SOLUTION y ' A = 7.5(15) (150) + 90(150) (15) + 215(p)(50) 2. = mm 2. A = 15(150) + 150(15) + p(50) 2. =
|
|
|
- Jesse Aldous Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9 58. Determine the location of the centroidal ais - of the beam s cross-sectional area. Neglect the size of the corner welds at A and B for the calculation. 15 mm 15 mm B 15 mm 15 mm A = 7.5(15) (15) + 9(15) (15) + 215(p)(5) 2 A C = mm 2 5 mm A = 15(15) + 15(15) + p(5) 2 = mm 2 = A A = = 154 mm
2 9 63. Determine the location (, ) of the centroid C of the crosssectional area for the structural member constructed from two equal-sized channels welded together as shown. Assume all corners are square. Neglect the size of the welds..5 in. _ C A = in. _ = in 3 A = = 13 in 2.5 in. 4 in. 2 in. 4 in. = A A = = 4.74 in. 13 A = = in 3 = A A = = 2.99 in. 13
3 9 82. Determine the distance h to which a 1-mm diameter hole must be bored into the base of the cone so that the center of mass of the resulting shape is located at z = 115 mm. The material has a densit of 8 Mg>m 3. z 1 3 p A.5 4 B - p h2A h 2 B 1 3 p p h2 = mm h = h 2 h h -.3 = h 5 mm C 15 mm _ z Choosing the positive root, h = 323 mm
4 9 83. Determine the distance z to the centroid of the shape which consists of a cone with a hole of height h = 5 mm bored into its base. z 5 mm z V = 1 3 p (.15)2 A.5B a.5 4 b - p (.5)2 (.5) a.5 2 b = 1.463(1-3 )m 4 h 5 mm C 15 mm z V = 1 3 p (.15)2 (.5) - p(.5) 2 (.5) =.1139 m 3 z = z V V = (1-3 ) = m = 128 mm.1139
5 9 89. Locate the center of mass z of the assembl. The clinder and the cone are made from materials having densities of 5Mg>m 3 and 9Mg>m 3, respectivel. z Center of mass: The assembl is broken into two composite segments, as shown in Figs. a and b. z = z m m = 5(.4)Cp(.2 2 )(.8)D + 9( )c 1 3 p(.42 )(.6) d 5Cp(.2 2 )(.8)D + 9c 1 3 p(.42 )(.6) d.4 m.2 m.6 m.8 m = =.754 m = 754 mm
6 9 16. Determine the volume of an ellipsoid formed b revolving the shaded area about the ais using the second theorem of Pappus Guldinus. The area and centroid of the shaded area should first be obtained b using integration a 2 b 2 b Area and Centroid: The differential element parallel to the ais is shown shaded in Fig. a. The area of this element is given b Integrating, da = d = a b 2b2-2 d a b a A = da = LA L b 2b2-2 d = pab 4 The centroid can be obtained b appling Eq. 9 4 with =. da = LA da LA b = L c a b 2b2-2 d d pab 4 = 4b 3p Volume: Appling the second theorem of Pappus Guldinus and using the results obtained above, we have V = 2pA = 2pa 4b 3p bapab 4 b = 2 3 pab2
7 9 19. Determine the volume of the solid formed b revolving the shaded area about the u u ais using the second theorem of Pappus Guldinus. The area and centroid of the area should first be obtained b using integration. u Area and Centroid: The differential element parallel to the ais is shown shaded in Fig. a. The area of this element is given b da = d = d 2 ft Integrating, u 1 A = da = LA L 9 3 d = A = 2.25 ft 2 The centroid can be obtained b appling Eq. 9 4 with =. da = LA da LA = L a db 2.25 = L Volume: Appling the second theorem of Pappus-Guldinus and using the results obtained above, we have d = = 2.4 ft 2.25 V = 2p ra = 2p( )(2.25) = 36.8 ft 3
8 Determine the surface area of the roof of the structure if it is formed b rotating the parabola about the ais. 16 ( 2 /16) 16 m Centroid: The length of the differential element is dl = 2d 2 + d 2 d = 1 + a d 2 and its centroid is =. Here,. Evaluating the d = - C d b d 8 integrals, we nave 16 m L = L dl = L 16 m Appling Eq. 9 5, we have L 16 m dl = d = m2 L C d = m C 64 dl = L L dl = = m Surface Area: Appling the theorem of Pappus and Guldinus, Eq. 9 7, with u = 2p, L = m, r = = 9.178, we have A = url = 2p(9.178) (23.663) = 1365 m 2
9 Determine the magnitude of the resultant hdrostatic force acting on the dam and its location, measured from the top surface of the water. The width of the dam is 8 m; r w = 1. Mg>m 3. 6 m p = 6(1)(1 3 )(9.81) = N/m 2 F = 1 2 (6)(8)(58 86) = 1.41(16 )N = 1.41 MN h = 2 3 (6) = 4 m
10 Determine the magnitude of the hdrostatic force acting per foot of length on the seawall. g w = 62.4 lb>ft ft A = da = -d = 2 2 d = 2 LA L L w = b g h = 1(62.4)(8) = lb>ft F = 5.333(1)(62.4) = lb -2 = ft F = 1 (499.2)(8) = 1997 lb 2 F R = 2(332.8) 2 + (1997) 2 = 224 lb = 2.2 kip
SOLUTION Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded area about the x axis. I x = y 2 da = 2 y 2 (xdy) = 2 y y dy
 5. Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded area about the ais. 4 4m 4 4 I = da = (d) 4 = 4 - d I = B (5 + (4)() + 8(4) ) (4 - ) 3-5 4 R m m I = 39. m 4 6. Determine the moment of inertia for the
5. Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded area about the ais. 4 4m 4 4 I = da = (d) 4 = 4 - d I = B (5 + (4)() + 8(4) ) (4 - ) 3-5 4 R m m I = 39. m 4 6. Determine the moment of inertia for the
10 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the x axis.
 10 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the ais. m m 10 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the ais. m m 10 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area about
10 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the ais. m m 10 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the ais. m m 10 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area about
9.3 Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus
 9.3 Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus 9.3 Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving a the Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus
9.3 Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus 9.3 Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving a the Theorems of Pappus and Guldinus
Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia
 Distributed Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction Moments of nertia of an Area Moments of nertia of an Area b ntegration Polar Moments of nertia Radius of Gration of an Area Sample Problems Parallel
Distributed Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction Moments of nertia of an Area Moments of nertia of an Area b ntegration Polar Moments of nertia Radius of Gration of an Area Sample Problems Parallel
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 --review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
--review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
STATICS. Moments of Inertia VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Ninth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 N E 9 Distributed CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction
N E 9 Distributed CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction
STATICS. Moments of Inertia VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Seventh Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer
 00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, nc. All rights reserved. Seventh E CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: 9 STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Distributed Forces: Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler
00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, nc. All rights reserved. Seventh E CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: 9 STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Distributed Forces: Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler
ME 141. Lecture 8: Moment of Inertia
 ME 4 Engineering Mechanics Lecture 8: Moment of nertia Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil679@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
ME 4 Engineering Mechanics Lecture 8: Moment of nertia Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil679@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
I xx + I yy + I zz = (y 2 + z 2 )dm + (x 2 + y 2 )dm. (x 2 + z 2 )dm + (x 2 + y 2 + z 2 )dm = 2
 9196_1_s1_p095-0987 6/8/09 1:09 PM Page 95 010 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. ll rights reserved. This material is protected under all copright laws as the currentl 1 1. Show that the
9196_1_s1_p095-0987 6/8/09 1:09 PM Page 95 010 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. ll rights reserved. This material is protected under all copright laws as the currentl 1 1. Show that the
Chapter 5. Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity
 Chapter 5 Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity Application There are many examples in engineering analysis of distributed loads. It is convenient in some cases to represent such loads as
Chapter 5 Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity Application There are many examples in engineering analysis of distributed loads. It is convenient in some cases to represent such loads as
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3
 Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
A = (cosh x sinh x) dx = (sinh x cosh x) = sinh1 cosh1 sinh 0 + cosh 0 =
 Calculus 7 Review Consider the region between curves y= cosh, y= sinh, =, =.. Find the area of the region. e + e e e Solution. Recall that cosh = and sinh =, whence sinh cosh. Therefore the area is given
Calculus 7 Review Consider the region between curves y= cosh, y= sinh, =, =.. Find the area of the region. e + e e e Solution. Recall that cosh = and sinh =, whence sinh cosh. Therefore the area is given
SOLUTION (y 2 + z 2 )dm + (x 2 + y 2 )dm. (x 2 + z 2 )dm + I xx + I yy + I zz = = 2. (x 2 + y 2 + z 2 )dm
 1 1. Show that the sum of the moments of inertia of a bod, I + I + I, is independent of the orientation of the,, aes and thus depends onl on the location of its origin. I + I + I = Lm ( + )dm + Lm ( +
1 1. Show that the sum of the moments of inertia of a bod, I + I + I, is independent of the orientation of the,, aes and thus depends onl on the location of its origin. I + I + I = Lm ( + )dm + Lm ( +
276 Calculus and Structures
 76 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER THE CONJUGATE BEA ETHOD Calculus and Structures 77 Copyright Chapter THE CONJUGATE BEA ETHOD.1 INTRODUCTION To find the deflection of a beam you must solve the equation,
76 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER THE CONJUGATE BEA ETHOD Calculus and Structures 77 Copyright Chapter THE CONJUGATE BEA ETHOD.1 INTRODUCTION To find the deflection of a beam you must solve the equation,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) 2
 Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
Second Moments or Moments of Inertia
 Second Moments or Moments of Inertia The second moment of inertia of an element of area such as da in Figure 1 with respect to any axis is defined as the product of the area of the element and the square
Second Moments or Moments of Inertia The second moment of inertia of an element of area such as da in Figure 1 with respect to any axis is defined as the product of the area of the element and the square
( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION
![( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION ( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION](/thumbs/86/93981005.jpg) Math 6 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION A curve is rectifiable if it has a finite arc length. It is sufficient that f be continuous on [ab, ] in order for f to be rectifiable between
Math 6 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION A curve is rectifiable if it has a finite arc length. It is sufficient that f be continuous on [ab, ] in order for f to be rectifiable between
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at C of the beam shown in Fig. 1 4a.
 E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
MAC 2311 Chapter 5 Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function
 MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
(a) Use washer cross sections: a washer has
 Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
Exercises. . Evaluate f (, ) xydawhere. 2, 1 x< 3, 0 y< (Answer: 14) 3, 3 x 4, 0 y 2. (Answer: 12) ) f x. ln 2 1 ( ) = (Answer: 1)
 Eercises Eercises. Let = {(, : 4, }. Evaluate f (,,
Eercises Eercises. Let = {(, : 4, }. Evaluate f (,,
(Refer Slide Time: 2:08 min)
 Applied Mechanics Prof. R. K. Mittal Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. 11 Properties of Surfaces (Contd.) Today we will take up lecture eleven which is a
Applied Mechanics Prof. R. K. Mittal Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. 11 Properties of Surfaces (Contd.) Today we will take up lecture eleven which is a
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
5. What is the moment of inertia about the x - x axis of the rectangular beam shown?
 1 of 5 Continuing Education Course #274 What Every Engineer Should Know About Structures Part D - Bending Strength Of Materials NOTE: The following question was revised on 15 August 2018 1. The moment
1 of 5 Continuing Education Course #274 What Every Engineer Should Know About Structures Part D - Bending Strength Of Materials NOTE: The following question was revised on 15 August 2018 1. The moment
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 Third E CHAPTER 6 Shearing MECHANCS OF MATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Stresses in Beams and Thin- Walled Members Shearing
Third E CHAPTER 6 Shearing MECHANCS OF MATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Stresses in Beams and Thin- Walled Members Shearing
By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Engineering Materials Design Lecture.6 the design of beams By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh 6.1 INTRODUCTION Finding the shear forces and bending moments is an essential step in the design of any beam. we usually
Engineering Materials Design Lecture.6 the design of beams By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh 6.1 INTRODUCTION Finding the shear forces and bending moments is an essential step in the design of any beam. we usually
Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts COURSE CONTENT
 Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts Dr. Harlan H. Bengtson, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction This course is about measurement of the flow rate of a fluid flowing under pressure in a closed conduit.
Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts Dr. Harlan H. Bengtson, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction This course is about measurement of the flow rate of a fluid flowing under pressure in a closed conduit.
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
MTE 119 STATICS LECTURE MATERIALS FINAL REVIEW PAGE NAME & ID DATE. Example Problem F.1: (Beer & Johnston Example 9-11)
 Eample Problem F.: (Beer & Johnston Eample 9-) Determine the mass moment of inertia with respect to: (a) its longitudinal ais (-ais) (b) the y-ais SOLUTION: a) Mass moment of inertia about the -ais: Step
Eample Problem F.: (Beer & Johnston Eample 9-) Determine the mass moment of inertia with respect to: (a) its longitudinal ais (-ais) (b) the y-ais SOLUTION: a) Mass moment of inertia about the -ais: Step
MATH 52 MIDTERM 1. April 23, 2004
 MATH 5 MIDTERM April 3, Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the honor code. During the test, you may not use
MATH 5 MIDTERM April 3, Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the honor code. During the test, you may not use
CHAPTER 6 Applications of Integration
 PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
Problem d d d B C E D. 0.8d. Additional lecturebook examples 29 ME 323
 Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
ME 201 Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 ME 01 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Unit 5.3 Reduction of a Simple Distributed Loading Distributed Loads Thus far we ve been working with loads that are concentrated at a point: Many times in engineering
ME 01 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Unit 5.3 Reduction of a Simple Distributed Loading Distributed Loads Thus far we ve been working with loads that are concentrated at a point: Many times in engineering
STATICS VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity. Tenth Edition CHAPTER
 Tenth E CHAPTER 5 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. David F. Mazurek Lecture Notes: John Chen California Polytechnic State University Distributed Forces:
Tenth E CHAPTER 5 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. David F. Mazurek Lecture Notes: John Chen California Polytechnic State University Distributed Forces:
Quizzam Module 1 : Statics
 Structural Steel Design Quizzam odule : Statics NAE Draw shear and moment diagrams for the following loading conditions. Note the reactions. Calculate the maximum amount of internal bending moment. 0 500
Structural Steel Design Quizzam odule : Statics NAE Draw shear and moment diagrams for the following loading conditions. Note the reactions. Calculate the maximum amount of internal bending moment. 0 500
Fluid force problems
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 5: Basic applications of integration Section 1 Fluid force problems What ou need to know alread: How to use the four step process to set up an integral. What
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 5: Basic applications of integration Section 1 Fluid force problems What ou need to know alread: How to use the four step process to set up an integral. What
h p://edugen.wileyplus.com/edugen/courses/crs1404/pc/c08/c2hlch...
 Digital Vision/PictureQuestW... 1 of 2 30-Sep-12 18:41 CHAPTER 8 DISTRIBUTED FORCE Digital Vision/PictureQuest We have looked at a variety of systems and defined the conditions under which they are in
Digital Vision/PictureQuestW... 1 of 2 30-Sep-12 18:41 CHAPTER 8 DISTRIBUTED FORCE Digital Vision/PictureQuest We have looked at a variety of systems and defined the conditions under which they are in
Math 1B Calculus Test 3 Spring 10 Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show your work for credit.
 ath B Calculus Test Spring Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show our work for credit.. Determine whether each integral is convergent or divergent. Evaluate those that are convergent. a. / 4
ath B Calculus Test Spring Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show our work for credit.. Determine whether each integral is convergent or divergent. Evaluate those that are convergent. a. / 4
Calculus and Structures
 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER 8 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS FOR BEAMS WITH CONTINUOUS FORCES Calculus and Structures 11 Copyright Chapter 8 CONTINUOUS FORCE 8.1 INTRODUCTION The last section was
Calculus and Structures CHAPTER 8 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS FOR BEAMS WITH CONTINUOUS FORCES Calculus and Structures 11 Copyright Chapter 8 CONTINUOUS FORCE 8.1 INTRODUCTION The last section was
Failure in Flexure. Introduction to Steel Design, Tensile Steel Members Modes of Failure & Effective Areas
 Introduction to Steel Design, Tensile Steel Members Modes of Failure & Effective Areas MORGAN STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARCHITECTURE AND PLANNING LECTURE VIII Dr. Jason E. Charalambides Failure in Flexure!
Introduction to Steel Design, Tensile Steel Members Modes of Failure & Effective Areas MORGAN STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARCHITECTURE AND PLANNING LECTURE VIII Dr. Jason E. Charalambides Failure in Flexure!
REVIEW FOR EXAM II. Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2002
 REVIEW FOR EXM II. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering b Dr. Ibrahim. ssakkaf SPRING 00 ENES 0 Mechanics of Materials Department of Civil and Environmental
REVIEW FOR EXM II. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering b Dr. Ibrahim. ssakkaf SPRING 00 ENES 0 Mechanics of Materials Department of Civil and Environmental
From Table 1 4. DL = [12 lb/ft 2 # in.(6 in.)] (15 ft)(10 ft) = 10,800 lb. LL = (250 lb/ft 2 )(15 ft)(10 ft) = 37,500 lb.
![From Table 1 4. DL = [12 lb/ft 2 # in.(6 in.)] (15 ft)(10 ft) = 10,800 lb. LL = (250 lb/ft 2 )(15 ft)(10 ft) = 37,500 lb. From Table 1 4. DL = [12 lb/ft 2 # in.(6 in.)] (15 ft)(10 ft) = 10,800 lb. LL = (250 lb/ft 2 )(15 ft)(10 ft) = 37,500 lb.](/thumbs/86/93354768.jpg) 1 1. The floor of a heavy storage warehouse building is made of 6-in.-thick stone concrete. If the floor is a slab having a length of 15 ft and width of 10 ft, determine the resultant force caused by the
1 1. The floor of a heavy storage warehouse building is made of 6-in.-thick stone concrete. If the floor is a slab having a length of 15 ft and width of 10 ft, determine the resultant force caused by the
Exam 04: Chapters 08 and 09
 Name: Exam 04: Chapters 08 and 09 Select and solve four of the following problems to the best of your ability. You must choose two problem from each column. Please notice that it is possible to select
Name: Exam 04: Chapters 08 and 09 Select and solve four of the following problems to the best of your ability. You must choose two problem from each column. Please notice that it is possible to select
Chapter 9 Moment of Inertia
 Chapter 9 Moment of Inertia Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my PARALLEL-AXIS THEOREM,
Chapter 9 Moment of Inertia Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my PARALLEL-AXIS THEOREM,
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
Department of Mathematical x 1 x 2 1
 Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
Distributed Force Acting on a Boundary
 Outline: Centres of Mass and Centroids Centre of Mass Integration Centroids Composite Bodies Distributed Force Acting on a Boundary Line (Beams External Effects) Areas 1 Up to now all forces have been
Outline: Centres of Mass and Centroids Centre of Mass Integration Centroids Composite Bodies Distributed Force Acting on a Boundary Line (Beams External Effects) Areas 1 Up to now all forces have been
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration
 Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
Chapter 6 Notes, Stewart 8e
 Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
3.5 Reinforced Concrete Section Properties
 CHAPER 3: Reinforced Concrete Slabs and Beams 3.5 Reinforced Concrete Section Properties Description his application calculates gross section moment of inertia neglecting reinforcement, moment of inertia
CHAPER 3: Reinforced Concrete Slabs and Beams 3.5 Reinforced Concrete Section Properties Description his application calculates gross section moment of inertia neglecting reinforcement, moment of inertia
Force System Resultants Distributed Loads. A hole has been found in the nudist camp wall. The police are looking into it.
 Force System Resultants A hole has been found in the nudist camp wall. The police are looking into it. Objectives Understand the concept and representation of a distributed load Understand how to convert
Force System Resultants A hole has been found in the nudist camp wall. The police are looking into it. Objectives Understand the concept and representation of a distributed load Understand how to convert
1 1. Round off the following numbers to three significant figures: (a) m, (b) s, (c) 4555 N, and (d) 2768 kg.
 1 1. Round off the following numbers to three significant figures: (a) 4.65735 m, (b) 55.578 s, (c) 4555 N, and (d) 2768 kg. a) 4.66 m b) 55.6 s c) 4.56 kn d) 2.77 Mg Ans 1 2. Represent each of the following
1 1. Round off the following numbers to three significant figures: (a) 4.65735 m, (b) 55.578 s, (c) 4555 N, and (d) 2768 kg. a) 4.66 m b) 55.6 s c) 4.56 kn d) 2.77 Mg Ans 1 2. Represent each of the following
Semester: BE 3 rd Subject :Mechanics of Solids ( ) Year: Faculty: Mr. Rohan S. Kariya. Tutorial 1
 Semester: BE 3 rd Subject :Mechanics of Solids (2130003) Year: 2018-19 Faculty: Mr. Rohan S. Kariya Class: MA Tutorial 1 1 Define force and explain different type of force system with figures. 2 Explain
Semester: BE 3 rd Subject :Mechanics of Solids (2130003) Year: 2018-19 Faculty: Mr. Rohan S. Kariya Class: MA Tutorial 1 1 Define force and explain different type of force system with figures. 2 Explain
Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the x axis Determine the moment of inertia of the area about the y axis.
 10 Solutions 44918 1/28/09 4:21 PM Page 941 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copright laws as the currentl eist. No portion
10 Solutions 44918 1/28/09 4:21 PM Page 941 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copright laws as the currentl eist. No portion
Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity
 Distriuted Forces: Centroids nd Centers of Grvit Introduction Center of Grvit of D Bod Centroids nd First Moments of Ares nd Lines Centroids of Common Shpes of Ares Centroids of Common Shpes of Lines Composite
Distriuted Forces: Centroids nd Centers of Grvit Introduction Center of Grvit of D Bod Centroids nd First Moments of Ares nd Lines Centroids of Common Shpes of Ares Centroids of Common Shpes of Lines Composite
Math 122 Fall Solutions to Homework #5. ( ) 2 " ln x. y = x 2
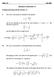 Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending
 EA 3702 echanics & aterials Science (echanics of aterials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending Pure Bending Ch 2 Aial Loading & Parallel Loading: uniform normal stress and shearing stress distribution Ch 3 Torsion:
EA 3702 echanics & aterials Science (echanics of aterials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending Pure Bending Ch 2 Aial Loading & Parallel Loading: uniform normal stress and shearing stress distribution Ch 3 Torsion:
Stress Transformation Equations: u = +135 (Fig. a) s x = 80 MPa s y = 0 t xy = 45 MPa. we obtain, cos u + t xy sin 2u. s x = s x + s y.
 014 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently 9 7. Determine the normal stress and shear stress acting
014 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently 9 7. Determine the normal stress and shear stress acting
AISC LRFD Beam Design in the RAM Structural System
 Model: Verification11_3 Typical Floor Beam #10 W21x44 (10,3,10) AISC 360-05 LRFD Beam Design in the RAM Structural System Floor Loads: Slab Self-weight: Concrete above flute + concrete in flute + metal
Model: Verification11_3 Typical Floor Beam #10 W21x44 (10,3,10) AISC 360-05 LRFD Beam Design in the RAM Structural System Floor Loads: Slab Self-weight: Concrete above flute + concrete in flute + metal
Lecture 5: Pure bending of beams
 Lecture 5: Pure bending of beams Each end of an initiall straight, uniform beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples. The moment of the couples is denoted b (units of F-L. t is shown in solid mechanics
Lecture 5: Pure bending of beams Each end of an initiall straight, uniform beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples. The moment of the couples is denoted b (units of F-L. t is shown in solid mechanics
Chapter Objectives. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
 Chapter Objectives To generalize the procedure by formulating equations that can be plotted so that they describe the internal shear and moment throughout a member. To use the relations between distributed
Chapter Objectives To generalize the procedure by formulating equations that can be plotted so that they describe the internal shear and moment throughout a member. To use the relations between distributed
Steel Cross Sections. Structural Steel Design
 Steel Cross Sections Structural Steel Design PROPERTIES OF SECTIONS Perhaps the most important properties of a beam are the depth and shape of its cross section. There are many to choose from, and there
Steel Cross Sections Structural Steel Design PROPERTIES OF SECTIONS Perhaps the most important properties of a beam are the depth and shape of its cross section. There are many to choose from, and there
2.0 Introduction. F i. [Eq. 2.1] M i. [Eq. 2.2]
![2.0 Introduction. F i. [Eq. 2.1] M i. [Eq. 2.2] 2.0 Introduction. F i. [Eq. 2.1] M i. [Eq. 2.2]](/thumbs/89/98509785.jpg) Chapter Statics.0 Introduction A Statics analysis is generally the first step in determining how an engineering system deforms under load, and how the system supports the load internally. For equilibrium,
Chapter Statics.0 Introduction A Statics analysis is generally the first step in determining how an engineering system deforms under load, and how the system supports the load internally. For equilibrium,
MATH141: Calculus II Exam #1 review 6/8/2017 Page 1
 MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
8.1 Internal Forces in Structural Members
 8.1 Internal Forces in Structural Members 8.1 Internal Forces in Structural Members xample 1, page 1 of 4 1. etermine the normal force, shear force, and moment at sections passing through a) and b). 4
8.1 Internal Forces in Structural Members 8.1 Internal Forces in Structural Members xample 1, page 1 of 4 1. etermine the normal force, shear force, and moment at sections passing through a) and b). 4
6.5 Cables: Concentrated Loads
 6.5 ables: oncentrated Loads 6.5 ables: oncentrated Loads Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 3 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving ables With oncentrated Loads 1. Pass sections through
6.5 ables: oncentrated Loads 6.5 ables: oncentrated Loads Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 3 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving ables With oncentrated Loads 1. Pass sections through
Math 262 Exam 1 - Practice Problems. 1. Find the area between the given curves:
 Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 6 Shearing Stress in Beams & Thin-Walled Members
 EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 6 Shearing Stress in Beams & Thin-Walled Members Beams Bending & Shearing EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018)
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 6 Shearing Stress in Beams & Thin-Walled Members Beams Bending & Shearing EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018)
1.1 The Equations of Motion
 1.1 The Equations of Motion In Book I, balance of forces and moments acting on an component was enforced in order to ensure that the component was in equilibrium. Here, allowance is made for stresses which
1.1 The Equations of Motion In Book I, balance of forces and moments acting on an component was enforced in order to ensure that the component was in equilibrium. Here, allowance is made for stresses which
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints)
 Page Number Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Description of Correction Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 11 Figure
Page Number Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Description of Correction Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 11 Figure
Exam 05: Chapters 10 and 11
 Name: Exam 05: Chapters 10 and 11 Select and solve five of the following problems to the best of your ability. You must choose two problem from each column, and a final problem at your own discretion.
Name: Exam 05: Chapters 10 and 11 Select and solve five of the following problems to the best of your ability. You must choose two problem from each column, and a final problem at your own discretion.
Chapter 4 Pure Bending
 Chapter Pure endg INTRODUCTION endg tress W W L endg of embers made of everal aterials 0 5 lumum 0.5 TYP rass teel rass 2.5 2 lumum 2.5 1.5 12 Cross-section, Cross-section, tress Concentrations r r D d
Chapter Pure endg INTRODUCTION endg tress W W L endg of embers made of everal aterials 0 5 lumum 0.5 TYP rass teel rass 2.5 2 lumum 2.5 1.5 12 Cross-section, Cross-section, tress Concentrations r r D d
[4] Properties of Geometry
![[4] Properties of Geometry [4] Properties of Geometry](/thumbs/91/107196493.jpg) [4] Properties of Geometr Page 1 of 6 [4] Properties of Geometr [4.1] Center of Gravit and Centroid [4.] Composite Bodies [4.3] Moments of Inertia [4.4] Composite reas and Products of Inertia [4] Properties
[4] Properties of Geometr Page 1 of 6 [4] Properties of Geometr [4.1] Center of Gravit and Centroid [4.] Composite Bodies [4.3] Moments of Inertia [4.4] Composite reas and Products of Inertia [4] Properties
Chapter 8. Applications of Definite Integrals. π π. 1 and 2. The graph is. x 2x + 3 = 0 has no real solutions, since
 Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
(Please write your Roll No. immediately) Mid Term Examination. Regular (Feb 2017)
 (Please write your Roll No. immediately) Roll No... Mid Term Examination Regular (Feb 2017) B.Tech-II sem Sub-Engineering Mechanics Paper code- ETME-110 Time-1.5 hours Max Marks-30 Note: 1. Q.No. 1 is
(Please write your Roll No. immediately) Roll No... Mid Term Examination Regular (Feb 2017) B.Tech-II sem Sub-Engineering Mechanics Paper code- ETME-110 Time-1.5 hours Max Marks-30 Note: 1. Q.No. 1 is
Math 21a Homework 07 Solutions Spring, 2014
 Math a Homework 7 Solutions Spring, 4. valuate the iterated integral. a) Stewart.7 # 6 ) e d d d We perform the iterated integral: e d d d e d d e d [ e [ ] 4 e + 4e. Note that we ve twice done an integral
Math a Homework 7 Solutions Spring, 4. valuate the iterated integral. a) Stewart.7 # 6 ) e d d d We perform the iterated integral: e d d d e d d e d [ e [ ] 4 e + 4e. Note that we ve twice done an integral
MOMENT OF INERTIA. Applications. Parallel-Axis Theorem
 MOMENT OF INERTIA Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Determine the mass moment of inertia of a rigid body or a system of rigid bodies. In-Class Activities: Applications Mass Moment of Inertia
MOMENT OF INERTIA Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Determine the mass moment of inertia of a rigid body or a system of rigid bodies. In-Class Activities: Applications Mass Moment of Inertia
Purdue University Study Guide for MA Credit Exam
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 60 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA60. The credit exam is a twohour long exam with 5 multiple choice questions. No books or notes
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 60 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA60. The credit exam is a twohour long exam with 5 multiple choice questions. No books or notes
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints)
 Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 Page Number Description of Correction 15 Example
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 Page Number Description of Correction 15 Example
Shear Stress Example: 1 (3/30/00)
 Shear Stress Example: 1 (3/30/00) Shear Stress Example Determine the largest shear stress for the beam shown. Given the 7' beam with the cross-section shown above left, what is the largest shear stress
Shear Stress Example: 1 (3/30/00) Shear Stress Example Determine the largest shear stress for the beam shown. Given the 7' beam with the cross-section shown above left, what is the largest shear stress
Ch. 5: Distributed Forces
 234 5.0 Outline 234 Introduction 235 Center of Mass 236 Centroids (Line, Area, Volume) 241 Composite Bodies and Figures 257 Theorem of Pappus 265 Fluid Statics 272 5.0 Outline 5.0 Introduction Ch. 5: Distributed
234 5.0 Outline 234 Introduction 235 Center of Mass 236 Centroids (Line, Area, Volume) 241 Composite Bodies and Figures 257 Theorem of Pappus 265 Fluid Statics 272 5.0 Outline 5.0 Introduction Ch. 5: Distributed
Virginia Tech Math 1226 : Past CTE problems
 Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
BEAMS: SHEAR AND MOMENT DIAGRAMS (FORMULA)
 LETURE Third Edition BEMS: SHER ND MOMENT DGRMS (FORMUL). J. lark School of Engineering Department of ivil and Environmental Engineering 1 hapter 5.1 5. b Dr. brahim. ssakkaf SPRNG 00 ENES 0 Mechanics
LETURE Third Edition BEMS: SHER ND MOMENT DGRMS (FORMUL). J. lark School of Engineering Department of ivil and Environmental Engineering 1 hapter 5.1 5. b Dr. brahim. ssakkaf SPRNG 00 ENES 0 Mechanics
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Objectives
 Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
CHAPTER 2. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 2 PROBLEM 2.1 Two forces are applied as shown to a hook. Determinee graphicall the magnitude and direction of their resultant using (a) the parallelogram law, (b) the triangle rule. (a) Parallelogram
CHAPTER 2 PROBLEM 2.1 Two forces are applied as shown to a hook. Determinee graphicall the magnitude and direction of their resultant using (a) the parallelogram law, (b) the triangle rule. (a) Parallelogram
B. Incorrect! Presence of all three variables in the equation makes it not cylindrical.
 Calculus III - Problem Drill 08: Clindrical and Quadric Surfaces Question No. of 0 Instructions: () Read the problem and answer choices carefull () Work the problems on paper as needed () Pick the. Which
Calculus III - Problem Drill 08: Clindrical and Quadric Surfaces Question No. of 0 Instructions: () Read the problem and answer choices carefull () Work the problems on paper as needed () Pick the. Which
Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS
 CHAPTER 5. MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS Matri Transformations Definition Let A and B be sets. A function f : A B
CHAPTER 5. MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS Matri Transformations Definition Let A and B be sets. A function f : A B
Rectangular box of sizes (dimensions) w,l,h wlh Right cylinder of radius r and height h r 2 h
 Volumes: Slicing Method, Method of Disks and Washers -.,.. Volumes of Some Regular Solids: Solid Volume Rectangular bo of sizes (dimensions) w,l,h wlh Right clinder of radius r and height h r h Right cone
Volumes: Slicing Method, Method of Disks and Washers -.,.. Volumes of Some Regular Solids: Solid Volume Rectangular bo of sizes (dimensions) w,l,h wlh Right clinder of radius r and height h r h Right cone
Arnie Pizer Rochester Problem Library Fall 2005 WeBWorK assignment VMultIntegrals1Double due 04/03/2008 at 02:00am EST.
 WeBWorK assignment VMultIntegralsouble due 04/03/2008 at 02:00am ST.. ( pt) rochesterlibrary/setvmultintegralsouble/ur vc 8.pg Consider the solid that lies above the square = [0,2] [0,2] and below the
WeBWorK assignment VMultIntegralsouble due 04/03/2008 at 02:00am ST.. ( pt) rochesterlibrary/setvmultintegralsouble/ur vc 8.pg Consider the solid that lies above the square = [0,2] [0,2] and below the
Triple integrals in Cartesian coordinates (Sect. 15.5)
 Triple integrals in Cartesian coordinates (Sect. 5.5) Triple integrals in rectangular boes. Triple integrals in arbitrar domains. Volume on a region in space. Triple integrals in rectangular boes Definition
Triple integrals in Cartesian coordinates (Sect. 5.5) Triple integrals in rectangular boes. Triple integrals in arbitrar domains. Volume on a region in space. Triple integrals in rectangular boes Definition
SET-I SECTION A SECTION B. General Instructions. Time : 3 hours Max. Marks : 100
 General Instructions. All questions are compulsor.. This question paper contains 9 questions.. Questions - in Section A are ver short answer tpe questions carring mark each.. Questions 5- in Section B
General Instructions. All questions are compulsor.. This question paper contains 9 questions.. Questions - in Section A are ver short answer tpe questions carring mark each.. Questions 5- in Section B
APRIL Conquering the FE & PE exams Formulas, Examples & Applications. Topics covered in this month s column:
 APRIL 2015 DR. Z s CORNER Conquering the FE & PE exams Formulas, Examples & Applications Topics covered in this month s column: PE Exam Specifications (Geotechnical) Transportation (Horizontal Curves)
APRIL 2015 DR. Z s CORNER Conquering the FE & PE exams Formulas, Examples & Applications Topics covered in this month s column: PE Exam Specifications (Geotechnical) Transportation (Horizontal Curves)
( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x 2 = - 8y.
 PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
STATICS VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: and Centers of Gravity. Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 007 The McGrw-Hill Compnies, Inc. All rights reserved. Eighth E CHAPTER 5 Distriuted VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinnd P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Wlt Oler Tes Tech
007 The McGrw-Hill Compnies, Inc. All rights reserved. Eighth E CHAPTER 5 Distriuted VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinnd P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Wlt Oler Tes Tech
Three torques act on the shaft. Determine the internal torque at points A, B, C, and D.
 ... 7. Three torques act on the shaft. Determine the internal torque at points,, C, and D. Given: M 1 M M 3 300 Nm 400 Nm 00 Nm Solution: Section : x = 0; T M 1 M M 3 0 T M 1 M M 3 T 100.00 Nm Section
... 7. Three torques act on the shaft. Determine the internal torque at points,, C, and D. Given: M 1 M M 3 300 Nm 400 Nm 00 Nm Solution: Section : x = 0; T M 1 M M 3 0 T M 1 M M 3 T 100.00 Nm Section
Department of Mathematical 1 Limits. 1.1 Basic Factoring Example. x 1 x 2 1. lim
 Contents 1 Limits 2 1.1 Basic Factoring Example...................................... 2 1.2 One-Sided Limit........................................... 3 1.3 Squeeze Theorem..........................................
Contents 1 Limits 2 1.1 Basic Factoring Example...................................... 2 1.2 One-Sided Limit........................................... 3 1.3 Squeeze Theorem..........................................
APPENDIX A Thickness of Base Metal
 APPENDIX A Thickness of Base Metal For uncoated steel sheets, the thickness of the base metal is listed in Table A.1. For galvanized steel sheets, the thickness of the base metal can be obtained by subtracting
APPENDIX A Thickness of Base Metal For uncoated steel sheets, the thickness of the base metal is listed in Table A.1. For galvanized steel sheets, the thickness of the base metal can be obtained by subtracting
