MATRIX ANALYSIS HOMEWORK
|
|
|
- Emily Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATRIX ANALYSIS HOMEWORK VERN I. PAULSEN 1. Due 9/25 We let S n denote the group of all permutations of {1,..., n}. 1. Compute the determinants of the elementary matrices: U(k, l), D(k, λ), and S(k, l; λ) 2. Let J n M n be the matrix of all 1 s. (i) Use Laplace s formula and induction to prove that det(j n ) = 0 for all n. (ii) Use (i) to prove that there is an equal number of even and odd permutations in S n. 3. Given a permutation σ S n, let P σ, Q σ M n be the matrices defined by Q σ = n i=1 E i,σ(i) and P σ = n j=1 E σ(j),j. (i) Prove that P σ Q σ = Q σ P σ = I n (ii) Prove that det(p σ ) = det(q σ ) = sgn(σ).(so this can be used to define sgn(σ).) (iii) Given A M n describe P σ A, Q σ A, AP σ, and AQ σ. (iv) Prove that σ S n P σ = (n 1)! J n. (v) If π : {1,..., n} {1,..., n} is another permutation, prove that P σ P π = P σ π and Q σ Q π = Q π σ where (f g)(i) = f(g(i)) is the composition of two functions. (vi) Find the mistake in the Wiki page on permutation matrices! 4. A matrix P M n is called a permutation matrix provided that each row and column of P has exactly one 1 and the remaining entries are 0 s. Prove that P is a permutation matrix if and only if there is a permutation σ such that P = P σ (hence the name). 5. A matrix T = (t i,j ) is upper(resp., lower) triangular provided that t i,j = 0 for i > j(resp., i < j). Use induction to prove that if T M n is upper or lower triangular then det(t ) = n i=1 t i,i. 6. Let B n = (min{i, j}) M n. Prove that det(b n ) = Let C n = (max{i, j}) M n. Find and prove a formula for det(c n ). 8. Prove that perm(b n ) (n!) 2 perm(c n ). 1
2 2 V. I. PAULSEN 2. Due 10/2 [ ] A1,1 A 1. Let A M n1 +n 2 have block form A = 1,2, where A 0 A i,j 2,2 M ni,n j and A 2,1 = 0. It is easy to see, but messy to write down a proof that det(a) = det(a 1,1 )det(a 2,2 ). From this it follows that A is invertible det(a) 0 det(a 1,1 ) 0 and det(a 2,2 ) 0 A 1,1 and A 2,2 are invertible. The purpose of this exercise is to prove this fact without using determinants. (i) Prove that A is invertible if and only if A 1,1 and A 2,2 are invertible by expressing A 1 in block form. (ii) Prove, more generally, that σ(a) = σ(a 1,1 ) σ(a 2,2 ). 2. Let A M n. (i) Let q be a polynomial such that q(λ) 0 for all λ σ(a). Prove that q(a) is invertible. (ii) Prove that for q as in (i) and any other polynomial p, we have that p(a)q(a) 1 = q 1 (A)p(A). (iii) Let p 1, p 2, q 1, q 2 be polynomials such that q i (λ) 0, for all λ σ(a), i = 1, 2 and such that p 1 q 2 = p 2 q 1. Prove that p 1 (A)q 1 (A) 1 = p 2 (A)q 2 (A) 1. (iv) For q as in (i) and p any polynomial, the rational function r(x) = p(x)/q(x) is defined on σ(a) and we set r(a) = p(a)q(a) 1. Prove that σ(r(a)) = {r(λ) : λ σ(a)}. [ ] λ 1 3. Let λ C and let A = M 0 λ 2 and let B = λ λ λ M 3. (i) Prove that σ(a) = σ(b) = {λ}. (ii) Prove formulas for the entries of A n and B n. (ii) Let p, q be polynomials, with q(λ) 0 and let r(x) = p(x)/q(x). Give and prove explicit formulas for the entries of r(a) and r(b). 4. Let 1 d < n, and let A = (a i,j ) M n with A = A, a i,i = a j,j, i, j and p A (t) = t n d (t 1) d. (Such matrices do exist.) (i) Find the values of the symmetric functions, S k, 1 k n for this matrix. (ii) Find the common value of the diagonal entries. (iii) Find the sum of the squares of all the strictly upper triangular entries of A, i.e., 1 i<j n a i,j 2.
3 3. Due 10/9 1. Let x, y F n M n,1, B Mn 1 (. Prove ) that det(b xy ) = 1 y det(b)(1 B 1 x, y ). HInt: Consider. x B 2. Suppose that A M n, n 2 is singular and that σ(a)\{0} is non-empty. Let r = min{ λ : λ σ(a), λ 0}. (i) Prove that for 0 < z < r A + zi n Mn 1. (ii) Prove that for any A = (a i,j ) M n and any ɛ > 0, there is B = (b i,j ) Mn 1 with n i,j=1 a i,j b i,j 2 < ɛ 2. This is often referred to as the density of the invertibles. 3. Give an example of a matrix A M n such that λ is an e-value of A of geometric multiplicity 1, and such that for any S 1, we have that λ is an e-value of A[S, S].(This shows that b = a is false in the persistence of e-values theorem.) 4. Let A M m,n. Prove that A is rank 1 iff there exist non-zero x M m,1, y M n,1 such that A = xy. 5. Let A = xy as in 4, with n = m 2. (i) Show that if x, y are linearly independent, then σ(xy ) = {0}. (ii) Show that if y = αx, α 0 then σ(xy ) = {0, α x 2 2}. 3
4 4 V. I. PAULSEN 4. Due 10/16 1. Let V : F n F m be an isometry. Prove that p V V (t) = t m n (t 1) n. 2. Prove that the n vectors v j = (cos(2πj/n), sin(2πj/n)), 0 j n 1 are a uniform Parseval frame for R 2 and that in the case n = 3 they are an equiangular uniform Parseval frame. 3. Let {v 1,..., v m } F n be an equiangular uniform Parseval frame for F n (m n). Compute the value of the constant v i, v j, i j. 4. Let A M n and let {v 1,..., v k } be eigenvectors of A corresponding to distinct, i.e., λ i λ j, i j eigenvalues {λ 1,..., λ k }. Prove that {v 1,..., v k } are linearly independent.
5 5. Due 10/30 Given subspaces V, W F n we set V +W = {v+w : v V, w W }. 1. Show that if V, W F n are subspaces such that V + W = F n and V W = (0), then there is a well-defined linear map L : F n F n such that L(v + w) = v. We call L the projection onto V along W. Show that L 2 = L, and conclude that if A is the matrix of this linear map, then A 2 = A. A linear map L : F n F n is called a projection iff there is a pair of subspaces V, W such that L is the projection onto V along W. 2. A matrix A M n is called idempotent if A 2 = A. Let A be idempotent. (i) Prove that N (A) R(A) = (0) and that N (A) + R(A) = F n. (ii) Prove that L A is the projection onto R(A) along N (A). (iii) Prove that ( dim(r(a)) ) = T r(a) Let A =, which is idempotent. Describe the set of vector 0 0 such that L A x = (1, 0). 4. We call L as in 1, an orthogonal projection iff V W. Prove that L is an orthogonal projection iff the matrix of L, A satisfies A = A 2 = A. 5. Prove that every projection is similar to an orthogonal projection. 5
6 6 V. I. PAULSEN 6. Due 11/6 The purpose of these exercises is to use our theorems to derive some results in spectral graph theory. By a graph on n vertices, we mean a pair G = (V, E) where for now V = {1,..., n} denotes the vertex set and E V V satisfies, (i, j) E = (j, i) E and (i, i) / E, i. We say that i and j are adjacent and write i j (i, j) E. A clique in G is a subset S V such that for all i, j S, i j = (i, j) E. For graph theorists, note that the cardinality of E, E is equal to twice the number of edges. The adjacency matrix of a graph is the matrix A G M n, is the self-adjoint matrix given by A G = (i,j) E E i,j. We set λ i = λ i (A G ). 1. Prove that n i=1 λ2 i = E. 2. Prove that i k=1 λ k 0 for 1 i n. 3. Prove that λ n E. n 4. Prove that if G has a clique S with S = k, then λ i 1, for 1 i k 1 and λ n k 1.
7 7. Due 11/16 1. Let V : C d C n be an isometry, which we identify with its matrix V M n,d. Prove that V V M n is the orthogonal projection onto R(V ). 2. Let {v 1,..., v n } C d. Prove that {v 1,..., v n } is a Parseval frame for C d iff the Grammian G = ( v j, v i ) satisfies G = G 2 and T r(g) = d. 3. Let A, B M n and let k N. Prove that if A 0, B 0 and A k = B k then A = B.(This shows the uniqueness of the k-th root of a positive semidefinite matrix.) 7
8 8 V. I. PAULSEN 8. Due 11/23 1. Let A M n. A = USV { be a singular valued decomposition. For a real number set t t 1 t 0 = 0 t = 0. If S = diag(s 1,..., s n ) then set S = diag(s 1,..., s n). Define A = V S U. Prove: (1) if A = U 1 SV 1 with possibly different unitaries then V1 S U1 = V S U. (2) when A is invertible, A = A 1. (3) AA A = A and A AA = A 2. Let A M n. A least squares solution to the equation Ax = b is a vector x such that: 1) Ax b 2 Ay b 2, y i.e., the error is minimized, 2) among all x satisfying 1), x 2 is minimized. Let P denote the orthogonal projection onto the range of A and let Q denote the orthogonal projection onto N (A). Prove that x is the least squares solution to Ax = b iff Ax = P (b) and Q(x) = x. Deduce that the least squares solution is unique. 3. Prove that A b is the least squares solution to Ax = b. 4. Prove that if A, B M n are positive definite, then A B is positive definite.
9 9. Due 12/8 1. Let A M n, 0 A. let γ = sup{a 1,σ(1) a n,σ(n) where the sup is taken over all permutations σ of 1,..., n. Prove that γ 1/n ρ(a). 2. Let A M n, 0 A and let x = (x 1,..., x n ) be the Perron vector for A. If min i n j=1 a i,j = ρ(a) then prove that x 1 =... = x n. Prove that if max i n j=1 a i,j = ρ(a) then x 1 =... = x n. 3. Let A M n, 0 A and let H = Re(A). Prove that ρ(a) λ n (H). Department of Pure Mathematics, University of Waterloo address: vpaulsen@uwaterloo.ca 9
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004.
 Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Linear Systems. Class 27. c 2008 Ron Buckmire. TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5.4
 Linear Systems Math Spring 8 c 8 Ron Buckmire Fowler 9 MWF 9: am - :5 am http://faculty.oxy.edu/ron/math//8/ Class 7 TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5. Summary
Linear Systems Math Spring 8 c 8 Ron Buckmire Fowler 9 MWF 9: am - :5 am http://faculty.oxy.edu/ron/math//8/ Class 7 TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5. Summary
Therefore, A and B have the same characteristic polynomial and hence, the same eigenvalues.
 Similar Matrices and Diagonalization Page 1 Theorem If A and B are n n matrices, which are similar, then they have the same characteristic equation and hence the same eigenvalues. Proof Let A and B be
Similar Matrices and Diagonalization Page 1 Theorem If A and B are n n matrices, which are similar, then they have the same characteristic equation and hence the same eigenvalues. Proof Let A and B be
Diagonalization. MATH 322, Linear Algebra I. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Diagonalization MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Motivation Today we consider two fundamental questions: Given an n n matrix A, does there exist a basis
Diagonalization MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Motivation Today we consider two fundamental questions: Given an n n matrix A, does there exist a basis
Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C.
 Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Problem Set (T) If A is an m n matrix, B is an n p matrix and D is a p s matrix, then show
 MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
There are six more problems on the next two pages
 Math 435 bg & bu: Topics in linear algebra Summer 25 Final exam Wed., 8/3/5. Justify all your work to receive full credit. Name:. Let A 3 2 5 Find a permutation matrix P, a lower triangular matrix L with
Math 435 bg & bu: Topics in linear algebra Summer 25 Final exam Wed., 8/3/5. Justify all your work to receive full credit. Name:. Let A 3 2 5 Find a permutation matrix P, a lower triangular matrix L with
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2
 Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
ANSWERS. E k E 2 E 1 A = B
 MATH 7- Final Exam Spring ANSWERS Essay Questions points Define an Elementary Matrix Display the fundamental matrix multiply equation which summarizes a sequence of swap, combination and multiply operations,
MATH 7- Final Exam Spring ANSWERS Essay Questions points Define an Elementary Matrix Display the fundamental matrix multiply equation which summarizes a sequence of swap, combination and multiply operations,
Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices
 Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices A common data structure for statistical analysis is a rectangular array or matris. Rows represent individual observational units, or just observations,
Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices A common data structure for statistical analysis is a rectangular array or matris. Rows represent individual observational units, or just observations,
Math 102, Winter Final Exam Review. Chapter 1. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination
 Math 0, Winter 07 Final Exam Review Chapter. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination { x + x =,. Different forms of a system of linear equations. Example: The x + 4x = 4. [ ] [ ] [ ] vector form (or the column
Math 0, Winter 07 Final Exam Review Chapter. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination { x + x =,. Different forms of a system of linear equations. Example: The x + 4x = 4. [ ] [ ] [ ] vector form (or the column
Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra
 Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra Chi-Kwong Li Chapter 4 Hermitian and symmetric matrices Basic properties Theorem Let A M n. The following are equivalent. Remark (a) A is Hermitian, i.e., A = A. (b) x
Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra Chi-Kwong Li Chapter 4 Hermitian and symmetric matrices Basic properties Theorem Let A M n. The following are equivalent. Remark (a) A is Hermitian, i.e., A = A. (b) x
Question: Given an n x n matrix A, how do we find its eigenvalues? Idea: Suppose c is an eigenvalue of A, then what is the determinant of A-cI?
 Section 5. The Characteristic Polynomial Question: Given an n x n matrix A, how do we find its eigenvalues? Idea: Suppose c is an eigenvalue of A, then what is the determinant of A-cI? Property The eigenvalues
Section 5. The Characteristic Polynomial Question: Given an n x n matrix A, how do we find its eigenvalues? Idea: Suppose c is an eigenvalue of A, then what is the determinant of A-cI? Property The eigenvalues
235 Final exam review questions
 5 Final exam review questions Paul Hacking December 4, 0 () Let A be an n n matrix and T : R n R n, T (x) = Ax the linear transformation with matrix A. What does it mean to say that a vector v R n is an
5 Final exam review questions Paul Hacking December 4, 0 () Let A be an n n matrix and T : R n R n, T (x) = Ax the linear transformation with matrix A. What does it mean to say that a vector v R n is an
j=1 x j p, if 1 p <, x i ξ : x i < ξ} 0 as p.
 LINEAR ALGEBRA Fall 203 The final exam Almost all of the problems solved Exercise Let (V, ) be a normed vector space. Prove x y x y for all x, y V. Everybody knows how to do this! Exercise 2 If V is a
LINEAR ALGEBRA Fall 203 The final exam Almost all of the problems solved Exercise Let (V, ) be a normed vector space. Prove x y x y for all x, y V. Everybody knows how to do this! Exercise 2 If V is a
MAT Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams
 MAT 342 - Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams A-x. (0 pts Give the precise definition of the row echelon form. 2. ( 0 pts After performing row reductions on the augmented matrix for a certain system
MAT 342 - Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams A-x. (0 pts Give the precise definition of the row echelon form. 2. ( 0 pts After performing row reductions on the augmented matrix for a certain system
Elementary linear algebra
 Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
Foundations of Matrix Analysis
 1 Foundations of Matrix Analysis In this chapter we recall the basic elements of linear algebra which will be employed in the remainder of the text For most of the proofs as well as for the details, the
1 Foundations of Matrix Analysis In this chapter we recall the basic elements of linear algebra which will be employed in the remainder of the text For most of the proofs as well as for the details, the
Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2
 Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2 Department of Mathematics Boise State University January 16, 2019 Math 566 Linear Algebra Review: Part 2 January 16, 2019 1 / 22 Vector spaces A set
Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2 Department of Mathematics Boise State University January 16, 2019 Math 566 Linear Algebra Review: Part 2 January 16, 2019 1 / 22 Vector spaces A set
Linear Algebra. Workbook
 Linear Algebra Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: November 21 Student: Fall 2011 Checklist Name: A B C D E F F G H I J 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 xxx xxx xxx
Linear Algebra Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: November 21 Student: Fall 2011 Checklist Name: A B C D E F F G H I J 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 xxx xxx xxx
MATH 235. Final ANSWERS May 5, 2015
 MATH 235 Final ANSWERS May 5, 25. ( points) Fix positive integers m, n and consider the vector space V of all m n matrices with entries in the real numbers R. (a) Find the dimension of V and prove your
MATH 235 Final ANSWERS May 5, 25. ( points) Fix positive integers m, n and consider the vector space V of all m n matrices with entries in the real numbers R. (a) Find the dimension of V and prove your
LINEAR ALGEBRA QUESTION BANK
 LINEAR ALGEBRA QUESTION BANK () ( points total) Circle True or False: TRUE / FALSE: If A is any n n matrix, and I n is the n n identity matrix, then I n A = AI n = A. TRUE / FALSE: If A, B are n n matrices,
LINEAR ALGEBRA QUESTION BANK () ( points total) Circle True or False: TRUE / FALSE: If A is any n n matrix, and I n is the n n identity matrix, then I n A = AI n = A. TRUE / FALSE: If A, B are n n matrices,
Math Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet
 Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
OHSx XM511 Linear Algebra: Solutions to Online True/False Exercises
 This document gives the solutions to all of the online exercises for OHSx XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Answers are in square brackets [. Lecture 02 ( 1.1)
This document gives the solutions to all of the online exercises for OHSx XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Answers are in square brackets [. Lecture 02 ( 1.1)
Ir O D = D = ( ) Section 2.6 Example 1. (Bottom of page 119) dim(v ) = dim(l(v, W )) = dim(v ) dim(f ) = dim(v )
 Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
MATH 31 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL
 MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
1 Linear Algebra Problems
 Linear Algebra Problems. Let A be the conjugate transpose of the complex matrix A; i.e., A = A t : A is said to be Hermitian if A = A; real symmetric if A is real and A t = A; skew-hermitian if A = A and
Linear Algebra Problems. Let A be the conjugate transpose of the complex matrix A; i.e., A = A t : A is said to be Hermitian if A = A; real symmetric if A is real and A t = A; skew-hermitian if A = A and
MH1200 Final 2014/2015
 MH200 Final 204/205 November 22, 204 QUESTION. (20 marks) Let where a R. A = 2 3 4, B = 2 3 4, 3 6 a 3 6 0. For what values of a is A singular? 2. What is the minimum value of the rank of A over all a
MH200 Final 204/205 November 22, 204 QUESTION. (20 marks) Let where a R. A = 2 3 4, B = 2 3 4, 3 6 a 3 6 0. For what values of a is A singular? 2. What is the minimum value of the rank of A over all a
4. Linear transformations as a vector space 17
 4 Linear transformations as a vector space 17 d) 1 2 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 32 Let a linear transformation in R 2 be the reflection in the line = x 2 Find its matrix 33 For each linear transformation
4 Linear transformations as a vector space 17 d) 1 2 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 32 Let a linear transformation in R 2 be the reflection in the line = x 2 Find its matrix 33 For each linear transformation
Matrix Algebra: Summary
 May, 27 Appendix E Matrix Algebra: Summary ontents E. Vectors and Matrtices.......................... 2 E.. Notation.................................. 2 E..2 Special Types of Vectors.........................
May, 27 Appendix E Matrix Algebra: Summary ontents E. Vectors and Matrtices.......................... 2 E.. Notation.................................. 2 E..2 Special Types of Vectors.........................
2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution.
 1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
LinGloss. A glossary of linear algebra
 LinGloss A glossary of linear algebra Contents: Decompositions Types of Matrices Theorems Other objects? Quasi-triangular A matrix A is quasi-triangular iff it is a triangular matrix except its diagonal
LinGloss A glossary of linear algebra Contents: Decompositions Types of Matrices Theorems Other objects? Quasi-triangular A matrix A is quasi-triangular iff it is a triangular matrix except its diagonal
Remark 1 By definition, an eigenvector must be a nonzero vector, but eigenvalue could be zero.
 Sec 5 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues In this chapter, vector means column vector Definition An eigenvector of an n n matrix A is a nonzero vector x such that A x λ x for some scalar λ A scalar λ is called
Sec 5 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues In this chapter, vector means column vector Definition An eigenvector of an n n matrix A is a nonzero vector x such that A x λ x for some scalar λ A scalar λ is called
Chapter 3. Matrices. 3.1 Matrices
 40 Chapter 3 Matrices 3.1 Matrices Definition 3.1 Matrix) A matrix A is a rectangular array of m n real numbers {a ij } written as a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =.... a m1 a m2 a mn The array has m rows
40 Chapter 3 Matrices 3.1 Matrices Definition 3.1 Matrix) A matrix A is a rectangular array of m n real numbers {a ij } written as a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =.... a m1 a m2 a mn The array has m rows
Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture)
 Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture) Travis Schedler Thurs, Dec 9, 2010 (version: Monday, Dec 13, 3:52 PM) Goals (2) Recall χ T (x) = (x λ 1 ) (x λ n ) = x n tr(t )x n 1 + +( 1) n det(t
Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture) Travis Schedler Thurs, Dec 9, 2010 (version: Monday, Dec 13, 3:52 PM) Goals (2) Recall χ T (x) = (x λ 1 ) (x λ n ) = x n tr(t )x n 1 + +( 1) n det(t
18.S34 linear algebra problems (2007)
 18.S34 linear algebra problems (2007) Useful ideas for evaluating determinants 1. Row reduction, expanding by minors, or combinations thereof; sometimes these are useful in combination with an induction
18.S34 linear algebra problems (2007) Useful ideas for evaluating determinants 1. Row reduction, expanding by minors, or combinations thereof; sometimes these are useful in combination with an induction
Notes on Linear Algebra and Matrix Theory
 Massimo Franceschet featuring Enrico Bozzo Scalar product The scalar product (a.k.a. dot product or inner product) of two real vectors x = (x 1,..., x n ) and y = (y 1,..., y n ) is not a vector but a
Massimo Franceschet featuring Enrico Bozzo Scalar product The scalar product (a.k.a. dot product or inner product) of two real vectors x = (x 1,..., x n ) and y = (y 1,..., y n ) is not a vector but a
Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices
 Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The main aim of this lecture note is to prepare your background for semidefinite programming. We have already seen some linear algebra.
Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The main aim of this lecture note is to prepare your background for semidefinite programming. We have already seen some linear algebra.
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra
 Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #2 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
MATH 240 Spring, Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Matrices
 MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1
 Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1 Written up by Mikhail Belkin and Moon Duchin Instructor: Laszlo Babai June 17, 2001 1 Basic Linear Algebra Exercise 1.1 Let V and W be linear subspaces
Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1 Written up by Mikhail Belkin and Moon Duchin Instructor: Laszlo Babai June 17, 2001 1 Basic Linear Algebra Exercise 1.1 Let V and W be linear subspaces
Remark By definition, an eigenvector must be a nonzero vector, but eigenvalue could be zero.
 Sec 6 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Definition An eigenvector of an n n matrix A is a nonzero vector x such that A x λ x for some scalar λ A scalar λ is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial
Sec 6 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Definition An eigenvector of an n n matrix A is a nonzero vector x such that A x λ x for some scalar λ A scalar λ is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial
EE/ACM Applications of Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications Lecture 2
 EE/ACM 150 - Applications of Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications Lecture 2 Andre Tkacenko Signal Processing Research Group Jet Propulsion Laboratory April 5, 2012 Andre Tkacenko
EE/ACM 150 - Applications of Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications Lecture 2 Andre Tkacenko Signal Processing Research Group Jet Propulsion Laboratory April 5, 2012 Andre Tkacenko
MATH 315 Linear Algebra Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018
 Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018 Review the following subjects involving systems of equations and matrices from Calculus II. Linear systems of equations Converting systems to matrix form Pivot entry
Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018 Review the following subjects involving systems of equations and matrices from Calculus II. Linear systems of equations Converting systems to matrix form Pivot entry
Linear Algebra in Actuarial Science: Slides to the lecture
 Linear Algebra in Actuarial Science: Slides to the lecture Fall Semester 2010/2011 Linear Algebra is a Tool-Box Linear Equation Systems Discretization of differential equations: solving linear equations
Linear Algebra in Actuarial Science: Slides to the lecture Fall Semester 2010/2011 Linear Algebra is a Tool-Box Linear Equation Systems Discretization of differential equations: solving linear equations
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra
 MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University March 2, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University March 2, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
2018 Fall 2210Q Section 013 Midterm Exam II Solution
 08 Fall 0Q Section 0 Midterm Exam II Solution True or False questions points 0 0 points) ) Let A be an n n matrix. If the equation Ax b has at least one solution for each b R n, then the solution is unique
08 Fall 0Q Section 0 Midterm Exam II Solution True or False questions points 0 0 points) ) Let A be an n n matrix. If the equation Ax b has at least one solution for each b R n, then the solution is unique
ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 12/31/2014 at 10:36pm CST
 me me ft-uiowa-math255 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 2/3/2 at :3pm CST. ( pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem3.pg Give a geometric description of the following
me me ft-uiowa-math255 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 2/3/2 at :3pm CST. ( pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem3.pg Give a geometric description of the following
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008
 Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Answer any eight)
 Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2
 Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511
 This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
1 Last time: least-squares problems
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
Conceptual Questions for Review
 Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Warm-up. True or false? Baby proof. 2. The system of normal equations for A x = y has solutions iff A x = y has solutions
 Warm-up True or false? 1. proj u proj v u = u 2. The system of normal equations for A x = y has solutions iff A x = y has solutions 3. The normal equations are always consistent Baby proof 1. Let A be
Warm-up True or false? 1. proj u proj v u = u 2. The system of normal equations for A x = y has solutions iff A x = y has solutions 3. The normal equations are always consistent Baby proof 1. Let A be
Homework Set #8 Solutions
 Exercises.2 (p. 19) Homework Set #8 Solutions Assignment: Do #6, 8, 12, 14, 2, 24, 26, 29, 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 40, 42 6. Reducing the matrix to echelon form: 1 5 2 1 R2 R2 R1 1 5 0 18 12 2 1 R R 2R1 1 5
Exercises.2 (p. 19) Homework Set #8 Solutions Assignment: Do #6, 8, 12, 14, 2, 24, 26, 29, 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 40, 42 6. Reducing the matrix to echelon form: 1 5 2 1 R2 R2 R1 1 5 0 18 12 2 1 R R 2R1 1 5
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m
 Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 2012
 MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 22 NAME: INSTRUCTOR S NAME:. There are a total of 25 problems. You should show work on the exam sheet, and pencil in the correct answer on the scantron. 2. No books, notes, or calculators
MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 22 NAME: INSTRUCTOR S NAME:. There are a total of 25 problems. You should show work on the exam sheet, and pencil in the correct answer on the scantron. 2. No books, notes, or calculators
LINEAR ALGEBRA 1, 2012-I PARTIAL EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
Diagonalization of Matrix
 of Matrix King Saud University August 29, 2018 of Matrix Table of contents 1 2 of Matrix Definition If A M n (R) and λ R. We say that λ is an eigenvalue of the matrix A if there is X R n \ {0} such that
of Matrix King Saud University August 29, 2018 of Matrix Table of contents 1 2 of Matrix Definition If A M n (R) and λ R. We say that λ is an eigenvalue of the matrix A if there is X R n \ {0} such that
1. What is the determinant of the following matrix? a 1 a 2 4a 3 2a 2 b 1 b 2 4b 3 2b c 1. = 4, then det
 What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
EXERCISES ON DETERMINANTS, EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS. 1. Determinants
 EXERCISES ON DETERMINANTS, EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS. Determinants Ex... Let A = 0 4 4 2 0 and B = 0 3 0. (a) Compute 0 0 0 0 A. (b) Compute det(2a 2 B), det(4a + B), det(2(a 3 B 2 )). 0 t Ex..2. For
EXERCISES ON DETERMINANTS, EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS. Determinants Ex... Let A = 0 4 4 2 0 and B = 0 3 0. (a) Compute 0 0 0 0 A. (b) Compute det(2a 2 B), det(4a + B), det(2(a 3 B 2 )). 0 t Ex..2. For
Linear Algebra Lecture Notes-II
 Linear Algebra Lecture Notes-II Vikas Bist Department of Mathematics Panjab University, Chandigarh-64 email: bistvikas@gmail.com Last revised on March 5, 8 This text is based on the lectures delivered
Linear Algebra Lecture Notes-II Vikas Bist Department of Mathematics Panjab University, Chandigarh-64 email: bistvikas@gmail.com Last revised on March 5, 8 This text is based on the lectures delivered
Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2018 Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet 1 Randomized Algorithm Expectation: For a random variable X with domain, the discrete set S, E [X] = s S P [X = s]
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2018 Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet 1 Randomized Algorithm Expectation: For a random variable X with domain, the discrete set S, E [X] = s S P [X = s]
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Linear Algebra Practice Problems Page of 7 Linear Algebra Practice Problems These problems cover Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 7 of Elementary Linear Algebra, 6th ed, by Ron Larson and David Falvo (ISBN-3 = 978--68-78376-2,
Linear Algebra Practice Problems Page of 7 Linear Algebra Practice Problems These problems cover Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 7 of Elementary Linear Algebra, 6th ed, by Ron Larson and David Falvo (ISBN-3 = 978--68-78376-2,
4. Determinants.
 4. Determinants 4.1. Determinants; Cofactor Expansion Determinants of 2 2 and 3 3 Matrices 2 2 determinant 4.1. Determinants; Cofactor Expansion Determinants of 2 2 and 3 3 Matrices 3 3 determinant 4.1.
4. Determinants 4.1. Determinants; Cofactor Expansion Determinants of 2 2 and 3 3 Matrices 2 2 determinant 4.1. Determinants; Cofactor Expansion Determinants of 2 2 and 3 3 Matrices 3 3 determinant 4.1.
MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006
 MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006 Sherod Eubanks HOMEWORK 2 2.1 : 2, 5, 9, 12 2.3 : 3, 6 2.4 : 2, 4, 5, 9, 11 Section 2.1: Unitary Matrices Problem 2 If λ σ(u) and U M n is unitary, show that
MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006 Sherod Eubanks HOMEWORK 2 2.1 : 2, 5, 9, 12 2.3 : 3, 6 2.4 : 2, 4, 5, 9, 11 Section 2.1: Unitary Matrices Problem 2 If λ σ(u) and U M n is unitary, show that
(a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? Solution: dim N(A) 1, since rank(a) 3. Ax =
 . (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
. (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
Topics in Graph Theory
 Topics in Graph Theory September 4, 2018 1 Preliminaries A graph is a system G = (V, E) consisting of a set V of vertices and a set E (disjoint from V ) of edges, together with an incidence function End
Topics in Graph Theory September 4, 2018 1 Preliminaries A graph is a system G = (V, E) consisting of a set V of vertices and a set E (disjoint from V ) of edges, together with an incidence function End
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra
 CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS FROM STRANG S LINEAR ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS (4TH EDITION)
 HOMEWORK PROBLEMS FROM STRANG S LINEAR ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS (4TH EDITION) PROFESSOR STEVEN MILLER: BROWN UNIVERSITY: SPRING 2007 1. CHAPTER 1: MATRICES AND GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION Page 9, # 3: Describe
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS FROM STRANG S LINEAR ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS (4TH EDITION) PROFESSOR STEVEN MILLER: BROWN UNIVERSITY: SPRING 2007 1. CHAPTER 1: MATRICES AND GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION Page 9, # 3: Describe
Lecture Summaries for Linear Algebra M51A
 These lecture summaries may also be viewed online by clicking the L icon at the top right of any lecture screen. Lecture Summaries for Linear Algebra M51A refers to the section in the textbook. Lecture
These lecture summaries may also be viewed online by clicking the L icon at the top right of any lecture screen. Lecture Summaries for Linear Algebra M51A refers to the section in the textbook. Lecture
ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA Kent State University Department of Mathematical Sciences Compiled and Maintained by Donald L. White Version: August 29, 2017 CONTENTS LINEAR ALGEBRA AND
ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA Kent State University Department of Mathematical Sciences Compiled and Maintained by Donald L. White Version: August 29, 2017 CONTENTS LINEAR ALGEBRA AND
Math 554 Qualifying Exam. You may use any theorems from the textbook. Any other claims must be proved in details.
 Math 554 Qualifying Exam January, 2019 You may use any theorems from the textbook. Any other claims must be proved in details. 1. Let F be a field and m and n be positive integers. Prove the following.
Math 554 Qualifying Exam January, 2019 You may use any theorems from the textbook. Any other claims must be proved in details. 1. Let F be a field and m and n be positive integers. Prove the following.
Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 2015
 Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 205. If A is a 3 3 triangular matrix, explain why det(a) is equal to the product of entries on the diagonal. If A is a lower triangular or diagonal
Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 205. If A is a 3 3 triangular matrix, explain why det(a) is equal to the product of entries on the diagonal. If A is a lower triangular or diagonal
Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012
 Instructions Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012 The exam consists of four problems, each having multiple parts. You should attempt to solve all four problems. 1.
Instructions Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012 The exam consists of four problems, each having multiple parts. You should attempt to solve all four problems. 1.
and let s calculate the image of some vectors under the transformation T.
 Chapter 5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 5. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Let T : R n R n be a linear transformation. Then T can be represented by a matrix (the standard matrix), and we can write T ( v) =
Chapter 5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 5. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Let T : R n R n be a linear transformation. Then T can be represented by a matrix (the standard matrix), and we can write T ( v) =
G1110 & 852G1 Numerical Linear Algebra
 The University of Sussex Department of Mathematics G & 85G Numerical Linear Algebra Lecture Notes Autumn Term Kerstin Hesse (w aw S w a w w (w aw H(wa = (w aw + w Figure : Geometric explanation of the
The University of Sussex Department of Mathematics G & 85G Numerical Linear Algebra Lecture Notes Autumn Term Kerstin Hesse (w aw S w a w w (w aw H(wa = (w aw + w Figure : Geometric explanation of the
Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review
 Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review. Let A be invertible. Show that, if v, v, v 3 are linearly independent vectors, so are Av, Av, Av 3. NOTE: It should be clear from your answer that you know the definition.
Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review. Let A be invertible. Show that, if v, v, v 3 are linearly independent vectors, so are Av, Av, Av 3. NOTE: It should be clear from your answer that you know the definition.
Calculating determinants for larger matrices
 Day 26 Calculating determinants for larger matrices We now proceed to define det A for n n matrices A As before, we are looking for a function of A that satisfies the product formula det(ab) = det A det
Day 26 Calculating determinants for larger matrices We now proceed to define det A for n n matrices A As before, we are looking for a function of A that satisfies the product formula det(ab) = det A det
Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces
 Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces 1. Hilbert spaces A Hilbert space H is a complete real or complex inner product space. Consider complex Hilbert spaces for definiteness. If (, ) : H H
Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces 1. Hilbert spaces A Hilbert space H is a complete real or complex inner product space. Consider complex Hilbert spaces for definiteness. If (, ) : H H
Linear Algebra Formulas. Ben Lee
 Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
BASIC ALGORITHMS IN LINEAR ALGEBRA. Matrices and Applications of Gaussian Elimination. A 2 x. A T m x. A 1 x A T 1. A m x
 BASIC ALGORITHMS IN LINEAR ALGEBRA STEVEN DALE CUTKOSKY Matrices and Applications of Gaussian Elimination Systems of Equations Suppose that A is an n n matrix with coefficents in a field F, and x = (x,,
BASIC ALGORITHMS IN LINEAR ALGEBRA STEVEN DALE CUTKOSKY Matrices and Applications of Gaussian Elimination Systems of Equations Suppose that A is an n n matrix with coefficents in a field F, and x = (x,,
LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM
 LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM Unless otherwise stated, all vector spaces in this worksheet are finite dimensional and the scalar field F is R or C. Definition 1. A linear operator
LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM Unless otherwise stated, all vector spaces in this worksheet are finite dimensional and the scalar field F is R or C. Definition 1. A linear operator
1 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations. a 1n a 2n
 March 31, 2013 16-1 16. Systems of Linear Equations 1 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations An m n matrix is an array A = (a ij ) of the form a 11 a 21 a m1 a 1n a 2n... a mn where each a ij is a real
March 31, 2013 16-1 16. Systems of Linear Equations 1 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations An m n matrix is an array A = (a ij ) of the form a 11 a 21 a m1 a 1n a 2n... a mn where each a ij is a real
Equality: Two matrices A and B are equal, i.e., A = B if A and B have the same order and the entries of A and B are the same.
 Introduction Matrix Operations Matrix: An m n matrix A is an m-by-n array of scalars from a field (for example real numbers) of the form a a a n a a a n A a m a m a mn The order (or size) of A is m n (read
Introduction Matrix Operations Matrix: An m n matrix A is an m-by-n array of scalars from a field (for example real numbers) of the form a a a n a a a n A a m a m a mn The order (or size) of A is m n (read
Math 407: Linear Optimization
 Math 407: Linear Optimization Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II Math Dept, University of Washington February 28, 2018 Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II (Math Dept, University
Math 407: Linear Optimization Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II Math Dept, University of Washington February 28, 2018 Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II (Math Dept, University
ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST
 me me ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST 1. (1 pt) local/library/ui/eigentf.pg A is n n an matrices.. There are an infinite number
me me ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST 1. (1 pt) local/library/ui/eigentf.pg A is n n an matrices.. There are an infinite number
Basic Elements of Linear Algebra
 A Basic Review of Linear Algebra Nick West nickwest@stanfordedu September 16, 2010 Part I Basic Elements of Linear Algebra Although the subject of linear algebra is much broader than just vectors and matrices,
A Basic Review of Linear Algebra Nick West nickwest@stanfordedu September 16, 2010 Part I Basic Elements of Linear Algebra Although the subject of linear algebra is much broader than just vectors and matrices,
Section 3.9. Matrix Norm
 3.9. Matrix Norm 1 Section 3.9. Matrix Norm Note. We define several matrix norms, some similar to vector norms and some reflecting how multiplication by a matrix affects the norm of a vector. We use matrix
3.9. Matrix Norm 1 Section 3.9. Matrix Norm Note. We define several matrix norms, some similar to vector norms and some reflecting how multiplication by a matrix affects the norm of a vector. We use matrix
NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES
 NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES. Operator Norms on Space of linear maps Let A be an n n real matrix and x 0 be a vector in R n. We would like to use the Picard iteration method to solve for the following system
NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES. Operator Norms on Space of linear maps Let A be an n n real matrix and x 0 be a vector in R n. We would like to use the Picard iteration method to solve for the following system
1. General Vector Spaces
 1.1. Vector space axioms. 1. General Vector Spaces Definition 1.1. Let V be a nonempty set of objects on which the operations of addition and scalar multiplication are defined. By addition we mean a rule
1.1. Vector space axioms. 1. General Vector Spaces Definition 1.1. Let V be a nonempty set of objects on which the operations of addition and scalar multiplication are defined. By addition we mean a rule
Symmetric matrices and dot products
 Symmetric matrices and dot products Proposition An n n matrix A is symmetric iff, for all x, y in R n, (Ax) y = x (Ay). Proof. If A is symmetric, then (Ax) y = x T A T y = x T Ay = x (Ay). If equality
Symmetric matrices and dot products Proposition An n n matrix A is symmetric iff, for all x, y in R n, (Ax) y = x (Ay). Proof. If A is symmetric, then (Ax) y = x T A T y = x T Ay = x (Ay). If equality
Linear algebra I Homework #1 due Thursday, Oct Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another.
 Homework # due Thursday, Oct. 0. Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another. Hint: Place the vertices of the square along the axes and then introduce coordinates. 2. Find the equation
Homework # due Thursday, Oct. 0. Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another. Hint: Place the vertices of the square along the axes and then introduce coordinates. 2. Find the equation
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 2.1 Matrix Operations. Definition: A : m n, B : n p. Example: Compute AB, if possible.
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 2.1 Matrix Operations Definition: A : m n, B : n p ( 1 2 p ) ( 1 2 p ) AB = A b b b = Ab Ab Ab Example: Compute AB, if possible. 1 Row-column rule: i-j-th entry of AB:
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 2.1 Matrix Operations Definition: A : m n, B : n p ( 1 2 p ) ( 1 2 p ) AB = A b b b = Ab Ab Ab Example: Compute AB, if possible. 1 Row-column rule: i-j-th entry of AB:
Algebra C Numerical Linear Algebra Sample Exam Problems
 Algebra C Numerical Linear Algebra Sample Exam Problems Notation. Denote by V a finite-dimensional Hilbert space with inner product (, ) and corresponding norm. The abbreviation SPD is used for symmetric
Algebra C Numerical Linear Algebra Sample Exam Problems Notation. Denote by V a finite-dimensional Hilbert space with inner product (, ) and corresponding norm. The abbreviation SPD is used for symmetric
ACM 104. Homework Set 4 Solutions February 14, 2001
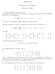 ACM 04 Homework Set 4 Solutions February 4, 00 Franklin Chapter, Problem 4, page 55 Suppose that we feel that some observations are more important or reliable than others Redefine the function to be minimized
ACM 04 Homework Set 4 Solutions February 4, 00 Franklin Chapter, Problem 4, page 55 Suppose that we feel that some observations are more important or reliable than others Redefine the function to be minimized
Contents. Preface for the Instructor. Preface for the Student. xvii. Acknowledgments. 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2
 Contents Preface for the Instructor xi Preface for the Student xv Acknowledgments xvii 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2 Complex Numbers 2 Lists 5 F n 6 Digression on Fields 10 Exercises 1.A 11 1.B Definition
Contents Preface for the Instructor xi Preface for the Student xv Acknowledgments xvii 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2 Complex Numbers 2 Lists 5 F n 6 Digression on Fields 10 Exercises 1.A 11 1.B Definition
