X X + 1 " P n ) = P m "
|
|
|
- Wilfred Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLiVIAW University of New IVSexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico Send all communications regarding Elementary Problems and Solutions to Professor A. P. Hillman, Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87106, Each problem or solution should be submitted in legible form, preferably typed in double spacing, on a separate sheet or sheets, in the format used below. Solutions should be received within three months of the publication date. Contributors (in the United States) who desire acknowledgement of r e - ceipt of their contributions are asked to enclose self-addressed stamped postcards, NOTATION: t = F 2 = 1 and F n + 2 = F n F n ; Li = 1, L 2 = 3, and L n + 2 = L f l L n. PROPOSED PROBLEMS B-220 Proposed by Guy A R. Guillotte, Montreal, P. Q., Canada. Let p be the m prime. Prove that p and p - are twin primes (i. e., p + = p + 2) if and only if m X X + 1 " P n ) = P m " B-221 Proposed by R. Garfield, College of Insurance, New York, N. Y. Prove that 545
2 546 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS [Dec. B-222 Proposed by V. E. Hoggatt, Jr., San Jose State College, San Jose, California. Find a formula for K where Kj = 1 and K n + 1 = ( K 1 + K K n ) + F 2 n + 1. B-223 Proposed by Edgar Karst, University of Arizona, Tuscon, Arizona. Find a solution of x y + (x + 3) y - (x + 4 ) y = u V + (u + 3) V - (u + 4) V in the form x = F, Jy = F, u = L, and v = L. m n* v s B-224 Proposed by Lawrence Somer, Champaign, Illinois. Let m be a fixed positive integer. Prove that no t e r m in the sequence Fj[, F 3, F 5, F 7, is divisible by 4m - 1. B-225 Proposed by John Me, Berkeley, California. satisfying Let ao> " ' ', a. «be constants and let {f } be a sequence of integers f. = a...f., + a. 0 f a f ; n = 0, 1, 2, ' ". n+j j - 1 n+j-1 j - 2 n+j-2 o n Find a n e c e s s a r y and sufficient condition for every integer m is an exact divisor of some f.. {f } to have the property that SOLUTIONS A SEQUENCE OF MULTIPLES OF 12 B-202 Proposed by Richard M. Grassl, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico. Let F, F 2, ' be the Fibonacci Sequence 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, with F n+2,_o = F n+1 _,.- + F n. Let
3 1971] ELEMENTARY PEOBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS 547 G n = F 4n-2 + F 4n + F 4n + 2 (i) Find a recursion formula for the sequence G l9 G 2, (ii) Show that each G is a multiple of 12. Solution by Phil Mana, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico. (i) The sequence {G } satisfies G «= 7G - - G since each of the sequences {F 4 _ 2 } 5 {F. }, and {F. 2} has this recursion relation. (ii) Since GQ = 0 and Gj = 12, mathematical induction using Part (i) proves that 12 G for n ^ 0. Also solved by T. Stanley, Gregory Wulczyn, and the Proposer. A SEQUENCE OF MULTIPLES OF 168 B-203 Proposed by Richard M. Grassl, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico. Show that F g _ 4 + F g + F g. is always a multiple of 168 Solution by T. Stanley, City University, London, England. The following generalizes on B-202 and B-203. Let The formulas E(n,k,r) = F. + F. + F.. kn-r kn kn+r F kn+r F r - l F k n + F r F k n + l F k n - r = ( - 1 } ( F r - l F k n - F r F k n - l } are well-known. Thus? if r is even, we have E(n,k 5 r) = ( F r + )F r _ 1 + l ) F k n. Now F, divides F, for each n and so E(n,k s r) is a multiple of
4 548 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS [Dec. (F + 2F - + 1)F. r r - 1 k for even r. Then E(n,8,4) is a multiple of ( ) 2 1 = 168, which establishes B-203. Also solved by Gregory Wulczyn and the Proposer. Editor f s Note; Combining thoughts from the solutions of B-202 and B-203, one can show that F, _ 2 + F. + F. 2 is a multiple of (L + 1)F, for n = 1, 2, 3,. GENERATING FUNCTION FOR F 0-2 n - l B-204 Proposed by V. Hoggatt, Jr., San Jose State College, San Jose, California. Let Fi = Fo = 1 and F j 0 = F ^ + F. Show that 1 L n+2 n+1 n (i) F t x + F 2 x 2 + Fgx 3 + F 7 x 4 + = (x - x 2 ) / ( l - 3x + x 2 ) for x < (3 - N / 5 ) / 2. (ii) 1 + 2x + 3x 2 + 4x 3 + = 1/(1 - x) 2 for x ^ 1. (iii) nfi + (n - 1)F, + (n - 2)F F 3 n _ 2 + F ^ = F 2 n Solution by Phil Mana, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico. (i) Let f(x) = (1 - x ) / ( l - 3x + x 2 ) and let its Maclaurin expansion be (1) f(x) = c 0 + Cjx + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +. Then (1) converges for x ^ r, where r is the root of 1-3x + x 2 = 0 of l e a s t absolute value* i. e., r = (3 - \ f 5 ) / 2. Multiplying both sides of (1) by 1-3x + x 2 gives us (2) 1 - x = (1-3x + x 2 )c 0 + Cjx + c 2 x ).
5 1971] ELEMENTAEY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS 549 Expanding the right r side of (2) and equating coefficients of x m of (2), leads to on both sides (3) c 0 = 1, c t = 2 5 c n c n c n = 0 for n > 0. This implies that c = F 9 - and Part (i) is proved. (ii) This follows by term-by-term differentiation of 1 + X + X? + = 1/(1 - X), [x < 1. (iii) Let G n = nf t + (n - 1)F 3 + 2F 2 n _ 2 + F 2 n _ r Then the generating function for the G is found by multiplying the series of Parts (i) and (ii) to be 1/[(1 - x)(l - 3x + x 2 )] = Gt + G 2 x + G 3 x 2 + e9. This implies that G t = 1, G 2 = 4? G 3 = 12, and (4) G ±Q - 4G ^ + 4G ± 1 - G = 0. v ' n+3 n+2 n+1 n Since F 0 M - 1 satisfies the same initial conditions and the same recur- 2n+l rence relation (4) as G, Part (iii) is established. Also solved by the Proposer. ANOTHER CONVOLUTION FOR? 2 ± B-205 Proposed by V. Hoggatt, Jr., San Jose State College, San Jose, California. Show that (2n - l ) F j + (2n - 3)F 3 + (2n - 5)F F 2 n _ 3 + F ^ ^ = L 2 n - 2. fin where L is the n. Lucas number (i. e., Lj = 1, L 2 = 3, L = L n+i + L ). n
6 550 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS [Dec, Solution by Phil Mana, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico. one uses The solution is s i m i l a r to that of B-204. Instead of P a r t (ii) of B-204, 1 + 3x + 5x 2 +. = (1 + x ) / ( l - x) 2, x < 1, which may be obtained by differentiating t e r m - b y - t e r m in y + y3 + y = y / ( l - y2) f x < l, and then substituting y 2 = x. A GEOMETRIC SERIES B-206 Proposed by Guy A. Guillotte, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Let a = (1 + \J'E)/2 and sum 00 E: af,- + F n n+1 n Solution by C. B. A. Peck, State College, Pennsylvania. F r o m the Fibonacci Quarterly; Vol. 1, No. 3, p. 54, a V _L T? = af,- + F n+1 n Hence the sum is ( l / a 2 ) [ l - (1/a)] = l/(a 2 - a) = 1, since a 2 - a - 1 = 0. Also solved by Gregory Wulczyn and the Proposer.
7 1971] ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS 551 ANOTHER GEOMETRIC SERIES B-207 Proposed by Guy A Guillotte, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Sum ~ * F + \f5 F,- + F l 0 n n+1 n+2 Solution by C. B. A. Peck, State College, Pennsylvania. The equation F + ^ F ± 1 + F _ L O = L ± 1 + \ 5 F ± 1 = 2 a n + 1 n n+1 n+2 n+1 n+1 along with B-206, show that the sum desired here is l/2 8 Also solved by Gregory Wulczyn and the Proposer. FIBONACCI NOTE SERVICE The Fibonacci Quarterly i s offering a s e r v i c e in which it will be p o s - sible for its r e a d e r s to secure background notes for a r t i c l e s. This will apply to the following: (1) Short abstracts of extensive r e s u l t s, derivations, and numerical data. (2) Brief articles summarizing a large amount of r e s e a r c h. (3) Articles of standard size for which additional background m a t e r i a l may be obtained. Articles in the Quarterly for which this note service is available will indicate the fact together with the number of pages in question. Requests for these notes should be made to: Brother Alfred Brousseau S t Mary? s College Moraga, Calif The notes will be Xeroxed* The price for this service is four cents a page (including postage, m a - t e r i a l s, and labor).
ALGORITHMS FOR THIRD-ORDER RECURSION SEQUENCES
 ALGORITHMS FOR THIRD-ORDER RECURSION SEQUENCES BROTHER ALFRED BROUSSEAU St. Mary's College, Moraga, California 947 Given a third-order recursion relation (D T n + 1 = a l T n " a 2 T n _ i + a T n Let
ALGORITHMS FOR THIRD-ORDER RECURSION SEQUENCES BROTHER ALFRED BROUSSEAU St. Mary's College, Moraga, California 947 Given a third-order recursion relation (D T n + 1 = a l T n " a 2 T n _ i + a T n Let
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by A. P. HILLMAN University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 873 Send all communications regarding ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to PROFESSOR A. P. HILLMAN, 79
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 873 Send all communications regarding ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to PROFESSOR A. P. HILLMAN, 79
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA PA 17745, This department
Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA PA 17745, This department
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz
 Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz IMPORTANT NOTICE: There is a new editor of this department and a new address for all submissions. Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to DR. STANLEY
Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz IMPORTANT NOTICE: There is a new editor of this department and a new address for all submissions. Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to DR. STANLEY
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lk Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania 17745 Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lk Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania 17745 Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
PROBLEMS PROPOSED IN THIS ISSUE
 Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should be on a separate sheet (or
Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should be on a separate sheet (or
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by A. P. Hillman
 Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should be on a separate sheet (or
Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should be on a separate sheet (or
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
AND RELATED NUMBERS. GERHARD ROSENBERGER Dortmund, Federal Republic of Germany (Submitted April 1982)
 ON SOME D I V I S I B I L I T Y PROPERTIES OF FIBONACCI AND RELATED NUMBERS Universitat GERHARD ROSENBERGER Dortmund, Federal Republic of Germany (Submitted April 1982) 1. Let x be an arbitrary natural
ON SOME D I V I S I B I L I T Y PROPERTIES OF FIBONACCI AND RELATED NUMBERS Universitat GERHARD ROSENBERGER Dortmund, Federal Republic of Germany (Submitted April 1982) 1. Let x be an arbitrary natural
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Assistant Editors GLORIA C. PADILLA and CHARLES R. WALL Send all communications regarding ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS and SOLUTIONS to PROFESSOR
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Assistant Editors GLORIA C. PADILLA and CHARLES R. WALL Send all communications regarding ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS and SOLUTIONS to PROFESSOR
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania
 ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney,
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz
 Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD f AM 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to the problem editor by electronic
Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD f AM 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to the problem editor by electronic
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by A. P. Hillman
 Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should he on a separate sheet (or sheets) and must be received within
Edited by A. P. Hillman Please send all material for to Dr. A. P. HILLMAN; 709 SOLANO DR., S.E.; ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87108. Each solution should he on a separate sheet (or sheets) and must be received within
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by Florian Luca Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLU- TIONS to FLORIAN LUCA, IMATE, UNAM, AP. POSTAL 61-3 (XANGARI),CP 58 089, MORELIA, MICHOACAN, MEXICO, or by e-mail
Edited by Florian Luca Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLU- TIONS to FLORIAN LUCA, IMATE, UNAM, AP. POSTAL 61-3 (XANGARI),CP 58 089, MORELIA, MICHOACAN, MEXICO, or by e-mail
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Uiversity of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A. P. Hillma, Departmet
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Uiversity of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A. P. Hillma, Departmet
^ ) = ^ : g ' f ^4(x)=a(xr + /xxr,
 Edited by Stanley Rablnowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to
Edited by Stanley Rablnowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to
LONGEST SUCCESS RUNS AND FIBONACCI-TYPE POLYNOMIALS
 LONGEST SUCCESS RUNS AND FIBONACCI-TYPE POLYNOMIALS ANDREAS N. PHILIPPOU & FROSSO S. MAKRI University of Patras, Patras, Greece (Submitted January 1984; Revised April 1984) 1. INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY
LONGEST SUCCESS RUNS AND FIBONACCI-TYPE POLYNOMIALS ANDREAS N. PHILIPPOU & FROSSO S. MAKRI University of Patras, Patras, Greece (Submitted January 1984; Revised April 1984) 1. INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY
COMPOSITIONS AND FIBONACCI NUMBERS
 COMPOSITIONS AND FIBONACCI NUMBERS V. E. HOGGATT, JR., and D. A. LIND San Jose State College, San Jose, California and University of Cambridge, England 1, INTRODUCTION A composition of n is an ordered
COMPOSITIONS AND FIBONACCI NUMBERS V. E. HOGGATT, JR., and D. A. LIND San Jose State College, San Jose, California and University of Cambridge, England 1, INTRODUCTION A composition of n is an ordered
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek
 Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
GENERATING FUNCTIONS OF CENTRAL VALUES IN GENERALIZED PASCAL TRIANGLES. CLAUDIA SMITH and VERNER E. HOGGATT, JR.
 GENERATING FUNCTIONS OF CENTRAL VALUES CLAUDIA SMITH and VERNER E. HOGGATT, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, CA 95. INTRODUCTION In this paper we shall examine the generating functions of the central
GENERATING FUNCTIONS OF CENTRAL VALUES CLAUDIA SMITH and VERNER E. HOGGATT, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, CA 95. INTRODUCTION In this paper we shall examine the generating functions of the central
(1.1) A j y ( t + j) = 9
 LIEAR HOOGEEOUS DIFFERECE EQUATIOS ROBERT.GIULI San Jose State College, San Jose, California 1. LIEAE HOOGEEOUS DIFFERECE EQUATIOS Since Its founding, this quarterly has essentially devoted its effort
LIEAR HOOGEEOUS DIFFERECE EQUATIOS ROBERT.GIULI San Jose State College, San Jose, California 1. LIEAE HOOGEEOUS DIFFERECE EQUATIOS Since Its founding, this quarterly has essentially devoted its effort
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. H1LLMASM Uiversity of Mew Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A. P. Hillma, Departmet
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. H1LLMASM Uiversity of Mew Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A. P. Hillma, Departmet
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA VEN, PA 17745. This
Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA VEN, PA 17745. This
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA VEN, PA 17745. This
Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HA VEN, PA 17745. This
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz
 Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to the problem editor by electronic mail
Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also be sent to the problem editor by electronic mail
GENERALIZED RABBITS FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS. V.E.Hoggatt^Jro. San Jose State College, San Jose, Calif e 1. INTRODUCTION
 GENERALIZED RABBITS FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS V.E.Hoggatt^ro San ose State College, San ose, Calif e 1. INTRODUCTION The original Fibonacci number sequence arose from an academic rabbit production
GENERALIZED RABBITS FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS V.E.Hoggatt^ro San ose State College, San ose, Calif e 1. INTRODUCTION The original Fibonacci number sequence arose from an academic rabbit production
Divisibility in the Fibonacci Numbers. Stefan Erickson Colorado College January 27, 2006
 Divisibility in the Fibonacci Numbers Stefan Erickson Colorado College January 27, 2006 Fibonacci Numbers F n+2 = F n+1 + F n n 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 F n 1 1 2 3 8 13 21 34 89 144 n 13 14 1 16 17 18
Divisibility in the Fibonacci Numbers Stefan Erickson Colorado College January 27, 2006 Fibonacci Numbers F n+2 = F n+1 + F n n 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 F n 1 1 2 3 8 13 21 34 89 144 n 13 14 1 16 17 18
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr. Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY, 4063, or by
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr. Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY, 4063, or by
ADVANCED PEOBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ADVANCED PEOBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by Raymond E* Whitney Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND K WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 7745. This department
ADVANCED PEOBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by Raymond E* Whitney Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND K WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 7745. This department
ON SOME RECIPROCAL SUMS OF BROUSSEAU: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH TO THAT OF CARLITZ
 ON SOME RECIPROCAL SUMS OF BROUSSEAU: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH TO THAT OF CARLITZ In [2], it was shown that R. S. Melham Department of Math. Sciences, University oftechnology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway,
ON SOME RECIPROCAL SUMS OF BROUSSEAU: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH TO THAT OF CARLITZ In [2], it was shown that R. S. Melham Department of Math. Sciences, University oftechnology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway,
CLASSES OF IDENTITIES FOR THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS G n = G n _ t + G n _ c FROM MATRICES WITH CONSTANT VALUED DETERMINANTS
 CLASSES OF IDENTITIES FOR THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS G n = G n _ t + G n _ c FROM MATRICES WITH CONSTANT VALUED DETERMINANTS Marjorle Bicknell-Johnson 665 Fairlane Avenue, Santa Clara, CA 955 Colin
CLASSES OF IDENTITIES FOR THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS G n = G n _ t + G n _ c FROM MATRICES WITH CONSTANT VALUED DETERMINANTS Marjorle Bicknell-Johnson 665 Fairlane Avenue, Santa Clara, CA 955 Colin
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek
 Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
f = 0 (n < 0), fj = 1, f = J2 f. (n > 1).
 GENERALIZED FIBONACCI KSEQUENCES HYMAM GABAI York College (CUNY) and University of Illinois (UICSM) 1* INTRODUCTION For k > 2, the Fibonacci ksequence F(k) maybe defined recursively by n l f = 0 (n < 0),
GENERALIZED FIBONACCI KSEQUENCES HYMAM GABAI York College (CUNY) and University of Illinois (UICSM) 1* INTRODUCTION For k > 2, the Fibonacci ksequence F(k) maybe defined recursively by n l f = 0 (n < 0),
Summation of certain infinite Fibonacci related series
 arxiv:52.09033v (30 Dec 205) Summation of certain infinite Fibonacci related series Bakir Farhi Laboratoire de Mathématiques appliquées Faculté des Sciences Exactes Université de Bejaia 06000 Bejaia Algeria
arxiv:52.09033v (30 Dec 205) Summation of certain infinite Fibonacci related series Bakir Farhi Laboratoire de Mathématiques appliquées Faculté des Sciences Exactes Université de Bejaia 06000 Bejaia Algeria
GOLDEN SEQUENCES OF MATRICES WITH APPLICATIONS TO FIBONACCI ALGEBRA
 GOLDEN SEQUENCES OF MATRICES WITH APPLICATIONS TO FIBONACCI ALGEBRA JOSEPH ERCOLANO Baruch College, CUNY, New York, New York 10010 1. INTRODUCTION As is well known, the problem of finding a sequence of
GOLDEN SEQUENCES OF MATRICES WITH APPLICATIONS TO FIBONACCI ALGEBRA JOSEPH ERCOLANO Baruch College, CUNY, New York, New York 10010 1. INTRODUCTION As is well known, the problem of finding a sequence of
EXPANSION OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS IN TERMS INVOLVING LUCAS NUMBERS OR SIMILAR NUMBER SEQUENCES
 EXPANSION OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS IN TERMS INVOLVING LUCAS NUMBERS OR SIMILAR NUMBER SEQUENCES PAUL F. BYRD San Jose State College, San Jose, California 1. INTRODUCTION In a previous article [_ 1J, certain
EXPANSION OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS IN TERMS INVOLVING LUCAS NUMBERS OR SIMILAR NUMBER SEQUENCES PAUL F. BYRD San Jose State College, San Jose, California 1. INTRODUCTION In a previous article [_ 1J, certain
REDUCTION FORMULAS FOR THE SUMMATION OF RECIPROCALS IN CERTAIN SECOND-ORDER RECURRING SEQUENCES
 REDUCTION FORMULAS FOR THE SUMMATION OF RECIPROCALS IN CERTAIN SECOND-ORDER RECURRING SEQUENCES R. S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 23, Broadway, NSW
REDUCTION FORMULAS FOR THE SUMMATION OF RECIPROCALS IN CERTAIN SECOND-ORDER RECURRING SEQUENCES R. S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 23, Broadway, NSW
Integrated Arithmetic and Basic Algebra
 211 771 406 III T H I R D E D I T I O N Integrated Arithmetic and Basic Algebra Bill E. Jordan Seminole Community College William P. Palow Miami-Dade College Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto
211 771 406 III T H I R D E D I T I O N Integrated Arithmetic and Basic Algebra Bill E. Jordan Seminole Community College William P. Palow Miami-Dade College Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto
DIFFERENTIAL PROPERTIES OF A GENERAL CLASS OF POLYNOMIALS. Richard Andre-Jeannin IUT GEA, Route de Romain, Longwy, France (Submitted April 1994)
 DIFFERENTIAL PROPERTIES OF A GENERAL CLASS OF POLYNOMIALS Richard Andre-Jeannin IUT GEA, Route de Romain, 54400 Longwy, France (Submitted April 1994) 1. INTRODUCTION Let us consider the generalized Fibonacci
DIFFERENTIAL PROPERTIES OF A GENERAL CLASS OF POLYNOMIALS Richard Andre-Jeannin IUT GEA, Route de Romain, 54400 Longwy, France (Submitted April 1994) 1. INTRODUCTION Let us consider the generalized Fibonacci
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited By RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Lock Haven State College, Lock Haven, Pennsylvania
 ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited By RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Loc Haven State College, Loc Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney, Mathematics
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited By RAYMOND E.WHITNEY Loc Haven State College, Loc Haven, Pennsylvania Send all communications concerning Advanced Problems and Solutions to Raymond E. Whitney, Mathematics
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY 4063, or by email
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY 4063, or by email
DIVISIBILITY BY FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SQUARES
 DIVISIBILITY BY FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SQUARES V. E. HOGGATT, JR., and MARJORIE B5CKNELL JOHNSON San Jose State University, San Jose, California 95192 1. INTRODUCTION In Matijasevic's paper [1] on Hilbert's
DIVISIBILITY BY FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SQUARES V. E. HOGGATT, JR., and MARJORIE B5CKNELL JOHNSON San Jose State University, San Jose, California 95192 1. INTRODUCTION In Matijasevic's paper [1] on Hilbert's
A Probabilistic View of Certain Weighted Fibonacci Sums
 Claremont Colleges Scholarship @ Claremont All HMC Faculty Publications and Research HMC Faculty Scholarship 8-1-2003 A Probabilistic View of Certain Weighted Fibonacci Sums Arthur T. Benjamin Harvey Mudd
Claremont Colleges Scholarship @ Claremont All HMC Faculty Publications and Research HMC Faculty Scholarship 8-1-2003 A Probabilistic View of Certain Weighted Fibonacci Sums Arthur T. Benjamin Harvey Mudd
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. H1LLMAN Uiversity of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mex. Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A* P. Hillma, Departmet
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. H1LLMAN Uiversity of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mex. Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary Problems ad Solutios to Professor A* P. Hillma, Departmet
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. Mathematical Induction in zybooks
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications Mathematical Induction 6.4 6.6 in zybooks Why induction? Prove algorithm correctness (CS320 is full of it) The inductive proof will sometimes point out
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications Mathematical Induction 6.4 6.6 in zybooks Why induction? Prove algorithm correctness (CS320 is full of it) The inductive proof will sometimes point out
GENERALIZED FIBONACCI POLYNOMIALS AND ZECKENDORFS THEOREM 1. INTRODUCTION
 GENERALIZED FIBONACCI POLYNOMIALS AND ZECKENDORFS THEOREM VERIER E. HOGGATT, Jr., and MARJORSE BtCKNELL San Jose State University, San Jose, California 1. INTRODUCTION The Zeckendorf Theorem states that
GENERALIZED FIBONACCI POLYNOMIALS AND ZECKENDORFS THEOREM VERIER E. HOGGATT, Jr., and MARJORSE BtCKNELL San Jose State University, San Jose, California 1. INTRODUCTION The Zeckendorf Theorem states that
NEW UNITARY PERFECT NUMBERS HAVE AT LEAST NINE ODD COMPONENTS
 NEW UNITARY PERFECT NUMBERS HAVE AT LEAST NINE ODD COMPONENTS CHARLES R. WALL Trident Technical College, Charleston, SC 29411 (Submitted November 1986) 1. INTRODUCTION We say that a divisor d of an integer
NEW UNITARY PERFECT NUMBERS HAVE AT LEAST NINE ODD COMPONENTS CHARLES R. WALL Trident Technical College, Charleston, SC 29411 (Submitted November 1986) 1. INTRODUCTION We say that a divisor d of an integer
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 EDITED BY RUSS EULER AND JAWAD SADEK Please submit all new problem proposals their solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics Statistics, Northwest Missouri State University,
EDITED BY RUSS EULER AND JAWAD SADEK Please submit all new problem proposals their solutions to the Problems Editor, DR. RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics Statistics, Northwest Missouri State University,
G E N E R A L I Z E D C O N V O L U T I O N A R R A Y S
 G E N E R A L I Z E D C O N V O L U T I O N A R R A Y S V. E. HOGGATT,JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California 00192 G. E. BERGUM South Dakota State University, Brookings, Sooth Dakota 57006
G E N E R A L I Z E D C O N V O L U T I O N A R R A Y S V. E. HOGGATT,JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California 00192 G. E. BERGUM South Dakota State University, Brookings, Sooth Dakota 57006
DYNAMICS OF THE ZEROS OF FIBONACCI POLYNOMIALS M. X. He Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL. D, Simon
 M. X. He Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL D, Simon Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL P. E. Ricci Universita degli Studi di Roma "La Sapienza," Rome, Italy (Submitted December
M. X. He Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL D, Simon Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL P. E. Ricci Universita degli Studi di Roma "La Sapienza," Rome, Italy (Submitted December
Y. H. Harris Kwong SUNY College at Fredonia, Fredonia, NY (Submitted May 1987)
 Y. H. Harris Kwong SUNY College at Fredonia, Fredonia, NY 14063 (Submitted May 1987) 1. Introduction The Stirling number of the second kind, S(n, k), is defined as the number of ways to partition a set
Y. H. Harris Kwong SUNY College at Fredonia, Fredonia, NY 14063 (Submitted May 1987) 1. Introduction The Stirling number of the second kind, S(n, k), is defined as the number of ways to partition a set
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by Raymond E 0 Whitney Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
Edited by Raymond E 0 Whitney Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
SOME FORMULAE FOR THE FIBONACCI NUMBERS
 SOME FORMULAE FOR THE FIBONACCI NUMBERS Brian Curtin Department of Mathematics, University of South Florida, 4202 E Fowler Ave PHY4, Tampa, FL 33620 e-mail: bcurtin@mathusfedu Ena Salter Department of
SOME FORMULAE FOR THE FIBONACCI NUMBERS Brian Curtin Department of Mathematics, University of South Florida, 4202 E Fowler Ave PHY4, Tampa, FL 33620 e-mail: bcurtin@mathusfedu Ena Salter Department of
Editorial Comment 21. Golden Rectangle Figure 1. Tree. Figure FIBONACCI-TRIBONACCJ [ O c t 1963] ,? Silver H Rectangle.
![Editorial Comment 21. Golden Rectangle Figure 1. Tree. Figure FIBONACCI-TRIBONACCJ [ O c t 1963] ,? Silver H Rectangle. Editorial Comment 21. Golden Rectangle Figure 1. Tree. Figure FIBONACCI-TRIBONACCJ [ O c t 1963] ,? Silver H Rectangle.](/thumbs/76/73329679.jpg) 70 FIBONACCI-TRIBONACCJ [ O c t 1963] Editorial Comment Mark Feinberg is a fourteen-year-old student in the ninth grade of the Susquehanna Township Junior High School and recently became the Pennsylvania
70 FIBONACCI-TRIBONACCJ [ O c t 1963] Editorial Comment Mark Feinberg is a fourteen-year-old student in the ninth grade of the Susquehanna Township Junior High School and recently became the Pennsylvania
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Stanley Rablnowitz
 Edited by Stanley Rablnowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTLONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWLTZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also he sent to
Edited by Stanley Rablnowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTLONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWLTZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also he sent to
CONVOLUTION TREES AND PASCAL-T TRIANGLES. JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 1986) 1.
 JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 986). INTRODUCTION Pascal (6-66) made extensive use of the famous arithmetical triangle which now bears his name. He wrote
JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 986). INTRODUCTION Pascal (6-66) made extensive use of the famous arithmetical triangle which now bears his name. He wrote
MATH 55 - HOMEWORK 6 SOLUTIONS. 1. Section = 1 = (n + 1) 3 = 2. + (n + 1) 3. + (n + 1) 3 = n2 (n + 1) 2.
 MATH 55 - HOMEWORK 6 SOLUTIONS Exercise Section 5 Proof (a) P () is the statement ( ) 3 (b) P () is true since ( ) 3 (c) The inductive hypothesis is P (n): ( ) n(n + ) 3 + 3 + + n 3 (d) Assuming the inductive
MATH 55 - HOMEWORK 6 SOLUTIONS Exercise Section 5 Proof (a) P () is the statement ( ) 3 (b) P () is true since ( ) 3 (c) The inductive hypothesis is P (n): ( ) n(n + ) 3 + 3 + + n 3 (d) Assuming the inductive
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Uiversity of Mew Mexico, Albuquerque, IMew Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary P r o b l e m s ad Solutios to P r o f e s s o r A, P.
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Edited by A. P. HILLMAN Uiversity of Mew Mexico, Albuquerque, IMew Mexico Sed all commuicatios regardig Elemetary P r o b l e m s ad Solutios to P r o f e s s o r A, P.
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY RUSS EULER AND JAWAD SADEK Please submit all new problem proposals and their solutions to the Problems Editor, DR RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY RUSS EULER AND JAWAD SADEK Please submit all new problem proposals and their solutions to the Problems Editor, DR RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
Section 11.1 Sequences
 Math 152 c Lynch 1 of 8 Section 11.1 Sequences A sequence is a list of numbers written in a definite order: a 1, a 2, a 3,..., a n,... Notation. The sequence {a 1, a 2, a 3,...} can also be written {a
Math 152 c Lynch 1 of 8 Section 11.1 Sequences A sequence is a list of numbers written in a definite order: a 1, a 2, a 3,..., a n,... Notation. The sequence {a 1, a 2, a 3,...} can also be written {a
EQUATIONS WHOSE ROOTS ARE T I E nth POWERS OF T I E ROOTS OF A GIVEN CUBIC EQUATION
 EQUATIONS WHOSE ROOTS ARE T I E nth POWERS OF T I E ROOTS OF A GIVEN CUBIC EQUATION N. A, DRAiMand MARJORIE BICKNELL Ventura, Calif, and Wilcox High School, Santa Clara, Calif. Given the cubic equation
EQUATIONS WHOSE ROOTS ARE T I E nth POWERS OF T I E ROOTS OF A GIVEN CUBIC EQUATION N. A, DRAiMand MARJORIE BICKNELL Ventura, Calif, and Wilcox High School, Santa Clara, Calif. Given the cubic equation
PRIMITIVE PERIODS OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI SEQUENCES
 PRIMITIVE PERIODS O GENERALIZED IBONACCI SEQUENCES CLAUDIA SMIT and VERWER E. OGGATT, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California 95192 1. IWTRODUCTIOW In this paper we are concerned with the primitive
PRIMITIVE PERIODS O GENERALIZED IBONACCI SEQUENCES CLAUDIA SMIT and VERWER E. OGGATT, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California 95192 1. IWTRODUCTIOW In this paper we are concerned with the primitive
Mathematical Induction. Rosen Chapter 4.1,4.2 (6 th edition) Rosen Ch. 5.1, 5.2 (7 th edition)
 Mathematical Induction Rosen Chapter 4.1,4.2 (6 th edition) Rosen Ch. 5.1, 5.2 (7 th edition) Motivation Suppose we want to prove that for every value of n: 1 + 2 + + n = n(n + 1)/2. Let P(n) be the predicate
Mathematical Induction Rosen Chapter 4.1,4.2 (6 th edition) Rosen Ch. 5.1, 5.2 (7 th edition) Motivation Suppose we want to prove that for every value of n: 1 + 2 + + n = n(n + 1)/2. Let P(n) be the predicate
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz
 Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also he sent to
Edited by Stanley Rabinowitz Please send all material for ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to Dr. STANLEY RABINOWITZ; 12 VINE BROOK RD; WESTFORD, MA 01886-4212 USA. Correspondence may also he sent to
Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek
 Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
Edited by Russ Euler and Jawad Sadek Please submit all new problem proposals and corresponding solutions to the Problems Editor, DR RUSS EULER, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Missouri
SECOND-ORDER RECURRENCES. Lawrence Somer Department of Mathematics, Catholic University of America, Washington, D.C
 p-stability OF DEGENERATE SECOND-ORDER RECURRENCES Lawrence Somer Department of Mathematics, Catholic University of America, Washington, D.C. 20064 Walter Carlip Department of Mathematics and Computer
p-stability OF DEGENERATE SECOND-ORDER RECURRENCES Lawrence Somer Department of Mathematics, Catholic University of America, Washington, D.C. 20064 Walter Carlip Department of Mathematics and Computer
Supplementary Information
 If f - - x R f z (F ) w () () f F >, f E jj E, V G >, G >, E G,, f ff f FILY f jj ff LO_ N_ j:rer_ N_ Y_ fg LO_; LO_ N_; N_ j:rer_; j:rer_ N_ Y_ f LO_ N_ j:rer_; j:rer_; N_ j:rer_ Y_ fn LO_ N_ - N_ Y_
If f - - x R f z (F ) w () () f F >, f E jj E, V G >, G >, E G,, f ff f FILY f jj ff LO_ N_ j:rer_ N_ Y_ fg LO_; LO_ N_; N_ j:rer_; j:rer_ N_ Y_ f LO_ N_ j:rer_; j:rer_; N_ j:rer_ Y_ fn LO_ N_ - N_ Y_
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS. Edited by Raymond E. Whitney
 Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 7745. This department
Edited by Raymond E. Whitney Please send all communications concerning ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 7745. This department
SOME IDENTITIES INVOLVING DIFFERENCES OF PRODUCTS OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS
 SOME IDENTITIES INVOLVING DIFFERENCES OF PRODUCTS OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS CURTIS COOPER Abstract. Melham discovered the Fibonacci identity F n+1f n+2f n+6 F 3 n+3 = 1 n F n. Melham then considered
SOME IDENTITIES INVOLVING DIFFERENCES OF PRODUCTS OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS CURTIS COOPER Abstract. Melham discovered the Fibonacci identity F n+1f n+2f n+6 F 3 n+3 = 1 n F n. Melham then considered
Infinite arctangent sums involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers
 Infinite arctangent sums involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers Kunle Adegoke Department of Physics and Engineering Physics, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, 0005 Nigeria Saturday 3 rd July, 06, 6:43
Infinite arctangent sums involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers Kunle Adegoke Department of Physics and Engineering Physics, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, 0005 Nigeria Saturday 3 rd July, 06, 6:43
(Submitted November 1999) 1. INTRODUCTION - F. n+k 2. n=1f" n+k l. <... < k m
 REDUCTION FORMULAS FOR THE SUMMATION OF RECIPROCALS IN CERTAIN SECOND-ORDER RECURRING SEQUENCES R. S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway,
REDUCTION FORMULAS FOR THE SUMMATION OF RECIPROCALS IN CERTAIN SECOND-ORDER RECURRING SEQUENCES R. S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway,
arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 29 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 29 Jul 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 29 Jul 2017](/thumbs/88/116041514.jpg) Fibonacci and Lucas Numbers Associated with Brocard-Ramanujan Equation arxiv:1509.07898v2 [math.nt] 29 Jul 2017 Prapanpong Pongsriiam Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Silpakorn University
Fibonacci and Lucas Numbers Associated with Brocard-Ramanujan Equation arxiv:1509.07898v2 [math.nt] 29 Jul 2017 Prapanpong Pongsriiam Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Silpakorn University
C O M P L E X FACTORIZATIONS O F T H E F I B O N A C C I AND LUCAS NUMBERS
 C O M P L E X FACTORIZATIONS O F T H E F I B O N A C C I AND LUCAS NUMBERS Nathan D. Cahill, John R. D'Errico, and John P* Spence Eastman Kodak Company, 343 State Street, Rochester, NY 4650 {natfaan. cahill,
C O M P L E X FACTORIZATIONS O F T H E F I B O N A C C I AND LUCAS NUMBERS Nathan D. Cahill, John R. D'Errico, and John P* Spence Eastman Kodak Company, 343 State Street, Rochester, NY 4650 {natfaan. cahill,
Section 4.1: Sequences and Series
 Section 4.1: Sequences and Series In this section, we shall introduce the idea of sequences and series as a necessary tool to develop the proof technique called mathematical induction. Most of the material
Section 4.1: Sequences and Series In this section, we shall introduce the idea of sequences and series as a necessary tool to develop the proof technique called mathematical induction. Most of the material
ON A KIND OF GENERALIZED ARITHMETIC-GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION
 ON A KIND OF GENERALIZED ARITHMETIC-GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION Leetsch C. Hsu* Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China (Submitted August 1995) 1. INTRODUCTION Let (t\h) p denote the generalized
ON A KIND OF GENERALIZED ARITHMETIC-GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION Leetsch C. Hsu* Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China (Submitted August 1995) 1. INTRODUCTION Let (t\h) p denote the generalized
F O R M U L A S F O R CONVOLUTION F I B O N A C C I NUMBERS AND P O L Y N O M I A L S
 F O R M U L A S F O R CONVOLUTION F I B O N A C C I NUMBERS AND P O L Y N O M I A L S Guodong Liu Dept. of Mathematics, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516015, People's Republic of China (Submitted
F O R M U L A S F O R CONVOLUTION F I B O N A C C I NUMBERS AND P O L Y N O M I A L S Guodong Liu Dept. of Mathematics, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516015, People's Republic of China (Submitted
YE OLDE FIBONACCI CURIOSITY SHOPPE REVISITED
 R.S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway, NSW 2007 Australia (Submitted. September 2001) 1. INTRODUCTION There are many Fibonacci identities
R.S. Melham Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box 123, Broadway, NSW 2007 Australia (Submitted. September 2001) 1. INTRODUCTION There are many Fibonacci identities
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY VERNER E, HOGGATT 9 JR 0, SAN JOSE STATE COLLEGE Sed all commuicatios cocerig Advaced P r o b l e m s ad Solutios to Verer E. Hoggatt, J r., Mathematics Departmet,
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY VERNER E, HOGGATT 9 JR 0, SAN JOSE STATE COLLEGE Sed all commuicatios cocerig Advaced P r o b l e m s ad Solutios to Verer E. Hoggatt, J r., Mathematics Departmet,
SOME PROPERTIES OF THIRD-ORDER RECURRENCE RELATIONS
 SOME PROPERTIES OF THIRD-ORDER RECURRENCE RELATIONS A. G. SHANNON* University of Papua New Guinea, Boroko, T. P. N. G. A. F. HORADAIVS University of New Engl, Armidale, Australia. INTRODUCTION In this
SOME PROPERTIES OF THIRD-ORDER RECURRENCE RELATIONS A. G. SHANNON* University of Papua New Guinea, Boroko, T. P. N. G. A. F. HORADAIVS University of New Engl, Armidale, Australia. INTRODUCTION In this
UNIT DETERMINANTS IN GENERALIZED PASCAL TRIANGLES
 UNI DEERMINANS IN GENERALIZED PASCAL RIANGLES MARJORf E BtCKNELL and V. E. HOGGA, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California here are many ways in which one can select a square array from Pascal's
UNI DEERMINANS IN GENERALIZED PASCAL RIANGLES MARJORf E BtCKNELL and V. E. HOGGA, JR. San Jose State University, San Jose, California here are many ways in which one can select a square array from Pascal's
Fibonacci numbers. Chapter The Fibonacci sequence. The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by
 Chapter Fibonacci numbers The Fibonacci sequence The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by F n+ = F n + F n, F 0 = 0, F = The first few Fibonacci numbers are n 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 F n 0 5 8 55 89
Chapter Fibonacci numbers The Fibonacci sequence The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by F n+ = F n + F n, F 0 = 0, F = The first few Fibonacci numbers are n 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 F n 0 5 8 55 89
COMPLETE PADOVAN SEQUENCES IN FINITE FIELDS. JUAN B. GIL Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Altoona, PA 16601
 COMPLETE PADOVAN SEQUENCES IN FINITE FIELDS JUAN B. GIL Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Altoona, PA 16601 MICHAEL D. WEINER Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Altoona, PA 16601 CATALIN ZARA
COMPLETE PADOVAN SEQUENCES IN FINITE FIELDS JUAN B. GIL Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Altoona, PA 16601 MICHAEL D. WEINER Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Altoona, PA 16601 CATALIN ZARA
Yi Wang Department of Applied Mathematics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian , China (Submitted June 2002)
 SELF-INVERSE SEQUENCES RELATED TO A BINOMIAL INVERSE PAIR Yi Wang Department of Applied Mathematics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China (Submitted June 2002) 1 INTRODUCTION Pairs of
SELF-INVERSE SEQUENCES RELATED TO A BINOMIAL INVERSE PAIR Yi Wang Department of Applied Mathematics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China (Submitted June 2002) 1 INTRODUCTION Pairs of
±i-iy (j)^> = P"±(-iy (j)#> (2)
 I D E N T I T I E S AND CONGRUENCES INVOLVING H I G H E R - O R D E R EULER-BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND P O L Y N O M I A L S Giiodong Liu Dept. of Mathematics, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong 516015,
I D E N T I T I E S AND CONGRUENCES INVOLVING H I G H E R - O R D E R EULER-BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND P O L Y N O M I A L S Giiodong Liu Dept. of Mathematics, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong 516015,
1. INTRODUCTION. Figure 1: An ellipse with b < 0. are the image of the n th roots of unity under the mapping. n,j ) + (a n + b n ) (2) j=0
 PRODUCTS OF ELLIPTICAL CHORD LENGTHS AND THE FIBONACCI NUMBERS Thomas E. Price Department of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics, The University of Akron, Akron, OH 44325 e-mail: teprice@uakron.edu (Submitted
PRODUCTS OF ELLIPTICAL CHORD LENGTHS AND THE FIBONACCI NUMBERS Thomas E. Price Department of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics, The University of Akron, Akron, OH 44325 e-mail: teprice@uakron.edu (Submitted
#A67 INTEGERS 18 (2018) ON THE NESTED LOCAL POSTAGE STAMP PROBLEM
 #A67 INTEGERS 18 (2018) ON THE NESTED LOCAL POSTAGE STAMP PROBLEM Edgar Federico Elizeche Department of Mathematics, St. Stephen s College, University of Delhi, Delhi 110007, India edgar.federico@elizeche.com
#A67 INTEGERS 18 (2018) ON THE NESTED LOCAL POSTAGE STAMP PROBLEM Edgar Federico Elizeche Department of Mathematics, St. Stephen s College, University of Delhi, Delhi 110007, India edgar.federico@elizeche.com
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY, 4063, or by
ELEMENTARY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS EDITED BY HARRIS KWONG Please submit solutions and problem proposals to Dr Harris Kwong, Department of Mathematical Sciences, SUNY Fredonia, Fredonia, NY, 4063, or by
9 MODULARITY AND GCD PROPERTIES OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS
 #A55 INTEGERS 14 (2014) 9 MODULARITY AND GCD PROPERTIES OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS Rigoberto Flórez 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, The Citadel, Charleston, South Carolina rigo.florez@citadel.edu
#A55 INTEGERS 14 (2014) 9 MODULARITY AND GCD PROPERTIES OF GENERALIZED FIBONACCI NUMBERS Rigoberto Flórez 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, The Citadel, Charleston, South Carolina rigo.florez@citadel.edu
MATRICES AND LINEAR RECURRENCES IN FINITE FIELDS
 Owen J. Brison Departamento de Matemática, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Bloco C6, Piso 2, Campo Grande, 1749-016 LISBOA, PORTUGAL e-mail: brison@ptmat.fc.ul.pt J. Eurico Nogueira Departamento
Owen J. Brison Departamento de Matemática, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Bloco C6, Piso 2, Campo Grande, 1749-016 LISBOA, PORTUGAL e-mail: brison@ptmat.fc.ul.pt J. Eurico Nogueira Departamento
ALGEBRA AND ALGEBRAIC COMPUTING ELEMENTS OF. John D. Lipson. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
 ELEMENTS OF ALGEBRA AND ALGEBRAIC COMPUTING John D. Lipson University of Toronto PRO Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. Redwood City, California Menlo Park, California Reading, Massachusetts Amsterdam
ELEMENTS OF ALGEBRA AND ALGEBRAIC COMPUTING John D. Lipson University of Toronto PRO Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. Redwood City, California Menlo Park, California Reading, Massachusetts Amsterdam
1. INTRODUCTION. n=. A few applications are also presented at the end of the Note. The following Theorem is established in the present Note:
 CONVOLVING THE m-th POWERS OF THE CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS WITH THE GENERAL FIBONACCI SEQUENCE USING CARLITZ S WEIGHTED STIRLING POLYNOMIALS OF THE SECOND KIND N. Gauthier Department of Physics, The Royal
CONVOLVING THE m-th POWERS OF THE CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS WITH THE GENERAL FIBONACCI SEQUENCE USING CARLITZ S WEIGHTED STIRLING POLYNOMIALS OF THE SECOND KIND N. Gauthier Department of Physics, The Royal
Twin primes are pairs of natural numbers (p, p + 2) such that both p and p + 2 are primes.
 SOLUTIONS TO QUIZ - MATH 170 - SUMMER SESSION I (2012) Name: INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The duration of this quiz is 1 hour - from 4:05 p.m. till 5:05 p.m. 2. No calculators, electronic watches, cellphones etc.
SOLUTIONS TO QUIZ - MATH 170 - SUMMER SESSION I (2012) Name: INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The duration of this quiz is 1 hour - from 4:05 p.m. till 5:05 p.m. 2. No calculators, electronic watches, cellphones etc.
Induction. Induction. Induction. Induction. Induction. Induction 2/22/2018
 The principle of mathematical induction is a useful tool for proving that a certain predicate is true for all natural numbers. It cannot be used to discover theorems, but only to prove them. If we have
The principle of mathematical induction is a useful tool for proving that a certain predicate is true for all natural numbers. It cannot be used to discover theorems, but only to prove them. If we have
Existence of Poluet numbers in square form D. Narasimha Murty 1 and Prof. Dr. K. Raja Rama Gandhi 2
 The Bulletin of Society for Mathematical Services and Standards Online: 2014-06-02 ISSN: 2277-8020, Vol. 10, pp 26-30 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/bsmass.10.26 2014 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Existence
The Bulletin of Society for Mathematical Services and Standards Online: 2014-06-02 ISSN: 2277-8020, Vol. 10, pp 26-30 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/bsmass.10.26 2014 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Existence
2301 Assignment 1 Due Friday 19th March, 2 pm
 Show all your work. Justify your solutions. Answers without justification will not receive full marks. Only hand in the problems on page 2. Practice Problems Question 1. Prove that if a b and a 3c then
Show all your work. Justify your solutions. Answers without justification will not receive full marks. Only hand in the problems on page 2. Practice Problems Question 1. Prove that if a b and a 3c then
Order Notation and the Mathematics for Analysis of Algorithms
 Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Order Notation and the Mathematics for Analysis of Algorithms Name: Email: Code: 19704 Always choose the best or most general answer, unless otherwise instructed.
Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Order Notation and the Mathematics for Analysis of Algorithms Name: Email: Code: 19704 Always choose the best or most general answer, unless otherwise instructed.
A CURIOUS PROPERTY OF UNIT FRACTIONS OF THE FORM 1/d WHERE (d, 10) = 1 INTRODUCTION
 A CURIOUS PROPERTY OF UNIT FRACTIONS OF THE FORM 1/d WHERE (d, 10) = 1 BROTHER ALFRED BROUSSEAU l St. Mary's College, California HAROLD ANDERSEN 2 and JEROME POVSE 3 San Carlos High School, San Carlos,
A CURIOUS PROPERTY OF UNIT FRACTIONS OF THE FORM 1/d WHERE (d, 10) = 1 BROTHER ALFRED BROUSSEAU l St. Mary's College, California HAROLD ANDERSEN 2 and JEROME POVSE 3 San Carlos High School, San Carlos,
On sets of integers whose shifted products are powers
 On sets of integers whose shifted products are powers C.L. Stewart 1 Department of Pure Mathematics, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, NL 3G1 Abstract Let N be a positive integer and let
On sets of integers whose shifted products are powers C.L. Stewart 1 Department of Pure Mathematics, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, NL 3G1 Abstract Let N be a positive integer and let
Discrete Mathematics. Spring 2017
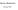 Discrete Mathematics Spring 2017 Previous Lecture Principle of Mathematical Induction Mathematical Induction: Rule of Inference Mathematical Induction: Conjecturing and Proving Mathematical Induction:
Discrete Mathematics Spring 2017 Previous Lecture Principle of Mathematical Induction Mathematical Induction: Rule of Inference Mathematical Induction: Conjecturing and Proving Mathematical Induction:
