Status and Prospect of Laser Fusion Research at ILE Osaka University
|
|
|
- Blaise Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fusion Power Associates 39th Annual Meeting and Symposium Fusion Energy: Strategies and Expectations through the 2020s Status and Prospect of Laser Fusion Research at ILE Osaka University Introduction of a Fast Ignition project: FIREX project Recent Progress of the fast ignition research Prospect of the next generation laser facility: J EPoCH project Ryosuke KODAMA Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University on DECEMBER 4 5, 2018 at GRAND HYATT WASHINGTON HOTEL, Washington, DC US 1
2 FIREX I project is now under going at ILE Osaka Advantage of the FI scheme: Heating and compression processes are separately optimized, resulting in simple combination of the optimized conditions for efficient fusion process. Now compression heating Ignition FIREX I: Scaling to efficiently realize the Fast Ignition FIREX: Fast Ignition Realization Experiment Future FIREX II: Ignition and Burning Single shot facility Multi kj/ns laser GEKKO XII kj/short pulse laser LFEX + Heating with plasma devices Cone guiding of heating laser pulse Guiding of REB with laser induced magnetic field. R. Kodama et al., Nature (2001) R. Kodama et al., Nature (2002) S. Fujioka et al., Sci. Rep (2013) S. Fujioka et al., Phys. Plasma (2016) New scheme of fuel compression H. Sawada et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. (2016) Scaling for efficient ignition with the FI scheme 2
3 Guiding of the MeV REB into the Core Plasma to Efficiently Heat up the Compressed Plasmas with a Strong Magnetic Field Taking account of the core size and MeV energy of the REB, we would need a magnetic field of more than kilo tesla. Gyro-radius of electron Gyro-radius of electron must be smaller than fuel core radius. Heating laser pulse Electron generation Core Plasma 1 MeV 10 MeV 10 kt 1 kt Cone guiding of heating laser pulse REB guiding with Strong Magnetic Field Diverged electron beam Necessity to guide or focus the REB into the small core plasma T. Johzaki et al., Nucl. Fusion 3(2017). 3
4 Progress of Generation of Strong Magnetic Fields by High Power Lasers over the past 30 years >10k T kt 800 T Strong Compression of a Magnetic Field with a Laser Accelerated Foil H. Yoneda, et al.,phys. Rev. Lett. 60 T Whispering gallery effect in relativistic optics Y. Abe et al., JETP Letters Kilotesla Magnetic Field due to a (2018) Capacitor Coil Target Driven by LFEX laser High Power Laser S. Fujioka et al., Sci Rep 30, (2013) , (2012) Generation of a strong magnetic field by an intense CO2 laser pulse H. Daido, et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 846 (1986) 4
5 Energy Coupling to the Core with the Magnetic Field was Improved by Twice of that without the Field. Energy coupling of the heating pulse to the core 4% 8% The coupling also depends on the electron stopping : the density of the compressed fuel as well as the temperature of heating electron beam. Only implosion w/ heating w/ heating + w/ B-field B-field 100 μm No heating pulse 100 μm Diverged electron beam 100 μm Guided electron beam Magnetic field lines Raw spatial profile of monochromatic Ka (8.05 kev) 5
6 Energy deposition of the electron beam to the imploded core plasmas at different times. The isochoric heating of the compressed core [1] was improved by collimation of the REB with kilo tesla magnetic field generated by power laser[2]. [1] R. Kodama et al., Nature 412,798(2001) [2] S. Sakata et al., Nature Comm. 9, 3937 (2018) ρl=0.08 g cm 2 / ρ=5.7 g cm 3 ρl=0.16 g cm 2/ρ=11.3 g cm 3 at t = ns. at t = ns, 6
7 The Compressed Plasma with a density of 16 g/cm 3 was heated by the REB guided by the kilo Tesla Magnetic field to be 2keV. Density profile@0.72ns Plasma density profile was obtained with x ray backlighting technique. X ray X ray spectrum contains also emissions from a Ni coil and Au cone. FLYCHK simulation FLYCHK reproduces the spectrum. cone Cu-K Ni-K Cu-Li-like Cu-He Au L-lines #40528 Density: 10 17g/cm 3 2 kev The core with a pressure : > 20Gbar 7
8 Prospect of FIREX I project by 2020 Fusion Plasma experiments as the FIREX I Heating experiments: Heating with a 2 color laser pulse and/or a longer pulse to increase the coupling efficiency from the laser to the core plasma to be >20% from 8%. Compression experiments: Demonstration of higher density with a solid ball target with a tailored laser pulse to be ρr >0.3 g/cm 2 from ρr 0.1 g/cm 2. Reactor Technology Development Fuel target fabrication technology High repetition laser technology 8
9 Solid Fuel Ball is Compressed as a New Approach for the FI Solid fuel ball compression would have more advantages for the FI scheme as compared with the shell implosion. Hydro Instability: smaller Achievable density : High enough Target quality: Relatively Lower level Fuel Target production: Simple Data base: rare data base Solid ball Solid ball Cone Red: advantage Black: disadvantage Shell Hydro Instability: critical Achievable density : High enough Target quality: High level Fuel Target production: Complexity Data base: many experiences Shell 9
10 High Density could be obtained with Solid Fuel Ball Compression Compression was demonstrated of Solid ball target Solid ball target is scalable to the. ignition with a tailored laser pulse. Density profiles around max comp. 中実球 [g/cm 3 ] ns 50.86ns 50.90ns R~ 2 g/cm 2 from 1 D simulation High density compression of solid ball, which could be hydro dynamically stable was experimentally demonstrated to be ρr 0.1 g/cm 2. H. Sawada et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. (2016) Solid (or liquid) ball DT target with CH ablator 815 m Solid (or liquid) DT 790 m r [ m] CH ablator 25 m t 1E15 1E14 1E13 7 steps laser pulse E L = 200 kj L = 0.35 µm 1E t [ms] 4 10
11 Strategies and Expectations through the 2020s Fusion Plasma Research as the FIREX I project Optimization of the heating and the compression schemes separately and demonstration of the integration towards FIREX II for realization of the fast ignition. Technology Development Fuel Target Technology for the FIREX project: Cryogenic target fabrication technologies are being developed, focusing on the FI scheme. Laser Technology as the J EPoCH project: The J EPoCH project is to realize a multi purpose facility base on a high repetition 10kJ laser system consisted of 100Hz/kJ lasers, which has multi 10 PW lasers and multi radiation sources based on laser accelerators.. This facility will promote more the FIREX project as a new approach of the laser fusion research. J EPoCH:Japan Establishment for a Power laser Community Harvest 11
12 Fuel target development focusing on the FI scheme Cone attached Cryogenic fuel targets with a polystyrene shell and foam shell are being developed. The IR heating method has been modified for the FIREX target. An ice layer with 95 % sphericity was achieved in a 800 µm PS shell target by the combination of IR heating and cone temperature control. The solidification process without residual voids in a foam layer was examined based on simulation result. The void fraction was reduced to be near 1 % in the foam shell. Both of the shells need more higher quality from a point of view of hydrodynamic instability of the shell implosion. Solid or liquid fuel ball targets development is now on going. We start development of solid ball target and its compression experiment. Based on the simulation results, solid (or liquid) ball DT target with CH ablator will be developed for the FI experiment. 中実球 Ice layer with 95 % sphericity CH ablator Solid (or liquid) DT 12
13 Strategies and Expectations through the 2020s Fusion Plasma Research as the FIREX I project Optimization of the heating and the compression schemes separately and demonstration of the integration towards FIREX II for realization of the fast ignition. Technology Development Fuel Target Technology for the FIREX project: Cryogenic target fabrication technologies are being developed, focusing on the FI scheme. Laser Technology as the J EPoCH* project: The J EPoCH project is to realize a multi purpose facility based on a high repetition 10kJ laser system consisted of a number of 100Hz/100J lasers, which has multi 10 PW lasers and multi radiation sources with laser accelerators. This facility will promote more the FIREX project as a new approach of the laser fusion research. The system would expand the potential of high power lasers into more large field of science and industry and increases the number of people who support laser fusion. *J EPoCH:Japan Establishment for a Power laser Community Harvest 13
14 Power Laser Integration for the Next Generation, which riches diversity and opens new field of sciences Conceptual view of the J EPoCH system 8kJ/ns 12 beam Symmetry PW/ ps Area 1 16Hz 96Hz 80Hz 16beam lets of 96Hz/1kJ Area 3 Area 2 Area 1: High density Ultra High Density Phys. Laser Fusion Plasma Phys. Laser Fusion Reactor Eng. Laser Astro Phys. Laser Nuclear Physics 20PW 30fs/8kJ ns single side Area 2: High field & pressure Quantum Vacuum Phys. Laser Nuclear Phys. Ultra High Field Phys. Laser Astro Phys. Ultra High Pressure Phys. and Chem. fssec sec/100 kj/pw Thz EM EUV,X ray, ray Electron,/Ion/ Neutron beam Area 3:Diversity Material Science Condensed Matter Physics and Chemistry Life Science Beam Sci. and Nuclear Photo. 14
15 High repetition Power Laser Development is a Critical Issues to Realize the J EPoCH system. Big power laser facility for Science Multi kj/ns laser GEKKO XII kj/short pulse laser LFEX Pulse energy (J) NIF(US) kW 0.1 kw Thales Jena Flash lump 10 kw LULI LD 励起 ns fs LBNL High Rep. & Big power Laser for Academic and Industry Applications HiLASE/STFC HAPLS LLNL CAEP 100 kw J-EPoCHLaser Fusion System Eng. Space Debris Removal (on the ground) Amplitude ILE(Osaka) STFC Tsinghua Univ. MPQ Jena MBI Repetition (Hz) Neutron source GeV accelerator -ray source Radiation therapy J EPoCH 160beams /100Hz Key Technology 25cm Beam Combining Laser Diode 35cm Laser Ceramic 15
16 Road Map of the High Repetition Energetic Lasers to realize the J EPoCH system 16 Beam Combining Technology reduces the Beam Aperture Size, resulting in High repetition 10kJ system. GEKKO 30 cm x12bams Hz cm J EPoCH <10cm 10J/100Hz 100J/100Hz 1kW 10kW Establishment of element technologies of the 100Hz/kJ laser supported by laser accelerator project 35cm 1beamlet/kJ/100Hz 100kW 160beams/16kJ/16Hz 200kW Laser accelerator technology has been almost established Laser plasma accelerator technologies, which are now developed under several programmatic projects, expand the potential of high power laser. e.g. X ray source, g ray source, ion source and neutron source Well Stable and reliable near GeV e beam J EPoCH project Neutrons 2x10 11 nin 4 pulse
17 Summary and comments Plasma Research for the FI as the FIREX I project Investigation of the reliable scaling to realize efficient Fast ignition towards FIREX II project. Technology Development Fuel Target Technology for the FIREX project: Cryogenic target fabrication technologies are being developed, focusing on the FI scheme. High Rep. Laser Technology as the J EPoCH project: Developing a 100Hz/100J high power laser to realize the J EPoCH system With this system, we expect a new stage of laser fusion research with big data based on the high rep. facility, from the single shot base facility. Extra Comments : The project name of EPoCH is better than the J EPoCH for the International Community to get on the track towards achieving Millennium Development Goals. I expect more progress of US Japan collaboration on HED science including laser fusion and power laser development under a new frame work. 17
18 Thank you for your attention! Institute of Laser Engineering Osaka University (ILE Osaka) is one of the world leading laboratory developing laser technologies and researching the applications since the foundation of its forerunner under the Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University in Since then for 47 years, ILE Osaka has independently developed one of the world s largest power laser facilities, and takes full advantage of this equipment in its research endeavors. In 2022, ILE will celebrate its 50th anniversary. 18
Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX)
 1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets
 Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition. H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University
 Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition and Related Laser Plasma Physics H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University Y. Sentoku University of Nevada
Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition and Related Laser Plasma Physics H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University Y. Sentoku University of Nevada
Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I
 1 IF/P7-18 Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I H. Nagatomo 1), T. Johzaki 1), H. Sakagami 2) Y. Sentoku 3), A. Sunahara 4), T. Taguchi 5), Y. Nakao 6), H. Shiraga 1), H. Azechi 1), K.
1 IF/P7-18 Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I H. Nagatomo 1), T. Johzaki 1), H. Sakagami 2) Y. Sentoku 3), A. Sunahara 4), T. Taguchi 5), Y. Nakao 6), H. Shiraga 1), H. Azechi 1), K.
Integrated simulation of magnetic-field-assist fast ignition laser fusion
 Integrated simulation of magnetic-field-assist fast ignition laser fusion T. Johzaki 1, H. Nagatomo 2, A. Sunahara 3, Y. Sentoku 4, H. Sakagami 5, M. Hata 2, T. Taguchi 6, K. Mima 7, Y. Kai 1, D. Ajimi
Integrated simulation of magnetic-field-assist fast ignition laser fusion T. Johzaki 1, H. Nagatomo 2, A. Sunahara 3, Y. Sentoku 4, H. Sakagami 5, M. Hata 2, T. Taguchi 6, K. Mima 7, Y. Kai 1, D. Ajimi
Laser Fusion Research with GEKKO XII and PW Laser System at Osaka
 1 Laser Fusion Research with GEKKO XII and PW Laser System at Osaka Y. Izawa 1), K. Mima1), H. Azechi1), S. Fujioka 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Fujimoto 1), T. Jitsuno 1), Y. Johzaki 1),Y. Kitagawa 1), R. Kodama
1 Laser Fusion Research with GEKKO XII and PW Laser System at Osaka Y. Izawa 1), K. Mima1), H. Azechi1), S. Fujioka 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Fujimoto 1), T. Jitsuno 1), Y. Johzaki 1),Y. Kitagawa 1), R. Kodama
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE
 Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability
 Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016
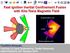 B-generation coil Cone Dense plasma core FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016 1 Summary Fast ignition with external B-field A critical problem
B-generation coil Cone Dense plasma core FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016 1 Summary Fast ignition with external B-field A critical problem
ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion
 ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion Riccardo Betti Fusion Science Center Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester Seminar Massachusetts Institute of Technology, January 0, 010, Cambridge
ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion Riccardo Betti Fusion Science Center Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester Seminar Massachusetts Institute of Technology, January 0, 010, Cambridge
Monochromatic 8.05-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets
 Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments
 Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA
 High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA D.D. Meyerhofer 1), R.L. McCrory 1), R. Betti 1), T.R. Boehly 1), D.T. Casey, 2), T.J.B. Collins 1), R.S. Craxton 1), J.A. Delettrez
High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA D.D. Meyerhofer 1), R.L. McCrory 1), R. Betti 1), T.R. Boehly 1), D.T. Casey, 2), T.J.B. Collins 1), R.S. Craxton 1), J.A. Delettrez
PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA
 PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA K.MIMA, H.AZECHI, H.FUJITA, N.IZUMI, T.JITSUNO, Y.KATO, T.KANABE, Y.KITAGAWA, R.KODAMA, N.MIYANAGA, M.NAKAI, M.NAKATSUKA, S.NAKAI, H.NAGATOMO,
PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA K.MIMA, H.AZECHI, H.FUJITA, N.IZUMI, T.JITSUNO, Y.KATO, T.KANABE, Y.KITAGAWA, R.KODAMA, N.MIYANAGA, M.NAKAI, M.NAKATSUKA, S.NAKAI, H.NAGATOMO,
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA
 Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF
 Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION
 ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION R. KODAMA, H. FUJITA, N. IZUMI, T. KANABE, Y. KATO*, Y. KITAGAWA, Y. SENTOKU, S. NAKAI, M. NAKATSUKA, T. NORIMATSU,
ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION R. KODAMA, H. FUJITA, N. IZUMI, T. KANABE, Y. KATO*, Y. KITAGAWA, Y. SENTOKU, S. NAKAI, M. NAKATSUKA, T. NORIMATSU,
Relativistic Laser self-focusing
 Relativistic Laser self-focusing Kazuo A. Tanaka Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Suita, Osaka 565-0871 Japan GRE OLUG Workshop on HEDS Rochester, N.Y., U.S.A. Apr. 27, 2010 Ne/Nc Concept
Relativistic Laser self-focusing Kazuo A. Tanaka Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Suita, Osaka 565-0871 Japan GRE OLUG Workshop on HEDS Rochester, N.Y., U.S.A. Apr. 27, 2010 Ne/Nc Concept
Update on Fast Ignition Fusion Energy
 Update on Fast Ignition Fusion Energy R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy Science and Technology Ottawa,
Update on Fast Ignition Fusion Energy R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy Science and Technology Ottawa,
Fukuoka, Japan. 23 August National Ignition Facility (NIF) Laboratory for Laser Energetics (OPERA)
 Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
From Fast Ignition Realization Experiments (FIREX) to Electric Power Generation (LIFT)
 1 OV/4-1 From Fast Ignition Realization Experiments (FIREX) to Electric Power Generation (LIFT) H. Azechi 1), K. Mima 1), Y. Fujimoto 1), S. Fujioka 1), H. Homma 1), M. Isobe 3), A. Iwamoto 3), T. Jitsuno
1 OV/4-1 From Fast Ignition Realization Experiments (FIREX) to Electric Power Generation (LIFT) H. Azechi 1), K. Mima 1), Y. Fujimoto 1), S. Fujioka 1), H. Homma 1), M. Isobe 3), A. Iwamoto 3), T. Jitsuno
Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions
 Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF )
 High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
Ignition Regime and Burn Dynamics of D T-Seeded D 3 He Fuel for Fast Ignition Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Ignition Regime and Burn Dynamics of D T-Seeded D 3 He Fuel for Fast Ignition Inertial Confinement Fusion Y. Nakao, K. Tsukida, K. Shinkoda, Y. Saito Department of Applied Quantum Physics and Nuclear Engineering,
Ignition Regime and Burn Dynamics of D T-Seeded D 3 He Fuel for Fast Ignition Inertial Confinement Fusion Y. Nakao, K. Tsukida, K. Shinkoda, Y. Saito Department of Applied Quantum Physics and Nuclear Engineering,
Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
The National Ignition Campaign: Status and Progress
 1 The National Ignition Campaign: Status and Progress E. I. Moses Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94450 Abstract. The National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National
1 The National Ignition Campaign: Status and Progress E. I. Moses Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94450 Abstract. The National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National
Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Inertial Confinement Fusion Prof. Dr. Mathias Groth Aalto University School of Science, Department of Applied Physics Outline Principles of inertial confinement fusion Implosion/compression physics Direct
Inertial Confinement Fusion Prof. Dr. Mathias Groth Aalto University School of Science, Department of Applied Physics Outline Principles of inertial confinement fusion Implosion/compression physics Direct
Path to a direct-drive ignition facility for fusion energy research that requires substantially less laser energy
 Path to a direct-drive ignition facility for fusion energy research that requires substantially less laser energy NRL Laser Fusion High Average Power Laser Program Workshop Lawrence Livermore National
Path to a direct-drive ignition facility for fusion energy research that requires substantially less laser energy NRL Laser Fusion High Average Power Laser Program Workshop Lawrence Livermore National
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics
 1 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics R.L. McCrory 1), D.D. Meyerhofer 1), S.J. Loucks 1), S. Skupsky 1) R.E. Bahr 1), R. Betti 1), T.R.
1 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics R.L. McCrory 1), D.D. Meyerhofer 1), S.J. Loucks 1), S. Skupsky 1) R.E. Bahr 1), R. Betti 1), T.R.
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil
 Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets
 Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability Recent citations - Experimental study of shock-accelerated inclined heavy gas
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability Recent citations - Experimental study of shock-accelerated inclined heavy gas
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility
 Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ. Lindsay M. Mitchel. Spencerport High School. Spencerport, New York
 Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER. Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc.
 D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc. SONOFUSION Sonofusion is making some noise A bit short in energy, ~mj
D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc. SONOFUSION Sonofusion is making some noise A bit short in energy, ~mj
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA
 First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
Where are we with laser fusion?
 Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale
 Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Inertial fusion advance toward ignition and gain (Summary talk)
 Inertial fusion advance toward ignition and gain (Summary talk) X. T. He Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, P. O. Box 8009, Beijing 100088, P. R. China Email: xthe@iapcm.ac.cn
Inertial fusion advance toward ignition and gain (Summary talk) X. T. He Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, P. O. Box 8009, Beijing 100088, P. R. China Email: xthe@iapcm.ac.cn
HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe
 HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe Prof Mike Dunne Director, Central Laser Facility, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK m.dunne@rl.ac.uk www.hiper-laser.eu We are entering a new era Demonstration
HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe Prof Mike Dunne Director, Central Laser Facility, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK m.dunne@rl.ac.uk www.hiper-laser.eu We are entering a new era Demonstration
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy
 Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy Tara Desai 1 *, J.T. Mendonca 2, Dimitri Batani 1 and Andrea Bernardinello 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Ò G.Occhialini Ó and INFM, Universitˆ
Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy Tara Desai 1 *, J.T. Mendonca 2, Dimitri Batani 1 and Andrea Bernardinello 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Ò G.Occhialini Ó and INFM, Universitˆ
Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled, cone-in-shell, fast-ignitor targets on the OMEGA Laser
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF
 Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System
 Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress To cite this article: M. J. Edwards and Ignition Team 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 688 1217
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress To cite this article: M. J. Edwards and Ignition Team 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 688 1217
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA
 Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Non-cryogenic ICF-target
 Non-cryogenic ICF-target 1, V.E. Sherman, 3 N.V. Zmitrenko 1 P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, RF St.-Petersburg Polytechnic State Iniversity, RF M.V. Keldish Instititute
Non-cryogenic ICF-target 1, V.E. Sherman, 3 N.V. Zmitrenko 1 P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, RF St.-Petersburg Polytechnic State Iniversity, RF M.V. Keldish Instititute
Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks. 26 June 2009
 PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Laser in Fusion. Department of Electronics of TEI of Crete. Dr Petridis Kostantinos Lecturer Optoelectronics, Laser and Plasma Technologies Group
 Laser in Fusion Department of Electronics of TEI of Crete Dr Petridis Kostantinos Lecturer Optoelectronics, Laser and Plasma Technologies Group Nuclear Fusion Since we have tried any energy source in our
Laser in Fusion Department of Electronics of TEI of Crete Dr Petridis Kostantinos Lecturer Optoelectronics, Laser and Plasma Technologies Group Nuclear Fusion Since we have tried any energy source in our
Physics of Fast Ignition
 (some aspects of the) Physics of Fast Ignition and target studies for the HiPER project Stefano Atzeni Dipartimento di Energetica, Università di Roma La Sapienza and CNISM,Italy IOP Plasma Physics Group
(some aspects of the) Physics of Fast Ignition and target studies for the HiPER project Stefano Atzeni Dipartimento di Energetica, Università di Roma La Sapienza and CNISM,Italy IOP Plasma Physics Group
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid. P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M.
 Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
INVESTIGATION OF THE DEGENERACY EFFECT IN FAST IGNITION FOR HETEROGENEOUS FUEL
 INVESTIGATION OF THE DEGENERACY EFFECT IN FAST IGNITION FOR HETEROGENEOUS FUEL M. MAHDAVI 1, B. KALEJI 1 Sciences Faculty, Department of Physics, University of Mazandaran P. O. Box 47415-416, Babolsar,
INVESTIGATION OF THE DEGENERACY EFFECT IN FAST IGNITION FOR HETEROGENEOUS FUEL M. MAHDAVI 1, B. KALEJI 1 Sciences Faculty, Department of Physics, University of Mazandaran P. O. Box 47415-416, Babolsar,
Figure 1: The current target chamber and beam diagnostic station for the NDCX-I beamline will be used during commissioning of NDCX-II in 2012
 Progress in U.S. Heavy Ion Fusion Research* IAEA-10 IFE/P6-06 B G Logan, J J Barnard, F M Bieniosek, R H Cohen, R C Davidson, P C Efthimion, A Friedman, E P Gilson, L R Grisham, D P Grote, E Henestroza,
Progress in U.S. Heavy Ion Fusion Research* IAEA-10 IFE/P6-06 B G Logan, J J Barnard, F M Bieniosek, R H Cohen, R C Davidson, P C Efthimion, A Friedman, E P Gilson, L R Grisham, D P Grote, E Henestroza,
The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF)
 PSFC/JA-16-32 The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) J.A. Frenje 1 T.J. Hilsabeck 2, C. Wink1, P. Bell 3,
PSFC/JA-16-32 The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) J.A. Frenje 1 T.J. Hilsabeck 2, C. Wink1, P. Bell 3,
Nuclear Fusion with Polarized Fuel
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Nuclear Fusion with Polarized Fuel -Some thoughts on the PREFER collaboration - Workshop on Nuclear Fusion with Polarized Fuel Ferrara 2/3 October 2017 Markus Büscher
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Nuclear Fusion with Polarized Fuel -Some thoughts on the PREFER collaboration - Workshop on Nuclear Fusion with Polarized Fuel Ferrara 2/3 October 2017 Markus Büscher
ILE, Osaka University ILE, Osaka February 3, 2014
 Summary of Today s Workshop Hideaki Takabe (Aki) ILE, Osaka University ILE, Osaka February 3, 2014 Brief Summary Basic Science on (Astrophysics) Nuclear Physics with ps and ns Intense Lasers 1. NEEC (NEET)
Summary of Today s Workshop Hideaki Takabe (Aki) ILE, Osaka University ILE, Osaka February 3, 2014 Brief Summary Basic Science on (Astrophysics) Nuclear Physics with ps and ns Intense Lasers 1. NEEC (NEET)
Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques
 Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy
Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy
University of Alberta And. Edmonton, November 4, 2017
 Laser Fusion in Canada Robert Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta And Alberta/Canada Fusion Technology Alliance Presented at the Fusion Forum Edmonton, November
Laser Fusion in Canada Robert Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta And Alberta/Canada Fusion Technology Alliance Presented at the Fusion Forum Edmonton, November
Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia B.Yu. Sharkov*, N.N. Alexeev, M.D. Churazov, A.A. Golubev, D.G. Koshkarev, P.R. Zenkevich
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia B.Yu. Sharkov*, N.N. Alexeev, M.D. Churazov, A.A. Golubev, D.G. Koshkarev, P.R. Zenkevich
X ray and XUV phase contrast diagnostics for ELI NP
 X ray and XUV phase contrast diagnostics for ELI NP D. Stutman 1,2, F. Negoita 1 and D. Ursescu 1 1 ELI NP, Bucharest Magurele, Romania 2 Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, USA CARPATHIAN SUMMER SCHOOL
X ray and XUV phase contrast diagnostics for ELI NP D. Stutman 1,2, F. Negoita 1 and D. Ursescu 1 1 ELI NP, Bucharest Magurele, Romania 2 Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, USA CARPATHIAN SUMMER SCHOOL
Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width
 Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Laboratory experiments on the formation and recoil jet transport of aerosol by laser ablation
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Laboratory experiments on the formation and recoil jet transport of aerosol by laser ablation To cite this article: Yoshi Hirooka et al 2016 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Laboratory experiments on the formation and recoil jet transport of aerosol by laser ablation To cite this article: Yoshi Hirooka et al 2016 J. Phys.:
Z-Pinch Inertial Fusion Energy
 Z-Pinch Inertial Fusion Energy Capsule compression Z-Pinch Power Plant Chamber Repetitive Driver experiments on Z LTD Technology Craig L. Olson Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM 87185 RCM on
Z-Pinch Inertial Fusion Energy Capsule compression Z-Pinch Power Plant Chamber Repetitive Driver experiments on Z LTD Technology Craig L. Olson Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM 87185 RCM on
Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums
 Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL
 PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast ignition with heavy ions
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 (2003) A125 A132 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION PII: S0741-3335(03)68658-6 New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 (2003) A125 A132 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION PII: S0741-3335(03)68658-6 New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast
The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA
 The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA Yield Exp (#1 14 ) 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4 1-D campaign neutron yields.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.2.4.6.8 1. 1.2 LILAC 4 8.
The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA Yield Exp (#1 14 ) 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4 1-D campaign neutron yields.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.2.4.6.8 1. 1.2 LILAC 4 8.
Content. Laser structure. Laser principle. Lecture 1. Introduction. a.laser b.light matter interaction c.laser driven nuclear fusion
 13 Content Lecture 1 Introduction a.laser b.light matter interaction c.laser driven nuclear fusion 1 Laser principle Laser structure 1. gain medium. pumping source 3. high reflector 4. output coupler 5.
13 Content Lecture 1 Introduction a.laser b.light matter interaction c.laser driven nuclear fusion 1 Laser principle Laser structure 1. gain medium. pumping source 3. high reflector 4. output coupler 5.
ICF Burn-History Measurements Using 17-MeV Fusion Gamma Rays
 V ICF Burn-History Measurements Using 17-MeV Fusion Gamma Rays R. A. Lerche M.D.Cable, P. G. Dendooven This paper was prepared for submittal to the 12th International Conference on Laser Interaction and
V ICF Burn-History Measurements Using 17-MeV Fusion Gamma Rays R. A. Lerche M.D.Cable, P. G. Dendooven This paper was prepared for submittal to the 12th International Conference on Laser Interaction and
Extreme Light Road Map
 Gérard MOUROU IZEST Ecole Polytechnique IZEST ENABLING TECHNOLOGY Extreme Light Road Map LMJ/NIF, 2MJ, 3B Vacuum Polarization E p =m p c 2 MJ XCELS kj IZEST C 3 TeV GeV ELI, kj.3 B E e =m 0 c 2 J MeV mj
Gérard MOUROU IZEST Ecole Polytechnique IZEST ENABLING TECHNOLOGY Extreme Light Road Map LMJ/NIF, 2MJ, 3B Vacuum Polarization E p =m p c 2 MJ XCELS kj IZEST C 3 TeV GeV ELI, kj.3 B E e =m 0 c 2 J MeV mj
Laser-based proton sources for medical applications
 Laser-based proton sources for medical applications V. Yu. Bychenkov, A. V. Brantov Lebedev Physics Institute, Moscow Center for Fundamental and Applied Research (CFAR), VNIIA, ROSATOM, Moscow ICAN Scientific
Laser-based proton sources for medical applications V. Yu. Bychenkov, A. V. Brantov Lebedev Physics Institute, Moscow Center for Fundamental and Applied Research (CFAR), VNIIA, ROSATOM, Moscow ICAN Scientific
Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas
 2014 US-Japan JIFT Workshop on Progress in kinetic plasma simulations Oct.31-Nov.1, 2014, Salon F, New Orleans Marriott, New Orleans, LA, U.S.A Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas T. Johzaki
2014 US-Japan JIFT Workshop on Progress in kinetic plasma simulations Oct.31-Nov.1, 2014, Salon F, New Orleans Marriott, New Orleans, LA, U.S.A Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas T. Johzaki
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr
 D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition
 The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor. Katherine Manfred
 Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine Manfred Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine M. Manfred Fairport High
Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine Manfred Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine M. Manfred Fairport High
Pellet Injector for Inertial Fusion
 Abstract Pellet Injector for Inertial Fusion J. P. PERIN (*),(*), E BOULEAU (*), B. RUS (**) (*) CEA/INAC/SBT, 17 Rue des Martyrs 38054 GRENOBLE cedex 9 FRANCE (**) Institute of Physics of the ASCR, v.v.i.18221
Abstract Pellet Injector for Inertial Fusion J. P. PERIN (*),(*), E BOULEAU (*), B. RUS (**) (*) CEA/INAC/SBT, 17 Rue des Martyrs 38054 GRENOBLE cedex 9 FRANCE (**) Institute of Physics of the ASCR, v.v.i.18221
D-T ignition in a Z-pinch compressed by imploding liner
 D-gnition in a Z-pinch compressed by imploding. Bilbao 1),.Bernal 1), J. G. inhart ), G. Verri ) 1) nstituto de Física del Plasma Universidad de Buenos Aires Buenos Aires (Argentina) ) NFM, Dipartimento
D-gnition in a Z-pinch compressed by imploding. Bilbao 1),.Bernal 1), J. G. inhart ), G. Verri ) 1) nstituto de Física del Plasma Universidad de Buenos Aires Buenos Aires (Argentina) ) NFM, Dipartimento
Nuclear Science with High Intensity Lasers
 Nuclear Science with High Intensity Lasers Dr. Tomaž Žagar GEN energija, d.o.o. Krško, Slovenija Jožef Stefan Institute, Reactor Physics Department, Ljubljana, Slovenija European Commission, Joint Research
Nuclear Science with High Intensity Lasers Dr. Tomaž Žagar GEN energija, d.o.o. Krško, Slovenija Jožef Stefan Institute, Reactor Physics Department, Ljubljana, Slovenija European Commission, Joint Research
Proton Beam Generated by Multi-Lasers Interaction with Rear-Holed Target
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 67 (2017) 322 326 Vol. 67, No. 3, March 1, 2017 Proton Beam Generated by Multi-Lasers Interaction with Rear-Holed Target Peng Yang ( 杨鹏 ), Da-Peng Fan ( 范大鹏 ), and Yu-Xiao Li ( 李玉晓
Commun. Theor. Phys. 67 (2017) 322 326 Vol. 67, No. 3, March 1, 2017 Proton Beam Generated by Multi-Lasers Interaction with Rear-Holed Target Peng Yang ( 杨鹏 ), Da-Peng Fan ( 范大鹏 ), and Yu-Xiao Li ( 李玉晓
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) with high magnetic fields
 Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) with high magnetic fields B. Grant Logan BGLogan Scientific, Inc., Danville, CA, USA Visiting scientist at U.Orsay-Paris-Sud, CEA-DIF, Ecole Polytechnique Consultant for
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) with high magnetic fields B. Grant Logan BGLogan Scientific, Inc., Danville, CA, USA Visiting scientist at U.Orsay-Paris-Sud, CEA-DIF, Ecole Polytechnique Consultant for
Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility
 2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
BIG A Gamma Ray Source at FACET-II
 BIG A Gamma Ray Source at FACET-II Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear Applications, GWU, December 13-15, 2015 Carsten Hast SLAC Outline FACET-II in a Nutshell BIG: Beams of Intense Gamma-Rays at
BIG A Gamma Ray Source at FACET-II Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear Applications, GWU, December 13-15, 2015 Carsten Hast SLAC Outline FACET-II in a Nutshell BIG: Beams of Intense Gamma-Rays at
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser
 Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
MIT Research using High-Energy Density Plasmas at OMEGA and the NIF
 MIT Research using High-Energy Density Plasmas at OMEGA and the NIF 860 μm 2.3 μm SiO 2 D 3 He gas 1 10 11 D-D 3 He D-D T Yield D-D p D- 3 He 0 0 5 10 15 Energy (MeV) D- 3 He p Hans Rinderknecht Wednesday,
MIT Research using High-Energy Density Plasmas at OMEGA and the NIF 860 μm 2.3 μm SiO 2 D 3 He gas 1 10 11 D-D 3 He D-D T Yield D-D p D- 3 He 0 0 5 10 15 Energy (MeV) D- 3 He p Hans Rinderknecht Wednesday,
Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets
 Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets new prospects in tumor therapy and laboratory astroparticle physics C. Roedel SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory & Friedrich-Schiller-University
Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets new prospects in tumor therapy and laboratory astroparticle physics C. Roedel SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory & Friedrich-Schiller-University
PONDEROMOTIVE ION ACCELERATION AND FAST ION IGNITION WITH ULTRAINTENSE LASER PULSES
 PONDEROMOTIVE ION ACCELERATION AND FAST ION IGNITION WITH ULTRAINTENSE LASER PULSES V.Tikhonchuk Centre Lasers Intenses et Applications Université Bordeaux 1, France Senigallia, June 15, 2009 COULOMB 09
PONDEROMOTIVE ION ACCELERATION AND FAST ION IGNITION WITH ULTRAINTENSE LASER PULSES V.Tikhonchuk Centre Lasers Intenses et Applications Université Bordeaux 1, France Senigallia, June 15, 2009 COULOMB 09
EXTENSION OF FREE-STANDING TARGET TECHNOLOGIES ON IFE REQUIREMENTS
 EXTENSION OF FREE-STANDING TARGET TECHNOLOGIES ON IFE REQUIREMENTS I.V. ALEKSANDROVA, S.V. BAZDENKOV, V.I. CHTCHERBAKOV, E.R. KORESHEVA, I.E.OSIPOV Lebedev Physical Institute of RAS, Moscow, Russia Abstract
EXTENSION OF FREE-STANDING TARGET TECHNOLOGIES ON IFE REQUIREMENTS I.V. ALEKSANDROVA, S.V. BAZDENKOV, V.I. CHTCHERBAKOV, E.R. KORESHEVA, I.E.OSIPOV Lebedev Physical Institute of RAS, Moscow, Russia Abstract
Monoenergetic proton backlighter for measuring E and B fields and for radiographing implosions and high-energy density plasmas invited
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 10E725 2006 Monoenergetic proton backlighter for measuring E and B fields and for radiographing implosions and high-energy density plasmas invited C. K. Li, a F. H.
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 10E725 2006 Monoenergetic proton backlighter for measuring E and B fields and for radiographing implosions and high-energy density plasmas invited C. K. Li, a F. H.
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil.
 Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
Generation and application of ultra-short high-intensity laser pulses
 Generation and application of ultra-short high-intensity laser pulses J. Limpouch Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Department of Physical Electronics
Generation and application of ultra-short high-intensity laser pulses J. Limpouch Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Department of Physical Electronics
BEAM PROPAGATION FOR THE LASER INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION-FISSION ENERGY ENGINE. S. C. Wilks, B. I. Cohen, J. F. Latkowski, and E. A.
 BEAM PROPAGATION FOR THE LASER INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION-FISSION ENERGY ENGINE S. C. Wilks, B. I. Cohen, J. F. Latkowski, and E. A. Williams Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory L-211, Livermore, CA,
BEAM PROPAGATION FOR THE LASER INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION-FISSION ENERGY ENGINE S. C. Wilks, B. I. Cohen, J. F. Latkowski, and E. A. Williams Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory L-211, Livermore, CA,
Laser Ion Acceleration: Status and Perspectives for Fusion
 Laser Ion Acceleration: Status and Perspectives for Fusion Peter G. Thirolf, LMU Munich Outline: laser-particle acceleration fission-fusion mechanism: with ultra-dense ion beams towards r-process path
Laser Ion Acceleration: Status and Perspectives for Fusion Peter G. Thirolf, LMU Munich Outline: laser-particle acceleration fission-fusion mechanism: with ultra-dense ion beams towards r-process path
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
Update on MJ Laser Target Physics
 Update on MJ Laser Target Physics P.A.Holstein, J.Giorla, M.Casanova, F.Chaland, C.Cherfils, E. Dattolo, D.Galmiche, S.Laffite, E.Lefebvre, P.Loiseau, M.C. Monteil, F.Poggi, G.Riazuelo, Y.Saillard CEA
Update on MJ Laser Target Physics P.A.Holstein, J.Giorla, M.Casanova, F.Chaland, C.Cherfils, E. Dattolo, D.Galmiche, S.Laffite, E.Lefebvre, P.Loiseau, M.C. Monteil, F.Poggi, G.Riazuelo, Y.Saillard CEA
High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP
 High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP Channel 1 Crystal chamber X-ray streak camera Chamber wall Re-entrant tube with collimators Normalized signal 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Pulse
High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP Channel 1 Crystal chamber X-ray streak camera Chamber wall Re-entrant tube with collimators Normalized signal 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Pulse
