Introduction to Quantum Error Correction
|
|
|
- Gabriel Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Quantum Error Correction Nielsen & Chuang Quantum Information and Quantum Computation, CUP 2000, Ch. 10 Gottesman quant-ph/ Steane quant-ph/ Gottesman quant-ph/
2 Errors in QIP unitary # $ # $e! " U i( + ) %%& M non-unitary! 0 + " 1 ##$ p! 0 general: pure mixed states! " " 2 # f tr f <! = " " #! = E! E = E " " E 1 $ $ from! f = tr env " U! $! env U # f % & = $ = ' e U! e0 e0 U e! ' E! E E = e U e0 U sys+env trace preserving:! EE = 1 E! E = " " tae ρ and randomly replace by, ( ) with probability (! ) p = tr E E
3 Bit flip channel Quantum noise: channel representation! " # E! E! 1 0"! 0 1" E0 = p $, E1 1 p, 0 1 % = # $ 1 0 % & ' & ' Phase flip channel E0 = p! $ ", E1 1 p! " 0 1 % = # $ 0 # 1 % & ' & ' Bit-phase flip channel 1 0 0!i E0 = p " $ #, E1 1 py 1 p " # 0 1 % =! =! $ i 0 % & ' & ' Amplitude damping channel " 1 0 # " 0! # E0 =, E1 = $ 2 0 1! % $ % ' & ( ' 0 0 ( p! " = 1# p " + X " X + Y " Y + Z " Z 3 Depolarizing channel ( ) ( ) ( ) Geometrical interpretation: Bloch sphere in r-space (NC p. 376) I + r #! " =,! =!,!,!, =,, 2 { } r { r r r } x y z x y z
4 Repetition codes classical error, e.g. 010, corrected to majority value 000 note: learned value of bits in doing so prob. for bit error p < 1: multi-bit error prob. = 3p 2 (1-p)+p 3 =3p 2-2p 3 < p when p < quantum??! ""#!!! No cloning theorem! n bits, majority n/2+1 error prob. p n/2+1 + error prob. as n (p < 0.5) suppose! #!! and " # " " then but (! + " )#(! + " )(! + " )! + " #!! + "" =!! + "" + "! +!" by linearity cannot copy unnown quantum states
5 Encode/Error/Recovery quantum information is encoded into ρ C an error occurs! (" ) = # E " E C C recovery procedure undertaen R [! ] (" ) R E " E R = # # C l C l l regain the encoded state ρ C R [ ( )]! " = " C C
6 Encoding and Recovery R encode error diagnose error fix encoding qubits ancillas measurement error and recovery are superoperators ( ) # A A! = S " =! Unitary operations Recovery operator R restores state to the code after error from environment encode into a subspace no meaurement of state, only of error achieve by adding ancilla qubits measure ancillas syndrome of error perform unitaries conditional on syndrome to correct erroneous qubits
7 Encoding e.g., 3-qubit bit flip code 0 L >= 000> 1 L >= 111>! = " 0 + # 1 $! = " 0 + # 1 C L L! 0 0! C ( ) ( )! 0 + " 1 # 0 $! 00 + " 11! 00 + " 11 # 0 $! " 111 %! 0 + " 1 L L
8 Continuous Errors R " i! / 2 # 1 0 $ i! / 2 e 0! / 2 e i! i! / 2 # $ = % 0 e & = % & ' ( ' 0 e ( (! ) (! ) = cos / 2 I " isin / 2 Z add ancilla(s), transfer error info to ancilla (c-u) Z! 0 + " 1 # 0 $ Z! 0 + " 1 # Z ( ) ( ) L L anc L L anc (! 0 " 1 ) 0 (! 0 " 1 ) I + # $ I + # noerror L L anc L L anc ancilla superposition $! % cos I " 0 # 1 ' ( ) 2 * ( ) + & no error L L anc $! % + isin' ( Z (" 0 + # 1 )& Z ) 2 * L L anc measure ancilla 2 $! % prob. sin ' ( Z (" 0 1 ) L + # L & Zanc ) 2 * 2 $! % prob. cos ' ( I (" 0 + # 1 )& no error ) 2 * L L anc invert either one restore initial state
9 3-qubit Bit Flip Code 0 L >= 000> 1 L >= 111> α+β 1> Error X with prob. p R ψ> anc M encode error diagnose fix I II III IV M X I: (α+β 1>) α 000>+β 111> II: 8 possibilities from errors XII, IXI, IIX, XXI, XIX, IXX, XXX, III
10 state after error α 000>+β 111> (1-p) 3 α 100>+β 011> p(1-p) 2 α 010>+β 101> p(1-p) 2 α 001>+β 110> p(1-p) 2 α 110>+β 001> p 2 (1-p) α 101>+β 010> p 2 (1-p) α 011>+β 100> p 2 (1-p) α 111>+β 000> p 3 Prob. of getting state 1 or no error III: a) perform CNOT between qubits 1 & 2 with ancilla 1 b) perform CNOT between qubits 1 & 3 with ancilla 2 α 000>+β 111> 00> (1-p) 3 α 100>+β 011> 11> p(1-p) 2 α 010>+β 101> 10> p(1-p) 2 α 001>+β 110> 01> p(1-p) 2 α 110>+β 001> 01> p 2 (1-p) α 101>+β 010> 10> p 2 (1-p) α 011>+β 100> 11> p 2 (1-p) α 111>+β 000> 00> p 3 syndrome syndrome redundant for 1 and 2 (0 and 3) errors, but unequal probabilities
11 III. c) M = measure ancillas: assume only 1 (or 0) error syndrome uniquely identifies error failure rate of code = rate of 2 errors = 3p 2 (1-p)+p 3 = 3p 2-2p 3 < p for p < 0.5 IV. fix by applying unitary conditional on M syndrome: 00 do nothing 01 apply σ x to 3 rd qubit 10 apply σ x to 2 nd qubit 11 apply σ x to 1 st qubit α 000>+β 111> 00> α 100>+β 011> 11> α 010>+β 101> 10> α 001>+β 110> 01> recover encoded state α 000>+β 111>
12 Decoding e.g. from syndrome 10 after IV. have α 000>+β 111> with p(1-p) 2 extract original qubit α+β 1> with circuit: i) ii) i) α 000>+β 111> α 00>+β 1> 10> ii) α 00>+β 1> 10> α 00>+β 1> 00> = (α+β 1>) 00> get correct qubit state with prob. > 1-p prob. of failure = 3p 2-2p 3 < p for p < 0.5 success = 100% if no 2 or 3 errors error prob. reduced from p to O(p 2 )
13 3-bit Phase Code σ z (α+β 1>) = α-β 1> not classical! change basis: +> =1/ 2(+ 1>) ->=1/ 2(- 1>)! + " 1! 1 1 "! 1"! 1" # = = H % $ # 2 1 % 1 $# 1 $ # 1 $ & ' & '& ' & ' H σ z H=σ x or H= +><0 + -><1 then σ z +>= -> σ z ->= +> lie bit flip! R ψ> H H H H H H Z M M X I II
14 effectively encoded into 0 L >= +++>, 1 L >= ---> I, II α +++> + β ---> phase errors ZII, IZI, ZII act as Z on 000>, 111> e.g., ZII 000> = 000> ZII 111> = > but as X on +++>, --->
15 Both bit flip and phase errors: concatenate these two codes: 0 L >=( 000>+ 111>)( 000>+ 111>)( 000>+ 111>) 1 L >=( 000>- 111>)( 000>- 111>)( 000>- 111>) inner layer corrects bit flips 000, 111 outer layer corrects phase flips +++, ---- define Bell basis: 000>± 111> 001> ± 110> 010> ± 101> 100> ± 011> Shor PRA 52, R2493 (1995) consider decoherence of qubit 1: e a 0 +a 1 1> e 1> a 2 +a 3 1> e, a 0, a 3 = states of env first triple: 000>+ 111> (a 0 +a 1 1>) 00>+ (a 2 +a 3 1>) 11> = a 0 000>+a a 2 011>+a 3 111>
16 put in Bell basis =1/2 (a 0 +a 3 ) ( 000> + 111>) +1/2 (a 0 -a 3 ) ( 000> - 111>) +1/2 (a 1 +a 2 ) ( 100> + 011>) +1/2 (a 1 -a 2 ) ( 100> - 111>) similarly 000> - 111> goes to =1/2 (a 0 +a 3 ) ( 000> - 111>) +1/2 (a 0 -a 3 ) ( 000> + 111>) +1/2 (a 1 +a 2 ) ( 100> - 011>) +1/2 (a 1 -a 2 ) ( 100> + 111>) output 2 (syndrome 2) assume 1 error only: compare all 3 triples, see which differs majority sign indicates 0 L > or 1 L > find which qubit decohered (measure 9 ancillas which syndrome) restore qubit state with a unitary operation e.g. from 000> - 111>) 1/2 (a 0 +a 3 ) ( 000> - 111>) no error output 2 1/2 (a 0 -a 3 ) ( 000> + 111>) Z error 1/2 (a 1 +a 2 ) ( 100> + 011>) X error 1/2 (a 1 -a 2 ) ( 100> - 011>) ZX=Y error
17 have diagnosed error on 1 st qubit correct with appropriate unitary Encoder: ψ> H H H [9,1,3] code: 9 physical qubits 1 logical qubit (3-1)/2=1 arbitrary error corrected not most efficient code: [7,1,3] and [5,1,3] cannot compute easily (logical X, Z OK logical H, CNOT, T hard)
Example: sending one bit of information across noisy channel. Effects of the noise: flip the bit with probability p.
 Lecture 20 Page 1 Lecture 20 Quantum error correction Classical error correction Modern computers: failure rate is below one error in 10 17 operations Data transmission and storage (file transfers, cell
Lecture 20 Page 1 Lecture 20 Quantum error correction Classical error correction Modern computers: failure rate is below one error in 10 17 operations Data transmission and storage (file transfers, cell
D.5 Quantum error correction
 D. QUANTUM ALGORITHMS 157 Figure III.34: E ects of decoherence on a qubit. On the left is a qubit yi that is mostly isoloated from its environment i. Ontheright,aweakinteraction between the qubit and the
D. QUANTUM ALGORITHMS 157 Figure III.34: E ects of decoherence on a qubit. On the left is a qubit yi that is mostly isoloated from its environment i. Ontheright,aweakinteraction between the qubit and the
Quantum Error Correction and Fault Tolerance. Classical Repetition Code. Quantum Errors. Barriers to Quantum Error Correction
 Quantum Error Correction and Fault Tolerance Daniel Gottesman Perimeter Institute The Classical and Quantum Worlds Quantum Errors A general quantum error is a superoperator: ρ ΣA k ρ A k (Σ A k A k = I)
Quantum Error Correction and Fault Tolerance Daniel Gottesman Perimeter Institute The Classical and Quantum Worlds Quantum Errors A general quantum error is a superoperator: ρ ΣA k ρ A k (Σ A k A k = I)
Lectures on Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation
 Lectures on Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation B.M. Terhal, IBM Research I. Descriptions of Noise and Quantum States II. Quantum Coding and Error-Correction III. Fault-Tolerant Error-Correction. Surface
Lectures on Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation B.M. Terhal, IBM Research I. Descriptions of Noise and Quantum States II. Quantum Coding and Error-Correction III. Fault-Tolerant Error-Correction. Surface
Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity
 Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity Mark M. Wilde The quantum capacity theorem is one of the most important theorems in quantum hannon theory. It is a fundamentally quantum theorem
Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity Mark M. Wilde The quantum capacity theorem is one of the most important theorems in quantum hannon theory. It is a fundamentally quantum theorem
The information content of a quantum
 The information content of a quantum A few words about quantum computing Bell-state measurement Quantum dense coding Teleportation (polarisation states) Quantum error correction Teleportation (continuous
The information content of a quantum A few words about quantum computing Bell-state measurement Quantum dense coding Teleportation (polarisation states) Quantum error correction Teleportation (continuous
6. Quantum error correcting codes
 6. Quantum error correcting codes Error correcting codes (A classical repetition code) Preserving the superposition Parity check Phase errors CSS 7-qubit code (Steane code) Too many error patterns? Syndrome
6. Quantum error correcting codes Error correcting codes (A classical repetition code) Preserving the superposition Parity check Phase errors CSS 7-qubit code (Steane code) Too many error patterns? Syndrome
QUANTUM COMPUTING 10.
 QUANTUM COMPUTING 10. Jozef Gruska Faculty of Informatics Brno Czech Republic December 20, 2011 10. QUANTUM ERROR CORRECTION CODES Quantum computing based on pure states and unitary evolutions is an idealization
QUANTUM COMPUTING 10. Jozef Gruska Faculty of Informatics Brno Czech Republic December 20, 2011 10. QUANTUM ERROR CORRECTION CODES Quantum computing based on pure states and unitary evolutions is an idealization
Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs
 Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs Workshop on Quantum Computing and its Application March 16, 2017 Qubits Unitary transformations Quantum Circuits Quantum Measurements Quantum
Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs Workshop on Quantum Computing and its Application March 16, 2017 Qubits Unitary transformations Quantum Circuits Quantum Measurements Quantum
Magic States. Presented by Nathan Babcock
 Magic States Presented by Nathan Babcock Overview I will discuss the following points:. Quantum Error Correction. The Stabilizer Formalism. Clifford Group Quantum Computation 4. Magic States 5. Derivation
Magic States Presented by Nathan Babcock Overview I will discuss the following points:. Quantum Error Correction. The Stabilizer Formalism. Clifford Group Quantum Computation 4. Magic States 5. Derivation
Quantum Computer Architecture
 Quantum Computer Architecture Scalable and Reliable Quantum Computers Greg Byrd (ECE) CSC 801 - Feb 13, 2018 Overview 1 Sources 2 Key Concepts Quantum Computer 3 Outline 4 Ion Trap Operation The ion can
Quantum Computer Architecture Scalable and Reliable Quantum Computers Greg Byrd (ECE) CSC 801 - Feb 13, 2018 Overview 1 Sources 2 Key Concepts Quantum Computer 3 Outline 4 Ion Trap Operation The ion can
Talk by Johannes Vrana
 Decoherence and Quantum Error Correction Talk by Johannes Vrana Seminar on Quantum Computing - WS 2002/2003 Page 1 Content I Introduction...3 II Decoherence and Errors...4 1. Decoherence...4 2. Errors...6
Decoherence and Quantum Error Correction Talk by Johannes Vrana Seminar on Quantum Computing - WS 2002/2003 Page 1 Content I Introduction...3 II Decoherence and Errors...4 1. Decoherence...4 2. Errors...6
Techniques for fault-tolerant quantum error correction
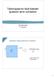 Techniques for fault-tolerant quantum error correction Ben Reichardt UC Berkeley Quantum fault-tolerance problem C 0/1 Fault-tolerant, larger High tolerable noise Low overhead 1 Encoding for fault tolerance
Techniques for fault-tolerant quantum error correction Ben Reichardt UC Berkeley Quantum fault-tolerance problem C 0/1 Fault-tolerant, larger High tolerable noise Low overhead 1 Encoding for fault tolerance
Quantum Error Correction
 qitd213 Quantum Error Correction Robert B. Griffiths Version of 9 April 2012 References: QCQI = Quantum Computation and Quantum Information by Nielsen and Chuang(Cambridge, 2000), Secs. 10.1, 10.2, 10.3.
qitd213 Quantum Error Correction Robert B. Griffiths Version of 9 April 2012 References: QCQI = Quantum Computation and Quantum Information by Nielsen and Chuang(Cambridge, 2000), Secs. 10.1, 10.2, 10.3.
Non-Zero Syndromes and Syndrome Measurement Order for the [[7,1,3]] Quantum Error Correction Code
![Non-Zero Syndromes and Syndrome Measurement Order for the [[7,1,3]] Quantum Error Correction Code Non-Zero Syndromes and Syndrome Measurement Order for the [[7,1,3]] Quantum Error Correction Code](/thumbs/87/97094643.jpg) Non-Zero Syndromes and Syndrome Measurement Order for the [[,,]] Quantum Error Correction Code Yaakov S. Weinstein Quantum Information Science Group, Mitre, Forrestal Rd. Princeton, NJ, USA The[[,,]] quantum
Non-Zero Syndromes and Syndrome Measurement Order for the [[,,]] Quantum Error Correction Code Yaakov S. Weinstein Quantum Information Science Group, Mitre, Forrestal Rd. Princeton, NJ, USA The[[,,]] quantum
Summary: Types of Error
 Summary: Types of Error Unitary errors (including leakage and cross-talk) due to gates, interactions. How does this scale up (meet resonance conditions for misc. higher-order photon exchange processes
Summary: Types of Error Unitary errors (including leakage and cross-talk) due to gates, interactions. How does this scale up (meet resonance conditions for misc. higher-order photon exchange processes
A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs
 A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs Preetum Nairan preetum@bereley.edu Mar 3, 05 Abstract This survey aims to highlight some interesting ideas in
A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs Preetum Nairan preetum@bereley.edu Mar 3, 05 Abstract This survey aims to highlight some interesting ideas in
Logical error rate in the Pauli twirling approximation
 Logical error rate in the Pauli twirling approximation Amara Katabarwa and Michael R. Geller Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602, USA (Dated: April 10, 2015)
Logical error rate in the Pauli twirling approximation Amara Katabarwa and Michael R. Geller Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602, USA (Dated: April 10, 2015)
Quantum secret sharing based on quantum error-correcting codes
 Quantum secret sharing based on quantum error-correcting codes Zhang Zu-Rong( ), Liu Wei-Tao( ), and Li Cheng-Zu( ) Department of Physics, School of Science, National University of Defense Technology,
Quantum secret sharing based on quantum error-correcting codes Zhang Zu-Rong( ), Liu Wei-Tao( ), and Li Cheng-Zu( ) Department of Physics, School of Science, National University of Defense Technology,
Quantum Error Correcting Codes and Quantum Cryptography. Peter Shor M.I.T. Cambridge, MA 02139
 Quantum Error Correcting Codes and Quantum Cryptography Peter Shor M.I.T. Cambridge, MA 02139 1 We start out with two processes which are fundamentally quantum: superdense coding and teleportation. Superdense
Quantum Error Correcting Codes and Quantum Cryptography Peter Shor M.I.T. Cambridge, MA 02139 1 We start out with two processes which are fundamentally quantum: superdense coding and teleportation. Superdense
Analog quantum error correction with encoding a qubit into an oscillator
 17th Asian Quantum Information Science Conference 6 September 2017 Analog quantum error correction with encoding a qubit into an oscillator Kosuke Fukui, Akihisa Tomita, Atsushi Okamoto Graduate School
17th Asian Quantum Information Science Conference 6 September 2017 Analog quantum error correction with encoding a qubit into an oscillator Kosuke Fukui, Akihisa Tomita, Atsushi Okamoto Graduate School
Quantum Error-Correcting Codes by Concatenation
 Second International Conference on Quantum Error Correction University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA December 5 9, 2011 Quantum Error-Correcting Codes by Concatenation Markus Grassl joint work
Second International Conference on Quantum Error Correction University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA December 5 9, 2011 Quantum Error-Correcting Codes by Concatenation Markus Grassl joint work
A scheme for protecting one-qubit information against erasure. error. Abstract
 A scheme for protecting one-qubit information against erasure error Chui-Ping Yang 1, Shih-I Chu 1, and Siyuan Han 1 Department of Chemistry, University of Kansas, and Kansas Center for Advanced Scientific
A scheme for protecting one-qubit information against erasure error Chui-Ping Yang 1, Shih-I Chu 1, and Siyuan Han 1 Department of Chemistry, University of Kansas, and Kansas Center for Advanced Scientific
2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor. 2.1 Classical information processing The carrier of information
 QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
arxiv:quant-ph/ v3 26 Aug 1997
 CALT-68-2112 QUIC-97-030 quant-ph/9705031 eliable Quantum Computers arxiv:quant-ph/9705031v3 26 Aug 1997 John Preskill 1 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA Abstract The new field
CALT-68-2112 QUIC-97-030 quant-ph/9705031 eliable Quantum Computers arxiv:quant-ph/9705031v3 26 Aug 1997 John Preskill 1 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA Abstract The new field
General Qubit Errors Cannot Be Corrected
 arxiv:quant-ph/0206144v4 27 Jun 2002 General Qubit Errors Cannot Be Corrected Subhash Kak June27, 2002 Abstract Error correction in the standard meaning of the term implies the ability to correct all small
arxiv:quant-ph/0206144v4 27 Jun 2002 General Qubit Errors Cannot Be Corrected Subhash Kak June27, 2002 Abstract Error correction in the standard meaning of the term implies the ability to correct all small
Quantum Computing with Very Noisy Gates
 Quantum Computing with Very Noisy Gates Produced with pdflatex and xfig Fault-tolerance thresholds in theory and practice. Available techniques for fault tolerance. A scheme based on the [[4, 2, 2]] code.
Quantum Computing with Very Noisy Gates Produced with pdflatex and xfig Fault-tolerance thresholds in theory and practice. Available techniques for fault tolerance. A scheme based on the [[4, 2, 2]] code.
Quantum Error Correction Codes - From Qubit to Qudit
 Quantum Error Correction Codes - From Qubit to Qudit Xiaoyi Tang Paul McGuirk December 7, 005 1 Introduction Quantum computation (QC), with inherent parallelism from the superposition principle of quantum
Quantum Error Correction Codes - From Qubit to Qudit Xiaoyi Tang Paul McGuirk December 7, 005 1 Introduction Quantum computation (QC), with inherent parallelism from the superposition principle of quantum
More advanced codes 0 1 ( , 1 1 (
 p. 1/24 More advanced codes The Shor code was the first general-purpose quantum error-correcting code, but since then many others have been discovered. An important example, discovered independently of
p. 1/24 More advanced codes The Shor code was the first general-purpose quantum error-correcting code, but since then many others have been discovered. An important example, discovered independently of
b) (5 points) Give a simple quantum circuit that transforms the state
 C/CS/Phy191 Midterm Quiz Solutions October 0, 009 1 (5 points) Short answer questions: a) (5 points) Let f be a function from n bits to 1 bit You have a quantum circuit U f for computing f If you wish
C/CS/Phy191 Midterm Quiz Solutions October 0, 009 1 (5 points) Short answer questions: a) (5 points) Let f be a function from n bits to 1 bit You have a quantum circuit U f for computing f If you wish
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes
 CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last lecture we learned of the quantum error
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last lecture we learned of the quantum error
5. Communication resources
 5. Communication resources Classical channel Quantum channel Entanglement How does the state evolve under LOCC? Properties of maximally entangled states Bell basis Quantum dense coding Quantum teleportation
5. Communication resources Classical channel Quantum channel Entanglement How does the state evolve under LOCC? Properties of maximally entangled states Bell basis Quantum dense coding Quantum teleportation
Fault-Tolerant Universality from Fault-Tolerant Stabilizer Operations and Noisy Ancillas
 Fault-Tolerant Universality from Fault-Tolerant Stabilizer Operations and Noisy Ancillas Ben W. Reichardt UC Berkeley NSF, ARO [quant-ph/0411036] stabilizer operations, Q: Do form a universal set? prepare
Fault-Tolerant Universality from Fault-Tolerant Stabilizer Operations and Noisy Ancillas Ben W. Reichardt UC Berkeley NSF, ARO [quant-ph/0411036] stabilizer operations, Q: Do form a universal set? prepare
Quantum Error Correction Codes Spring 2005 : EE229B Error Control Coding Milos Drezgic
 Quantum Error Correction Codes Spring 2005 : EE229B Error Control Coding Milos Drezgic Abstract This report contains the comprehensive explanation of some most important quantum error correction codes.
Quantum Error Correction Codes Spring 2005 : EE229B Error Control Coding Milos Drezgic Abstract This report contains the comprehensive explanation of some most important quantum error correction codes.
What is a quantum computer? Quantum Architecture. Quantum Mechanics. Quantum Superposition. Quantum Entanglement. What is a Quantum Computer (contd.
 What is a quantum computer? Quantum Architecture by Murat Birben A quantum computer is a device designed to take advantage of distincly quantum phenomena in carrying out a computational task. A quantum
What is a quantum computer? Quantum Architecture by Murat Birben A quantum computer is a device designed to take advantage of distincly quantum phenomena in carrying out a computational task. A quantum
Recovery in quantum error correction for general noise without measurement
 Quantum Information and Computation, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2011) 000 000 c Rinton Press Recovery in quantum error correction for general noise without measurement CHI-KWONG LI Department of Mathematics, College
Quantum Information and Computation, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2011) 000 000 c Rinton Press Recovery in quantum error correction for general noise without measurement CHI-KWONG LI Department of Mathematics, College
Teleportation-based approaches to universal quantum computation with single-qubit measurements
 Teleportation-based approaches to universal quantum computation with single-qubit measurements Andrew Childs MIT Center for Theoretical Physics joint work with Debbie Leung and Michael Nielsen Resource
Teleportation-based approaches to universal quantum computation with single-qubit measurements Andrew Childs MIT Center for Theoretical Physics joint work with Debbie Leung and Michael Nielsen Resource
Single qubit + CNOT gates
 Lecture 6 Universal quantum gates Single qubit + CNOT gates Single qubit and CNOT gates together can be used to implement an arbitrary twolevel unitary operation on the state space of n qubits. Suppose
Lecture 6 Universal quantum gates Single qubit + CNOT gates Single qubit and CNOT gates together can be used to implement an arbitrary twolevel unitary operation on the state space of n qubits. Suppose
arxiv:quant-ph/ v1 18 Apr 2000
 Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics arxiv:quant-ph/0004072 v1 18 Apr 2000 An Introduction to Quantum Error Correction Daniel Gottesman Abstract. Quantum states are very delicate, so it is likely
Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics arxiv:quant-ph/0004072 v1 18 Apr 2000 An Introduction to Quantum Error Correction Daniel Gottesman Abstract. Quantum states are very delicate, so it is likely
Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871
 Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871 Lecture 1 (2017) Jon Yard QNC 3126 jyard@uwaterloo.ca TAs Nitica Sakharwade nsakharwade@perimeterinstitute.ca
Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871 Lecture 1 (2017) Jon Yard QNC 3126 jyard@uwaterloo.ca TAs Nitica Sakharwade nsakharwade@perimeterinstitute.ca
Optimal Controlled Phasegates for Trapped Neutral Atoms at the Quantum Speed Limit
 with Ultracold Trapped Atoms at the Quantum Speed Limit Michael Goerz May 31, 2011 with Ultracold Trapped Atoms Prologue: with Ultracold Trapped Atoms Classical Computing: 4-Bit Full Adder Inside the CPU:
with Ultracold Trapped Atoms at the Quantum Speed Limit Michael Goerz May 31, 2011 with Ultracold Trapped Atoms Prologue: with Ultracold Trapped Atoms Classical Computing: 4-Bit Full Adder Inside the CPU:
How Often Must We Apply Syndrome Measurements?
 How Often Must We Apply Syndrome Measurements? Y. S. Weinstein Quantum Information Science Group, MITRE, 200 Forrestal Rd., Princeton, NJ 08540 ABSTRACT Quantum error correction requires encoding quantum
How Often Must We Apply Syndrome Measurements? Y. S. Weinstein Quantum Information Science Group, MITRE, 200 Forrestal Rd., Princeton, NJ 08540 ABSTRACT Quantum error correction requires encoding quantum
Introduction to quantum information processing
 Introduction to quantum information processing Fidelity and other distance metrics Brad Lackey 3 November 2016 FIDELITY AND OTHER DISTANCE METRICS 1 of 17 OUTLINE 1 Noise channels 2 Fidelity 3 Trace distance
Introduction to quantum information processing Fidelity and other distance metrics Brad Lackey 3 November 2016 FIDELITY AND OTHER DISTANCE METRICS 1 of 17 OUTLINE 1 Noise channels 2 Fidelity 3 Trace distance
High Fidelity to Low Weight. Daniel Gottesman Perimeter Institute
 High Fidelity to Low Weight Daniel Gottesman Perimeter Institute A Word From Our Sponsor... Quant-ph/0212066, Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices, D.G., H.-K. Lo, N. Lutkenhaus,
High Fidelity to Low Weight Daniel Gottesman Perimeter Institute A Word From Our Sponsor... Quant-ph/0212066, Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices, D.G., H.-K. Lo, N. Lutkenhaus,
Quantum error correction on a hybrid spin system. Christoph Fischer, Andrea Rocchetto
 Quantum error correction on a hybrid spin system Christoph Fischer, Andrea Rocchetto Christoph Fischer, Andrea Rocchetto 17/05/14 1 Outline Error correction: why we need it, how it works Experimental realization
Quantum error correction on a hybrid spin system Christoph Fischer, Andrea Rocchetto Christoph Fischer, Andrea Rocchetto 17/05/14 1 Outline Error correction: why we need it, how it works Experimental realization
Introduction to Quantum Computation
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Quantum Computation 1.1 Motivations The main task in this course is to discuss application of quantum mechanics to information processing (or computation). Why? Education:Asingleq-bitisthesmallestpossiblequantummechanical
Chapter 1 Introduction to Quantum Computation 1.1 Motivations The main task in this course is to discuss application of quantum mechanics to information processing (or computation). Why? Education:Asingleq-bitisthesmallestpossiblequantummechanical
Unconditional Security of the Bennett 1992 quantum key-distribution protocol over a lossy and noisy channel
 Unconditional Security of the Bennett 1992 quantum key-distribution protocol over a lossy and noisy channel Kiyoshi Tamaki *Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics Collaboration with Masato Koashi
Unconditional Security of the Bennett 1992 quantum key-distribution protocol over a lossy and noisy channel Kiyoshi Tamaki *Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics Collaboration with Masato Koashi
Quantum Computing. 6. Quantum Computer Architecture 7. Quantum Computers and Complexity
 Quantum Computing 1. Quantum States and Quantum Gates 2. Multiple Qubits and Entangled States 3. Quantum Gate Arrays 4. Quantum Parallelism 5. Examples of Quantum Algorithms 1. Grover s Unstructured Search
Quantum Computing 1. Quantum States and Quantum Gates 2. Multiple Qubits and Entangled States 3. Quantum Gate Arrays 4. Quantum Parallelism 5. Examples of Quantum Algorithms 1. Grover s Unstructured Search
Large-Scale Quantum Architectures
 Large-Scale Quantum Architectures Fred Chong Director of Computer Engineering Professor of Computer Science University of California at Santa Barbara With Daniel Kudrow, Tzvetan Metodi, Darshan Thaker,
Large-Scale Quantum Architectures Fred Chong Director of Computer Engineering Professor of Computer Science University of California at Santa Barbara With Daniel Kudrow, Tzvetan Metodi, Darshan Thaker,
M. Grassl, Grundlagen der Quantenfehlerkorrektur, Universität Innsbruck, WS 2007/ , Folie 127
 M Grassl, Grundlagen der Quantenfehlerkorrektur, Universität Innsbruck, WS 2007/2008 2008-01-11, Folie 127 M Grassl, Grundlagen der Quantenfehlerkorrektur, Universität Innsbruck, WS 2007/2008 2008-01-11,
M Grassl, Grundlagen der Quantenfehlerkorrektur, Universität Innsbruck, WS 2007/2008 2008-01-11, Folie 127 M Grassl, Grundlagen der Quantenfehlerkorrektur, Universität Innsbruck, WS 2007/2008 2008-01-11,
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics
 Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Seminar 1. Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Seminar 1 Introduction to Quantum Computing Before going in I am also a beginner in this field If you are interested, you can search more using: Quantum Computing since Democritus (Scott Aaronson) Quantum
Seminar 1 Introduction to Quantum Computing Before going in I am also a beginner in this field If you are interested, you can search more using: Quantum Computing since Democritus (Scott Aaronson) Quantum
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 16 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 16 Mar 2014 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 16 Mar 2014](/thumbs/92/109364927.jpg) Approximate quantum error correction for generalized amplitude damping errors Carlo Cafaro 1, and Peter van Loock 1 Max-Planck Institute for the Science of Light, 91058 Erlangen, Germany and Institute
Approximate quantum error correction for generalized amplitude damping errors Carlo Cafaro 1, and Peter van Loock 1 Max-Planck Institute for the Science of Light, 91058 Erlangen, Germany and Institute
Quantum Error Correction Codes-From Qubit to Qudit. Xiaoyi Tang, Paul McGuirk
 Quantum Error Correction Codes-From Qubit to Qudit Xiaoyi Tang, Paul McGuirk Outline Introduction to quantum error correction codes (QECC) Qudits and Qudit Gates Generalizing QECC to Qudit computing Need
Quantum Error Correction Codes-From Qubit to Qudit Xiaoyi Tang, Paul McGuirk Outline Introduction to quantum error correction codes (QECC) Qudits and Qudit Gates Generalizing QECC to Qudit computing Need
Jian-Wei Pan
 Lecture Note 6 11.06.2008 open system dynamics 0 E 0 U ( t) ( t) 0 E ( t) E U 1 E ( t) 1 1 System Environment U() t ( ) 0 + 1 E 0 E ( t) + 1 E ( t) 0 1 0 0 1 1 2 * 0 01 E1 E0 q() t = TrEq+ E = * 2 1 0
Lecture Note 6 11.06.2008 open system dynamics 0 E 0 U ( t) ( t) 0 E ( t) E U 1 E ( t) 1 1 System Environment U() t ( ) 0 + 1 E 0 E ( t) + 1 E ( t) 0 1 0 0 1 1 2 * 0 01 E1 E0 q() t = TrEq+ E = * 2 1 0
QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING THEOREM p.1/36
 QUANTUM INFORMATION - THE NO-HIDING THEOREM Arun K Pati akpati@iopb.res.in Instititute of Physics, Bhubaneswar-751005, Orissa, INDIA and Th. P. D, BARC, Mumbai-400085, India QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING
QUANTUM INFORMATION - THE NO-HIDING THEOREM Arun K Pati akpati@iopb.res.in Instititute of Physics, Bhubaneswar-751005, Orissa, INDIA and Th. P. D, BARC, Mumbai-400085, India QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING
X row 1 X row 2, X row 2 X row 3, Z col 1 Z col 2, Z col 2 Z col 3,
 1 Ph 219c/CS 219c Exercises Due: Thursday 9 March 2017.1 A cleaning lemma for CSS codes In class we proved the cleaning lemma for stabilizer codes, which says the following: For an [[n, k]] stabilizer
1 Ph 219c/CS 219c Exercises Due: Thursday 9 March 2017.1 A cleaning lemma for CSS codes In class we proved the cleaning lemma for stabilizer codes, which says the following: For an [[n, k]] stabilizer
Teleportation of Quantum States (1993; Bennett, Brassard, Crepeau, Jozsa, Peres, Wootters)
 Teleportation of Quantum States (1993; Bennett, Brassard, Crepeau, Jozsa, Peres, Wootters) Rahul Jain U. Waterloo and Institute for Quantum Computing, rjain@cs.uwaterloo.ca entry editor: Andris Ambainis
Teleportation of Quantum States (1993; Bennett, Brassard, Crepeau, Jozsa, Peres, Wootters) Rahul Jain U. Waterloo and Institute for Quantum Computing, rjain@cs.uwaterloo.ca entry editor: Andris Ambainis
Quantum Control of Qubits
 Quantum Control of Qubits K. Birgitta Whaley University of California, Berkeley J. Zhang J. Vala S. Sastry M. Mottonen R. desousa Quantum Circuit model input 1> 6> = 1> 0> H S T H S H x x 7 k = 0 e 3 π
Quantum Control of Qubits K. Birgitta Whaley University of California, Berkeley J. Zhang J. Vala S. Sastry M. Mottonen R. desousa Quantum Circuit model input 1> 6> = 1> 0> H S T H S H x x 7 k = 0 e 3 π
Hilbert Space, Entanglement, Quantum Gates, Bell States, Superdense Coding.
 CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
Quantum Subsystem Codes Their Theory and Use
 Quantum Subsystem Codes Their Theory and Use Nikolas P. Breuckmann - September 26, 2011 Bachelor thesis under supervision of Prof. Dr. B. M. Terhal Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften
Quantum Subsystem Codes Their Theory and Use Nikolas P. Breuckmann - September 26, 2011 Bachelor thesis under supervision of Prof. Dr. B. M. Terhal Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften
Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation
 Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Channel-Adapted Quantum Error Correction. Andrew Stephen Fletcher
 Channel-Adapted Quantum Error Correction by Andrew Stephen Fletcher Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Channel-Adapted Quantum Error Correction by Andrew Stephen Fletcher Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
High-fidelity Z-measurement error encoding of optical qubits
 Griffith Research Online https://research-repository.griffith.edu.au High-fidelity Z-measurement error encoding of optical qubits Author O'Brien, J., Pryde, G., White, A., Ralph, T. Published 2005 Journal
Griffith Research Online https://research-repository.griffith.edu.au High-fidelity Z-measurement error encoding of optical qubits Author O'Brien, J., Pryde, G., White, A., Ralph, T. Published 2005 Journal
Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2
![Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2](/thumbs/78/77811482.jpg) Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, 2007 Quantum decoherence p. 2/2 Outline Quantum decoherence: 1. Basics of quantum
Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, 2007 Quantum decoherence p. 2/2 Outline Quantum decoherence: 1. Basics of quantum
Degradable Quantum Channels
 Degradable Quantum Channels Li Yu Department of Physics, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA May 27, 2010 References The capacity of a quantum channel for simultaneous transmission of classical
Degradable Quantum Channels Li Yu Department of Physics, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA May 27, 2010 References The capacity of a quantum channel for simultaneous transmission of classical
Memory Hierarchies for Quantum Data
 Memory ierarchies for Quantum Data Dean Copsey z, Mark Oskin y, Frederic T. Chong z, Isaac Chuang Π and Khaled Abdel-Ghaffar z z University of California at Davis y University of Washington Π Massachusetts
Memory ierarchies for Quantum Data Dean Copsey z, Mark Oskin y, Frederic T. Chong z, Isaac Chuang Π and Khaled Abdel-Ghaffar z z University of California at Davis y University of Washington Π Massachusetts
Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6
 University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6 Due 12:30pm Monday, May 14, 2018 1. Brainwarmers on Kraus operators. (a) Check that
University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6 Due 12:30pm Monday, May 14, 2018 1. Brainwarmers on Kraus operators. (a) Check that
Quantum gate. Contents. Commonly used gates
 Quantum gate From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In quantum computing and specifically the quantum circuit model of computation, a quantum gate (or quantum logic gate) is a basic quantum circuit operating
Quantum gate From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In quantum computing and specifically the quantum circuit model of computation, a quantum gate (or quantum logic gate) is a basic quantum circuit operating
Grover s algorithm. We want to find aa. Search in an unordered database. QC oracle (as usual) Usual trick
 Grover s algorithm Search in an unordered database Example: phonebook, need to find a person from a phone number Actually, something else, like hard (e.g., NP-complete) problem 0, xx aa Black box ff xx
Grover s algorithm Search in an unordered database Example: phonebook, need to find a person from a phone number Actually, something else, like hard (e.g., NP-complete) problem 0, xx aa Black box ff xx
Decodiy for surface. Quantum Error Correction. path integral. theory versus. Decoding for GKP code. experiment. Correcting
 Quantum Error Correction 1 3X 1100 ( 230 ntro : theory versus experiment Quantum Error i Bosonic Codes # } \ Correcting Conditions stalilizer Codes ( including conthuoqsoyueagjask \ # Decoding Decoding
Quantum Error Correction 1 3X 1100 ( 230 ntro : theory versus experiment Quantum Error i Bosonic Codes # } \ Correcting Conditions stalilizer Codes ( including conthuoqsoyueagjask \ # Decoding Decoding
Quantum Computing: From Circuit To Architecture
 POLITECNICO DI MILANO Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Quantum Computing: From Circuit To Architecture Nicholas Mainardi Email: nicholas.mainardi@polimi.it home.deib.polimi.it/nmainardi
POLITECNICO DI MILANO Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Quantum Computing: From Circuit To Architecture Nicholas Mainardi Email: nicholas.mainardi@polimi.it home.deib.polimi.it/nmainardi
Solution 4 for USTC class Physics of Quantum Information
 Solution 4 for 2018 2019 USTC class Physics of Quantum Information Shuai Zhao, Xin-Yu Xu, Kai Chen National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale and Department of Modern Physics, University of
Solution 4 for 2018 2019 USTC class Physics of Quantum Information Shuai Zhao, Xin-Yu Xu, Kai Chen National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale and Department of Modern Physics, University of
quantum error-rejection
 Lecture Note 7 Decoherence-free sub-space space and quantum error-rejection rejection.06.006 open system dynamics ψ = α 0 + α 0 Decoherence System Environment 0 E 0 U ( t) ( t) 0 E ( t) E U E ( t) U()
Lecture Note 7 Decoherence-free sub-space space and quantum error-rejection rejection.06.006 open system dynamics ψ = α 0 + α 0 Decoherence System Environment 0 E 0 U ( t) ( t) 0 E ( t) E U E ( t) U()
Approaches to Quantum Error Correction
 Séminaire Poincaré 1 (005) 65 93 Séminaire Poincaré Approaches to Quantum Error Correction Julia Kempe CNRS & LRI Laboratoire de Recherche Informatique Bât. 490, Université de Paris-Sud 91405 Orsay Cedex
Séminaire Poincaré 1 (005) 65 93 Séminaire Poincaré Approaches to Quantum Error Correction Julia Kempe CNRS & LRI Laboratoire de Recherche Informatique Bât. 490, Université de Paris-Sud 91405 Orsay Cedex
Quantum Information Processing and Diagrams of States
 Quantum Information and Diagrams of States September 17th 2009, AFSecurity Sara Felloni sara@unik.no / sara.felloni@iet.ntnu.no Quantum Hacking Group: http://www.iet.ntnu.no/groups/optics/qcr/ UNIK University
Quantum Information and Diagrams of States September 17th 2009, AFSecurity Sara Felloni sara@unik.no / sara.felloni@iet.ntnu.no Quantum Hacking Group: http://www.iet.ntnu.no/groups/optics/qcr/ UNIK University
Physics ; CS 4812 Problem Set 4
 Physics 4481-7681; CS 4812 Problem Set 4 Six problems (six pages), all short, covers lectures 11 15, due in class 25 Oct 2018 Problem 1: 1-qubit state tomography Consider a 1-qubit state ψ cos θ 2 0 +
Physics 4481-7681; CS 4812 Problem Set 4 Six problems (six pages), all short, covers lectures 11 15, due in class 25 Oct 2018 Problem 1: 1-qubit state tomography Consider a 1-qubit state ψ cos θ 2 0 +
Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo
 CS 497 Frontiers of Computer Science Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture of http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cleve/cs497-f7 Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum
CS 497 Frontiers of Computer Science Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture of http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cleve/cs497-f7 Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum
Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation. Tatiana G. Rappoport Advanced Summer School Cinvestav 2005
 Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation Advanced Summer School 1 I. Background II. Spintronics Spin generation (magnetic semiconductors) Spin detection III. Spintronics - electron
Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation Advanced Summer School 1 I. Background II. Spintronics Spin generation (magnetic semiconductors) Spin detection III. Spintronics - electron
CS120, Quantum Cryptography, Fall 2016
 CS10, Quantum Cryptography, Fall 016 Homework # due: 10:9AM, October 18th, 016 Ground rules: Your homework should be submitted to the marked bins that will be by Annenberg 41. Please format your solutions
CS10, Quantum Cryptography, Fall 016 Homework # due: 10:9AM, October 18th, 016 Ground rules: Your homework should be submitted to the marked bins that will be by Annenberg 41. Please format your solutions
1 Readings. 2 Unitary Operators. C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9/22/09 Fall 2009 Lecture 8
 C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9//09 Fall 009 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Kaye et al: Ch. 1.1-1.5,
C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9//09 Fall 009 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Kaye et al: Ch. 1.1-1.5,
A Tutorial on Quantum Error Correction
 Proceedings of the International School of Physics Enrico Fermi, course CLXII, Quantum Computers, Algorithms and Chaos, G. Casati, D. L. Shepelyansky and P. Zoller, eds., pp. 1 32 (IOS Press, Amsterdam
Proceedings of the International School of Physics Enrico Fermi, course CLXII, Quantum Computers, Algorithms and Chaos, G. Casati, D. L. Shepelyansky and P. Zoller, eds., pp. 1 32 (IOS Press, Amsterdam
Introduction to Quantum Error Correction
 Introduction to Quantum Error Correction E. Knill, R. Laflamme, A. Ashikhmin, H. Barnum, L. Viola and W. H. Zurek arxiv:quant-ph/007170v1 30 Jul 00 Contents February 1, 008 1 Concepts and Examples 4 1.1
Introduction to Quantum Error Correction E. Knill, R. Laflamme, A. Ashikhmin, H. Barnum, L. Viola and W. H. Zurek arxiv:quant-ph/007170v1 30 Jul 00 Contents February 1, 008 1 Concepts and Examples 4 1.1
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9/22/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 8. a b b d. w. Therefore, U preserves norms and angles (up to sign).
 C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9//05 Fall 005 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Universality Ch. 3.5-3.6
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9//05 Fall 005 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Universality Ch. 3.5-3.6
Introduction to Quantum Error Correction
 Introduction to Quantum Error Correction Emanuel Knill, Raymond Laflamme, Alexei Ashikhmin, Howard N. Barnum, Lorenza Viola, and Wojciech H. Zurek 188 Los Alamos Science Number 27 2002 W hen physically
Introduction to Quantum Error Correction Emanuel Knill, Raymond Laflamme, Alexei Ashikhmin, Howard N. Barnum, Lorenza Viola, and Wojciech H. Zurek 188 Los Alamos Science Number 27 2002 W hen physically
arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 15 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 15 Oct 2010 arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 15 Oct 2010](/thumbs/86/94003821.jpg) 5-qubit Quantum error correction in a charge qubit quantum computer Dave Touchette, Haleemur Ali and Michael Hilke Department of Physics, McGill University, Montreal, Québec, H3A 2T8, Canada (Dated: October
5-qubit Quantum error correction in a charge qubit quantum computer Dave Touchette, Haleemur Ali and Michael Hilke Department of Physics, McGill University, Montreal, Québec, H3A 2T8, Canada (Dated: October
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation
 MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture 2
 Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Quantum Entanglement and Error Correction
 Quantum Entanglement and Error Correction Fall 2016 Bei Zeng University of Guelph Course Information Instructor: Bei Zeng, email: beizeng@icloud.com TA: Dr. Cheng Guo, email: cheng323232@163.com Wechat
Quantum Entanglement and Error Correction Fall 2016 Bei Zeng University of Guelph Course Information Instructor: Bei Zeng, email: beizeng@icloud.com TA: Dr. Cheng Guo, email: cheng323232@163.com Wechat
1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics
 1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics How to describe the states of an ideally controlled system? How to describe changes in an ideally controlled system? How to describe measurements on an ideally controlled
1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics How to describe the states of an ideally controlled system? How to describe changes in an ideally controlled system? How to describe measurements on an ideally controlled
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation and the Threshold Theorem
 CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation and the Threshold Theorem Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last few lectures, we
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation and the Threshold Theorem Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last few lectures, we
Quantum Memory Hierarchies
 Quantum Memory Hierarchies Efficient Designs that Match Available Parallelism in Quantum Processors Darshan D. Thaker Tzvetan S. Metodi UC Davis Andrew W. Cross Issac L. Chuang MIT Frederic T. Chong UC
Quantum Memory Hierarchies Efficient Designs that Match Available Parallelism in Quantum Processors Darshan D. Thaker Tzvetan S. Metodi UC Davis Andrew W. Cross Issac L. Chuang MIT Frederic T. Chong UC
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 14 May 2017
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 14 May 2017 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 14 May 2017](/thumbs/95/122522131.jpg) A Low-Overhead Hybrid Approach for Universal Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation Eesa Nikahd, Morteza Saheb Zamani, and Mehdi Sedighi Quantum Design Automation Lab Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran,
A Low-Overhead Hybrid Approach for Universal Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation Eesa Nikahd, Morteza Saheb Zamani, and Mehdi Sedighi Quantum Design Automation Lab Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran,
Reliable quantum computers
 Reliable quantum computers BY JOHN PRESKILL Charles C. Lauritsen Laboratory of High Energy Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA The new field of quantum error correction
Reliable quantum computers BY JOHN PRESKILL Charles C. Lauritsen Laboratory of High Energy Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA The new field of quantum error correction
QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY QUANTUM COMPUTING. Philippe Grangier, Institut d'optique, Orsay. from basic principles to practical realizations.
 QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY QUANTUM COMPUTING Philippe Grangier, Institut d'optique, Orsay 1. Quantum cryptography : from basic principles to practical realizations. 2. Quantum computing : a conceptual revolution
QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY QUANTUM COMPUTING Philippe Grangier, Institut d'optique, Orsay 1. Quantum cryptography : from basic principles to practical realizations. 2. Quantum computing : a conceptual revolution
Energetics and Error Rates of Self-Correcting Quantum Memories
 Energetics and Error Rates of Self-Correcting Quantum Memories John Schulman Quantum codes allow for the robust storage of quantum information despite interaction with the environment. In a quantum code,
Energetics and Error Rates of Self-Correcting Quantum Memories John Schulman Quantum codes allow for the robust storage of quantum information despite interaction with the environment. In a quantum code,
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 5 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 5 Jan 2015 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 5 Jan 2015](/thumbs/78/77987229.jpg) Comparison of a quantum error correction threshold for exact and approximate errors arxiv:1501.00068v2 [quant-ph] 5 Jan 2015 Mauricio Gutiérrez and Kenneth R. Brown Schools of Chemistry and Biochemistry;
Comparison of a quantum error correction threshold for exact and approximate errors arxiv:1501.00068v2 [quant-ph] 5 Jan 2015 Mauricio Gutiérrez and Kenneth R. Brown Schools of Chemistry and Biochemistry;
The Deutsch-Josza Algorithm in NMR
 December 20, 2010 Matteo Biondi, Thomas Hasler Introduction Algorithm presented in 1992 by Deutsch and Josza First implementation in 1998 on NMR system: - Jones, JA; Mosca M; et al. of a quantum algorithm
December 20, 2010 Matteo Biondi, Thomas Hasler Introduction Algorithm presented in 1992 by Deutsch and Josza First implementation in 1998 on NMR system: - Jones, JA; Mosca M; et al. of a quantum algorithm
arxiv:quant-ph/ v2 18 Feb 1997
 CALT-68-2100, QUIC-97-004 A Theory of Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation Daniel Gottesman California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 arxiv:quant-ph/9702029 v2 18 Feb 1997 Abstract In order
CALT-68-2100, QUIC-97-004 A Theory of Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation Daniel Gottesman California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 arxiv:quant-ph/9702029 v2 18 Feb 1997 Abstract In order
