JĄDRA ATOMOWE. Badania naukowe: struktura jądra atomowego. Profesor Stefan Ćwiok Jądra stabilne. Jądra znane. Jądra ciężkie i superciężkie
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ur. 1933r. Przeryty Bór k. Tarnowa. Studia: Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Moskiewskiego im.łomonosowa. Doktorat: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (1969) Adiunkt: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego ( ) Od 1973: Instytut Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej 1998: tytuł Profesora Fizyki Wieloletni z-ca Dyrektora Instytutu Fizyki PW i Kierownik Zakładu Fizyki Jądrowej Badania naukowe: struktura jądra atomowego JĄDRA ATOMOWE Jądra stabilne? Jądra ciężkie i superciężkie Profesor Stefan Ćwiok Jądra znane protony Neutron Gwiazdy star neutronowe neutrony
2 ur. 1933r. Przeryty Bór k. Tarnowa. Studia: Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Moskiewskiego im.łomonosowa. Doktorat: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (1969) Adiunkt: Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego ( ) Od 1973: Instytut Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej 1998: tytuł Profesora Fizyki Wieloletni z-ca Dyrektora Instytutu Fizyki PW i Kierownik Zakładu Fizyki Jądrowej Badania naukowe: struktura jądra atomowego Profesor Stefan Ćwiok Osiągnięcia: -hipoteza stabilności bardzo ciężkich jąder o N=162 potwierdzona przez doświadczenia w GSI Darmstadt i Berkeley (USA). -wyjaśnienie zagadki istnienia dwóch kanałów rozszczepienia w izotopach fermu. -hipoteza istnienia (metastabilnych) stanów hiperzdeformowanych w aktynowcach - potwierdzona eksperymentalnie. -systematyczne obliczenia dla nieparzystych jąder superciężkich (do dziś interpretacja wielu eksperymentów bazuje na tych wynikach). -hipoteza istnienia liczby magicznej Z=126, a nie Z=114 jak dotychczas sądzono. -hipoteza współistnienia kształtów w jądrach superciężkich (Nature, 433(2005)705)
3 O pewnych własnościach kwantowych gazów atomowych Piotr Magierski (WF PW) Współpracownicy: Aurel Bulgac, Joaquin E. Drut (University of Washington, Seattle)
4 Outline Particle scattering at low energies. BCS-BEC BEC crossover. What is the unitary regime? How one can manipulate the two-body interaction in experiments with atomic gases? Theoretical approach: path integral description of strongly interacting Fermi gases. Equation of state for the Fermi gas in the unitary regime. Critical temperature. Conclusions.
5 Scattering at low energies (s-wave scattering) If ik r e ikr ψ () r = e + f ; f - r 1 f = 1 1 ik + r0 k a 2 2 2π λ = >> R k R - radius of the interaction potential scattering amplitude, a - scattering length, r - effective range k 0 then the interaction is determined by the scattering length alone. 0
6 Scattering at low energies: attractive interaction 1) 2) 3) a < 0 there is no bound state a = ± V(r) ψ () r What is the energy of the dilute Fermi gas? kf kf εf = ; n = ( k 2 Fr 0 << 1) 2m 3π a > 0 a bound state exists Fermi gas? E( k a ) =? F - particle density Perturbation series: E 10 6 = 1+ ( ka F ) 1 ( ka F )( 11 2ln2 )... EFG 9π π 3 EFG = εfn - Energy of the noninteracting Fermi gas 5 PAIRING NOT INCLUDED YET!
7 a < 0 Fermi gas How pairing emerges? Cooper s argument (1956) Gap 2 Cooper pair = kf π 1 1 ε exp, iff 1 and F BCS k a - size of the Cooper pair 2 F << << η = 2m 2k k k e Fa F F 2 EHF+BCS 10 5 BCS 10 = 40 + kfa + = + kfa + 4 EFG 9π 8 εf 9π e π 1 ( )... 1 ( )... exp kfa Hartree-Fock term BCS term
8 Superconductivity and superfluidity in Fermi systems 20 orders of magnitude over a century of (low temperature) physics Dilute atomic Fermi gases T c ev Liquid 3 He T c 10-7 ev Metals, composite materials T c ev Nuclei, neutron stars T c ev QCD color superconductivity T c ev units (1 ev 10 4 K)
9 What is the unitary regime? A gas of interacting fermions is in the unitary regime if the average separation between particles is large compared to their size (range of interaction), but small compared to their scattering length. n r 3 n a 3 1 n - particle density 0 1 a - scattering length r 0 - effective range ie.. r 0, 0 The only scale: E a FG ± N = 3 ε 5 ( ) UNIVERSALITY: ( ) = ξ T ε E T E FG QUESTIONS: What is the shape of? What is the critical temperature for the superfluid-to-normal transition?... F F NONPERTURBATIVE REGIME System is dilute but strongly interacting! σ = ξ ( ) T ε F 4π a 2
10 Expected phases of a two species dilute Fermi system BCS-BEC BEC crossover EASY! weak interaction BCS Superfluid T Strong interaction UNITARY REGIME? EASY! weak interactions Molecular BEC and Atomic+Molecular Superfluids 1/a a<0 no 2-body bound state a>0 shallow 2-body bound state Bose molecule
11 A little bit of history Bertsch Many-Body X challenge, Seattle, 1999 What are the ground state properties of the many-body system composed of spin ½ fermions interacting via a zero-range, range, infinite scattering-length contact interaction. Why? Besides pure theoretical curiosity, this problem is relevant t to neutron stars! In 1999 it was not yet clear, either theoretically or experimentally, whether such fermion matter is stable or not! A number of people argued that under such conditions fermionic matter is unstable. - systems of bosons are unstable (Efimov effect) - systems of three or more fermion species are unstable (Efimov effect) Baker (winner of the MBX challenge) concluded that the system is stable. See also Heiselberg (entry to the same competition) Carlson et al (2003) Fixed-Node Green Function Monte Carlo and Astrakharchik et al. (2004) FN-DMC provided the best theoretical estimates for the ground state energy of such systems: ξ ( T = 0) 0.44 Thomas Duke group (2002) demonstrated experimentally that such systems are (meta)stable.
12 In dilute atomic systems experimenters can control nowadays almost anything: The number of atoms in the trap: typicallyt about atoms divided among the lowest two hyperfine states. The density of atoms Mixtures of various atoms The temperature of the atomic cloud The strength of this interaction is fully tunable! Who does experiments? Jin s group at Boulder Grimm s group in Innsbruck Thomas group at Duke Ketterle s group at MIT Salomon s group in Paris Hulet s group at Rice Physics Today, v54, 20 (2001)
13 One fermionic atom in magnetic field Fm F F= I+ J ; J= L+ S Nuclear spin Electronic spin Two hypefine states are populated in the trap Collision of two atoms: At low energies (low density of atoms) only L=0 (s-wave) scattering is effective. Due to the high diluteness atoms in the same hyperfine state do not interact with one another. Atoms in different hyperfine states experience interactions only in s-wave. s
14 Feshbach resonance 2 2 p H = + ( V + V ) + V ( r) P + V ( r) P + V 2µ i= 1 hf Z d i i hf ahf Z V = I J, V = ( γ ) 2 ejz γniz B Tiesinga, Verhaar, Stoof, Phys. Rev. A47, 4114 (1993) Channel coupling E resonance: a ± Regal and Jin, PRL 90, (2003) Interatomic distance
15 Theoretical approach: Fermions on 3D lattice Coordinate space L limit for the spatial correlations in the system kcut π = ; x x - Spin up fermion: - Spin down fermion: External conditions: T µ - temperature - chemical potential n(k) Momentum space 2π/L k cut =π/ x k π x k y π x k x 2π/L 2 2 π εf,, kt << 2 m ( x ) π δε > 2 ml 2π δ p > L 2
16 Hamiltonian 2 ˆ ˆ ˆ 3 3 H = T + V = d r ψˆs ( r) ψˆs( r) g d r nˆ ( r) nˆ ( r) s= 2m N d r n ( r) n ( r) ; n ( r) ( r) ( r) ˆ 3 ( ) = ˆ + ˆ ˆs = ψˆs ψˆ s 1 g mk cut m = + 4π a 2π Grand-canonical ensemble: { ρ } Running coupling constant g defined by lattice 1 g = m 2π 2 x ˆ 1 { ˆ ˆ ˆ } 1 E( T ) = H = Tr H ρ ( H, N, T ) = En e Z ( T ) Z - UNITARY LIMIT 1 kt ( E µ N ) 1 ( E µ N ) ( H µ N ) 1 ˆ ˆ n n kt kt Z ( T ) = Tr ( Hˆ, Nˆ, T ) = e ; ρ( Hˆ, Nˆ, T )= e Eigenenergies of the Hamiltonian are unknown! n n n n
17 Single-particle Path integral approach: particle quantum mechanics: r e r = D[ r( t)] e ihˆ ( t t ) 1 1 ( ) 0 t0 ( ( ), ( )) t ( ( ), ( ) mr () t ) = = 2 i L r t r t dt is[ r ( t)] t0 L r(), t r() t V ( r); e e Quantum statistical mechanics: t i L r t r t dt is 1 r 1 is 2 e e { } Z( β) = Tr exp( β ( Hˆ µ Nˆ) = nexp( β ( Hˆ µ Nˆ) n β = 1 ; imaginary time: τ = it kt n many body states [ ] + σ β = ln{det[1 Uˆ ({ })]} Z( ) D σ( r, τ) e S[ σ( r, τ)] = ln{det[1 + Uˆ ({ σ})]} - action
18 1 kt τ β 0 Uˆ({ σ}) = T exp{ dτ[ hˆ({ σ }) µ ]}; hˆ({ σ}) one-body operator U({ σ}) = ψ Uˆ ({ σ}) ψ ; ψ - single-particle wave function kl k l l S [ σ ] σ τ = ˆ D[ ( r, )] e ET ( ) H = EU [ ({ σ })] ZT ( ) EU [ ({ σ })]- Quantum Monte-Carlo: Sigma space sampling energy associated with a given sigma field σ N σ 1 ET ( ) = EU({ k}) N σ k= 1 ( σ ) E( T) - stochastic variable E( T) = E( T) P( σ) e S[ σ ] N σ 2 E( T) E( T) number of uncorrelated samples N σ
19 Quantum Monte-Carlo: parallel computing τ β 0 Uˆ({ σ}) = T exp{ dτ[ hˆ({ σ }) µ ]}; hˆ({ σ}) one-body operator U({ σ}) = ψ Uˆ ({ σ}) ψ ; ψ - single-particle wave function kl k l l For each sigma n single particle states have to be evolved.... ψ n ψ 3 ψ 2 ψ 1 U ˆ({ σ }) ˆ({ σ}) ˆ({ }) U U σ... U ˆ({ σ }) U({ σ}) = ψ Uˆ ({ σ}) ψ kl k l
20 More details of the calculations: Lattice sizes used from 8 3 x 257 (high Ts) to 8 3 x (low Ts),, <N>=50, and 6 3 x 257 (high Ts) to 6 3 x (low Ts),, <N>=30. Effective use of FFT(W) makes all imaginary time propagators diagonal (either in real space or momentum space) and there is no need to store large e matrices. Update field configurations using the Metropolis importance sampling algorithm. Change randomly at a fraction of all space and time sites the signs s the auxiliary fields σ(x, (x,τ)) so as to maintain a running average of the acceptance rate between 0.4 and 0.6. Thermalize for 50, ,000 MC steps or/and use as a start-up field configuration a σ(x, (x,τ)-field configuration from a different T At low temperatures use Singular Value Decomposition of the evolution operator U({σ}) to stabilize the numerics. Use 200,000-2,000,000 σ(x, (x,τ)- field configurations for calculations MC correlation time time steps at T T c
21 a = ± Superfluid to Normal Fermi Liquid Transition Normal Fermi Gas (with vertical offset, solid line) ξ ( T= 0) 0.41(2) Bogoliubov-Anderson phonons and quasiparticle contribution (dashed line ) Bogoliubov-Anderson phonons contribution only (dotted( line) People never consider this??? Quasi-particle contribution only (dotted line) π T E ( T) = ε N exp T quasi-particles F ε F 7/3 2 π = ε F exp e 2 kfa 4 3 3π T Ephonons( T) = εfn, /2 ξs 5 16ξs εf A. Bulgac, J.E. Drut, P. Magierski, cond-mat/
22 Phase transition Ideal Fermi gas entropy S E µ 3 T E = µ N - PV + TS = εf ( n) N e = ε( n) nv 5 ε F ( n) N kf kf n = =, ε ( ) = 2 F n V 3π 2m 5 en ( ) µ 2 = 3 T S N = Nσ, P = e( n) n T ε F ( n) 3
23 Low temperature behaviour of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime 3 T µ ( T) ET ( ) = ε Nξ and ξ 0.41(2) for T < T εf εf 5 F s C de( T) T 2 T T µ ( T) = = ε ξ ξ F εfξs dn εf 5 εf εf 5/2 T T ξ = ξs + ςs, ςs 11(1) εf εf 3 T ET ( ) = εfn ξs + ςs 5 εf n Lattice results disfavor either n 3 or n 2 and suggest n=2.5(0.25) This is the same behavior as for a gas of noninteracting (!) bosons below the condensation temperature.
24 Conclusions Fully non-perturbative calculations for a spin ½ many fermion system in the unitary regime at finite temperatures are feasible and apparently the system undergoes a phase transition in the bulk at a T c = 0.23 (2) ε F (Exp: T c = 0.27(2) ε F, J. Kinast et al. Science,, 307, 1296 (2005): Based on theoretical assumptions). Chemical potential is constant up to the critical temperature note similarity with Bose systems! Below the transition temperature, both phonons and fermionic quasiparticles contribute almost equaly to the specific heat. In more than one way the system is at crossover between a Bose and Fermi systems. There are reasons to believe that below the critical temperature this system is a new type of fermionic superfluid, with unusual properties.
25 Quest for unitaryu point critical temperature Analytics Numerics 0.55 Experiment + assumptionns 0.50 This work T c /E F M. Holland, S. J. J. M. F. Kokkelmans, M. L. Chiofalo, and R. Walser, PRL 87, (2001) P. Nozieres, S. Schmitt-Rink, J. Low. Temp. Phys 59, 195 (1985) J. Kinhast, A. Turlapov, J.E. Thomas, Q. Chen, J. Stajic, K. Levin, Science 307, 1296 (2005) A. Ours Bulgac, J. E. Drut, P. Magierski, cond-mat/ X.-J. Liu, H. Hu, cond-mat/ T.Lee, D. Schafer, nucl-th/ E. Burovski, N. Prokofev, B. Svistunov, M. Troyer Private communication M. Wingate, cond-mat/ Boris Svistunov s talk (updated), Seattle 2005
26 Evidence for fermionic superfluidity: vortices! 6 system of fermionic Li atoms Feshbach resonance: B=834G BEC side: a>0 UNITARY REGIME BCS side: a<0 M.W. Zwierlein et al., Nature, 435, 1047 (2005)
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC. BEC regime a new type of superfluid?
 Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps
 Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw Outline Some general remarks Path
Specific heat of a fermionic atomic cloud in the bulk and in traps Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw Outline Some general remarks Path
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations
 Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime?
 What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime? Aurel Bulgac,, George F. Bertsch,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski, Yongle Yu University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw
What do we know about the state of cold fermions in the unitary regime? Aurel Bulgac,, George F. Bertsch,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski, Yongle Yu University of Washington, Seattle, WA Also in Warsaw
Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases. Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology
 Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Path Integral (Auxiliary Field) Monte Carlo approach to ultracold atomic gases Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas
 Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the s If the energy is small only the s--wave is re wave is r levant.
 The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now at OSU, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at
The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now at OSU, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas. Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology
 Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (U. Washington) Kenneth J. Roche (PNNL) Joaquin E. Drut (U. North
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (U. Washington) Kenneth J. Roche (PNNL) Joaquin E. Drut (U. North
Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina. Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej)
 Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej) 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity in Fermi systems Discovery: H. Kamerlingh
Pomiędzy nadprzewodnictwem a kondensacją Bosego-Einsteina Piotr Magierski (Wydział Fizyki Politechniki Warszawskiej) 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity in Fermi systems Discovery: H. Kamerlingh
Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle
 Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle People I have been lucky to work with on these problems: Clockwise (starting
Why strongly interacting fermion gases are interesting to a many-body theorist? Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle People I have been lucky to work with on these problems: Clockwise (starting
Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute Fermi Gases near a Feshbach Resonance
 Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute ermi Gases near a eshbach Resonance A. Bulgac (Seattle), Y. Yu (Seattle Lund) P.. Bedaque (Berkeley), G.. Bertsch (Seattle), R.A. Broglia (Milan), A.C. onseca (Lisbon)
Signatures of Superfluidity in Dilute ermi Gases near a eshbach Resonance A. Bulgac (Seattle), Y. Yu (Seattle Lund) P.. Bedaque (Berkeley), G.. Bertsch (Seattle), R.A. Broglia (Milan), A.C. onseca (Lisbon)
r 0 range of interaction a scattering length
 The Incredible Many Facets of the Unitary Fermi Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now in Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, soon at
The Incredible Many Facets of the Unitary Fermi Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Joaquin E. Drut (Seattle, now in Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, soon at
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary Fermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo
 Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary ermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Equilibrium and nonequilibrium properties of unitary ermi gas from Quantum Monte Carlo Piotr Magierski Warsaw University of Technology Collaborators: A. Bulgac - University of Washington J.E. Drut - University
Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas
 Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle) Joaquin E. Drut (LANL)
Thermodynamics, pairing properties of a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle) Joaquin E. Drut (LANL)
Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems
 Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems Part A Comments on papers of E. Burovski,, N. Prokof ev ev,, B. Svistunov and M.
Part A - Comments on the papers of Burovski et al. Part B - On Superfluid Properties of Asymmetric Dilute Fermi Systems Part A Comments on papers of E. Burovski,, N. Prokof ev ev,, B. Svistunov and M.
Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC FERMI GASES
 1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover
 Institut für Experimentalphysik Universität Innsbruck Dresden, 12.10. 2004 BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover Johannes Hecker Denschlag The lithium team Selim Jochim Markus Bartenstein
Institut für Experimentalphysik Universität Innsbruck Dresden, 12.10. 2004 BEC of 6 Li 2 molecules: Exploring the BEC-BCS crossover Johannes Hecker Denschlag The lithium team Selim Jochim Markus Bartenstein
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the ss--wave is r wave is e r levant.
 The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: JoaquinE. Drut (Seattle, now inosu, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at LANL)
The Unitary Fermi Gas: so simple yet so complex! Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: JoaquinE. Drut (Seattle, now inosu, Columbus) Michael McNeil Forbes (Seattle, now at LANL)
Reference for most of this talk:
 Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding ultracold Fermi gases. in Ultracold Fermi Gases, Proceedings of the International School
Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding ultracold Fermi gases. in Ultracold Fermi Gases, Proceedings of the International School
Cold fermions, Feshbach resonance, and molecular condensates (II)
 Cold fermions, Feshbach resonance, and molecular condensates (II) D. Jin JILA, NIST and the University of Colorado I. Cold fermions II. III. Feshbach resonance BCS-BEC crossover (Experiments at JILA) $$
Cold fermions, Feshbach resonance, and molecular condensates (II) D. Jin JILA, NIST and the University of Colorado I. Cold fermions II. III. Feshbach resonance BCS-BEC crossover (Experiments at JILA) $$
BCS-BEC Crossover. Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke
 BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin. Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
 Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Bardeen Bardeen, Cooper Cooper and Schrieffer and Schrieffer 1957
 Unexpected aspects of large amplitude nuclear collective motion Aurel Bulgac University of Washington Collaborators: Sukjin YOON (UW) Kenneth J. ROCHE (ORNL) Yongle YU (now at Wuhan Institute of Physics
Unexpected aspects of large amplitude nuclear collective motion Aurel Bulgac University of Washington Collaborators: Sukjin YOON (UW) Kenneth J. ROCHE (ORNL) Yongle YU (now at Wuhan Institute of Physics
ICAP Summer School, Paris, Three lectures on quantum gases. Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT
 ICAP Summer School, Paris, 2012 Three lectures on quantum gases Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding
ICAP Summer School, Paris, 2012 Three lectures on quantum gases Wolfgang Ketterle, MIT Cold fermions Reference for most of this talk: W. Ketterle and M. W. Zwierlein: Making, probing and understanding
Quantum Quantum Optics Optics VII, VII, Zakopane Zakopane, 11 June 09, 11
 Quantum Optics VII, Zakopane, 11 June 09 Strongly interacting Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center for Quantum Optics in Innsbruck University of Innsbruck Austrian Academy of Sciences ultracold fermions: species
Quantum Optics VII, Zakopane, 11 June 09 Strongly interacting Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center for Quantum Optics in Innsbruck University of Innsbruck Austrian Academy of Sciences ultracold fermions: species
Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation. Randy Hulet
 Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation Randy Hulet Outline Introduction to methods and concepts of cold atom physics Interactions Feshbach resonances Quantum Gases Quantum regime nλ
Introduction to Cold Atoms and Bose-Einstein Condensation Randy Hulet Outline Introduction to methods and concepts of cold atom physics Interactions Feshbach resonances Quantum Gases Quantum regime nλ
Lecture 4. Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules
 Lecture 4 Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules 95 Reminder: scattering length V(r) a tan 0( k) lim k0 k r a: scattering length Single-channel scattering a 96 Multi-channel scattering alkali-metal atom:
Lecture 4 Feshbach resonances Ultracold molecules 95 Reminder: scattering length V(r) a tan 0( k) lim k0 k r a: scattering length Single-channel scattering a 96 Multi-channel scattering alkali-metal atom:
Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover
 Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei and CNISM, Università di Padova INO-CNR, Research
Broad and Narrow Fano-Feshbach Resonances: Condensate Fraction in the BCS-BEC Crossover Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei and CNISM, Università di Padova INO-CNR, Research
From BEC to BCS. Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs. Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI. and
 From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas
 Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/4/04 Workshop
Bose-Einstein condensation of lithium molecules and studies of a strongly interacting Fermi gas Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/4/04 Workshop
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas
 Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.quant-gas] 9 May 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.quant-gas] 9 May 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.quant-gas] 9 May 2011](/thumbs/92/110300221.jpg) Atomic Fermi gas at the unitary limit by quantum Monte Carlo methods: Effects of the interaction range Xin Li, Jindřich Kolorenč,,2 and Lubos Mitas Department of Physics, North Carolina State University,
Atomic Fermi gas at the unitary limit by quantum Monte Carlo methods: Effects of the interaction range Xin Li, Jindřich Kolorenč,,2 and Lubos Mitas Department of Physics, North Carolina State University,
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP
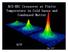 BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas
 Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas Introduction / Motivation Homogeneous Gas Momentum Distribution Quasi-Particle Spectrum Low Energy Excitations and Static Structure Function Inhomogeneous
Low- and High-Energy Excitations in the Unitary Fermi Gas Introduction / Motivation Homogeneous Gas Momentum Distribution Quasi-Particle Spectrum Low Energy Excitations and Static Structure Function Inhomogeneous
What ar e t e scatter engt e e ect ve range If the energy is small only the s If the energy is small only the s--wave is re wave is r levant.
 Generation and Dynamics of Vortices in a Superfluid Unitary Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Yuan Lung (Alan) Luo (Seattle) Piotr Magierski (Warsaw/Seattle) Kenneth
Generation and Dynamics of Vortices in a Superfluid Unitary Gas Aurel Bulgac University of Washington, Seattle, WA Collaborators: Yuan Lung (Alan) Luo (Seattle) Piotr Magierski (Warsaw/Seattle) Kenneth
Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter. National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
 Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter Stefano Gandolfi Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
Nuclear structure III: Nuclear and neutron matter Stefano Gandolfi Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) National Nuclear Physics Summer School Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) July 18-29, 2016
Equation of State of Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas
 he 19 th Particle and Nuclei International Conference (PANIC11) Equation of State of Strongly Interacting ermi Gas Mark Ku, Ariel Sommer, Lawrence Cheuk, Andre Schirotzek, Martin Zwierlein heory collaborators
he 19 th Particle and Nuclei International Conference (PANIC11) Equation of State of Strongly Interacting ermi Gas Mark Ku, Ariel Sommer, Lawrence Cheuk, Andre Schirotzek, Martin Zwierlein heory collaborators
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids. C. Salomon
 A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon Enrico Fermi School Quantum Matter at Ultralow Temperatures Varenna, July 8, 2014 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner, C.S. Lithium
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon Enrico Fermi School Quantum Matter at Ultralow Temperatures Varenna, July 8, 2014 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner, C.S. Lithium
F. Chevy Seattle May 2011
 THERMODYNAMICS OF ULTRACOLD GASES F. Chevy Seattle May 2011 ENS FERMION GROUPS Li S. Nascimbène Li/K N. Navon L. Tarruell K. Magalhaes FC C. Salomon S. Chaudhuri A. Ridinger T. Salez D. Wilkowski U. Eismann
THERMODYNAMICS OF ULTRACOLD GASES F. Chevy Seattle May 2011 ENS FERMION GROUPS Li S. Nascimbène Li/K N. Navon L. Tarruell K. Magalhaes FC C. Salomon S. Chaudhuri A. Ridinger T. Salez D. Wilkowski U. Eismann
Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid?
 Nuclear Physics A 830 (2009) 665c 672c www.elsevier.com/locate/nuclphysa Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid? J. E. Thomas Physics Department, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708-0305,
Nuclear Physics A 830 (2009) 665c 672c www.elsevier.com/locate/nuclphysa Is an Ultra-Cold Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas a Perfect Fluid? J. E. Thomas Physics Department, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708-0305,
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids. C. Salomon
 A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon INT workshop Frontiers in quantum simulation with cold atoms University of Washington, April 2, 2015 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner,
A Mixture of Bose and Fermi Superfluids C. Salomon INT workshop Frontiers in quantum simulation with cold atoms University of Washington, April 2, 2015 The ENS Fermi Gas Team F. Chevy, Y. Castin, F. Werner,
Strongly paired fermions
 Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
FOUR-BODY EFIMOV EFFECT
 FOUR-BODY EFIMOV EFFECT Yvan Castin, Christophe Mora LKB and LPA, Ecole normale supérieure (Paris, France) Ludovic Pricoupenko LPTMC, Université Paris 6 OUTLINE OF THE TALK Cold atoms in short Introduction
FOUR-BODY EFIMOV EFFECT Yvan Castin, Christophe Mora LKB and LPA, Ecole normale supérieure (Paris, France) Ludovic Pricoupenko LPTMC, Université Paris 6 OUTLINE OF THE TALK Cold atoms in short Introduction
The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other
 1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA
 Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA Lianyi He ( 何联毅 ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University 2016 Hangzhou Workshop on Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gases,
Dynamic Density and Spin Responses in the BCS-BEC Crossover: Toward a Theory beyond RPA Lianyi He ( 何联毅 ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University 2016 Hangzhou Workshop on Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gases,
Superfluidity in bosonic systems
 Superfluidity in bosonic systems Rico Pires PI Uni Heidelberg Outline Strongly coupled quantum fluids 2.1 Dilute Bose gases 2.2 Liquid Helium Wieman/Cornell A. Leitner, from wikimedia When are quantum
Superfluidity in bosonic systems Rico Pires PI Uni Heidelberg Outline Strongly coupled quantum fluids 2.1 Dilute Bose gases 2.2 Liquid Helium Wieman/Cornell A. Leitner, from wikimedia When are quantum
Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases
 Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases The ideal Fermi gas: a reminder Interacting Fermions BCS theory in a nutshell The BCS-BEC crossover and quantum simulation Many-Body Physics with Cold Gases Diluteness:
Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases The ideal Fermi gas: a reminder Interacting Fermions BCS theory in a nutshell The BCS-BEC crossover and quantum simulation Many-Body Physics with Cold Gases Diluteness:
Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance
 Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance Dietrich Roscher [D. Roscher, J. Braun, J.-W. Chen, J.E. Drut arxiv:1306.0798] Advances in quantum Monte Carlo techniques for non-relativistic
Tackling the Sign Problem of Ultracold Fermi Gases with Mass-Imbalance Dietrich Roscher [D. Roscher, J. Braun, J.-W. Chen, J.E. Drut arxiv:1306.0798] Advances in quantum Monte Carlo techniques for non-relativistic
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas
 Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases
 Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases Michael KöhlK ETH Zürich Z (www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch( www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch) Introduction Why should a condensed matter physicist
Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Ultracold Fermionic and Bosonic Gases Michael KöhlK ETH Zürich Z (www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch( www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch) Introduction Why should a condensed matter physicist
Fermi Condensates ULTRACOLD QUANTUM GASES
 Fermi Condensates Markus Greiner, Cindy A. Regal, and Deborah S. Jin JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology and University of Colorado, and Department of Physics, University of Colorado,
Fermi Condensates Markus Greiner, Cindy A. Regal, and Deborah S. Jin JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology and University of Colorado, and Department of Physics, University of Colorado,
Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics
 Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Unitarity limit Consider simple square well potential a < 0 a =, ǫ B = 0 a > 0, ǫ B > 0 Unitarity
Intersections of nuclear physics and cold atom physics Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Unitarity limit Consider simple square well potential a < 0 a =, ǫ B = 0 a > 0, ǫ B > 0 Unitarity
Super Efimov effect. Sergej Moroz University of Washington. together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son. Tuesday, April 1, 14
 Super Efimov effect together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son Sergej Moroz University of Washington Few-body problems They are challenging but useful: Newton gravity Quantum atoms Quantum molecules
Super Efimov effect together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son Sergej Moroz University of Washington Few-body problems They are challenging but useful: Newton gravity Quantum atoms Quantum molecules
High-Temperature Superfluidity
 High-Temperature Superfluidity Tomoki Ozawa December 10, 2007 Abstract With the recent advancement of the technique of cooling atomic gases, it is now possible to make fermionic atom gases into superfluid
High-Temperature Superfluidity Tomoki Ozawa December 10, 2007 Abstract With the recent advancement of the technique of cooling atomic gases, it is now possible to make fermionic atom gases into superfluid
Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations?
 Image: Peter Engels group at WSU Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations? Doerte Blume and Kevin M. Daily Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Washington State University,
Image: Peter Engels group at WSU Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations? Doerte Blume and Kevin M. Daily Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Washington State University,
Time-dependent density-functional theory for trapped strongly interacting fermionic atoms
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 70, 033612 (2004) Time-dependent density-functional theory for trapped strongly interacting fermionic atoms Yeong E. Kim* and Alexander L. Zubarev Purdue Nuclear and Many-Body Theory
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 70, 033612 (2004) Time-dependent density-functional theory for trapped strongly interacting fermionic atoms Yeong E. Kim* and Alexander L. Zubarev Purdue Nuclear and Many-Body Theory
The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas
 The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Finite-temperature auxiliary-field Monte Carlo (AFMC) method The trapped unitary Fermi gas
The nature of superfluidity in the cold atomic unitary Fermi gas Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Finite-temperature auxiliary-field Monte Carlo (AFMC) method The trapped unitary Fermi gas
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Aug 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Aug 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Aug 2005](/thumbs/88/115865929.jpg) Single-particle excitations in the BCS-BEC crossover region II: Broad Feshbach resonance arxiv:cond-mat/58213v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Aug 25 Y. Ohashi 1 and A. Griffin 2 1 Institute of Physics, University
Single-particle excitations in the BCS-BEC crossover region II: Broad Feshbach resonance arxiv:cond-mat/58213v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Aug 25 Y. Ohashi 1 and A. Griffin 2 1 Institute of Physics, University
Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW
 Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity Discovery: H. Kamerlingh Onnes in 1911 cooled a metallic sample
Nierównowagowe procesy w nadciekłych układach kwantowych. Piotr Magierski Wydział Fizyki PW 100 years of superconductivity and superfluidity Discovery: H. Kamerlingh Onnes in 1911 cooled a metallic sample
A study of the BEC-BCS crossover region with Lithium 6
 A study of the BEC-BCS crossover region with Lithium 6 T.Bourdel, L. Khaykovich, J. Cubizolles, J. Zhang, F. Chevy, M. Teichmann, L. Tarruell, S. Kokkelmans, Christophe Salomon Theory: D. Petrov, G. Shlyapnikov,
A study of the BEC-BCS crossover region with Lithium 6 T.Bourdel, L. Khaykovich, J. Cubizolles, J. Zhang, F. Chevy, M. Teichmann, L. Tarruell, S. Kokkelmans, Christophe Salomon Theory: D. Petrov, G. Shlyapnikov,
BEC-BCS Crossover in Cold Atoms
 BEC-BCS Crossover in Cold Atoms (2 years later...) Andrew Morris Pablo López Ríos Richard Needs Theory of Condensed Matter Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge TTI 31 st July 2009 Outline Theory
BEC-BCS Crossover in Cold Atoms (2 years later...) Andrew Morris Pablo López Ríos Richard Needs Theory of Condensed Matter Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge TTI 31 st July 2009 Outline Theory
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005](/thumbs/74/70382724.jpg) Released momentum distribution of a Fermi gas in the BCS-BEC crossover arxiv:cond-mat/5246v [cond-mat.other] 9 Dec 25 M.L. Chiofalo, S. Giorgini 2,3 and M. Holland 2 INFM and Classe di Scienze, Scuola
Released momentum distribution of a Fermi gas in the BCS-BEC crossover arxiv:cond-mat/5246v [cond-mat.other] 9 Dec 25 M.L. Chiofalo, S. Giorgini 2,3 and M. Holland 2 INFM and Classe di Scienze, Scuola
Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases
 Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases Quantum many-body system in attractive interaction Molecular condensate BEC Cooper pairs BCS Thomas Bourdel, J. Cubizolles, L. Khaykovich, J. Zhang, S. Kokkelmans,
Superfluidity in interacting Fermi gases Quantum many-body system in attractive interaction Molecular condensate BEC Cooper pairs BCS Thomas Bourdel, J. Cubizolles, L. Khaykovich, J. Zhang, S. Kokkelmans,
New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases
 New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases Joaquín E. Drut The Ohio State University INT Program Simulations and Symmetries Seattle, March 2010 In collaboration with Timo A. Lähde Aalto University,
New approaches to strongly interacting Fermi gases Joaquín E. Drut The Ohio State University INT Program Simulations and Symmetries Seattle, March 2010 In collaboration with Timo A. Lähde Aalto University,
Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas
 Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas The Pennsylvania State University Ken O Hara Jason Williams Eric Hazlett Ronald Stites John Huckans Overview New Physics with Three Component Fermi
Experiments with an Ultracold Three-Component Fermi Gas The Pennsylvania State University Ken O Hara Jason Williams Eric Hazlett Ronald Stites John Huckans Overview New Physics with Three Component Fermi
Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases. Michael Köhl Universität Bonn
 Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases Michael Köhl Universität Bonn Ultracold Fermi gases as model systems BEC/BCS crossover Search for the perfect fluid: Cold fermions vs. Quark-gluon plasma Cao et al.,
Two-dimensional atomic Fermi gases Michael Köhl Universität Bonn Ultracold Fermi gases as model systems BEC/BCS crossover Search for the perfect fluid: Cold fermions vs. Quark-gluon plasma Cao et al.,
Fluctuations between the BCS and BEC Limits in the System of Ultracold Alkali Atoms
 Vol. 109 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 5 Proceedings of the XI National School Collective Phenomena and Their Competition Kazimierz Dolny, September 25 29, 2005 Fluctuations between the BCS and
Vol. 109 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 5 Proceedings of the XI National School Collective Phenomena and Their Competition Kazimierz Dolny, September 25 29, 2005 Fluctuations between the BCS and
From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics
 From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics Alice Sinatra Quantum Fluids course - Complement 1 2013-2014 Plan 1 COOLING AND TRAPPING 2 CONDENSATION 3 NON-LINEAR PHYSICS AND
From laser cooling to BEC First experiments of superfluid hydrodynamics Alice Sinatra Quantum Fluids course - Complement 1 2013-2014 Plan 1 COOLING AND TRAPPING 2 CONDENSATION 3 NON-LINEAR PHYSICS AND
hal , version 1-9 Jan 2007
 Expansion of a lithium gas in the BEC-BCS crossover L. Tarruell 1, M. Teichmann 1, J. McKeever 1, T. Bourdel 1, J. Cubizolles 1, L. Khaykovich 2, J. Zhang 3, N. Navon 1, F. Chevy 1, and C. Salomon 1 1
Expansion of a lithium gas in the BEC-BCS crossover L. Tarruell 1, M. Teichmann 1, J. McKeever 1, T. Bourdel 1, J. Cubizolles 1, L. Khaykovich 2, J. Zhang 3, N. Navon 1, F. Chevy 1, and C. Salomon 1 1
Evidence for Efimov Quantum states
 KITP, UCSB, 27.04.2007 Evidence for Efimov Quantum states in Experiments with Ultracold Cesium Atoms Hanns-Christoph Nägerl bm:bwk University of Innsbruck TMR network Cold Molecules ultracold.atoms Innsbruck
KITP, UCSB, 27.04.2007 Evidence for Efimov Quantum states in Experiments with Ultracold Cesium Atoms Hanns-Christoph Nägerl bm:bwk University of Innsbruck TMR network Cold Molecules ultracold.atoms Innsbruck
BEC and superfluidity in ultracold Fermi gases
 Collège de France, 11 Apr 2005 BEC and superfluidity in ultracold Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center of Quantum Optics Innsbruck University Austrian Academy of Sciences two classes Bosons integer spin Fermions
Collège de France, 11 Apr 2005 BEC and superfluidity in ultracold Fermi gases Rudolf Grimm Center of Quantum Optics Innsbruck University Austrian Academy of Sciences two classes Bosons integer spin Fermions
Path-integrals and the BEC/BCS crossover in dilute atomic gases
 Path-integrals and the BEC/BCS crossover in dilute atomic gases J. Tempere TFVS, Universiteit Antwerpen, Universiteitsplein 1, B261 Antwerpen, Belgium. J.T. Devreese TFVS, Universiteit Antwerpen, Universiteitsplein
Path-integrals and the BEC/BCS crossover in dilute atomic gases J. Tempere TFVS, Universiteit Antwerpen, Universiteitsplein 1, B261 Antwerpen, Belgium. J.T. Devreese TFVS, Universiteit Antwerpen, Universiteitsplein
Unitary Fermi Gas: Quarky Methods
 Unitary Fermi Gas: Quarky Methods Matthew Wingate DAMTP, U. of Cambridge Outline Fermion Lagrangian Monte Carlo calculation of Tc Superfluid EFT Random matrix theory Fermion L Dilute Fermi gas, 2 spins
Unitary Fermi Gas: Quarky Methods Matthew Wingate DAMTP, U. of Cambridge Outline Fermion Lagrangian Monte Carlo calculation of Tc Superfluid EFT Random matrix theory Fermion L Dilute Fermi gas, 2 spins
Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars
 Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Prague, July 16, 2013 Collaboration
Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Prague, July 16, 2013 Collaboration
Effective Field Theory and. the Nuclear Many-Body Problem
 Effective Field Theory and the Nuclear Many-Body Problem Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Nuclear Effective Field Theory Low Energy Nucleons: Nucleons are point particles Interactions
Effective Field Theory and the Nuclear Many-Body Problem Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Nuclear Effective Field Theory Low Energy Nucleons: Nucleons are point particles Interactions
Density Waves and Supersolidity in Rapidly Rotating Atomic Fermi Gases
 Density Waves and Supersolidity in Rapidly Rotating Atomic Fermi Gases Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Quantum Gases Conference, Paris, 30 June 2007. Gunnar Möller
Density Waves and Supersolidity in Rapidly Rotating Atomic Fermi Gases Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Quantum Gases Conference, Paris, 30 June 2007. Gunnar Möller
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics. Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University
 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University January 25, 2011 2 Chapter 12 Collective modes in interacting Fermi
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University January 25, 2011 2 Chapter 12 Collective modes in interacting Fermi
BCS everywhere else: from Atoms and Nuclei to the Cosmos. Gordon Baym University of Illinois
 BCS everywhere else: from Atoms and Nuclei to the Cosmos Gordon Baym University of Illinois October 13, 2007 Wide applications of BCS beyond laboratory superconductors Pairing of nucleons in nuclei Neutron
BCS everywhere else: from Atoms and Nuclei to the Cosmos Gordon Baym University of Illinois October 13, 2007 Wide applications of BCS beyond laboratory superconductors Pairing of nucleons in nuclei Neutron
Diagrammatic Monte Carlo
 Sign Problems and Complex Actions, ECT*, Trento, March 2-6, 2009 Diagrammatic Monte Carlo Boris Svistunov University of Massachusetts, Amherst Nikolay Prokof ev Kris Van Houcke (Umass/Ghent) Evgeny Kozik
Sign Problems and Complex Actions, ECT*, Trento, March 2-6, 2009 Diagrammatic Monte Carlo Boris Svistunov University of Massachusetts, Amherst Nikolay Prokof ev Kris Van Houcke (Umass/Ghent) Evgeny Kozik
Thermodynamics of the unitary Fermi gas
 Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Faculty of Physics, Chair of Theoretical Solid State Physics, Theresienstr. 37, 80333 Munich, Germany E-mail: O.Goulko@physik.uni-muenchen.de M. Wingate DAMTP, University
Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Faculty of Physics, Chair of Theoretical Solid State Physics, Theresienstr. 37, 80333 Munich, Germany E-mail: O.Goulko@physik.uni-muenchen.de M. Wingate DAMTP, University
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas
 Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
BCS Pairing Dynamics. ShengQuan Zhou. Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois
 BCS Pairing Dynamics 1 ShengQuan Zhou Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois Abstract. Experimental control over inter-atomic interactions by adjusting external parameters is discussed.
BCS Pairing Dynamics 1 ShengQuan Zhou Dec.10, 2006, Physics Department, University of Illinois Abstract. Experimental control over inter-atomic interactions by adjusting external parameters is discussed.
Fermi gases in an optical lattice. Michael Köhl
 Fermi gases in an optical lattice Michael Köhl BEC-BCS crossover What happens in reduced dimensions? Sa de Melo, Physics Today (2008) Two-dimensional Fermi gases Two-dimensional gases: the grand challenge
Fermi gases in an optical lattice Michael Köhl BEC-BCS crossover What happens in reduced dimensions? Sa de Melo, Physics Today (2008) Two-dimensional Fermi gases Two-dimensional gases: the grand challenge
Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs
 Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs Karén Kheruntsyan and Peter Drummond Department of Physics, University of Queensland, Brisbane, AUSTRALIA Quantum superpositions
Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs Karén Kheruntsyan and Peter Drummond Department of Physics, University of Queensland, Brisbane, AUSTRALIA Quantum superpositions
BEC-BCS crossover, phase transitions and phase separation in polarized resonantly-paired superfluids
 BEC-BCS crossover, phase transitions and phase separation in polarized resonantly-paired superfluids Daniel E. Sheehy Ames Laboratory Iowa State University Work in collaboration with L. Radzihovsky (Boulder)
BEC-BCS crossover, phase transitions and phase separation in polarized resonantly-paired superfluids Daniel E. Sheehy Ames Laboratory Iowa State University Work in collaboration with L. Radzihovsky (Boulder)
Benchmarking the Many-body Problem
 Benchmarking the Many-body Problem Precision bounds on the Equation of State Michael McNeil Forbes Institute for Nuclear Theory (INT) and the University of Washington (Seattle) 18 May 2011 1 Benchmarks
Benchmarking the Many-body Problem Precision bounds on the Equation of State Michael McNeil Forbes Institute for Nuclear Theory (INT) and the University of Washington (Seattle) 18 May 2011 1 Benchmarks
Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics
 1 Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Instructor Eugene Demler Office: Lyman 322 Email: demler@physics.harvard.edu Teaching Fellow
1 Harvard University Physics 284 Spring 2018 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Instructor Eugene Demler Office: Lyman 322 Email: demler@physics.harvard.edu Teaching Fellow
Effective Field Theory and Ultracold Atoms
 Effective Field Theory and Ultracold Atoms Eric Braaten Ohio State University support Department of Energy Air Force Office of Scientific Research Army Research Office 1 Effective Field Theory and Ultracold
Effective Field Theory and Ultracold Atoms Eric Braaten Ohio State University support Department of Energy Air Force Office of Scientific Research Army Research Office 1 Effective Field Theory and Ultracold
Lecture 3. Bose-Einstein condensation Ultracold molecules
 Lecture 3 Bose-Einstein condensation Ultracold molecules 66 Bose-Einstein condensation Bose 1924, Einstein 1925: macroscopic occupation of the lowest energy level db h 2 mk De Broglie wavelength d 1/3
Lecture 3 Bose-Einstein condensation Ultracold molecules 66 Bose-Einstein condensation Bose 1924, Einstein 1925: macroscopic occupation of the lowest energy level db h 2 mk De Broglie wavelength d 1/3
Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007
 Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007 L.P. Pitaevskii Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, INFM BEC CNR,Trento, Italy; Kapitza Institute for Physical Problems, ul.
Superfluidity and superconductivity. IHP, Paris, May 7 and 9, 2007 L.P. Pitaevskii Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, INFM BEC CNR,Trento, Italy; Kapitza Institute for Physical Problems, ul.
Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas
 J Low Temp Phys (2009) 154: 1 29 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9850-2 Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas Le Luo J.E. Thomas Received: 25 July 2008 / Accepted: 12 October 2008 / Published
J Low Temp Phys (2009) 154: 1 29 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9850-2 Thermodynamic Measurements in a Strongly Interacting Fermi Gas Le Luo J.E. Thomas Received: 25 July 2008 / Accepted: 12 October 2008 / Published
An impurity in a Fermi sea on a narrow Feshbach resonance: A variational study of the polaronic and dimeronic branches
 An impurity in a Fermi sea on a narrow Feshbach resonance: A variational study of the polaronic and dimeronic branches Christian Trefzger Laboratoire Kastler Brossel ENS Paris Introduction: The system
An impurity in a Fermi sea on a narrow Feshbach resonance: A variational study of the polaronic and dimeronic branches Christian Trefzger Laboratoire Kastler Brossel ENS Paris Introduction: The system
Bose-condensed and BCS fermion superfluid states T ~ nano to microkelvin (coldest in the universe)
 Deconfined quark-gluon plasmas made in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions T ~ 10 2 MeV ~ 10 12 K (temperature of early universe at ~1µ sec) Bose-condensed and BCS fermion superfluid states T ~ nano
Deconfined quark-gluon plasmas made in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions T ~ 10 2 MeV ~ 10 12 K (temperature of early universe at ~1µ sec) Bose-condensed and BCS fermion superfluid states T ~ nano
Ultracold Fermi and Bose Gases and Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles
 October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
Superfluidity and Superconductivity Macroscopic Quantum Phenomena
 Superfluid Bose and Fermi gases Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/11/2013 Universal Themes of Bose-Einstein Condensation Leiden Superfluidity
Superfluid Bose and Fermi gases Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 3/11/2013 Universal Themes of Bose-Einstein Condensation Leiden Superfluidity
Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas
 Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas Introduction: 2D FG and a condensed matter perspective Auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo calculations - exact* here Results on spin-balanced
Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas Introduction: 2D FG and a condensed matter perspective Auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo calculations - exact* here Results on spin-balanced
Condensation of pairs of fermionic lithium atoms
 Condensation of pairs of fermionic lithium atoms Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 5/10/04 KITP workshop, Santa Barbara BEC I Ultracold fermions
Condensation of pairs of fermionic lithium atoms Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms 5/10/04 KITP workshop, Santa Barbara BEC I Ultracold fermions
Cold atoms and AdS/CFT
 Cold atoms and AdS/CFT D. T. Son Institute for Nuclear Theory, University of Washington Cold atoms and AdS/CFT p.1/27 History/motivation BCS/BEC crossover Unitarity regime Schrödinger symmetry Plan Geometric
Cold atoms and AdS/CFT D. T. Son Institute for Nuclear Theory, University of Washington Cold atoms and AdS/CFT p.1/27 History/motivation BCS/BEC crossover Unitarity regime Schrödinger symmetry Plan Geometric
EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS
 EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS DIAGRAMMATIC MONTE CARLO Kris Van Houcke (UMass Amherst & U of Ghent) Félix Werner (UMass Amherst) Evgeny Kozik Boris Svistunov & Nikolay Prokofev (UMass Amherst) (ETH
EQUATION OF STATE OF THE UNITARY GAS DIAGRAMMATIC MONTE CARLO Kris Van Houcke (UMass Amherst & U of Ghent) Félix Werner (UMass Amherst) Evgeny Kozik Boris Svistunov & Nikolay Prokofev (UMass Amherst) (ETH
A rigorous solution to unitary Bose Gases
 A rigorous solution to unitary Bose Gases Fei Zhou University of British Columbia, Vancouver and Canadian Institute for Advanced Research At INT cold gas workshop, University of Washington, April 16, 2015
A rigorous solution to unitary Bose Gases Fei Zhou University of British Columbia, Vancouver and Canadian Institute for Advanced Research At INT cold gas workshop, University of Washington, April 16, 2015
