this is the only recitation on chapter 7. My office is Skiles 244
Announcements Monday, November 26 Please fill out your CIOS survey! WeBWorK 6.6, 7.1, 7.2 are due on Wednesday. No quiz on Friday! But this is the only recitation on chapter 7. My office is Skiles 244
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Announcements Monday, September 18
 Announcements Monday, September 18 WeBWorK 1.4, 1.5 are due on Wednesday at 11:59pm. The first midterm is on this Friday, September 22. Midterms happen during recitation. The exam covers through 1.5. About
Announcements Monday, September 18 WeBWorK 1.4, 1.5 are due on Wednesday at 11:59pm. The first midterm is on this Friday, September 22. Midterms happen during recitation. The exam covers through 1.5. About
1.2 Graphs and Lines. Cartesian Coordinate System
 1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
8-2 Trigonometric Ratios
 8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Write each fraction as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth. 1. 2. 0.67 0.29 Solve each equation. 3. 4. x = 7.25
8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Write each fraction as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth. 1. 2. 0.67 0.29 Solve each equation. 3. 4. x = 7.25
f Illit staffd Eld V Exe 41,1 E A at E X E it E XII Find eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the matrix
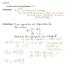 Fri Nov 30 Symmetric matrices and the spectral theorem, 7-7 Announcements: PCA principal component analysis Prof Tom Alberts guest lecture on Tues will at least by end of lecture indicate the ideas behind
Fri Nov 30 Symmetric matrices and the spectral theorem, 7-7 Announcements: PCA principal component analysis Prof Tom Alberts guest lecture on Tues will at least by end of lecture indicate the ideas behind
Fact: Every matrix transformation is a linear transformation, and vice versa.
 Linear Transformations Definition: A transformation (or mapping) T is linear if: (i) T (u + v) = T (u) + T (v) for all u, v in the domain of T ; (ii) T (cu) = ct (u) for all scalars c and all u in the
Linear Transformations Definition: A transformation (or mapping) T is linear if: (i) T (u + v) = T (u) + T (v) for all u, v in the domain of T ; (ii) T (cu) = ct (u) for all scalars c and all u in the
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Instructor Notes for Chapters 3 & 4
 Algebra for Calculus Fall 0 Section 3. Complex Numbers Goal for students: Instructor Notes for Chapters 3 & 4 perform computations involving complex numbers You might want to review the quadratic formula
Algebra for Calculus Fall 0 Section 3. Complex Numbers Goal for students: Instructor Notes for Chapters 3 & 4 perform computations involving complex numbers You might want to review the quadratic formula
(So SamID 1 ( ) = Ken W. Smith.)
 In an earlier lesson, we introduced functions by assigning US citizens a social security number (SSN ) or by assigning students and staff at Sam Houston State University a student ID (SamID) The function
In an earlier lesson, we introduced functions by assigning US citizens a social security number (SSN ) or by assigning students and staff at Sam Houston State University a student ID (SamID) The function
5) homogeneous and nonhomogeneous systems 5a) The homogeneous matrix equation, A x = 0 is always consistent.
 5) homogeneous and nonhomogeneous systems 5a) The homogeneous matrix equation, A x is always consistent. 5b) If A x b is also consistent, then the solution set to A x b is a translation of the solution
5) homogeneous and nonhomogeneous systems 5a) The homogeneous matrix equation, A x is always consistent. 5b) If A x b is also consistent, then the solution set to A x b is a translation of the solution
Chapter 3-1 Polynomials
 Chapter 3 notes: Chapter 3-1 Polynomials Obj: SWBAT identify, evaluate, add, and subtract polynomials A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables with whole number exponents
Chapter 3 notes: Chapter 3-1 Polynomials Obj: SWBAT identify, evaluate, add, and subtract polynomials A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables with whole number exponents
Graphing Linear Inequalities
 Graphing Linear Inequalities Linear Inequalities in Two Variables: A linear inequality in two variables is an inequality that can be written in the general form Ax + By < C, where A, B, and C are real
Graphing Linear Inequalities Linear Inequalities in Two Variables: A linear inequality in two variables is an inequality that can be written in the general form Ax + By < C, where A, B, and C are real
SUPPLEMENT I. Example. Graph the vector 4, 3. Definition. Given two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), the vector represented by # AB is # AB =,
 SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
Announcements Monday, October 29
 Announcements Monday, October 29 WeBWorK on determinents due on Wednesday at :59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 5., 5.2, 5.3. My office is Skiles 244 and Rabinoffice hours are: Mondays, 2 pm; Wednesdays,
Announcements Monday, October 29 WeBWorK on determinents due on Wednesday at :59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 5., 5.2, 5.3. My office is Skiles 244 and Rabinoffice hours are: Mondays, 2 pm; Wednesdays,
CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
 CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Use the concept of conservative forces and determine the potential energy of such forces.
CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Use the concept of conservative forces and determine the potential energy of such forces.
Unit Plan: Matrices (4 weeks or 20 instructional Days)
 Unit Plan: Matrices (4 weeks or 20 instructional Days) Day 1: Review of Systems of Equations in 2 and 3 Variables Objectives: (M.4HS.CVM.18 )(CCSS.Math.Content.HSF-IF.B.6) Students will be able to solve
Unit Plan: Matrices (4 weeks or 20 instructional Days) Day 1: Review of Systems of Equations in 2 and 3 Variables Objectives: (M.4HS.CVM.18 )(CCSS.Math.Content.HSF-IF.B.6) Students will be able to solve
Math 2210Q (Roby) Practice Midterm #1 Solutions Fall 2017
 Math Q (Roby) Practice Midterm # Solutions Fall 7 SHOW ALL YOUR WORK! Make sure you give reasons to support your answers. If you have any questions, do not hesitate to ask! For this exam no calculators
Math Q (Roby) Practice Midterm # Solutions Fall 7 SHOW ALL YOUR WORK! Make sure you give reasons to support your answers. If you have any questions, do not hesitate to ask! For this exam no calculators
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
Monday Tuesday Block Friday 13 22/ End of 9-wks Pep-Rally Operations Vectors Two Vectors
 Name: Period: Pre-Cal AB: Unit 6: Vectors Monday Tuesday Block Friday 13 14 15/16 PSAT/ASVAB 17 Pep Rally No School Solving Trig Equations TEST Vectors Intro 20 21 22/23 24 End of 9-wks Pep-Rally Operations
Name: Period: Pre-Cal AB: Unit 6: Vectors Monday Tuesday Block Friday 13 14 15/16 PSAT/ASVAB 17 Pep Rally No School Solving Trig Equations TEST Vectors Intro 20 21 22/23 24 End of 9-wks Pep-Rally Operations
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2026 Summer 2018 Problem Set #1 Assigned: May 14, 2018 Due: May 22, 2018 Reading: Chapter 1; App. A on Complex Numbers,
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2026 Summer 2018 Problem Set #1 Assigned: May 14, 2018 Due: May 22, 2018 Reading: Chapter 1; App. A on Complex Numbers,
Quiz 2 Practice Problems
 Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS. Points: 4+7+4 Ma 322 Solved First Exam February 7, 207 With supplements You are given an augmented matrix of a linear system of equations. Here t is a parameter: 0 4 4 t 0 3
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS. Points: 4+7+4 Ma 322 Solved First Exam February 7, 207 With supplements You are given an augmented matrix of a linear system of equations. Here t is a parameter: 0 4 4 t 0 3
1.) How many significant figures do the following numbers have? a.) Answer: d.) Answer: b.) Answer: e.) Answer:
 AP Physics 1 Intro Packet 2018 (Due August 13 th ) The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout
AP Physics 1 Intro Packet 2018 (Due August 13 th ) The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout
Announcements. CS243: Discrete Structures. Sequences, Summations, and Cardinality of Infinite Sets. More on Midterm. Midterm.
 Announcements CS43: Discrete Structures Sequences, Summations, and Cardinality of Infinite Sets Işıl Dillig Homework is graded, scores on Blackboard Graded HW and sample solutions given at end of this
Announcements CS43: Discrete Structures Sequences, Summations, and Cardinality of Infinite Sets Işıl Dillig Homework is graded, scores on Blackboard Graded HW and sample solutions given at end of this
Announcements Monday, October 02
 Announcements Monday, October 02 Please fill out the mid-semester survey under Quizzes on Canvas WeBWorK 18, 19 are due Wednesday at 11:59pm The quiz on Friday covers 17, 18, and 19 My office is Skiles
Announcements Monday, October 02 Please fill out the mid-semester survey under Quizzes on Canvas WeBWorK 18, 19 are due Wednesday at 11:59pm The quiz on Friday covers 17, 18, and 19 My office is Skiles
Vertex Form of a Parabola
 Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
( ) AP Physics 1 Math Review
 AP Physics 1 Math Review The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout the packet. All work must
AP Physics 1 Math Review The exercises below are a review of the prerequisite math skills that you need to succeed in AP Physics 1. Make sure to read all directions throughout the packet. All work must
MATH PRACTICE EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 2359 PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS SPRING 205 Throughout this exam, V and W will denote vector spaces over R Part I: True/False () For each of the following statements, determine whether the statement is
MATH 2359 PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS SPRING 205 Throughout this exam, V and W will denote vector spaces over R Part I: True/False () For each of the following statements, determine whether the statement is
264 CHAPTER 4. FRACTIONS cm in cm cm ft pounds
 6 CHAPTER. FRACTIONS 9. 7cm 61. cm 6. 6ft 6. 0in 67. 10cm 69. pounds .. DIVIDING FRACTIONS 6. Dividing Fractions Suppose that you have four pizzas and each of the pizzas has been sliced into eight equal
6 CHAPTER. FRACTIONS 9. 7cm 61. cm 6. 6ft 6. 0in 67. 10cm 69. pounds .. DIVIDING FRACTIONS 6. Dividing Fractions Suppose that you have four pizzas and each of the pizzas has been sliced into eight equal
MAT01A1: Inverse Functions
 MAT01A1: Inverse Functions Dr Craig 27 February 2018 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
MAT01A1: Inverse Functions Dr Craig 27 February 2018 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
Physics 8 Friday, November 8, 2013
 Physics 8 Friday, November 8, 2013 Turn in HW10 today. I ll put HW11 online tomorrow. Today & Monday: mainly trusses. Some beams next week. Monday reading: from Vossoughi ch5+8 (centroids + second moment
Physics 8 Friday, November 8, 2013 Turn in HW10 today. I ll put HW11 online tomorrow. Today & Monday: mainly trusses. Some beams next week. Monday reading: from Vossoughi ch5+8 (centroids + second moment
Section 1.3: slope fields and graphs of differential equation solutions: Consider the first order DE IVP for a function y x : y = f x, y, y x 0
 Section 1.3: slope fields and graphs of differential equation solutions: Consider the first order DE IVP for a function y x : y = f x, y, y x 0 = y 0. If y x is a solution to this IVP and if we consider
Section 1.3: slope fields and graphs of differential equation solutions: Consider the first order DE IVP for a function y x : y = f x, y, y x 0 = y 0. If y x is a solution to this IVP and if we consider
Do you know how to find the distance between two points?
 Some notation to understand: is the line through points A and B is the ray starting at point A and extending (infinitely) through B is the line segment connecting points A and B is the length of the line
Some notation to understand: is the line through points A and B is the ray starting at point A and extending (infinitely) through B is the line segment connecting points A and B is the length of the line
Announcements August 31
 Announcements August 31 Homeworks 1.1 and 1.2 are due Friday. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework. There will generally be a quiz every
Announcements August 31 Homeworks 1.1 and 1.2 are due Friday. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework. There will generally be a quiz every
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Kinematics of Linear Motion
 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: William and Mary February 24, 2015 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Learning Objectives Today, we will be looking at applications of derivatives in the field of kinematics. Learning
Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: William and Mary February 24, 2015 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Learning Objectives Today, we will be looking at applications of derivatives in the field of kinematics. Learning
5.6 Solving Equations Using Both the Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality
 5.6 Solving Equations Using Both the Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality Now that we have studied the Addition Property of Equality and the Multiplication Property of Equality, we can solve
5.6 Solving Equations Using Both the Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality Now that we have studied the Addition Property of Equality and the Multiplication Property of Equality, we can solve
MAT01A1. Numbers, Inequalities and Absolute Values. (Appendix A)
 MAT01A1 Numbers, Inequalities and Absolute Values (Appendix A) Dr Craig 8 February 2017 Leftovers from yesterday: lim n i=1 3 = lim n n 3 = lim n n n 3 i ) 2 ] + 1 n[( n ( n i 2 n n + 2 i=1 i=1 3 = lim
MAT01A1 Numbers, Inequalities and Absolute Values (Appendix A) Dr Craig 8 February 2017 Leftovers from yesterday: lim n i=1 3 = lim n n 3 = lim n n n 3 i ) 2 ] + 1 n[( n ( n i 2 n n + 2 i=1 i=1 3 = lim
Unit 1 Notes. Polynomials
 Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Class Note #14. In this class, we studied an algorithm for integer multiplication, which. 2 ) to θ(n
 Class Note #14 Date: 03/01/2006 [Overall Information] In this class, we studied an algorithm for integer multiplication, which improved the running time from θ(n 2 ) to θ(n 1.59 ). We then used some of
Class Note #14 Date: 03/01/2006 [Overall Information] In this class, we studied an algorithm for integer multiplication, which improved the running time from θ(n 2 ) to θ(n 1.59 ). We then used some of
New Topic PHYS 11: Pg 2
 New Topic PHYS 11: Pg 2 Instantaneous velocity is the slope of the position-vs-time curve PHYS 11: Pg 3 Displacement (not position!) is the area under the velocity-vs-time curve How would I calculate the
New Topic PHYS 11: Pg 2 Instantaneous velocity is the slope of the position-vs-time curve PHYS 11: Pg 3 Displacement (not position!) is the area under the velocity-vs-time curve How would I calculate the
MATH 3330 INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST 3 SPRING Test 3 will be in PKH 113 in class time, Tues April 21
 MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
May 2 nd May 6 th. Unit 10: Rational & Irrational Numbers
 Math 8: Week 33 Math Packet May 2 nd May 6 th Unit 10: Rational & Irrational Numbers Jump Start Directions: Fill out all the BINGO boards on pages 1-2 with the following perfect square numbers: 2, 4, 9,
Math 8: Week 33 Math Packet May 2 nd May 6 th Unit 10: Rational & Irrational Numbers Jump Start Directions: Fill out all the BINGO boards on pages 1-2 with the following perfect square numbers: 2, 4, 9,
