Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2
|
|
|
- Myrtle Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, 2007
2 Quantum decoherence p. 2/2 Outline Quantum decoherence: 1. Basics of quantum mechanics 2. The measurement problem 3. Quantum decoherence
3 1. Basics of quantum mechanics Quantum decoherence p. 3/2
4 Quantum decoherence p. 4/2 The very basics Quantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that replaces classical mechanics and classical electromagnetism at atomic and subatomic level. For instance, Newtonian mechanics and classical electromagnetism cannot explain why an electron is staying in its orbital whereas quantum mechanics does. Quantum mechanics is concerned with quanta which refers to discrete units that quantum theory assigns to physical quantity e.g.: Energy of an atom at rest, spin of a particle etc.
5 Quantum decoherence p. 5/2 Quantum phenomena Some phenomena that do not appear in classical physics that quantum mechanics describes: - Quantisation or discretisation of certain physical quantities - Wave-particle duality - Uncertainty principle - etc.
6 Quantum decoherence p. 6/2 Probabilities The orthodox description of quantum mechanics which I will present today is a probabilistic one. Indeed, quantum mechanics is content to give a probabilistic description of the quantum world. The point is important since the explanation of the measurement process I will give here via quantum decoherence do not explain how the quantum system finally evolves in a stable deterministic state but stops at the level of probabilities.
7 Quantum decoherence p. 7/2 The postulates Here is a summary of the mathematical framework in which quantum mechanics is expressed: (i) To each physical system is associated a (separable) complex Hilbert space H. One dimensional subspaces of H represents states of the system. (ii) Evolution is described by means of unitary transformations on H. (iii) Observables are self-adjoint operators on H. (iv) A composite system is the Hilbert space obtained via the tensor product of the component state spaces.
8 Quantum decoherence p. 8/2 Measurement in-depth Note: From now on, I ll speak about finitary quantum mechanics i.e. Dim(H) <. As I said in the previous slide, a measurable quantity (observable) is represented by a self-adjoint operator σ. The eigenvalues of σ {λ i } R represents the set of possible outcomes of the measurement. If I measure λ j then, the state of the system after the measurement is the eigenstate corresponding to the eigenvalue λ j.
9 Quantum decoherence p. 9/2 Measurement in-depth Recall that a hermitian matrix can be unitarily diagonalised. The eigenvectors obtained during the process spans the state space of the system in fact, this says that a state can be expressed as a superposition of the eigenstates of the observable.
10 Quantum decoherence p. 10/2 An example Now, let us consider the simplest quantum system: the qubit (quantum bit). A qubit is represented by a normalized vector φ H i.e. φ = α 0 + β 1 ; α,β C s.t. α 2 + β 2 = 1. Now, consider the following observable on H: σ := [ ] = 1 [ ] 1 [ ] = 1P 0 1P 1 Then expected value of the probability to observe 0 if I measure φ is φ P 0 φ = αα 0.
11 Quantum decoherence p. 11/2 Density operators Now, note that: φ P 0 φ = Tr(P 0 φ φ ). There, ρ φ := φ φ is called the density operator associated to φ. It is the projector that describes the one-dimensional subspace of H spanned by φ = α 0 + β 1 ; it is a positive matrix of trace one: [ αα αβ βα ββ The unitaries U then act on ρ as UρU. ]
12 Quantum decoherence p. 12/2 Density operators Density operator formalism has many advantages. If two state vectors ψ, φ H produce the same density matrix then, they are indistinguishable physically. Moreover, we can also consider probabilistic mixture of density operators.
13 Quantum decoherence p. 13/2 Density operators Concretely, Given a set of states and probabilities { φ i,p i } with i p i = 1, one can form the following density operator: p i φ i φ i i It corresponds to a probabilistic mixture of the states φ i hence, the points in the closure of the convex hull of pure states states of the form ψ ψ are density operators.
14 Quantum decoherence p. 14/2 Density operators The set of physical transformation on density operators is given by superoperators i.e. completely positive trace preserving operators. This includes, isometries, traces, measurements, adjoining an ancilla etc.
15 2. The measurement problem Quantum decoherence p. 15/2
16 Quantum decoherence p. 16/2 The measurement problem So far, I have just given the mathematical formalism describing quantum mechanics and I have said that an observable is just some hermitian operator. Returning to our toy-model, before the measurement, the qubit is in the state: [ αα αβ βα ββ after the measurement, it will be in the state 0 0 with probability αα and in the state 1 1 with probability ββ. This is the wavefunction collapse. ]
17 Quantum decoherence p. 17/2 The measurement problem We can also think of the measurement as an operator which has the following effect on our qubit: [ αα αβ βα ββ ] M [ αα 0 0 ββ Of course, this is nothing but P 0 ρ φ P 0 + P 1 ρ φ P 1. However, these probabilities are a mathematical artefact, we are left with either one of the two possible states in our hand. ]
18 Quantum decoherence p. 18/2 The measurement problem Vanishing of the off-diagonal elements in the density operator says that we no longer have a coherent superposition. Moreover, the outcome state is a classical mixture. Finally, note that the passage from coherent superposition to mixture is not unitary and fundamentally irreversible.
19 3. Quantum decoherence Quantum decoherence p. 19/2
20 Quantum decoherence p. 20/2 Quantum decoherence To this date, there seems to be no consensus on how we should explain the full process of measurement. However, there is some consensus on how we pass from a coherent quantum state to a statistical mixture (classical). Here is the key intuition: An observer is macroscopic (classical) while the objects exhibiting quantum phenomena are very small (a grain of dust is too big). However, for an observer to learn the outcome of a measurement on a quantum system, this system must become correlated with a measurement apparatus (big, classical) and this gives the illusion of a collapse.
21 Quantum decoherence p. 21/2 Quantum decoherence The remainder of this talk will be about explaining how this transition occurs that is, from the density operator point of view, the process of passing from a coherent superposition to a statistical mixture and that s what quantum decoherence is about.
22 Quantum decoherence p. 22/2 Quantum decoherence There are a few concepts I need to introduce in order to speak of decoherence namely, - Traces and - Quantum entanglement.
23 Quantum decoherence p. 23/2 Traces Working with density matrix yields a notion of trace in an obvious sense: If I have a density operator ρ acting on H H (which is a joint system), I can trace out the part which act over H or the part acting over H. Now what does the trace mean? It is just the expression of the ignorance of what happens in some subsystem (which is traced out) to which some observer doesn t have access.
24 Quantum decoherence p. 24/2 Quantum entanglement A state described by ρ acting on H H is unentangled if it factors as ρ H ρ H and it is said to be entangled otherwise. For instance, the 2 qubit state ρ AB = is entangled; simply put, it is quantum correlation.
25 Quantum decoherence p. 25/2 Quantum entanglement Indeed, suppose that the 2 qubit state described in the previous slide is shared between two observers (Alice and Bob) and Alice measures her share and obtain 0, then the state collapse to After, if Bob measure his share of the state then, he will obtain 0 with certainty.
26 Quantum decoherence p. 26/2 All this together Now, suppose that Alice and Bob know that they share an entangled qubit however, they can t communicate then, from their respective point of view, their state looks like Tr A (ρ AB ) = Tr B (ρ AB ) = 1 2 [ which is the completely mixed state. However, if they can communicate, Alice measures her share and communicates the result to Bob then, Bob knows the state of his qubit without having to measure it. ]
27 Quantum decoherence p. 27/2 Quantum decoherence Back to decoherence. What actually happens during a measurement? There is a quantum object that interacts with some macroscopic apparatus in such a way that the apparatus produces a signal which states the outcome of the measurement. In other words, there is an interaction between a quantum system, a macroscopic apparatus and the environment where the wave function becomes correlated (entangled) with both the environment, the apparatus and, moreover, the environment is inaccessible (traced) to observers.
28 Quantum decoherence p. 28/2 Quantum decoherence Formally, we have a state that represents a system S: ψ = α 0 + β 1 and a measurement apparatus A s.t. 0 A 0 0 A 0 and 1 A 0 1 A 1 and an environment E in the state ǫ.
29 Quantum decoherence p. 29/2 Quantum decoherence The joint system is, before the measurement in the state ψ A 0 ǫ. The measurement process is given by (α 0 +β 1 ) A 0 ǫ α 0 A 0 ǫ 0 +β 1 A 1 ǫ 1 s.t. ǫ 0 ǫ 1 = 0. As I said before, the environment is inaccessible to the observer thus, the reduced density operator is ρ SA = Tr E (ρ SAE ) = α 2 0 A 0 0 A 0 + β 2 1 A 1 1 A 1 Which contains only classical correlations.
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics
 Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix
 PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
Ph 219/CS 219. Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006
 1 Ph 219/CS 219 Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006 1.1 How far apart are two quantum states? Consider two quantum states described by density operators ρ and ρ in an N-dimensional Hilbert space, and
1 Ph 219/CS 219 Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006 1.1 How far apart are two quantum states? Consider two quantum states described by density operators ρ and ρ in an N-dimensional Hilbert space, and
Ensembles and incomplete information
 p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
Quantum Measurements: some technical background
 Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
b) (5 points) Give a simple quantum circuit that transforms the state
 C/CS/Phy191 Midterm Quiz Solutions October 0, 009 1 (5 points) Short answer questions: a) (5 points) Let f be a function from n bits to 1 bit You have a quantum circuit U f for computing f If you wish
C/CS/Phy191 Midterm Quiz Solutions October 0, 009 1 (5 points) Short answer questions: a) (5 points) Let f be a function from n bits to 1 bit You have a quantum circuit U f for computing f If you wish
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871
 Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871 Lecture 9 (2017) Jon Yard QNC 3126 jyard@uwaterloo.ca http://math.uwaterloo.ca/~jyard/qic710 1 More state distinguishing
Introduction to Quantum Information Processing QIC 710 / CS 768 / PH 767 / CO 681 / AM 871 Lecture 9 (2017) Jon Yard QNC 3126 jyard@uwaterloo.ca http://math.uwaterloo.ca/~jyard/qic710 1 More state distinguishing
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Private quantum subsystems and error correction
 Private quantum subsystems and error correction Sarah Plosker Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Brandon University September 26, 2014 Outline 1 Classical Versus Quantum Setting Classical Setting
Private quantum subsystems and error correction Sarah Plosker Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Brandon University September 26, 2014 Outline 1 Classical Versus Quantum Setting Classical Setting
Lecture 14: Quantum information revisited
 CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 4: Quantum information revisited March 4, 006 So far, this course has focused almost entirely on quantum algorithms The next
CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 4: Quantum information revisited March 4, 006 So far, this course has focused almost entirely on quantum algorithms The next
Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable,
 Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable, A qubit: a sphere of values, which is spanned in projective sense by two quantum
Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable, A qubit: a sphere of values, which is spanned in projective sense by two quantum
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
Compression and entanglement, entanglement transformations
 PHYSICS 491: Symmetry and Quantum Information April 27, 2017 Compression and entanglement, entanglement transformations Lecture 8 Michael Walter, Stanford University These lecture notes are not proof-read
PHYSICS 491: Symmetry and Quantum Information April 27, 2017 Compression and entanglement, entanglement transformations Lecture 8 Michael Walter, Stanford University These lecture notes are not proof-read
Hilbert Space, Entanglement, Quantum Gates, Bell States, Superdense Coding.
 CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics. 1 Inner Products and Outer Products for Single Particle States
 Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics Outer Products, Operators, Density Matrices In order to explore the complexity of many particle systems a different way to represent multiparticle states
Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics Outer Products, Operators, Density Matrices In order to explore the complexity of many particle systems a different way to represent multiparticle states
Quantum Computing Lecture 3. Principles of Quantum Mechanics. Anuj Dawar
 Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
The Framework of Quantum Mechanics
 The Framework of Quantum Mechanics We now use the mathematical formalism covered in the last lecture to describe the theory of quantum mechanics. In the first section we outline four axioms that lie at
The Framework of Quantum Mechanics We now use the mathematical formalism covered in the last lecture to describe the theory of quantum mechanics. In the first section we outline four axioms that lie at
The Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Pt. 1
 The Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Pt. 1 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 15, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University The Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Pt. 1 February 15, 2018
The Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Pt. 1 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 15, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University The Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Pt. 1 February 15, 2018
Lecture: Quantum Information
 Lecture: Quantum Information Transcribed by: Crystal Noel and Da An (Chi Chi) November 10, 016 1 Final Proect Information Find an issue related to class you are interested in and either: read some papers
Lecture: Quantum Information Transcribed by: Crystal Noel and Da An (Chi Chi) November 10, 016 1 Final Proect Information Find an issue related to class you are interested in and either: read some papers
Lectures 1 and 2: Axioms for Quantum Theory
 Lectures 1 and 2: Axioms for Quantum Theory Joseph Emerson Course: AMATH 900/AMATH 495/PHYS 490 Foundations and Interpretations of Quantum Theory Course Instructors: Joseph Emerson and Ray Laflamme Hosted
Lectures 1 and 2: Axioms for Quantum Theory Joseph Emerson Course: AMATH 900/AMATH 495/PHYS 490 Foundations and Interpretations of Quantum Theory Course Instructors: Joseph Emerson and Ray Laflamme Hosted
Chapter 5. Density matrix formalism
 Chapter 5 Density matrix formalism In chap we formulated quantum mechanics for isolated systems. In practice systems interect with their environnement and we need a description that takes this feature
Chapter 5 Density matrix formalism In chap we formulated quantum mechanics for isolated systems. In practice systems interect with their environnement and we need a description that takes this feature
Quantum Information Types
 qitd181 Quantum Information Types Robert B. Griffiths Version of 6 February 2012 References: R. B. Griffiths, Types of Quantum Information, Phys. Rev. A 76 (2007) 062320; arxiv:0707.3752 Contents 1 Introduction
qitd181 Quantum Information Types Robert B. Griffiths Version of 6 February 2012 References: R. B. Griffiths, Types of Quantum Information, Phys. Rev. A 76 (2007) 062320; arxiv:0707.3752 Contents 1 Introduction
Lecture 20: Bell inequalities and nonlocality
 CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 0: Bell inequalities and nonlocality April 4, 006 So far in the course we have considered uses for quantum information in the
CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 0: Bell inequalities and nonlocality April 4, 006 So far in the course we have considered uses for quantum information in the
Borromean Entanglement Revisited
 Borromean Entanglement Revisited Ayumu SUGITA Abstract An interesting analogy between quantum entangled states and topological links was suggested by Aravind. In particular, he emphasized a connection
Borromean Entanglement Revisited Ayumu SUGITA Abstract An interesting analogy between quantum entangled states and topological links was suggested by Aravind. In particular, he emphasized a connection
Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo
 CS 497 Frontiers of Computer Science Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture of http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cleve/cs497-f7 Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum
CS 497 Frontiers of Computer Science Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture of http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cleve/cs497-f7 Richard Cleve David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science Institute for Quantum
When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection?
 When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection? Robin Hanson Department of Economics George Mason University August 9, 2001 Abstract Deviations from exact decoherence make little difference
When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection? Robin Hanson Department of Economics George Mason University August 9, 2001 Abstract Deviations from exact decoherence make little difference
De-coherence and transition from Quantum to Classical
 De-coherence and transition from Quantum to Classical Ravi Mohan Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee March 22, 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Correlations and Measurements 3 Missing Information and Decoherence
De-coherence and transition from Quantum to Classical Ravi Mohan Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee March 22, 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Correlations and Measurements 3 Missing Information and Decoherence
QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING THEOREM p.1/36
 QUANTUM INFORMATION - THE NO-HIDING THEOREM Arun K Pati akpati@iopb.res.in Instititute of Physics, Bhubaneswar-751005, Orissa, INDIA and Th. P. D, BARC, Mumbai-400085, India QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING
QUANTUM INFORMATION - THE NO-HIDING THEOREM Arun K Pati akpati@iopb.res.in Instititute of Physics, Bhubaneswar-751005, Orissa, INDIA and Th. P. D, BARC, Mumbai-400085, India QUANTUM INFORMATION -THE NO-HIDING
SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION
 SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION YAQIAO LI This note tries to rephrase mathematically superdense coding and quantum teleportation explained in [] Section.3 and.3.7, respectively (as if I understood
SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION YAQIAO LI This note tries to rephrase mathematically superdense coding and quantum teleportation explained in [] Section.3 and.3.7, respectively (as if I understood
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity
 Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity Mark M. Wilde The quantum capacity theorem is one of the most important theorems in quantum hannon theory. It is a fundamentally quantum theorem
Lecture 6: Quantum error correction and quantum capacity Mark M. Wilde The quantum capacity theorem is one of the most important theorems in quantum hannon theory. It is a fundamentally quantum theorem
Does Quantum Measurement Violate the Conservation of Angular Momentum? A Paradox Resolved Rick Bradford, 6/12/16
 Does Quantum Measurement Violate the Conservation of Angular Momentum? A Parado Resolved Rick Bradford, 6//6 Presented here is a parado which took some considerable effort to resolve - and I don't think
Does Quantum Measurement Violate the Conservation of Angular Momentum? A Parado Resolved Rick Bradford, 6//6 Presented here is a parado which took some considerable effort to resolve - and I don't think
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation
 MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels
 JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
Unitary evolution: this axiom governs how the state of the quantum system evolves in time.
 CS 94- Introduction Axioms Bell Inequalities /7/7 Spring 7 Lecture Why Quantum Computation? Quantum computers are the only model of computation that escape the limitations on computation imposed by the
CS 94- Introduction Axioms Bell Inequalities /7/7 Spring 7 Lecture Why Quantum Computation? Quantum computers are the only model of computation that escape the limitations on computation imposed by the
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history
 Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
Stochastic Histories. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 8 Stochastic Histories 8.1 Introduction Despite the fact that classical mechanics employs deterministic dynamical laws, random dynamical processes often arise in classical physics, as well as in
Chapter 8 Stochastic Histories 8.1 Introduction Despite the fact that classical mechanics employs deterministic dynamical laws, random dynamical processes often arise in classical physics, as well as in
Decoherence and the Classical Limit
 Chapter 26 Decoherence and the Classical Limit 26.1 Introduction Classical mechanics deals with objects which have a precise location and move in a deterministic way as a function of time. By contrast,
Chapter 26 Decoherence and the Classical Limit 26.1 Introduction Classical mechanics deals with objects which have a precise location and move in a deterministic way as a function of time. By contrast,
CS257 Discrete Quantum Computation
 CS57 Discrete Quantum Computation John E Savage April 30, 007 Lect 11 Quantum Computing c John E Savage Classical Computation State is a vector of reals; e.g. Booleans, positions, velocities, or momenta.
CS57 Discrete Quantum Computation John E Savage April 30, 007 Lect 11 Quantum Computing c John E Savage Classical Computation State is a vector of reals; e.g. Booleans, positions, velocities, or momenta.
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing When Quantum Computers Fall Apart
 CSE 599d - Quantum Comuting When Quantum Comuters Fall Aart Dave Bacon Deartment of Comuter Science & Engineering, University of Washington In this lecture we are going to begin discussing what haens to
CSE 599d - Quantum Comuting When Quantum Comuters Fall Aart Dave Bacon Deartment of Comuter Science & Engineering, University of Washington In this lecture we are going to begin discussing what haens to
arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 7 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 7 Apr 2015 arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 7 Apr 2015](/thumbs/72/66522565.jpg) Statistical Mechanics Derived From Quantum Mechanics arxiv:1501.05402v2 [hep-th] 7 Apr 2015 Yu-Lei Feng 1 and Yi-Xin Chen 1 1 Zhejiang Institute of Modern Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027,
Statistical Mechanics Derived From Quantum Mechanics arxiv:1501.05402v2 [hep-th] 7 Apr 2015 Yu-Lei Feng 1 and Yi-Xin Chen 1 1 Zhejiang Institute of Modern Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027,
Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann
 Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Theoretische Physik III Summer school Bleubeuren July 014 Contents 1 Quantum Mechanics...........................
Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Theoretische Physik III Summer school Bleubeuren July 014 Contents 1 Quantum Mechanics...........................
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Density Matrices. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 15 Density Matrices 15.1 Introduction Density matrices are employed in quantum mechanics to give a partial description of a quantum system, one from which certain details have been omitted. For
Chapter 15 Density Matrices 15.1 Introduction Density matrices are employed in quantum mechanics to give a partial description of a quantum system, one from which certain details have been omitted. For
Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation
 Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics. A Modern View
 Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics A Modern View It s time to make decoherence mainstream QM is ~90 years old But it is still taught like the 1930s Modern textbooks still ignore measurement
Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics A Modern View It s time to make decoherence mainstream QM is ~90 years old But it is still taught like the 1930s Modern textbooks still ignore measurement
THE OBJECTIVE PAST OF
 THE OBJECTIVE PAST OF A QUANTUM UNIVERSE: REDUNDANT RECORDS OF CONSISTENT HISTORIES C. Jess Riedel with Charles Bennett, Wojciech Zurek, and Michael Zwolak arxiv:1312.0331 IBM Watson Research Lab arxiv:1310.4473
THE OBJECTIVE PAST OF A QUANTUM UNIVERSE: REDUNDANT RECORDS OF CONSISTENT HISTORIES C. Jess Riedel with Charles Bennett, Wojciech Zurek, and Michael Zwolak arxiv:1312.0331 IBM Watson Research Lab arxiv:1310.4473
Quantum Information Theory
 Quantum Information Theory Lectures 15 17 Quantum dynamics. III V. Superoperators and completely positive maps. 2002 November 5; modified 2005 September 30 and 2009 February 3 and 2014 October 3 1 Measurement
Quantum Information Theory Lectures 15 17 Quantum dynamics. III V. Superoperators and completely positive maps. 2002 November 5; modified 2005 September 30 and 2009 February 3 and 2014 October 3 1 Measurement
Chapter 2: Quantum Entanglement
 Y. D. Chong (018 PH4401: Quantum Mechanics III Chapter : Quantum Entanglement I. QUANTUM MECHANICS OF MULTI-PARTICLE SYSTEMS So far, we have studied quantum mechanical systems consisting of single particles.
Y. D. Chong (018 PH4401: Quantum Mechanics III Chapter : Quantum Entanglement I. QUANTUM MECHANICS OF MULTI-PARTICLE SYSTEMS So far, we have studied quantum mechanical systems consisting of single particles.
The tilde map can be rephased as we please; i.e.,
 To: C. Fuchs, K. Manne, J. Renes, and R. Schack From: C. M. Caves Subject: Linear dynamics that preserves maximal information is Hamiltonian 200 January 7; modified 200 June 23 to include the relation
To: C. Fuchs, K. Manne, J. Renes, and R. Schack From: C. M. Caves Subject: Linear dynamics that preserves maximal information is Hamiltonian 200 January 7; modified 200 June 23 to include the relation
The query register and working memory together form the accessible memory, denoted H A. Thus the state of the algorithm is described by a vector
 1 Query model In the quantum query model we wish to compute some function f and we access the input through queries. The complexity of f is the number of queries needed to compute f on a worst-case input
1 Query model In the quantum query model we wish to compute some function f and we access the input through queries. The complexity of f is the number of queries needed to compute f on a worst-case input
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture 2
 Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing
 Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
Quantum mechanics in one hour
 Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
Quantum Mechanics C (130C) Winter 2014 Final exam
 University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Quantum Mechanics C (130C Winter 014 Final exam Please remember to put your name on your exam booklet. This is a closed-book
University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Quantum Mechanics C (130C Winter 014 Final exam Please remember to put your name on your exam booklet. This is a closed-book
Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products
 CS903: Quantum computation and Information theory (Special Topics In TCS) Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products This lecture will formalize many of the notions introduced informally in the second
CS903: Quantum computation and Information theory (Special Topics In TCS) Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products This lecture will formalize many of the notions introduced informally in the second
Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 2 Solutions
 University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 39/139 Spring 018 Assignment Solutions Due 1:30pm Monday, April 16, 018 1. Classical circuits brain-warmer. (a) Show
University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 39/139 Spring 018 Assignment Solutions Due 1:30pm Monday, April 16, 018 1. Classical circuits brain-warmer. (a) Show
Principles of Quantum Mechanics Pt. 2
 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Pt. 2 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 9, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Principles of Quantum Mechanics Pt. 2 February 9, 2017 1 / 13 The
Principles of Quantum Mechanics Pt. 2 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 9, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Principles of Quantum Mechanics Pt. 2 February 9, 2017 1 / 13 The
Quantum Noise. Michael A. Nielsen. University of Queensland
 Quantum Noise Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To introduce a tool the density matrix that is used to describe noise in quantum systems, and to give some examples. Density matrices
Quantum Noise Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To introduce a tool the density matrix that is used to describe noise in quantum systems, and to give some examples. Density matrices
State. Bell State Exercises
 Bell State Exercises Frank Rioux he Bell states are maximally entangled superpositions of two-particle states. Consider two spin-/ particles created in the same event. here are four maximally entangled
Bell State Exercises Frank Rioux he Bell states are maximally entangled superpositions of two-particle states. Consider two spin-/ particles created in the same event. here are four maximally entangled
. Here we are using the standard inner-product over C k to define orthogonality. Recall that the inner-product of two vectors φ = i α i.
 CS 94- Hilbert Spaces, Tensor Products, Quantum Gates, Bell States 1//07 Spring 007 Lecture 01 Hilbert Spaces Consider a discrete quantum system that has k distinguishable states (eg k distinct energy
CS 94- Hilbert Spaces, Tensor Products, Quantum Gates, Bell States 1//07 Spring 007 Lecture 01 Hilbert Spaces Consider a discrete quantum system that has k distinguishable states (eg k distinct energy
Quantum Mechanics II: Examples
 Quantum Mechanics II: Examples Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To apply the principles introduced in the last lecture to some illustrative examples: superdense coding, and quantum
Quantum Mechanics II: Examples Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To apply the principles introduced in the last lecture to some illustrative examples: superdense coding, and quantum
A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories. Todd A. Brun University of Southern California
 A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories Todd A. Brun University of Southern California Outline 1. Review projective and generalized measurements. 2. A simple model of indirect measurement. 3. Weak measurements--jump-like
A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories Todd A. Brun University of Southern California Outline 1. Review projective and generalized measurements. 2. A simple model of indirect measurement. 3. Weak measurements--jump-like
Density Operators and Ensembles
 qitd422 Density Operators and Ensembles Robert B. Griffiths Version of 30 January 2014 Contents 1 Density Operators 1 1.1 Introduction.............................................. 1 1.2 Partial trace..............................................
qitd422 Density Operators and Ensembles Robert B. Griffiths Version of 30 January 2014 Contents 1 Density Operators 1 1.1 Introduction.............................................. 1 1.2 Partial trace..............................................
arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 5 Jun 2015
![arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 5 Jun 2015 arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 5 Jun 2015](/thumbs/88/117676319.jpg) Entanglement and swap of quantum states in two qubits Takaya Ikuto and Satoshi Ishizaka Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Higashihiroshima, 739-8521, Japan (Dated:
Entanglement and swap of quantum states in two qubits Takaya Ikuto and Satoshi Ishizaka Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Higashihiroshima, 739-8521, Japan (Dated:
Physics 4022 Notes on Density Matrices
 Physics 40 Notes on Density Matrices Definition: For a system in a definite normalized state ψ > the density matrix ρ is ρ = ψ >< ψ 1) From Eq 1 it is obvious that in the basis defined by ψ > and other
Physics 40 Notes on Density Matrices Definition: For a system in a definite normalized state ψ > the density matrix ρ is ρ = ψ >< ψ 1) From Eq 1 it is obvious that in the basis defined by ψ > and other
Entanglement Measures and Monotones
 Entanglement Measures and Monotones PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University March 30, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Entanglement Measures and Monotones March 30, 2017 1 / 11 Quantifying
Entanglement Measures and Monotones PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University March 30, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Entanglement Measures and Monotones March 30, 2017 1 / 11 Quantifying
This is the important completeness relation,
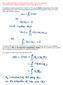 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection?
 When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection? arxiv:quant-ph/0108070v1 14 Aug 2001 Robin Hanson Department of Economics George Mason University August 9, 2001 Abstract Deviations from
When Worlds Collide: Quantum Probability From Observer Selection? arxiv:quant-ph/0108070v1 14 Aug 2001 Robin Hanson Department of Economics George Mason University August 9, 2001 Abstract Deviations from
Asymptotic Pure State Transformations
 Asymptotic Pure State Transformations PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University April 18, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Asymptotic Pure State Transformations April 18, 2017 1 / 15 Entanglement
Asymptotic Pure State Transformations PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University April 18, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Asymptotic Pure State Transformations April 18, 2017 1 / 15 Entanglement
3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D
 3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D 3.1 Introduction Last time, we derived the time dependent Schrödinger equation, starting from three basic postulates: 1) The time evolution of a state can be expressed as a unitary
3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D 3.1 Introduction Last time, we derived the time dependent Schrödinger equation, starting from three basic postulates: 1) The time evolution of a state can be expressed as a unitary
Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6
 University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6 Due 12:30pm Monday, May 14, 2018 1. Brainwarmers on Kraus operators. (a) Check that
University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Physics 239/139 Spring 2018 Assignment 6 Due 12:30pm Monday, May 14, 2018 1. Brainwarmers on Kraus operators. (a) Check that
CS/Ph120 Homework 1 Solutions
 CS/Ph0 Homework Solutions October, 06 Problem : State discrimination Suppose you are given two distinct states of a single qubit, ψ and ψ. a) Argue that if there is a ϕ such that ψ = e iϕ ψ then no measurement
CS/Ph0 Homework Solutions October, 06 Problem : State discrimination Suppose you are given two distinct states of a single qubit, ψ and ψ. a) Argue that if there is a ϕ such that ψ = e iϕ ψ then no measurement
Entanglement and Quantum Teleportation
 Entanglement and Quantum Teleportation Stephen Bartlett Centre for Advanced Computing Algorithms and Cryptography Australian Centre of Excellence in Quantum Computer Technology Macquarie University, Sydney,
Entanglement and Quantum Teleportation Stephen Bartlett Centre for Advanced Computing Algorithms and Cryptography Australian Centre of Excellence in Quantum Computer Technology Macquarie University, Sydney,
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
Structure of Unital Maps and the Asymptotic Quantum Birkhoff Conjecture. Peter Shor MIT Cambridge, MA Joint work with Anand Oza and Dimiter Ostrev
 Structure of Unital Maps and the Asymptotic Quantum Birkhoff Conjecture Peter Shor MIT Cambridge, MA Joint work with Anand Oza and Dimiter Ostrev The Superposition Principle (Physicists): If a quantum
Structure of Unital Maps and the Asymptotic Quantum Birkhoff Conjecture Peter Shor MIT Cambridge, MA Joint work with Anand Oza and Dimiter Ostrev The Superposition Principle (Physicists): If a quantum
Basic concepts from quantum theory
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games
 CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games Scribe: Zeyu Guo In the first lecture, we saw three equivalent variants of the classical PCP theorems in terms of CSP, proof checking,
CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games Scribe: Zeyu Guo In the first lecture, we saw three equivalent variants of the classical PCP theorems in terms of CSP, proof checking,
An Introduction to Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
 An to and Graduate Group in Applied Math University of California, Davis March 13, 009 A bit of history Benioff 198 : First paper published mentioning quantum computing Feynman 198 : Use a quantum computer
An to and Graduate Group in Applied Math University of California, Davis March 13, 009 A bit of history Benioff 198 : First paper published mentioning quantum computing Feynman 198 : Use a quantum computer
10 Interpreting Quantum Mechanics
 10 Interpreting Quantum Mechanics In this final chapter, I want to explore the process of measurement in quantum mechanics. 10.1 The Density Operator To get started, we must first come clean about an unrealistic
10 Interpreting Quantum Mechanics In this final chapter, I want to explore the process of measurement in quantum mechanics. 10.1 The Density Operator To get started, we must first come clean about an unrealistic
Open quantum systems
 Chapter 4 Open quantum systems 4. Quantum operations Let s go back for a second to the basic postulates of quantum mechanics. Recall that when we first establish the theory, we begin by postulating that
Chapter 4 Open quantum systems 4. Quantum operations Let s go back for a second to the basic postulates of quantum mechanics. Recall that when we first establish the theory, we begin by postulating that
CS286.2 Lecture 13: Quantum de Finetti Theorems
 CS86. Lecture 13: Quantum de Finetti Theorems Scribe: Thom Bohdanowicz Before stating a quantum de Finetti theorem for density operators, we should define permutation invariance for quantum states. Let
CS86. Lecture 13: Quantum de Finetti Theorems Scribe: Thom Bohdanowicz Before stating a quantum de Finetti theorem for density operators, we should define permutation invariance for quantum states. Let
Einselection without pointer states -
 Einselection without pointer states Einselection without pointer states - Decoherence under weak interaction Christian Gogolin Universität Würzburg 2009-12-16 C. Gogolin Universität Würzburg 2009-12-16
Einselection without pointer states Einselection without pointer states - Decoherence under weak interaction Christian Gogolin Universität Würzburg 2009-12-16 C. Gogolin Universität Würzburg 2009-12-16
HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes
 HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes Outline: 1. Homework 4 (discuss reading assignment) 2. The Measurement Problem 3. GRW theory Handouts: None Homework: Yes Vocabulary/Equations:
HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes Outline: 1. Homework 4 (discuss reading assignment) 2. The Measurement Problem 3. GRW theory Handouts: None Homework: Yes Vocabulary/Equations:
Redundant Information and the Quantum-Classical Transition
 University of California, Santa Barbara 22 August 2012 Redundant Information and the Quantum-Classical Transition C. Jess Riedel Acting advisor: Wojciech H. Zurek Theoretical Division Los Alamos National
University of California, Santa Barbara 22 August 2012 Redundant Information and the Quantum-Classical Transition C. Jess Riedel Acting advisor: Wojciech H. Zurek Theoretical Division Los Alamos National
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes
 CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last lecture we learned of the quantum error
CSE 599d - Quantum Computing Stabilizer Quantum Error Correcting Codes Dave Bacon Department of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington In the last lecture we learned of the quantum error
Detection of photonic Bell states
 LECTURE 3 Detection of photonic Bell states d a c Beam-splitter transformation: b ˆB ˆB EXERCISE 10: Derive these three relations V a H a ˆB Detection: or V b H b or Two photons detected in H a, H b, V
LECTURE 3 Detection of photonic Bell states d a c Beam-splitter transformation: b ˆB ˆB EXERCISE 10: Derive these three relations V a H a ˆB Detection: or V b H b or Two photons detected in H a, H b, V
Unitary Dynamics and Quantum Circuits
 qitd323 Unitary Dynamics and Quantum Circuits Robert B. Griffiths Version of 20 January 2014 Contents 1 Unitary Dynamics 1 1.1 Time development operator T.................................... 1 1.2 Particular
qitd323 Unitary Dynamics and Quantum Circuits Robert B. Griffiths Version of 20 January 2014 Contents 1 Unitary Dynamics 1 1.1 Time development operator T.................................... 1 1.2 Particular
Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 3: Superdense coding, quantum circuits, and partial measurements
 CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 3: Superdense coding, quantum circuits, and partial measurements Superdense Coding January 4, 006 Imagine a situation where two
CPSC 59/69: Quantum Computation John Watrous, University of Calgary Lecture 3: Superdense coding, quantum circuits, and partial measurements Superdense Coding January 4, 006 Imagine a situation where two
Operator Quantum Error Correcting Codes
 Operator Quantum Error Correcting Codes Vlad Gheorghiu Department of Physics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, U.S.A. June 18, 2008 Vlad Gheorghiu (CMU) Operator Quantum Error Correcting
Operator Quantum Error Correcting Codes Vlad Gheorghiu Department of Physics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, U.S.A. June 18, 2008 Vlad Gheorghiu (CMU) Operator Quantum Error Correcting
Indeterminate-length quantum coding
 Indeterminate-length quantum coding arxiv:quant-ph/0011014v1 2 Nov 2000 Benjamin Schumacher (1) and Michael D. Westmoreland (2) February 1, 2008 (1) Department of Physics, Kenyon College, Gambier, OH 43022
Indeterminate-length quantum coding arxiv:quant-ph/0011014v1 2 Nov 2000 Benjamin Schumacher (1) and Michael D. Westmoreland (2) February 1, 2008 (1) Department of Physics, Kenyon College, Gambier, OH 43022
Quantum Teleportation Pt. 3
 Quantum Teleportation Pt. 3 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University March 7, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Quantum Teleportation Pt. 3 March 7, 2017 1 / 9 A Bit of History on Teleportation
Quantum Teleportation Pt. 3 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University March 7, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Quantum Teleportation Pt. 3 March 7, 2017 1 / 9 A Bit of History on Teleportation
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Dirac Notation Formalism of Quantum Mechanics We can use a shorthand notation for the normalization integral I = "! (r,t) 2 dr = "! * (r,t)! (r,t) dr =!! The state! is called a ket. The complex conjugate
Dirac Notation Formalism of Quantum Mechanics We can use a shorthand notation for the normalization integral I = "! (r,t) 2 dr = "! * (r,t)! (r,t) dr =!! The state! is called a ket. The complex conjugate
Quantum information and quantum computing
 Middle East Technical University, Department of Physics January 7, 009 Outline Measurement 1 Measurement 3 Single qubit gates Multiple qubit gates 4 Distinguishability 5 What s measurement? Quantum measurement
Middle East Technical University, Department of Physics January 7, 009 Outline Measurement 1 Measurement 3 Single qubit gates Multiple qubit gates 4 Distinguishability 5 What s measurement? Quantum measurement
Consistent Histories. Chapter Chain Operators and Weights
 Chapter 10 Consistent Histories 10.1 Chain Operators and Weights The previous chapter showed how the Born rule can be used to assign probabilities to a sample space of histories based upon an initial state
Chapter 10 Consistent Histories 10.1 Chain Operators and Weights The previous chapter showed how the Born rule can be used to assign probabilities to a sample space of histories based upon an initial state
