Inovace bakalářského studijního oboru Aplikovaná chemie. Reg. č.: CZ.1.07/2.2.00/
|
|
|
- Hilary Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inovace bakalářského studijního oboru Aplikovaná chemie Reg. č.: CZ.1.07/2.2.00/
2 Introduction to Physical Chemistry Lecture 6 Thermodynamic laws zeroth first second
3 Lecture vocabulary: summarize prove experience contravene concept propagation of sound transmission of shock waves can be treated as heat transfer indefinitely small change exact partial energy conservation law proof consider keep in mind assumed independent expression tendency abundant internal energy hypothetical violate side effect sole driving force magnitude efficiency shrnovat dokázat zkušenost odporovat koncept, koncepce, představa šíření zvuku šíření rázových vln může být považován za přenos tepla nekonečně malá změna přesný částečný zákon o zachování energie důkaz uvažovat mít na mysli považován nezávislý výraz, vyjádření tendence přebytečná vnitřní energie hypotetický porušovat průvodní jev výhradný hybná síla velikost účinnost
4 Four laws of thermodynamics 4 laws of thermodynamics summarize the most important facts of thermodynamics. They: define fundamental physical quantities, such as temperature, energy, and entropy describe thermodynamic systems by virtue of these quantities describe the transfer of energy as heat and work in thermodynamic processes Thermodynamic laws have the character of axioms (i.e. they cannot be proved, but we have no experience which contravenes them
5 Recommended reading Hrbac recommends the web page as well Why do I recommend this web page? The termodynamic concepts are explained not only on basic problems, but are extended also to real-life phenomena and devices i.e. you can learn e.g. that propagation of sound through atmosphere is an isoentropic process or that transmission of shock waves in rocket motor can be treated as an isoenthalpic process
6 Zeroth thermodynamic law If the two thermodynamic objects are in equillibrium and stay in it after heat transfer is enabled, they have the same temperature C Objects in thermodynamic equilibrium have the same temperature. A B If two or more objects are in thermodynamic equilibrium with other object, all these objects are in equilibrium
7 First thermodynamic law The first law of thermodynamics defines the internal energy (U) as equal to the difference of the heat transfer (Q) into a system and the work (W) done by the system. U U Q ( W ) 2 1 Infinitezimal (indefinitely small change in internal energy) du Q ( W ) Differential of quantites which are not state quantities Exact (total) differential Partial (non-exact) differential First thermodynamic law is in fact the energy conservation law for the case when energy can be exchanged only in the form of heat or pressure-volume work
8 Internal energy of an ideal gas For those who can t remember that the internal energy of an ideal gas is dependent only on temperature, but not on the volume of the gas: Consult Alois Alzheimer ( ) The proof is on the next slide:
9 Internal energy of an ideal gas p 2 Consider two processes (and keep in mind that every process can be approximated by series of such processes) 1 For process 2: V du 2 For process 1: du C dt 1 V 1 This can be integrated because T is the only thing that is changing on the righthandside (C V is assumed to be independent of T and V ). 2 CpdT pdv C p is constant (i.e. not a function of T or V) so it can be integrated directly. Using the ideal gas law: pv = nrt we easily see that pdv+vdp=nrdt. For constant pressure Vdp is zero and therefore pdv=nrdt. Therefore: As we know Mayer s eq. (C p =C V +R) we see that du 2 =CvdT 2. Thus du C du CpdT nrdt 2 dt C dt V 2 V V C dt
10 Second thermodynamic law The second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. The law deduces: the principle of the increase of entropy explains the phenomenon of irreversibility in nature declares the impossibility of machines that generate usable energy from the abundant internal energy of nature by the processes called perpetual motion of the second kind
11 Perpetuum mobile Perpetual motion describes hypothetical machines that operate or produce useful work indefinitely and, more generally, hypothetical machines that produce more work or energy than they consume, whether they might operate indefinitely or not. The "Overbalanced Wheel "water screw" perpetual 1200 s motion machine Boyle's selfflowingflask A perpetual motion machine of the first kind produces work without the input of energy. It thus violates the first law of thermodynamics: the law of conservation of energy. A perpetual motion machine of the second kind is a machine which spontaneously converts thermal energy into mechanical work. When the thermal energy is equivalent to the work done, this does not violate the law of conservation of energy. However it does violate the more subtle second law of thermodynamics (see also entropy). The signature of a perpetual motion machine of the second kind is that there is only one heat reservoir involved, which is being spontaneously cooled without involving a transfer of heat to a cooler reservoir. This conversion of heat into useful work, without any side effect, is impossible, according to the second law of thermodynamics.
12 Second thermodynamic law Clausius statement No process is possible whose sole result is the transfer of heat from a body of lower temperature to a body of higher temperature William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin OM, GCVO, PC, PRS, PRSE, ( ) Kelvin statement Rudolf Clausius ( ) No cyclic process is possible in which the sole result is the absorption of heat from a reservoir and its complete conversion into work
13 Lord Kelvin OM, GCVO, PC, PRS, PRSE Privy Council of the United Kingdom President of the Royal Society (PRS) President of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Order of Merit
14 Carnot cycle Essay about the driving force of fire W 1. Isothermal. rev. expansion in bath T h accepts Q 2 releases -W 1 - W 1 = RT h ln(v 2 /V 1 ) = Q 2 (for 1 mole of ideal gas) 2. Adiabatic rev expansion Q = const, releases -W 2 - W 2 = - C v (T h T c ) = ΔU 3. Isothermal. rev. compression in bath Tc releases Q 1, accepts W 3 surroundings: (thermostatting bath or thermal insulation, depending on the phase of the cycle) W 3 = - RT c ln(v 4 /V 3 ) = - Q 1 4. Adiabat. Rev. compression Q = const, accepts W 4 W 4 = C v (T c T h ) = - C v (T c T h ) - W 4 = - C v (T c T h ) = ΔU
15 Carnot cycle 1. Izoth. rev. expansion in bath T h accepts Q 2 releases -W 1 - W 1 = RT h ln(v 2 /V 1 ) = Q 2 2. Adiabatic rev. expansion Q = const, releases -W 2 - W 2 = - C v (T h T c ) 3. Izoth. rev. compression in bath Tc releases Q 1, accepts W 3 W 3 = - RT c ln(v 4 /V 3 ) = - Q 1 4. Adiabat. rev. compression Q = const, accepts W 4 W 4 = C v (T c T h ) = - C v (T c T h ) - W 4 = - C v (T c T h ) Because during isothermal process the internal energy is not changed and the gas returns to its original state (i.e. to the state with original internal energy), the works -W 2 and W 4 are equal (u can see directly from the expressions that these works have the same magnitude). Therefore, the work made by the Carnot engine depends only on the difference between -W 1 and W 3. That is: -W = - W 1 - W 3 = RT h ln(v 2 /V 1 ) + RT c ln(v 4 /V 3 ).
16 Carnot cycle efficiency and entropy From the description of adiabatic phases T c V 2-1 = T h V 3-1 ; T h V 4-1 = T c V 1-1 follows: that V 2 /V 1 = V 3 /V 4 = - (V 4 /V 3 ) Therefore W = - W 1 - W 3 = R(T h - T c ) ln(v 2 /V 1 ) The engine efficiency : = - W/Q h = (Q h + Q c )/Q h = (T h T c )/T h QC TC Q QC Q C 1 1 H H Q or 0 Q T T T T T H H H C H C This can be generalized as an integral around a reversible cycle: dq 0 T (Clausius theorem) dq ds T A new thermodynamic state quantity called Entropy is introduced this way
17
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Motivation for a Second Law!! First law allows us to calculate the energy
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
Thermodynamic Third class Dr. Arkan J. Hadi
 5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Reversible Processes. Furthermore, there must be no friction (i.e. mechanical energy loss) or turbulence i.e. it must be infinitely slow.
 Reversible Processes A reversible thermodynamic process is one in which the universe (i.e. the system and its surroundings) can be returned to their initial conditions. Because heat only flows spontaneously
Reversible Processes A reversible thermodynamic process is one in which the universe (i.e. the system and its surroundings) can be returned to their initial conditions. Because heat only flows spontaneously
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 9 Heat Engines
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 9 Heat Engines
Irreversible Processes
 Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics
 Chapter 4 Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics 4.1 Heat engines In a cyclic transformation the final state of a system is by definition identical to the initial state. he overall change of the
Chapter 4 Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics 4.1 Heat engines In a cyclic transformation the final state of a system is by definition identical to the initial state. he overall change of the
Adiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0)
 Adiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0) Occurs if: change is made sufficiently quickly and/or with good thermal isolation. Governing formula: PV g = constant where g = C P /C V Adiabat P Isotherms V Because PV/T
Adiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0) Occurs if: change is made sufficiently quickly and/or with good thermal isolation. Governing formula: PV g = constant where g = C P /C V Adiabat P Isotherms V Because PV/T
Minimum Bias Events at ATLAS
 Camille Bélanger-Champagne McGill University Lehman College City University of New York Thermodynamics Charged Particle and Statistical Correlations Mechanics in Minimum Bias Events at ATLAS Thermodynamics
Camille Bélanger-Champagne McGill University Lehman College City University of New York Thermodynamics Charged Particle and Statistical Correlations Mechanics in Minimum Bias Events at ATLAS Thermodynamics
I.D The Second Law Q C
 I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
THERMODYNAMICS Lecture 5: Second Law of Thermodynamics
 HERMODYNAMICS Lecture 5: Second Law of hermodynamics Pierwsza strona Second Law of hermodynamics In the course of discussions on the First Law of hermodynamics we concluded that all kinds of energy are
HERMODYNAMICS Lecture 5: Second Law of hermodynamics Pierwsza strona Second Law of hermodynamics In the course of discussions on the First Law of hermodynamics we concluded that all kinds of energy are
Thermodynamics! for Environmentology!
 1 Thermodynamics! for Environmentology! Thermodynamics and kinetics of natural systems Susumu Fukatsu! Applied Quantum Physics Group! The University of Tokyo, Komaba Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
1 Thermodynamics! for Environmentology! Thermodynamics and kinetics of natural systems Susumu Fukatsu! Applied Quantum Physics Group! The University of Tokyo, Komaba Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0)
 Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
12 The Laws of Thermodynamics
 June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 2007
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 007 5.9 Energy Environment and Society (a Project Based First Year Subject supported by the d'arbeloff Program) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SPRING 007 5.9 Energy Environment and Society (a Project Based First Year Subject supported by the d'arbeloff Program) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Lecture 21: Introducing the Second Law, Irreversibilities
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Introducing the Second Law, Irreversibilities Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai,
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Introducing the Second Law, Irreversibilities Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai,
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H. Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK expansion?
 ...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy
 Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
S = S(f) S(i) dq rev /T. ds = dq rev /T
 In 1855, Clausius proved the following (it is actually a corollary to Clausius Theorem ): If a system changes between two equilibrium states, i and f, the integral dq rev /T is the same for any reversible
In 1855, Clausius proved the following (it is actually a corollary to Clausius Theorem ): If a system changes between two equilibrium states, i and f, the integral dq rev /T is the same for any reversible
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines
 Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
Thermodynamics Second Law Heat Engines Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 10, 2018 Last time entropy (microscopic perspective) Overview heat engines heat pumps Carnot engines Heat Engines Steam engines
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set.
 Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Chapter 16 Thermodynamics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are
 Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Physics 1501 Lecture 37
 Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL ANALYSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY Application in Materials Science Investigations
 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL ANALYSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY Application in Materials Science Investigations Analiza cieplna i kalorymetria różnicowa w badaniach materiałów Tomasz Czeppe Lecture
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL ANALYSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY Application in Materials Science Investigations Analiza cieplna i kalorymetria różnicowa w badaniach materiałów Tomasz Czeppe Lecture
First Law showed the equivalence of work and heat. Suggests engine can run in a cycle and convert heat into useful work.
 0.0J /.77J / 5.60J hermodynamics of Biomolecular Systems 0.0/5.60 Fall 005 Lecture #6 page he Second Law First Law showed the euivalence of work and heat U = + w, du = 0 for cyclic process = w Suggests
0.0J /.77J / 5.60J hermodynamics of Biomolecular Systems 0.0/5.60 Fall 005 Lecture #6 page he Second Law First Law showed the euivalence of work and heat U = + w, du = 0 for cyclic process = w Suggests
Reversibility. Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium
 Reversibility Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium Reversible process: idealized process infinitely close to thermodynamic equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) Necessary conditions
Reversibility Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium Reversible process: idealized process infinitely close to thermodynamic equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) Necessary conditions
Second Law of Thermodynamics: Concept of Entropy. While the first law of thermodynamics defines a relation between work and heat, in terms of
 Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics: Concept of Entropy The law that entropy always increases, holds, I think, the supreme position among the laws of Nature. If someone points out to you that your pet
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics: Concept of Entropy The law that entropy always increases, holds, I think, the supreme position among the laws of Nature. If someone points out to you that your pet
The Story of Spontaneity and Energy Dispersal. You never get what you want: 100% return on investment
 The Story of Spontaneity and Energy Dispersal You never get what you want: 100% return on investment Spontaneity Spontaneous process are those that occur naturally. Hot body cools A gas expands to fill
The Story of Spontaneity and Energy Dispersal You never get what you want: 100% return on investment Spontaneity Spontaneous process are those that occur naturally. Hot body cools A gas expands to fill
The Physics of Energy
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Corso di Laurea in FISICA II Introduction to thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni The Physics of Energy Use
Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Corso di Laurea in FISICA II Introduction to thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni The Physics of Energy Use
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements
 Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements Violation of Clausius statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Clausius statement Violation
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements Violation of Clausius statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Clausius statement Violation
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition. Chapter 3. The Second Law
 Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition Chapter 3. The Second Law The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 Entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific processes
Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition Chapter 3. The Second Law The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 Entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific processes
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Basic Thermodynamics. Prof. S. K. Som. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur.
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Second Law and its Corollaries I Good afternoon, I welcome you all to this
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Second Law and its Corollaries I Good afternoon, I welcome you all to this
Lecture Notes Set 4c: Heat engines and the Carnot cycle
 ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Matter exchange - type of wall Yes - permeable - absence of wall. Energy exchange - type of wall. - diathermic - moving wall. Yes
 I. The concept of work, expansion and additional (useful) work. II. The concept of heat. III. Definition of internal energy and its molecular interpretation. I. Different forms of the first law of thermodynamics..
I. The concept of work, expansion and additional (useful) work. II. The concept of heat. III. Definition of internal energy and its molecular interpretation. I. Different forms of the first law of thermodynamics..
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle
 Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle. Irreversible Processes. Reversible Processes. Carnot Cycle
 Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
CHEM Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
Physical Biochemistry. Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University
 Physical Biochemistry Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University Week 3 CHAPTER 2 The Second Law: Entropy of the Universe increases What is entropy Definition: measure of disorder The greater the disorder,
Physical Biochemistry Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University Week 3 CHAPTER 2 The Second Law: Entropy of the Universe increases What is entropy Definition: measure of disorder The greater the disorder,
October 18, 2011 Carnot cycle - 1
 Carnot Cycle In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (The book is now free online You should try it out) To construct an engine, Carnot noted, at
Carnot Cycle In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (The book is now free online You should try it out) To construct an engine, Carnot noted, at
Examples. Fire Piston (demo) Example (Comparison of processes)
 Examples Fire Piston (demo) Fire Piston istory http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fire_piston Example 19.68 (Comparison of processes) Fire piston calculations http://complex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262/soln/fire_piston.pdf
Examples Fire Piston (demo) Fire Piston istory http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fire_piston Example 19.68 (Comparison of processes) Fire piston calculations http://complex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262/soln/fire_piston.pdf
Chap. 3 The Second Law. Spontaneous change
 Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Lecture. Polymer Thermodynamics 0331 L First and Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1 Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. S. Enders Faculty III for Process Science Institute of Chemical Engineering Department of hermodynamics Lecture Polymer hermodynamics 0331 L 337 2.1. First Law of hermodynamics
1 Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. S. Enders Faculty III for Process Science Institute of Chemical Engineering Department of hermodynamics Lecture Polymer hermodynamics 0331 L 337 2.1. First Law of hermodynamics
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Chemistry 163B Refrigerators and Generalization of Ideal Gas Carnot (four steps to exactitude) E&R pp 86-91, Raff pp.
 statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics Chemistry 163B Refrigerators and Generalization of Ideal Gas Carnot (four steps to exactitude) E&R pp 86-91, 109-111 Raff pp. 159-164 1. Macroscopic properties
statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics Chemistry 163B Refrigerators and Generalization of Ideal Gas Carnot (four steps to exactitude) E&R pp 86-91, 109-111 Raff pp. 159-164 1. Macroscopic properties
CARNOT CYCLE = T = S ( U,V )
 hermodynamics CANO CYCE Do not trouble students with history In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (he book is now free online You should try it
hermodynamics CANO CYCE Do not trouble students with history In 1824, Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) published a short book, eflections on the Motive Power of Fire (he book is now free online You should try it
More Thermodynamics. Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes
 More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy
 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Examples Clausius uncertainty Carnot cycle Asymmetry of heat and work Perpetual mobile Heat pump 10 version of 2 nd law
 Chem 759 Entropy Part III Examples Clausius uncertainty Carnot cycle Asymmetry of heat and work Perpetual mobile Heat pump 10 version of 2 nd law Updated PowerPoints with in-class solutions, go to http://www.uweburghaus.us/classes/chem759
Chem 759 Entropy Part III Examples Clausius uncertainty Carnot cycle Asymmetry of heat and work Perpetual mobile Heat pump 10 version of 2 nd law Updated PowerPoints with in-class solutions, go to http://www.uweburghaus.us/classes/chem759
CHAPTER 2 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Instructor: Prof. Dr. Uğur Atikol
 CHAPTER 2 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Instructor: Prof. Dr. Uğur Atikol Chapter 2 The Second Law of Thrmodynamics Outline Closed Systems History One-thermal reservoir Reversibility and irreversible
CHAPTER 2 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Instructor: Prof. Dr. Uğur Atikol Chapter 2 The Second Law of Thrmodynamics Outline Closed Systems History One-thermal reservoir Reversibility and irreversible
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
Lecture 13. The Second Law
 MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 88 Lecture 13 The Second Law Last Time Consequences of an Ideal Gas Internal Energy a Function of T Only A New State Function for Any System: Enthalpy H = U + PV A New State
MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 88 Lecture 13 The Second Law Last Time Consequences of an Ideal Gas Internal Energy a Function of T Only A New State Function for Any System: Enthalpy H = U + PV A New State
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Second Law and its Corollaries-IV Good afternoon to all of you to this session
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Second Law and its Corollaries-IV Good afternoon to all of you to this session
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Heat What is heat? Work = 2. PdV 1
 eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
Lecture Ch. 2a. Lord Kelvin (a.k.a William Thomson) James P. Joule. Other Kinds of Energy What is the difference between E and U? Exact Differentials
 Lecture Ch. a Energy and heat capacity State functions or exact differentials Internal energy vs. enthalpy st Law of thermodynamics Relate heat, work, energy Heat/work cycles (and path integrals) Energy
Lecture Ch. a Energy and heat capacity State functions or exact differentials Internal energy vs. enthalpy st Law of thermodynamics Relate heat, work, energy Heat/work cycles (and path integrals) Energy
Chem Lecture Notes 6 Fall 2013 Second law
 Chem 340 - Lecture Notes 6 Fall 2013 Second law In the first law, we determined energies, enthalpies heat and work for any process from an initial to final state. We could know if the system did work or
Chem 340 - Lecture Notes 6 Fall 2013 Second law In the first law, we determined energies, enthalpies heat and work for any process from an initial to final state. We could know if the system did work or
Physics 53. Thermal Physics 1. Statistics are like a bikini. What they reveal is suggestive; what they conceal is vital.
 Physics 53 Thermal Physics 1 Statistics are like a bikini. What they reveal is suggestive; what they conceal is vital. Arthur Koestler Overview In the following sections we will treat macroscopic systems
Physics 53 Thermal Physics 1 Statistics are like a bikini. What they reveal is suggestive; what they conceal is vital. Arthur Koestler Overview In the following sections we will treat macroscopic systems
Inovace bakalářského studijního oboru Aplikovaná chemie. Reg. č.: CZ.1.07/2.2.00/
 Inovace bakalářského studijního oboru Aplikovaná chemie Reg. č.: CZ.1.07/2.2.00/15.0247 Lecture vocabulary: reaction heat specifies reactant ambient temperature circumstance initial / final conditions
Inovace bakalářského studijního oboru Aplikovaná chemie Reg. č.: CZ.1.07/2.2.00/15.0247 Lecture vocabulary: reaction heat specifies reactant ambient temperature circumstance initial / final conditions
THERMODYNAMICS b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
 THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Irreversible Processes
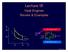 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Part1B(Advanced Physics) Statistical Physics
 PartB(Advanced Physics) Statistical Physics Course Overview: 6 Lectures: uesday, hursday only 2 problem sheets, Lecture overheads + handouts. Lent erm (mainly): Brief review of Classical hermodynamics:
PartB(Advanced Physics) Statistical Physics Course Overview: 6 Lectures: uesday, hursday only 2 problem sheets, Lecture overheads + handouts. Lent erm (mainly): Brief review of Classical hermodynamics:
MCQs THERMODYNAMICS. Physics Without Fear.
 MCQs THERMODYNAMICS Physics Without Fear Thermodynamics: At a glance Zeroth law of thermodynamics: Two systems A and B each in thermal equilibrium with a third system C are in thermal equilibrium with
MCQs THERMODYNAMICS Physics Without Fear Thermodynamics: At a glance Zeroth law of thermodynamics: Two systems A and B each in thermal equilibrium with a third system C are in thermal equilibrium with
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion. Prof. Bhaskar Roy. Prof. A. M. Pradeep. Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
Chemistry 163B Winter 2013 Clausius Inequality and ΔS ideal gas
 Chemistry 163B q rev, Clausius Inequality and calculating ΔS for ideal gas,, changes (HW#5) Challenged enmanship Notes 1 statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics 1. Macroscopic properties of an isolated
Chemistry 163B q rev, Clausius Inequality and calculating ΔS for ideal gas,, changes (HW#5) Challenged enmanship Notes 1 statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics 1. Macroscopic properties of an isolated
Classical thermodynamics
 Classical thermodynamics More about irreversibility chap. 6 Isentropic expansion of an ideal gas Sudden expansion of a gas into vacuum cf Kittel and Kroemer end of Cyclic engines cf Kittel and Kroemer
Classical thermodynamics More about irreversibility chap. 6 Isentropic expansion of an ideal gas Sudden expansion of a gas into vacuum cf Kittel and Kroemer end of Cyclic engines cf Kittel and Kroemer
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
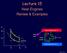 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Niraj Sir THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Physics 150. Thermodynamics. Chapter 15
 Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
Lecture 27: Entropy and Information Prof. WAN, Xin
 General Physics I Lecture 27: Entropy and Information Prof. WAN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ 1st & 2nd Laws of Thermodynamics The 1st law specifies that we cannot get more energy
General Physics I Lecture 27: Entropy and Information Prof. WAN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ 1st & 2nd Laws of Thermodynamics The 1st law specifies that we cannot get more energy
ΔU = Q W. Tue Dec 1. Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM WALTER 145. Thermodynamics 1st Law. 2 nd Law. Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
