ECE 598 JS Lecture 07 Nonideal Conductors and Dielectrics
|
|
|
- Bertram Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE 598 JS Lecture 07 Nonideal Conductors and Dielectrics Spring 2012 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois 1
2 μh E = t ε E H = J + t Material Medium J = σ E E = jωμ H H = J + jωε E σ: conductivity of material medium (Ω 1 m 1 ) since σ H = σ E + jωε E = E( σ + jωε ) = jωε 1+ E jωε ε ε 1+ σ jωε or then E ωμε = + σ E jωε 2
3 Wave in Material Medium 2 2 σ 2 E = ω με 1+ E = γ E jωε 2 2 σ γ = ω με 1+ jωε γ is complex propagation constant σ γ = jω με 1+ = α + jβ jωε α: associated with attenuation of wave β: associated with propagation of wave 3
4 Wave in Material Medium Solution: E = xe ˆ e = xe ˆ e e o γ z α z j β z o decaying exponential 2 με σ α = ω ωε 1/2 2 με σ β = ω ωε Magnetic field E H yˆ o α = e e η z jβ z 1/2 Complex intrinsic impedance η = jωμ σ + jωε 4
5 Skin Depth E = xe ˆ e = xe ˆ e e o γ z α z j β z o Wave decay The decay of electromagnetic wave propagating into a conductor is measured in terms of the skin depth Definition: skin depth δ is distance over which amplitude of wave drops by 1/e. δ = 1 α For good conductors: δ = 2 ωμσ 5
6 Skin Depth e -1 Wave motion I δ = z C V t For perfect conductor, δ = 0 and current only flows on the surface 6
7 DC Resistance R dc l σ wt = l: conductor length σ: conductivity 7
8 AC Resistance R ac l l l πμ f = = = σ wδ σw 2/ ωμσ w σ l: conductor length σ: conductivity f: frequency 8
9 Frequency-Dependent Resistance Jδ =1 α z J J e dz J 0 = = α δ Approximation is to assume that all the current is flowing uniformly within a skin depth 9
10 Frequency-Dependent Resistance Resistance changes with I z I = CL t R ac R dc Resistance is ~ constant when δ >t f 1 π f μ = w σ 1 = σ wt 10
11 Reference Plane Current R ac, ground l 6h πμ f σ 11
12 Skin Effect in Microstrip ε r H. A. Wheeler, "Formulas for the skin effect," Proc. IRE, vol. 30, pp ,
13 Skin Effect in Microstrip Current density varies as J = J e e o y/ δ jy/ δ Note that the phase of the current density varies as a function of y y/ δ jy/ δ Jw o δ o 1 j 0 I = J we e dy = + Jo σ Eo = Jo Eo = σ The voltage measured over a section of conductor of length D is: V = E D= o JD o σ 13
14 The skin effect impedance is where with V JD ( 1+ j) ( 1 ) o Zskin = = = + j π f I σ Jowδ w ρ = Skin Effect in Microstrip 1 σ D D R = skin X = skin f w π μσ μρ is the bulk resistivity of the conductor Zskin = Rskin + jxskin Skin effect has reactive (inductive) component 14
15 Internal Inductance The internal inductance can be calculated directly from the ac resistance L internal R ac = = ω R skin ω Skin effect resistance goes up with frequency Skin effect inductance goes down with frequency 15
16 Surface Roughness Copper surfaces are rough to facilitate adhesion to dielectric during PCB manufacturing When the tooth height is comparable to the skin depth, roughness effects cannot be ignored Surface roughness will increase ohmic losses 16
17 Hammerstad Model R H ( f ) KHRs f when δ < t = Rdc when δ t L H ( f ) L external ( f ) = RH ( fδ = t) + L external RH + when δ < t 2π f 2π f δ = t when δ t 17
18 Hammerstad Model K H 2 2 hrms = 1+ arctan 1.4 π δ h RMS : root mean square value of surface roughness height δ: skin depth f δ=t : frequency where the skin depth is equal to the thickness of the conductor 18
19 Hemispherical Model R L hemi hemi ( f ) ( f ) KhemiRs f when δ < t = Rdc when δ t L external ( f ) = Rhemi ( fδ = t ) + L external Rhemi + when δ < t 2π f 2π f δ = t when δ t 19
20 Hemispherical Model K hemi 1 when Ks 1 = Ks when Ks > 1 K s = 2 ( ) () () ( )( ) ( )( ) () 2 j 3 1 δ / r 1+ j α 1 = ( kr) δ /2r 1+ j ( + ) + ( o )( tile base ) ( μωδ/4) A Re η 3 π / 4k α 1 β 1 μ ωδ / 4 A A 2 () 2 j j/ k rδ 1/ 1 β 1 = ( kr) j/ k rδ 1/ 1 o tile ( )( ( j) ) ( )( ( j) ) 20
21 Huray Model R Huray ( f ) KHurayRs f when δ < t = Rdc when δ t L Huray ( f ) L external ( f ) = RHuray ( fδ = t ) + L external RHuray + when δ < t 2π f 2π f δ = t when δ t 21
22 Huray Model K P Huray = = P + P flat N _ spheres P ( μ ωδ /4) flat N 1 2 3π () () PN _ spheres = Re η Ho α 1 + β k n= 1 flat o tile ( )( ) ( )( ) () 2 j 3 1 δ / r 1+ j α 1 = ( kr) δ /2r 1+ j A η = μ / ε ε' ( )( ( j) ) ( )( ( j) ) 2 () 2 j j/ k rδ 1/ 1 β 1 = ( kr) j/ k rδ 1/ 1 o o n H o : magnitude of applied H field. 22
23 Dielectrics and Polarization No field Applied field Field causes the formation of dipoles polarization Bound surface charge density q sp on upper surface and +q sp on lower surface of the slab. 23
24 Dielectrics and Polarization D= ε E + P= ε E + ε χ E = ε + χ E = ε E ( 1 ) o a o a o e a o e a s a P : polarization vector D : electric flux density E : applied electric field a χ e ε o ε s : electric susceptibility : free space permittivity : static permittivity 24
25 Dielectric Constant Material Air Styrofoam Paraffin Teflon Plywood RT/duroid 5880 Polyethylene RT/duroid 5870 Glass-reinforced teflon (microfiber) Teflon quartz (woven) Glass-reinforced teflon (woven) Cross-linked polystyrene (unreinforced) Polyphenelene oxide (PPO) Glass-reinf orced polystyrene Amber Rubber Plexiglas ε r
26 Dielectric Constants Material Lucite Fused silica Nylon (solid) Quartz Bakelite Formica Lead glass Mica Beryllium oxide (BeO) Marble Flint glass Ferrite (FqO,) Silicon (Si) Gallium arsenide (GaAs) Ammonia (liquid) Glycerin Water ε r
27 AC Variations When a material is subjected to an applied electric field, the centroids of the positive and negative charges are displaced relative to each other forming a linear dipole. When the applied fields begin to alternate in polarity, the permittivities are affected and become functions of the frequency of the alternating fields. 27
28 AC Variations Reverses in polarity cause incremental changes in the static conductivity σ s heating of materials using microwaves (e.g. food cooking) When an electric field is applied, it is assumed that the positive charge remains stationary and the negative charge moves relative to the positive along a platform that exhibits a friction (damping) coefficient d. 28
29 Complex Permittivity N e ε = 1+ Q ε o ' r NQ e ε m o 2 ( 2 2 ω ) o ω 2 d m 2 ( 2 2) o ωo ω + ω ( 2 2) o : dipole density ω = : dipole charge : free space permittivity s : spring (tension) factor o ε " r s m = m ω o NQ e ε m 2 : mass d ω m 2 d ω ω + ω m d : damping coefficient : natural frequency ω: applied frequency 2 29
30 Complex Permittivity H = J i + J c + jωε E = J i + σ se + jω ( ε ' jε ") E H = J + σ + ωε " E+ jωε ' E = J + σ E+ jωε ' E ( ) i s i e σ = equivalent conductivity = σ + ωε" = σ + σ e s s a σ = a alternating field conductivity = ωε " σ s = static field conductivity σ e : total conductivity composed of the static portion σ s and the alternative part σ a caused by the rotation of the dipoles 30
31 Complex Permittivity J = J + J + J = J + σ E+ jωε ' E t i ce de i e J i J t : total electric current density : impressed (source) electric current density J ce J : effective electric conduction current density de : effective displacement electric current density σ e Jt = Ji + σee+ jωε' E = Ji + jωε' 1 j E = Ji + jωε' ( 1 jtanδe) E ωε ' σ e σs + σa σs σa tanδe = effective electric loss tangent = = = + ωε' ωε' ωε' ωε' 31
32 Complex Permittivity σ s ε " ε tanδe = + = tanδs + tanδa = ωε' ε' ε " e ' e tanδ a tanδ s = static electric loss tangent = σ s ωε ' σ a = alternating electric loss tangent = = ωε' " ε ' ε σ e Jcd = Jce + Jde = σee+ jωε' E = jωε' 1 j E = jωε' ( 1 jtanδe ) E ωε ' 32
33 Dielectric Properties Good Dielectrics: σ e 1 ωε ' σ e Jcd = jωε'1 j E jωε' E ωε ' Good Conductors: σ e 1 ωε ' σ e Jcd = jωε'1 j E σee ωε ' 33
34 Dielectric Properties Good Dielectrics: σ e 1 ωε ' σ e Jcd = jωε'1 j E jωε' E ωε ' Good Conductors: σ e 1 ωε ' σ e Jcd = jωε'1 j E σee ωε ' 34
35 Kramers-Kronig Relations There is a relation between the real and imaginary parts of the complex permittivity: 0 ( ') ( ω ') " ' 2 ' r ε r ( ω) = 1 + ω ε dω' 2 2 π ω ω 0 ( ') ( ω ) ' " 2ω 1 ε r ' ε r ( ω) = dω' 2 2 π ω ω Debye Equation ' ' " ' ε rs εr( ω) = εr( ω) jεr( ω) = εr ε ' r jωτ e 35
36 Kramers-Kronig Relations τ e is a relaxation time constant: τ e ε = τ ε ' rs ' r ' r ( ) ε ω ε ε ' ' r = r ε ' r 2 ( ωτ ) e ε " r ( ω) = ( ' ' ) ε ε ωτ r r e 1+ ( ωτ ) e 2 36
37 Dielectric Materials Material ε r tanδ Air Alcohol (ethyl) Aluminum oxide Bakelite Carbon dioxide Germanium Glass Ice Mica Nylon Paper Plexiglas Polystyrene Porcelain * x x x x10-4 2x x x x x
38 Dielectric Materials Material ε r tanδ Pyrex glass Quartz (fused) Rubber Silica (fused) Silicon Snow Sodium chloride Soil (dry) Styrofoam Teflon Titanium dioxide Water (distilled) Water (sea) Water (dehydrated) Wood (dry) x x x x x x x10-4 3x x x x
MAGNETIC FIELDS & UNIFORM PLANE WAVES
 MAGNETIC FIELDS & UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section Multiple Choice 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (8 Pts) 5. (8 Pts) Notes: 1. In the multiple choice questions, each question may have more than one
MAGNETIC FIELDS & UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section Multiple Choice 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (8 Pts) 5. (8 Pts) Notes: 1. In the multiple choice questions, each question may have more than one
MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES
 MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (6 Pts) 5. (6 Pts) 6. (4 Pts) 7. (20 Pts) 8. (20 Pts) 9. (20 Pts) Total Notes: 1. Please read over all questions
MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (6 Pts) 5. (6 Pts) 6. (4 Pts) 7. (20 Pts) 8. (20 Pts) 9. (20 Pts) Total Notes: 1. Please read over all questions
Chapter 3 Uniform Plane Waves Dr. Stuart Long
 3-1 Chapter 3 Uniform Plane Waves Dr. Stuart Long 3- What is a wave? Mechanism by which a disturbance is propagated from one place to another water, heat, sound, gravity, and EM (radio, light, microwaves,
3-1 Chapter 3 Uniform Plane Waves Dr. Stuart Long 3- What is a wave? Mechanism by which a disturbance is propagated from one place to another water, heat, sound, gravity, and EM (radio, light, microwaves,
Plane Waves GATE Problems (Part I)
 Plane Waves GATE Problems (Part I). A plane electromagnetic wave traveling along the + z direction, has its electric field given by E x = cos(ωt) and E y = cos(ω + 90 0 ) the wave is (a) linearly polarized
Plane Waves GATE Problems (Part I). A plane electromagnetic wave traveling along the + z direction, has its electric field given by E x = cos(ωt) and E y = cos(ω + 90 0 ) the wave is (a) linearly polarized
ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines
 ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 MAXWELL S EQUATIONS B E = t Faraday s Law of Induction
ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 MAXWELL S EQUATIONS B E = t Faraday s Law of Induction
ECE 107: Electromagnetism
 ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 7: Dynamic fields Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Maxwell s equations Maxwell
ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 7: Dynamic fields Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Maxwell s equations Maxwell
Plane Waves Part II. 1. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when
 Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Uniform Plane Waves Page 1. Uniform Plane Waves. 1 The Helmholtz Wave Equation
 Uniform Plane Waves Page 1 Uniform Plane Waves 1 The Helmholtz Wave Equation Let s rewrite Maxwell s equations in terms of E and H exclusively. Let s assume the medium is lossless (σ = 0). Let s also assume
Uniform Plane Waves Page 1 Uniform Plane Waves 1 The Helmholtz Wave Equation Let s rewrite Maxwell s equations in terms of E and H exclusively. Let s assume the medium is lossless (σ = 0). Let s also assume
Basics of Wave Propagation
 Basics of Wave Propagation S. R. Zinka zinka@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BITS Pilani, Hyderbad Campus May 7, 2015 Outline 1 Time Harmonic Fields 2 Helmholtz
Basics of Wave Propagation S. R. Zinka zinka@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BITS Pilani, Hyderbad Campus May 7, 2015 Outline 1 Time Harmonic Fields 2 Helmholtz
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 15
 ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 6 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 5 Attenuation Formula Waveguiding system (WG or TL): S z Waveguiding system Exyz (,, ) = E( xye, ) = E( xye, ) e γz jβz αz
ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 6 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 5 Attenuation Formula Waveguiding system (WG or TL): S z Waveguiding system Exyz (,, ) = E( xye, ) = E( xye, ) e γz jβz αz
ECE 598 JS Lecture 08 Lossy Transmission Lines
 ECE 598 JS Lecture 8 Lssy Transmissin Lines Spring 22 Jse E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Cmputer Engineering University f Illinis jesa@illinis.edu Lss in Transmissin Lines RF SOURCE Signal amplitude decreases
ECE 598 JS Lecture 8 Lssy Transmissin Lines Spring 22 Jse E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Cmputer Engineering University f Illinis jesa@illinis.edu Lss in Transmissin Lines RF SOURCE Signal amplitude decreases
ECE 6340 Fall Homework 2. Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish): Probs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12
 ECE 634 Fall 16 Homework Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish: Probs. 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 1 1 Consider two parallel infinite wires in free space each carrying
ECE 634 Fall 16 Homework Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish: Probs. 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 1 1 Consider two parallel infinite wires in free space each carrying
Nonideal Conductor Models
 Nonideal Conductor Models 吳瑞北 Rm. 340, Department of Electrical Engineering E-mail: rbwu@ew.ee.ntu.edu.tw url: cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~rbwu S. H. Hall et al., High-Speed Digital Designs, Chap.5 1 What will You
Nonideal Conductor Models 吳瑞北 Rm. 340, Department of Electrical Engineering E-mail: rbwu@ew.ee.ntu.edu.tw url: cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~rbwu S. H. Hall et al., High-Speed Digital Designs, Chap.5 1 What will You
Uniform Plane Waves. Ranga Rodrigo. University of Moratuwa. November 7, 2008
 Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
EECS 117. Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 22 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 22 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
Field and Wave Electromagnetic
 Field and Wave Electromagnetic Chapter7 The time varying fields and Maxwell s equation Introduction () Time static fields ) Electrostatic E =, id= ρ, D= εe ) Magnetostatic ib=, H = J, H = B μ note) E and
Field and Wave Electromagnetic Chapter7 The time varying fields and Maxwell s equation Introduction () Time static fields ) Electrostatic E =, id= ρ, D= εe ) Magnetostatic ib=, H = J, H = B μ note) E and
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad Electronics and Communicaton Engineering
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 Electronics and Communicaton Engineering Question Bank Course Name : Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines (EMTL) Course Code :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 Electronics and Communicaton Engineering Question Bank Course Name : Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines (EMTL) Course Code :
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 7
 ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 16 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 1 TEM Transmission Line conductors 4 parameters C capacitance/length [F/m] L inductance/length [H/m] R resistance/length
ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 16 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 1 TEM Transmission Line conductors 4 parameters C capacitance/length [F/m] L inductance/length [H/m] R resistance/length
Lecture 2 Review of Maxwell s Equations and the EM Constitutive Parameters
 Lecture 2 Review of Maxwell s Equations and the EM Constitutive Parameters Optional Reading: Steer Appendix D, or Pozar Section 1.2,1.6, or any text on Engineering Electromagnetics (e.g., Hayt/Buck) Time-domain
Lecture 2 Review of Maxwell s Equations and the EM Constitutive Parameters Optional Reading: Steer Appendix D, or Pozar Section 1.2,1.6, or any text on Engineering Electromagnetics (e.g., Hayt/Buck) Time-domain
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012
 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012 http://www.empowermentresources.com/stop_cointelpro/electromagnetic_warfare.htm RF Design In RF circuits RF energy has to be transported
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012 http://www.empowermentresources.com/stop_cointelpro/electromagnetic_warfare.htm RF Design In RF circuits RF energy has to be transported
Electromagnetism. 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless
 Electromagnetism 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Radio Spectrum use for Communications 2 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless 3 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Electromagnetism I Gauss
Electromagnetism 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Radio Spectrum use for Communications 2 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless 3 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Electromagnetism I Gauss
An improved planar cavity model for dielectric characterization
 Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2015 An improved planar cavity model for dielectric characterization Benjamin Jay Conley Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/masters_theses
Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2015 An improved planar cavity model for dielectric characterization Benjamin Jay Conley Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/masters_theses
1 Electromagnetic concepts useful for radar applications
 Electromagnetic concepts useful for radar applications The scattering of electromagnetic waves by precipitation particles and their propagation through precipitation media are of fundamental importance
Electromagnetic concepts useful for radar applications The scattering of electromagnetic waves by precipitation particles and their propagation through precipitation media are of fundamental importance
Accurate Modeling of Spiral Inductors on Silicon From Within Cadence Virtuoso using Planar EM Simulation. Agilent EEsof RFIC Seminar Spring 2004
 Accurate Modeling of Spiral Inductors on Silicon From Within Cadence Virtuoso using Planar EM Simulation Agilent EEsof RFIC Seminar Spring Overview Spiral Inductor Models Availability & Limitations Momentum
Accurate Modeling of Spiral Inductors on Silicon From Within Cadence Virtuoso using Planar EM Simulation Agilent EEsof RFIC Seminar Spring Overview Spiral Inductor Models Availability & Limitations Momentum
3 Constitutive Relations: Macroscopic Properties of Matter
 EECS 53 Lecture 3 c Kamal Sarabandi Fall 21 All rights reserved 3 Constitutive Relations: Macroscopic Properties of Matter As shown previously, out of the four Maxwell s equations only the Faraday s and
EECS 53 Lecture 3 c Kamal Sarabandi Fall 21 All rights reserved 3 Constitutive Relations: Macroscopic Properties of Matter As shown previously, out of the four Maxwell s equations only the Faraday s and
22 Phasor form of Maxwell s equations and damped waves in conducting media
 22 Phasor form of Maxwell s equations and damped waves in conducting media When the fields and the sources in Maxwell s equations are all monochromatic functions of time expressed in terms of their phasors,
22 Phasor form of Maxwell s equations and damped waves in conducting media When the fields and the sources in Maxwell s equations are all monochromatic functions of time expressed in terms of their phasors,
A Method to Extract Dielectric Parameters from Transmission Lines with Conductor Surface Roughness at Microwave Frequencies
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 48, 1 8, 2016 A Method to Extract Dielectric Parameters from Transmission Lines with Conductor Surface Roughness at Microwave Frequencies Binke Huang * and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 48, 1 8, 2016 A Method to Extract Dielectric Parameters from Transmission Lines with Conductor Surface Roughness at Microwave Frequencies Binke Huang * and
TC 412 Microwave Communications. Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines
 TC 412 Microwave Communications Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines RS 1 Review Input impedance for finite length line Quarter wavelength line Half wavelength line Smith chart A
TC 412 Microwave Communications Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines RS 1 Review Input impedance for finite length line Quarter wavelength line Half wavelength line Smith chart A
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM NOTES
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM NOTES PHYSICS B4B BAKERSFIELD COLLEGE Rick Darke (Instructor) CHARGE Electric charge is a fundamental property associated with 2 of the 3 subatomic particles making up most matter.
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM NOTES PHYSICS B4B BAKERSFIELD COLLEGE Rick Darke (Instructor) CHARGE Electric charge is a fundamental property associated with 2 of the 3 subatomic particles making up most matter.
Modeling frequency-dependent conductor losses and dispersion in serial data channel interconnects
 Modeling frequency-dependent conductor losses and dispersion in serial data channel interconnects Yuriy Shlepnev Simberian Inc., www.simberian.com Abstract: Models of transmission lines and transitions
Modeling frequency-dependent conductor losses and dispersion in serial data channel interconnects Yuriy Shlepnev Simberian Inc., www.simberian.com Abstract: Models of transmission lines and transitions
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 1
 ECE 6341 Spring 16 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 1 1 Fields in a Source-Free Region Sources Source-free homogeneous region ( ε, µ ) ( EH, ) Note: For a lossy region, we replace ε ε c ( / ) εc
ECE 6341 Spring 16 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 1 1 Fields in a Source-Free Region Sources Source-free homogeneous region ( ε, µ ) ( EH, ) Note: For a lossy region, we replace ε ε c ( / ) εc
Conventional Paper I (a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials?
 Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Dielectric and Conductor Roughness Models Identification for Successful PCB and Packaging Interconnect Design up to 50 GHz
 Dielectric and Conductor Roughness Models Identification for Successful PCB and Packaging Interconnect Design up to 50 GHz Yuriy Shlepnev Simberian Inc. Abstract: Meaningful interconnect design and compliance
Dielectric and Conductor Roughness Models Identification for Successful PCB and Packaging Interconnect Design up to 50 GHz Yuriy Shlepnev Simberian Inc. Abstract: Meaningful interconnect design and compliance
GLE 594: An introduction to applied geophysics
 GL 594: An introduction to applied geophysics Ground Penetrating Radar Fall 005 Ground Penetrating Radar Reading Today: 309-316 Next class: 316-39 Introduction to GPR Using the reflection (and sometimes
GL 594: An introduction to applied geophysics Ground Penetrating Radar Fall 005 Ground Penetrating Radar Reading Today: 309-316 Next class: 316-39 Introduction to GPR Using the reflection (and sometimes
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Time-harmonic form Phasor form. =0 (1.11d)
 Chapter 2 Wave in an Unbounded Medium Maxwell s Equations Time-harmonic form Phasor form (Real quantity) (complex quantity) B E = Eˆ = jωbˆ (1.11 a) t D= ρ Dˆ = ρ (1.11 b) D H = J + Hˆ = Jˆ+ jωdˆ ( 1.11
Chapter 2 Wave in an Unbounded Medium Maxwell s Equations Time-harmonic form Phasor form (Real quantity) (complex quantity) B E = Eˆ = jωbˆ (1.11 a) t D= ρ Dˆ = ρ (1.11 b) D H = J + Hˆ = Jˆ+ jωdˆ ( 1.11
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
EECS 117 Lecture 20: Plane Waves
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 20 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 20: Plane Waves Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 20 p.
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 20 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 20: Plane Waves Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 20 p.
Lecture contents Review: Few concepts from physics Electric field
 1 Lecture contents Review: Few concepts from physics Electric field Coulomb law, Gauss law, Poisson equation, dipole, capacitor Conductors and isolators 1 Electric current Dielectric constant Overview
1 Lecture contents Review: Few concepts from physics Electric field Coulomb law, Gauss law, Poisson equation, dipole, capacitor Conductors and isolators 1 Electric current Dielectric constant Overview
Lumped Modeling in Thermal Domain
 EEL55: Principles of MEMS ransducers (Fall 003) Instructor: Dr. Hui-Kai Xie Lumped Modeling in hermal Domain Last lecture oday: Lumped modeling Self-heating resistor Self-heating resistor Other dissipation
EEL55: Principles of MEMS ransducers (Fall 003) Instructor: Dr. Hui-Kai Xie Lumped Modeling in hermal Domain Last lecture oday: Lumped modeling Self-heating resistor Self-heating resistor Other dissipation
Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves
 4-1 Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves ECE 3317 Dr. Stuart Long www.bridgat.com www.ranamok.com Boundary Conditions 4- -The convention is that is the outward pointing normal at the boundary
4-1 Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves ECE 3317 Dr. Stuart Long www.bridgat.com www.ranamok.com Boundary Conditions 4- -The convention is that is the outward pointing normal at the boundary
Modeling copper cables and PCBs
 Chapter 2 Modeling copper cables and PCBs 2.1. Introduction A proper channel model is a good basis for a correct understanding of any transmission system. The goal of this chapter is to identify an accurate
Chapter 2 Modeling copper cables and PCBs 2.1. Introduction A proper channel model is a good basis for a correct understanding of any transmission system. The goal of this chapter is to identify an accurate
Kimmo Silvonen, Transmission lines, ver
 Kimmo Silvonen, Transmission lines, ver. 13.10.2008 1 1 Basic Theory The increasing operating and clock frequencies require transmission line theory to be considered more and more often! 1.1 Some practical
Kimmo Silvonen, Transmission lines, ver. 13.10.2008 1 1 Basic Theory The increasing operating and clock frequencies require transmission line theory to be considered more and more often! 1.1 Some practical
Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104
 Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104 Lab #7- Capacitors 1. Introduction The capacitor is one of the essential elements of analog circuitry. It is highly useful for its energy
Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104 Lab #7- Capacitors 1. Introduction The capacitor is one of the essential elements of analog circuitry. It is highly useful for its energy
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 2: Basic Electromagnetic Analysis
 Antennas and Propagation : Basic Electromagnetic Analysis Outline Vector Potentials, Wave Equation Far-field Radiation Duality/Reciprocity Transmission Lines Antennas and Propagation Slide 2 Antenna Theory
Antennas and Propagation : Basic Electromagnetic Analysis Outline Vector Potentials, Wave Equation Far-field Radiation Duality/Reciprocity Transmission Lines Antennas and Propagation Slide 2 Antenna Theory
Notes 24 Image Theory
 ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 24 Image Teory 1 Uniqueness Teorem S ρ v ( yz),, ( given) Given: Φ=ΦB 2 ρv Φ= ε Φ=Φ B on boundary Inside
ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 24 Image Teory 1 Uniqueness Teorem S ρ v ( yz),, ( given) Given: Φ=ΦB 2 ρv Φ= ε Φ=Φ B on boundary Inside
Steric stabilization. Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans
 Steric stabilization Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans Rates of flocculation Strength of interparticle forces The time for half
Steric stabilization Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans Rates of flocculation Strength of interparticle forces The time for half
toroidal iron core compass switch battery secondary coil primary coil
 Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Switched Mode Power Conversion
 Inductors Devices for Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors Transformers Capacitors Inductors Inductors Store Energy Inductors Store Energy in a Magnetic Field In Power Converters Energy Storage
Inductors Devices for Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors Transformers Capacitors Inductors Inductors Store Energy Inductors Store Energy in a Magnetic Field In Power Converters Energy Storage
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
Ansoft HFSS Material Manager
 Choose Perfect Conductor to define a perfectly conducting material that is, a material with infinite conductivity. No field solution is performed inside a perfect conductor. Solve Inside is set to No to
Choose Perfect Conductor to define a perfectly conducting material that is, a material with infinite conductivity. No field solution is performed inside a perfect conductor. Solve Inside is set to No to
Waves. Daniel S. Weile. ELEG 648 Waves. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware. Plane Waves Reflection of Waves
 Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Chapter 2 Circuit Elements
 Chapter Circuit Elements Chapter Circuit Elements.... Introduction.... Circuit Element Construction....3 Resistor....4 Inductor...4.5 Capacitor...6.6 Element Basics...8.6. Element Reciprocals...8.6. Reactance...8.6.3
Chapter Circuit Elements Chapter Circuit Elements.... Introduction.... Circuit Element Construction....3 Resistor....4 Inductor...4.5 Capacitor...6.6 Element Basics...8.6. Element Reciprocals...8.6. Reactance...8.6.3
6 Chapter. Current and Resistance
 6 Chapter Current and Resistance 6.1 Electric Current... 6-2 6.1.1 Current Density... 6-2 6.2 Ohm s Law... 6-5 6.3 Summary... 6-8 6.4 Solved Problems... 6-9 6.4.1 Resistivity of a Cable... 6-9 6.4.2 Charge
6 Chapter Current and Resistance 6.1 Electric Current... 6-2 6.1.1 Current Density... 6-2 6.2 Ohm s Law... 6-5 6.3 Summary... 6-8 6.4 Solved Problems... 6-9 6.4.1 Resistivity of a Cable... 6-9 6.4.2 Charge
Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters
 Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters Yuriy Olegovich Shlepnev Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com 2015 EPEPS Conference, October 27, 2015 2015 Simberian Inc. Outline Introduction
Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters Yuriy Olegovich Shlepnev Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com 2015 EPEPS Conference, October 27, 2015 2015 Simberian Inc. Outline Introduction
Properties of Electric Charge
 1 Goals 2 Properties of Electric Charge 2 Atomic Structure: Composed of three main particles: 1. Proton 2. Neutron 3. Electron Things to Remember: 3 Everything is made of atoms. Electrons can move from
1 Goals 2 Properties of Electric Charge 2 Atomic Structure: Composed of three main particles: 1. Proton 2. Neutron 3. Electron Things to Remember: 3 Everything is made of atoms. Electrons can move from
Module I: Electromagnetic waves
 Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 3: Time dependent EM fields: relaxation, propagation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline Relaxation to a stationary state Electromagnetic waves Propagating plane wave
Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 3: Time dependent EM fields: relaxation, propagation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline Relaxation to a stationary state Electromagnetic waves Propagating plane wave
General review: - a) Dot Product
 General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS
 RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER- 2 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS By 4S7VJ 2.1 Sine-wave If a magnet rotates near a coil, an alternating e.m.f. (a.c.) generates in the coil. This e.m.f. gradually increase
RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER- 2 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS By 4S7VJ 2.1 Sine-wave If a magnet rotates near a coil, an alternating e.m.f. (a.c.) generates in the coil. This e.m.f. gradually increase
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations
 Chapter 7. Time-arying Fields and Maxwell s Equations Electrostatic & Time arying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are not
Chapter 7. Time-arying Fields and Maxwell s Equations Electrostatic & Time arying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are not
LOSSY TRANSMISSION LINE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SPECIAL FUNCTIONS
 LOSSY TRANSMISSION LINE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SPECIAL FUNCTIONS by Bing Zhong A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING In Partial Fulfillment
LOSSY TRANSMISSION LINE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SPECIAL FUNCTIONS by Bing Zhong A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING In Partial Fulfillment
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b
 ECE b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b Instructor: Prof. Vitali Lomain Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of California, San Diego 1 Uniform Waveguide (1) Wave propagation
ECE b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b Instructor: Prof. Vitali Lomain Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of California, San Diego 1 Uniform Waveguide (1) Wave propagation
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 2: Uniform plane waves
 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 2: Uniform plane waves Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology March 25, 2010 Outline 1 Plane waves in lossless media General time dependence
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 2: Uniform plane waves Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology March 25, 2010 Outline 1 Plane waves in lossless media General time dependence
Overview in Images. S. Lin et al, Nature, vol. 394, p , (1998) T.Thio et al., Optics Letters 26, (2001).
 Overview in Images 5 nm K.S. Min et al. PhD Thesis K.V. Vahala et al, Phys. Rev. Lett, 85, p.74 (000) J. D. Joannopoulos, et al, Nature, vol.386, p.143-9 (1997) T.Thio et al., Optics Letters 6, 197-1974
Overview in Images 5 nm K.S. Min et al. PhD Thesis K.V. Vahala et al, Phys. Rev. Lett, 85, p.74 (000) J. D. Joannopoulos, et al, Nature, vol.386, p.143-9 (1997) T.Thio et al., Optics Letters 6, 197-1974
ENGINEERING APPROACH TO MODELLING FRE- QUENCY DISPERSION WITHIN NORMAL METALS AT ROOM TEMPERATURE FOR THz APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 257 275, 2010 ENGINEERING APPROACH TO MODELLING FRE- QUENCY DISPERSION WITHIN NORMAL METALS AT ROOM TEMPERATURE FOR THz APPLICATIONS S. Lucyszyn and Y.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 257 275, 2010 ENGINEERING APPROACH TO MODELLING FRE- QUENCY DISPERSION WITHIN NORMAL METALS AT ROOM TEMPERATURE FOR THz APPLICATIONS S. Lucyszyn and Y.
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department. Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE
 Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE Practice 8 Determining The Resistivity of the Electroinsulating Materials 1. Behavior of the dielectric in
Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE Practice 8 Determining The Resistivity of the Electroinsulating Materials 1. Behavior of the dielectric in
Combined thickness and permittivity measurement of layers using an open-ended coaxial probe
 Combined thickness and permittivity measurement of layers using an open-ended coaxial probe Andreas Soto Peterson A thesis submitted for the degree of Master in Measurement Technology and Instrumentation
Combined thickness and permittivity measurement of layers using an open-ended coaxial probe Andreas Soto Peterson A thesis submitted for the degree of Master in Measurement Technology and Instrumentation
Polarization. D =e i E=k i e o E =e o E+ P
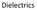 Dielectrics Polarization a perfect insulator or a dielectric is the material with no free charge carriers. if an electric field, E, is applied to the insulator no charge flow. However in the presence of
Dielectrics Polarization a perfect insulator or a dielectric is the material with no free charge carriers. if an electric field, E, is applied to the insulator no charge flow. However in the presence of
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY Classification of Materials: Insulator: An insulator is a material that offers a very low level (or negligible) of conductivity when voltage is applied. Eg: Paper,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY Classification of Materials: Insulator: An insulator is a material that offers a very low level (or negligible) of conductivity when voltage is applied. Eg: Paper,
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
Lecture ( 9 ) Chapter Three : Electric Field in Material Space
 Lecture ( 9 ) Chapter Three : Electric Field in Material Space Properties of Materials, Convection and Conduction Currents, and Conductors 3.1 Properties of Materials Just as electric fields can exist
Lecture ( 9 ) Chapter Three : Electric Field in Material Space Properties of Materials, Convection and Conduction Currents, and Conductors 3.1 Properties of Materials Just as electric fields can exist
Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant
 Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant Name: ID: 1. Objective: (i) To measure the dielectric constant of paper and plastic film. (ii) To examine the energy storage capacity of a practical capacitor.
Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant Name: ID: 1. Objective: (i) To measure the dielectric constant of paper and plastic film. (ii) To examine the energy storage capacity of a practical capacitor.
3.1 The Helmoltz Equation and its Solution. In this unit, we shall seek the physical significance of the Maxwell equations, summarized
 Unit 3 TheUniformPlaneWaveand Related Topics 3.1 The Helmoltz Equation and its Solution In this unit, we shall seek the physical significance of the Maxwell equations, summarized at the end of Unit 2,
Unit 3 TheUniformPlaneWaveand Related Topics 3.1 The Helmoltz Equation and its Solution In this unit, we shall seek the physical significance of the Maxwell equations, summarized at the end of Unit 2,
ELE3310: Basic ElectroMagnetic Theory
 A summary for the final examination EE Department The Chinese University of Hong Kong November 2008 Outline Mathematics 1 Mathematics Vectors and products Differential operators Integrals 2 Integral expressions
A summary for the final examination EE Department The Chinese University of Hong Kong November 2008 Outline Mathematics 1 Mathematics Vectors and products Differential operators Integrals 2 Integral expressions
Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to
Chapter 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation
 Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation Electrostatic & Time Varying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation Electrostatic & Time Varying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are
Geophysical Applications GPR Ground Penetrating Radar
 Overview: Basics of GPR Radar-wave velocity, attenuation and skin depth Modes of acquisition The Radar-range equation Dielectric properties of materials and relation to porosity Case studies [Archeology,
Overview: Basics of GPR Radar-wave velocity, attenuation and skin depth Modes of acquisition The Radar-range equation Dielectric properties of materials and relation to porosity Case studies [Archeology,
A Circuit Approach to Teaching Skin Effect
 35 A Circuit Approach to Teaching Skin Effect James H. Spreen Indiana Institute of Technology Abstract: This paper presents a circuits-based approach to describing skin effect. A student project in library
35 A Circuit Approach to Teaching Skin Effect James H. Spreen Indiana Institute of Technology Abstract: This paper presents a circuits-based approach to describing skin effect. A student project in library
ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism. Spring Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 25 Capacitance
 EE 3318 pplied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 25 apacitance 1 apacitance apacitor [F] + V - +Q ++++++++++++++++++ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Q ε r
EE 3318 pplied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 25 apacitance 1 apacitance apacitor [F] + V - +Q ++++++++++++++++++ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Q ε r
A New, Accurate Quasi-Static Model for Conductor Loss in Coplanar Waveguide
 A New, Accurate Quasi-Static Model for Conductor Loss in Coplanar Waveguide M. S. Islam, E. Tuncer, D. P. Neikirk Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Austin, Texas Conductor loss calculation techniques
A New, Accurate Quasi-Static Model for Conductor Loss in Coplanar Waveguide M. S. Islam, E. Tuncer, D. P. Neikirk Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Austin, Texas Conductor loss calculation techniques
remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the remaining two
 Unit 2 Maxwell s Equations Time-Varying Form While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the
Unit 2 Maxwell s Equations Time-Varying Form While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the
Theory of Electromagnetic Fields
 Theory of Electromagnetic Fields Andrzej Wolski University of Liverpool, and the Cockcroft Institute, UK Abstract We discuss the theory of electromagnetic fields, with an emphasis on aspects relevant to
Theory of Electromagnetic Fields Andrzej Wolski University of Liverpool, and the Cockcroft Institute, UK Abstract We discuss the theory of electromagnetic fields, with an emphasis on aspects relevant to
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2013 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2013 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
ECE357H1S ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS TERM TEST March 2016, 18:00 19:00. Examiner: Prof. Sean V. Hum
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE357H1S ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS TERM TEST 2 21 March 2016, 18:00
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE357H1S ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS TERM TEST 2 21 March 2016, 18:00
Chapter 5 Electric Fields in Material Space
 Chapter 5 Electric Fields in Material Space Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Introduction In chapter 4, Electrostatic fields in free space were considered.
Chapter 5 Electric Fields in Material Space Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Introduction In chapter 4, Electrostatic fields in free space were considered.
White Paper: Transparent High Dielectric Nanocomposite
 Zhiyun (Gene) Chen, Ph.D., Vice President of Engineering Pixelligent Technologies 64 Beckley Street, Baltimore, Maryland 2224 Email: zchen@pixelligent.com February 205 Abstract High dielectric constant
Zhiyun (Gene) Chen, Ph.D., Vice President of Engineering Pixelligent Technologies 64 Beckley Street, Baltimore, Maryland 2224 Email: zchen@pixelligent.com February 205 Abstract High dielectric constant
Engineering Services Examination - UPSC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 Engineering Services Examination - UPSC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Topic-wise Conventional Papers I & II 994 to 3 3 By Engineers Institute of India ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the
Engineering Services Examination - UPSC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Topic-wise Conventional Papers I & II 994 to 3 3 By Engineers Institute of India ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the
Broadband transmission line models for analysis of serial data channel interconnects
 PCB Design Conference East, Durham NC, October 23, 2007 Broadband transmission line models for analysis of serial data channel interconnects Y. O. Shlepnev, Simberian, Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com Simberian:
PCB Design Conference East, Durham NC, October 23, 2007 Broadband transmission line models for analysis of serial data channel interconnects Y. O. Shlepnev, Simberian, Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com Simberian:
Macroscopic dielectric theory
 Macroscopic dielectric theory Maxwellʼs equations E = 1 c E =4πρ B t B = 4π c J + 1 c B = E t In a medium it is convenient to explicitly introduce induced charges and currents E = 1 B c t D =4πρ H = 4π
Macroscopic dielectric theory Maxwellʼs equations E = 1 c E =4πρ B t B = 4π c J + 1 c B = E t In a medium it is convenient to explicitly introduce induced charges and currents E = 1 B c t D =4πρ H = 4π
Chapter 23. Electric Fields
 Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electricity and Magnetism The laws of electricity and magnetism play a central role in the operation of many modern devices. The interatomic and intermolecular forces responsible
Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electricity and Magnetism The laws of electricity and magnetism play a central role in the operation of many modern devices. The interatomic and intermolecular forces responsible
Modeling of Overhead Power Lines for Broadband PLC Applications.
 Modeling of Overhead Power Lines for Broadband PLC Applications. T. A. Papadopoulos, G. K. Papagiannis, D. P. Labridis Power Systems Laboratory Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Aristotle University
Modeling of Overhead Power Lines for Broadband PLC Applications. T. A. Papadopoulos, G. K. Papagiannis, D. P. Labridis Power Systems Laboratory Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Aristotle University
Water activity and dielectric properties of gels in frequency range 200MHz to 6GHz
 Water activity and dielectric properties of gels in frequency range 200MHz to 6GHz Sylvie CLERJON, Jean-Dominique DAUDIN, Jean-Louis DAMEZ Centre INRA de Clermont-Ferrand-Theix 1 About gels Water Activity
Water activity and dielectric properties of gels in frequency range 200MHz to 6GHz Sylvie CLERJON, Jean-Dominique DAUDIN, Jean-Louis DAMEZ Centre INRA de Clermont-Ferrand-Theix 1 About gels Water Activity
ECEN 3741 Electromagnetic Fields 1
 ECEN 3741 Electromagnetic Fields 1 Lecture Notes No. 1 Waves & Phasors Dr. Lin Sun Dept. of ECE Youngstown State University Youngstown, Ohio, 44555 Spring 2015 http://people.ysu.edu/~lsun/ecen3741 1 Chapter
ECEN 3741 Electromagnetic Fields 1 Lecture Notes No. 1 Waves & Phasors Dr. Lin Sun Dept. of ECE Youngstown State University Youngstown, Ohio, 44555 Spring 2015 http://people.ysu.edu/~lsun/ecen3741 1 Chapter
Steric stabilization i the role of polymers
 Steric stabilization i the role of polymers Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecture 4
Steric stabilization i the role of polymers Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecture 4
CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters. Passive components. Prof. Alfred Rufer
 CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters Passive components Prof. Alfred Rufer Overview Part 1: (to be designed) Part 2: Capacitors (to be selected) Part 3: A new component: The Supercapacitor, component
CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters Passive components Prof. Alfred Rufer Overview Part 1: (to be designed) Part 2: Capacitors (to be selected) Part 3: A new component: The Supercapacitor, component
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( z) ( )
 EE433-08 Planer Micrwave Circuit Design Ntes Returning t the incremental sectin, we will nw slve fr V and I using circuit laws. We will assume time-harmnic excitatin. v( z,t ) = v(z)cs( ωt ) jωt { s }
EE433-08 Planer Micrwave Circuit Design Ntes Returning t the incremental sectin, we will nw slve fr V and I using circuit laws. We will assume time-harmnic excitatin. v( z,t ) = v(z)cs( ωt ) jωt { s }
Lecture 21 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics
 Lecture 1 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics Program: 1. Maxwell s Equations.. Magnetic induction and electric displacement. 3. Origins of the electric permittivity and magnetic permeability. 4. Wave
Lecture 1 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics Program: 1. Maxwell s Equations.. Magnetic induction and electric displacement. 3. Origins of the electric permittivity and magnetic permeability. 4. Wave
A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories
 A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820)
A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820)
