Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas. Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology
|
|
|
- Duane Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology
2 Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (U. Washington) Kenneth J. Roche (PNNL) Joaquin E. Drut (U. North Carolina) Gabriel Wlazłowski (PW/ U. Washington) Michael M. Forbes (INT) Yongle Yu (Wuhan) Yuan-Lung (Alan) Luo (U. Washington)
3 What is a unitary gas? A gas of interacting fermions is in the unitary regime if the average separation between particles is large compared to their size (range of interaction), but small compared to their scattering length. n r 0 3 << 1 n a 3 >> 1 n - particle density a - scattering length r 0 - effective range NONPERTURBATIVE REGIME Universality: E x x E ; x= (0) 0.37(1) EFG FG System is dilute but strongly interacting! T - Exp. estimate - Energy of noninteracting Fermi gas F
4 Cold atomic gases and high Tc superconductors 0.5 F T c 0.16 F From Fischer et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 353 (2007) & P. Magierski, G. Wlazłowski, A. Bulgac, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
5 Expected phases of a two species dilute Fermi system BCS-BEC crossover Characteristic temperature: T C superfluid-normal phase transition T Strong interaction UNITARY REGIME Characteristic temperatures: superfluid-normal phase transition break up of Bose molecule T C T T T c weak interaction BCS Superfluid? weak interactions Molecular BEC and Atomic+Molecular Superfluids 1/a a<0 no 2-body bound state a>0 shallow 2-body bound state Bose molecule
6 Unitary limit in 2 and 4 dimensions: 1 a R r O r Two body wave function for r r 4d : ( ) ( ), 0. d 2 Intuitive arguments: - For d=4 R() r 2 d d r diverges at the origin - For d=2 the singularity of the wave function disappears = interaction also disappears. 4D: noninteracting bosons d 4 1 ka F BCS Strong interaction BEC 1 ka F d 2 2D: noninteracting Fermi gas The only nontrivial case of unitary regime is in 3D Nussinov,Nussinov, Phys.Rev. A74, (2006)
7 Effective Hamiltonian of an atom-atom system 2 2 p hf Z H ( Vi V i ) V0 ( r ) P0 V1 ( r ) P hf 2 i1 hf a V I J, V Coulomb term i Tiesinga, Verhaar, Stoof, Phys. Rev. A47, 4114 (1993) Channel coupling Feshbach resonance E Z V ( J I ) B e z n z Regal and Jin, PRL 90, (2003) Interatomic distance
8 Short (selective) history: In 1999 DeMarco and Jin created a degenerate atomic Fermi gas. In 2005 Zwierlein/Ketterle group observed quantum vortices which survived when passing from BEC to unitarity evidence for superfluidity! system of fermionic 6 Li atoms Feshbach resonance: B=834G BEC side: a>0 UNITARY REGIME BCS side: a<0 M.W. Zwierlein et al., Nature, 435, 1047 (2005)
9 L limit for the spatial correlations in the system 2 ˆ ˆ ˆ 3 3 H T V d r ˆs ( r) ˆs( r) g d r nˆ ( r) nˆ ( r) s 2m ˆ 3 ˆ ˆ ˆs ˆs ˆ s N d r n ( r) n ( r) ; n ( r) ( r) ( r) Path Integral Monte Carlo for fermions on 3D lattice Coordinate space Hamiltonian Volume L lattice spacing x 3 - Spin up fermion: kcut x ; x - Spin down fermion: External conditions: T - temperature - chemical potential Periodic boundary conditions imposed
10 2 ˆ ˆ ˆ 3 3 H T V d r ˆs ( r) ˆs( r) g d r nˆ ( r) nˆ ( r) s 2m ˆ 3 ˆ ˆ ˆs ˆs ˆ s N d r n ( r) n ( r) ; n ( r) ( r) ( r) 1 g Basics of Auxiliary Field Monte Carlo (Path Integral MC) mk cut m 4 a Running coupling constant g defined by lattice 2 1 kt 0 1 g 2 m 2 x - UNITARY LIMIT Uˆ ({ }) T exp{ d[ hˆ ({ }) ]}; hˆ ({ }) one-body operator U({ }) Uˆ ({ }) ; - single-particle wave function kl k l l S[ ] ˆ D[ ( r, )] e E( T) H E[ U({ })] ZT ( ) EU [ ({ })]- energy associated with a given sigma field 2 Tr Uˆ({ }) {det[1 Uˆ ( )]} exp[ S({ })] 0 - No sign problem for spin symmetric system!
11 Details of calculations, improvements and problems Currently we can reach 16 3 lattice and perform calcs. down to x = 0.06 (x temperature in Fermi energy units) at the densities of the order of Effective use of FFT(W) makes all imaginary time propagators diagonal (either in real space or momentum space) and there is no need to store large matrices. Update field configurations using the Metropolis importance sampling algorithm. QMC calculations can be split into two independent processes: 1) sample generation (generation of sigma fields), 2) calculations of observables. Change randomly at a fraction of all space and time sites the signs the auxiliary fields σ(r,) so as to maintain a running average of the acceptance rate between 0.4 and 0.6. At low temperatures use Singular Value Decomposition of the evolution operator U({σ}) to stabilize the numerics. MC correlation time 200 time steps at T T c for lattices Unfortunately when increasing the lattice size the correlation time also increases. One needs few thousands uncorrelated samples (we usually take about ) to decrease the statistical error to the level of 1%.
12 Diagram. MC Burovski et al. PRL96, (2006) QMC Bulgac, Drut, Magierski, PRL99, (2006) Diagram. + analytic Haussmann et al. PRA75, (2007) Experiment S. Nascimbene et al. Nature 463, 1057 (2010) Courtesy of C. Salomon exp( )
13 Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas - current status Experiment: M.J.H. Ku, A.T. Sommer, L.W. Cheuk, M.W. Zwierlein, Science 335, 563 (2012) QMC (PIMC + Hybrid Monte Carlo): J.E.Drut, T.Lähde, G.Wlazłowski, P.Magierski, Phys. Rev. A 85, (2012)
14 Local density approximation (LDA) from QMC Uniform system Nonuniform system (gradient corrections neglected) 3 F N ( x ) F N N d r F ( r ) ( x( r )) U ( r) n( r) 5 T 2 x( r ) ; F ( r) 3 n( r) ( r) 2m F The overall chemical potential and the temperature T are constant throughout the system. The density profile will depend on the shape of the trap as dictated by: ( F N) ( x( r)) U( r) 0 n( r) n( r) Using as an input the Monte Carlo results for the uniform system and experimental data (trapping potential, number of particles), we determine the density profiles. 2 2 / 3
15 Comparison with experiment John Thomas group at Duke University, L.Luo, et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, , (2007) THEORY EXP. THEORY ho E0 N F Entropy as a function of energy (relative to the ground state) for the unitary Fermi gas in the harmonic trap. Theory: Ratio of the mean square cloud size at B=1200G to its value at unitarity (B=840G) as a function of the energy. Experimental data are denoted by point with error bars. B 1200G 1/ k a 0.75 F
16 From Sa de Melo, Physics Today (2008) Pairing pseudogap: suppression of low-energy spectral weight function due to incoherent pairing in the normal state (T >T c ) Important issue related to pairing pseudogap: - Are there sharp gapless quasiparticles in a normal Fermi liquid YES: Landau s Fermi liquid theory; NO: breakdown of Fermi liquid paradigm
17 Spectral weight function at unitarity: 1 ( kfa) 0 T 0.12 F T 0.17 F T 0.15 F T C T 0.21 F
18 Gap in the single particle fermionic spectrum - theory Magierski, Wlazłowski, Bulgac, Phys. Rev. Lett.107,145304(2011) Magierski, Wlazłowski, Bulgac, Drut, Phys. Rev. Lett.103,210403(2009)
19 RF spectroscopy in ultracold atomic gases Stewart, Gaebler, Jin, Using photoemission spectroscopy to probe a strongly interacting Fermi gas, Nature, 454, 744 (2008) Experiment (blue dots): D. Jin s group Gaebler et al. Nature Physics 6, 569(2010) Theory (red line): Magierski, Wlazłowski, Bulgac, Phys.Rev.Lett.107,145304(2011)
20 Viscosity in strongly correlated quantum systems:
21 In the light of the kinetic theory of gases molecules are moving mostly along straight lines and occasionally bump onto each other. Mean free path This leads to the Maxwell s formula for viscosity (1860): Consequences: - Non interacting gas is a pathological example of the system with an infinite viscosity - Strongly interacting system can have low viscosity since the mean free path is short but
22 but when the system is strongly correlated then the kinetic theory fails! However: If we blindly use this formula we may notice that the Heisenberg uncertainty principle would give the following relation: ~ pl p - average momentum For any physical fluid: S 4 kb KSS conjecture Kovtun, Son, Starinets, Phys.Rev.Lett. 94, , (2005) from AdS/CFT correspondence
23 Perfect fluid - strongly interacting quantum system = S k 4 B Candidates: quark gluon plasma, atomic gas No well defined quasiparticles Extremely high temperatures: thousands billion degrees Despite of energy scales differing by many orders of magnitude, expansion of both system is pretty much similar and in particular exhibts the so-called elliptic flow.
24 Shear viscosity ( ) ( q 0, ) / xyxy G q d r ˆ r ˆ e 3 xyxy (, ) xy (, ) xy (0,0) cosh ( / 2) Gxyxy ( q, ) xyxy ( q, ) d sinh / 2 i ˆ j ( ), ˆ ˆ k r H lkl ( r) 0 iqr Additional symmetries and sum rules: ε energy density
25 Shear viscosity to entropy ratio experiment vs. theory (from A. Adams et al. New Journal of Physics, "Focus on Strongly Correlated Quantum Fluids: from Ultracold Quantum Gases to QCD Plasmas arxive: ) Lattice QCD ( SU(3) gluodynamics ): H.B. Meyer, Phys. Rev. D 76, (2007) QMC calculations for UFG: G. Wlazłowski, P. Magierski, J.E. Drut, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, (2012)
26 Shear viscosity to entropy density ratio T 8 T 3/2 G.Wlazłowski, P.Magierski,J.E.Drut, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, (2012)
27 Shear viscosity per unit density as a function of temperature C. Chafin, T. Schafer, PRA87,023629(2013) P.Romatschke, R.E. Young, arxiv: Wlazłowski, Magierski, Bulgac, Roche, Phys. Rev. A88, (2012)
28 Spin susceptibility and spin drag rate Wlazłowski, Magierski, Bulgac, Drut, Roche, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, ,(2013) n s ( ) ( q 0, ) / s - spin drag rate 0 s - spin conductivity ˆ z ˆ z ˆ z ˆ z 1 Gs ( q, ) j ( ) j ( ) j (0) j (0) q q q q V cosh ( / 2) Gs( q, ) s( q, ) d sinh / 2
29 Formalism for Time Dependent Phenomena: TDSLDA Density functional contains normal densities, anomalous density (pairing) and currents: Density functional for unitary Fermi gas Nuclear energy functional: SLy4, SkP, SkM*, Both codes: SLDA and TDSLDA are formulated on the 3D lattice without any symmetry restrictions. SLDA generates initial conditions for TDSLDA.
30 Road to quantum turbulence Classical turbulence: energy is transfered from large scales to small scales where it eventually dissipates. Kolmogorov spectrum: E(k)=C ε 2/3 k -5/3 E kinetic energy per unit mass associated with the scale 1/k ε - energy rate (per unit mass) transfered to the system at large scales. k - wave number (from Fourier transformation of the velocity field). C dimensionless constant. Superfluid turbulence (quantum turbulence): disordered set of quantized vortices. The friction between the superfluid and normal part of the fluid serves as a source of energy dissipation. Problem: how the energy is dissipated in the superfluid system at small scales at T=0? - pure quantum turbulence Possibility: vortex reconnections Kelvin waves phonon radiation
31 Vortex reconnections Bulgac, Luo, Magierski, Roche, Yu, Science 332, 1288 (2011)
32 Soliton dynamics vs ring vortex a controversy MIT Experiment: Nature 499 (2013) 426 Theory prefers ring vortices: A. Bulgac, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, (2014) G. Wlazłowski, et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. (in press)
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo
 Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary ermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary ermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases. Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology
 Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina. Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej)
 Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej) 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity in Fermi systems Discovery: H. Kamerlingh
Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej) 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity in Fermi systems Discovery: H. Kamerlingh
Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas
 Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle) Joaquin E. Drut (LANL)
Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle) Joaquin E. Drut (LANL)
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas
 Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC. BEC regime a new type of superfluid?
 Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
Od kwantowej turbulencji do rozszczepienia jądra atomowego. (Wyzwania fizyki układów kwantowych daleko od stanu równowagi.)
 Od kwantowej turbulencji do rozszczepienia jądra atomowego. (Wyzwania fizyki układów kwantowych daleko od stanu równowagi.) Provocative statement: In comparison to many body quantum systems, few body quantum
Od kwantowej turbulencji do rozszczepienia jądra atomowego. (Wyzwania fizyki układów kwantowych daleko od stanu równowagi.) Provocative statement: In comparison to many body quantum systems, few body quantum
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations
 Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin. Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
 Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Zależna od czasu metoda funkcjonału gęstości energii teoria i praktyka opisu dynamiki układów nadciekłych. Piotr Magierski (Politechnika Warszawska)
 Zależna od czasu metoda funkcjonału gęstości energii teoria i praktyka opisu dynamiki układów nadciekłych Piotr Magierski (Politechnika Warszawska) GOAL: Description of fermionic superfluids (nuclei and
Zależna od czasu metoda funkcjonału gęstości energii teoria i praktyka opisu dynamiki układów nadciekłych Piotr Magierski (Politechnika Warszawska) GOAL: Description of fermionic superfluids (nuclei and
Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW
 Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity Discovery: H. Kamerlingh Onnes in 1911 cooled a metallic sample
Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity Discovery: H. Kamerlingh Onnes in 1911 cooled a metallic sample
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the s If the energy is small only the s--wave is re wave is r levant.
 The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now at OSU, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at
The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now at OSU, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at
Quantum limited spin transport in ultracold atomic gases
 Quantum limited spin transport in ultracold atomic gases Searching for the perfect SPIN fluid... Tilman Enss (Uni Heidelberg) Rudolf Haussmann (Uni Konstanz) Wilhelm Zwerger (TU München) Technical University
Quantum limited spin transport in ultracold atomic gases Searching for the perfect SPIN fluid... Tilman Enss (Uni Heidelberg) Rudolf Haussmann (Uni Konstanz) Wilhelm Zwerger (TU München) Technical University
What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime?
 What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime? Aurel Bulgac,, George F. Bertsch,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski, Yongle Yu University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw
What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime? Aurel Bulgac,, George F. Bertsch,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski, Yongle Yu University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw
Bardeen Bardeen, Cooper Cooper and Schrieffer and Schrieffer 1957
 Unexpected aspects of large amplitude nuclear collective motion Aurel Bulgac University of Washington Collaborators: Sukjin YOON (UW) Kenneth J. ROCHE (ORNL) Yongle YU (now at Wuhan Institute of Physics
Unexpected aspects of large amplitude nuclear collective motion Aurel Bulgac University of Washington Collaborators: Sukjin YOON (UW) Kenneth J. ROCHE (ORNL) Yongle YU (now at Wuhan Institute of Physics
Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps
 Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw Outline Some general remarks Path
Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw Outline Some general remarks Path
Towards the shear viscosity of a cold unitary fermi gas
 Towards the shear viscosity of a cold unitary fermi gas Jiunn-Wei Chen National Taiwan U. Shear viscosity y V x (y) x Frictional force T ij iv j ( x) V 2 j i ( x) 1 ij V ( x). 3 Shear viscosity measures
Towards the shear viscosity of a cold unitary fermi gas Jiunn-Wei Chen National Taiwan U. Shear viscosity y V x (y) x Frictional force T ij iv j ( x) V 2 j i ( x) 1 ij V ( x). 3 Shear viscosity measures
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Reactions within Superfluid TDDFT
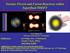 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Reactions within Superfluid TDDFT Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Univ. of Washington) Kenneth J. Roche (PNNL) Ionel Stetcu (LANL)
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Reactions within Superfluid TDDFT Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Univ. of Washington) Kenneth J. Roche (PNNL) Ionel Stetcu (LANL)
Pairing dynamics in low energy nuclear reactions.
 Pairing dynamics in low energy nuclear reactions. Collaborators: Warsaw Univ. of Technology Janina Grineviciute Kazuyuki Sekizawa Gabriel Wlazłowski Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Bugra
Pairing dynamics in low energy nuclear reactions. Collaborators: Warsaw Univ. of Technology Janina Grineviciute Kazuyuki Sekizawa Gabriel Wlazłowski Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Bugra
r 0 range of interaction a scattering length
 The Incredible Many Facets of the Unitary Fermi Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now in Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, soon at
The Incredible Many Facets of the Unitary Fermi Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now in Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, soon at
The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas
 The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Finite-temperature auxiliary-field Monte Carlo (AFMC) method The trapped unitary Fermi gas
The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Finite-temperature auxiliary-field Monte Carlo (AFMC) method The trapped unitary Fermi gas
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the ss--wave is r wave is e r levant.
 The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: JoaquinE. Drut (Seattle, now inosu, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at LANL)
The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: JoaquinE. Drut (Seattle, now inosu, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at LANL)
Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC FERMI GASES
 1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
Equation of State of Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas
 he 19 th Particle and Nuclei International Conference (PANIC11) Equation of State of Strongly Interacting ermi Gas Mark Ku, Ariel Sommer, Lawrence Cheuk, Andre Schirotzek, Martin Zwierlein heory collaborators
he 19 th Particle and Nuclei International Conference (PANIC11) Equation of State of Strongly Interacting ermi Gas Mark Ku, Ariel Sommer, Lawrence Cheuk, Andre Schirotzek, Martin Zwierlein heory collaborators
ICAP Summer School, Paris, Three lectures on quantum gases. Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT
 ICAP Summer School, Paris, 2012 Three lectures on quantum gases Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding
ICAP Summer School, Paris, 2012 Three lectures on quantum gases Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding
Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems
 Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems Part A Comments on papers of E. Burovski,, N. Prokof ev ev,, B. Svistunov and M.
Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems Part A Comments on papers of E. Burovski,, N. Prokof ev ev,, B. Svistunov and M.
Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA
 Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA Lianyi He ( 何联毅 ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University 2016 Hangzhou Workshop on Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gases,
Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA Lianyi He ( 何联毅 ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University 2016 Hangzhou Workshop on Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gases,
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas
 Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES
 College de France, May 14, 2013 SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INFM PLAN OF THE LECTURES Lecture 1. Superfluidity in ultra cold atomic gases: examples
College de France, May 14, 2013 SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INFM PLAN OF THE LECTURES Lecture 1. Superfluidity in ultra cold atomic gases: examples
Reference for most of this talk:
 Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding ultracold Fermi gases. in Ultracold Fermi Gases, Proceedings of the International School
Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding ultracold Fermi gases. in Ultracold Fermi Gases, Proceedings of the International School
BCS to BEC Crossover and the Unitarity Fermi Gas. Mohit Randeria Ohio State University Boulder School on Modern aspects of Superconductivity
 1 BCS to BEC Crossover and the Unitarity Fermi Gas Mohit Randeria Ohio State University 2014 Boulder School on Modern aspects of Superconductivity Review articles: 2 M. Randeria and E. Taylor, Ann. Rev.
1 BCS to BEC Crossover and the Unitarity Fermi Gas Mohit Randeria Ohio State University 2014 Boulder School on Modern aspects of Superconductivity Review articles: 2 M. Randeria and E. Taylor, Ann. Rev.
Universal quantum transport in ultracold Fermi gases
 Universal quantum transport in ultracold Fermi gases How slowly can spins diffuse? Tilman Enss (U Heidelberg) Rudolf Haussmann (U Konstanz) Wilhelm Zwerger (TU München) Aarhus, 26 June 24 Transport in
Universal quantum transport in ultracold Fermi gases How slowly can spins diffuse? Tilman Enss (U Heidelberg) Rudolf Haussmann (U Konstanz) Wilhelm Zwerger (TU München) Aarhus, 26 June 24 Transport in
From BEC to BCS. Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs. Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI. and
 From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases
 New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases Joaquín E. Drut The Ohio State University INT Program Simulations and Symmetries Seattle, March 2010 In collaboration with Timo A. Lähde Aalto University,
New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases Joaquín E. Drut The Ohio State University INT Program Simulations and Symmetries Seattle, March 2010 In collaboration with Timo A. Lähde Aalto University,
Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter. National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
 Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter Stefano Gandolfi Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter Stefano Gandolfi Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases. Michael Köhl Universität Bonn
 Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases Michael Köhl Universität Bonn Ultracold Fermi gases as model systems BEC/BCS crossover Search for the perfect fluid: Cold fermions vs. Quark-gluon plasma Cao et al.,
Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases Michael Köhl Universität Bonn Ultracold Fermi gases as model systems BEC/BCS crossover Search for the perfect fluid: Cold fermions vs. Quark-gluon plasma Cao et al.,
Lecture 4. Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules
 Lecture 4 Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules 95 Reminder: scattering length V(r) a tan 0( k) lim k0 k r a: scattering length Single-channel scattering a 96 Multi-channel scattering alkali-metal atom:
Lecture 4 Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules 95 Reminder: scattering length V(r) a tan 0( k) lim k0 k r a: scattering length Single-channel scattering a 96 Multi-channel scattering alkali-metal atom:
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas
 Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas
 Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas Introduction / Motivation Homogeneous Gas Momentum Distribution Quasi-Particle Spectrum Low Energy Excitations and Static Structure Function Inhomogeneous
Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas Introduction / Motivation Homogeneous Gas Momentum Distribution Quasi-Particle Spectrum Low Energy Excitations and Static Structure Function Inhomogeneous
Nuclear Fission: from more phenomenology and adjusted parameters to more fundamental theory and increased predictive power
 Nuclear Fission: from more phenomenology and adjusted parameters to more fundamental theory and increased predictive power Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac
Nuclear Fission: from more phenomenology and adjusted parameters to more fundamental theory and increased predictive power Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac
Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle
 Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle People I have been lucky to work with on these problems: Clockwise (starting
Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle People I have been lucky to work with on these problems: Clockwise (starting
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids
 Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the s If the energy is small only the s--wave is re wave is r levant.
 Generation and Dynamics of Vortices in a Superfluid Unitary Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Yuan Lung (Alan) Luo (Seattle) Piotr Magierski (Warsaw/Seattle) Kenneth
Generation and Dynamics of Vortices in a Superfluid Unitary Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Yuan Lung (Alan) Luo (Seattle) Piotr Magierski (Warsaw/Seattle) Kenneth
Quantum Quantum Optics Optics VII, VII, Zakopane Zakopane, 11 June 09, 11
 Quantum Optics VII, Zakopane, 11 June 09 Strongly interacting Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center for Quantum Optics in Innsbruck University of Innsbruck Austrian Academy of Sciences ultracold fermions: species
Quantum Optics VII, Zakopane, 11 June 09 Strongly interacting Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center for Quantum Optics in Innsbruck University of Innsbruck Austrian Academy of Sciences ultracold fermions: species
The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other
 1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation. Randy Hulet
 Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation Randy Hulet Outline Introduction to methods and concepts of cold atom physics Interactions Feshbach resonances Quantum Gases Quantum regime nλ
Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation Randy Hulet Outline Introduction to methods and concepts of cold atom physics Interactions Feshbach resonances Quantum Gases Quantum regime nλ
Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases
 Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases Michael KöhlK ETH Zürich Z (www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch( www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch) Introduction Why should a condensed matter physicist
Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases Michael KöhlK ETH Zürich Z (www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch( www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch) Introduction Why should a condensed matter physicist
Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute Fermi Gases near a Feshbach Resonance
 Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute ermi Gases near a eshbach Resonance A. Bulgac (Seattle), Y. Yu (Seattle Lund) P.. Bedaque (Berkeley), G.. Bertsch (Seattle), R.A. Broglia (Milan), A.C. onseca (Lisbon)
Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute ermi Gases near a eshbach Resonance A. Bulgac (Seattle), Y. Yu (Seattle Lund) P.. Bedaque (Berkeley), G.. Bertsch (Seattle), R.A. Broglia (Milan), A.C. onseca (Lisbon)
The BCS-BEC Crossover and the Unitary Fermi Gas
 Lecture Notes in Physics 836 The BCS-BEC Crossover and the Unitary Fermi Gas Bearbeitet von Wilhelm Zwerger 1. Auflage 2011. Taschenbuch. xvi, 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 642 21977 1 Format (B x L): 15,5
Lecture Notes in Physics 836 The BCS-BEC Crossover and the Unitary Fermi Gas Bearbeitet von Wilhelm Zwerger 1. Auflage 2011. Taschenbuch. xvi, 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 642 21977 1 Format (B x L): 15,5
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP
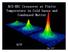 BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms
 Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms Predrag Nikolić Rice University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Sponsors W.M.Keck Program in Quantum
Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms Predrag Nikolić Rice University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Sponsors W.M.Keck Program in Quantum
BCS-BEC Crossover. Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke
 BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv: v1)
 Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv:1205.4536v1) Christof Weitenberg, Rémi Desbuquois, Lauriane Chomaz, Tarik Yefsah, Julian Leonard, Jérôme Beugnon, Jean Dalibard Trieste 18.07.2012 Phase transitions
Superfluidity of a 2D Bose gas (arxiv:1205.4536v1) Christof Weitenberg, Rémi Desbuquois, Lauriane Chomaz, Tarik Yefsah, Julian Leonard, Jérôme Beugnon, Jean Dalibard Trieste 18.07.2012 Phase transitions
Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics
 Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Unitarity limit Consider simple square well potential a < 0 a =, ǫ B = 0 a > 0, ǫ B > 0 Unitarity
Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Unitarity limit Consider simple square well potential a < 0 a =, ǫ B = 0 a > 0, ǫ B > 0 Unitarity
Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas
 Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas The Pennsylvania State University Ken O Hara Jason Williams Eric Hazlett Ronald Stites John Huckans Overview New Physics with Three Component Fermi
Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas The Pennsylvania State University Ken O Hara Jason Williams Eric Hazlett Ronald Stites John Huckans Overview New Physics with Three Component Fermi
Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas
 Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/4/04 Workshop
Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/4/04 Workshop
Dimensional BCS-BEC crossover
 Dimensional BCS-BEC crossover Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, Heidelberg University ERG 2014 Outline Ultracold atoms BCS-BEC Crossover 2D Experiments with... Theory Experiment C. Wetterich
Dimensional BCS-BEC crossover Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, Heidelberg University ERG 2014 Outline Ultracold atoms BCS-BEC Crossover 2D Experiments with... Theory Experiment C. Wetterich
BCS Pairing Dynamics. ShengQuan Zhou. Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois
 BCS Pairing Dynamics 1 ShengQuan Zhou Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois Abstract. Experimental control over inter-atomic interactions by adjusting external parameters is discussed.
BCS Pairing Dynamics 1 ShengQuan Zhou Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois Abstract. Experimental control over inter-atomic interactions by adjusting external parameters is discussed.
Contents. 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks Physical phenomena and theoretical tools The path integrals... 9
 Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas
 Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases
 Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases The ideal Fermi gas: a reminder Interacting Fermions BCS theory in a nutshell The BCS-BEC crossover and quantum simulation Many-Body Physics with Cold Gases Diluteness:
Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases The ideal Fermi gas: a reminder Interacting Fermions BCS theory in a nutshell The BCS-BEC crossover and quantum simulation Many-Body Physics with Cold Gases Diluteness:
Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas
 J Low Temp Phys (2009) 154: 1 29 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9850-2 Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas Le Luo J.E. Thomas Received: 25 July 2008 / Accepted: 12 October 2008 / Published
J Low Temp Phys (2009) 154: 1 29 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9850-2 Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas Le Luo J.E. Thomas Received: 25 July 2008 / Accepted: 12 October 2008 / Published
Strongly paired fermions
 Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
High-Temperature Superfluidity
 High-Temperature Superfluidity Tomoki Ozawa December 10, 2007 Abstract With the recent advancement of the technique of cooling atomic gases, it is now possible to make fermionic atom gases into superfluid
High-Temperature Superfluidity Tomoki Ozawa December 10, 2007 Abstract With the recent advancement of the technique of cooling atomic gases, it is now possible to make fermionic atom gases into superfluid
Universality in Few- and Many-Body Systems
 Universality in Few- and Many-Body Systems Lucas Platter Institute for Nuclear Theory University of Washington Collaborators: Braaten, Hammer, Kang, Phillips, Ji Ultracold Gases the scattering length a
Universality in Few- and Many-Body Systems Lucas Platter Institute for Nuclear Theory University of Washington Collaborators: Braaten, Hammer, Kang, Phillips, Ji Ultracold Gases the scattering length a
Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance
 Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance Dietrich Roscher [D. Roscher, J. Braun, J.-W. Chen, J.E. Drut arxiv:1306.0798] Advances in quantum Monte Carlo techniques for non-relativistic
Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance Dietrich Roscher [D. Roscher, J. Braun, J.-W. Chen, J.E. Drut arxiv:1306.0798] Advances in quantum Monte Carlo techniques for non-relativistic
Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover
 Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei and CNISM, Università di Padova INO-CNR, Research
Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei and CNISM, Università di Padova INO-CNR, Research
Fermi gases in an optical lattice. Michael Köhl
 Fermi gases in an optical lattice Michael Köhl BEC-BCS crossover What happens in reduced dimensions? Sa de Melo, Physics Today (2008) Two-dimensional Fermi gases Two-dimensional gases: the grand challenge
Fermi gases in an optical lattice Michael Köhl BEC-BCS crossover What happens in reduced dimensions? Sa de Melo, Physics Today (2008) Two-dimensional Fermi gases Two-dimensional gases: the grand challenge
BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover
 Institut für Experimentalphysik Universität Innsbruck Dresden, 12.10. 2004 BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover Johannes Hecker Denschlag The lithium team Selim Jochim Markus Bartenstein
Institut für Experimentalphysik Universität Innsbruck Dresden, 12.10. 2004 BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover Johannes Hecker Denschlag The lithium team Selim Jochim Markus Bartenstein
Benchmarking the Many-body Problem
 Benchmarking the Many-body Problem Precision bounds on the Equation of State Michael McNeil Forbes Institute for Nuclear Theory (INT) and the University of Washington (Seattle) 18 May 2011 1 Benchmarks
Benchmarking the Many-body Problem Precision bounds on the Equation of State Michael McNeil Forbes Institute for Nuclear Theory (INT) and the University of Washington (Seattle) 18 May 2011 1 Benchmarks
Cold atoms and AdS/CFT
 Cold atoms and AdS/CFT D. T. Son Institute for Nuclear Theory, University of Washington Cold atoms and AdS/CFT p.1/27 History/motivation BCS/BEC crossover Unitarity regime Schrödinger symmetry Plan Geometric
Cold atoms and AdS/CFT D. T. Son Institute for Nuclear Theory, University of Washington Cold atoms and AdS/CFT p.1/27 History/motivation BCS/BEC crossover Unitarity regime Schrödinger symmetry Plan Geometric
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids. C. Salomon
 A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon INT workshop Frontiers in quantum simulation with cold atoms University of Washington, April 2, 2015 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner,
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon INT workshop Frontiers in quantum simulation with cold atoms University of Washington, April 2, 2015 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner,
Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid?
 Nuclear Physics A 830 (2009) 665c 672c www.elsevier.com/locate/nuclphysa Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid? J. E. Thomas Physics Department, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708-0305,
Nuclear Physics A 830 (2009) 665c 672c www.elsevier.com/locate/nuclphysa Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid? J. E. Thomas Physics Department, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708-0305,
F. Chevy Seattle May 2011
 THERMODYNAMICS OF ULTRACOLD GASES F. Chevy Seattle May 2011 ENS FERMION GROUPS Li S. Nascimbène Li/K N. Navon L. Tarruell K. Magalhaes FC C. Salomon S. Chaudhuri A. Ridinger T. Salez D. Wilkowski U. Eismann
THERMODYNAMICS OF ULTRACOLD GASES F. Chevy Seattle May 2011 ENS FERMION GROUPS Li S. Nascimbène Li/K N. Navon L. Tarruell K. Magalhaes FC C. Salomon S. Chaudhuri A. Ridinger T. Salez D. Wilkowski U. Eismann
We can then linearize the Heisenberg equation for in the small quantity obtaining a set of linear coupled equations for and :
 Wednesday, April 23, 2014 9:37 PM Excitations in a Bose condensate So far: basic understanding of the ground state wavefunction for a Bose-Einstein condensate; We need to know: elementary excitations in
Wednesday, April 23, 2014 9:37 PM Excitations in a Bose condensate So far: basic understanding of the ground state wavefunction for a Bose-Einstein condensate; We need to know: elementary excitations in
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals
 2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
Strongly Interacting Fermi Gases: Universal Thermodynamics, Spin Transport, and Dimensional Crossover
 NewSpin, College Station, 1/16/011 Strongly Interacting ermi Gases: Universal hermodynamics, Spin ransport, and Dimensional Crossover Martin Zwierlein Massachusetts Institute of echnology Center for Ultracold
NewSpin, College Station, 1/16/011 Strongly Interacting ermi Gases: Universal hermodynamics, Spin ransport, and Dimensional Crossover Martin Zwierlein Massachusetts Institute of echnology Center for Ultracold
Lecture 2: Ultracold fermions
 Lecture 2: Ultracold fermions Fermions in optical lattices. Fermi Hubbard model. Current state of experiments Lattice modulation experiments Doublon lifetimes Stoner instability Ultracold fermions in optical
Lecture 2: Ultracold fermions Fermions in optical lattices. Fermi Hubbard model. Current state of experiments Lattice modulation experiments Doublon lifetimes Stoner instability Ultracold fermions in optical
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
JĄDRA ATOMOWE. Badania naukowe: struktura jądra atomowego. Profesor Stefan Ćwiok Jądra stabilne. Jądra znane. Jądra ciężkie i superciężkie
 ur. 1933r. Przeryty Bór k. Tarnowa. Studia: Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Moskiewskiego im.łomonosowa. Doktorat: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (1969) Adiunkt:
ur. 1933r. Przeryty Bór k. Tarnowa. Studia: Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Moskiewskiego im.łomonosowa. Doktorat: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (1969) Adiunkt:
Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University RHIC serves the perfect fluid Experiments at RHIC are consistent with the idea that a thermalized
Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University RHIC serves the perfect fluid Experiments at RHIC are consistent with the idea that a thermalized
Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007
 Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007 L.P. Pitaevskii Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, INFM BEC CNR,Trento, Italy; Kapitza Institute for Physical Problems, ul.
Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007 L.P. Pitaevskii Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, INFM BEC CNR,Trento, Italy; Kapitza Institute for Physical Problems, ul.
Superfluid Phase Transition in Gaseous Two Component Lithium-6 System: Critical Temperature. Abstract
 Superfluid Phase Transition in Gaseous Two Component Lithium-6 System: Critical Temperature Benjamin M. Fregoso Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1110 West Green Street,
Superfluid Phase Transition in Gaseous Two Component Lithium-6 System: Critical Temperature Benjamin M. Fregoso Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1110 West Green Street,
Spin Diffusion and Dynamical Defects in a Strongly interacting Fermi gas
 ECT Workshop, May 13 th, 2014 Spin Diffusion and Dynamical Defects in a Strongly interacting Fermi gas Tarik Yefsah Massachusetts Institute of Technology 10-15 m Many-body physics Length scales 1 m 10
ECT Workshop, May 13 th, 2014 Spin Diffusion and Dynamical Defects in a Strongly interacting Fermi gas Tarik Yefsah Massachusetts Institute of Technology 10-15 m Many-body physics Length scales 1 m 10
Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases
 Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases Quantum many-body system in attractive interaction Molecular condensate BEC Cooper pairs BCS Thomas Bourdel, J. Cubizolles, L. Khaykovich, J. Zhang, S. Kokkelmans,
Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases Quantum many-body system in attractive interaction Molecular condensate BEC Cooper pairs BCS Thomas Bourdel, J. Cubizolles, L. Khaykovich, J. Zhang, S. Kokkelmans,
The Big Picture. Thomas Schaefer. North Carolina State University
 The Big Picture Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Big Questions What is QCD? What is a Phase of QCD? What is a Plasma? What is a (perfect) Liquid? What is a wqgp/sqgp? 2 What is QCD (Quantum
The Big Picture Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Big Questions What is QCD? What is a Phase of QCD? What is a Plasma? What is a (perfect) Liquid? What is a wqgp/sqgp? 2 What is QCD (Quantum
Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices
 Goal of these lectures Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices Discuss some aspect of the physics of quantum low dimensional systems Planar fluids Quantum wells and MOS structures High T c
Goal of these lectures Low dimensional quantum gases, rotation and vortices Discuss some aspect of the physics of quantum low dimensional systems Planar fluids Quantum wells and MOS structures High T c
Simulation of neutron-rich dilute nuclear matter using ultracold Fermi gases
 APCTP Focus Program on Quantum Condensation (QC12) Simulation of neutron-rich dilute nuclear matter using ultracold Fermi gases Munekazu Horikoshi Photon Science Center of University of Tokyo Grant-In-Aid
APCTP Focus Program on Quantum Condensation (QC12) Simulation of neutron-rich dilute nuclear matter using ultracold Fermi gases Munekazu Horikoshi Photon Science Center of University of Tokyo Grant-In-Aid
Thermodynamics of the unitary Fermi gas
 Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Faculty of Physics, Chair of Theoretical Solid State Physics, Theresienstr. 37, 80333 Munich, Germany E-mail: O.Goulko@physik.uni-muenchen.de M. Wingate DAMTP, University
Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Faculty of Physics, Chair of Theoretical Solid State Physics, Theresienstr. 37, 80333 Munich, Germany E-mail: O.Goulko@physik.uni-muenchen.de M. Wingate DAMTP, University
Sarma phase in relativistic and non-relativistic systems
 phase in relativistic and non-relativistic systems Tina Katharina Herbst In Collaboration with I. Boettcher, J. Braun, J. M. Pawlowski, D. Roscher, N. Strodthoff, L. von Smekal and C. Wetterich arxiv:149.5232
phase in relativistic and non-relativistic systems Tina Katharina Herbst In Collaboration with I. Boettcher, J. Braun, J. M. Pawlowski, D. Roscher, N. Strodthoff, L. von Smekal and C. Wetterich arxiv:149.5232
Publications. Articles:
 Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory
 Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
Exact relations for two-component Fermi gases with contact interactions
 QMATH13, Oct. 8-11, 2016 Exact relations for two-component Fermi gases with contact interactions Shina Tan, Georgia Institute of Technology 1 Outline The system Hamiltonian Energy functional The contact
QMATH13, Oct. 8-11, 2016 Exact relations for two-component Fermi gases with contact interactions Shina Tan, Georgia Institute of Technology 1 Outline The system Hamiltonian Energy functional The contact
NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering
 NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering Few x 10 5 Yb atoms 250mm 400 nk 250 nk < 200 nk Control of atomic c.m. position and momentum. Today: Bose-Fermi double superfluid Precision BEC interferometry Ultracold
NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering Few x 10 5 Yb atoms 250mm 400 nk 250 nk < 200 nk Control of atomic c.m. position and momentum. Today: Bose-Fermi double superfluid Precision BEC interferometry Ultracold
Universal Quantum Viscosity in a Unitary Fermi Gas
 Universal Quantum Viscosity in a Unitary Fermi Gas Chenglin Cao Duke University July 5 th, 011 Advisor: Prof. John E Thomas Dr.Ilya Arakelyan Dr.James Joseph Dr.Haibin Wu Yingyi Zhang Ethan Elliott Willie
Universal Quantum Viscosity in a Unitary Fermi Gas Chenglin Cao Duke University July 5 th, 011 Advisor: Prof. John E Thomas Dr.Ilya Arakelyan Dr.James Joseph Dr.Haibin Wu Yingyi Zhang Ethan Elliott Willie
Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics
 1 Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Instructor Eugene Demler Office: Lyman 322 Email: demler@physics.harvard.edu Teaching Fellow
1 Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Instructor Eugene Demler Office: Lyman 322 Email: demler@physics.harvard.edu Teaching Fellow
K two systems. fermionic species mixture of two spin states. K 6 Li mass imbalance! cold atoms: superfluidity in Fermi gases
 Bad Honnef, 07 July 2015 Impurities in a Fermi sea: Decoherence and fast dynamics impurity physics: paradigms of condensed matter-physics Fermi sea fixed scalar impurity orthogonality catastrophe P.W.
Bad Honnef, 07 July 2015 Impurities in a Fermi sea: Decoherence and fast dynamics impurity physics: paradigms of condensed matter-physics Fermi sea fixed scalar impurity orthogonality catastrophe P.W.
Diagrammatic Monte Carlo
 Sign Problems and Complex Actions, ECT*, Trento, March 2-6, 2009 Diagrammatic Monte Carlo Boris Svistunov University of Massachusetts, Amherst Nikolay Prokof ev Kris Van Houcke (Umass/Ghent) Evgeny Kozik
Sign Problems and Complex Actions, ECT*, Trento, March 2-6, 2009 Diagrammatic Monte Carlo Boris Svistunov University of Massachusetts, Amherst Nikolay Prokof ev Kris Van Houcke (Umass/Ghent) Evgeny Kozik
EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS
 EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS DIAGRAMMATIC MONTE CARLO Kris Van Houcke (UMass Amherst & U of Ghent) Félix Werner (UMass Amherst) Evgeny Kozik Boris Svistunov & Nikolay Prokofev (UMass Amherst) (ETH
EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS DIAGRAMMATIC MONTE CARLO Kris Van Houcke (UMass Amherst & U of Ghent) Félix Werner (UMass Amherst) Evgeny Kozik Boris Svistunov & Nikolay Prokofev (UMass Amherst) (ETH
Ultracold Fermi and Bose Gases and Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles
 October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
