New Tools for Analysing Power System Dynamics
|
|
|
- Laurel Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 New Tools for Analysing Power System Dynamics Ian A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison (With support from many talented people.) PSerc Research Tele-Seminar March 2, 2004 PSERC
2 Two main themes 2 Dealing with parameter uncertainty How much confidence is there in load model parameters? Generator parameters? Simulation is too time-consuming to repeat studies for multiple parameter sets. Inverse problems What does this mean? Trajectory sensitivities form a common link between these two areas.
3 3 Inverse problems Direct problem: input x process K model output? Inverse problem (system identification): input process output x? model y Inverse problem (causation): input process output? K y model
4 Inverse problems (continued) 4 Power system context Identification problems Load models and parameters Generator parameters What controller parameters ensure appropriate fault-recovery dynamics? What load changes maintain dynamic security? Under what conditions could a fault induce incidental protection operation? Protection operation caused by post-fault transients.
5 Trajectory sensitivities 5 Let φ(t; λ) describe the trajectory (flow), at time t, due to parameters λ. Determined by simulation. The corresponding trajectory sensitivities are Φ(t; λ) φ λ (t; λ). Characteristics of sensitivities Φ: Quantify the change in a trajectory due to a small change in parameters. Can be computed efficiently, as a by-product of simulating the nominal trajectory. Well defined for nonlinear non-smooth systems. Provide gradient information that underlies Newton-type algorithms (shooting methods).
6 Trajectory approximation 6 Taylor series expansion of the flow gives, φ(t; λ + λ) =φ(t; λ)+φ(t; λ) λ Example: Generator field voltage Field voltage, E fd (pu) Actual computed trajectory, t cl =0.23 sec, E fdmax =5.8 0 Approximate perturbed trajectory, t cl =0.21 sec, E fdmax =5.0 Actual perturbed trajectory (for comparison) Time (sec)
7 Error bounds 7 Many system parameters are not known precisely, but are better described by probability distributions. Select parameter sets using a Monte-Carlo process. Form an approximate trajectory for each set Terminal voltage (pu) Nominal trajectory Error bound Time (sec)
8 Parameter estimation 8 Desire a systematic approach to: Determine which parameters are well conditioned (identifiable). Estimate those parameters Algorithm: Minimize the nonlinear least-squares cost J (λ) = 1 m ( ) 2 φ(t k ; λ) ms(t k ) 2 k=1 via the Gauss-Newton iterative scheme Φ(λ j ) T Φ(λ j ) λ j+1 =Φ(λ j ) T ( φ(λ j ) ms ) λ j+1 = λ j α j+1 λ j+1
9 Parameter estimation (continued) 9 Nordel example 450 Bus 12 voltage, V 12 (kv) Measured Initial parameter values Estimated parameter values Time (s)
10 Performance specification (grazing) 10 Trajectory is tangential to a performance boundary. Parameter values λ g λ+ λ Boundary x + x g
11 11 Performance specification (continued) Example: Generator field control. What value of E fd,max ensures voltage does not overshoot abnormally following a fault? V ref E fdmax + V t 1 1+sT R Σ 1+sT C 1+sT B K A 1+sT A E fd + V PSS E fdmin V max 1+sT 1 1+sT 2 V min st w 1+sT w K PSS ω
12 Performance specification (continued) 12 Terminal voltage constrained below 1.2 pu during initial transient Hypersurface b(x,y): V t 1.2= Terminal voltage, V t (pu) Initial parameter value Grazing parameter value Time (sec)
13 Performance specification (continued) 13 Example: Distance protection. How far can load be increased before a fault disturbance induces incidental protection operation? 1.2 Initial trajectory Grazing trajectory 1 b(x,y)= X c 2 c 1 a 2 a 1 0 b b R
14 Performance specification (continued) 14 Example: Distance protection with timing. Replace conditions enforcing tangential contact by conditions specifying time inside mho characteristic. Initial trajectory 1.2 Time constraint trajectory 1 b(x,y)= X a 2 a 1 c 2 0 b 2 c b R
15 Performance specification (continued) 15 Initial, grazing, and time-constraint cases. 3 Initial trajectory 2.5 Grazing trajectory Time constraint trajectory b(x,y) τ=0.3 s Time (s)
16 Dynamic embedded optimization 16 Minimize the cost J (λ) =ϕ ( φ(t f ; λ),λ,t f ) + tf t 0 ψ ( φ(t; λ),λ,t ) dt where φ(t; λ) satisfies the dynamic model. Closely related to optimal control, but optimizing over finite dimensional design parameters. Some technical issues arise for hybrid (switched) systems if event order changes.
17 17 Dynamic embedded optimization (continued) Example: AVR/PSS tuning What values of PSS output limits give best damping? V ref E fdmax + V t 1 1+sT R Σ 1+sT C 1+sT B K A 1+sT A E fd + V PSS E fdmin V max 1+sT 1 1+sT 2 V min st w 1+sT w K PSS ω
18 Dynamic embedded optimization (continued) 18 Optimization adjusted the lower PSS limit from -0.1 to pu. Noticable damping improvement Generator angle, δ (rad) Initial limit values Optimal limit values Time (sec)
19 Conclusions 19 Parameter uncertainty is unavoidable in power systems, and should be considered in decision making. This is computationally feasible using first-order approximations of trajectories. Many analysis and design processes are effectively inverse problems. Such problems can be solved using gradient-based iterative algorithms. In both cases, efficient computation of trajectory sensitivities underlies practical algorithms.
20 20 Extra Material
21 Simulation model 21 Differential Algebraic Impulsive Switched (DAIS) model ẋ = f(x, y)+ r i=1 0=g(x, y) g (0) (x, y)+ where ( ) δ(y r,i ) h i (x, y) x s g (j) (x, y) j=1 ẋ = f(x, y) x + = h i (x,y ), y r,i =0 g (j) (x, y) = g (j ) (x, y) g (j+) (x, y) y s,j < 0 y s,j > 0 j =1,..., s
22 Trajectory sensitivity computation 22 Smooth sections of trajectories evolve according to ẋ = f(x, y) 0=g(x, y) Differentiating with respect to x 0 gives Initial conditions Φ x = f x (t)φ x + f y (t)φ y 0= g x (t)φ x + g y (t)φ y Φ x (t 0 )=I
23 ff Trajectory sensitivities at events 23 At an event (at time τ), sensitivities evolve according to jump conditions, Φ x (τ + )=Φ x (τ ) ( f + f ) τ x 0 Nominal trajectory @ Φ x 0 Ω ΩΩffi@ f τ - ΦΦ* x(τ)+ x Triggering f + τ Φ + x Φ ΦΦΦΦ 0 Φ ΦΦΦΦ ff x(τ + τ)
24 Grazing and time-constraint formulation 24 For simplicity, the ODE form of equations is presented rather than the DAE form. Grazing φ(t g ; λ) x g =0 b(x g )=0 b x (x g )f(x g )=0 Time constraint φ(t 1 ; λ) x 1 =0 φ(t 2 ; λ) x 2 =0 b(x 1 )=0 b(x 2 )=0 t 1 t 2 τ spec =0
Systematic Tuning of Nonlinear Power System Controllers
 Proceedings of the 22 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications September 8-2, 22 Glasgow, Scotland, U.K. Systematic Tuning of Nonlinear Power System Controllers Ian A. Hiskens Department of
Proceedings of the 22 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications September 8-2, 22 Glasgow, Scotland, U.K. Systematic Tuning of Nonlinear Power System Controllers Ian A. Hiskens Department of
VALUE-ADDED SIMULATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS. Ian A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison
 VALUE-ADDED SIMULATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS Ian A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Email: hiskens@engr.wisc.edu Abstract Analytical investigations
VALUE-ADDED SIMULATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS Ian A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Email: hiskens@engr.wisc.edu Abstract Analytical investigations
Shooting Methods for Locating Grazing Phenomena in Hybrid Systems
 Shooting Methods for Locating Grazing Phenomena in Hybrid Systems Vaibhav Donde Ian A. Hiskens Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Dept. of Elect. and Comp. Engineering Cyclotron Road University of Wisconsin-Madison
Shooting Methods for Locating Grazing Phenomena in Hybrid Systems Vaibhav Donde Ian A. Hiskens Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Dept. of Elect. and Comp. Engineering Cyclotron Road University of Wisconsin-Madison
IEEE PES Task Force on Benchmark Systems for Stability Controls
 IEEE PES Task Force on Benchmark Systems for Stability Controls Ian Hiskens November 9, 3 Abstract This report summarizes a study of an IEEE -generator, 39-bus system. Three types of analysis were performed:
IEEE PES Task Force on Benchmark Systems for Stability Controls Ian Hiskens November 9, 3 Abstract This report summarizes a study of an IEEE -generator, 39-bus system. Three types of analysis were performed:
POWER system dynamic behavior is subject to performance
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 20, NO 4, NOVEMBER 2005 1967 Dynamic Performance Assessment: Grazing and Related Phenomena Vaibhav Donde, Member, IEEE, and Ian A Hiskens, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 20, NO 4, NOVEMBER 2005 1967 Dynamic Performance Assessment: Grazing and Related Phenomena Vaibhav Donde, Member, IEEE, and Ian A Hiskens, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
Iterative Computation of Marginally Stable Trajectories
 Iterative Computation of Marginally Stable Trajectories I.A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, WI 53706, USA August 4, 2003 Abstract Stability
Iterative Computation of Marginally Stable Trajectories I.A. Hiskens Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, WI 53706, USA August 4, 2003 Abstract Stability
Phase Boundary Computation for Fault Induced Delayed Voltage Recovery
 IEEE th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) December -,. Osaka, Japan Phase Boundary Computation for Fault Induced Delayed Voltage Recovery Michael W. Fisher Ian A. Hiskens Abstract Distribution
IEEE th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) December -,. Osaka, Japan Phase Boundary Computation for Fault Induced Delayed Voltage Recovery Michael W. Fisher Ian A. Hiskens Abstract Distribution
Significance of Load Modelling in Power System Dynamics
 X SEPOPE 21 a 25 de maio de 2006 May 21 rst to 25 th 2006 FLORIANÓPOLIS (SC) BRASIL X SIMPÓSIO DE ESPECIALISTAS EM PLANEJAMENTO DA OPERAÇÃO E EXPANSÃO ELÉTRICA X SYMPOSIUM OF SPECIALISTS IN ELECTRIC OPERATIONAL
X SEPOPE 21 a 25 de maio de 2006 May 21 rst to 25 th 2006 FLORIANÓPOLIS (SC) BRASIL X SIMPÓSIO DE ESPECIALISTAS EM PLANEJAMENTO DA OPERAÇÃO E EXPANSÃO ELÉTRICA X SYMPOSIUM OF SPECIALISTS IN ELECTRIC OPERATIONAL
A Stable Finite Horizon Model Predictive Control for Power System Voltage Collapse Prevention
 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 2011 A Stable Finite Horizon Model Predictive Control for Power System Voltage
2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 2011 A Stable Finite Horizon Model Predictive Control for Power System Voltage
ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II : 7 - Transient Stability
 ECE 4/5 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II : 7 - Transient Stability Spring 014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 Transient Stability The ability of the power system to maintain synchronism
ECE 4/5 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II : 7 - Transient Stability Spring 014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 Transient Stability The ability of the power system to maintain synchronism
IEOR 265 Lecture 14 (Robust) Linear Tube MPC
 IEOR 265 Lecture 14 (Robust) Linear Tube MPC 1 LTI System with Uncertainty Suppose we have an LTI system in discrete time with disturbance: x n+1 = Ax n + Bu n + d n, where d n W for a bounded polytope
IEOR 265 Lecture 14 (Robust) Linear Tube MPC 1 LTI System with Uncertainty Suppose we have an LTI system in discrete time with disturbance: x n+1 = Ax n + Bu n + d n, where d n W for a bounded polytope
Behaviour of synchronous machine during a short-circuit (a simple example of electromagnetic transients)
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability (a simple example of electromagnetic transients) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 25 Objectives
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability (a simple example of electromagnetic transients) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 25 Objectives
Nonlinear Dynamic Model Evaluation From Disturbance Measurements
 702 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 16, NO 4, NOVEMBER 2001 Nonlinear Dynamic Model Evaluation From Disturbance Measurements Ian A Hiskens, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract The nonlinear nonsmooth
702 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 16, NO 4, NOVEMBER 2001 Nonlinear Dynamic Model Evaluation From Disturbance Measurements Ian A Hiskens, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract The nonlinear nonsmooth
Accelerated Block-Coordinate Relaxation for Regularized Optimization
 Accelerated Block-Coordinate Relaxation for Regularized Optimization Stephen J. Wright Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin, Madison October 09, 2012 Problem descriptions Consider where f is smooth
Accelerated Block-Coordinate Relaxation for Regularized Optimization Stephen J. Wright Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin, Madison October 09, 2012 Problem descriptions Consider where f is smooth
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Self-Tuning Control for Synchronous Machine Stabilization
 http://dx.doi.org/.5755/j.eee.2.4.2773 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 392-25, VOL. 2, NO. 4, 25 Self-Tuning Control for Synchronous Machine Stabilization Jozef Ritonja Faculty of Electrical Engineering
http://dx.doi.org/.5755/j.eee.2.4.2773 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 392-25, VOL. 2, NO. 4, 25 Self-Tuning Control for Synchronous Machine Stabilization Jozef Ritonja Faculty of Electrical Engineering
SHOOTING METHODS FOR LOCATING GRAZING PHENOMENA IN HYBRID SYSTEMS *
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 6, No. 3 (26) 67 692 c World Scientific Publishing Company SHOOTING METHODS FOR LOCATING GRAZING PHENOMENA IN HYBRID SYSTEMS * VAIBHAV DONDE Lawrence
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 6, No. 3 (26) 67 692 c World Scientific Publishing Company SHOOTING METHODS FOR LOCATING GRAZING PHENOMENA IN HYBRID SYSTEMS * VAIBHAV DONDE Lawrence
Ch 6.4: Differential Equations with Discontinuous Forcing Functions
 Ch 6.4: Differential Equations with Discontinuous Forcing Functions! In this section focus on examples of nonhomogeneous initial value problems in which the forcing function is discontinuous. Example 1:
Ch 6.4: Differential Equations with Discontinuous Forcing Functions! In this section focus on examples of nonhomogeneous initial value problems in which the forcing function is discontinuous. Example 1:
Simulating a Power System
 Simulating a Power System Presented by Prof. Tyrone Fernando School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EECE), University of Western Australia (UWA) 1. Motivations In an actual power system, it is
Simulating a Power System Presented by Prof. Tyrone Fernando School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EECE), University of Western Australia (UWA) 1. Motivations In an actual power system, it is
max clear Figure 1 below illustrates a stable case. P post (f) (g) (e) A 2 (d) (c)
 Stability 4. Introduction In the previous notes (Stability 3, we developed the equal area iterion, which says that For stability, A =A, which means the decelerating energy (A must equal the accelerating
Stability 4. Introduction In the previous notes (Stability 3, we developed the equal area iterion, which says that For stability, A =A, which means the decelerating energy (A must equal the accelerating
Computers and Mathematics with Applications. Chaos suppression via periodic pulses in a class of piece-wise continuous systems
 Computers and Mathematics with Applications 64 (2012) 849 855 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Computers and Mathematics with Applications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa
Computers and Mathematics with Applications 64 (2012) 849 855 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Computers and Mathematics with Applications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa
MPC-Based Load Shedding for Voltage Stability Enhancement
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 2005 Seville, Spain, December 2-5, 2005 WeA09.6 MPC-Based Load Shedding for Voltage Stability Enhancement
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 2005 Seville, Spain, December 2-5, 2005 WeA09.6 MPC-Based Load Shedding for Voltage Stability Enhancement
MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Basics of Optimization Problems
 MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Basics of Optimization Problems Xiaojing Ye Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Xiaojing Ye, Math & Stat, Georgia State University 0 A standard minimization
MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Basics of Optimization Problems Xiaojing Ye Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Xiaojing Ye, Math & Stat, Georgia State University 0 A standard minimization
Power System Stability GENERATOR CONTROL AND PROTECTION
 Power System Stability Outline Basis for Steady-State Stability Transient Stability Effect of Excitation System on Stability Small Signal Stability Power System Stabilizers Speed Based Integral of Accelerating
Power System Stability Outline Basis for Steady-State Stability Transient Stability Effect of Excitation System on Stability Small Signal Stability Power System Stabilizers Speed Based Integral of Accelerating
1.2 Derivation. d p f = d p f(x(p)) = x fd p x (= f x x p ). (1) Second, g x x p + g p = 0. d p f = f x g 1. The expression f x gx
 PDE-constrained optimization and the adjoint method Andrew M. Bradley November 16, 21 PDE-constrained optimization and the adjoint method for solving these and related problems appear in a wide range of
PDE-constrained optimization and the adjoint method Andrew M. Bradley November 16, 21 PDE-constrained optimization and the adjoint method for solving these and related problems appear in a wide range of
EXCITATION CONTROL OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR USING A FUZZY LOGIC BASED BACKSTEPPING APPROACH
 EXCITATION CONTROL OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR USING A FUZZY LOGIC BASED BACKSTEPPING APPROACH Abhilash Asekar 1 1 School of Engineering, Deakin University, Waurn Ponds, Victoria 3216, Australia ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
EXCITATION CONTROL OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR USING A FUZZY LOGIC BASED BACKSTEPPING APPROACH Abhilash Asekar 1 1 School of Engineering, Deakin University, Waurn Ponds, Victoria 3216, Australia ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
Introduction to State Estimation of Power Systems ECG 740
 Introduction to State Estimation of Power Systems ECG 740 Introduction To help avoid major system failures, electric utilities have installed extensive supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA)
Introduction to State Estimation of Power Systems ECG 740 Introduction To help avoid major system failures, electric utilities have installed extensive supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA)
QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers
 45-E-PSS-75 QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Seyyed Mohammad Mahdi Alavi, Roozbeh Izadi-Zamanabadi Department of Control Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark Correspondence
45-E-PSS-75 QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Seyyed Mohammad Mahdi Alavi, Roozbeh Izadi-Zamanabadi Department of Control Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark Correspondence
TIME-domain simulation is an important approach for
 1 Application of Pseudo-Transient Continuation Method in Dynamic Stability Analysis Xiaozhe Wang, Student Member, IEEE, Hsiao-Dong Chiang, Fellow, IEEE. arxiv:142.4159v1 [cs.sy] 17 Feb 214 Abstract In
1 Application of Pseudo-Transient Continuation Method in Dynamic Stability Analysis Xiaozhe Wang, Student Member, IEEE, Hsiao-Dong Chiang, Fellow, IEEE. arxiv:142.4159v1 [cs.sy] 17 Feb 214 Abstract In
Design of PSS and SVC Controller Using PSO Algorithm to Enhancing Power System Stability
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar Apr. 2015), PP 01-09 www.iosrjournals.org Design of PSS and SVC Controller
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar Apr. 2015), PP 01-09 www.iosrjournals.org Design of PSS and SVC Controller
SPEED-GRADIENT-BASED CONTROL OF POWER NETWORK: CASE STUDY
 CYBERNETICS AND PHYSICS, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 2016, 85 90 SPEED-GRADIENT-BASED CONTROL OF POWER NETWORK: CASE STUDY Igor Furtat Control of Complex Systems ITMO University Russia cainenash@mail.ru Nikita Tergoev
CYBERNETICS AND PHYSICS, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 2016, 85 90 SPEED-GRADIENT-BASED CONTROL OF POWER NETWORK: CASE STUDY Igor Furtat Control of Complex Systems ITMO University Russia cainenash@mail.ru Nikita Tergoev
Review: control, feedback, etc. Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization
 Plan of the Lecture Review: control, feedback, etc Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization Goal: a general framework that encompasses all examples of interest Once we have mastered
Plan of the Lecture Review: control, feedback, etc Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization Goal: a general framework that encompasses all examples of interest Once we have mastered
Dynamic Security Analysis of Power Systems by a Sampling-based Algorithm
 1 Dynamic Security Analysis of Power Systems by a Sampling-based Algorithm Qiang Wu, T. John Koo, Yoshihiko Susuki Abstract arxiv:1811.03301v1 [cs.sy] 8 Nov 2018 Dynamic security analysis is an important
1 Dynamic Security Analysis of Power Systems by a Sampling-based Algorithm Qiang Wu, T. John Koo, Yoshihiko Susuki Abstract arxiv:1811.03301v1 [cs.sy] 8 Nov 2018 Dynamic security analysis is an important
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
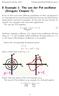 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Modeling and Experimentation: Compound Pendulum
 Modeling and Experimentation: Compound Pendulum Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2014 Overview This lab focuses on developing a mathematical
Modeling and Experimentation: Compound Pendulum Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2014 Overview This lab focuses on developing a mathematical
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS
 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 3 NEWTONS SHOOTING METHOD 4 SUMMARY OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 3 NEWTONS SHOOTING
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 3 NEWTONS SHOOTING METHOD 4 SUMMARY OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 3 NEWTONS SHOOTING
Trajectory Sensitivity Analysis as a Means of Performing Dynamic Load Sensitivity Studies in Power System Planning
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2014 Grid of the Future Symposium Trajectory Sensitivity Analysis as a Means of Performing Dynamic Load Sensitivity Studies
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2014 Grid of the Future Symposium Trajectory Sensitivity Analysis as a Means of Performing Dynamic Load Sensitivity Studies
Dynamic simulation of a five-bus system
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamic simulation of a five-bus system Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 16 System modelling
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamic simulation of a five-bus system Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 16 System modelling
MVE165/MMG631 Linear and integer optimization with applications Lecture 13 Overview of nonlinear programming. Ann-Brith Strömberg
 MVE165/MMG631 Overview of nonlinear programming Ann-Brith Strömberg 2015 05 21 Areas of applications, examples (Ch. 9.1) Structural optimization Design of aircraft, ships, bridges, etc Decide on the material
MVE165/MMG631 Overview of nonlinear programming Ann-Brith Strömberg 2015 05 21 Areas of applications, examples (Ch. 9.1) Structural optimization Design of aircraft, ships, bridges, etc Decide on the material
Lecture 10: Singular Perturbations and Averaging 1
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.243j (Fall 2003): DYNAMICS OF NONLINEAR SYSTEMS by A. Megretski Lecture 10: Singular Perturbations and
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.243j (Fall 2003): DYNAMICS OF NONLINEAR SYSTEMS by A. Megretski Lecture 10: Singular Perturbations and
Transient Stability Analysis with PowerWorld Simulator
 Transient Stability Analysis with PowerWorld Simulator T1: Transient Stability Overview, Models and Relationships 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 support@powerworld.com
Transient Stability Analysis with PowerWorld Simulator T1: Transient Stability Overview, Models and Relationships 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 support@powerworld.com
Design and Application of Fuzzy PSS for Power Systems Subject to Random Abrupt Variations of the Load
 Design and Application of Fuzzy PSS for Power Systems Subject to Random Abrupt Variations of the Load N. S. D. Arrifano, V. A. Oliveira and R. A. Ramos Abstract In this paper, a design method and application
Design and Application of Fuzzy PSS for Power Systems Subject to Random Abrupt Variations of the Load N. S. D. Arrifano, V. A. Oliveira and R. A. Ramos Abstract In this paper, a design method and application
Test Case: Power System Voltage Stability
 Test Case: Power System Voltage Stability Mats Larsson Corporate Research Mats Larsson / 2002-02-18 / 1 2002 Corporate Research Ltd, Baden, Switzerland Preview The People from Characteristics of Power
Test Case: Power System Voltage Stability Mats Larsson Corporate Research Mats Larsson / 2002-02-18 / 1 2002 Corporate Research Ltd, Baden, Switzerland Preview The People from Characteristics of Power
Plan of the Lecture. Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control
 Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic:
Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic:
SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL, MECHANICAL AND MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS. Transient Stability LECTURE NOTES SPRING SEMESTER, 2008
 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL, MECHANICAL AND MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS LECTURE NOTES Transient Stability SPRING SEMESTER, 008 October 7, 008 Transient Stability Transient stability refers to the ability of a synchronous
SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL, MECHANICAL AND MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS LECTURE NOTES Transient Stability SPRING SEMESTER, 008 October 7, 008 Transient Stability Transient stability refers to the ability of a synchronous
Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control
 Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control Goal: understand the difference between open-loop and closed-loop (feedback)
Plan of the Lecture Review: stability; Routh Hurwitz criterion Today s topic: basic properties and benefits of feedback control Goal: understand the difference between open-loop and closed-loop (feedback)
Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs. 1 Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs
 Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs.. Finite difference scheme. We consider a simple example u := subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions ( ) u
Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs.. Finite difference scheme. We consider a simple example u := subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions ( ) u
APPLICATION OF D-K ITERATION TECHNIQUE BASED ON H ROBUST CONTROL THEORY FOR POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER DESIGN
 APPLICATION OF D-K ITERATION TECHNIQUE BASED ON H ROBUST CONTROL THEORY FOR POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER DESIGN Amitava Sil 1 and S Paul 2 1 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Neotia Institute
APPLICATION OF D-K ITERATION TECHNIQUE BASED ON H ROBUST CONTROL THEORY FOR POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER DESIGN Amitava Sil 1 and S Paul 2 1 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Neotia Institute
Optimal Control of Switching Surfaces
 Optimal Control of Switching Surfaces Y. Wardi, M. Egerstedt, M. Boccadoro, and E. Verriest {ywardi,magnus,verriest}@ece.gatech.edu School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
Optimal Control of Switching Surfaces Y. Wardi, M. Egerstedt, M. Boccadoro, and E. Verriest {ywardi,magnus,verriest}@ece.gatech.edu School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
Funnel control in mechatronics: An overview
 Funnel control in mechatronics: An overview Position funnel control of stiff industrial servo-systems C.M. Hackl 1, A.G. Hofmann 2 and R.M. Kennel 1 1 Institute for Electrical Drive Systems and Power Electronics
Funnel control in mechatronics: An overview Position funnel control of stiff industrial servo-systems C.M. Hackl 1, A.G. Hofmann 2 and R.M. Kennel 1 1 Institute for Electrical Drive Systems and Power Electronics
sc Control Systems Design Q.1, Sem.1, Ac. Yr. 2010/11
 sc46 - Control Systems Design Q Sem Ac Yr / Mock Exam originally given November 5 9 Notes: Please be reminded that only an A4 paper with formulas may be used during the exam no other material is to be
sc46 - Control Systems Design Q Sem Ac Yr / Mock Exam originally given November 5 9 Notes: Please be reminded that only an A4 paper with formulas may be used during the exam no other material is to be
Convexity of the Reachable Set of Nonlinear Systems under L 2 Bounded Controls
 1 1 Convexity of the Reachable Set of Nonlinear Systems under L 2 Bounded Controls B.T.Polyak Institute for Control Science, Moscow, Russia e-mail boris@ipu.rssi.ru Abstract Recently [1, 2] the new convexity
1 1 Convexity of the Reachable Set of Nonlinear Systems under L 2 Bounded Controls B.T.Polyak Institute for Control Science, Moscow, Russia e-mail boris@ipu.rssi.ru Abstract Recently [1, 2] the new convexity
Power System Transient Stability Analysis Using Sum Of Squares Programming
 Power System Transient Stability Analysis Using Sum Of Squares Programming M. Tacchi, B. Marinescu, M. Anghel, S. Kundu, S. Benahmed and C. Cardozo Ecole Centrale Nantes-LS2N-CNRS, France sif-eddine.benahmed@eleves.ec-nantes.fr,
Power System Transient Stability Analysis Using Sum Of Squares Programming M. Tacchi, B. Marinescu, M. Anghel, S. Kundu, S. Benahmed and C. Cardozo Ecole Centrale Nantes-LS2N-CNRS, France sif-eddine.benahmed@eleves.ec-nantes.fr,
Module 6 : Preventive, Emergency and Restorative Control. Lecture 27 : Normal and Alert State in a Power System. Objectives
 Module 6 : Preventive, Emergency and Restorative Control Lecture 27 : Normal and Alert State in a Power System Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Different states in a power system
Module 6 : Preventive, Emergency and Restorative Control Lecture 27 : Normal and Alert State in a Power System Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Different states in a power system
I R TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT. Sampled-Data Modeling and Analysis of PWM DC-DC Converters Under Hysteretic Control. by C.-C. Fang, E.H.
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Sampled-Data Modeling and Analysis of PWM DC-DC Converters Under Hysteretic Control by C.-C. Fang, E.H. Abed T.R. 98-56 I R INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH ISR develops, applies
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Sampled-Data Modeling and Analysis of PWM DC-DC Converters Under Hysteretic Control by C.-C. Fang, E.H. Abed T.R. 98-56 I R INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH ISR develops, applies
and cables for offshore wind connection
 Transient analysis of transformers and cables for offshore wind connection Bjørn Gustavsen SINTEF Energy Research Trondheim, Norway Wind power R&D seminar deep sea offshore wind: Trondheim, Norway, 20-21
Transient analysis of transformers and cables for offshore wind connection Bjørn Gustavsen SINTEF Energy Research Trondheim, Norway Wind power R&D seminar deep sea offshore wind: Trondheim, Norway, 20-21
REAL-TIME TRANSIENT STABILITY ASSESSMENT
 CHAPTER 3 REAL-TIME TRANSIENT STABILITY ASSESSMENT In Chapter 2, the basic multimachine theory and the different dynamic, state and transient energy equations have been presented and the basic criterion
CHAPTER 3 REAL-TIME TRANSIENT STABILITY ASSESSMENT In Chapter 2, the basic multimachine theory and the different dynamic, state and transient energy equations have been presented and the basic criterion
VOLTAGE stability has become a major concern for the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 171 Continuation-Based Quasi-Steady-State Analysis Qin Wang, Member, IEEE, Hwachang Song, Member, IEEE, and Venkataramana Ajjarapu, Senior
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 171 Continuation-Based Quasi-Steady-State Analysis Qin Wang, Member, IEEE, Hwachang Song, Member, IEEE, and Venkataramana Ajjarapu, Senior
Summary The paper considers the problem of nding points of maximum loadability which are closest (in a local
 Calculation of Power System Critical Loading Conditions Ian A. Hiskens Yuri V. Makarov Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Newcastle, Callaghan, NSW, 8, Australia Summary
Calculation of Power System Critical Loading Conditions Ian A. Hiskens Yuri V. Makarov Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Newcastle, Callaghan, NSW, 8, Australia Summary
Forecasting Regime Shifts in Natural and Man-made Infrastructure
 Forecasting Regime Shifts in Natural and Man-made Infrastructure M.D. Lemmon Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame, USA UCONN - August, 2014 M.D. Lemmon (ND) Forecasting Regime
Forecasting Regime Shifts in Natural and Man-made Infrastructure M.D. Lemmon Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame, USA UCONN - August, 2014 M.D. Lemmon (ND) Forecasting Regime
Architectures and Algorithms for Distributed Generation Control of Inertia-Less AC Microgrids
 Architectures and Algorithms for Distributed Generation Control of Inertia-Less AC Microgrids Alejandro D. Domínguez-García Coordinated Science Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Architectures and Algorithms for Distributed Generation Control of Inertia-Less AC Microgrids Alejandro D. Domínguez-García Coordinated Science Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Abstract. 2. Dynamical model of power system
 Optimization Of Controller Parametersfornon-Linear Power Systems Using Different Optimization Techniques Rekha 1,Amit Kumar 2, A. K. Singh 3 1, 2 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engg. Dept. NIT Jamshedpur
Optimization Of Controller Parametersfornon-Linear Power Systems Using Different Optimization Techniques Rekha 1,Amit Kumar 2, A. K. Singh 3 1, 2 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engg. Dept. NIT Jamshedpur
Power system modelling under the phasor approximation
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 16 Electromagnetic transient vs. phasor-mode simulations
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 16 Electromagnetic transient vs. phasor-mode simulations
Verified High-Order Optimal Control in Space Flight Dynamics
 Verified High-Order Optimal Control in Space Flight Dynamics R. Armellin, P. Di Lizia, F. Bernelli-Zazzera K. Makino and M. Berz Fourth International Workshop on Taylor Methods Boca Raton, December 16
Verified High-Order Optimal Control in Space Flight Dynamics R. Armellin, P. Di Lizia, F. Bernelli-Zazzera K. Makino and M. Berz Fourth International Workshop on Taylor Methods Boca Raton, December 16
Reduced Size Rule Set Based Fuzzy Logic Dual Input Power System Stabilizer
 772 NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE, NPSC 2002 Reduced Size Rule Set Based Fuzzy Logic Dual Input Power System Stabilizer Avdhesh Sharma and MLKothari Abstract-- The paper deals with design of fuzzy
772 NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE, NPSC 2002 Reduced Size Rule Set Based Fuzzy Logic Dual Input Power System Stabilizer Avdhesh Sharma and MLKothari Abstract-- The paper deals with design of fuzzy
Minimax Approximation Synthesis in PSS Design by Embedding
 Minimax Approximation Synthesis in PSS Design by Embedding Gravitational Search Algorithm Dr. Akash Saxena Department of Electrical Engineering Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Jaipur, India Power
Minimax Approximation Synthesis in PSS Design by Embedding Gravitational Search Algorithm Dr. Akash Saxena Department of Electrical Engineering Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Jaipur, India Power
AMONG POWER SYSTEM CONTROLS IMPACT OF INTERACTIONS EPRI/NSF WORKSHOP PLAYACAR, APRIL 2002 GLOBAL DYNAMIC OPTIMISATION OF THE ELECTRIC POWER GRID
 EPRI/NSF WORKSHOP PLAYACAR, APRIL 00 GLOBAL DYNAMIC OPTIMISATION OF THE ELECTRIC POWER GRID IMPACT OF INTERACTIONS AMONG POWER SYSTEM CONTROLS NELSON MARTINS JULIO C.R. FERRAZ, SERGIO GOMES JR. CEPEL COPPE/UFRJ
EPRI/NSF WORKSHOP PLAYACAR, APRIL 00 GLOBAL DYNAMIC OPTIMISATION OF THE ELECTRIC POWER GRID IMPACT OF INTERACTIONS AMONG POWER SYSTEM CONTROLS NELSON MARTINS JULIO C.R. FERRAZ, SERGIO GOMES JR. CEPEL COPPE/UFRJ
Transient stability analysis and control of power systems with considering flux decay by energy function approach
 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 60, No. 1, 2012 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-012-0001-1 Transient stability analysis and control of power systems with considering flux decay
BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 60, No. 1, 2012 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-012-0001-1 Transient stability analysis and control of power systems with considering flux decay
Bounding Uncertainty in Power System Dynamic Simulations
 Bounding Uncertainty in Power System Dynamic Simulations Ian A. Hiskens M.A. Pai Trong B, Nguyen Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at IJrbana-Champaign 1406 W. Green
Bounding Uncertainty in Power System Dynamic Simulations Ian A. Hiskens M.A. Pai Trong B, Nguyen Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at IJrbana-Champaign 1406 W. Green
1. Introduction. Keywords Transient Stability Analysis, Power System, Swing Equation, Three-Phase Fault, Fault Clearing Time
 Energy and Power 17, 7(1): -36 DOI: 1.593/j.ep.1771.3 Numerical Simulations for Transient Stability Analysis of Two-Machine Power System Considering Three-Phase Fault under Different Fault Clearing Times
Energy and Power 17, 7(1): -36 DOI: 1.593/j.ep.1771.3 Numerical Simulations for Transient Stability Analysis of Two-Machine Power System Considering Three-Phase Fault under Different Fault Clearing Times
Excitation control for improving transient stability limit and voltage regulation with dynamic loads
 Excitation control for improving transient stability limit and voltage regulation with dynamic loads M. J. Hossain, H. R. Pota, M. A. Mahmud, R. A. Ramos, SEIT, UNSW@ADFA, Canberra, ACT-2600, Australia.
Excitation control for improving transient stability limit and voltage regulation with dynamic loads M. J. Hossain, H. R. Pota, M. A. Mahmud, R. A. Ramos, SEIT, UNSW@ADFA, Canberra, ACT-2600, Australia.
CHAPTER 10: Numerical Methods for DAEs
 CHAPTER 10: Numerical Methods for DAEs Numerical approaches for the solution of DAEs divide roughly into two classes: 1. direct discretization 2. reformulation (index reduction) plus discretization Direct
CHAPTER 10: Numerical Methods for DAEs Numerical approaches for the solution of DAEs divide roughly into two classes: 1. direct discretization 2. reformulation (index reduction) plus discretization Direct
CHAPTER 2 DYNAMIC STABILITY MODEL OF THE POWER SYSTEM
 20 CHAPTER 2 DYNAMIC STABILITY MODEL OF THE POWER SYSTEM 2. GENERAL Dynamic stability of a power system is concerned with the dynamic behavior of the system under small perturbations around an operating
20 CHAPTER 2 DYNAMIC STABILITY MODEL OF THE POWER SYSTEM 2. GENERAL Dynamic stability of a power system is concerned with the dynamic behavior of the system under small perturbations around an operating
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
Shallow water approximations for water waves over a moving bottom. Tatsuo Iguchi Department of Mathematics, Keio University
 Shallow water approximations for water waves over a moving bottom Tatsuo Iguchi Department of Mathematics, Keio University 1 Tsunami generation and simulation Submarine earthquake occures with a seabed
Shallow water approximations for water waves over a moving bottom Tatsuo Iguchi Department of Mathematics, Keio University 1 Tsunami generation and simulation Submarine earthquake occures with a seabed
Prediction of Instability Points Using System Identification
 Prediction of Instability Points Using System Identification Hassan Ghasemi laudio A. añizares John Reeve hassan@thunderbox.uwaterloo.ca ccanizar@engmail.uwaterloo.ca J.Reeve@ece.uwaterloo.ca Department
Prediction of Instability Points Using System Identification Hassan Ghasemi laudio A. añizares John Reeve hassan@thunderbox.uwaterloo.ca ccanizar@engmail.uwaterloo.ca J.Reeve@ece.uwaterloo.ca Department
The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System
 1 The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System M. M. Alomari and B. S. Rodanski University of Technology, Sydney (UTS) P.O. Box 123, Broadway NSW 2007, Australia
1 The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System M. M. Alomari and B. S. Rodanski University of Technology, Sydney (UTS) P.O. Box 123, Broadway NSW 2007, Australia
CHATTERING-FREE SMC WITH UNIDIRECTIONAL AUXILIARY SURFACES FOR NONLINEAR SYSTEM WITH STATE CONSTRAINTS. Jian Fu, Qing-Xian Wu and Ze-Hui Mao
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 12, December 2013 pp. 4793 4809 CHATTERING-FREE SMC WITH UNIDIRECTIONAL
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 12, December 2013 pp. 4793 4809 CHATTERING-FREE SMC WITH UNIDIRECTIONAL
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
Introduction to Controls
 EE 474 Review Exam 1 Name Answer each of the questions. Show your work. Note were essay-type answers are requested. Answer with complete sentences. Incomplete sentences will count heavily against the grade.
EE 474 Review Exam 1 Name Answer each of the questions. Show your work. Note were essay-type answers are requested. Answer with complete sentences. Incomplete sentences will count heavily against the grade.
ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/ Power Systems Analysis II 3 Load Modeling
 ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/ Power Systems Analysis II 3 Load Modeling Spring 2014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 References 1. Load Performance for Dynamic Performance Analysis, IEEE Committee
ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/ Power Systems Analysis II 3 Load Modeling Spring 2014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 References 1. Load Performance for Dynamic Performance Analysis, IEEE Committee
Optimization. Escuela de Ingeniería Informática de Oviedo. (Dpto. de Matemáticas-UniOvi) Numerical Computation Optimization 1 / 30
 Optimization Escuela de Ingeniería Informática de Oviedo (Dpto. de Matemáticas-UniOvi) Numerical Computation Optimization 1 / 30 Unconstrained optimization Outline 1 Unconstrained optimization 2 Constrained
Optimization Escuela de Ingeniería Informática de Oviedo (Dpto. de Matemáticas-UniOvi) Numerical Computation Optimization 1 / 30 Unconstrained optimization Outline 1 Unconstrained optimization 2 Constrained
CHAPTER 3 THE MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE: MIXED INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS. p. 1/73
 CHAPTER 3 THE MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE: MIXED INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS p. 1/73 THE MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE: MIXED INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS Mixed Inequality Constraints: Inequality constraints involving control and possibly
CHAPTER 3 THE MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE: MIXED INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS p. 1/73 THE MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE: MIXED INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS Mixed Inequality Constraints: Inequality constraints involving control and possibly
θ α W Description of aero.m
 Description of aero.m Determination of the aerodynamic forces, moments and power by means of the blade element method; for known mean wind speed, induction factor etc. Simplifications: uniform flow (i.e.
Description of aero.m Determination of the aerodynamic forces, moments and power by means of the blade element method; for known mean wind speed, induction factor etc. Simplifications: uniform flow (i.e.
Theorem 1. ẋ = Ax is globally exponentially stable (GES) iff A is Hurwitz (i.e., max(re(σ(a))) < 0).
 Linear Systems Notes Lecture Proposition. A M n (R) is positive definite iff all nested minors are greater than or equal to zero. n Proof. ( ): Positive definite iff λ i >. Let det(a) = λj and H = {x D
Linear Systems Notes Lecture Proposition. A M n (R) is positive definite iff all nested minors are greater than or equal to zero. n Proof. ( ): Positive definite iff λ i >. Let det(a) = λj and H = {x D
Outline. Classical Control. Lecture 1
 Outline Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Prerequisites Block diagram for system modeling Modeling Mechanical Electrical Outline Introduction Background Basic Systems Models/Transfers functions 1 Introduction
Outline Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Prerequisites Block diagram for system modeling Modeling Mechanical Electrical Outline Introduction Background Basic Systems Models/Transfers functions 1 Introduction
Application of Monte Carlo Simulation to Multi-Area Reliability Calculations. The NARP Model
 Application of Monte Carlo Simulation to Multi-Area Reliability Calculations The NARP Model Any power system reliability model using Monte Carlo simulation consists of at least the following steps: 1.
Application of Monte Carlo Simulation to Multi-Area Reliability Calculations The NARP Model Any power system reliability model using Monte Carlo simulation consists of at least the following steps: 1.
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 4, pp. 373-38, 23. Copyright 23,. ISSN 68-963. ETNA A NOTE ON THE RELATION BETWEEN THE NEWTON HOMOTOPY METHOD AND THE DAMPED NEWTON METHOD XUPING ZHANG
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 4, pp. 373-38, 23. Copyright 23,. ISSN 68-963. ETNA A NOTE ON THE RELATION BETWEEN THE NEWTON HOMOTOPY METHOD AND THE DAMPED NEWTON METHOD XUPING ZHANG
The estimation problem ODE stability The embedding method The simultaneous method In conclusion. Stability problems in ODE estimation
 Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University HPSC Hanoi 2006 Outline The estimation problem ODE stability The embedding method The simultaneous method In conclusion Estimation Given the
Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University HPSC Hanoi 2006 Outline The estimation problem ODE stability The embedding method The simultaneous method In conclusion Estimation Given the
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models
 Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Constrained Optimization Theory
 Constrained Optimization Theory Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Constrained Optimization Theory IMA, August
Constrained Optimization Theory Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Constrained Optimization Theory IMA, August
Passive control. Carles Batlle. II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July
 Passive control theory II Carles Batlle II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July 18-22 2005 Contents of this lecture Interconnection and
Passive control theory II Carles Batlle II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July 18-22 2005 Contents of this lecture Interconnection and
Alberto Bressan. Department of Mathematics, Penn State University
 Non-cooperative Differential Games A Homotopy Approach Alberto Bressan Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Differential Games d dt x(t) = G(x(t), u 1(t), u 2 (t)), x(0) = y, u i (t) U i
Non-cooperative Differential Games A Homotopy Approach Alberto Bressan Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Differential Games d dt x(t) = G(x(t), u 1(t), u 2 (t)), x(0) = y, u i (t) U i
Lecture 1: Introduction to System Modeling and Control. Introduction Basic Definitions Different Model Types System Identification
 Lecture 1: Introduction to System Modeling and Control Introduction Basic Definitions Different Model Types System Identification What is Mathematical Model? A set of mathematical equations (e.g., differential
Lecture 1: Introduction to System Modeling and Control Introduction Basic Definitions Different Model Types System Identification What is Mathematical Model? A set of mathematical equations (e.g., differential
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Tools (NMPC Tools)
 Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Tools (NMPC Tools) Rishi Amrit, James B. Rawlings April 5, 2008 1 Formulation We consider a control system composed of three parts([2]). Estimator Target calculator Regulator
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Tools (NMPC Tools) Rishi Amrit, James B. Rawlings April 5, 2008 1 Formulation We consider a control system composed of three parts([2]). Estimator Target calculator Regulator
Comparative Study of Synchronous Machine, Model 1.0 and Model 1.1 in Transient Stability Studies with and without PSS
 Comparative Study of Synchronous Machine, Model 1.0 and Model 1.1 in Transient Stability Studies with and without PSS Abhijit N Morab, Abhishek P Jinde, Jayakrishna Narra, Omkar Kokane Guide: Kiran R Patil
Comparative Study of Synchronous Machine, Model 1.0 and Model 1.1 in Transient Stability Studies with and without PSS Abhijit N Morab, Abhishek P Jinde, Jayakrishna Narra, Omkar Kokane Guide: Kiran R Patil
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification
 Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification Lecture 9: Sensitivity Analysis ST 2018 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Repetition of Previous Lecture Sparse grids in Uncertainty Quantification
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification Lecture 9: Sensitivity Analysis ST 2018 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Repetition of Previous Lecture Sparse grids in Uncertainty Quantification
Optimal tunning of lead-lag and fuzzy logic power system stabilizers using particle swarm optimization
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Expert Systems with Applications Expert Systems with Applications xxx (2008) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/eswa Optimal tunning of lead-lag and fuzzy logic power
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Expert Systems with Applications Expert Systems with Applications xxx (2008) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/eswa Optimal tunning of lead-lag and fuzzy logic power
Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations
 Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations Alan Champneys Department of Engineering Mathematics, University of Bristol Mario di Bernardo, Chris Budd, Piotr Kowalczyk Gabor Licsko,...
Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations Alan Champneys Department of Engineering Mathematics, University of Bristol Mario di Bernardo, Chris Budd, Piotr Kowalczyk Gabor Licsko,...
