Zen and The Art of Grammar Maintenance
|
|
|
- Hector Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LIFO, Université d Orléans 6 June 2008 / TAG+9 Tutorial
2 Outline 1 2 3
3 Factorization and Reuse N N N N V N N V N V V Cl V V Jean mange une pomme Jean la mange la pomme que Jean mange
4 Jean mange une pomme N V N V V N V V V N Canonical ubject Active Verb Form Canonical Object
5 Jean la mange N V Cl V N V V Cl V V V Canonical ubject Clitic Object Active Verb Form
6 La pomme que Jean mange N N N N N V N V V N N V V Relative Object Canonical ubject Active Verb Form
7 Jean qui mange la pomme N N N N V N N V V N V V V N Relative ubject Active Verb Form Canonical Object
8 Jean qui la mange N N N N V N V V Cl V N V Cl V V Relative ubject Clitic Object Active Verb Form
9 Outline 1 2 3
10 ubject ubjectcanonical N V N N ubjectrelative N V ubject ubjectcanonical ubjectrelative
11 Object ObjectCanonical V V N ObjectClitic Cl N V N ObjectRelative N Object ObjectCanonical ObjectClitic ObjectRelative
12 Transitive Active Verb VerbActiveMorph V VerbActiveTransitive ubject VerbActiveMorph Object V
13 Metagrammars as DCGs a metagrammar is a DCG terminals are tree descriptions a metagrammar is the grammar of a grammar
14 Metagrammars as DCGs a metagrammar is a DCG terminals are tree descriptions a metagrammar is the grammar of a grammar
15 Model-Theoretic View et of tree descriptions = Metagrammar Lexical entry = et of tree descriptions
16 Operational View a metagrammar is a logic program its execution accumulates tree descriptions which are then processed by a solver resulting in the production of a lexical entry backtrack to obtain the rest of the lexicon
17 Outline 1 2 3
18 Type definitions type CAT={n,v,p} type PER=[1..3] type FLEX=[num:NUMBER, gen:gender, pers:per]
19 Property definitions property extraction : bool
20 Property definitions property extraction : bool {extra = +} extra extraction = +
21 Feature definitions feature num : NUMBER
22 Class definitions class C1 import C2[] export?x?y declare?x?y!z { tatement }
23 Restricted imports class C1 import C2[] as [?X1,...,?Xn] export?x?y declare?x?y!z { tatement }
24 Renamings class C1 import C2[] as [?X1=?Y1,...,?Xn] export?x=?u?y declare?x?y!z { tatement }
25 tatements ::= 1 ; E 1 = E 2 Class[E 1,..., E n ] Dim {... } = [f = E,...]
26 Expressions E ::=?X!X Atom Int Atom}?X = [f 1 = E 1,..., f n = E n ] E 1.E 2 E(E 1,..., E n ) E 1 E 2 (E)
27 Dimension-specific description languages Dim {... } tree descriptions hole semantics AVM, (semi-)lattices There are currently 3 built-in dimensions: <syn> <sem> <dyn>
28 Tree Description Language <syn> { yn } yn ::= yn; yn yn yn node?x (p = E,...) [f = E,...] E -> E E -> + E E -> E E >> E E >> + E E >> E E = E E<E 1,..., E n >
29 Alternative yntax dominance node { node } node {...+ node } node {... node } precedence node node node,,,+ node node,,, node
30 Flat emantics Description Language <sem> { em } em ::= em; em em em Var : E(E,..., E) Var : E(E,..., E) Var << Var
31 Mutual Exclusion ets mutex UBJ-INV mutex UBJ-INV += CanonicalObject mutex UBJ-INV += InvertedNominalubject 2 classes in the same mutex cannot both be used in the same derivation
32 Principles
Grammar Implementation: XMG
 Grammar Implementation: XMG XMG Tutorial Laura Kallmeyer & Benjamin Burkhardt (Slides partly by Timm Lichte and Simon Petitjean) HHU Düsseldorf WS 2017/2018 1 / 20 Defining abstractions Classes allow to:
Grammar Implementation: XMG XMG Tutorial Laura Kallmeyer & Benjamin Burkhardt (Slides partly by Timm Lichte and Simon Petitjean) HHU Düsseldorf WS 2017/2018 1 / 20 Defining abstractions Classes allow to:
Dynamics, Dependency Grammar and Incremental Interpretation
 Dynamic, Dependency Grammar and Incremental Interpretation David Milward Iri Perkmann 11.05.2016 Lexicalied Dependency Grammar: provide (flat) tree-tructure analye of entence. Dynamic Dependency Grammar:
Dynamic, Dependency Grammar and Incremental Interpretation David Milward Iri Perkmann 11.05.2016 Lexicalied Dependency Grammar: provide (flat) tree-tructure analye of entence. Dynamic Dependency Grammar:
Unterspezifikation in der Semantik Scope Semantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars
 in der emantik cope emantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2011/2012 LTAG: The Formalism (1) Tree Adjoining Grammars (TAG): Tree-rewriting
in der emantik cope emantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2011/2012 LTAG: The Formalism (1) Tree Adjoining Grammars (TAG): Tree-rewriting
Tree Adjoining Grammars
 Tree Adjoining Grammars Feature Structure Based TAG Laura Kallmeyer & Benjamin Burkhardt HHU Düsseldorf WS 2017/2018 1 / 20 Outline 1 Why feature structures? 2 Basics of feature structure logic 3 Feature
Tree Adjoining Grammars Feature Structure Based TAG Laura Kallmeyer & Benjamin Burkhardt HHU Düsseldorf WS 2017/2018 1 / 20 Outline 1 Why feature structures? 2 Basics of feature structure logic 3 Feature
Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features
 Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features Denys Duchier Thi-Bich-Hanh Dao firstname.lastname@univ-orleans.fr Yannick Parmentier Abstract In this paper, we present a model-theoretic description of
Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features Denys Duchier Thi-Bich-Hanh Dao firstname.lastname@univ-orleans.fr Yannick Parmentier Abstract In this paper, we present a model-theoretic description of
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars
 Parsing with Context-Free Grammars Berlin Chen 2005 References: 1. Natural Language Understanding, chapter 3 (3.1~3.4, 3.6) 2. Speech and Language Processing, chapters 9, 10 NLP-Berlin Chen 1 Grammars
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars Berlin Chen 2005 References: 1. Natural Language Understanding, chapter 3 (3.1~3.4, 3.6) 2. Speech and Language Processing, chapters 9, 10 NLP-Berlin Chen 1 Grammars
Conflict Removal. Less Than, Equals ( <= ) Conflict
 Conflict Removal As you have observed in a recent example, not all context free grammars are simple precedence grammars. You have also seen that a context free grammar that is not a simple precedence grammar
Conflict Removal As you have observed in a recent example, not all context free grammars are simple precedence grammars. You have also seen that a context free grammar that is not a simple precedence grammar
Bringing machine learning & compositional semantics together: central concepts
 Bringing machine learning & compositional semantics together: central concepts https://githubcom/cgpotts/annualreview-complearning Chris Potts Stanford Linguistics CS 244U: Natural language understanding
Bringing machine learning & compositional semantics together: central concepts https://githubcom/cgpotts/annualreview-complearning Chris Potts Stanford Linguistics CS 244U: Natural language understanding
A Constructor-Based Reachability Logic for Rewrite Theories
 A Constructor-Based Reachability Logic for Rewrite Theories Stephen Skeirik, Andrei Stefanescu, Jose Meseguer October 10th, 2017 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Reachability Logic Semantics 3 The Invariant Paradox
A Constructor-Based Reachability Logic for Rewrite Theories Stephen Skeirik, Andrei Stefanescu, Jose Meseguer October 10th, 2017 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Reachability Logic Semantics 3 The Invariant Paradox
A new semantics for logic programs capturing the stable model semantics: the extension semantics
 A new semantics for logic programs capturing the stable model semantics: the extension semantics Belaïd Benhamou and Pierre Siegel Université Aix-Marseille, CMI Laboratoire des Sciences de L Information
A new semantics for logic programs capturing the stable model semantics: the extension semantics Belaïd Benhamou and Pierre Siegel Université Aix-Marseille, CMI Laboratoire des Sciences de L Information
Semantics and Generative Grammar. Expanding Our Formalism, Part 1 1
 Expanding Our Formalism, Part 1 1 1. Review of Our System Thus Far Thus far, we ve built a system that can interpret a very narrow range of English structures: sentences whose subjects are proper names,
Expanding Our Formalism, Part 1 1 1. Review of Our System Thus Far Thus far, we ve built a system that can interpret a very narrow range of English structures: sentences whose subjects are proper names,
Proseminar on Semantic Theory Fall 2010 Ling 720. Remko Scha (1981/1984): Distributive, Collective and Cumulative Quantification
 1. Introduction Remko Scha (1981/1984): Distributive, Collective and Cumulative Quantification (1) The Importance of Scha (1981/1984) The first modern work on plurals (Landman 2000) There are many ideas
1. Introduction Remko Scha (1981/1984): Distributive, Collective and Cumulative Quantification (1) The Importance of Scha (1981/1984) The first modern work on plurals (Landman 2000) There are many ideas
Predicate Logic. Xinyu Feng 09/26/2011. University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) 09/26/2011 Overview Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic?
University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) 09/26/2011 Overview Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic?
Principles of Program Analysis: A Sampler of Approaches
 Principles of Program Analysis: A Sampler of Approaches Transparencies based on Chapter 1 of the book: Flemming Nielson, Hanne Riis Nielson and Chris Hankin: Principles of Program Analysis Springer Verlag
Principles of Program Analysis: A Sampler of Approaches Transparencies based on Chapter 1 of the book: Flemming Nielson, Hanne Riis Nielson and Chris Hankin: Principles of Program Analysis Springer Verlag
Introduction to Semantics. The Formalization of Meaning 1
 The Formalization of Meaning 1 1. Obtaining a System That Derives Truth Conditions (1) The Goal of Our Enterprise To develop a system that, for every sentence S of English, derives the truth-conditions
The Formalization of Meaning 1 1. Obtaining a System That Derives Truth Conditions (1) The Goal of Our Enterprise To develop a system that, for every sentence S of English, derives the truth-conditions
Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis
 Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Logic in Automatic Verification
 Logic in Automatic Verification Javier Esparza Sofware Reliability and Security Group Institute for Formal Methods in Computer Science University of Stuttgart Many thanks to Abdelwaheb Ayari, David Basin,
Logic in Automatic Verification Javier Esparza Sofware Reliability and Security Group Institute for Formal Methods in Computer Science University of Stuttgart Many thanks to Abdelwaheb Ayari, David Basin,
Predicate Logic. x. x + 0 = x. Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example. Why discuss predicate logic?
 Predicate Logic Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic? It is an example of a simple language It has simple denotational
Predicate Logic Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic? It is an example of a simple language It has simple denotational
Top Down and Bottom Up Composition. 1 Notes on Notation and Terminology. 2 Top-down and Bottom-Up Composition. Two senses of functional application
 Elizabeth Coppock Compositional Semantics coppock@phil.hhu.de Heinrich Heine University Wed. ovember 30th, 2011 Winter Semester 2011/12 Time: 14:30 16:00 Room: 25.22-U1.72 Top Down and Bottom Up Composition
Elizabeth Coppock Compositional Semantics coppock@phil.hhu.de Heinrich Heine University Wed. ovember 30th, 2011 Winter Semester 2011/12 Time: 14:30 16:00 Room: 25.22-U1.72 Top Down and Bottom Up Composition
Parsing Algorithms. CS 4447/CS Stephen Watt University of Western Ontario
 Parsing Algorithms CS 4447/CS 9545 -- Stephen Watt University of Western Ontario The Big Picture Develop parsers based on grammars Figure out properties of the grammars Make tables that drive parsing engines
Parsing Algorithms CS 4447/CS 9545 -- Stephen Watt University of Western Ontario The Big Picture Develop parsers based on grammars Figure out properties of the grammars Make tables that drive parsing engines
Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7. Wed, Feb 18, 2009
 The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
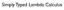 Simply Typed Lambda Calculus Language (ver1) Lambda calculus with boolean values t ::= x variable x : T.t abstraction tt application true false boolean values if ttt conditional expression Values v ::=
Simply Typed Lambda Calculus Language (ver1) Lambda calculus with boolean values t ::= x variable x : T.t abstraction tt application true false boolean values if ttt conditional expression Values v ::=
Natural Language Processing : Probabilistic Context Free Grammars. Updated 5/09
 Natural Language Processing : Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Updated 5/09 Motivation N-gram models and HMM Tagging only allowed us to process sentences linearly. However, even simple sentences require
Natural Language Processing : Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Updated 5/09 Motivation N-gram models and HMM Tagging only allowed us to process sentences linearly. However, even simple sentences require
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Top-Down Parsing, Part II
 op-down Parsing, Part II Announcements Programming Project 1 due Friday, 11:59PM Office hours every day until then. ubmission instructions will be emailed out tonight. Where We Are ource Code Lexical Analysis
op-down Parsing, Part II Announcements Programming Project 1 due Friday, 11:59PM Office hours every day until then. ubmission instructions will be emailed out tonight. Where We Are ource Code Lexical Analysis
Alessandro Mazzei MASTER DI SCIENZE COGNITIVE GENOVA 2005
 Alessandro Mazzei Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Torino MATER DI CIENZE COGNITIVE GENOVA 2005 04-11-05 Natural Language Grammars and Parsing Natural Language yntax Paolo ama Francesca yntactic
Alessandro Mazzei Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Torino MATER DI CIENZE COGNITIVE GENOVA 2005 04-11-05 Natural Language Grammars and Parsing Natural Language yntax Paolo ama Francesca yntactic
Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics
 Chair of Software Engineering Trusted Components Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics Reading assignment for next week Ariane paper and response (see course page) Axiomatic semantics
Chair of Software Engineering Trusted Components Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics Reading assignment for next week Ariane paper and response (see course page) Axiomatic semantics
On the Correctness of the Krivine Machine
 On the Correctness of the Krivine Machine Mitchell Wand Northeastern University 2003-10-03 15:55:00 wand October 3, 2003 Abstract We provide a short proof of the correctness of the Krivine machine by showing
On the Correctness of the Krivine Machine Mitchell Wand Northeastern University 2003-10-03 15:55:00 wand October 3, 2003 Abstract We provide a short proof of the correctness of the Krivine machine by showing
Multiword Expression Identification with Tree Substitution Grammars
 Multiword Expression Identification with Tree Substitution Grammars Spence Green, Marie-Catherine de Marneffe, John Bauer, and Christopher D. Manning Stanford University EMNLP 2011 Main Idea Use syntactic
Multiword Expression Identification with Tree Substitution Grammars Spence Green, Marie-Catherine de Marneffe, John Bauer, and Christopher D. Manning Stanford University EMNLP 2011 Main Idea Use syntactic
Roy L. Crole. Operational Semantics Abstract Machines and Correctness. University of Leicester, UK
 Midlands Graduate School, University of Birmingham, April 2008 1 Operational Semantics Abstract Machines and Correctness Roy L. Crole University of Leicester, UK Midlands Graduate School, University of
Midlands Graduate School, University of Birmingham, April 2008 1 Operational Semantics Abstract Machines and Correctness Roy L. Crole University of Leicester, UK Midlands Graduate School, University of
Decidability of SHI with transitive closure of roles
 1/20 Decidability of SHI with transitive closure of roles Chan LE DUC INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes - LIG 2/20 Example : Transitive Closure in Concept Axioms Devices have as their direct part a battery :
1/20 Decidability of SHI with transitive closure of roles Chan LE DUC INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes - LIG 2/20 Example : Transitive Closure in Concept Axioms Devices have as their direct part a battery :
Verification Using Temporal Logic
 CMSC 630 February 25, 2015 1 Verification Using Temporal Logic Sources: E.M. Clarke, O. Grumberg and D. Peled. Model Checking. MIT Press, Cambridge, 2000. E.A. Emerson. Temporal and Modal Logic. Chapter
CMSC 630 February 25, 2015 1 Verification Using Temporal Logic Sources: E.M. Clarke, O. Grumberg and D. Peled. Model Checking. MIT Press, Cambridge, 2000. E.A. Emerson. Temporal and Modal Logic. Chapter
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics Yi Li Software School Fudan University March 13, 2017 Yi Li (Fudan University) Discrete Mathematics March 13, 2017 1 / 1 Review of Lattice Ideal Special Lattice Boolean Algebra Yi
Discrete Mathematics Yi Li Software School Fudan University March 13, 2017 Yi Li (Fudan University) Discrete Mathematics March 13, 2017 1 / 1 Review of Lattice Ideal Special Lattice Boolean Algebra Yi
Modular Grammar Design with Typed Parametric Principles
 1 Modular Grammar Design with Typed Parametric Principles 1.1 Introduction Extensible Dependency Grammar (xdg) (Debusmann et al., 2004) is a general framework for dependency grammar, with multiple levels
1 Modular Grammar Design with Typed Parametric Principles 1.1 Introduction Extensible Dependency Grammar (xdg) (Debusmann et al., 2004) is a general framework for dependency grammar, with multiple levels
Predicate Logic. Xinyu Feng 11/20/2013. University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) 11/20/2013 Overview Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic?
University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) 11/20/2013 Overview Predicate logic over integer expressions: a language of logical assertions, for example x. x + 0 = x Why discuss predicate logic?
Floyd-Hoare Style Program Verification
 Floyd-Hoare Style Program Verification Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 9 Feb 2017 Outline of this talk 1 Overview 2 Hoare Triples 3
Floyd-Hoare Style Program Verification Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 9 Feb 2017 Outline of this talk 1 Overview 2 Hoare Triples 3
NICTA Advanced Course. Theorem Proving Principles, Techniques, Applications
 NICTA Advanced Course Theorem Proving Principles, Techniques, Applications λ 1 CONTENT Intro & motivation, getting started with Isabelle Foundations & Principles Lambda Calculus Higher Order Logic, natural
NICTA Advanced Course Theorem Proving Principles, Techniques, Applications λ 1 CONTENT Intro & motivation, getting started with Isabelle Foundations & Principles Lambda Calculus Higher Order Logic, natural
Spring 2016 Program Analysis and Verification. Lecture 3: Axiomatic Semantics I. Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University
 Spring 2016 Program Analysis and Verification Lecture 3: Axiomatic Semantics I Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University Warm-up exercises 1. Define program state: 2. Define structural semantics configurations:
Spring 2016 Program Analysis and Verification Lecture 3: Axiomatic Semantics I Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University Warm-up exercises 1. Define program state: 2. Define structural semantics configurations:
Outline. Learning. Overview Details Example Lexicon learning Supervision signals
 Outline Learning Overview Details Example Lexicon learning Supervision signals 0 Outline Learning Overview Details Example Lexicon learning Supervision signals 1 Supervision in syntactic parsing Input:
Outline Learning Overview Details Example Lexicon learning Supervision signals 0 Outline Learning Overview Details Example Lexicon learning Supervision signals 1 Supervision in syntactic parsing Input:
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
The Complexity of First-Order Extensible Dependency Grammar
 The Complexity of First-Order Extensible Dependency Grammar Ralph Debusmann Programming Systems Lab Universität des Saarlandes Postfach 15 11 50 66041 Saarbrücken, Germany rade@ps.uni-sb.de Abstract We
The Complexity of First-Order Extensible Dependency Grammar Ralph Debusmann Programming Systems Lab Universität des Saarlandes Postfach 15 11 50 66041 Saarbrücken, Germany rade@ps.uni-sb.de Abstract We
CoTAGs and ACGs. Gregory M. Kobele 1 and Jens Michaelis 2
 CoTAGs and ACGs Gregory M. Kobele 1 and Jens Michaelis 2 1 University of Chicago Chicago Illinois USA 2 Bielefeld University Bielefeld Germany Abstract. Our main concern is to provide a complete picture
CoTAGs and ACGs Gregory M. Kobele 1 and Jens Michaelis 2 1 University of Chicago Chicago Illinois USA 2 Bielefeld University Bielefeld Germany Abstract. Our main concern is to provide a complete picture
Chapter 6: Computation Tree Logic
 Chapter 6: Computation Tree Logic Prof. Ali Movaghar Verification of Reactive Systems Outline We introduce Computation Tree Logic (CTL), a branching temporal logic for specifying system properties. A comparison
Chapter 6: Computation Tree Logic Prof. Ali Movaghar Verification of Reactive Systems Outline We introduce Computation Tree Logic (CTL), a branching temporal logic for specifying system properties. A comparison
Parsing -3. A View During TD Parsing
 Parsing -3 Deterministic table-driven parsing techniques Pictorial view of TD and BU parsing BU (shift-reduce) Parsing Handle, viable prefix, items, closures, goto s LR(k): SLR(1), LR(1) Problems with
Parsing -3 Deterministic table-driven parsing techniques Pictorial view of TD and BU parsing BU (shift-reduce) Parsing Handle, viable prefix, items, closures, goto s LR(k): SLR(1), LR(1) Problems with
Design of Embedded Systems: Models, Validation and Synthesis (EE 249) Lecture 9
 Design of Embedded Systems: Models, Validation and Synthesis (EE 249) Lecture 9 Prof. Dr. Reinhard von Hanxleden Christian-Albrechts Universität Kiel Department of Computer Science Real-Time Systems and
Design of Embedded Systems: Models, Validation and Synthesis (EE 249) Lecture 9 Prof. Dr. Reinhard von Hanxleden Christian-Albrechts Universität Kiel Department of Computer Science Real-Time Systems and
Model Checking with CTL. Presented by Jason Simas
 Model Checking with CTL Presented by Jason Simas Model Checking with CTL Based Upon: Logic in Computer Science. Huth and Ryan. 2000. (148-215) Model Checking. Clarke, Grumberg and Peled. 1999. (1-26) Content
Model Checking with CTL Presented by Jason Simas Model Checking with CTL Based Upon: Logic in Computer Science. Huth and Ryan. 2000. (148-215) Model Checking. Clarke, Grumberg and Peled. 1999. (1-26) Content
Parsing with CFGs L445 / L545 / B659. Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring Parsing with CFGs. Direction of processing
 L445 / L545 / B659 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2016 1 / 46 : Overview Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the
L445 / L545 / B659 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2016 1 / 46 : Overview Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the
Parsing with CFGs. Direction of processing. Top-down. Bottom-up. Left-corner parsing. Chart parsing CYK. Earley 1 / 46.
 : Overview L545 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2013 Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the problem as searching
: Overview L545 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2013 Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the problem as searching
Suppose h maps number and variables to ɛ, and opening parenthesis to 0 and closing parenthesis
 1 Introduction Parenthesis Matching Problem Describe the set of arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis. Arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis cannot be described
1 Introduction Parenthesis Matching Problem Describe the set of arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis. Arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis cannot be described
Verifying Java-KE Programs
 Verifying Java-KE Programs A Small Case Study Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter July 22, 2014 Abstract This report investigates the specification and verification of a simple list class. The example was designed such
Verifying Java-KE Programs A Small Case Study Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter July 22, 2014 Abstract This report investigates the specification and verification of a simple list class. The example was designed such
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation (Feodor F. Dragan) Department of Computer Science Kent State University Spring, 2018 Theory of Computation, Feodor F. Dragan, Kent State University 1 Before we go into details, what
Theory of Computation (Feodor F. Dragan) Department of Computer Science Kent State University Spring, 2018 Theory of Computation, Feodor F. Dragan, Kent State University 1 Before we go into details, what
Introduction to Semantic Parsing with CCG
 Introduction to Semantic Parsing with CCG Kilian Evang Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 2018-04-24 Table of contents 1 Introduction to CCG Categorial Grammar (CG) Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG)
Introduction to Semantic Parsing with CCG Kilian Evang Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 2018-04-24 Table of contents 1 Introduction to CCG Categorial Grammar (CG) Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG)
INF Models of concurrency
 Monitors INF4140 - Models of concurrency Monitors, lecture 4 Fall 2017 27. September 2017 2 / 49 Overview Concurrent execution of different processes Communication by shared variables Processes may interfere
Monitors INF4140 - Models of concurrency Monitors, lecture 4 Fall 2017 27. September 2017 2 / 49 Overview Concurrent execution of different processes Communication by shared variables Processes may interfere
Functional Database Query Languages as. Typed Lambda Calculi of Fixed Order. Gerd G. Hillebrand and Paris C. Kanellakis
 Functional Database Query Languages as Typed Lambda Calculi of Fixed Order Gerd G. Hillebrand and Paris C. Kanellakis Department of Computer Science Brown University Providence, Rhode Island 02912 CS-94-26
Functional Database Query Languages as Typed Lambda Calculi of Fixed Order Gerd G. Hillebrand and Paris C. Kanellakis Department of Computer Science Brown University Providence, Rhode Island 02912 CS-94-26
THEORY OF COMPILATION
 Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture
 Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture Pedro Domingos Dept. Computer Science & Eng. University of Washington Joint work with Hoifung Poon 1 Graphical Models: Challenges Bayesian Network Markov Network
Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture Pedro Domingos Dept. Computer Science & Eng. University of Washington Joint work with Hoifung Poon 1 Graphical Models: Challenges Bayesian Network Markov Network
Automata-Theoretic Model Checking of Reactive Systems
 Automata-Theoretic Model Checking of Reactive Systems Radu Iosif Verimag/CNRS (Grenoble, France) Thanks to Tom Henzinger (IST, Austria), Barbara Jobstmann (CNRS, Grenoble) and Doron Peled (Bar-Ilan University,
Automata-Theoretic Model Checking of Reactive Systems Radu Iosif Verimag/CNRS (Grenoble, France) Thanks to Tom Henzinger (IST, Austria), Barbara Jobstmann (CNRS, Grenoble) and Doron Peled (Bar-Ilan University,
Introduction to ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition)
 Introduction to ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition) Jon Eyolfson University of Waterloo September 27 - October 1, 2010 Outline Introduction Usage Example Demonstration Conclusion Jon Eyolfson
Introduction to ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition) Jon Eyolfson University of Waterloo September 27 - October 1, 2010 Outline Introduction Usage Example Demonstration Conclusion Jon Eyolfson
Axiomatic Semantics. Semantics of Programming Languages course. Joosep Rõõmusaare
 Axiomatic Semantics Semantics of Programming Languages course Joosep Rõõmusaare 2014 Direct Proofs of Program Correctness Partial correctness properties are properties expressing that if a given program
Axiomatic Semantics Semantics of Programming Languages course Joosep Rõõmusaare 2014 Direct Proofs of Program Correctness Partial correctness properties are properties expressing that if a given program
Notes on Inductive Sets and Induction
 Notes on Inductive Sets and Induction Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT21 Ana Bove, March 15th 2018 Contents 1 Induction over the Natural Numbers 2 1.1 Mathematical (Simple) Induction........................
Notes on Inductive Sets and Induction Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT21 Ana Bove, March 15th 2018 Contents 1 Induction over the Natural Numbers 2 1.1 Mathematical (Simple) Induction........................
Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung
 Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung Parsing with Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Phrase-Structure Parse Trees Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Parsing with PCFG Other
Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung Parsing with Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Phrase-Structure Parse Trees Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Parsing with PCFG Other
Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung
 Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung Parsing with Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Phrase-Structure Parse Trees Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Parsing with PCFG Other
Maschinelle Sprachverarbeitung Parsing with Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Phrase-Structure Parse Trees Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Parsing with PCFG Other
Introduction to Semantics. Common Nouns and Adjectives in Predicate Position 1
 Common Nouns and Adjectives in Predicate Position 1 (1) The Lexicon of Our System at Present a. Proper Names: [[ Barack ]] = Barack b. Intransitive Verbs: [[ smokes ]] = [ λx : x D e. IF x smokes THEN
Common Nouns and Adjectives in Predicate Position 1 (1) The Lexicon of Our System at Present a. Proper Names: [[ Barack ]] = Barack b. Intransitive Verbs: [[ smokes ]] = [ λx : x D e. IF x smokes THEN
Grammar and Feature Unification
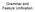 Grammar and Feature Unification Problems with CF Phrase Structure Grammars Difficult to capture dependencies between constituents the boy runs the boys run * the boy run * the boys runs Problems with CF
Grammar and Feature Unification Problems with CF Phrase Structure Grammars Difficult to capture dependencies between constituents the boy runs the boys run * the boy run * the boys runs Problems with CF
Context-free grammars for natural languages
 Context-free grammars Basic definitions Context-free grammars for natural languages Context-free grammars can be used for a variety of syntactic constructions, including some non-trivial phenomena such
Context-free grammars Basic definitions Context-free grammars for natural languages Context-free grammars can be used for a variety of syntactic constructions, including some non-trivial phenomena such
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web. Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012
 CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
Heuristics for Efficient SAT Solving. As implemented in GRASP, Chaff and GSAT.
 Heuristics for Efficient SAT Solving As implemented in GRASP, Chaff and GSAT. Formulation of famous problems as SAT: k-coloring (1/2) The K-Coloring problem: Given an undirected graph G(V,E) and a natural
Heuristics for Efficient SAT Solving As implemented in GRASP, Chaff and GSAT. Formulation of famous problems as SAT: k-coloring (1/2) The K-Coloring problem: Given an undirected graph G(V,E) and a natural
Temporal Logic of Actions
 Advanced Topics in Distributed Computing Dominik Grewe Saarland University March 20, 2008 Outline Basic Concepts Transition Systems Temporal Operators Fairness Introduction Definitions Example TLC - A
Advanced Topics in Distributed Computing Dominik Grewe Saarland University March 20, 2008 Outline Basic Concepts Transition Systems Temporal Operators Fairness Introduction Definitions Example TLC - A
Temporal Logic Model Checking
 18 Feb, 2009 Thomas Wahl, Oxford University Temporal Logic Model Checking 1 Temporal Logic Model Checking Thomas Wahl Computing Laboratory, Oxford University 18 Feb, 2009 Thomas Wahl, Oxford University
18 Feb, 2009 Thomas Wahl, Oxford University Temporal Logic Model Checking 1 Temporal Logic Model Checking Thomas Wahl Computing Laboratory, Oxford University 18 Feb, 2009 Thomas Wahl, Oxford University
EDA045F: Program Analysis LECTURE 10: TYPES 1. Christoph Reichenbach
 EDA045F: Program Analysis LECTURE 10: TYPES 1 Christoph Reichenbach In the last lecture... Performance Counters Challenges in Dynamic Performance Analysis Taint Analysis Binary Instrumentation 2 / 44 Types
EDA045F: Program Analysis LECTURE 10: TYPES 1 Christoph Reichenbach In the last lecture... Performance Counters Challenges in Dynamic Performance Analysis Taint Analysis Binary Instrumentation 2 / 44 Types
Information Flow Inference for ML
 POPL 02 INRIA Rocquencourt Projet Cristal Francois.Pottier@inria.fr http://cristal.inria.fr/~fpottier/ Vincent.Simonet@inria.fr http://cristal.inria.fr/~simonet/ Information flow analysis account number
POPL 02 INRIA Rocquencourt Projet Cristal Francois.Pottier@inria.fr http://cristal.inria.fr/~fpottier/ Vincent.Simonet@inria.fr http://cristal.inria.fr/~simonet/ Information flow analysis account number
Statistical Processing of Natural Language
 Statistical Processing of Natural Language and DMKM - Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya and 1 2 and 3 1. Observation Probability 2. Best State Sequence 3. Parameter Estimation 4 Graphical and Generative
Statistical Processing of Natural Language and DMKM - Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya and 1 2 and 3 1. Observation Probability 2. Best State Sequence 3. Parameter Estimation 4 Graphical and Generative
A brief introduction to Logic. (slides from
 A brief introduction to Logic (slides from http://www.decision-procedures.org/) 1 A Brief Introduction to Logic - Outline Propositional Logic :Syntax Propositional Logic :Semantics Satisfiability and validity
A brief introduction to Logic (slides from http://www.decision-procedures.org/) 1 A Brief Introduction to Logic - Outline Propositional Logic :Syntax Propositional Logic :Semantics Satisfiability and validity
A Probabilistic Forest-to-String Model for Language Generation from Typed Lambda Calculus Expressions
 A Probabilistic Forest-to-String Model for Language Generation from Typed Lambda Calculus Expressions Wei Lu and Hwee Tou Ng National University of Singapore 1/26 The Task (Logical Form) λx 0.state(x 0
A Probabilistic Forest-to-String Model for Language Generation from Typed Lambda Calculus Expressions Wei Lu and Hwee Tou Ng National University of Singapore 1/26 The Task (Logical Form) λx 0.state(x 0
Axiomatic Semantics. Stansifer Ch 2.4, Ch. 9 Winskel Ch.6 Slonneger and Kurtz Ch. 11 CSE
 Axiomatic Semantics Stansifer Ch 2.4, Ch. 9 Winskel Ch.6 Slonneger and Kurtz Ch. 11 CSE 6341 1 Outline Introduction What are axiomatic semantics? First-order logic & assertions about states Results (triples)
Axiomatic Semantics Stansifer Ch 2.4, Ch. 9 Winskel Ch.6 Slonneger and Kurtz Ch. 11 CSE 6341 1 Outline Introduction What are axiomatic semantics? First-order logic & assertions about states Results (triples)
EXAM. CS331 Compiler Design Spring Please read all instructions, including these, carefully
 EXAM Please read all instructions, including these, carefully There are 7 questions on the exam, with multiple parts. You have 3 hours to work on the exam. The exam is open book, open notes. Please write
EXAM Please read all instructions, including these, carefully There are 7 questions on the exam, with multiple parts. You have 3 hours to work on the exam. The exam is open book, open notes. Please write
Modal and Temporal Logics
 Modal and Temporal Logics Colin Stirling School of Informatics University of Edinburgh July 23, 2003 Why modal and temporal logics? 1 Computational System Modal and temporal logics Operational semantics
Modal and Temporal Logics Colin Stirling School of Informatics University of Edinburgh July 23, 2003 Why modal and temporal logics? 1 Computational System Modal and temporal logics Operational semantics
Intensionality. 1. Intensional Propositional Logic (IntPL).
 Ling255: Sem and CogSci Maribel Romero April 5, 2005 1. Intensional Propositional Logic (IntPL). Intensionality Intensional PL adds some operators O to our standard PL. The crucial property of these operators
Ling255: Sem and CogSci Maribel Romero April 5, 2005 1. Intensional Propositional Logic (IntPL). Intensionality Intensional PL adds some operators O to our standard PL. The crucial property of these operators
Equational Logic and Term Rewriting: Lecture I
 Why so many logics? You all know classical propositional logic. Why would we want anything more? Equational Logic and Term Rewriting: Lecture I One reason is that we might want to change some basic logical
Why so many logics? You all know classical propositional logic. Why would we want anything more? Equational Logic and Term Rewriting: Lecture I One reason is that we might want to change some basic logical
CAS LX 523 Syntax II Spring 2001 March 13, (1) A qp. Kayne, Richard (1995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
 CAS LX 52 Syntax II Spring 200 March, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 7: Antisymmetry Kayne, Richard (995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Koopman, Hilda (2000). The spec-head configuration.
CAS LX 52 Syntax II Spring 200 March, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 7: Antisymmetry Kayne, Richard (995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Koopman, Hilda (2000). The spec-head configuration.
A Global Constraint for Parallelizing the Execution of Task Sets in Non-Preemptive Scheduling
 A Global Constraint for Parallelizing the Execution of Task Sets in Non-Preemptive Scheduling 1 Introduction Michael Marte 1 Institut für Informatik, Universität München Oettingenstr. 67, 80538 München,
A Global Constraint for Parallelizing the Execution of Task Sets in Non-Preemptive Scheduling 1 Introduction Michael Marte 1 Institut für Informatik, Universität München Oettingenstr. 67, 80538 München,
Gecco 2007 Tutorial / Grammatical Evolution
 Gecco 2007 Grammatical Evolution Tutorial Conor Ryan Biocomputing and Developmental Systems Group Department of Computer Science and Information Systems University of Limerick Copyright is held by the
Gecco 2007 Grammatical Evolution Tutorial Conor Ryan Biocomputing and Developmental Systems Group Department of Computer Science and Information Systems University of Limerick Copyright is held by the
Model Answers to Problem Set 2
 Dr. Elizabeth Coppock Compositional emantics coppock@phil.hhu.de Heinrich Heine University Nov 2nd, 2011 Winter emester 2011/12 Model Answers to Problem et 2 Reading: Dowty, Wall and Peters (1981), pp.
Dr. Elizabeth Coppock Compositional emantics coppock@phil.hhu.de Heinrich Heine University Nov 2nd, 2011 Winter emester 2011/12 Model Answers to Problem et 2 Reading: Dowty, Wall and Peters (1981), pp.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Pushdown Automata Parsing
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
Computer Science 160 Translation of Programming Languages
 Computer Science 160 Translation of Programming Languages Instructor: Christopher Kruegel Top-Down Parsing Top-down Parsing Algorithm Construct the root node of the parse tree, label it with the start
Computer Science 160 Translation of Programming Languages Instructor: Christopher Kruegel Top-Down Parsing Top-down Parsing Algorithm Construct the root node of the parse tree, label it with the start
Axiomatic Semantics. Operational semantics. Good for. Not good for automatic reasoning about programs
 Review Operational semantics relatively l simple many flavors (small vs. big) not compositional (rule for while) Good for describing language implementation reasoning about properties of the language eg.
Review Operational semantics relatively l simple many flavors (small vs. big) not compositional (rule for while) Good for describing language implementation reasoning about properties of the language eg.
Parsing. Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford)
 Parsing Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford) S N VP V NP D N John hit the ball Levels of analysis Level Morphology/Lexical POS (morpho-synactic), WSD Elements
Parsing Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford) S N VP V NP D N John hit the ball Levels of analysis Level Morphology/Lexical POS (morpho-synactic), WSD Elements
Synchronous Grammars
 ynchronous Grammars ynchronous grammars are a way of simultaneously generating pairs of recursively related strings ynchronous grammar w wʹ ynchronous grammars were originally invented for programming
ynchronous Grammars ynchronous grammars are a way of simultaneously generating pairs of recursively related strings ynchronous grammar w wʹ ynchronous grammars were originally invented for programming
Chapter 5. Finite Automata
 Chapter 5 Finite Automata 5.1 Finite State Automata Capable of recognizing numerous symbol patterns, the class of regular languages Suitable for pattern-recognition type applications, such as the lexical
Chapter 5 Finite Automata 5.1 Finite State Automata Capable of recognizing numerous symbol patterns, the class of regular languages Suitable for pattern-recognition type applications, such as the lexical
Semantic Solutions to Program Analysis Problems
 Semantic Solutions to Program Analysis Problems Sam Tobin-Hochstadt and David Van Horn PLDI FIT 2011 A talk in three parts. 1. A provocative claim. (The thought) 2. A idea about modular program analysis.
Semantic Solutions to Program Analysis Problems Sam Tobin-Hochstadt and David Van Horn PLDI FIT 2011 A talk in three parts. 1. A provocative claim. (The thought) 2. A idea about modular program analysis.
Syntax Analysis Part III
 Syntax Analysis Part III Chapter 4: Top-Down Parsing Slides adapted from : Robert van Engelen, Florida State University Eliminating Ambiguity stmt if expr then stmt if expr then stmt else stmt other The
Syntax Analysis Part III Chapter 4: Top-Down Parsing Slides adapted from : Robert van Engelen, Florida State University Eliminating Ambiguity stmt if expr then stmt if expr then stmt else stmt other The
This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free Grammars
 This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free rammars (Context-free) rammars (Leftmost and Rightmost) Derivations Parse Trees An quivalence between Derivations and Parse Trees Ambiguity in rammars
This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free rammars (Context-free) rammars (Leftmost and Rightmost) Derivations Parse Trees An quivalence between Derivations and Parse Trees Ambiguity in rammars
COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS
 CST.2016.6.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IB Thursday 2 June 2016 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 6 Answer five questions. Submit the answers in five separate bundles, each with its own cover sheet.
CST.2016.6.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IB Thursday 2 June 2016 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 6 Answer five questions. Submit the answers in five separate bundles, each with its own cover sheet.
Quantification in the predicate calculus
 Quantification in the predicate calculus PHIL 43916 eptember 5, 2012 1. The problem posed by quantified sentences... 1 2. yntax of PC... 2 3. Bound and free iables... 3 4. Models and assignments... 4 5.
Quantification in the predicate calculus PHIL 43916 eptember 5, 2012 1. The problem posed by quantified sentences... 1 2. yntax of PC... 2 3. Bound and free iables... 3 4. Models and assignments... 4 5.
Decision Procedures for Satisfiability and Validity in Propositional Logic
 Decision Procedures for Satisfiability and Validity in Propositional Logic Meghdad Ghari Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM) School of Mathematics-Isfahan Branch Logic Group http://math.ipm.ac.ir/isfahan/logic-group.htm
Decision Procedures for Satisfiability and Validity in Propositional Logic Meghdad Ghari Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM) School of Mathematics-Isfahan Branch Logic Group http://math.ipm.ac.ir/isfahan/logic-group.htm
TALP at GeoQuery 2007: Linguistic and Geographical Analysis for Query Parsing
 TALP at GeoQuery 2007: Linguistic and Geographical Analysis for Query Parsing Daniel Ferrés and Horacio Rodríguez TALP Research Center Software Department Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya {dferres,horacio}@lsi.upc.edu
TALP at GeoQuery 2007: Linguistic and Geographical Analysis for Query Parsing Daniel Ferrés and Horacio Rodríguez TALP Research Center Software Department Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya {dferres,horacio}@lsi.upc.edu
Finite State Model Checking
 Finite State Model Checking Finite State Model Checking Finite State Systems System Descrition A Requirement F CTL TOOL No! Debugging Information Yes, Prototyes Executable Code Test sequences Tools: visualstate,
Finite State Model Checking Finite State Model Checking Finite State Systems System Descrition A Requirement F CTL TOOL No! Debugging Information Yes, Prototyes Executable Code Test sequences Tools: visualstate,
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05
 Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence
 Ling255: Sem & Cogsci Maribel Romero February 17, 2005 Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence 1. Introduction. We have seen that Determiners express a relation between two sets of individuals
Ling255: Sem & Cogsci Maribel Romero February 17, 2005 Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence 1. Introduction. We have seen that Determiners express a relation between two sets of individuals
An Efficient Decision Procedure for Functional Decomposable Theories Based on Dual Constraints
 An Efficient Decision Procedure for Functional Decomposable Theories Based on Dual Constraints Khalil Djelloul Laboratoire d Informatique Fondamentale d Orléans. Bat. 3IA, rue Léonard de Vinci. 45067 Orléans,
An Efficient Decision Procedure for Functional Decomposable Theories Based on Dual Constraints Khalil Djelloul Laboratoire d Informatique Fondamentale d Orléans. Bat. 3IA, rue Léonard de Vinci. 45067 Orléans,
