The JEFF-3.0 Nuclear Data Library
|
|
|
- Clifton Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data Bank ISBN The JEFF-3.0 Nuclear Data Library JEFF Report 19 Synopsis of the General Purpose File OECD 2005 NEA No NUCLEAR ENERGY AGENCY ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT
2 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT The OECD is a unique forum where the governments of 30 democracies work together to address the economic, social and environmental challenges of globalisation. The OECD is also at the forefront of efforts to understand and to help governments respond to new developments and concerns, such as corporate governance, the information economy and the challenges of an ageing population. The Organisation provides a setting where governments can compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practice and work to co-ordinate domestic and international policies. The OECD member countries are: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Slovak Republic, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom and the United States. The Commission of the European Communities takes part in the work of the OECD. OECD Publishing disseminates widely the results of the Organisation s statistics gathering and research on economic, social and environmental issues, as well as the conventions, guidelines and standards agreed by its members. * * * This work is published on the responsibility of the Secretary-General of the OECD. The opinions expressed and arguments employed herein do not necessarily reflect the official views of the Organisation or of the governments of its member countries. NUCLEAR ENERGY AGENCY The OECD Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) was established on 1 st February 1958 under the name of the OEEC European Nuclear Energy Agency. It received its present designation on 20 th April 1972, when Japan became its first non-european full member. NEA membership today consists of 28 OECD member countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Republic of Korea, the Slovak Republic, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom and the United States. The Commission of the European Communities also takes part in the work of the Agency. The mission of the NEA is: to assist its member countries in maintaining and further developing, through international co-operation, the scientific, technological and legal bases required for a safe, environmentally friendly and economical use of nuclear energy for peaceful purposes, as well as to provide authoritative assessments and to forge common understandings on key issues, as input to government decisions on nuclear energy policy and to broader OECD policy analyses in areas such as energy and sustainable development. Specific areas of competence of the NEA include safety and regulation of nuclear activities, radioactive waste management, radiological protection, nuclear science, economic and technical analyses of the nuclear fuel cycle, nuclear law and liability, and public information. The NEA Data Bank provides nuclear data and computer program services for participating countries. In these and related tasks, the NEA works in close collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna, with which it has a Co-operation Agreement, as well as with other international organisations in the nuclear field. OECD 2005 No reproduction, copy, transmission or translation of this publication may be made without written permission. Applications should be sent to OECD Publishing: rights@oecd.org or by fax (+33-1) Permission to photocopy a portion of this work should be addressed to the Centre Français d exploitation du droit de Copie, 20 rue des Grands-Augustins, Paris, France (contact@cfcopies.com).
3 FOREWORD The Joint Evaluated Fission and Fusion (JEFF) project is a collaborative effort among NEA Data Bank member countries to develop a reference nuclear data library for use in different nuclear energy applications. The third, improved version of the JEFF general-purpose data library (JEFF-3.0) was recently released. This library contains evaluated nuclear data for 340 materials from 1-H-1 to 99-Es-255. The present report describes the content of this library. 3
4
5 TABLE OF CONTENTS Foreword... 3 Introduction... 7 Content of the JEFF-3.0 library... 7 Origin of the JEFF-3.0 evaluations... 8 Library testing and quality assurance... 8 References Figures Tables Annex Annex
6
7 Introduction The Joint Evaluated Fission and Fusion File (JEFF) Project is a collaborative effort involving the member countries of the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency Data Bank. The project provides a framework for co-operative activities between participating countries while seeking to make the most rational and efficient use of the available resources. As with other NEA activities, participation is on a voluntary basis, and each participating organisation is responsible for covering the cost of its own contributions. This project brings together experts in different areas such as measurements, evaluations, file processing and verification and validation of nuclear data. The compilation of the data is mainly performed at the NEA Data Bank under strict quality assurance procedures. The project also maintains close links with other similar international efforts or projects aimed at producing evaluated nuclear data, for example through active participation in the NEA Nuclear Science Committee Working Party on International Nuclear Data Evaluation Co-operation (WPEC). The flow chart in Figure 1 shows the organisation of the JEFF project. In the past, two different evaluated data libraries were produced from two separate groups in the Data Bank member countries: the JEF library and the EFF library. The JEF library addressed the needs of fission applications, while the EFF library was mainly concerned with fusion technology studies. The difference in the application areas is reflected in the content of these libraries and in their validation. The set of materials in the EFF-2.4 [1] library is a subset of the JEF library, but the evaluations are in many cases improvements compared to those of [2], especially for the structural materials and nuclides that are of special interest to fusion (Li, Be, etc.). The JEF and EFF projects worked closely together, but with different time scales, as illustrated in Figure 2. They now co-operate to produce a single new library, JEFF-3. Content of the JEFF-3.0 library The JEFF-3.0 library comprises at present only a general-purpose library, including thermal scattering law data for five materials. This general-purpose library was released in April 2002 and contains data for 340 materials from 1-H-1 to 99-Es-255. Table 1 provides the list of materials in the library. A material corresponds to a nucleus of a single isotope or to a nucleus of a natural element. A nucleus is either in its ground state or in an isomeric state. In the first column of Table 1, the material is represented as ZZZ-SY-AAA where AAA and ZZZ are the atomic charge and mass given as three-digit integers. SY is the symbol of the material represented with two characters. Note that AAA is equal to zero when the material represents a natural element. In addition, when the nucleus is in its first isomeric state, the letter m is appended to the end of the column (e.g. 95-Am-242m). The materials are classified in ascending atomic charge order. The second column provides the material number used to identify the isotope or the element in the library. The third column gives the name of the file, which contains the evaluated data for this specific material and which can be found on the enclosed CD-ROM. The last five materials in the table represent neutron thermal scattering data for the following compounds: hydrogen in light water, deuterium in heavy water, beryllium in beryllium oxide, carbon in graphite and hydrogen in polyethylene. The JEFF-3.0 library is given in the ENDF-6 format. This format stores nuclear data in various sections (MF). Each file contains data for different reactions (MT). Annexes 1 and 2 give the list of MF and MT numbers and their meaning in the ENDF-6 format. 7
8 Table 2 provides details concerning the content of each evaluated file. Reactions for which cross-section data is given in File 3 (MF=3) are listed in the second column. The reactions are listed using ENDF-6 nomenclature. This nomenclature is briefly described in Annex 1. Columns 3 through 5 list the reactions for which angular distributions, energy distributions or energy-angle distributions are given in File 4, 5 or 6 (MF=4, 5 or 6). Table 3 gives a list of materials for which resonance data is give in File 2 (MF=2). This table includes information about the formalism used in the resolved resonance region, the energy limits of the different resonance regions and a list of the energies of the first three s-wave resonances. Table 4 gives a list of materials for which photon production data is available in Files 12 to 15 (MF=12 to 15). Table 5 provides a list of materials for which covariance data is available in Files 31 through 35 (MF=31 to 35). Origin of the JEFF-3.0 evaluations The choice of evaluated data was guided by the feedback accumulated from the validation of the and EFF-2.4 libraries. Consequently, and EFF-2.4 formed the basic skeletons of the JEFF-3.0 library. Other evaluated files (e.g. JENDL-3.2, ENDF/B-VI, CENDL-2.1 or BROND-2.2) were adopted when data were not available in the JEF(F) libraries or when other evaluated files where considered to be of better quality. New evaluated files were also created for JEFF-3.0 (e.g. Be, Si, V, Ni, Cr, Fe, 240 Pu). Finally, modifications to existing files were made to obtain better agreement with integral data (e.g. 143 Nd, 149 Sm, 238 U and 241 Pu). Table 6 lists the origin of all evaluated files in the JEFF-3.0 library. The general recommendations for the selection of files for JEFF-3.0 are described in Ref. [1]. Adjustments to these choices were made for specific nuclides. The corresponding references are given below: x Aluminium [2]. x Fission products [3-5]. x x x 239 Pu [6,7]. 240 Pu [8]. 241 Pu [9]. x Energy release in fission [10]. x Photon production data [11]. Library testing and quality assurance The JEFF-3.0 starter file has undergone thorough testing at the NEA Data Bank. The tests were performed according to recently developed QA procedures, which included running the BNL checking 8
9 codes (CHECKER, FIZCON and PSYCHE) on every evaluated data set. The results of the checking codes are given in the CD-ROM appended to this report. In addition, the files were processed with the latest version of NJOY. Integral data, such as Maxwellian average cross-sections and resonance integrals, were also generated using the INTER code version The temperature used was 293 K and E 0 = ev for the thermal spectrum temperature. The results were compared to those of. This test helped identify and correct a few inconsistencies, which had not been detected by the QA checks. The JEFF-3.0 integral data can be found in Table 7. The feedback emerging from JEFF-3.0 testing and processing is available on the following website: Refs. [12-14] provide more details as concerns this feedback. 9
10
11 REFERENCES Electronic copies of the JEF/DOC documents below are included in the CD-ROM appended to the paper version of this report. [1] Rowlands, J.L., Proposed Selection of Data for JEFF-3, JEFDOC-657. [2] Leal, L.C., et al., Aluminium Data Measurements and Evaluation for Criticality Safety Applications, JEFDOC-913. [3] Chabert, C., A. Courcelle, B. Roque, O. Serot, Progress Report on Main FPs Qualification. Recommendation for 154 Eu, 155 Eu, 143 Nd and 149 Sm, JEFDOC-885. [4] Serot, O., et al., 133 Cs Fission Product: Recommendation for JEFF3, JEFDOC-874. [5] Serot, O., et al., Progress Report on Main Fission Products: Recommendations for 103 Rh, 152 Eu and 153 Eu, JEF/DOC-912. [6] Romain, P., et al., New Evaluation of 239 Pu Data, JEF/DOC-919. [7] Serot, O., B. Morillon, E. Fort, Energy Release in Thermal Neutron Induced Fission of 239 Pu, JEF/DOC-900. [8] Courcelle, A., A. Santamarina, C. Chabert, O. Litaize, Validation of the Current 241 Pu Evaluations Against Integral Experiments. Proposed JEFF3.0 Evaluation, JEF/DOC-884. [9] Derrien, H., A. Courcelle, A. Santamarina, Re-evaluation and Validation of the 241 Pu Resonance Parameters in the Energy Range Thermal to 20 ev, JEF/DOC-916. [10] Serot, O., A. Courcelle, Energy Released in Fission: Short Review for JEFF3, JEF/DOC-887. [11] Courcelle, A., Gamma Production Data, Prompt Gamma Emitted in Fission: Short Review, JEF/DOC-886. [12] Sublet, J-Ch. and P. Ribon, NJOY99 and CALENDF-2002 Processing Viewpoint, Prospect and Solutions, JEFDOC-934. [13] Nouri, A., JEFF-3.0 Feedback: Status April 2003, JEFDOC-967. [14] Sublet, J-Ch., B. Roque, F. Laugier, J. Tommasi, JEFF-3.0 Feedbacks Pre-JEFF-3.1 Proposals, JEF/DOC
12
13 FIGURES 13
14
15 Figure 1. Organisation of the project Figure 2. Time scales of the JEF and EFF projects 15
16
17 TABLES 17
18
19 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 1-H JEFF30N125_1.ASC 1-H JEFF30N128_1.ASC 1-H JEFF30N131_1.ASC 2-He JEFF30N225_1.ASC 2-He JEFF30N228_1.ASC 3-Li JEFF30N325_1.ASC 3-Li JEFF30N328_1.ASC 4-Be JEFF30N425_2.ASC 5-B JEFF30N525_1.ASC 5-B JEFF30N528_1.ASC 6-C-nat 600 JEFF30N600_1.ASC 7-N JEFF30N725_2.ASC 7-N JEFF30N728_2.ASC 8-O JEFF30N825_1.ASC 8-O JEFF30N828_1.ASC 9-F JEFF30N925_1.ASC 11-Na JEFF30N1122_1.ASC 11-Na JEFF30N1125_2.ASC 12-Mg-nat 1200 JEFF30N1200_1.ASC 13-Al JEFF30N1325_2.ASC 14-Si JEFF30N1425_4.ASC 14-Si JEFF30N1428_2.ASC 14-Si JEFF30N1431_2.ASC 15-P JEFF30N1525_1.ASC 16-S-nat 1600 JEFF30N1600_2.ASC 17-Cl-nat 1700 JEFF30N1700_1.ASC 18-Ar JEFF30N1825_1.ASC 18-Ar JEFF30N1831_1.ASC 18-Ar JEFF30N1837_1.ASC 19-K-nat 1900 JEFF30N1900_2.ASC 20-Ca-nat 2000 JEFF30N2000_2.ASC 21-Sc JEFF30N2125_1.ASC 22-Ti-nat 2200 JEFF30N2200_1.ASC 23-V-nat 2300 JEFF30N2300_1.ASC 24-Cr JEFF30N2425_1.ASC 24-Cr JEFF30N2431_1.ASC 24-Cr JEFF30N2434_3.ASC 24-Cr JEFF30N2437_3.ASC 25-Mn JEFF30N2525_1.ASC 26-Fe JEFF30N2625_1.ASC 26-Fe JEFF30N2631_2.ASC 19
20 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 26-Fe JEFF30N2634_1.ASC 26-Fe JEFF30N2637_1.ASC 27-Co JEFF30N2722_3.ASC 27-Co-58m 2723 JEFF30N2723_2.ASC 27-Co JEFF30N2725_1.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2825_2.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2828_1.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2831_2.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2834_1.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2837_1.ASC 28-Ni JEFF30N2843_1.ASC 29-Cu JEFF30N2925_1.ASC 29-Cu JEFF30N2931_1.ASC 30-Zn-nat 3000 JEFF30N3000_1.ASC 31-Ga-nat 3100 JEFF30N3100_1.ASC 32-Ge JEFF30N3225_1.ASC 32-Ge JEFF30N3231_1.ASC 32-Ge JEFF30N3234_1.ASC 32-Ge JEFF30N3237_1.ASC 32-Ge JEFF30N3243_1.ASC 33-As JEFF30N3325_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3425_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3431_2.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3434_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3437_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3440_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3443_1.ASC 34-Se JEFF30N3449_1.ASC 35-Br JEFF30N3525_1.ASC 35-Br JEFF30N3531_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3625_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3631_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3637_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3640_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3643_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3646_1.ASC 36-Kr JEFF30N3649_1.ASC 37-Rb JEFF30N3725_1.ASC 37-Rb JEFF30N3728_1.ASC 37-Rb JEFF30N3731_1.ASC 38-Sr JEFF30N3825_1.ASC 20
21 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 38-Sr JEFF30N3831_1.ASC 38-Sr JEFF30N3834_1.ASC 38-Sr JEFF30N3837_1.ASC 38-Sr JEFF30N3840_1.ASC 38-Sr JEFF30N3843_1.ASC 39-Y JEFF30N3925_1.ASC 39-Y JEFF30N3928_1.ASC 39-Y JEFF30N3931_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4025_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4028_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4031_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4034_2.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4037_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4040_1.ASC 40-Zr JEFF30N4043_1.ASC 41-Nb JEFF30N4125_1.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4225_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4231_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4234_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4237_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4240_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4243_2.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4246_1.ASC 42-Mo JEFF30N4249_2.ASC 43-Tc JEFF30N4331_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4425_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4431_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4434_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4437_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4440_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4443_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4446_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4449_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4452_1.ASC 44-Ru JEFF30N4455_1.ASC 45-Rh JEFF30N4525_2.ASC 45-Rh JEFF30N4531_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4625_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4631_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4634_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4637_1.ASC 21
22 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 46-Pd JEFF30N4640_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4643_1.ASC 46-Pd JEFF30N4649_1.ASC 47-Ag JEFF30N4725_1.ASC 47-Ag JEFF30N4731_1.ASC 47-Ag JEFF30N4737_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4825_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4831_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4837_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4840_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4843_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4846_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4849_1.ASC 48-Cd-115m 4853 JEFF30N4853_1.ASC 48-Cd JEFF30N4855_1.ASC 49-In JEFF30N4925_1.ASC 49-In JEFF30N4931_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5025_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5031_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5034_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5037_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5040_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5043_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5046_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5049_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5055_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5058_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5061_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5064_1.ASC 50-Sn JEFF30N5067_1.ASC 51-Sb JEFF30N5125_2.ASC 51-Sb JEFF30N5131_2.ASC 51-Sb JEFF30N5134_1.ASC 51-Sb JEFF30N5137_1.ASC 51-Sb JEFF30N5140_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5225_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5231_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5234_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5237_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5240_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5243_1.ASC 22
23 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 52-Te-127m 5247 JEFF30N5247_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5249_1.ASC 52-Te-129m 5253 JEFF30N5253_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5255_1.ASC 52-Te JEFF30N5261_1.ASC 53-I JEFF30N5325_1.ASC 53-I JEFF30N5331_1.ASC 53-I JEFF30N5334_1.ASC 53-I JEFF30N5337_1.ASC 53-I JEFF30N5349_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5425_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5431_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5437_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5440_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5443_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5446_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5449_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5452_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5455_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5458_1.ASC 54-Xe JEFF30N5461_1.ASC 55-Cs JEFF30N5525_2.ASC 55-Cs JEFF30N5528_1.ASC 55-Cs JEFF30N5531_1.ASC 55-Cs JEFF30N5534_1.ASC 55-Cs JEFF30N5537_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5625_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5631_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5637_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5640_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5643_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5646_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5649_1.ASC 56-Ba JEFF30N5655_1.ASC 57-La JEFF30N5725_1.ASC 57-La JEFF30N5728_1.ASC 57-La JEFF30N5731_1.ASC 58-Ce JEFF30N5837_1.ASC 58-Ce JEFF30N5840_1.ASC 58-Ce JEFF30N5843_1.ASC 58-Ce JEFF30N5846_1.ASC 23
24 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 58-Ce JEFF30N5849_1.ASC 59-Pr JEFF30N5925_1.ASC 59-Pr JEFF30N5928_1.ASC 59-Pr JEFF30N5931_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6025_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6028_2.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6031_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6034_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6037_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6040_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6043_1.ASC 60-Nd JEFF30N6049_1.ASC 61-Pm JEFF30N6149_2.ASC 61-Pm JEFF30N6152_1.ASC 61-Pm-148m 6153 JEFF30N6153_1.ASC 61-Pm JEFF30N6155_1.ASC 61-Pm JEFF30N6161_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6225_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6234_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6237_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6240_2.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6243_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6246_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6249_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6252_1.ASC 62-Sm JEFF30N6255_1.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6325_2.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6328_2.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6331_2.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6334_2.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6337_2.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6340_1.ASC 63-Eu JEFF30N6343_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6425_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6431_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6434_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6437_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6440_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6443_1.ASC 64-Gd JEFF30N6449_1.ASC 65-Tb JEFF30N6525_1.ASC 24
25 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 65-Tb JEFF30N6528_1.ASC 66-Dy JEFF30N6637_1.ASC 66-Dy JEFF30N6640_1.ASC 66-Dy JEFF30N6643_1.ASC 66-Dy JEFF30N6646_1.ASC 66-Dy JEFF30N6649_1.ASC 67-Ho JEFF30N6725_1.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6825_2.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6831_1.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6837_1.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6840_1.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6843_2.ASC 68-Er JEFF30N6846_1.ASC 71-Lu JEFF30N7125_1.ASC 71-Lu JEFF30N7128_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7225_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7231_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7234_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7237_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7240_1.ASC 72-Hf JEFF30N7243_2.ASC 73-Ta JEFF30N7328_1.ASC 73-Ta JEFF30N7331_2.ASC 74-W JEFF30N7431_2.ASC 74-W JEFF30N7434_2.ASC 74-W JEFF30N7437_2.ASC 74-W JEFF30N7443_2.ASC 75-Re JEFF30N7525_1.ASC 75-Re JEFF30N7531_1.ASC 76-Os-nat 7600 JEFF30N7600_1.ASC 77-Ir-nat 7700 JEFF30N7700_2.ASC 78-Pt-nat 7800 JEFF30N7800_1.ASC 79-Au JEFF30N7925_1.ASC 80-Hg-nat 8000 JEFF30N8000_2.ASC 81-Tl-nat 8100 JEFF30N8100_2.ASC 82-Pb JEFF30N8225_2.ASC 82-Pb JEFF30N8231_3.ASC 82-Pb JEFF30N8234_3.ASC 82-Pb JEFF30N8237_3.ASC 83-Bi JEFF30N8325_1.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9025_2.ASC 25
26 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 90-Th JEFF30N9028_2.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9031_2.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9034_2.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9040_2.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9043_2.ASC 90-Th JEFF30N9046_2.ASC 91-Pa JEFF30N9131_1.ASC 91-Pa JEFF30N9137_2.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9219_1.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9222_2.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9225_1.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9228_3.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9231_1.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9234_2.ASC 92-U JEFF30N9237_4.ASC 93-Np JEFF30N9343_1.ASC 93-Np JEFF30N9346_2.ASC 93-Np JEFF30N9349_1.ASC 93-Np JEFF30N9352_2.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9428_2.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9431_2.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9434_3.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9437_3.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9440_3.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9443_3.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9446_2.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9449_1.ASC 94-Pu JEFF30N9452_2.ASC 95-Am JEFF30N9543_2.ASC 95-Am JEFF30N9546_3.ASC 95-Am-242m 9547 JEFF30N9547_2.ASC 95-Am JEFF30N9549_2.ASC 95-Am JEFF30N9552_1.ASC 95-Am-244m 9553 JEFF30N9553_1.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9628_2.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9631_2.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9634_2.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9637_2.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9640_1.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9643_1.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9646_2.ASC 26
27 Table 1. List of materials in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide or element MAT and isomeric state number Evaluation file 96-Cm JEFF30N9649_3.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9652_1.ASC 96-Cm JEFF30N9655_1.ASC 97-Bk JEFF30N9752_2.ASC 97-Bk JEFF30N9755_2.ASC 98-Cf JEFF30N9852_2.ASC 98-Cf JEFF30N9855_1.ASC 98-Cf JEFF30N9858_1.ASC 98-Cf JEFF30N9861_2.ASC 98-Cf JEFF30N9867_1.ASC 99-Es JEFF30N9914_2.ASC 99-Es JEFF30N9915_1.ASC H in H20 thermal scattering data 1 JEFF30TS1_1.ASC D in D20 thermal scattering data 11 JEFF30TS11_1.ASC Be thermal scattering data 26 JEFF30TS26_1.ASC Graphite thermal scattering data 31 JEFF30TS31_1.ASC H in CH2 thermal scattering data 37 JEFF30TS37_1.ASC 27
28 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 1 H 1, 2, H 1, 2, 16, H 1, 2, 16, 17 2, He 1, 2, He 1, 2, Li 1, 2, 4, 24, 51-81, 102, 103, 105 2, 24, 51-81, Li 1, 2, 4, 16, 24, 25, 28, 51-53, 91, 102, 104 2, 51, 52 16, 24, 25, 28, 53, 91 9 Be 1-3, 16, , 107, , 107, B 1, 2, 4, 51-85, , 107, 113, , 800, 801 2, B 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, 102, 103, 105, 107 2, , 22, 28, 91, 103, , 24, 28, 32, 33, 41, 91, nat C 1-4, 16, 24, 28, 32, 33, 41, 51-73, 91, , 107, 111, 112, 115, 116, , N 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-90, , 107, 108, , , 700, 701, , 16, 24, 28, 32, 33, 41, 51-73, 91 2, N 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-57, 91, , 107 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-57, 91 16, 22, 28, O 1, 2, 4, 51-88, , 107, , O 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 107 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, 22, 28, F 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-71, 91, , 107 2, , 22, 28, 91, 102, 103, Na 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-61, 91, , 107, 108, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-61, 91 16, Na 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-77, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-77, 91 16, 22, 28, 91 nat Mg 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, , 22, 28, Al 1-5, 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 45, 51-89, 91, , 107, 108, 111, 112, 117, , , , 749, , Si 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-67, 91, , 111, , 649, , Si 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-79, 91, 102, 103, 107, 111, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-79, 91 16, 22, 28, Si 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-69, 91, 102, 103, 107, 111, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-69, 91 16, 22, 28, P 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-56, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-56, 91 16, 22, 28, , 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 45, 51-89, 91, 108, 111, 112, 117, , , , 749, , , 22, 28, 51-67, 91, , 649, ,
29 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 nat S 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-73, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-73, 91 16, 22, 28, 91 nat Cl 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 22, 28, 51-63, 91 16, 22, 28, Ar 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-71, 91, , 107, 108, 251, 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-71, 91 16, Ar 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-69, 91, , 107, 108, 251, 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-69, 91 16, Ar 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-71, 91, , 107, 251, 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-71, 91 16, 17, nat K 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-61, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-61, 91 16, 22, 28, 91 nat Ca 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-84, 91, 102, 103, 107, 111, 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-84, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 45 Sc 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-64, 91, , 16, 22, 28, 51-64, 91 16, 22, 28, 91 nat Ti 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-87, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-87, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 91 nat V 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 32, 51-74, 91, , 111, 112 2, 32, , 22, 28, 91, 103, Cr 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-56, 91, , , 22, 28, 51-56, 91, 103, Cr 1-5, 51-66, 102, , , 51-66, , Cr 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, 102, 103, , 22, 28, 51-63, 91, 103, Cr 1-4, 16, 51-54, 91, 102, 103, , 51-54, 91, 103, Mn 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-66, 91, , , 251 2, , 22, 28, 91, Fe 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-57, 91, , , 22, 28, 51-57, 91, 103, Fe 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-82, 91, , , 649, 2, 51-82, , , 22, 28, 91, 649, , Fe 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-65, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-65, 91 16, 22, 28, Fe 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-67, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-67, 91 16, 22, 28, Co 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, 91 58m Co 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, Co 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-69, 91, , 111, 2, 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-69, 91 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, Ni 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-58, 91, , , 22, 28, 51-58, 91, 103,
30 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 59 Ni 1-3, 16, 22, 28, 32, 34, , 111 2, 16, 22, 28, 32, Ni 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-61, 91, , 22, 28, 51-61, 91, 103, Ni 1-4, 16, 28, 51-58, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 28, 51-58, 91, 103, Ni 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-54, 91, , , 22, 28, 51-54, 91, 103, Ni 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51, 52, 91, , , 22, 28, 51, 52, 91, 103, Cu 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-72, 91, , 106, , 22, 28, 51-72, 91, 103, Cu 1-4, 16, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, , 22, 28, 51-63, 91, 103, 107 nat Zn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51, 91, 102, 103, 105, 107, nat Ga 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-88, 91, , 111, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 91 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-88, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Ge 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-74, 91, , 111, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-74, 91 16, 22, 28, Ge 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111 2, 51-55, Ge 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111, , 51-54, Ge 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111, , 51-55, Ge 1, 2, 4, 51, 52, 91, , 111, , 51, 52, As 1, 2, 4, 51-63, 91, , 111, , 51-63, Se 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Se 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111, , 51-54, Se 1, 2, 4, 51-60, 91, , 111, , 51-60, Se 1, 2, 4, 51-59, 91, , 111, , 51-59, Se 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-79, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-79, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Se 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, , 111, , 51-58, Se 1, 2, 4, 51-53, 91, , 111, , 51-53, Br 1, 2, 4, 51-61, 91, , 111, , 51-61, Br 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111, , 51-54, Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-53, 91, , 111, , 16, 51-53, 91 16, Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-56, 91, , 111, , 16, 51-56, 91 16, Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-59, 91, , 111, , 16, 51-59, 91 16, 91 30
31 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 83 Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-56, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 51-56, 91 16, 17, Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-63, 91, , 111, , 16, 51-63, 91 16, Kr 1, 2, 4, 51, 91, , 111 2, 51, Kr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-64, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 51-64, 91 16, 17, Rb 1, 2, 4, 51-53, 91, , 111, , 51-53, Rb 1, 2, 4, 51, 91, , 111 2, 51, Rb 1, 2, 4, 51, 52, 91, , 111, , 51, 52, Sr 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, Sr 1, 2, 4, 51-57, 91, , 111, , 51-57, Sr 1, 2, 4, 51-57, 91, , 111, , 51-57, Sr 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111, , 51-55, Sr 1, 2, 4, 51-62, 91, , 111 2, 51-62, Sr 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111 2, 51-54, Y 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, 22, 28, Y 1, 2, 4, 51, 52, 91, , 111 2, 51, 52, Y 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, 102, , 111 2, 51-58, Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91, , 111, 251 2, 16, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91 16, 22, 28, 32, Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-64, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-64, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-67, 91, , 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, , , Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, 22, 28, Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-64, 91, , 107, 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-64, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 95 Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Zr 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-57, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Nb 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-73, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, , Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 51-66, 91, , 111, , 2, , 22, 28, 91,
32 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 94 Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-69, 91, , 111, 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, , Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-65, 91, , , 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-67, 91, , 107, 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, , , 207, Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, , , 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-64, 91, , 107, 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, , , 207, Mo 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 51-56, Mo 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-54, 91, , 107, , 207, Tc 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, 91 2, , 17, 22, 28, 91, , , 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, Ru 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Ru 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Ru 1, 2, 4, 51-62, 91, , 111, , 51-62, Ru 1, 2, 4, 51-57, 91, , 111, , 51-57, Ru 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-65, 91, 102, 103, 107, 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-65, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Ru 1, 2, 4, 51-69, 91, , 111 2, 51-69, Ru 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-89, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-89, 91 16, Ru 1, 2, 4, 51, 52, 91, , 111, , 51, 52, Ru 1, 2, 4, 51-59, 91, , 111 2, 51-59, Ru 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111 2, 51-54, Rh 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, 102 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Rh 1, 2, 4, 51-53, 91, 102 2, 51-53, Pd 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, 91 32
33 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 105 Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, , Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-70, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-70, 91 16, Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-67, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-67, 91 16, Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-60, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-60, 91 16, Pd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-60, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-60, 91 16, Ag 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-56, 91, , 111, , 16, 51-56, 91 16, Ag 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Ag 1, 2, 4, 51-60, 91, , 111 2, 51-60, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-55, 91, , 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-55, 91 16, 22, 28, 32, 33, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-64, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-64, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-61, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-61, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-58, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-58, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-62, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-62, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, m Cd 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, Cd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-56, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, , In 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-74, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-74, In 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-63, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-63, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-73, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-73, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-76, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-76, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 91 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 33
34 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 115 Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-66, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-66, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-62, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-62, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-57, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-70, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-70, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-66, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-66, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 51-59, 91, , 111 2, 51-59, Sn 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-70, 91, , 107 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-70, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sn 1, 2, 4, 51-53, 91, , 111 2, 51-53, Sn 1, 2, 4, 51-60, 91, , 111 2, 51-60, Sb 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-63, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sb 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-58, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-58, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Sb 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, , 107, 111 2, 51-58, Sb 1, 2, 4, 51-69, 91, , 111 2, 51-69, Sb 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111 2, 51-55, Te 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Te 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111, , 51-54, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, , 111, , 51-58, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-61, 91, , 111, , 51-61, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111, , 51-56, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-63, 91, , 111, , 51-63, m Te 1, 2, 4, 91, 102 2, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-59, 91, , 111, 251 2, 51-59, m Te 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-60, 91, , 111, , 51-60, Te 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 51-56, I 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-62, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-62, 91 16, 91 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 34
35 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 129 I 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, 102, 103, 107, Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, I 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, I 1, 2, 4, 51-54, 91, , 111 2, 51-54, I 1, 2, 4, 91, 102 2, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-54, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-54, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-54, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-54, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-53, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-53, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-56, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-56, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-56, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 51-56, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-54, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 51-54, 91 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 51, 91, , 111 2, 51, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-53, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 51-53, 91, 16, 17, Xe 1, 2, 4, 51, 91, 102 2, 51, 91, Xe 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-53, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 51-53, 91 16, 17, Cs 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-55, 91, 102, 103, 107 2, 16, 51-55, 91 16, Cs 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111, , 51-55, Cs 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-68, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-68, 91 16, Cs 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Cs 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-60, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-60, 91 16, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-63, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-63, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-58, 91, , 107, 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 51-58, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-69, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-69, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, 91 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 35
36 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 140 Ba 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 17, 91 16, 17, La 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-65, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, , La 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-73, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-73, 91 16, La 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, 102, , 111 2, 51-56, Ce 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, , 111 2, 51-58, Ce 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-62, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-62, 91 16, Ce 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-56, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 17, 51-56, 91 16, 17, Ce 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, Ce 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-68, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 17, 51-68, 91 16, 17, Pr 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-74, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-74, 91 16, Pr 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111 2, Pr 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 51-56, Nd 1, 2, 4, 51-58, 91, , 111, , 51-58, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-76, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-76, 91 16, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-63, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-63, 91 16, Nd 1, 2, 4, 51-53, 91, , 111, , 51-53, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-57, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-57, 91 16, Nd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91, , 111, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Pm 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-61, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-61, 91 16, Pm 1, 2, 4, 91, 102 2, m Pm 1, 2, 4, 91, 102, , Pm 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 51-56, Pm 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 111 2, 51-56, Sm 1, 2, 4, 91, , 111, , Sm 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, 91 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 36
37 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 148 Sm 1, 2, 4, 51-66, 91, , 111 2, 51-66, Sm 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-60, 91, 102, 103, 107 2, 16, 17, 51-60, 91 16, 17, Sm 1, 2, 4, 51-66, 91, , 111, , 51-66, Sm 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, , Sm 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-63, 91, , 111, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-63, 91 16, Sm 1, 2, 4, 51-62, 91, , 111 2, 51-62, Sm 1, 2, 4, 51-69, 91, , 111, , 51-69, Eu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91, , 111 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Eu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-61, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, , Eu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-61, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-61, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Eu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-55, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-55, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Eu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91, , 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-59, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Eu 1, 2, 4, 51-55, 91, , 111 2, 51-55, Eu 1, 2, 4, 91, 102 2, Gd 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-79, 91, , 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 51-79, Gd 1, 2, 4, 51-65, 91, , 111 2, 51-65, Gd 1, 2, 4, 51-79, 91, , 111, 251 2, 51-79, Gd 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-64, 91, , 111 2, 16, 51-64, 91 16, Gd 1, 2, 4, 51-78, 91, , 111, 251 2, 51-78, Gd 1, 2, 4, 51-61, 91, , 111 2, 51-61, Gd 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, , 107 2, 51-56, Tb 1, 2, 4, 16, 51-66, 91, 102, 251, 252 2, 16, 51-66, 91 16, Tb 1, 2, 4, 91, 102, , Dy 1, 2, 4, 51-64, 91, 102, , 51-64, Dy 1, 2, 4, 51-57, 91, 102, , 51-57, Dy 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, 102, , 51-56, Dy 1, 2, 4, 51-56, 91, 102, , 51-56, , 17, 22, 28, 32, 33, 91 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 37
38 Table 2. List of reactions for which cross-sections, angular, energy and energy-angle distributions are available in the JEFF-3.0 library (cont.) Nuclide Reactions described in MF=3 Reactions with angular distributions in MF=4 Reactions with energy distributions in MF=5 Reactions with energy-angle distributions in MF=6 164 Dy 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-62, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-62, 91 16, 17, Ho 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 37, 51-63, 91, 102 2, 16, 17, 37, 51-63, 91 16, 17, 37, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-58, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 28, 51-58, 91 16, 17, 28, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-60, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 28, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-57, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-57, 91 16, 17, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-57, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 28, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 28, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-59, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 28, 51-59, 91 16, 17, 28, Er 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-57, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 28, 51-57, 91 16, 17, 28, Lu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-58, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-58, 91 16, 17, Lu 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-58, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-58, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-68, 91, 102, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-68, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-73, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-73, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-66, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-66, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-71, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-71, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-62, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-62, 91 16, 17, Hf 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-61, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 51-61, 91 16, 17, Ta 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 28, 51-64, 91, 102, 103, 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 28, 51-64, 91 16, 17, 28, Ta1 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-58, 91, 102, 107, , 16, 17, 51-58, 91 16, 17, W 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-70, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-70, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, W 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, W 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-60, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, W 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-62, 91, , 107, 251 2, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-62, 91 16, 17, 22, 28, Re 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-59, 91, 102 2, 16, 17, 51-59, 91 16, 17, Re 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-66, 91, 102 2, 16, 17, 51-66, 91 16, 17, 91 nat Os 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-67, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-67, 91 16, 17, 91 nat Ir 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 51-58, 91, 102, 103, 107, , 16, 17, 51-58, 91 16, 17, 91 nat Pt 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 91, 102, , 17, Au 1, 2, 4, 16, 17, 37, 51-63, 91, 102, 103, 107 2, 16, 17, 37, 51-63, 91 16, 17, 37, 91 nat Hg 1-4, 16, 17, 22, 28, 51-80, 91, , 107 2, 51-80, 16, 17, 22, 28, 91 38
Element Cube Project (x2)
 Element Cube Project (x2) Background: As a class, we will construct a three dimensional periodic table by each student selecting two elements in which you will need to create an element cube. Helpful Links
Element Cube Project (x2) Background: As a class, we will construct a three dimensional periodic table by each student selecting two elements in which you will need to create an element cube. Helpful Links
The European Activation File: EAF-2005 decay data library
 UKAEA FUS 516 EURATOM/UKAEA Fusion The European Activation File: EAF-2005 decay data library R.A. Forrest January 2005 UKAEA EURATOM/UKAEA Fusion Association Culham Science Centre Abingdon Oxfordshire
UKAEA FUS 516 EURATOM/UKAEA Fusion The European Activation File: EAF-2005 decay data library R.A. Forrest January 2005 UKAEA EURATOM/UKAEA Fusion Association Culham Science Centre Abingdon Oxfordshire
The Periodic Table. Periodic Properties. Can you explain this graph? Valence Electrons. Valence Electrons. Paramagnetism
 Periodic Properties Atomic & Ionic Radius Energy Electron Affinity We want to understand the variations in these properties in terms of electron configurations. The Periodic Table Elements in a column
Periodic Properties Atomic & Ionic Radius Energy Electron Affinity We want to understand the variations in these properties in terms of electron configurations. The Periodic Table Elements in a column
Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Atoms and the Periodic Table Parts of the Atom Proton Found in the nucleus Number of protons defines the element Charge +1, mass 1 Parts of the Atom Neutron Found in the nucleus Stabilizes the nucleus
Atoms and the Periodic Table Parts of the Atom Proton Found in the nucleus Number of protons defines the element Charge +1, mass 1 Parts of the Atom Neutron Found in the nucleus Stabilizes the nucleus
CLASS TEST GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials 1
 CLASS TEST GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials MARKS: 45 TIME: hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators. 3. You
CLASS TEST GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials MARKS: 45 TIME: hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators. 3. You
Radiometric Dating (tap anywhere)
 Radiometric Dating (tap anywhere) Protons Neutrons Electrons Elements on the periodic table are STABLE Elements can have radioactive versions of itself called ISOTOPES!! Page 1 in your ESRT has your list!
Radiometric Dating (tap anywhere) Protons Neutrons Electrons Elements on the periodic table are STABLE Elements can have radioactive versions of itself called ISOTOPES!! Page 1 in your ESRT has your list!
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT
 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
Nucleus. Electron Cloud
 Atomic Structure I. Picture of an Atom Nucleus Electron Cloud II. Subatomic particles Particle Symbol Charge Relative Mass (amu) protons p + +1 1.0073 neutrons n 0 1.0087 electrons e - -1 0.00054858 Compare
Atomic Structure I. Picture of an Atom Nucleus Electron Cloud II. Subatomic particles Particle Symbol Charge Relative Mass (amu) protons p + +1 1.0073 neutrons n 0 1.0087 electrons e - -1 0.00054858 Compare
Ch. 9 NOTES ~ Chemical Bonding NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics.
 Ch. 9 NOTES ~ Chemical Bonding NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Review: Comparison of ionic and molecular compounds Molecular compounds Ionic
Ch. 9 NOTES ~ Chemical Bonding NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Review: Comparison of ionic and molecular compounds Molecular compounds Ionic
Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (005) pp. 709 718 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No. 4, April 15, 005 Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (005) pp. 709 718 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No. 4, April 15, 005 Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS
 Useful Constants and equations: K = o C + 273 Avogadro's number = 6.022 x 10 23 d = density = mass/volume R H = 2.178 x 10-18 J c = E = h = hc/ h = 6.626 x 10-34 J s c = 2.998 x 10 8 m/s E n = -R H Z 2
Useful Constants and equations: K = o C + 273 Avogadro's number = 6.022 x 10 23 d = density = mass/volume R H = 2.178 x 10-18 J c = E = h = hc/ h = 6.626 x 10-34 J s c = 2.998 x 10 8 m/s E n = -R H Z 2
Last 4 Digits of USC ID:
 Chemistry 05 B Practice Exam Dr. Jessica Parr First Letter of last Name PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Name: Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 8 2 4 3 9 4 0
Chemistry 05 B Practice Exam Dr. Jessica Parr First Letter of last Name PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Name: Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 8 2 4 3 9 4 0
Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table
 Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table William B. Jensen Department of Chemistry University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 452201-0172 The extended step-pyramid table recognizes that elements
Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table William B. Jensen Department of Chemistry University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 452201-0172 The extended step-pyramid table recognizes that elements
610B Final Exam Cover Page
 1 st Letter of Last Name NAME: 610B Final Exam Cover Page No notes or calculators of any sort allowed. You have 3 hours to complete the exam. CHEM 610B, 50995 Final Exam Fall 2003 Instructor: Dr. Brian
1 st Letter of Last Name NAME: 610B Final Exam Cover Page No notes or calculators of any sort allowed. You have 3 hours to complete the exam. CHEM 610B, 50995 Final Exam Fall 2003 Instructor: Dr. Brian
Metallurgical Chemistry. An Audio Course for Students
 Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi February, 1987 Metallurgical Chemistry. An Audio Course for Students Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/27/ METALLURGICAL
Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi February, 1987 Metallurgical Chemistry. An Audio Course for Students Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/27/ METALLURGICAL
CHEM 10113, Quiz 5 October 26, 2011
 CHEM 10113, Quiz 5 October 26, 2011 Name (please print) All equations must be balanced and show phases for full credit. Significant figures count, show charges as appropriate, and please box your answers!
CHEM 10113, Quiz 5 October 26, 2011 Name (please print) All equations must be balanced and show phases for full credit. Significant figures count, show charges as appropriate, and please box your answers!
The Periodic Table of the Elements
 The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
Using the Periodic Table
 MATH SKILLS TRANSPARENCY WORKSHEET Using the Periodic Table 6 Use with Chapter 6, Section 6.2 1. Identify the number of valence electrons in each of the following elements. a. Ne e. O b. K f. Cl c. B g.
MATH SKILLS TRANSPARENCY WORKSHEET Using the Periodic Table 6 Use with Chapter 6, Section 6.2 1. Identify the number of valence electrons in each of the following elements. a. Ne e. O b. K f. Cl c. B g.
CHEM 130 Exp. 8: Molecular Models
 CHEM 130 Exp. 8: Molecular Models In this lab, we will learn and practice predicting molecular structures from molecular formulas. The Periodic Table of the Elements IA 1 H IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 3 5
CHEM 130 Exp. 8: Molecular Models In this lab, we will learn and practice predicting molecular structures from molecular formulas. The Periodic Table of the Elements IA 1 H IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 3 5
(C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1
 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach
(C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach
Made the FIRST periodic table
 Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
The Periodic Table of Elements
 The Periodic Table of Elements 8 Uuo Uus Uuh (9) Uup (88) Uuq (89) Uut (8) Uub (8) Rg () 0 Ds (9) 09 Mt (8) 08 Hs (9) 0 h () 0 Sg () 0 Db () 0 Rf () 0 Lr () 88 Ra () 8 Fr () 8 Rn () 8 At (0) 8 Po (09)
The Periodic Table of Elements 8 Uuo Uus Uuh (9) Uup (88) Uuq (89) Uut (8) Uub (8) Rg () 0 Ds (9) 09 Mt (8) 08 Hs (9) 0 h () 0 Sg () 0 Db () 0 Rf () 0 Lr () 88 Ra () 8 Fr () 8 Rn () 8 At (0) 8 Po (09)
PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids
 Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:1 Trim:165 240MM TS: Integra, India PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:2
Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:1 Trim:165 240MM TS: Integra, India PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:2
Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Solutions and Ions. Pure Substances
 Class #4 Solutions and Ions CHEM 107 L.S. Brown Texas A&M University Pure Substances Pure substance: described completely by a single chemical formula Fixed composition 1 Mixtures Combination of 2 or more
Class #4 Solutions and Ions CHEM 107 L.S. Brown Texas A&M University Pure Substances Pure substance: described completely by a single chemical formula Fixed composition 1 Mixtures Combination of 2 or more
HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY II
 HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY II Periodic Table of the Elements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He 1.00794 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.00262 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.9898
HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY II Periodic Table of the Elements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He 1.00794 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.00262 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.9898
Chapter 12 The Atom & Periodic Table- part 2
 Chapter 12 The Atom & Periodic Table- part 2 Electrons found outside the nucleus; negatively charged Protons found in the nucleus; positive charge equal in magnitude to the electron s negative charge Neutrons
Chapter 12 The Atom & Periodic Table- part 2 Electrons found outside the nucleus; negatively charged Protons found in the nucleus; positive charge equal in magnitude to the electron s negative charge Neutrons
02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr
 Chemistry 05 B First Letter of PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Exam last Name Name: 02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 2 2 9 3 9 4 2
Chemistry 05 B First Letter of PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Exam last Name Name: 02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 2 2 9 3 9 4 2
(please print) (1) (18) H IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA He (2) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17)
 CHEM 10113, Quiz 3 September 28, 2011 Name (please print) All equations must be balanced and show phases for full credit. Significant figures count, show charges as appropriate, and please box your answers!
CHEM 10113, Quiz 3 September 28, 2011 Name (please print) All equations must be balanced and show phases for full credit. Significant figures count, show charges as appropriate, and please box your answers!
9/20/2017. Elements are Pure Substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical change (contain Only One Type of Atom)
 CAPTER 6: TE PERIODIC TABLE Elements are Pure Substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical change (contain Only One Type of Atom) The Periodic Table (Mendeleev) In 1872, Dmitri
CAPTER 6: TE PERIODIC TABLE Elements are Pure Substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical change (contain Only One Type of Atom) The Periodic Table (Mendeleev) In 1872, Dmitri
Secondary Support Pack. be introduced to some of the different elements within the periodic table;
 Secondary Support Pack INTRODUCTION The periodic table of the elements is central to chemistry as we know it today and the study of it is a key part of every student s chemical education. By playing the
Secondary Support Pack INTRODUCTION The periodic table of the elements is central to chemistry as we know it today and the study of it is a key part of every student s chemical education. By playing the
Chemistry 431 Practice Final Exam Fall Hours
 Chemistry 431 Practice Final Exam Fall 2018 3 Hours R =8.3144 J mol 1 K 1 R=.0821 L atm mol 1 K 1 R=.08314 L bar mol 1 K 1 k=1.381 10 23 J molecule 1 K 1 h=6.626 10 34 Js N A = 6.022 10 23 molecules mol
Chemistry 431 Practice Final Exam Fall 2018 3 Hours R =8.3144 J mol 1 K 1 R=.0821 L atm mol 1 K 1 R=.08314 L bar mol 1 K 1 k=1.381 10 23 J molecule 1 K 1 h=6.626 10 34 Js N A = 6.022 10 23 molecules mol
NAME: FIRST EXAMINATION
 1 Chemistry 64 Winter 1994 NAME: FIRST EXAMINATION THIS EXAMINATION IS WORTH 100 POINTS AND CONTAINS 4 (FOUR) QUESTIONS THEY ARE NOT EQUALLY WEIGHTED! YOU SHOULD ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS AND ALLOCATE YOUR
1 Chemistry 64 Winter 1994 NAME: FIRST EXAMINATION THIS EXAMINATION IS WORTH 100 POINTS AND CONTAINS 4 (FOUR) QUESTIONS THEY ARE NOT EQUALLY WEIGHTED! YOU SHOULD ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS AND ALLOCATE YOUR
If anything confuses you or is not clear, raise your hand and ask!
 CHM 1045 Dr. Light s Section December 10, 2002 FINAL EXAM Name (please print) Recitation Section Meeting Time This exam consists of six pages. Make sure you have one of each. Print your name at the top
CHM 1045 Dr. Light s Section December 10, 2002 FINAL EXAM Name (please print) Recitation Section Meeting Time This exam consists of six pages. Make sure you have one of each. Print your name at the top
Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in the Columns!
 Chemistry 1304.001 Name (please print) Exam 5 (100 points) April 18, 2018 On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in
Chemistry 1304.001 Name (please print) Exam 5 (100 points) April 18, 2018 On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in
1 Genesis 1:1. Chapter 10 Matter. Lesson. Genesis 1:1 In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. (NKJV)
 1 Genesis 1:1 Genesis 1:1 In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. (NKJV) 1 Vocabulary Saturated having all the solute that can be dissolved at that temperature Neutron a particle with no
1 Genesis 1:1 Genesis 1:1 In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. (NKJV) 1 Vocabulary Saturated having all the solute that can be dissolved at that temperature Neutron a particle with no
CHM 101 PRACTICE TEST 1 Page 1 of 4
 CHM 101 PRACTICE TEST 1 Page 1 of 4 Please show calculations (stuffed equations) on all mathematical problems!! On the actual test, "naked answers, with no work shown, will receive no credit even if correct.
CHM 101 PRACTICE TEST 1 Page 1 of 4 Please show calculations (stuffed equations) on all mathematical problems!! On the actual test, "naked answers, with no work shown, will receive no credit even if correct.
Chemistry 2 Exam Roane State Academic Festival. Name (print neatly) School
 Name (print neatly) School There are fifteen question on this exam. Each question is weighted equally. n the answer sheet, write your name in the space provided and your answers in the blanks provided.
Name (print neatly) School There are fifteen question on this exam. Each question is weighted equally. n the answer sheet, write your name in the space provided and your answers in the blanks provided.
Modified from: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School IB Chemistry 1-2.1
 Modified from: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School IB Chemistry 1-2.1 The development of the periodic table brought a system of order to what was otherwise an collection of thousands of pieces of information.
Modified from: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School IB Chemistry 1-2.1 The development of the periodic table brought a system of order to what was otherwise an collection of thousands of pieces of information.
Lab Day and Time: Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
BROOKLYN COLLEGE Department of Chemistry. Chemistry 1 Second Lecture Exam Nov. 27, Name Page 1 of 5
 BROOKLYN COLLEGE Department of Chemistry Chemistry 1 Second Lecture Exam Nov. 27, 2002 Name Page 1 of 5 Circle the name of your lab instructor Kobrak, Zhou, Girotto, Hussey, Du Before you begin the exam,
BROOKLYN COLLEGE Department of Chemistry Chemistry 1 Second Lecture Exam Nov. 27, 2002 Name Page 1 of 5 Circle the name of your lab instructor Kobrak, Zhou, Girotto, Hussey, Du Before you begin the exam,
1 of 5 14/10/ :21
 X-ray absorption s, characteristic X-ray lines... 4.2.1 Home About Table of Contents Advanced Search Copyright Feedback Privacy You are here: Chapter: 4 Atomic and nuclear physics Section: 4.2 Absorption
X-ray absorption s, characteristic X-ray lines... 4.2.1 Home About Table of Contents Advanced Search Copyright Feedback Privacy You are here: Chapter: 4 Atomic and nuclear physics Section: 4.2 Absorption
7. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1215 Exam II John II. Gelder October 7, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 5 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and a solubility
CHEM 1215 Exam II John II. Gelder October 7, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 5 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and a solubility
Chemistry 1 First Lecture Exam Fall Abbasi Khajo Levine Mathias Mathias/Ortiz Metlitsky Rahi Sanchez-Delgado Vasserman
 Chemistry 1 First Lecture Exam Fall 2011 Page 1 of 9 NAME Circle the name of your recitation/lab instructor(s) Abbasi Khajo Levine Mathias Mathias/Ortiz Metlitsky Rahi Sanchez-Delgado Vasserman Before
Chemistry 1 First Lecture Exam Fall 2011 Page 1 of 9 NAME Circle the name of your recitation/lab instructor(s) Abbasi Khajo Levine Mathias Mathias/Ortiz Metlitsky Rahi Sanchez-Delgado Vasserman Before
The exam must be written in ink. No calculators of any sort allowed. You have 2 hours to complete the exam. Periodic table 7 0
 Email: The exam must be written in ink. No calculators of any sort allowed. You have 2 hours to complete the exam. CEM 610B Exam 3 Spring 2002 Instructor: Dr. Brian Pagenkopf Page Points 2 6 3 7 4 9 5
Email: The exam must be written in ink. No calculators of any sort allowed. You have 2 hours to complete the exam. CEM 610B Exam 3 Spring 2002 Instructor: Dr. Brian Pagenkopf Page Points 2 6 3 7 4 9 5
PROOF/ÉPREUVE ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Space environment (natural and artificial) Galactic cosmic ray model
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15390 First edition 2004-##-## Space environment (natural and artificial) Galactic cosmic ray model Environnement spatial (naturel et artificiel) Modèle de rayonnement cosmique
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15390 First edition 2004-##-## Space environment (natural and artificial) Galactic cosmic ray model Environnement spatial (naturel et artificiel) Modèle de rayonnement cosmique
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1515 Exam II John II. Gelder October 14, 1993 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last two pages include a periodic table, a
CHEM 1515 Exam II John II. Gelder October 14, 1993 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last two pages include a periodic table, a
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Chem 6A Michael J. Sailor, UC San Diego 1 Announcements: Thursday (Sep 29) quiz: Bring student ID or we cannot accept your quiz! No notes, no calculators Covers chapters 1 and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Chem 6A Michael J. Sailor, UC San Diego 1 Announcements: Thursday (Sep 29) quiz: Bring student ID or we cannot accept your quiz! No notes, no calculators Covers chapters 1 and
Lab Day and Time: Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Chem Exam 1. September 26, Dr. Susan E. Bates. Name 9:00 OR 10:00
 Chem 1711 Exam 1 September 26, 2013 Dr. Susan E. Bates Name 9:00 OR 10:00 N A = 6.022 x 10 23 mol 1 I A II A III B IV B V B VI B VII B VIII I B II B III A IV A V A VI A VII A inert gases 1 H 1.008 3 Li
Chem 1711 Exam 1 September 26, 2013 Dr. Susan E. Bates Name 9:00 OR 10:00 N A = 6.022 x 10 23 mol 1 I A II A III B IV B V B VI B VII B VIII I B II B III A IV A V A VI A VII A inert gases 1 H 1.008 3 Li
DO NOW: Retrieve your projects. We will be reviewing them again today. Textbook pg 23, answer questions 1-3. Use the section 1.2 to help you.
 DO NOW: Retrieve your projects. We will be reviewing them again today. Textbook pg, answer questions. Use the section. to help you. Chapter test is FRIDAY. The Periodic Table of Elements 8 Uuo Uus Uuh
DO NOW: Retrieve your projects. We will be reviewing them again today. Textbook pg, answer questions. Use the section. to help you. Chapter test is FRIDAY. The Periodic Table of Elements 8 Uuo Uus Uuh
Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation
 Nuclear Science NEA/WPEC-32 NEA/NSC/WPEC/DOC(2011)430 International Evaluation Co-operation Volume 32 Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation A
Nuclear Science NEA/WPEC-32 NEA/NSC/WPEC/DOC(2011)430 International Evaluation Co-operation Volume 32 Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation A
Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in the Columns! (3 points each)
 Chemistry 1304.001 Name (please print) Exam 4 (100 points) April 12, 2017 On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in
Chemistry 1304.001 Name (please print) Exam 4 (100 points) April 12, 2017 On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Circle the letters only. NO ANSWERS in
HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY I
 HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY I Periodic Table of the Elements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He 1.00794 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.00262 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.9898
HANDOUT SET GENERAL CHEMISTRY I Periodic Table of the Elements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He 1.00794 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.00262 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.9898
INSTRUCTIONS: Exam III. November 10, 1999 Lab Section
 CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 10, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 10, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
Speed of light c = m/s. x n e a x d x = 1. 2 n+1 a n π a. He Li Ne Na Ar K Ni 58.
 Physical Chemistry II Test Name: KEY CHEM 464 Spring 18 Chapters 7-11 Average = 1. / 16 6 questions worth a total of 16 points Planck's constant h = 6.63 1-34 J s Speed of light c = 3. 1 8 m/s ħ = h π
Physical Chemistry II Test Name: KEY CHEM 464 Spring 18 Chapters 7-11 Average = 1. / 16 6 questions worth a total of 16 points Planck's constant h = 6.63 1-34 J s Speed of light c = 3. 1 8 m/s ħ = h π
MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15
 MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15 Electron-Electron Repulsions (15.5-15.9) The hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation is exactly solvable yielding the wavefunctions and orbitals of chemistry. Howev er, the Schrödinger
MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15 Electron-Electron Repulsions (15.5-15.9) The hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation is exactly solvable yielding the wavefunctions and orbitals of chemistry. Howev er, the Schrödinger
Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department. Semester Test 1. Analytical Chemistry CMY 283. Time: 120 min Marks: 100 Pages: 6
 Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department Semester Test 1 Analytical Chemistry CMY 283 Date: 5 September 2016 Lecturers : Prof P Forbes, Dr Laurens, Mr SA Nsibande Time: 120 min
Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department Semester Test 1 Analytical Chemistry CMY 283 Date: 5 September 2016 Lecturers : Prof P Forbes, Dr Laurens, Mr SA Nsibande Time: 120 min
Essential Chemistry for Biology
 1 Chapter 2 Essential Chemistry for Biology Biology and Society: More Precious than Gold A drought is a period of abnormally dry weather that changes the environment and one of the most devastating disasters.
1 Chapter 2 Essential Chemistry for Biology Biology and Society: More Precious than Gold A drought is a period of abnormally dry weather that changes the environment and one of the most devastating disasters.
The updated version of the Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) and China nuclear data evaluation activities
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07570 Invited The updated version of the Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) and China nuclear
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07570 Invited The updated version of the Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) and China nuclear
CMSC 313 Lecture 17 Postulates & Theorems of Boolean Algebra Semiconductors CMOS Logic Gates
 CMSC 313 Lecture 17 Postulates & Theorems of Boolean Algebra Semiconductors CMOS Logic Gates UMBC, CMSC313, Richard Chang Last Time Overview of second half of this course Logic gates &
CMSC 313 Lecture 17 Postulates & Theorems of Boolean Algebra Semiconductors CMOS Logic Gates UMBC, CMSC313, Richard Chang Last Time Overview of second half of this course Logic gates &
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1014 Exam I John I. Gelder September 16, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post your course scores on homework, laboratories and exams. If you do not
CHEM 1014 Exam I John I. Gelder September 16, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post your course scores on homework, laboratories and exams. If you do not
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1314.03 Exam I John I. Gelder September 25, 1997 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post, by the last 4 digits of your student I.D. number, your course scores
CHEM 1314.03 Exam I John I. Gelder September 25, 1997 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post, by the last 4 digits of your student I.D. number, your course scores
What is the periodic table?
 The periodic table of the elements represents one of the greatest discoveries in the history of science that certain elements, the basic chemical substances from which all matter is made, resemble each
The periodic table of the elements represents one of the greatest discoveries in the history of science that certain elements, the basic chemical substances from which all matter is made, resemble each
INTERNATIONAL BULLETIN ON ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR DATA FOR FUSION
 INTERNATIONAL BULLETIN ON ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR DATA FOR FUSION Number 70 November 2016 Contributors: M. Imai, A. Kramida, D.-H. Kwon, A. Lasa Esquisabel, H. Lee, W.-W. Lee, K.-M. Lim, I. Murakami, M.-Y.
INTERNATIONAL BULLETIN ON ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR DATA FOR FUSION Number 70 November 2016 Contributors: M. Imai, A. Kramida, D.-H. Kwon, A. Lasa Esquisabel, H. Lee, W.-W. Lee, K.-M. Lim, I. Murakami, M.-Y.
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 11, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 11, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
INSTRUCTIONS: CHEM Exam I. September 13, 1994 Lab Section
 CHEM 1314.05 Exam I John I. Gelder September 13, 1994 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post, by the last 4 digits of your student I.D. number, your course scores
CHEM 1314.05 Exam I John I. Gelder September 13, 1994 Name TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post, by the last 4 digits of your student I.D. number, your course scores
5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible. 26 Fe Cu Ni Co Pd Ag Ru 101.
 Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding
 Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Chapter Outline Review of Atomic Structure Atomic Bonding Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest structural units of all solids, liquids & gases. Atom: The smallest
Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Chapter Outline Review of Atomic Structure Atomic Bonding Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest structural units of all solids, liquids & gases. Atom: The smallest
Lab Day and Time: Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
CHEM 107 (Spring-2005) Exam 3 (100 pts)
 CHEM 107 (Spring-2005) Exam 3 (100 pts) Name: ------------------------------------------------------------------------, Clid # ------------------------------ LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
CHEM 107 (Spring-2005) Exam 3 (100 pts) Name: ------------------------------------------------------------------------, Clid # ------------------------------ LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1225 Exam I John I. Gelder February 4, 1999 Name KEY TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post your course scores on homework, laboratories and exams. If you do
CHEM 1225 Exam I John I. Gelder February 4, 1999 Name KEY TA's Name Lab Section Please sign your name below to give permission to post your course scores on homework, laboratories and exams. If you do
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE : 10
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE : 0 TIME : hour TOTAL : 75 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Write your full name on your answer book in the appropriate place. 2. The question paper consists of SEVEN questions. Answer
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE : 0 TIME : hour TOTAL : 75 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Write your full name on your answer book in the appropriate place. 2. The question paper consists of SEVEN questions. Answer
Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating
 Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Patterns What Patterns have you observed in your life? Where to Get Help If you don t understand concepts in chapter
Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Why all the repeating Patterns What Patterns have you observed in your life? Where to Get Help If you don t understand concepts in chapter
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 2
 CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 2 March 7, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (13 points)
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 2 March 7, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (13 points)
M10/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX+ CHEMISTRY. Wednesday 12 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M10/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ/XX+ 106116 CHEMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 1 May 010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
M10/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ/XX+ 106116 CHEMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 1 May 010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
K. 27 Co. 28 Ni. 29 Cu Rb. 46 Pd. 45 Rh. 47 Ag Cs Ir. 78 Pt.
 1 IA 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 Atomic number Element symbol Element name Atomic mass VIIIA 1 H 1.01 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 2 He 4.00 Metalloids 3 Li 6.94 4 Be 9.01 5 B 10.81 6 C 12.01 7 N 14.01 8 O 16.00 9 F
1 IA 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 Atomic number Element symbol Element name Atomic mass VIIIA 1 H 1.01 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 2 He 4.00 Metalloids 3 Li 6.94 4 Be 9.01 5 B 10.81 6 C 12.01 7 N 14.01 8 O 16.00 9 F
single-layer transition metal dichalcogenides MC2
 single-layer transition metal dichalcogenides MC2 Period 1 1 H 18 He 2 Group 1 2 Li Be Group 13 14 15 16 17 18 B C N O F Ne 3 4 Na K Mg Ca Group 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Al Ga
single-layer transition metal dichalcogenides MC2 Period 1 1 H 18 He 2 Group 1 2 Li Be Group 13 14 15 16 17 18 B C N O F Ne 3 4 Na K Mg Ca Group 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Al Ga
CHEM 167 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, MAY 2 9:45 11:45 A.M GILMAN HALL
 PROF. JOHN VERKADE SPRING 2005 THIS EXAM CONSISTS OF 12 QUESTIONS ON 9 PAGES CHEM 167 HOUR EXAM IV APRIL 20, 2005 SEAT NO. NAME RECIT. INSTR. RECIT. SECT. GRADING PAGE Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page
PROF. JOHN VERKADE SPRING 2005 THIS EXAM CONSISTS OF 12 QUESTIONS ON 9 PAGES CHEM 167 HOUR EXAM IV APRIL 20, 2005 SEAT NO. NAME RECIT. INSTR. RECIT. SECT. GRADING PAGE Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page
 lectures accompanying the book: Solid State Physics: An Introduction, by Philip ofmann (2nd edition 2015, ISBN-10: 3527412824, ISBN-13: 978-3527412822, Wiley-VC Berlin. www.philiphofmann.net 1 Bonds between
lectures accompanying the book: Solid State Physics: An Introduction, by Philip ofmann (2nd edition 2015, ISBN-10: 3527412824, ISBN-13: 978-3527412822, Wiley-VC Berlin. www.philiphofmann.net 1 Bonds between
Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department. Semester Test 1 MEMO. Analytical Chemistry CMY 283
 Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department Semester Test 1 MEMO Analytical Chemistry CMY 283 Date: 5 September 2016 Lecturers : Prof P Forbes, Dr Laurens, Mr SA Nsibande Time: 90
Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Chemistry Department Semester Test 1 MEMO Analytical Chemistry CMY 283 Date: 5 September 2016 Lecturers : Prof P Forbes, Dr Laurens, Mr SA Nsibande Time: 90
Part 2. Multiple choice (use answer card). 90 pts. total. 3 pts. each.
 1 Exam I CHEM 1303.001 Name (print legibly) Seat no. On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Part 1. Nomenclature. 10 pts. total. 2 pts. each. Fill in
1 Exam I CHEM 1303.001 Name (print legibly) Seat no. On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exam. Signed Date Part 1. Nomenclature. 10 pts. total. 2 pts. each. Fill in
CHEM 171 EXAMINATION 1. October 9, Dr. Kimberly M. Broekemeier. NAME: Key
 CHEM 171 EXAMINATION 1 October 9, 008 Dr. Kimberly M. Broekemeier NAME: Key I A II A III B IV B V B VI B VII B VIII I B II B III A IV A V A VI A VII A inert gase s 1 H 1.008 Li.941 11 Na.98 19 K 9.10 7
CHEM 171 EXAMINATION 1 October 9, 008 Dr. Kimberly M. Broekemeier NAME: Key I A II A III B IV B V B VI B VII B VIII I B II B III A IV A V A VI A VII A inert gase s 1 H 1.008 Li.941 11 Na.98 19 K 9.10 7
CHEM Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 1.5 hours. Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 1.5 hours. Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1)
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 2, August 2011, pp. 1052 1056 The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) Z. G. Ge, Z. X. Zhao and H. H. Xia China Nuclear
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 2, August 2011, pp. 1052 1056 The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) Z. G. Ge, Z. X. Zhao and H. H. Xia China Nuclear
M11/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX CHEMISTRY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 1. Monday 9 May 2011 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M11/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ/XX 116116 CHEMISTRY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 1 Monday 9 May 011 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
M11/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ/XX 116116 CHEMISTRY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 1 Monday 9 May 011 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
Atomic Emission Spectra. and. Flame Tests. Burlingame High School Chemistry
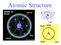 Atomic Structure Atomic Emission Spectra and Flame Tests Flame Tests Sodium potassium lithium When electrons are excited they bump up to a higher energy level. As they bounce back down they release energy
Atomic Structure Atomic Emission Spectra and Flame Tests Flame Tests Sodium potassium lithium When electrons are excited they bump up to a higher energy level. As they bounce back down they release energy
Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets.
![Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets. Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets.](/thumbs/77/75878580.jpg) Name Student Number CHEMISTRY 140 FINAL EXAM December 10, 2002 Numerical answers must be given with appropriate units and significant figures. Please place all answers in the space provided for the question.
Name Student Number CHEMISTRY 140 FINAL EXAM December 10, 2002 Numerical answers must be given with appropriate units and significant figures. Please place all answers in the space provided for the question.
High Accuracy EUV Reflectometry and Scattering at the Advanced Light Source
 High Accuracy EUV Reflectometry and Scattering at the Advanced Light Source Eric Gullikson Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 Reflectometry and Scattering Beamline (ALS 6.3.2) Commissioned Fall 1994
High Accuracy EUV Reflectometry and Scattering at the Advanced Light Source Eric Gullikson Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 Reflectometry and Scattering Beamline (ALS 6.3.2) Commissioned Fall 1994
Lab Day and Time: Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Chemistry Standard level Paper 1
 M15/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2015 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
M15/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2015 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
CHEM 172 EXAMINATION 1. January 15, 2009
 CHEM 17 EXAMINATION 1 January 15, 009 Dr. Kimberly M. Broekemeier NAME: Circle lecture time: 9:00 11:00 Constants: c = 3.00 X 10 8 m/s h = 6.63 X 10-34 J x s J = kg x m /s Rydberg Constant = 1.096776 x
CHEM 17 EXAMINATION 1 January 15, 009 Dr. Kimberly M. Broekemeier NAME: Circle lecture time: 9:00 11:00 Constants: c = 3.00 X 10 8 m/s h = 6.63 X 10-34 J x s J = kg x m /s Rydberg Constant = 1.096776 x
Upper Limit in Mendeleev s Periodic Table
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Physical Science (IJARPS) Volume 4, Issue 3, 2017, PP 14-18 ISSN 2349-7874 (Print) & ISSN 2349-7882 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Upper Limit in Mendeleev s
International Journal of Advanced Research in Physical Science (IJARPS) Volume 4, Issue 3, 2017, PP 14-18 ISSN 2349-7874 (Print) & ISSN 2349-7882 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Upper Limit in Mendeleev s
CHEM 107 (Spring-2004) Exam 2 (100 pts)
 CHEM 107 (Spring-2004) Exam 2 (100 pts) Name: ------------------------------------------------------------------------, SSN -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
CHEM 107 (Spring-2004) Exam 2 (100 pts) Name: ------------------------------------------------------------------------, SSN -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
Unit 1 Part 2 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Introduction to the Periodic Table UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE Contents 1. The Structure of the Periodic Table 2. Trends in the Periodic Table Key words: group, period, block,
UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE Contents 1. The Structure of the Periodic Table 2. Trends in the Periodic Table Key words: group, period, block,
PHYSICAL SCIENCES MARCH CONTROLLED TEST GRADE
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES MARCH CONTROLLED TEST GRADE 11 018 MARKS : 75 TIME : 1.5 Hrs INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Write your NAME and CLASS in your ANSWER BOOK.. This question paper consists of SIX questions.
PHYSICAL SCIENCES MARCH CONTROLLED TEST GRADE 11 018 MARKS : 75 TIME : 1.5 Hrs INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Write your NAME and CLASS in your ANSWER BOOK.. This question paper consists of SIX questions.
Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES
 1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
Chemistry Standard level Paper 1
 Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 12 May 2016 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all the questions. For each question,
Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 12 May 2016 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all the questions. For each question,
K. 27 Co. 28 Ni. 29 Cu Rb. 46 Pd. 45 Rh. 47 Ag Cs Ir. 78 Pt.
 1 IA 1 ydrogen 1.01 Atomic number Element symbol Element name Atomic mass VIIIA 1 1.01 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 2 e 4.00 Metalloids 3 Li 6.94 4 Be 9.01 5 B 10.81 6 C 12.01 7 N 14.01 8 O 16.00 9 F 19.00
1 IA 1 ydrogen 1.01 Atomic number Element symbol Element name Atomic mass VIIIA 1 1.01 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 2 e 4.00 Metalloids 3 Li 6.94 4 Be 9.01 5 B 10.81 6 C 12.01 7 N 14.01 8 O 16.00 9 F 19.00
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1225 Exam III John III. Gelder April 8, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table and
CHEM 1225 Exam III John III. Gelder April 8, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table and
