Finding the Planck Length Independent of Newton s Gravitational Constant and the Planck Constant The Compton Clock Model of Matter
|
|
|
- Molly Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Finding the Plank Length Independent of Newton s Gravitational Constant and the Plank Constant The Compton Clok Model of Matter Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sienes September 9, 08 In modern physis, it is assumed that the Plank length is a derived onstant from Newton s gravitational onstant, the Plank onstant and the speed of light, = G 3 This was first disovered by Max Plank in 899 We suggest a way to find the Plank length independent of any knowledge of Newton s gravitational onstant or the Plank onstant, but still dependent on the speed of light (diretly or indiretly) Key words: Plank length, Plank onstant, Newton s gravitational onstant, Compton frequeny, Shwarzshild radius I INTRODUCTION In 899, Max Plank [, ] introdued what he alled the natural units : the Plank mass, the Plank length, the Plank time, and the Plank energy He derived these units using dimensional analysis, assuming that Newton s gravitational onstant, the Plank onstant, and the speed of light were the most important universal onstants The Max Plank formula for the Plank length is given by = G 3 () In other words, it seems that we need to know Newton s gravitational onstant G and the Plank onstant and the speed of light to find the Plank length It has therefore been assumed that the Plank length is a derived onstant and that Newton s gravitational onstant is a more fundamental onstant, a view we will hallenge here II PLANCK LENGTH INDEPENDENT OF G AND First, find the redued Compton wavelength of an eletron by Compton sattering The redued Compton frequeny is then given by f C = λe () where f C stands for the redued Compton frequeny, and λ e is the redued Compton wavelength of the eletron Further, the Cylotron frequeny is linearly proportional to the redued Compton frequeny Conduting a ylotron experiment, one an find the redued Compton frequeny ratio between the proton and the eletron For example, [3] measured it to be about λ P λ e = f C,P f C,e = (76) (3) In fat, [3] measured the Proton eletron mass ratio this way, but the redued Compton frequeny is only a deeper aspet of mass, that has reently also been more or less onfirmed by experimental researh Theoretially, it is no surprise that f C,P f C,e = m P m e We simply laim that a simpler and deeper way to express mass is through the redued Compton frequeny in matter; see [4] Next, from the Shwarzshild metri [5, 6] solution of the Einstein field equation [7], we have the well-known formula for the Shwarzshild radius r s = GM (4) Haug [4] reently pointed out that the Shwarzshild radius is also equal to twie the redued Compton frequeny of the gravity objet over a time period of one Plank seond, multiplied by the Plank length That is, we must have r s = GM = f C t p = λ = l p λ (5) This means that the Shwarzshild radius ontains the Plank length Still, is there a way to extrat this without knowing the mass and Newton s gravitational onstant? Haug [8] reently showed that the Shwarzshild radius an be measured in a series of ways with no knowledge of the mass size or Newton s gravitational onstant For example, the Shwarzshild radius of the earth an be found from the gravitational aeleration field, the speed of light and the radius of the earth
2 r s = gr (6) where g is the gravitational aeleration and R is the radius of the gravity objet For smaller size objets, we an find the Shwarzshild radius using a Cavendish apparatus; it is given by r s = L4π R θ T (7) where L is the distane between the small balls and R is the distane, enter to enter, between the small and large ball T is the natural resonant osillation period of a torsion balane, θ is the defletion angle of the balane This is somewhat different than the known use of a Cavendish apparatus used to find the weight of the Earth or to find G, where one needs to know the mass size (weight) of the lead balls Again, we do not need to know the mass size in the normal sense nor do we need to know anything about Newton s gravitational onstant to find the Shwarzshild radius So, in pratie, take a lump of matter, divide it in two and make two idential balls of it Plae the two balls in the Cavendish apparatus In addition, one needs two muh smaller balls By measuring T, L, R and θ, we know the Shwarzshild radius of the large balls in the apparatus Assume that we measure a Shwarzshild radius of meters Next, we find the redued Compton frequeny of an eletron: it is f C,e = λe (8) Next, we use the ylotron to find the redued Compton frequeny of a Proton f C,P = λe (9) Next, we break the large balls up into piees and ount the number of protons in it Or, alternatively, we an pak a known amount of atoms together in a ball, and keep trak of the number of protons This is, in theory at least, possible Assume that we ount approximately protons in the mass, and we next divide it into two The redued Compton frequeny is additive for a larger mass, so based on the proton ount the redued Compton frequeny in eah of the large balls must be approximately f C = (0) Remember that the Shwarzshild radius that we measured was m To find the Plank length, we an use the following formula This gives us r s = f C r s = () f C m This also means that the Plank length is always the square root of half the Shwarzshild radius times the redued Compton wavelength of the mass = r s λ () The whole method requires no knowledge of traditional mass size measures, whih also means no knowledge of the Plank onstant, and no knowledge of Newton s gravitational onstant G III THE PLANCK TIME AND THE PLANCK MASS After we have found the Plank length, ompletely independent of the Plank onstant and the gravitational onstant, we an naturally easily find the Plank time as it is simply the Plank length divided by the speed of light However, the Plank mass and all masses at the deepest level an be desribed as Compton frequeny per Plank seond This means that the Plank mass in this view is ˆm p = f C t p = = (3) That is, the Plank mass is one in terms of frequeny per Plank seond That mass is related to Compton time has also been supported in reent experimental researh Dole and Perali [9] onlude that the rest-mass of a partile is assoiated to a rest periodiity known as Compton periodiity Additionally, [0] onluded that This diretly demonstrates the onnetion between time and mass In our view, the redued Compton frequeny hidden inside matter is the key to really understand how to extrat the Plank length independent of the Plank onstant and to understand mass and gravity from a deeper perspetive
3 3 IV AN ALTERNATIVE WAY THAT IS INDEPENDENT OF G BUT DEPENDENT ON KNOWING At a deeper level then, the Plank onstant must somehow ontain an embedded redued Compton frequeny for one kg The redued Compton wavelength for kg is λ = kg = The redued Compton frequeny of kg is therefore f C,kg = kg = kg (4) (5) That is, is simply the frequeny of kg Next, let us make two balls with weight kg and also two muh smaller balls to use in a Cavendish apparatus Next, we measure the Shwarzshild radius using the apparatus There is no need to know the Plank onstant or the weight of the balls to find the Shwarzshild radius It is when we are going to extrat the Plank length from the Shwarzshild radius that we, in this method, will utilize the Plank onstant This is beause the Plank onstant is needed to extrat the redued Compton frequeny in the matter when working with kg In the setion above, we had to ount the number of protons, but if working from kg instead we an use the Plank onstant to extrat the redued Compton frequeny The Plank length from the measured Shwarzshild radius in kg is simply equal to = r s,kg f C m (6) s It is also worth mentioning that the Plank frequeny is given by the redued Compton frequeny of the matter in question multiplied by the Plank length divided by half the Shwarzshild radius f C,p = f C r s = (7) V RELATION TO MASS AS KG In the above setions, we have shown that we an find the Plank length independent of any knowledge of Newton s gravitational onstant We have also laimed that the Plank mass ould simply be desribed by its Compton frequeny It is only if we want to onvert the Plank mass frequeny per Plank seond into kg that we really need the Plank onstant Any mass in kg an be found if we know the redued Compton wavelength of the mass in question m = λ (8) We have found the Plank length independent of G and, but need the Plank onstant to find the Plank mass in terms of kg This gives m p = = kg (9) The redued Compton frequeny of kg is, as we laimed earlier in this paper, f C,kg = kg = (0) This means the Plank onstant is equal to = () Now let us replae this into the mass equation m = λ = λ = λ = f C f C,kg () That is, any mass in kg form is simply the redued Compton frequeny of the mass in question divided by the redued Compton frequeny of kg So, the Plank onstant is simply needed to make our mass unit into a kg measure/definition of mass An alternative would be to desribe mass as the redued Compton frequeny over one Plank seond This means that all rest-masses an now be simply desribed as ˆm = f C t p = λ l = p λ λ (3) Any mass smaller than a Plank mass will then somehow be probabilisti as it means a frequeny of less than one per Plank seond This ould explain why quantum mehanis is neessary for the quantum world, but not in the marosopi world; see [4] for more details along these lines
4 4 VI WHY NEWTON S GRAVITATIONAL CONSTANT IS A COMPOSITE CONSTANT Haug has, in a series of papers [ 3], suggested that Newton s gravitational onstant is a omposite onstant of the form G = l p 3 (4) whih is basially the same as the MCulloh [4] onstant m sine m p = p Here, we will list some reasons that seem to support the fat that Newton s gravitational onstant is a Composite onstant rather than a deep fundamental onstant Already, when looking at the output units of Newton s gravitational onstant m 3 kg s, one should beome suspiious that this must be a omposite onstant It is highly unlikely that the universe invented something fundamental that has some omplex units Muh more likely is that the Plank length is something very fundamental Everyone an intuitively understand, to a ertain extent, what a length is One an also, to a large degree, understand what the speed of light is: it is how far the light travels in a given time period The Plank length is the shortest possible redued Compton wavelength The Plank length an be found ompletely independent of any knowledge of Newton s gravitational onstant; it an also be found independent of the Plank onstant, as shown in this paper The Plank onstant in the Max Plank formula, in our view, is atually needed in that formula to anel out the Plank onstant embedded in Newton s gravitational onstant By re-formulating G as a omposite of the form G = l p 3, a long series of Plank units is dramatially simplified and beomes more logial; see [] G 5 The Plank time desribed as t p = gives minimal intuition We may ask, what is the logial meaning of 5 and what is the deep logi behind the gravitational onstant? First, when replaing G with its omposite form, we see that the Plank time is simply t p = lp, so the time it takes for light to travel the Plank length is naturally known All the Plank units seem mystial when alulated from Newton s gravitational onstant and the Plank onstant Only when we have an output in kg, do we need the Plank onstant We do not question that Newton s gravitational onstant is a universal onstant, but it is, in our view, learly a omposite onstant that onsists of more fundamental entities VII CONCLUSION We have, for the first time, shown how the Plank length an be measured without any knowledge of Newton s gravitational onstant and the Plank onstant It seems that the Compton frequeny of matter is what is important for understanding mass at a deeper level Further, the Shwarzshild radius is the redued Compton frequeny over the Plank time period multiplied by the Plank length All we need to extrat the Plank length is to know the redued Compton frequeny of matter and the Shwarzshild radius The Shwarzshild radius also seems to play a entral role for gravity We laim that it is the redued Compton frequeny in matter, over the shortest time intervaossible, multiplied by the shortest length possible This view on the Shwarzshild radius seems to possibly be key to understanding gravity at a deeper level This should enourage further investigation, theoretially and experimentally [] Max Plank Naturlishe Maasseinheiten Der Königlih Preussishen Akademie Der Wissenshaften, p 479, 899 [] Max Plank Vorlesungen über die Theorie der Wärmestrahlung Leipzig: JA Barth, p 63, see also the English translation The Theory of Radiation (959) Dover, 906 [3] RS Van Dyk, FL Moore, DL Farnham, and PB Shwinberg New measurement of the proton-eletron mass ratio International Journal of Mass Spetrometry and Ion Proesses, 66 [4] E G Haug Revisiting the derivation of Heisenberg s unertainty priniple: The ollapse of unertainty at the Plank sale preprintsorg, 08 [5] K Shwarzshild Über das gravitationsfeld eines massenpunktes nah der einsteinshen theorie Sitzungsberihte der Deutshen Akademie der Wissenshaften zu Berlin, Klasse fur Mathematik, Physik, und Tehnik, page 89, 96 [6] K Shwarzshild über das gravitationsfeld einer kugel aus inkompressibler flussigkeit nah der einsteinshen theorie Sitzungsberihte der Deutshen Akademie der Wissenshaften zu Berlin, Klasse fur Mathematik, Physik, und Tehnik, page 44, 96 [7] Albert Einstein Näherungsweise integration der feldgleihungen der gravitation Sitzungsberihte der Königlih Preussishen Akademie der Wissenshaften Berlin, 96 [8] E G Haug Gravity without Newton s gravitational onstant and no knowledge of mass size preprintsorg, 08 [9] D Dole and Perali On the Compton lok and the undulatory nature of partile mass in graphene systems The European Physial Journal Plus, 30(4), 05 [0] S Lan, P Kuan, B Estey, D English, J M Brown, M A Hohensee, and Müller A lok diretly linking
5 5 time to a partile s mass Siene, 339, 03 [] E G Haug The gravitational onstant and the Plank units a deeper understanding of the quantum realm wwwvixraorg , 06 [] E G Haug Plank quantization of newton and einstein gravitation International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysis, 6(), 06 [3] E G Haug Newton and Einstein s gravity in a new perspetive for Plank masses and smaller sized objets International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysis, 08 [4] M E MCulloh Gravity from the unertainty priniple Astrophysis and Spae Siene, 349(), 04
A Modified Newtonian Quantum Gravity Theory Derived from Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle that Predicts the Same Bending of Light as GR
 A Modified Newtonian Quantum Gravity Theory Derived from Heisenberg s Unertainty Priniple that Predits the Same Bending of Light as GR Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sienes Marh 6, 208
A Modified Newtonian Quantum Gravity Theory Derived from Heisenberg s Unertainty Priniple that Predits the Same Bending of Light as GR Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sienes Marh 6, 208
Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sciences April 4, 2017
 The Mass Gap, Kg, the Plank Constant and the Gravity Gap The Plank Constant Is a Composite Constant One kg Is 85465435748 0 36 Collisions per Seond The Mass Gap Is.734 0 5 kg and also m p The Possibility
The Mass Gap, Kg, the Plank Constant and the Gravity Gap The Plank Constant Is a Composite Constant One kg Is 85465435748 0 36 Collisions per Seond The Mass Gap Is.734 0 5 kg and also m p The Possibility
A Motion Paradox from Einstein s Relativity of Simultaneity
 Motion Paradox from Einstein s Relativity of Simultaneity Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sienes November 5, 7 bstrat We are desribing a new and potentially important paradox related to
Motion Paradox from Einstein s Relativity of Simultaneity Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sienes November 5, 7 bstrat We are desribing a new and potentially important paradox related to
Does Heisenberg s Uncertainty Collapse at the Planck Scale? Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle Becomes the Certainty Principle
 Does Heisenberg s Unertainty Collapse at the Plank Sale? Heisenberg s Unertainty Priniple Beomes the Certainty Priniple Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian Uniersity of Life Sienes June 7, 08 Abstrat In this
Does Heisenberg s Unertainty Collapse at the Plank Sale? Heisenberg s Unertainty Priniple Beomes the Certainty Priniple Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian Uniersity of Life Sienes June 7, 08 Abstrat In this
Gravity from the Uncertainty Principle.
 Gravity from the Unertainty Priniple. M.E. MCulloh Otober 29, 2013 Abstrat It is shown here that Newton's gravity law an be derived from the unertainty priniple. The idea is that as the distane between
Gravity from the Unertainty Priniple. M.E. MCulloh Otober 29, 2013 Abstrat It is shown here that Newton's gravity law an be derived from the unertainty priniple. The idea is that as the distane between
Matter-light duality and speed greater than light
 Matter-light duality and speed greater than light Shalender Singh* and Vishnu Priya Singh Parmar Priza Tehnologies In. R&D, 155 MCarthy Blvd, Ste 1111, Milpitas, California, USA 95035 Email: shalender@prizateh.om
Matter-light duality and speed greater than light Shalender Singh* and Vishnu Priya Singh Parmar Priza Tehnologies In. R&D, 155 MCarthy Blvd, Ste 1111, Milpitas, California, USA 95035 Email: shalender@prizateh.om
Origin of the Expansive Homogeneous and Isotropic Relativistic-Quantum-Mechanical Universe
 Adv. Studies Theor. hys., Vol. 5, 011, no. 16, 783-790 Origin of the Expansive Homogeneous and Isotropi Relativisti-Quantum-Mehanial Universe Vladimír Skalský Faulty of Material Sienes and Tehnology of
Adv. Studies Theor. hys., Vol. 5, 011, no. 16, 783-790 Origin of the Expansive Homogeneous and Isotropi Relativisti-Quantum-Mehanial Universe Vladimír Skalský Faulty of Material Sienes and Tehnology of
Newton s Gravity from Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle An In-Depth Study of the McCulloch Derivation
 Newton s Gravity from Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle An In-Depth Study of the McCulloch Derivation Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sciences March 5, 208 Abstract Mike McCulloch has
Newton s Gravity from Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle An In-Depth Study of the McCulloch Derivation Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sciences March 5, 208 Abstract Mike McCulloch has
Gravity without Newton s Gravitational Constant and No Knowledge of Mass Size
 Gravity without Newton s Gravitational Constant and No Knowledge of Mass Size Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sciences Chr. Magnus Falsens Road, 1430 Ås, Norway (Dated: June 9, 018) Abstract:
Gravity without Newton s Gravitational Constant and No Knowledge of Mass Size Espen Gaarder Haug Norwegian University of Life Sciences Chr. Magnus Falsens Road, 1430 Ås, Norway (Dated: June 9, 018) Abstract:
Planck Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gravitation
 Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
CHAPTER 26 The Special Theory of Relativity
 CHAPTER 6 The Speial Theory of Relativity Units Galilean-Newtonian Relativity Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relativity Simultaneity Time Dilation and the Twin Paradox Length Contration Four-Dimensional
CHAPTER 6 The Speial Theory of Relativity Units Galilean-Newtonian Relativity Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relativity Simultaneity Time Dilation and the Twin Paradox Length Contration Four-Dimensional
Chapter 26 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 26 Leture Notes Physis 2424 - Strauss Formulas: t = t0 1 v L = L0 1 v m = m0 1 v E = m 0 2 + KE = m 2 KE = m 2 -m 0 2 mv 0 p= mv = 1 v E 2 = p 2 2 + m 2 0 4 v + u u = 2 1 + vu There were two revolutions
Chapter 26 Leture Notes Physis 2424 - Strauss Formulas: t = t0 1 v L = L0 1 v m = m0 1 v E = m 0 2 + KE = m 2 KE = m 2 -m 0 2 mv 0 p= mv = 1 v E 2 = p 2 2 + m 2 0 4 v + u u = 2 1 + vu There were two revolutions
Particle-wave symmetry in Quantum Mechanics And Special Relativity Theory
 Partile-wave symmetry in Quantum Mehanis And Speial Relativity Theory Author one: XiaoLin Li,Chongqing,China,hidebrain@hotmail.om Corresponding author: XiaoLin Li, Chongqing,China,hidebrain@hotmail.om
Partile-wave symmetry in Quantum Mehanis And Speial Relativity Theory Author one: XiaoLin Li,Chongqing,China,hidebrain@hotmail.om Corresponding author: XiaoLin Li, Chongqing,China,hidebrain@hotmail.om
The Laws of Acceleration
 The Laws of Aeleration The Relationships between Time, Veloity, and Rate of Aeleration Copyright 2001 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat Presented is a theory in fundamental theoretial physis that establishes the
The Laws of Aeleration The Relationships between Time, Veloity, and Rate of Aeleration Copyright 2001 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat Presented is a theory in fundamental theoretial physis that establishes the
Physics 486. Classical Newton s laws Motion of bodies described in terms of initial conditions by specifying x(t), v(t).
 Physis 486 Tony M. Liss Leture 1 Why quantum mehanis? Quantum vs. lassial mehanis: Classial Newton s laws Motion of bodies desribed in terms of initial onditions by speifying x(t), v(t). Hugely suessful
Physis 486 Tony M. Liss Leture 1 Why quantum mehanis? Quantum vs. lassial mehanis: Classial Newton s laws Motion of bodies desribed in terms of initial onditions by speifying x(t), v(t). Hugely suessful
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE?
 THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
Time and Energy, Inertia and Gravity
 Time and Energy, Inertia and Gravity The Relationship between Time, Aeleration, and Veloity and its Affet on Energy, and the Relationship between Inertia and Gravity Copyright 00 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat
Time and Energy, Inertia and Gravity The Relationship between Time, Aeleration, and Veloity and its Affet on Energy, and the Relationship between Inertia and Gravity Copyright 00 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat
TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER
 TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER (WHY IS THE SPEED OF LIGHT CONSTANT?) Dr. Tamas Lajtner Correspondene via web site: www.lajtnemahine.om. ABSTRACT... 2 2. SPACETIME CONTINUUM BY
TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER (WHY IS THE SPEED OF LIGHT CONSTANT?) Dr. Tamas Lajtner Correspondene via web site: www.lajtnemahine.om. ABSTRACT... 2 2. SPACETIME CONTINUUM BY
TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER
 TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER (No general ausality without superluminal veloities) by Dr. Tamas Lajtner Correspondene via web site: www.lajtnemahine.om ABSTRACT...2 1. SPACETIME
TWO WAYS TO DISTINGUISH ONE INERTIAL FRAME FROM ANOTHER (No general ausality without superluminal veloities) by Dr. Tamas Lajtner Correspondene via web site: www.lajtnemahine.om ABSTRACT...2 1. SPACETIME
Name Solutions to Test 1 September 23, 2016
 Name Solutions to Test 1 September 3, 016 This test onsists of three parts. Please note that in parts II and III, you an skip one question of those offered. Possibly useful formulas: F qequb x xvt E Evpx
Name Solutions to Test 1 September 3, 016 This test onsists of three parts. Please note that in parts II and III, you an skip one question of those offered. Possibly useful formulas: F qequb x xvt E Evpx
Line Radiative Transfer
 http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
arxiv:gr-qc/ v2 6 Feb 2004
 Hubble Red Shift and the Anomalous Aeleration of Pioneer 0 and arxiv:gr-q/0402024v2 6 Feb 2004 Kostadin Trenčevski Faulty of Natural Sienes and Mathematis, P.O.Box 62, 000 Skopje, Maedonia Abstrat It this
Hubble Red Shift and the Anomalous Aeleration of Pioneer 0 and arxiv:gr-q/0402024v2 6 Feb 2004 Kostadin Trenčevski Faulty of Natural Sienes and Mathematis, P.O.Box 62, 000 Skopje, Maedonia Abstrat It this
Special and General Relativity
 9/16/009 Speial and General Relativity Inertial referene frame: a referene frame in whih an aeleration is the result of a fore. Examples of Inertial Referene Frames 1. This room. Experiment: Drop a ball.
9/16/009 Speial and General Relativity Inertial referene frame: a referene frame in whih an aeleration is the result of a fore. Examples of Inertial Referene Frames 1. This room. Experiment: Drop a ball.
Blackbody radiation and Plank s law
 lakbody radiation and Plank s law blakbody problem: alulating the intensity o radiation at a given wavelength emitted by a body at a speii temperature Max Plank, 900 quantization o energy o radiation-emitting
lakbody radiation and Plank s law blakbody problem: alulating the intensity o radiation at a given wavelength emitted by a body at a speii temperature Max Plank, 900 quantization o energy o radiation-emitting
Relativistic Dynamics
 Chapter 7 Relativisti Dynamis 7.1 General Priniples of Dynamis 7.2 Relativisti Ation As stated in Setion A.2, all of dynamis is derived from the priniple of least ation. Thus it is our hore to find a suitable
Chapter 7 Relativisti Dynamis 7.1 General Priniples of Dynamis 7.2 Relativisti Ation As stated in Setion A.2, all of dynamis is derived from the priniple of least ation. Thus it is our hore to find a suitable
The gravitational phenomena without the curved spacetime
 The gravitational phenomena without the urved spaetime Mirosław J. Kubiak Abstrat: In this paper was presented a desription of the gravitational phenomena in the new medium, different than the urved spaetime,
The gravitational phenomena without the urved spaetime Mirosław J. Kubiak Abstrat: In this paper was presented a desription of the gravitational phenomena in the new medium, different than the urved spaetime,
Einstein s Three Mistakes in Special Relativity Revealed. Copyright Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Einstein s Three Mistakes in Speial Relativity Revealed Copyright Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat When the evidene supported priniples of eletromagneti propagation are properly applied, the derived theory is
Einstein s Three Mistakes in Speial Relativity Revealed Copyright Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat When the evidene supported priniples of eletromagneti propagation are properly applied, the derived theory is
Physical Laws, Absolutes, Relative Absolutes and Relativistic Time Phenomena
 Page 1 of 10 Physial Laws, Absolutes, Relative Absolutes and Relativisti Time Phenomena Antonio Ruggeri modexp@iafria.om Sine in the field of knowledge we deal with absolutes, there are absolute laws that
Page 1 of 10 Physial Laws, Absolutes, Relative Absolutes and Relativisti Time Phenomena Antonio Ruggeri modexp@iafria.om Sine in the field of knowledge we deal with absolutes, there are absolute laws that
Critical Reflections on the Hafele and Keating Experiment
 Critial Refletions on the Hafele and Keating Experiment W.Nawrot In 1971 Hafele and Keating performed their famous experiment whih onfirmed the time dilation predited by SRT by use of marosopi loks. As
Critial Refletions on the Hafele and Keating Experiment W.Nawrot In 1971 Hafele and Keating performed their famous experiment whih onfirmed the time dilation predited by SRT by use of marosopi loks. As
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 8 Aug 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 8 Aug 2003 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 8 Aug 2003](/thumbs/89/99934791.jpg) arxiv:physis/0308036v1 [physis.lass-ph] 8 Aug 003 On the meaning of Lorentz ovariane Lszl E. Szab Theoretial Physis Researh Group of the Hungarian Aademy of Sienes Department of History and Philosophy
arxiv:physis/0308036v1 [physis.lass-ph] 8 Aug 003 On the meaning of Lorentz ovariane Lszl E. Szab Theoretial Physis Researh Group of the Hungarian Aademy of Sienes Department of History and Philosophy
). In accordance with the Lorentz transformations for the space-time coordinates of the same event, the space coordinates become
 Relativity and quantum mehanis: Jorgensen 1 revisited 1. Introdution Bernhard Rothenstein, Politehnia University of Timisoara, Physis Department, Timisoara, Romania. brothenstein@gmail.om Abstrat. We first
Relativity and quantum mehanis: Jorgensen 1 revisited 1. Introdution Bernhard Rothenstein, Politehnia University of Timisoara, Physis Department, Timisoara, Romania. brothenstein@gmail.om Abstrat. We first
Astrophysics and Space Science, Volume 330, Number 2 / December 2010, pp DOI: /s
 Astrophysis and Spae Siene, Volume 0, Number / Deember 010, pp. 7-98 DOI: 10.1007/s10509-010-0409-8 The model of a flat (Eulidean) expansive homogeneous and isotropi relativisti universe in the light of
Astrophysis and Spae Siene, Volume 0, Number / Deember 010, pp. 7-98 DOI: 10.1007/s10509-010-0409-8 The model of a flat (Eulidean) expansive homogeneous and isotropi relativisti universe in the light of
Gravitation is a Gradient in the Velocity of Light ABSTRACT
 1 Gravitation is a Gradient in the Veloity of Light D.T. Froedge V5115 @ http://www.arxdtf.org Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om ABSTRACT It has long been known that a photon entering
1 Gravitation is a Gradient in the Veloity of Light D.T. Froedge V5115 @ http://www.arxdtf.org Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om ABSTRACT It has long been known that a photon entering
The Possibility of FTL Space Travel by using the Quantum Tunneling Effect through the Light Barrier
 ISSN: 19-98 The Possibility of FTL Spae Travel by using the Quantum Tunneling Effet through the Light Barrier Musha T Advaned Si-Teh Researh Organization, -11-7-61, Namiki, Kanazawa-Ku, Yokohama 65, Japan
ISSN: 19-98 The Possibility of FTL Spae Travel by using the Quantum Tunneling Effet through the Light Barrier Musha T Advaned Si-Teh Researh Organization, -11-7-61, Namiki, Kanazawa-Ku, Yokohama 65, Japan
Millennium Relativity Acceleration Composition. The Relativistic Relationship between Acceleration and Uniform Motion
 Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
Physics 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton Effect
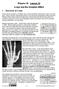 I. Disovery of x-rays Physis 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton ffet During all the researh on athode rays, several sientists missed their hane at some glory. Hertz narrowly missed disovering x-rays during
I. Disovery of x-rays Physis 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton ffet During all the researh on athode rays, several sientists missed their hane at some glory. Hertz narrowly missed disovering x-rays during
Relativity in Classical Physics
 Relativity in Classial Physis Main Points Introdution Galilean (Newtonian) Relativity Relativity & Eletromagnetism Mihelson-Morley Experiment Introdution The theory of relativity deals with the study of
Relativity in Classial Physis Main Points Introdution Galilean (Newtonian) Relativity Relativity & Eletromagnetism Mihelson-Morley Experiment Introdution The theory of relativity deals with the study of
Lecture #1: Quantum Mechanics Historical Background Photoelectric Effect. Compton Scattering
 561 Fall 2017 Leture #1 page 1 Leture #1: Quantum Mehanis Historial Bakground Photoeletri Effet Compton Sattering Robert Field Experimental Spetrosopist = Quantum Mahinist TEXTBOOK: Quantum Chemistry,
561 Fall 2017 Leture #1 page 1 Leture #1: Quantum Mehanis Historial Bakground Photoeletri Effet Compton Sattering Robert Field Experimental Spetrosopist = Quantum Mahinist TEXTBOOK: Quantum Chemistry,
Chapter 35. Special Theory of Relativity (1905)
 Chapter 35 Speial Theory of Relatiity (1905) 1. Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relatiity: A. The laws of physis are the same in all oordinate systems either at rest or moing at onstant eloity with
Chapter 35 Speial Theory of Relatiity (1905) 1. Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relatiity: A. The laws of physis are the same in all oordinate systems either at rest or moing at onstant eloity with
Simple Considerations on the Cosmological Redshift
 Apeiron, Vol. 5, No. 3, July 8 35 Simple Considerations on the Cosmologial Redshift José Franiso Garía Juliá C/ Dr. Maro Mereniano, 65, 5. 465 Valenia (Spain) E-mail: jose.garia@dival.es Generally, the
Apeiron, Vol. 5, No. 3, July 8 35 Simple Considerations on the Cosmologial Redshift José Franiso Garía Juliá C/ Dr. Maro Mereniano, 65, 5. 465 Valenia (Spain) E-mail: jose.garia@dival.es Generally, the
DO PHYSICS ONLINE. SPECIAL RELATIVITY Frames of Reference
 DO PHYSICS ONLINE SPACE SPECIAL RELATIVITY Frames of Referene Spae travel Apollo 11 spaeraft: Earth Moon v ~ 40x10 3 km.h -1 Voyager spaeraft: v ~ 60x10 3 km.h -1 (no sling shot effet) Ulysses spaeraft:
DO PHYSICS ONLINE SPACE SPECIAL RELATIVITY Frames of Referene Spae travel Apollo 11 spaeraft: Earth Moon v ~ 40x10 3 km.h -1 Voyager spaeraft: v ~ 60x10 3 km.h -1 (no sling shot effet) Ulysses spaeraft:
On the Quantum Theory of Radiation.
 Physikalishe Zeitshrift, Band 18, Seite 121-128 1917) On the Quantum Theory of Radiation. Albert Einstein The formal similarity between the hromati distribution urve for thermal radiation and the Maxwell
Physikalishe Zeitshrift, Band 18, Seite 121-128 1917) On the Quantum Theory of Radiation. Albert Einstein The formal similarity between the hromati distribution urve for thermal radiation and the Maxwell
Bäcklund Transformations: Some Old and New Perspectives
 Bäklund Transformations: Some Old and New Perspetives C. J. Papahristou *, A. N. Magoulas ** * Department of Physial Sienes, Helleni Naval Aademy, Piraeus 18539, Greee E-mail: papahristou@snd.edu.gr **
Bäklund Transformations: Some Old and New Perspetives C. J. Papahristou *, A. N. Magoulas ** * Department of Physial Sienes, Helleni Naval Aademy, Piraeus 18539, Greee E-mail: papahristou@snd.edu.gr **
Introduction to Quantum Chemistry
 Chem. 140B Dr. J.A. Mak Introdution to Quantum Chemistry Without Quantum Mehanis, how would you explain: Periodi trends in properties of the elements Struture of ompounds e.g. Tetrahedral arbon in ethane,
Chem. 140B Dr. J.A. Mak Introdution to Quantum Chemistry Without Quantum Mehanis, how would you explain: Periodi trends in properties of the elements Struture of ompounds e.g. Tetrahedral arbon in ethane,
Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy. Mathematics, Physics and Philosophy in the Interpretations of Relativity Theory
 Zero-energy spae anels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola, www.si.fi/~suntola/, Finland Mathematis, Physis and Philosophy in the Interpretations of Relativity Theory 1 Latest PhysisWeb Summaries 20.7.2007:
Zero-energy spae anels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola, www.si.fi/~suntola/, Finland Mathematis, Physis and Philosophy in the Interpretations of Relativity Theory 1 Latest PhysisWeb Summaries 20.7.2007:
Special Relativity. Relativity
 10/17/01 Speial Relativity Leture 17 Relativity There is no absolute motion. Everything is relative. Suppose two people are alone in spae and traveling towards one another As measured by the Doppler shift!
10/17/01 Speial Relativity Leture 17 Relativity There is no absolute motion. Everything is relative. Suppose two people are alone in spae and traveling towards one another As measured by the Doppler shift!
Theoretical background of T.T. Brown Electro-Gravity Communication System
 Theoretial bakground of T.T. Brown Eletro-Gravity Communiation System Algirdas Antano Maknikas Institute of Mehanis, Vilnius Gediminas Tehnial University September 1, 2014 Abstrat The author proposed theory
Theoretial bakground of T.T. Brown Eletro-Gravity Communiation System Algirdas Antano Maknikas Institute of Mehanis, Vilnius Gediminas Tehnial University September 1, 2014 Abstrat The author proposed theory
The Concept of Mass as Interfering Photons, and the Originating Mechanism of Gravitation D.T. Froedge
 The Conept of Mass as Interfering Photons, and the Originating Mehanism of Gravitation D.T. Froedge V04 Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om Abstrat For most purposes in physis the onept
The Conept of Mass as Interfering Photons, and the Originating Mehanism of Gravitation D.T. Froedge V04 Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om Abstrat For most purposes in physis the onept
The Electromagnetic Radiation and Gravity
 International Journal of Theoretial and Mathematial Physis 016, 6(3): 93-98 DOI: 10.593/j.ijtmp.0160603.01 The Eletromagneti Radiation and Gravity Bratianu Daniel Str. Teiului Nr. 16, Ploiesti, Romania
International Journal of Theoretial and Mathematial Physis 016, 6(3): 93-98 DOI: 10.593/j.ijtmp.0160603.01 The Eletromagneti Radiation and Gravity Bratianu Daniel Str. Teiului Nr. 16, Ploiesti, Romania
( x vt) m (0.80)(3 10 m/s)( s) 1200 m m/s m/s m s 330 s c. 3.
 Solutions to HW 10 Problems and Exerises: 37.. Visualize: At t t t 0 s, the origins of the S, S, and S referene frames oinide. Solve: We have 1 ( v/ ) 1 (0.0) 1.667. (a) Using the Lorentz transformations,
Solutions to HW 10 Problems and Exerises: 37.. Visualize: At t t t 0 s, the origins of the S, S, and S referene frames oinide. Solve: We have 1 ( v/ ) 1 (0.0) 1.667. (a) Using the Lorentz transformations,
UNCERTAINTY RELATIONS AS A CONSEQUENCE OF THE LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS. V. N. Matveev and O. V. Matvejev
 UNCERTAINTY RELATIONS AS A CONSEQUENCE OF THE LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS V. N. Matveev and O. V. Matvejev Joint-Stok Company Sinerta Savanoriu pr., 159, Vilnius, LT-315, Lithuania E-mail: matwad@mail.ru Abstrat
UNCERTAINTY RELATIONS AS A CONSEQUENCE OF THE LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS V. N. Matveev and O. V. Matvejev Joint-Stok Company Sinerta Savanoriu pr., 159, Vilnius, LT-315, Lithuania E-mail: matwad@mail.ru Abstrat
The Exact Solution of the Pioneer Anomaly and Flyby Anomaly and the Interpretation of Inertia from an asymmetric Casimir effect
 The Exat Solution of the Pioneer Anomaly and Flyby Anomaly and the Interpretation of Inertia from an asymmetri Casimir effet Abstrat Azzam Almosallami Zurih, Switzerland a.almosallami71@gmail.om In this
The Exat Solution of the Pioneer Anomaly and Flyby Anomaly and the Interpretation of Inertia from an asymmetri Casimir effet Abstrat Azzam Almosallami Zurih, Switzerland a.almosallami71@gmail.om In this
The experimental plan of displacement- and frequency-noise free laser interferometer
 7th Edoardo Amaldi Conferene on Gravitational Waves (Amaldi7) Journal of Physis: Conferene Series 122 (2008) 012022 The experimental plan of displaement- and frequeny-noise free laser interferometer K
7th Edoardo Amaldi Conferene on Gravitational Waves (Amaldi7) Journal of Physis: Conferene Series 122 (2008) 012022 The experimental plan of displaement- and frequeny-noise free laser interferometer K
Where Standard Physics Runs into Infinite Challenges, Atomism Predicts Exact Limits
 Where Standard Phyi Run into Infinite Challenge, Atomim Predit Exat Limit Epen Gaarder Haug Norwegian Univerity of Life Siene Deember, 07 Abtrat Where tandard phyi run into infinite hallenge, atomim predit
Where Standard Phyi Run into Infinite Challenge, Atomim Predit Exat Limit Epen Gaarder Haug Norwegian Univerity of Life Siene Deember, 07 Abtrat Where tandard phyi run into infinite hallenge, atomim predit
arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 5 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 5 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 5 Jan 2018](/thumbs/76/73479335.jpg) The Real Quaternion Relativity Viktor Ariel arxiv:1801.03393v1 [physis.gen-ph] 5 Jan 2018 In this work, we use real quaternions and the basi onept of the final speed of light in an attempt to enhane the
The Real Quaternion Relativity Viktor Ariel arxiv:1801.03393v1 [physis.gen-ph] 5 Jan 2018 In this work, we use real quaternions and the basi onept of the final speed of light in an attempt to enhane the
New Potential of the. Positron-Emission Tomography
 International Journal of Modern Physis and Appliation 6; 3(: 39- http://www.aasit.org/journal/ijmpa ISSN: 375-387 New Potential of the Positron-Emission Tomography Andrey N. olobuev, Eugene S. Petrov,
International Journal of Modern Physis and Appliation 6; 3(: 39- http://www.aasit.org/journal/ijmpa ISSN: 375-387 New Potential of the Positron-Emission Tomography Andrey N. olobuev, Eugene S. Petrov,
Control Theory association of mathematics and engineering
 Control Theory assoiation of mathematis and engineering Wojieh Mitkowski Krzysztof Oprzedkiewiz Department of Automatis AGH Univ. of Siene & Tehnology, Craow, Poland, Abstrat In this paper a methodology
Control Theory assoiation of mathematis and engineering Wojieh Mitkowski Krzysztof Oprzedkiewiz Department of Automatis AGH Univ. of Siene & Tehnology, Craow, Poland, Abstrat In this paper a methodology
Towards an Absolute Cosmic Distance Gauge by using Redshift Spectra from Light Fatigue.
 Towards an Absolute Cosmi Distane Gauge by using Redshift Spetra from Light Fatigue. Desribed by using the Maxwell Analogy for Gravitation. T. De Mees - thierrydemees @ pandora.be Abstrat Light is an eletromagneti
Towards an Absolute Cosmi Distane Gauge by using Redshift Spetra from Light Fatigue. Desribed by using the Maxwell Analogy for Gravitation. T. De Mees - thierrydemees @ pandora.be Abstrat Light is an eletromagneti
LECTURE 22. Electromagnetic. Spectrum 11/11/15. White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO)
 LECTURE 22 Eletromagneti Spetrum 2 White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) 1. Add together magenta, yan, and yellow. Play with intensities of eah to get white light.
LECTURE 22 Eletromagneti Spetrum 2 White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) 1. Add together magenta, yan, and yellow. Play with intensities of eah to get white light.
The Reason of Photons Angular Distribution at Electron-Positron Annihilation in a Positron-Emission Tomograph
 Advanes in Natural Siene ol 7, No,, pp -5 DOI: 3968/66 ISSN 75-786 [PRINT] ISSN 75-787 [ONLINE] wwwsanadanet wwwsanadaorg The Reason of Photons Angular Distribution at Eletron-Positron Annihilation in
Advanes in Natural Siene ol 7, No,, pp -5 DOI: 3968/66 ISSN 75-786 [PRINT] ISSN 75-787 [ONLINE] wwwsanadanet wwwsanadaorg The Reason of Photons Angular Distribution at Eletron-Positron Annihilation in
Tutorial 8: Solutions
 Tutorial 8: Solutions 1. * (a) Light from the Sun arrives at the Earth, an average of 1.5 10 11 m away, at the rate 1.4 10 3 Watts/m of area perpendiular to the diretion of the light. Assume that sunlight
Tutorial 8: Solutions 1. * (a) Light from the Sun arrives at the Earth, an average of 1.5 10 11 m away, at the rate 1.4 10 3 Watts/m of area perpendiular to the diretion of the light. Assume that sunlight
Aharonov-Bohm effect. Dan Solomon.
 Aharonov-Bohm effet. Dan Solomon. In the figure the magneti field is onfined to a solenoid of radius r 0 and is direted in the z- diretion, out of the paper. The solenoid is surrounded by a barrier that
Aharonov-Bohm effet. Dan Solomon. In the figure the magneti field is onfined to a solenoid of radius r 0 and is direted in the z- diretion, out of the paper. The solenoid is surrounded by a barrier that
The Special Theory of Relativity
 The Speial Theory of Relatiity Galilean Newtonian Relatiity Galileo Galilei Isaa Newton Definition of an inertial referene frame: One in whih Newton s first law is alid. onstant if F0 Earth is rotating
The Speial Theory of Relatiity Galilean Newtonian Relatiity Galileo Galilei Isaa Newton Definition of an inertial referene frame: One in whih Newton s first law is alid. onstant if F0 Earth is rotating
The Unified Geometrical Theory of Fields and Particles
 Applied Mathematis, 014, 5, 347-351 Published Online February 014 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/am) http://dx.doi.org/10.436/am.014.53036 The Unified Geometrial Theory of Fields and Partiles Amagh Nduka
Applied Mathematis, 014, 5, 347-351 Published Online February 014 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/am) http://dx.doi.org/10.436/am.014.53036 The Unified Geometrial Theory of Fields and Partiles Amagh Nduka
Investigation of the de Broglie-Einstein velocity equation s. universality in the context of the Davisson-Germer experiment. Yusuf Z.
 Investigation of the de Broglie-instein veloity equation s universality in the ontext of the Davisson-Germer experiment Yusuf Z. UMUL Canaya University, letroni and Communiation Dept., Öğretmenler Cad.,
Investigation of the de Broglie-instein veloity equation s universality in the ontext of the Davisson-Germer experiment Yusuf Z. UMUL Canaya University, letroni and Communiation Dept., Öğretmenler Cad.,
PY Modern Physics
 PY 351 - Modern Physis Assignment 6 - Otober 19, 2017. Due in lass on Otober 26, 2017. Assignment 6: Do all six problems. After a base of 4 points (to make the maximum sore equal to 100), eah orret solution
PY 351 - Modern Physis Assignment 6 - Otober 19, 2017. Due in lass on Otober 26, 2017. Assignment 6: Do all six problems. After a base of 4 points (to make the maximum sore equal to 100), eah orret solution
22.01 Fall 2015, Problem Set 6 (Normal Version Solutions)
 .0 Fall 05, Problem Set 6 (Normal Version Solutions) Due: November, :59PM on Stellar November 4, 05 Complete all the assigned problems, and do make sure to show your intermediate work. Please upload your
.0 Fall 05, Problem Set 6 (Normal Version Solutions) Due: November, :59PM on Stellar November 4, 05 Complete all the assigned problems, and do make sure to show your intermediate work. Please upload your
A Derivation of the Etherington s Distance-Duality Equation
 International Journal of Astrophysis and Spae Siene 215; 3(4): 65-69 Published online July 9, 215 (http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ijass) doi: 1.11648/j.ijass.21534.13 ISSN: 2376-714 (Print); ISSN:
International Journal of Astrophysis and Spae Siene 215; 3(4): 65-69 Published online July 9, 215 (http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ijass) doi: 1.11648/j.ijass.21534.13 ISSN: 2376-714 (Print); ISSN:
Contradictions in the Definition, Creation, and Existence of Black Holes
 International Journal of Engineering & Tehnology IJET-IJENS Vol: No: 0 Contraditions in the Definition, Creation, and Existene of Blak Holes Shahriar Khan Independent University, Bangladesh Abstrat Although
International Journal of Engineering & Tehnology IJET-IJENS Vol: No: 0 Contraditions in the Definition, Creation, and Existene of Blak Holes Shahriar Khan Independent University, Bangladesh Abstrat Although
Velocity Addition in Space/Time David Barwacz 4/23/
 Veloity Addition in Spae/Time 003 David arwaz 4/3/003 daveb@triton.net http://members.triton.net/daveb Abstrat Using the spae/time geometry developed in the previous paper ( Non-orthogonal Spae- Time geometry,
Veloity Addition in Spae/Time 003 David arwaz 4/3/003 daveb@triton.net http://members.triton.net/daveb Abstrat Using the spae/time geometry developed in the previous paper ( Non-orthogonal Spae- Time geometry,
A derivation of the Etherington s distance-duality equation
 A derivation of the Etherington s distane-duality equation Yuri Heymann 1 Abstrat The Etherington s distane-duality equation is the relationship between the luminosity distane of standard andles and the
A derivation of the Etherington s distane-duality equation Yuri Heymann 1 Abstrat The Etherington s distane-duality equation is the relationship between the luminosity distane of standard andles and the
9 Geophysics and Radio-Astronomy: VLBI VeryLongBaseInterferometry
 9 Geophysis and Radio-Astronomy: VLBI VeryLongBaseInterferometry VLBI is an interferometry tehnique used in radio astronomy, in whih two or more signals, oming from the same astronomial objet, are reeived
9 Geophysis and Radio-Astronomy: VLBI VeryLongBaseInterferometry VLBI is an interferometry tehnique used in radio astronomy, in whih two or more signals, oming from the same astronomial objet, are reeived
Lecture 3 - Lorentz Transformations
 Leture - Lorentz Transformations A Puzzle... Example A ruler is positioned perpendiular to a wall. A stik of length L flies by at speed v. It travels in front of the ruler, so that it obsures part of the
Leture - Lorentz Transformations A Puzzle... Example A ruler is positioned perpendiular to a wall. A stik of length L flies by at speed v. It travels in front of the ruler, so that it obsures part of the
Planck unit theory: Fine structure constant alpha and sqrt of Planck momentum
 Plank unit theory: Fine struture onstant alpha and sqrt of Plank momentum Malolm Maleod e-mail: mail4malolm@gmx.de The primary onstants; G,, h, e, α, k B, m e... range in preision from low G (4-digits)
Plank unit theory: Fine struture onstant alpha and sqrt of Plank momentum Malolm Maleod e-mail: mail4malolm@gmx.de The primary onstants; G,, h, e, α, k B, m e... range in preision from low G (4-digits)
Wave-Particle Duality: de Broglie Waves and Uncertainty
 Gauge Institute Journal Vol. No 4, November 6 Wave-Partile Duality: de Broglie Waves and Unertainty vik@adn.om November 6 Abstrat In 195, de Broglie ypotesized tat any material partile as an assoiated
Gauge Institute Journal Vol. No 4, November 6 Wave-Partile Duality: de Broglie Waves and Unertainty vik@adn.om November 6 Abstrat In 195, de Broglie ypotesized tat any material partile as an assoiated
EINSTEIN FIELD EQUATIONS OBTAINED ONLY WITH GAUSS CURVATURE AND ZOOM UNIVERSE MODEL CHARACTERISTICS
 EINSTEIN FIELD EQUATIONS OBTAINED ONLY WITH GAUSS CURVATURE AND ZOOM UNIVERSE MODEL CHARACTERISTICS Sergio Garia Chimeno Abstrat Demonstration how to obtain the Einstein Field Equations without using the
EINSTEIN FIELD EQUATIONS OBTAINED ONLY WITH GAUSS CURVATURE AND ZOOM UNIVERSE MODEL CHARACTERISTICS Sergio Garia Chimeno Abstrat Demonstration how to obtain the Einstein Field Equations without using the
Relativity fundamentals explained well (I hope) Walter F. Smith, Haverford College
 Relativity fundamentals explained well (I hope) Walter F. Smith, Haverford College 3-14-06 1 Propagation of waves through a medium As you ll reall from last semester, when the speed of sound is measured
Relativity fundamentals explained well (I hope) Walter F. Smith, Haverford College 3-14-06 1 Propagation of waves through a medium As you ll reall from last semester, when the speed of sound is measured
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
Four-dimensional equation of motion for viscous compressible substance with regard to the acceleration field, pressure field and dissipation field
 Four-dimensional equation of motion for visous ompressible substane with regard to the aeleration field, pressure field and dissipation field Sergey G. Fedosin PO box 6488, Sviazeva str. -79, Perm, Russia
Four-dimensional equation of motion for visous ompressible substane with regard to the aeleration field, pressure field and dissipation field Sergey G. Fedosin PO box 6488, Sviazeva str. -79, Perm, Russia
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
The Janus Cosmological Model and the fluctuations of the CMB
 The anus Cosmologial Model and the flutuations of the CMB.P. PETIT E-mail: p.petit@mailaps.org It is shown than, in the framework of the anus Cosmologial Model the gravitational instability whih ours in
The anus Cosmologial Model and the flutuations of the CMB.P. PETIT E-mail: p.petit@mailaps.org It is shown than, in the framework of the anus Cosmologial Model the gravitational instability whih ours in
New Chapter 3 The Universal Constants
 New Chapter 3 The Universal Constants 3. Our Set of Universal Constants The ten dimensionless universal onstants to be used here have already been listed at the beginning of.. In this hapter we desribe
New Chapter 3 The Universal Constants 3. Our Set of Universal Constants The ten dimensionless universal onstants to be used here have already been listed at the beginning of.. In this hapter we desribe
Cherenkov Radiation. Bradley J. Wogsland August 30, 2006
 Cherenkov Radiation Bradley J. Wogsland August 3, 26 Contents 1 Cherenkov Radiation 1 1.1 Cherenkov History Introdution................... 1 1.2 Frank-Tamm Theory......................... 2 1.3 Dispertion...............................
Cherenkov Radiation Bradley J. Wogsland August 3, 26 Contents 1 Cherenkov Radiation 1 1.1 Cherenkov History Introdution................... 1 1.2 Frank-Tamm Theory......................... 2 1.3 Dispertion...............................
arxiv:gr-qc/ v7 14 Dec 2003
 Propagation of light in non-inertial referene frames Vesselin Petkov Siene College, Conordia University 1455 De Maisonneuve Boulevard West Montreal, Quebe, Canada H3G 1M8 vpetkov@alor.onordia.a arxiv:gr-q/9909081v7
Propagation of light in non-inertial referene frames Vesselin Petkov Siene College, Conordia University 1455 De Maisonneuve Boulevard West Montreal, Quebe, Canada H3G 1M8 vpetkov@alor.onordia.a arxiv:gr-q/9909081v7
Metric of Universe The Causes of Red Shift.
 Metri of Universe The Causes of Red Shift. ELKIN IGOR. ielkin@yande.ru Annotation Poinare and Einstein supposed that it is pratially impossible to determine one-way speed of light, that s why speed of
Metri of Universe The Causes of Red Shift. ELKIN IGOR. ielkin@yande.ru Annotation Poinare and Einstein supposed that it is pratially impossible to determine one-way speed of light, that s why speed of
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysisAndMathsTutor.om. (a (i beam splitter [or semi-silvered mirror] (ii a ompensator [or a glass blok] allows for the thikness of the (semi-silvered mirror to obtain equal optial path lengths in the
PhysisAndMathsTutor.om. (a (i beam splitter [or semi-silvered mirror] (ii a ompensator [or a glass blok] allows for the thikness of the (semi-silvered mirror to obtain equal optial path lengths in the
a) What is the duration of the trip according to Ginette? b) What is the duration of the trip according to Tony?
 Ginette stays on Earth while Tony travels towards a star loated 4.6 lightyears away from Earth. The speed of Tony s ship is 80% of the speed of light. www.how-to-draw-artoons-online.om/artoon-earth.html
Ginette stays on Earth while Tony travels towards a star loated 4.6 lightyears away from Earth. The speed of Tony s ship is 80% of the speed of light. www.how-to-draw-artoons-online.om/artoon-earth.html
QUANTUM MECHANICS II PHYS 517. Solutions to Problem Set # 1
 QUANTUM MECHANICS II PHYS 57 Solutions to Problem Set #. The hamiltonian for a lassial harmoni osillator an be written in many different forms, suh as use ω = k/m H = p m + kx H = P + Q hω a. Find a anonial
QUANTUM MECHANICS II PHYS 57 Solutions to Problem Set #. The hamiltonian for a lassial harmoni osillator an be written in many different forms, suh as use ω = k/m H = p m + kx H = P + Q hω a. Find a anonial
Quantum Gravity via Newton
 4 Pearson: Quantum Gravity via Newton Vol. 9 Quantum Gravity via Newton Ron Pearson UK e-mail: pearson98@googlemail.om Sine relativity theories are unsatisfatory and annot provide quantum gravity an alternative
4 Pearson: Quantum Gravity via Newton Vol. 9 Quantum Gravity via Newton Ron Pearson UK e-mail: pearson98@googlemail.om Sine relativity theories are unsatisfatory and annot provide quantum gravity an alternative
finalsol.nb In my frame, I am at rest. So the time it takes for the missile to reach me is just 8µ106 km
 finalsol.n Physis D, Winter 005 Final Exam Solutions Top gun a v enemy = 0.4 in my enemy's frame, v' missile = 0.7 0.4 + 0.7 so, in my frame, v missile = Å º 0.859 +H0.4 H0.7 (it must e less than!) In
finalsol.n Physis D, Winter 005 Final Exam Solutions Top gun a v enemy = 0.4 in my enemy's frame, v' missile = 0.7 0.4 + 0.7 so, in my frame, v missile = Å º 0.859 +H0.4 H0.7 (it must e less than!) In
Nuclear Shell Structure Evolution Theory
 Nulear Shell Struture Evolution Theory Zhengda Wang (1) Xiaobin Wang () Xiaodong Zhang () Xiaohun Wang () (1) Institute of Modern physis Chinese Aademy of SienesLan Zhou P. R. China 70000 () Seagate Tehnology
Nulear Shell Struture Evolution Theory Zhengda Wang (1) Xiaobin Wang () Xiaodong Zhang () Xiaohun Wang () (1) Institute of Modern physis Chinese Aademy of SienesLan Zhou P. R. China 70000 () Seagate Tehnology
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe December 21, 2013 Prof. Alan Guth QUIZ 3 SOLUTIONS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physis Department Physis 8.286: The Early Universe Deember 2, 203 Prof. Alan Guth QUIZ 3 SOLUTIONS Quiz Date: Deember 5, 203 PROBLEM : DID YOU DO THE READING? (35
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physis Department Physis 8.286: The Early Universe Deember 2, 203 Prof. Alan Guth QUIZ 3 SOLUTIONS Quiz Date: Deember 5, 203 PROBLEM : DID YOU DO THE READING? (35
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter J2
 Answers to Courseook questions Chapter J 1 a Partiles are produed in ollisions one example out of many is: a ollision of an eletron with a positron in a synhrotron. If we produe a pair of a partile and
Answers to Courseook questions Chapter J 1 a Partiles are produed in ollisions one example out of many is: a ollision of an eletron with a positron in a synhrotron. If we produe a pair of a partile and
ES 247 Fracture Mechanics Zhigang Suo
 ES 47 Frature Mehanis Zhigang Suo The Griffith Paper Readings. A.A. Griffith, The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philosophial Transations of the Royal Soiety of London, Series A, Volume 1 (191)
ES 47 Frature Mehanis Zhigang Suo The Griffith Paper Readings. A.A. Griffith, The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philosophial Transations of the Royal Soiety of London, Series A, Volume 1 (191)
Berry s phase for coherent states of Landau levels
 Berry s phase for oherent states of Landau levels Wen-Long Yang 1 and Jing-Ling Chen 1, 1 Theoretial Physis Division, Chern Institute of Mathematis, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.R.China Adiabati
Berry s phase for oherent states of Landau levels Wen-Long Yang 1 and Jing-Ling Chen 1, 1 Theoretial Physis Division, Chern Institute of Mathematis, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.R.China Adiabati
Section 3. Interstellar absorption lines. 3.1 Equivalent width
 Setion 3 Interstellar absorption lines 3.1 Equivalent width We an study diuse interstellar louds through the absorption lines they produe in the spetra of bakground stars. Beause of the low temperatures
Setion 3 Interstellar absorption lines 3.1 Equivalent width We an study diuse interstellar louds through the absorption lines they produe in the spetra of bakground stars. Beause of the low temperatures
Chapter 28 Special Relativity
 Galilean Relatiity Chapter 8 Speial Relatiity A passenger in an airplane throws a ball straight up. It appears to oe in a ertial path. The law of graity and equations of otion under unifor aeleration are
Galilean Relatiity Chapter 8 Speial Relatiity A passenger in an airplane throws a ball straight up. It appears to oe in a ertial path. The law of graity and equations of otion under unifor aeleration are
Physics; Watching the Game From the Outside
 Physis; Wathing the Game From the Outside Roald C. Maximo Feb It is a good thing to have two ways of looking at a subjet, and also admit that there are two ways of looking at it. James Clerk Maxwell, on
Physis; Wathing the Game From the Outside Roald C. Maximo Feb It is a good thing to have two ways of looking at a subjet, and also admit that there are two ways of looking at it. James Clerk Maxwell, on
Stellar Aberration, Relative Motion, and the Lorentz Factor
 ong Beah 010 PROCEEDINGS of the NP 1 Stellar berration, Relatie Motion, and the orentz Fator Joseph. Rybzyk 139 Stetson Drie, Chalfont, P 18914-3751 e-mail: jarybzyk@erizon.net Presented are the results
ong Beah 010 PROCEEDINGS of the NP 1 Stellar berration, Relatie Motion, and the orentz Fator Joseph. Rybzyk 139 Stetson Drie, Chalfont, P 18914-3751 e-mail: jarybzyk@erizon.net Presented are the results
A unified field theory; atomic, gravitational orbitals as anti-photons
 (plankmomentum.om) A unified field theory; atomi, gravitational orbitals as anti-photons Malolm Maleod E-mail: malem@plankmomentum.om In this essay I propose an alternate interpretation whereby partiles
(plankmomentum.om) A unified field theory; atomi, gravitational orbitals as anti-photons Malolm Maleod E-mail: malem@plankmomentum.om In this essay I propose an alternate interpretation whereby partiles
