Anomalous scaling at non-thermal fixed points of Gross-Pitaevskii and KPZ turbulence
|
|
|
- Phillip Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anomalous scaling at non-thermal fixed points of Gross-Pitaevskii and KPZ turbulence Thomas Gasenzer Steven Mathey Jan M. Pawlowski ITP - Heidelberg 24 September 2014
2 Non-thermal fixed points Non-thermal fixed point are far from equilibrium quasi stationary states of matter. X Scale invariance ɛ(k) k d+η Depending on the initial conditions, the system may take an algebraically long time on the way to thermalisation.
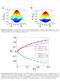
3 Introduction GPE KPZ DDGPE to KPZ Conclusions Plan Ultra-cold Bose gases, Gross-Pitaevskii Equation (GPE) Interface dynamics, Kardar-Parisi-Zhang (KPZ) z/ξ 1.5 ξ/lc 50 0 x/ξ t2 α = 2.5 α=3 α=4 α=6 α = 10 t y/ξ t3 0.5 FIG. 5: Vortex tangle structures emerging in the gas for the t2 t1 Burn paper by CrazzHky, used under CC BYα/ = Cropped, two different extremes of initial 2.5, at time t3 0 NIST/JILA/CU-Boulder; Nowak etconditions, al., arxiv: v t = 2424 τ (left) and α = 10, at time t = 606 τ (right). ξ/ld 1
4 Driven-Dissipative GPE Classical field equation for the average Bose wave-function φ(x, t): i t φ(x, t) = [ ( ) ] 1 2m iν 2 + µ + g φ(x, t) 2 φ(x, t) + ζ(x, t) With complex parameters µ = µ 1 + iµ 2 g = g 1 ig 2 Single particle pump 2 particle losses and stochastic driving ζ(x, t) = 0 ζ(x, t)ζ(x, t ) = γ δ(t t )δ(x x ) Sieberer et al., PRL 110, (2013); Sieberer et al., Phys. Rev. B 89, (2014); Täuber et al., Phys. Rev. X, (2014)
5 Driven-Dissipative GPE Classical field equation for the average Bose wave-function φ(x, t): i t φ(x, t) = [ ( ) ] 1 2m iν 2 + µ + g φ(x, t) 2 φ(x, t) + ζ(x, t) With complex parameters µ = µ 1 + iµ 2 g = g 1 ig 2 Single particle pump 2 particle losses and stochastic driving ζ(x, t) = 0 ζ(x, t)ζ(x, t ) = γ δ(t t )δ(x x ) Sieberer et al., PRL 110, (2013); Sieberer et al., Phys. Rev. B 89, (2014); Täuber et al., Phys. Rev. X, (2014)
6 Driven-Dissipative GPE Classical field equation for the average Bose wave-function φ(x, t): i t φ(x, t) = [ ( ) ] 1 2m iν 2 + µ + g φ(x, t) 2 φ(x, t) + ζ(x, t) With complex parameters µ = µ 1 + iµ 2 g = g 1 ig 2 Single particle pump 2 particle losses and stochastic driving ζ(x, t) = 0 ζ(x, t)ζ(x, t ) = γ δ(t t )δ(x x ) Sieberer et al., PRL 110, (2013); Sieberer et al., Phys. Rev. B 89, (2014); Täuber et al., Phys. Rev. X, (2014)
7 Scaling in ultra-cold Bose gases We focus on the kinetic energy density, ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = ɛ(k) k Scaling from dimensional analysis with an anomalous correction ɛ(k) = ɛ kin k d (kξ) η d η num 1 small small Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011)
8 Scaling in ultra-cold Bose gases We focus on the kinetic energy density, ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = ɛ(k) k Scaling from dimensional analysis with an anomalous correction ɛ(k) = ɛ kin k d (kξ) η d η num 1 small small Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011)
9 Scaling in ultra-cold Bose gases We focus on the kinetic energy density, ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = ɛ(k) k Scaling from dimensional analysis with an anomalous correction ɛ(k) = ɛ kin k d (kξ) η d η num 1 small small Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011)
10 Scaling in ultra-cold Bose gases We focus on the kinetic energy density, ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = ɛ(k) k Scaling from dimensional analysis with an anomalous correction ɛ(k) ɛ kin k d+η kξ d η num 1 small small Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011)
11 Kardar Parisi Zhang equation A model for interface growth, t θ(x, t) = ν 2 θ(x, t) + λ 2 [ θ(x, t)]2 + η(x, t) with diffusion, perpendicular expansion and stochastic driving, η(x, t) = 0 η(x, t)η(x, t ) = D δ(t t )δ(x x ) θ(x,t) x
12 Kardar Parisi Zhang equation A model for interface growth, t θ(x, t) = ν 2 θ(x, t) + λ 2 [ θ(x, t)]2 + η(x, t) with diffusion, perpendicular expansion and stochastic driving, η(x, t) = 0 η(x, t)η(x, t ) = D δ(t t )δ(x x ) θ(x,t) x
13 Kardar Parisi Zhang equation A model for interface growth, t θ(x, t) = ν 2 θ(x, t) + λ 2 [ θ(x, t)]2 + η(x, t) with diffusion, perpendicular expansion and stochastic driving, η(x, t) = 0 η(x, t)η(x, t ) = D δ(t t )δ(x x ) θ(x,t) x
14 Kardar Parisi Zhang equation A model for interface growth, t θ(x, t) = ν 2 θ(x, t) + λ 2 [ θ(x, t)]2 + η(x, t) with diffusion, perpendicular expansion and stochastic driving, η(x, t) = 0 η(x, t)η(x, t ) = D δ(t t )δ(x x ) θ(x,t) x
15 Scaling in interface growth The stationary state has scaling correlation functions, with exponents given by: θ(t + τ, x + r)θ(t, x) c = r 2χ g (τ/r z ) d χ 1/ ? z = 2 χ 3/ ? Kloss et al., Phys. Rev. E 86, (2012) and references therein
16 From DDGPE to KPZ Density and phase decomposition φ(x, t) = n(x, t) e iθ(x,t) t θ 1 2m ( θ)2 ν 2 θ = U, t n 1 m (n θ) = S, with sources of phase and density fluctuations, U = U[θ, n] + Re(ζeiθ ) n S = S[θ, n] + 2 n Im(ζe iθ ). Altman et al., arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech]
17 From DDGPE to KPZ Density and phase decomposition φ(x, t) = n(x, t) e iθ(x,t) t θ 1 2m ( θ)2 ν 2 θ = U, KPZ equation t n 1 m (n θ) = S, with sources of phase and density fluctuations, U = U[θ, n] + Re(ζeiθ ) n S = S[θ, n] + 2 n Im(ζe iθ ). Altman et al., arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech]
18 ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = n 2m Comparing scaling exponents ɛ kin (k) k d+η η = z χ k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ kin (k) k z d χ GPE simulations KPZ literature X
19 ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 = n 2m Comparing scaling exponents ɛ kin (k) k d+η η = z χ k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ kin (k) k z d χ GPE simulations d η num 1 small small KPZ literature X d η Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011)
20 volution in d = 3 Introduction GPE FIG. 3: Single-particle KPZ mode DDGPE occupation to KPZ numbers as Conclusions functions of the radial momentum k = [ d ensity falls below e: g = i=1, 4sin2 (k i /2)] 1/2, k = 2πn/N s, n = (n 1,..., n d ), n i = N s /2,..., N s /2, for the four = 103 (top right) different Comparing times ofscaling the run inexponents d = 2 dimensions shown in Fig. 1. right) Note the double-logarithmic scale. An early development of ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 a scaling n(k) k 4 ɛ kin is (k) followed k d+η by a bimodal scaling with n(k) k η = z χ garithmic scale. = n 2m k 2 at larger wave numbers. k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ kin (k) k z d χ During the inidually spread to n(k) antivortex d = 2pairs n 10 observed. Durphase two dis- n i (k) GPE simulations q (k) KPZ literature n c (k) ɛ(k) = k 2 n(k) d to be in excelction k X 4 10 ν of = Ref. µ 2 [6]. = 0 4 k 3 g k = ζ = 0 Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (R) (2011) UV = d = 2 exed the exponent q. (2), corrobo- 4]. Note that in V = 2 is identi- Rayleigh-Jeans momentum dishown again, for Occupation number n(k) initial occupation k ξ Radial momentum k
21 Comparing scaling exponents FIG. 3: Single-particle mode occupation numbers as functions of the radial momentum k = [ d 2πn/N s, n = (n 1,..., n d), n i = N s/2,..., N s/2, for the four different times of the run in = n d = 2 dimensions shown in Fig. 1. Note the double-logarithmic scale. An early development of 2m a scaling n(k) k 4 is followed by a bimodal scaling with n(k) k 2 at larger wave numbers. Occupation number n(k) ɛ kin = 1 2m φ 2 ɛ kin (k) k d+η i=1 4sin2 (k i/2)] 1/2, k = η = z χ k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ kin (k) k z d χ initial occupation d = 2 d = 3 GPE simulations k ξ Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 4 k 3 k 4.66 Occupation number n(k) X initial occupation KPZ literature k ξ 3 Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 5 k 4 k 5.66 Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, FIG (R) 4: Single-particle (2011) occupation numbers of different FIG. fractions of the system, at time t = 10 5 of the d = 2 run shown in Fig. 2, at the time t = 1640 of the situation in 5: Same as in Fig. 4, for the run in d = 3 dimensions its 5.66
22 ɛ cin = 1 2m φ 2 = n 2m Compressible excitations ɛ c (k) k d+η+1 η = z χ 1 k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ c (k) k z d χ GPE simulations d η num 0 small small KPZ literature X d η Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. A 85, (2012)
23 ɛ cin = 1 2m φ 2 = n 2m Compressible excitations ɛ c (k) k d+η+1 η = z χ 1 k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ c (k) k z d χ Occupation number n(k) d = 2 d = 3 GPE simulations Occupation number n(k) 10 6 X k ξ 1 3 Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 3 k 2 1 KPZ literature k ξ 3 Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 4 k 2 Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. A 85, (2012)
24 ɛ cin = 1 2m φ 2 = n 2m Compressible excitations ɛ c (k) k d+η+1 η = z χ 1 k k2 θ(k, t) 2 ɛ c (k) k z d χ Occupation number n(k) d = 2 d = 3 GPE simulations Occupation number n(k) 10 6 X k ξ 1 3 Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 3 k 2 k KPZ literature k ξ 3 Radial momentum k n(k) n q(k) n c(k) n i(k) k 4 k 2 k 3.6 Nowak et al., Phys. Rev. A 85, (2012)
25 Conclusions Interface dynamics described by KPZ equation does not capture vortex dynamics. It does captures the rest. We have made an estimation of anomalous scaling exponents of the ultra-cold Bose gas at a non-thermal fixed point. Gasenzer, SM, Pawlowski, arxiv: [cond-mat.quant-gas]
Vortices, Superfluid turbulence & Nonthermal Fixed Points in Bose Gases
 Vortices, Superfluid turbulence & Nonthermal Fixed Points in Bose Gases Institut für Theoretische Physik Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg Germany email: www: t.gasenzer@uni-heidelberg.de
Vortices, Superfluid turbulence & Nonthermal Fixed Points in Bose Gases Institut für Theoretische Physik Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg Germany email: www: t.gasenzer@uni-heidelberg.de
The Turbulent Universe
 The Turbulent Universe WMAP Science Team J. Berges ALICE/CERN Universität Heidelberg JILA/NIST Festkolloquium der Karl Franzens Universität Graz FWF Doktoratskolleg Hadrons in Vacuum, Nuclei and Stars
The Turbulent Universe WMAP Science Team J. Berges ALICE/CERN Universität Heidelberg JILA/NIST Festkolloquium der Karl Franzens Universität Graz FWF Doktoratskolleg Hadrons in Vacuum, Nuclei and Stars
Dynamic properties of interacting bosons and magnons
 Ultracold Quantum Gases beyond Equilibrium Natal, Brasil, September 27 October 1, 2010 Dynamic properties of interacting bosons and magnons Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaboration: A. Kreisel,
Ultracold Quantum Gases beyond Equilibrium Natal, Brasil, September 27 October 1, 2010 Dynamic properties of interacting bosons and magnons Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaboration: A. Kreisel,
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics.
 Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Driven-dissipative polariton quantum fluids in and out of equilibrium
 Driven-dissipative polariton quantum fluids in and out of equilibrium Marzena Szymańska Designer Quantum Systems Out of Equilibrium KITP, November 2016 Acknowledgements Group: A. Zamora G. Dagvadorj In
Driven-dissipative polariton quantum fluids in and out of equilibrium Marzena Szymańska Designer Quantum Systems Out of Equilibrium KITP, November 2016 Acknowledgements Group: A. Zamora G. Dagvadorj In
Topological Excitations, Superfluid Turbulence & Non-Thermal Fixed Points in Ultracold Gases
 Topological Excitations, Superfluid Turbulence & Non-Thermal Fixed Points in Ultracold Gases Institut für Theoretische Physik Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg Germany
Topological Excitations, Superfluid Turbulence & Non-Thermal Fixed Points in Ultracold Gases Institut für Theoretische Physik Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg Germany
Non-equilibrium Bose gases with c-fields
 Non-equilibrium Bose gases with c-fields Matthew Davis Collaborators: Tod Wright, Mike Garrett, Geoff Lee, Chao Feng, Jacopo Sabbatini, Blair Blakie, Karen Kheruntsyan, Ashton Bradley School of Mathematics
Non-equilibrium Bose gases with c-fields Matthew Davis Collaborators: Tod Wright, Mike Garrett, Geoff Lee, Chao Feng, Jacopo Sabbatini, Blair Blakie, Karen Kheruntsyan, Ashton Bradley School of Mathematics
Critical Physics far from Equilibrium
 Critical Physics far from Equilibrium Institut für Theoretische Physik Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg, Germany email: www: t.gasenzer@uni-heidelberg.de www.thphys.uni-heidelberg.de/~gasenzer Nonequilibrium
Critical Physics far from Equilibrium Institut für Theoretische Physik Philosophenweg 16 69120 Heidelberg, Germany email: www: t.gasenzer@uni-heidelberg.de www.thphys.uni-heidelberg.de/~gasenzer Nonequilibrium
Bethe Ansatz Solutions and Excitation Gap of the Attractive Bose-Hubbard Model
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 39, No., August 001, pp. 03 08 Bethe Ansatz Solutions and Excitation Gap of the Attractive Bose-Hubbard Model Deok-Sun Lee and Doochul Kim School of Physics,
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 39, No., August 001, pp. 03 08 Bethe Ansatz Solutions and Excitation Gap of the Attractive Bose-Hubbard Model Deok-Sun Lee and Doochul Kim School of Physics,
le LPTMS en Bretagne... photo extraite du site
 le LPTMS en Bretagne... 1 photo extraite du site http://www.chateau-du-val.com le LPTMS en Bretagne... 1 2 Quantum signature of analog Hawking radiation in momentum space Nicolas Pavloff LPTMS, CNRS, Univ.
le LPTMS en Bretagne... 1 photo extraite du site http://www.chateau-du-val.com le LPTMS en Bretagne... 1 2 Quantum signature of analog Hawking radiation in momentum space Nicolas Pavloff LPTMS, CNRS, Univ.
The one-dimensional KPZ equation and its universality
 The one-dimensional KPZ equation and its universality T. Sasamoto Based on collaborations with A. Borodin, I. Corwin, P. Ferrari, T. Imamura, H. Spohn 28 Jul 2014 @ SPA Buenos Aires 1 Plan of the talk
The one-dimensional KPZ equation and its universality T. Sasamoto Based on collaborations with A. Borodin, I. Corwin, P. Ferrari, T. Imamura, H. Spohn 28 Jul 2014 @ SPA Buenos Aires 1 Plan of the talk
Theory of fractional Lévy diffusion of cold atoms in optical lattices
 Theory of fractional Lévy diffusion of cold atoms in optical lattices, Erez Aghion, David Kessler Bar-Ilan Univ. PRL, 108 230602 (2012) PRX, 4 011022 (2014) Fractional Calculus, Leibniz (1695) L Hospital:
Theory of fractional Lévy diffusion of cold atoms in optical lattices, Erez Aghion, David Kessler Bar-Ilan Univ. PRL, 108 230602 (2012) PRX, 4 011022 (2014) Fractional Calculus, Leibniz (1695) L Hospital:
Aging Scaling in Driven Systems
 Aging Scaling in Driven Systems George L. Daquila Goldman Sachs, New York, USA Sebastian Diehl Universität zu Köln, Germany Sheng Chen, Weigang Liu, and Uwe C. Täuber Department of Physics & Center for
Aging Scaling in Driven Systems George L. Daquila Goldman Sachs, New York, USA Sebastian Diehl Universität zu Köln, Germany Sheng Chen, Weigang Liu, and Uwe C. Täuber Department of Physics & Center for
Stochastic nonlinear Schrödinger equations and modulation of solitary waves
 Stochastic nonlinear Schrödinger equations and modulation of solitary waves A. de Bouard CMAP, Ecole Polytechnique, France joint work with R. Fukuizumi (Sendai, Japan) Deterministic and stochastic front
Stochastic nonlinear Schrödinger equations and modulation of solitary waves A. de Bouard CMAP, Ecole Polytechnique, France joint work with R. Fukuizumi (Sendai, Japan) Deterministic and stochastic front
Vortex dynamics in finite temperature two-dimensional superfluid turbulence. Andrew Lucas
 Vortex dynamics in finite temperature two-dimensional superfluid turbulence Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics King s College London, Condensed Matter Theory Special Seminar August 15, 2014 Collaborators 2 Paul
Vortex dynamics in finite temperature two-dimensional superfluid turbulence Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics King s College London, Condensed Matter Theory Special Seminar August 15, 2014 Collaborators 2 Paul
Supplementary Figure 3: Interaction effects in the proposed state preparation with Bloch oscillations. The numerical results are obtained by
 Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium
 Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium Dénes Sexty Uni Heidelberg Collaborators: Jürgen Berges, Sören Schlichting March, 01, Seattle Gauge Field Dynamics In and Out of Equilibrium
Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium Dénes Sexty Uni Heidelberg Collaborators: Jürgen Berges, Sören Schlichting March, 01, Seattle Gauge Field Dynamics In and Out of Equilibrium
Exploring Geometry Dependence of Kardar-Parisi-Zhang Interfaces
 * This is a simplified ppt intended for public opening Exploring Geometry Dependence of Kardar-Parisi-Zhang Interfaces Kazumasa A. Takeuchi (Tokyo Tech) Joint work with Yohsuke T. Fukai (Univ. Tokyo &
* This is a simplified ppt intended for public opening Exploring Geometry Dependence of Kardar-Parisi-Zhang Interfaces Kazumasa A. Takeuchi (Tokyo Tech) Joint work with Yohsuke T. Fukai (Univ. Tokyo &
STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES F STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW
 STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW University of L Aquila 1 July 2014 GGI Firenze References L. Bertini; A. De Sole; D. G. ; G. Jona-Lasinio; C. Landim
STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW University of L Aquila 1 July 2014 GGI Firenze References L. Bertini; A. De Sole; D. G. ; G. Jona-Lasinio; C. Landim
AGAT 2016, Cargèse a point-vortex toy model
 AGAT 2016, Cargèse a point-vortex toy model Jean-François Pinton CNRS & ENS de Lyon M.P. Rast, JFP, PRE 79 (2009) M.P. Rast, JFP, PRL 107 (2011) M.P. Rast, JFP, P.D. Mininni, PRE 93 (2009) Motivations
AGAT 2016, Cargèse a point-vortex toy model Jean-François Pinton CNRS & ENS de Lyon M.P. Rast, JFP, PRE 79 (2009) M.P. Rast, JFP, PRL 107 (2011) M.P. Rast, JFP, P.D. Mininni, PRE 93 (2009) Motivations
Roton Mode in Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates
 Roton Mode in Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates Sandeep Indian Institute of Science Department of Physics, Bangalore March 14, 2013 BECs vs Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates Although quantum gases are
Roton Mode in Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates Sandeep Indian Institute of Science Department of Physics, Bangalore March 14, 2013 BECs vs Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates Although quantum gases are
BEC in one dimension
 BEC in one dimension Tilmann John 11. Juni 2013 Outline 1 one-dimensional BEC 2 theoretical description Tonks-Girardeau gas Interaction exact solution (Lieb and Liniger) 3 experimental realization 4 conclusion
BEC in one dimension Tilmann John 11. Juni 2013 Outline 1 one-dimensional BEC 2 theoretical description Tonks-Girardeau gas Interaction exact solution (Lieb and Liniger) 3 experimental realization 4 conclusion
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 15 Jul 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 15 Jul 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 15 Jul 2005](/thumbs/72/66469333.jpg) Correlation functions of one-dimensional Bose-Fermi mixtures Holger Frahm and Guillaume Palacios Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Hannover, Appelstr. 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany (Dated: July
Correlation functions of one-dimensional Bose-Fermi mixtures Holger Frahm and Guillaume Palacios Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Hannover, Appelstr. 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany (Dated: July
Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids
 Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids Hong Liu Paolo Glorioso Michael Crossley arxiv: 1511.03646 Conserved quantities Consider a long wavelength disturbance of a system in thermal equilibrium non-conserved
Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids Hong Liu Paolo Glorioso Michael Crossley arxiv: 1511.03646 Conserved quantities Consider a long wavelength disturbance of a system in thermal equilibrium non-conserved
Spherical models of interface growth
 Spherical models of interface growth Malte Henkel Groupe de Physique Statistique Institut Jean Lamour, Université de Lorraine Nancy, France co-author: X. Durang (KIAS Seoul) CompPhys 14, Leipzig, 27 th
Spherical models of interface growth Malte Henkel Groupe de Physique Statistique Institut Jean Lamour, Université de Lorraine Nancy, France co-author: X. Durang (KIAS Seoul) CompPhys 14, Leipzig, 27 th
Discrete solid-on-solid models
 Discrete solid-on-solid models University of Alberta 2018 COSy, University of Manitoba - June 7 Discrete processes, stochastic PDEs, deterministic PDEs Table: Deterministic PDEs Heat-diffusion equation
Discrete solid-on-solid models University of Alberta 2018 COSy, University of Manitoba - June 7 Discrete processes, stochastic PDEs, deterministic PDEs Table: Deterministic PDEs Heat-diffusion equation
Non-perturbative statistical theory of intermittency in ITG drift wave turbulence with zonal flows
 Non-perturbative statistical theory of intermittency in ITG drift wave turbulence with zonal flows Johan Anderson 1 and Eun-jin Kim University of Sheffield Department of Applied Mathematics Hicks Building,
Non-perturbative statistical theory of intermittency in ITG drift wave turbulence with zonal flows Johan Anderson 1 and Eun-jin Kim University of Sheffield Department of Applied Mathematics Hicks Building,
Introduction Efficiency bounds Source dependence Saturation Shear Flows Conclusions STIRRING UP TROUBLE
 STIRRING UP TROUBLE Multi-scale mixing measures for steady scalar sources Charles Doering 1 Tiffany Shaw 2 Jean-Luc Thiffeault 3 Matthew Finn 3 John D. Gibbon 3 1 University of Michigan 2 University of
STIRRING UP TROUBLE Multi-scale mixing measures for steady scalar sources Charles Doering 1 Tiffany Shaw 2 Jean-Luc Thiffeault 3 Matthew Finn 3 John D. Gibbon 3 1 University of Michigan 2 University of
Theory Seminar Uni Marburg. Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems
 Theory Seminar Uni Marburg 11 November, 2010 Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Bose-Einstein condensation 2.) Interacting magnons in
Theory Seminar Uni Marburg 11 November, 2010 Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Bose-Einstein condensation 2.) Interacting magnons in
Progress and Plans on Physics and Validation
 Progress and Plans on Physics and Validation T.S. Hahm Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory Princeton, New Jersey Momentum Transport Studies: Turbulence and Neoclassical Physics Role of Trapped Electrons
Progress and Plans on Physics and Validation T.S. Hahm Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory Princeton, New Jersey Momentum Transport Studies: Turbulence and Neoclassical Physics Role of Trapped Electrons
FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H
 FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H Albert-Läszlö Barabäs i H. Eugene Stanley Preface Notation guide x v xi x PART 1 Introduction 1 1 Interfaces in nature 1 1.1 Interface motion in disordered media 3
FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H Albert-Läszlö Barabäs i H. Eugene Stanley Preface Notation guide x v xi x PART 1 Introduction 1 1 Interfaces in nature 1 1.1 Interface motion in disordered media 3
Phase Transitions in Nonequilibrium Steady States and Power Laws and Scaling Functions of Surface Growth Processes
 Phase Transitions in Nonequilibrium Steady States and Power Laws and Scaling Functions of Surface Growth Processes Term-paper for PHY563 Xianfeng Rui, UIUC Physics Abstract: Three models of surface growth
Phase Transitions in Nonequilibrium Steady States and Power Laws and Scaling Functions of Surface Growth Processes Term-paper for PHY563 Xianfeng Rui, UIUC Physics Abstract: Three models of surface growth
Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas
 / 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
/ 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
Low-dimensional Bose gases Part 1: BEC and interactions
 Low-dimensional Bose gases Part 1: BEC and interactions Hélène Perrin Laboratoire de physique des lasers, CNRS-Université Paris Nord Photonic, Atomic and Solid State Quantum Systems Vienna, 2009 Introduction
Low-dimensional Bose gases Part 1: BEC and interactions Hélène Perrin Laboratoire de physique des lasers, CNRS-Université Paris Nord Photonic, Atomic and Solid State Quantum Systems Vienna, 2009 Introduction
Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium
 Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium Dénes Sexty Uni Heidelberg Collaborators: Jürgen Berges, Sören Schlichting July 1, 01, Swansea SEWM 01 Non-equilibrium initial state Turbulent
Turbulence and Bose-Einstein condensation Far from Equilibrium Dénes Sexty Uni Heidelberg Collaborators: Jürgen Berges, Sören Schlichting July 1, 01, Swansea SEWM 01 Non-equilibrium initial state Turbulent
Thermalisation and vortex formation in a mechanically perturbed condensate. Vortex Lattice Formation. This Talk. R.J. Ballagh and Tod Wright
 Thermalisation and vortex formation in a mechanically perturbed condensate Jack Dodd Centre ACQAO R.J. Ballagh and Tod Wright Jack Dodd centre for Photonics and Ultra-cold Atoms Department of Physics University
Thermalisation and vortex formation in a mechanically perturbed condensate Jack Dodd Centre ACQAO R.J. Ballagh and Tod Wright Jack Dodd centre for Photonics and Ultra-cold Atoms Department of Physics University
Far-from-equilibrium universality classes In heavy-ion collisions and cosmology
 Far-from-equilibrium universality classes In heavy-ion collisions and cosmology Kirill Boguslavski J. Berges, KB, S. Schlichting and R. Venugopalan, PRD 92, 096006 (2015); PRL 114, 061601 (2015) Project:
Far-from-equilibrium universality classes In heavy-ion collisions and cosmology Kirill Boguslavski J. Berges, KB, S. Schlichting and R. Venugopalan, PRD 92, 096006 (2015); PRL 114, 061601 (2015) Project:
Fate of Kosterlitz-Thouless Physics in Driven Open Quantum Systems
 Functional Renormalization - from quantum gravity and dark energy to ultracold atoms and condensed matter March 07-10, 2017 IWH Heidelberg, Germany Fate of Kosterlitz-Thouless Physics in Driven Open Quantum
Functional Renormalization - from quantum gravity and dark energy to ultracold atoms and condensed matter March 07-10, 2017 IWH Heidelberg, Germany Fate of Kosterlitz-Thouless Physics in Driven Open Quantum
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point
 Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Anderson Localization Theoretical description and experimental observation in Bose Einstein-condensates
 Anderson Localization Theoretical description and experimental observation in Bose Einstein-condensates Conrad Albrecht ITP Heidelberg 22.07.2009 Conrad Albrecht (ITP Heidelberg) Anderson Localization
Anderson Localization Theoretical description and experimental observation in Bose Einstein-condensates Conrad Albrecht ITP Heidelberg 22.07.2009 Conrad Albrecht (ITP Heidelberg) Anderson Localization
Equilibrium correlations and heat conduction in the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam chain.
 Equilibrium correlations and heat conduction in the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam chain. Abhishek Dhar International centre for theoretical sciences TIFR, Bangalore www.icts.res.in Suman G. Das (Raman Research Institute,
Equilibrium correlations and heat conduction in the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam chain. Abhishek Dhar International centre for theoretical sciences TIFR, Bangalore www.icts.res.in Suman G. Das (Raman Research Institute,
Random Averaging. Eli Ben-Naim Los Alamos National Laboratory. Paul Krapivsky (Boston University) John Machta (University of Massachusetts)
 Random Averaging Eli Ben-Naim Los Alamos National Laboratory Paul Krapivsky (Boston University) John Machta (University of Massachusetts) Talk, papers available from: http://cnls.lanl.gov/~ebn Plan I.
Random Averaging Eli Ben-Naim Los Alamos National Laboratory Paul Krapivsky (Boston University) John Machta (University of Massachusetts) Talk, papers available from: http://cnls.lanl.gov/~ebn Plan I.
Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group
 March 14, 2013, Condensed Matter Journal Club University of Florida at Gainesville Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt
March 14, 2013, Condensed Matter Journal Club University of Florida at Gainesville Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt
The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence
 The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence Eleftherios Gkioulekas (1) and Ka-Kit Tung (2) (1) Department of Mathematics,
The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence Eleftherios Gkioulekas (1) and Ka-Kit Tung (2) (1) Department of Mathematics,
Bursty Transport in Tokamaks with Internal Transport Barriers
 Bursty Transport in Tokamaks with Internal Transport Barriers S. Benkadda 1), O. Agullo 1), P. Beyer 1), N. Bian 1), P. H. Diamond 3), C. Figarella 1), X. Garbet 2), P. Ghendrih 2), V. Grandgirard 1),
Bursty Transport in Tokamaks with Internal Transport Barriers S. Benkadda 1), O. Agullo 1), P. Beyer 1), N. Bian 1), P. H. Diamond 3), C. Figarella 1), X. Garbet 2), P. Ghendrih 2), V. Grandgirard 1),
6. Interference of BECs
 6. Interference of BECs Josephson effects Weak link: tunnel junction between two traps. Josephson oscillation An initial imbalance between the population of the double well potential leads to periodic
6. Interference of BECs Josephson effects Weak link: tunnel junction between two traps. Josephson oscillation An initial imbalance between the population of the double well potential leads to periodic
Present and future prospects of the (functional) renormalization group
 Schladming Winter School 2011: Physics at all scales: the renormalization group Present and future prospects of the (functional) renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt panel discussion
Schladming Winter School 2011: Physics at all scales: the renormalization group Present and future prospects of the (functional) renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt panel discussion
The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or. smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is
 1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
Ferromagnetism of electron gas. Abstract
 Ferromagnetism of electron gas H.Gholizade Engineering Science Department, University of Tehran, Enghelab Sq., Tehran, Iran. arxiv:090.533v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 00 D.Momeni Department of physics,faculty
Ferromagnetism of electron gas H.Gholizade Engineering Science Department, University of Tehran, Enghelab Sq., Tehran, Iran. arxiv:090.533v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 00 D.Momeni Department of physics,faculty
As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation. Week 8: Lectures 15, 16
 As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation. Week 8: Lectures 15, 16 Masses for Vectors: the Higgs mechanism April 6, 2012 The momentum-space propagator
As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation. Week 8: Lectures 15, 16 Masses for Vectors: the Higgs mechanism April 6, 2012 The momentum-space propagator
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 27 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 27 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 27 Nov 2017](/thumbs/72/67392053.jpg) Growing interfaces: A brief review on the tilt method M. F. Torres and R. C. Buceta arxiv:1711.09652v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 27 Nov 2017 Instituto de Investigaciones Físicas de Mar del Plata (UNMdP and
Growing interfaces: A brief review on the tilt method M. F. Torres and R. C. Buceta arxiv:1711.09652v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 27 Nov 2017 Instituto de Investigaciones Físicas de Mar del Plata (UNMdP and
Interaction between atoms
 Interaction between atoms MICHA SCHILLING HAUPTSEMINAR: PHYSIK DER KALTEN GASE INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE PHYSIK III UNIVERSITÄT STUTTGART 23.04.2013 Outline 2 Scattering theory slow particles / s-wave
Interaction between atoms MICHA SCHILLING HAUPTSEMINAR: PHYSIK DER KALTEN GASE INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE PHYSIK III UNIVERSITÄT STUTTGART 23.04.2013 Outline 2 Scattering theory slow particles / s-wave
Simulating Quantum Systems through Matrix Product States. Laura Foini SISSA Journal Club
 Simulating Quantum Systems through Matrix Product States Laura Foini SISSA Journal Club 15-04-2010 Motivations Theoretical interest in Matrix Product States Wide spectrum of their numerical applications
Simulating Quantum Systems through Matrix Product States Laura Foini SISSA Journal Club 15-04-2010 Motivations Theoretical interest in Matrix Product States Wide spectrum of their numerical applications
Patterns in the Kardar Parisi Zhang equation
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 71, No. 2 journal of August 2008 physics pp. 253 262 Patterns in the Kardar Parisi Zhang equation HANS C FOGEDBY Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 71, No. 2 journal of August 2008 physics pp. 253 262 Patterns in the Kardar Parisi Zhang equation HANS C FOGEDBY Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University,
Optimal paths on the road network as directed polymers
 1/12 Optimal paths on the road network as directed polymers Alex Solon, Guy Bunin, Sherry Chu, Mehran Kardar [arxiv:1706.00489] 2/12 Directed polymer in a random medium (DPRM) Statistics of a stretched
1/12 Optimal paths on the road network as directed polymers Alex Solon, Guy Bunin, Sherry Chu, Mehran Kardar [arxiv:1706.00489] 2/12 Directed polymer in a random medium (DPRM) Statistics of a stretched
Laminar Flow. Chapter ZERO PRESSURE GRADIENT
 Chapter 2 Laminar Flow 2.1 ZERO PRESSRE GRADIENT Problem 2.1.1 Consider a uniform flow of velocity over a flat plate of length L of a fluid of kinematic viscosity ν. Assume that the fluid is incompressible
Chapter 2 Laminar Flow 2.1 ZERO PRESSRE GRADIENT Problem 2.1.1 Consider a uniform flow of velocity over a flat plate of length L of a fluid of kinematic viscosity ν. Assume that the fluid is incompressible
The Johns Hopkins Turbulence Databases (JHTDB)
 The Johns Hopkins Turbulence Databases (JHTDB) HOMOGENEOUS BUOYANCY DRIVEN TURBULENCE DATA SET Data provenance: D. Livescu 1 Database Ingest and Web Services: C. Canada 1, K. Kalin 2, R. Burns 2 & IDIES
The Johns Hopkins Turbulence Databases (JHTDB) HOMOGENEOUS BUOYANCY DRIVEN TURBULENCE DATA SET Data provenance: D. Livescu 1 Database Ingest and Web Services: C. Canada 1, K. Kalin 2, R. Burns 2 & IDIES
Bogoliubov theory of disordered Bose-Einstein condensates
 Bogoliubov theory of disordered Bose-Einstein condensates Christopher Gaul Universidad Complutense de Madrid BENASQUE 2012 DISORDER Bogoliubov theory of disordered Bose-Einstein condensates Abstract The
Bogoliubov theory of disordered Bose-Einstein condensates Christopher Gaul Universidad Complutense de Madrid BENASQUE 2012 DISORDER Bogoliubov theory of disordered Bose-Einstein condensates Abstract The
Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations
 Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations Aleksandar Donev 1 Courant Institute, New York University & Alejandro L. Garcia, San Jose State University John B. Bell, Lawrence Berkeley
Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations Aleksandar Donev 1 Courant Institute, New York University & Alejandro L. Garcia, San Jose State University John B. Bell, Lawrence Berkeley
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations
 Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
The non-perturbative renormalization group approach to KPZ
 The non-perturbative renormalization group approach to KPZ Bertrand Delamotte, University Paris VI Kyoto, August 2014 Collaborators L. Canet (Grenoble, France) H. Chaté (Saclay, France) T. Kloss (Grenoble,
The non-perturbative renormalization group approach to KPZ Bertrand Delamotte, University Paris VI Kyoto, August 2014 Collaborators L. Canet (Grenoble, France) H. Chaté (Saclay, France) T. Kloss (Grenoble,
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms
 Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics
 From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics Alice Sinatra Quantum Fluids course - Complement 1 2013-2014 Plan 1 COOLING AND TRAPPING 2 CONDENSATION 3 NON-LINEAR PHYSICS AND
From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics Alice Sinatra Quantum Fluids course - Complement 1 2013-2014 Plan 1 COOLING AND TRAPPING 2 CONDENSATION 3 NON-LINEAR PHYSICS AND
Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv: v1)
 Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv:1205.4536v1) Christof Weitenberg, Rémi Desbuquois, Lauriane Chomaz, Tarik Yefsah, Julian Leonard, Jérôme Beugnon, Jean Dalibard Trieste 18.07.2012 Phase transitions
Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv:1205.4536v1) Christof Weitenberg, Rémi Desbuquois, Lauriane Chomaz, Tarik Yefsah, Julian Leonard, Jérôme Beugnon, Jean Dalibard Trieste 18.07.2012 Phase transitions
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999
![Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999](/thumbs/71/65846802.jpg) Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Quantum Turbulence, and How it is Related to Classical Turbulence
 Quantum Turbulence, and How it is Related to Classical Turbulence Xueying Wang xueying8@illinois.edu University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2018 Abstract Since the discovery of turbulence in
Quantum Turbulence, and How it is Related to Classical Turbulence Xueying Wang xueying8@illinois.edu University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2018 Abstract Since the discovery of turbulence in
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2012](/thumbs/92/110525878.jpg) arxiv:2.32v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jan 22 The nonextensive entropy approach versus the stochastic in describing subdiffusion Tadeusz Koszto lowicz Institute of Physics, Jan Kochanowski University, ul.
arxiv:2.32v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jan 22 The nonextensive entropy approach versus the stochastic in describing subdiffusion Tadeusz Koszto lowicz Institute of Physics, Jan Kochanowski University, ul.
Bessel-like SPDEs. Lorenzo Zambotti, Sorbonne Université (joint work with Henri Elad-Altman) 15th May 2018, Luminy
 Bessel-like SPDEs, Sorbonne Université (joint work with Henri Elad-Altman) Squared Bessel processes Let δ, y, and (B t ) t a BM. By Yamada-Watanabe s Theorem, there exists a unique (strong) solution (Y
Bessel-like SPDEs, Sorbonne Université (joint work with Henri Elad-Altman) Squared Bessel processes Let δ, y, and (B t ) t a BM. By Yamada-Watanabe s Theorem, there exists a unique (strong) solution (Y
Anisotropic KPZ growth in dimensions: fluctuations and covariance structure
 arxiv:0811.0682v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Nov 2008 Anisotropic KPZ growth in 2 + 1 dimensions: fluctuations and covariance structure Alexei Borodin, Patrik L. Ferrari November 4, 2008 Abstract In [5] we
arxiv:0811.0682v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Nov 2008 Anisotropic KPZ growth in 2 + 1 dimensions: fluctuations and covariance structure Alexei Borodin, Patrik L. Ferrari November 4, 2008 Abstract In [5] we
5. Gross-Pitaevskii theory
 5. Gross-Pitaevskii theory Outline N noninteracting bosons N interacting bosons, many-body Hamiltonien Mean-field approximation, order parameter Gross-Pitaevskii equation Collapse for attractive interaction
5. Gross-Pitaevskii theory Outline N noninteracting bosons N interacting bosons, many-body Hamiltonien Mean-field approximation, order parameter Gross-Pitaevskii equation Collapse for attractive interaction
Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices
 Goal of these lectures Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices Discuss some aspect of the physics of quantum low dimensional systems Planar fluids Quantum wells and MOS structures High T c
Goal of these lectures Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices Discuss some aspect of the physics of quantum low dimensional systems Planar fluids Quantum wells and MOS structures High T c
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field
 Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Some Topics in Stochastic Partial Differential Equations
 Some Topics in Stochastic Partial Differential Equations November 26, 2015 L Héritage de Kiyosi Itô en perspective Franco-Japonaise, Ambassade de France au Japon Plan of talk 1 Itô s SPDE 2 TDGL equation
Some Topics in Stochastic Partial Differential Equations November 26, 2015 L Héritage de Kiyosi Itô en perspective Franco-Japonaise, Ambassade de France au Japon Plan of talk 1 Itô s SPDE 2 TDGL equation
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Aug 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Aug 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Aug 2004](/thumbs/74/70749037.jpg) Ground state energy of a homogeneous Bose-Einstein condensate beyond Bogoliubov Christoph Weiss and André Eckardt Institut für Physik, Carl von Ossietzky Universität, D-6 Oldenburg, Germany (Dated: November
Ground state energy of a homogeneous Bose-Einstein condensate beyond Bogoliubov Christoph Weiss and André Eckardt Institut für Physik, Carl von Ossietzky Universität, D-6 Oldenburg, Germany (Dated: November
SPDEs, criticality, and renormalisation
 SPDEs, criticality, and renormalisation Hendrik Weber Mathematics Institute University of Warwick Potsdam, 06.11.2013 An interesting model from Physics I Ising model Spin configurations: Energy: Inverse
SPDEs, criticality, and renormalisation Hendrik Weber Mathematics Institute University of Warwick Potsdam, 06.11.2013 An interesting model from Physics I Ising model Spin configurations: Energy: Inverse
Bifurcations and multistability in turbulence
 Bifurcations and multistability in turbulence VKS team A. Chiffaudel L. Marié F. Ravelet F.Daviaud CEA/Saclay, France O. Dauchot A. Prigent Conceptual Aspects of turbulence, Vienna, February 28 1 Bifurcations
Bifurcations and multistability in turbulence VKS team A. Chiffaudel L. Marié F. Ravelet F.Daviaud CEA/Saclay, France O. Dauchot A. Prigent Conceptual Aspects of turbulence, Vienna, February 28 1 Bifurcations
Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection in a Rectangular Rayleigh-Bénard Cell
 Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
STRESS TRANSPORT MODELLING 2
 STRESS TRANSPORT MODELLING 2 T.J. Craft Department of Mechanical, Aerospace & Manufacturing Engineering UMIST, Manchester, UK STRESS TRANSPORT MODELLING 2 p.1 Introduction In the previous lecture we introduced
STRESS TRANSPORT MODELLING 2 T.J. Craft Department of Mechanical, Aerospace & Manufacturing Engineering UMIST, Manchester, UK STRESS TRANSPORT MODELLING 2 p.1 Introduction In the previous lecture we introduced
Non-Equilibrium Criticality in Driven Open Quantum Systems
 Cold Atoms meet Quantum Field Theory July 08 2015 Bad Honnef, Germany Non-Equilibrium Criticality in Driven Open Quantum Systems Sebastian Diehl Institute for Theoretical Physics, Technical University
Cold Atoms meet Quantum Field Theory July 08 2015 Bad Honnef, Germany Non-Equilibrium Criticality in Driven Open Quantum Systems Sebastian Diehl Institute for Theoretical Physics, Technical University
Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter
 Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi University of Camerino, Italy Naples, 24 May,2017 Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi (2017) Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter 2017
Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi University of Camerino, Italy Naples, 24 May,2017 Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi (2017) Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter 2017
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/113658716.jpg) arxiv:1901.01924v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 E-mail: sigtryggur.hauksson@mail.mcgill.ca Sangyong Jeon E-mail: jeon@physics.mcgill.ca Charles Gale E-mail: gale@physics.mcgill.ca Jets are a promising way to probe
arxiv:1901.01924v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 E-mail: sigtryggur.hauksson@mail.mcgill.ca Sangyong Jeon E-mail: jeon@physics.mcgill.ca Charles Gale E-mail: gale@physics.mcgill.ca Jets are a promising way to probe
Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow
 Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow Kai Schneider 1 1 Benjamin Kadoch, Wouter Bos & Marie Farge 3 1 CMI, Université Aix-Marseille, France 2 LMFA, Ecole Centrale, Lyon, France 3 LMD, Ecole
Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow Kai Schneider 1 1 Benjamin Kadoch, Wouter Bos & Marie Farge 3 1 CMI, Université Aix-Marseille, France 2 LMFA, Ecole Centrale, Lyon, France 3 LMD, Ecole
Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer
 Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer Elisabeth Agoritsas (1), Thierry Giamarchi (2) Vincent Démery (3), Alberto Rosso (4) Reinaldo García-García (3),
Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer Elisabeth Agoritsas (1), Thierry Giamarchi (2) Vincent Démery (3), Alberto Rosso (4) Reinaldo García-García (3),
Weak universality of the KPZ equation
 Weak universality of the KPZ equation M. Hairer, joint with J. Quastel University of Warwick Buenos Aires, July 29, 2014 KPZ equation Introduced by Kardar, Parisi and Zhang in 1986. Stochastic partial
Weak universality of the KPZ equation M. Hairer, joint with J. Quastel University of Warwick Buenos Aires, July 29, 2014 KPZ equation Introduced by Kardar, Parisi and Zhang in 1986. Stochastic partial
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Title. Statistical behaviour of optical vortex fields. F. Stef Roux. CSIR National Laser Centre, South Africa
 . p.1/37 Title Statistical behaviour of optical vortex fields F. Stef Roux CSIR National Laser Centre, South Africa Colloquium presented at School of Physics National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland
. p.1/37 Title Statistical behaviour of optical vortex fields F. Stef Roux CSIR National Laser Centre, South Africa Colloquium presented at School of Physics National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland
Many-body physics 2: Homework 8
 Last update: 215.1.31 Many-body physics 2: Homework 8 1. (1 pts) Ideal quantum gases (a)foranidealquantumgas,showthatthegrandpartitionfunctionz G = Tre β(ĥ µ ˆN) is given by { [ ] 1 Z G = i=1 for bosons,
Last update: 215.1.31 Many-body physics 2: Homework 8 1. (1 pts) Ideal quantum gases (a)foranidealquantumgas,showthatthegrandpartitionfunctionz G = Tre β(ĥ µ ˆN) is given by { [ ] 1 Z G = i=1 for bosons,
the renormalization group (RG) idea
 the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
Interface depinning in a disordered medium - numerical results
 Interface depinning in a disordered medium - numerical results Heiko Leschhorn Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Postfach 102148, D-4630 Bochum, Germany arxiv:cond-mat/9302039v1 26 Feb
Interface depinning in a disordered medium - numerical results Heiko Leschhorn Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Postfach 102148, D-4630 Bochum, Germany arxiv:cond-mat/9302039v1 26 Feb
Aspects of Kicked Quantum Dynamics
 Aspects of Kicked Quantum Dynamics Talk given at Meccanica - a Conference in honor of Sandro Graffi, Bologna Aug. 08 Italo Guarneri August 20, 2008 Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems - Universita
Aspects of Kicked Quantum Dynamics Talk given at Meccanica - a Conference in honor of Sandro Graffi, Bologna Aug. 08 Italo Guarneri August 20, 2008 Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems - Universita
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram
 Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
Non-equilibrium phase transitions
 Non-equilibrium phase transitions An Introduction Lecture III Haye Hinrichsen University of Würzburg, Germany March 2006 Third Lecture: Outline 1 Directed Percolation Scaling Theory Langevin Equation 2
Non-equilibrium phase transitions An Introduction Lecture III Haye Hinrichsen University of Würzburg, Germany March 2006 Third Lecture: Outline 1 Directed Percolation Scaling Theory Langevin Equation 2
1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology... 2
 Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
On growth, disorder, and field theory
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1 (1998) 995 995. Printed in the UK PII: S953-8984(98)96386-X REVIEW ARTICLE On growth, disorder, and field theory Michael Lässig Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1 (1998) 995 995. Printed in the UK PII: S953-8984(98)96386-X REVIEW ARTICLE On growth, disorder, and field theory Michael Lässig Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung
Turbulent spectra generated by singularities
 Turbulent spectra generated by singularities p. Turbulent spectra generated by singularities E.A. Kuznetsov Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Moscow Russia In collaboration with: V. Naulin A.H.
Turbulent spectra generated by singularities p. Turbulent spectra generated by singularities E.A. Kuznetsov Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Moscow Russia In collaboration with: V. Naulin A.H.
Quantum phase transitions of insulators, superconductors and metals in two dimensions
 Quantum phase transitions of insulators, superconductors and metals in two dimensions Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Outline 1. Phenomenology of the cuprate superconductors (and other
Quantum phase transitions of insulators, superconductors and metals in two dimensions Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Outline 1. Phenomenology of the cuprate superconductors (and other
Quantum quenches and thermalization on scale-free graphs
 Francesco Caravelli Quantum quenches and thermalization on scale-free graphs Francesco Caravelli arxiv:1307.4018v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Oct 2014 Full list of author information is available at the end
Francesco Caravelli Quantum quenches and thermalization on scale-free graphs Francesco Caravelli arxiv:1307.4018v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Oct 2014 Full list of author information is available at the end
Electronic quasiparticles and competing orders in the cuprate superconductors
 Electronic quasiparticles and competing orders in the cuprate superconductors Andrea Pelissetto Rome Subir Sachdev Ettore Vicari Pisa Yejin Huh Harvard Harvard Gapless nodal quasiparticles in d-wave superconductors
Electronic quasiparticles and competing orders in the cuprate superconductors Andrea Pelissetto Rome Subir Sachdev Ettore Vicari Pisa Yejin Huh Harvard Harvard Gapless nodal quasiparticles in d-wave superconductors
Scaling exponents for certain 1+1 dimensional directed polymers
 Scaling exponents for certain 1+1 dimensional directed polymers Timo Seppäläinen Department of Mathematics University of Wisconsin-Madison 2010 Scaling for a polymer 1/29 1 Introduction 2 KPZ equation
Scaling exponents for certain 1+1 dimensional directed polymers Timo Seppäläinen Department of Mathematics University of Wisconsin-Madison 2010 Scaling for a polymer 1/29 1 Introduction 2 KPZ equation
VIII.B Equilibrium Dynamics of a Field
 VIII.B Equilibrium Dynamics of a Field The next step is to generalize the Langevin formalism to a collection of degrees of freedom, most conveniently described by a continuous field. Let us consider the
VIII.B Equilibrium Dynamics of a Field The next step is to generalize the Langevin formalism to a collection of degrees of freedom, most conveniently described by a continuous field. Let us consider the
