Ab initio MCDHF calculations of electron-nucleus interactions
|
|
|
- Emery Bailey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ab initio MCDHF calculations of electron-nucleus interactions Jacek Bieroń Universitas Iagellonica Cracoviensis Zakład Optyki Atomowej Institute of Physics 1364 Trento 25 Aug 2015
2 Complete Active Space in Dirac-Hartee-Fock theory Zakład Optyki Jacek Bieroń Atomowej Uniwersytet Jagielloński Instytut Fizyki
3 Hartree-Fock theory in 10 minutes ( r 1, r 2,, r N ) ( r 1 ) ( r 2 ) ( r N )
4 Hyperfine structure in 10 minutes E ( atom) ( nucl ) B(el ) magnetic dipole hyperfine structure electric 2 quadrupolev (el ) E Q ( nucl ) z 2
5 CPT invariance by M. C. Escher P start C matter mirror image anti-particle e+ anti-matter time identical to start time exotic physics in 10 minutes Courtesy H.W. Wilschut particle e- T
6 Hartree-Fock theory in 10 minutes Hyperfine structure in 10 minutes exotic physics in 10 minutes
7 Central Field Approximation ( r 1 ) ( r 2 ) ( r N ) radial function ( r ) R( r ) Y (, ) spherical function
8 Double substitutions describe pair correlations Correlated fluctuations of 2 electrons In general, they are quartic in number. Empty levels Occupied levels Correlations decay (somewhat) rapidly with separation. Exponentially between functions of the same electron Algebraically (R-3) between the 2 electrons ( dispersion)
9 Hartree-Fock Approximation ( r 1 ) ( r 2 ) ( r N ) radial function ( r ) R( r ) Y (, ) spherical function wikipedia.org/wiki/fourier_series
10 Multi-Configuration Variational WaveFunction for the ground state of Carbon reference configuration 1s 2 s 2 p valence correlation core polarization targeting specific region single substitution double substitution triple substitution 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 2 1s 2 2 s 2 2 p3 p 1s 2 2 s 2 2 p 2 1s 2s 2 2 p 2 3s 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 2 1s 2 2s 2 p 2 3d s 2s 2 p 1s 2 s 2 p3s3 s3 p 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 2 1s 2 2s 2 2 p nl 1s 2 2 s 2 2 p 2 1s 2 s 2 2 p nln'l' 1s 2 2 s 2 2 p 2 1s 2 2s nln'l'n "l" spectroscopic orbitals virtual set active orbital set nl = all possible combinations of: n1l1, n2l2 ni li with ni n and li l
11 MultiConfiguration Hartree-Fock theory ( ) ( ( ( ) ) ( cn n ( N n N ) ) ( ) ) n Complete Active Space
12 Hartree-Fock Approximation ( r 1 ) ( r 2 ) ( r N ) radial function ( r ) R( r ) Y (, ) spherical function
13 systematic step by step n by n increase of active set
14 accuracy ~ 0.01% (10) (8)
15 Relativistic effects V c m m0 NR r rnr 1 for U 91 r rnr 0.75 Z
16 Aufbau Non-Rel. Rel. 1s
17 orthogonal radial orbitals
18 Relativistic aufbau 4f 4d Rel. Non-Rel. f - ekspansion d - ekspansion... s - contraction Non-Rel. Rel. 7s 3s 2s 1s
19 Complete Active Space in Dirac-Fock theory Relativistic wave equation: 2 (c p m c V ) Multiconfiguration wavefunction: ( ) ( c n ( N n n N n ) ( ) ) Complete Active Space
20 Aufbau: radium vs lithium Ra 1s s 2 Li 1s 2 2 s
21 multire fer lowest n quantum number of opened occupied shells systematic ence number of substitutions (SDTQ ) 5D-systematic ual set t r i v f o umbers n m u t n q ua angular highest n quantum number of virtual set
22 5 dimensions: size of virtual orbital set angular symmetry of virtual set: spdfgh number of opened core shells substitution number: SDTQ multireference set
23 nuclear Quadrupole moment of gold DF values: Q( 2 D5 2 ) Q( 2 D3 2 ) accuracy ~ 1%
24 2-3 virtual sets, oscillations, uncertainties
25 2-3 virtual sets, oscillations, uncertainties
26
27 discrete symmetry violation
28 Time reversal violation and the Electric Dipole Moment Why is EDM a TRV observable J d time time QM: J//d any particle will do dn em de < em de (SM) < em find suitable object Schiff need amplifier atomic (Z3) nuclear suitable structure Consider all nuclides EDM violates parity and time reversal Courtesy Klaus Jungmann
29 particle EDM within SM E Standard Model prediction of EDM of: electron ~ 10^-38 e.cm neutron ~ 10^-32 e.cm muon ~ 10^-26 e.cm tau ~ 10^-23 e.cm
30 EDM Now and in the Future The more Winnie the Pooh looked inside the more Piglet wasn t there. NUPECC list 199 Hg Radium potential Start TRI P de (SM) < Courtesy Klaus Jungmann
31 EDM Limits as of summer 2004 spring 2011 Particle e (Tl) n Tl (odd p) Hg (odd n) summer 2009 Possible Exp. Limit SM New Physics [10-27 e cm] [factor to go] [factor to go] < < 1.05 * < 3.1 * < < < various ~ 1 order of magnitude / decade if the electron were magnified to the size of the solar system, its EDM would be no bigger than the width of a human hair. Courtesy Klaus Jungmann
32 d-p amplitude p-s amplitude (14) from: Dzuba et al., Phys. Rev. A 61 (2000)
33 Tensor-pseudotensor contributions to EDM of: 225-Ra, 199-Hg, 171-Yb DF vs MCDHF
34 EDM of Copernicium
35 coffee time?
36 Co-Producers (in alphabetical order) Jacek Bieroń Charlotte Froese Fischer Stephan Fritzsche Gediminas Gaigalas Michel Godefroid Ian Grant Paul Indelicato Per Jönsson Pekka Pyykkö Uniwersytet Jagielloński Vanderbilt University & NIST Universität Jena Vilniaus Universitetas Université Libre Bruxelles University of Oxford l Université Paris VI Malmö Högskola Helsingin Yliopisto Thank you for your attention
37 Large Numbers Hypothesis as always, history goes back to Dirac (who was influenced by Weyl, Eddington, Milne, Lemaitre) P.A.M. Dirac "The Cosmological Constants Nature 139: 323 (1937) According to current cosmological theories, the universe had a beginning about 2 x 10^9 years ago, when all the spiral nebulae were shot out from a small region of space, or perhaps from a point. If we express this time, 2 x 10^9 years, in units provided by the atomic constants, say the unit e^2/mc^3, we obtain a number about 10^39. This suggests that the above-mentioned large numbers are to be regarded, not as constants, but as simple functions of our present epoch, expressed in atomic units.
38 Large Numbers Hypothesis ct T is the age of the universe re is the classical electron radius re 2 Fe e Fg 4 0 GM p me LNH hypothesis 1 G T
39 why alpha and not G? G (67) m3kg 1s CODATA G (30) m 3kg 1s 2 International Astronomical Union
40 e g L 2m s e B g 2 Ls mc electron gyromagnetic ratio g e s s ( s 1) mc Ls s( s 1) Dirac Schwinger Bohr magneton g C2 C4 ( ) C6 ( ) C8 ( ) C10 ( ) a ahadr aweak 2 C2, C4,C6 exact C (35) PRL 99, (2007) g = (15) PRL 100, (2008) 139 ((33 31) (39)CODATA
41 Foils with white background thanks to Victor Flambaum and Vladimir Dzuba Variation of Fundamental Constants from Big Bang to Atomic Clocks V.V. Flambaum School of Physics, UNSW, Sydney, Australia Co-authors: Atomic calculations V.Dzuba,M.Kozlov,E.Angstmann,J.Berengut,M.Marchenko,Cheng Chin,S.Karshenboim,A.Nevsky Nuclear and QCD calculations E.Shuryak,V.Dmitriev,D.Leinweber,A.Thomas,R.Young,A.Hoell, P.Jaikumar,C.Roberts,S.Wright,A.Tedesco,W.Wiringa Cosmology J.Barrow Quasar data analysis J.Webb,M.Murphy,M.Drinkwater,W.Walsh,P.Tsanavaris,S.Curran Quasar observations C.Churchill,J.Prochazka,A.Wolfe, thanks to W.Sargent,R.Simcoe
42 Search for variation of fundamental constants Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Oklo natural nuclear reactor Quasar Absorption Spectra 1 Atomic clocks 1 Enhanced effects in atoms 1, molecules1 and nuclei Dependence on gravity 1 Based on atomic and molecular calculations Courtesy Victor Flambaum and Vladimir Dzuba
43 Quasar absorption spectra Gas cloud Earth Quasar Light One needs to know E( 2) for each line to do the fitting Courtesy Victor Flambaum and Vladimir Dzuba
44 energy of a one electron atom E mc Z 2 QED ( n 2 2Z 2 ) mc Z mc Z n 3 Z 2 k 2 E mc ck ( ) QED n 2 n 4 k 3 n rest energy Balmer energy Sommerfeld energy Schrödinger equation Pauli equation Dirac equation Feynman diagrams
45 Results of calculations (in cm-1) Negative shifters Anchor lines Atom Atom q q Mg I Ni II Mg II Ni II Mg II Cr II Si II Cr II Si II Cr II Al II Fe II Al III Al III Ni II Also, many transitions in Mn II, Ti II, Si IV, C II, C IV, N V, O I, Ca I, Ca II, Ge II, O II, Pb II Different signs and magnitudes of q provides opportunity to study systematic errors! Positive shifters Atom q Fe II Fe II Fe II Fe II Fe II Fe II Zn II Zn II Courtesy Victor Flambaum and Vladimir Dzuba
46 Co-Producers (in alphabetical order) Jacek Bieroń Charlotte Froese Fischer Stephan Fritzsche Gediminas Gaigalas Michel Godefroid Ian Grant Paul Indelicato Per Jönsson Pekka Pyykkö Uniwersytet Jagielloński Vanderbilt University & NIST Universität Jena Vilniaus Universitetas Université Libre Bruxelles University of Oxford l Université Paris VI Malmö Högskola Helsingin Yliopisto Thank you for your attention
Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules
 Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules 1 Listening to an atom q Coulomb forces + Quantum Electro-Dynamics => a relatively simple interpretation q Unprecedented control over internal and
Tests of fundamental symmetries with atoms and molecules 1 Listening to an atom q Coulomb forces + Quantum Electro-Dynamics => a relatively simple interpretation q Unprecedented control over internal and
Nuclear structure aspects of Schiff Moments. N.Auerbach Tel Aviv University and MSU
 Nuclear structure aspects of Schiff Moments N.Auerbach Tel Aviv University and MSU T-P-odd electromagnetic moments In the absence of parity (P) and time (T) reversal violation the T P-odd moments for a
Nuclear structure aspects of Schiff Moments N.Auerbach Tel Aviv University and MSU T-P-odd electromagnetic moments In the absence of parity (P) and time (T) reversal violation the T P-odd moments for a
Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments. K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri
 Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri An observation of EDM of a non-degenerate physical system is a direct unambiguous evidence of
Closed-shell Atomic Electric Dipole Moments K. V. P. Latha Angom Dilip Kumar Singh B. P. Das Rajat Chaudhuri An observation of EDM of a non-degenerate physical system is a direct unambiguous evidence of
Academic Editor: Joseph Reader Received: 21 December 2016; Accepted:19 January 2017; Published: 27 January 2017
 atoms Article JJ2LSJ Transformation and Unique Labeling for Energy Levels Gediminas Gaigalas 1, *, Charlotte Froese Fischer 2, Pavel Rynkun 1 and Per Jönsson 3 1 Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy,
atoms Article JJ2LSJ Transformation and Unique Labeling for Energy Levels Gediminas Gaigalas 1, *, Charlotte Froese Fischer 2, Pavel Rynkun 1 and Per Jönsson 3 1 Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy,
Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects. Bhanu Pratap Das
 Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects Bhanu Pratap Das Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore 560 034, India Outline
Parity and Time Reversal Violations in Atoms: Present Status and Future Prospects Bhanu Pratap Das Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore 560 034, India Outline
14. Structure of Nuclei
 14. Structure of Nuclei Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 14. Structure of Nuclei 1 In this section... Magic Numbers The Nuclear Shell Model Excited States Dr. Tina Potter 14.
14. Structure of Nuclei Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 14. Structure of Nuclei 1 In this section... Magic Numbers The Nuclear Shell Model Excited States Dr. Tina Potter 14.
Relativistic corrections of energy terms
 Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
Relativistic effects in Ni II and the search for variation of the fine. structure constant. Abstract
 Relativistic effects in Ni II and the search for variation of the fine structure constant. V. A. Dzuba, V. V. Flambaum, M. T. Murphy and J. K. Webb School of Physics, University of New South Wales, UNSW
Relativistic effects in Ni II and the search for variation of the fine structure constant. V. A. Dzuba, V. V. Flambaum, M. T. Murphy and J. K. Webb School of Physics, University of New South Wales, UNSW
Evaluating the Accuracy of Theoretical Transition Data for Atoms
 Evaluating the Accuracy of Theoretical Transition Data for Atoms Per Jönsson Group for Materials Science and Applied Mathematics School of Engineering, Malmö University, Sweden 6 maj 2013 Code development
Evaluating the Accuracy of Theoretical Transition Data for Atoms Per Jönsson Group for Materials Science and Applied Mathematics School of Engineering, Malmö University, Sweden 6 maj 2013 Code development
MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15
 MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15 Electron-Electron Repulsions (15.5-15.9) The hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation is exactly solvable yielding the wavefunctions and orbitals of chemistry. Howev er, the Schrödinger
MANY ELECTRON ATOMS Chapter 15 Electron-Electron Repulsions (15.5-15.9) The hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation is exactly solvable yielding the wavefunctions and orbitals of chemistry. Howev er, the Schrödinger
arxiv:submit/ [physics.atom-ph] 2 Apr 2018
![arxiv:submit/ [physics.atom-ph] 2 Apr 2018 arxiv:submit/ [physics.atom-ph] 2 Apr 2018](/thumbs/88/117718723.jpg) Ab initio calculations of hyperfine structures of zinc and evaluation of the nuclear quadrupole moment Q( 67 Zn) arxiv:submit/2215204 [physics.atom-ph] 2 Apr 2018 Jacek Bieroń, 1, Livio Filippin, 2 Gediminas
Ab initio calculations of hyperfine structures of zinc and evaluation of the nuclear quadrupole moment Q( 67 Zn) arxiv:submit/2215204 [physics.atom-ph] 2 Apr 2018 Jacek Bieroń, 1, Livio Filippin, 2 Gediminas
Lecture 4: Nuclear Energy Generation
 Lecture 4: Nuclear Energy Generation Literature: Prialnik chapter 4.1 & 4.2!" 1 a) Some properties of atomic nuclei Let: Z = atomic number = # of protons in nucleus A = atomic mass number = # of nucleons
Lecture 4: Nuclear Energy Generation Literature: Prialnik chapter 4.1 & 4.2!" 1 a) Some properties of atomic nuclei Let: Z = atomic number = # of protons in nucleus A = atomic mass number = # of nucleons
Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments)
 T Symmetry EDM s Octupole Deformation Other Nuclei Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments) J. Engel University of North Carolina June 16, 2005 T
T Symmetry EDM s Octupole Deformation Other Nuclei Nuclear Structure V: Application to Time-Reversal Violation (and Atomic Electric Dipole Moments) J. Engel University of North Carolina June 16, 2005 T
Academic Editor: Joseph Reader Received: 25 November 2016; Accepted: 6 January 2017; Published: 12 January 2017
 atoms Article Combining Multiconfiguration and Perturbation Methods: Perturbative Estimates of Core Core Electron Correlation Contributions to Excitation Energies in Mg-Like Iron Stefan Gustafsson 1, Per
atoms Article Combining Multiconfiguration and Perturbation Methods: Perturbative Estimates of Core Core Electron Correlation Contributions to Excitation Energies in Mg-Like Iron Stefan Gustafsson 1, Per
Physics 228 Today: April 22, 2012 Ch. 43 Nuclear Physics. Website: Sakai 01:750:228 or
 Physics 228 Today: April 22, 2012 Ch. 43 Nuclear Physics Website: Sakai 01:750:228 or www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 Nuclear Sizes Nuclei occupy the center of the atom. We can view them as being more
Physics 228 Today: April 22, 2012 Ch. 43 Nuclear Physics Website: Sakai 01:750:228 or www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 Nuclear Sizes Nuclei occupy the center of the atom. We can view them as being more
The Tiny Muon versus the Standard Model. Paul Debevec Physics 403 November 14 th, 2017
 The Tiny Muon versus the Standard Model Paul Debevec Physics 403 November 14 th, 2017 BNL E821 Muon g-2 Collaboration Standard Model of Particle Physics Components of the Standard Model of Particle Physics
The Tiny Muon versus the Standard Model Paul Debevec Physics 403 November 14 th, 2017 BNL E821 Muon g-2 Collaboration Standard Model of Particle Physics Components of the Standard Model of Particle Physics
Lecture 4. Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects
 Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure
 Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford s α -particle scattering experiement? (i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford s α -particle scattering experiement? (i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The
An Introduction to Hyperfine Structure and Its G-factor
 An Introduction to Hyperfine Structure and Its G-factor Xiqiao Wang East Tennessee State University April 25, 2012 1 1. Introduction In a book chapter entitled Model Calculations of Radiation Induced Damage
An Introduction to Hyperfine Structure and Its G-factor Xiqiao Wang East Tennessee State University April 25, 2012 1 1. Introduction In a book chapter entitled Model Calculations of Radiation Induced Damage
Speed of light c = m/s. x n e a x d x = 1. 2 n+1 a n π a. He Li Ne Na Ar K Ni 58.
 Physical Chemistry II Test Name: KEY CHEM 464 Spring 18 Chapters 7-11 Average = 1. / 16 6 questions worth a total of 16 points Planck's constant h = 6.63 1-34 J s Speed of light c = 3. 1 8 m/s ħ = h π
Physical Chemistry II Test Name: KEY CHEM 464 Spring 18 Chapters 7-11 Average = 1. / 16 6 questions worth a total of 16 points Planck's constant h = 6.63 1-34 J s Speed of light c = 3. 1 8 m/s ħ = h π
Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das
 Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore Collaborators: H. S. Nataraj, B. K. Sahoo,
Theory of Electric Dipole Moments of Atoms and Molecules Bhanu Pratap Das Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore Collaborators: H. S. Nataraj, B. K. Sahoo,
Intro to Nuclear and Particle Physics (5110)
 Intro to Nuclear and Particle Physics (5110) March 13, 009 Nuclear Shell Model continued 3/13/009 1 Atomic Physics Nuclear Physics V = V r f r L r S r Tot Spin-Orbit Interaction ( ) ( ) Spin of e magnetic
Intro to Nuclear and Particle Physics (5110) March 13, 009 Nuclear Shell Model continued 3/13/009 1 Atomic Physics Nuclear Physics V = V r f r L r S r Tot Spin-Orbit Interaction ( ) ( ) Spin of e magnetic
Variation of Fundamental Constants
 Variation of Fundamental Constants V.V. Flambaum School of Physics, UNSW, Sydney, Australia Co-authors: Atomic calculations V.Dzuba, M.Kozlov, E.Angstmann,J.Berengut,M.Marchenko,Cheng Chin,S.Karshenboim,A.Nevsky
Variation of Fundamental Constants V.V. Flambaum School of Physics, UNSW, Sydney, Australia Co-authors: Atomic calculations V.Dzuba, M.Kozlov, E.Angstmann,J.Berengut,M.Marchenko,Cheng Chin,S.Karshenboim,A.Nevsky
Nuclear Schiff moment
 Nuclear Schiff moment V.F. Dmitriev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia R.A. Sen'kov, I.B. Khriplovich, V.V. Flambaum Schiff theorem The energy of a neutral atom with a point like
Nuclear Schiff moment V.F. Dmitriev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia R.A. Sen'kov, I.B. Khriplovich, V.V. Flambaum Schiff theorem The energy of a neutral atom with a point like
In this lecture, we will go through the hyperfine structure of atoms. The coupling of nuclear and electronic total angular momentum is explained.
 Lecture : Hyperfine Structure of Spectral Lines: Page- In this lecture, we will go through the hyperfine structure of atoms. Various origins of the hyperfine structure are discussed The coupling of nuclear
Lecture : Hyperfine Structure of Spectral Lines: Page- In this lecture, we will go through the hyperfine structure of atoms. Various origins of the hyperfine structure are discussed The coupling of nuclear
נושא מס' 8: המבנה האלקטרוני של אטומים. Electronic Structure of Atoms. 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren
 נושא מס' 8: המבנה האלקטרוני של אטומים Electronic Structure of Atoms 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 19.07.10 The Electron Spin From further experiments, it was evident that the e had additional magnetic properties
נושא מס' 8: המבנה האלקטרוני של אטומים Electronic Structure of Atoms 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 19.07.10 The Electron Spin From further experiments, it was evident that the e had additional magnetic properties
Atomic Parity Violation
 Atomic Parity Violation Junghyun Lee APV proposes new physics beyond the standard model of elementary particles. APV is usually measured through the weak nuclear charge Q w, quantifying the strength of
Atomic Parity Violation Junghyun Lee APV proposes new physics beyond the standard model of elementary particles. APV is usually measured through the weak nuclear charge Q w, quantifying the strength of
Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Sascha Vogel Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher Wednesday, 14:15-16:45 FIS Lecture Hall Lecturers Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher svogel@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de
Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Sascha Vogel Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher Wednesday, 14:15-16:45 FIS Lecture Hall Lecturers Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher svogel@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de
Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic Data for Ar XVI
 Journal of Modern Physics, 2015, 6, 1609-1630 Published Online September 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2015.611163 Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic
Journal of Modern Physics, 2015, 6, 1609-1630 Published Online September 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2015.611163 Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
Particle Behavior of Light 1. Calculate the energy of a photon, mole of photons 2. Find binding energy of an electron (know KE) 3. What is a quanta?
 Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Experiments Hyrogen, Dirac theory
 Modern Atomic Physics: Experiment and Theory Experiments Hyrogen, Dirac theory Lecture April nd 014 Lectures in Internet Find zipped.ppt &.PDF files with the lectures at: http://web-docs.gsi.de/~stoe_exp/lectures/lectures.php
Modern Atomic Physics: Experiment and Theory Experiments Hyrogen, Dirac theory Lecture April nd 014 Lectures in Internet Find zipped.ppt &.PDF files with the lectures at: http://web-docs.gsi.de/~stoe_exp/lectures/lectures.php
URL: / /49/18/ Publisher: IOP. This document has been downloaded from MUEP (http://muep.mah.se).
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
URL: Publisher: Elsevier. This document has been downloaded from MUEP (
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Computer Physics Communications. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination.
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Computer Physics Communications. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination.
Using quasar microwave spectra to study variation of fundamental constants
 Present limits on time-variation of fundamental constants Sensitivity of astrophysical observations to variation of fundamental constants Conclusions Using quasar microwave spectra to study variation of
Present limits on time-variation of fundamental constants Sensitivity of astrophysical observations to variation of fundamental constants Conclusions Using quasar microwave spectra to study variation of
Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Nuclear and Particle Physics W. S. С Williams Department of Physics, University of Oxford and St Edmund Hall, Oxford CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1991 Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Historical perspective 1 1.2
Nuclear and Particle Physics W. S. С Williams Department of Physics, University of Oxford and St Edmund Hall, Oxford CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1991 Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Historical perspective 1 1.2
Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method
 Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method D. Angom Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad 380 009 Symposium on 50 Years of Coupled Cluster
Atomic electric dipole moment calculation with perturbed coupled cluster method D. Angom Theoretical Physics Division, Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad 380 009 Symposium on 50 Years of Coupled Cluster
Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga
 Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
c E If photon Mass particle 8-1
 Nuclear Force, Structure and Models Readings: Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 10 (Nuclear Models) Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 5 (Nuclear Forces) and Chapter 6 (Nuclear Structure) Characterization
Nuclear Force, Structure and Models Readings: Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 10 (Nuclear Models) Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 5 (Nuclear Forces) and Chapter 6 (Nuclear Structure) Characterization
Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method
 Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method Nodoka Yamanaka (ithes Group, RIKEN) In collaboration with E. Hiyama (RIKEN), T. Yamada (Kanto-Gakuin Univ.), Y. Funaki (RIKEN) 2015/10/12
Nuclear electric dipole moment in the Gaussian expansion method Nodoka Yamanaka (ithes Group, RIKEN) In collaboration with E. Hiyama (RIKEN), T. Yamada (Kanto-Gakuin Univ.), Y. Funaki (RIKEN) 2015/10/12
8. Which of the following could be an isotope of chlorine? (A) 37 Cl 17 (B) 17 Cl 17 (C) 37 Cl 17 (D) 17 Cl 37.5 (E) 17 Cl 37
 Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
NERS 311 Current Old notes notes Chapter Chapter 1: Introduction to the course 1 - Chapter 1.1: About the course 2 - Chapter 1.
 NERS311/Fall 2014 Revision: August 27, 2014 Index to the Lecture notes Alex Bielajew, 2927 Cooley, bielajew@umich.edu NERS 311 Current Old notes notes Chapter 1 1 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to the course
NERS311/Fall 2014 Revision: August 27, 2014 Index to the Lecture notes Alex Bielajew, 2927 Cooley, bielajew@umich.edu NERS 311 Current Old notes notes Chapter 1 1 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to the course
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Bohr s Correspondence Principle Bohr s Correspondence Principle states that quantum mechanics is in agreement with classical physics when the energy differences between quantized
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Bohr s Correspondence Principle Bohr s Correspondence Principle states that quantum mechanics is in agreement with classical physics when the energy differences between quantized
Nuclear and Radiation Physics
 501503742 Nuclear and Radiation Physics Why nuclear physics? Why radiation physics? Why in Jordan? Interdisciplinary. Applied? 1 Subjects to be covered Nuclear properties. Nuclear forces. Nuclear matter.
501503742 Nuclear and Radiation Physics Why nuclear physics? Why radiation physics? Why in Jordan? Interdisciplinary. Applied? 1 Subjects to be covered Nuclear properties. Nuclear forces. Nuclear matter.
Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes. Dario Vretenar
 Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes Dario Vretenar vretenar@phy.hr 1. Evolution of shell structure with N and Z A. Modification of the effective single-nucleon potential Relativistic
Evolution Of Shell Structure, Shapes & Collective Modes Dario Vretenar vretenar@phy.hr 1. Evolution of shell structure with N and Z A. Modification of the effective single-nucleon potential Relativistic
New Trends in the Nuclear Shell Structure O. Sorlin GANIL Caen
 New Trends in the Nuclear Shell Structure O. Sorlin GANIL Caen I. General introduction to the atomic nucleus Charge density, shell gaps, shell occupancies, Nuclear forces, empirical monopoles, additivity,
New Trends in the Nuclear Shell Structure O. Sorlin GANIL Caen I. General introduction to the atomic nucleus Charge density, shell gaps, shell occupancies, Nuclear forces, empirical monopoles, additivity,
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM. Spin. Pseudo-scalar. s d
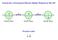 Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
CHEM 1311A. E. Kent Barefield. Course web page.
 CHEM 1311A E. Kent Barefield Course web page http://web.chemistry.gatech.edu/~barefield/1311/chem1311a.html Two requests: cell phones to silent/off no lap tops in operation during class Bring your transmitter
CHEM 1311A E. Kent Barefield Course web page http://web.chemistry.gatech.edu/~barefield/1311/chem1311a.html Two requests: cell phones to silent/off no lap tops in operation during class Bring your transmitter
Relativistic multiconfiguration methods. Atomic Structure Calculations using GRASP2K. What is needed. Grasp2K manual and references.
 Relativistic multiconfiguration methods Atomic Structure Calculations using GRASP2K Jörgen Ekman, Per Jönsson Group for Materials Science and Applied Mathematics Malmö University, Sweden 13 mars 2015 General
Relativistic multiconfiguration methods Atomic Structure Calculations using GRASP2K Jörgen Ekman, Per Jönsson Group for Materials Science and Applied Mathematics Malmö University, Sweden 13 mars 2015 General
Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants
 January 22, 2015 Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants MARIANNA SAFRONOVA University of Maryland Outline Blackbody radiation shifts in atomic clocks: Al +, Yb, Sr Theoretical
January 22, 2015 Atomic Clocks and the Search for Variation of Fundamental Constants MARIANNA SAFRONOVA University of Maryland Outline Blackbody radiation shifts in atomic clocks: Al +, Yb, Sr Theoretical
5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible. 26 Fe Cu Ni Co Pd Ag Ru 101.
 Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
ECE440 Nanoelectronics. Lecture 07 Atomic Orbitals
 ECE44 Nanoelectronics Lecture 7 Atomic Orbitals Atoms and atomic orbitals It is instructive to compare the simple model of a spherically symmetrical potential for r R V ( r) for r R and the simplest hydrogen
ECE44 Nanoelectronics Lecture 7 Atomic Orbitals Atoms and atomic orbitals It is instructive to compare the simple model of a spherically symmetrical potential for r R V ( r) for r R and the simplest hydrogen
Lesson 5 The Shell Model
 Lesson 5 The Shell Model Why models? Nuclear force not known! What do we know about the nuclear force? (chapter 5) It is an exchange force, mediated by the virtual exchange of gluons or mesons. Electromagnetic
Lesson 5 The Shell Model Why models? Nuclear force not known! What do we know about the nuclear force? (chapter 5) It is an exchange force, mediated by the virtual exchange of gluons or mesons. Electromagnetic
Atomic Structure. Atomic weight = m protons + m neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # of protons Isotope corresponds to # of neutrons
 Atomic Structure Neutrons: neutral Protons: positive charge (1.6x10 19 C, 1.67x10 27 kg) Electrons: negative charge (1.6x10 19 C, 9.11x10 31 kg) Atomic weight = m protons + m neutrons Atomic number (Z)
Atomic Structure Neutrons: neutral Protons: positive charge (1.6x10 19 C, 1.67x10 27 kg) Electrons: negative charge (1.6x10 19 C, 9.11x10 31 kg) Atomic weight = m protons + m neutrons Atomic number (Z)
Multiconfiguration Dirac-Hartree-Fock Calculations with Spectroscopic Accuracy: Applications to Astrophysics
 Review Multiconfiguration Dirac-Hartree-Fock Calculations with Spectroscopic Accuracy: Applications to Astrophysics Per Jönsson 1, *, Gediminas Gaigalas 2, Pavel Rynkun 2, Laima Radžiūtė 2, Jörgen Ekman
Review Multiconfiguration Dirac-Hartree-Fock Calculations with Spectroscopic Accuracy: Applications to Astrophysics Per Jönsson 1, *, Gediminas Gaigalas 2, Pavel Rynkun 2, Laima Radžiūtė 2, Jörgen Ekman
Nuclear Shell Model. Experimental evidences for the existence of magic numbers;
 Nuclear Shell Model It has been found that the nuclei with proton number or neutron number equal to certain numbers 2,8,20,28,50,82 and 126 behave in a different manner when compared to other nuclei having
Nuclear Shell Model It has been found that the nuclei with proton number or neutron number equal to certain numbers 2,8,20,28,50,82 and 126 behave in a different manner when compared to other nuclei having
Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (005) pp. 709 718 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No. 4, April 15, 005 Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (005) pp. 709 718 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No. 4, April 15, 005 Spin Cut-off Parameter of Nuclear Level Density and Effective Moment of Inertia
Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals
 Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals What are the more advanced theories of atomic structure? Richard Feynman, 1918 1988. Winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics. The modern scientific
Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals What are the more advanced theories of atomic structure? Richard Feynman, 1918 1988. Winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics. The modern scientific
Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Nuclear Structure Decay Data: Theory and Evaluation August Introduction to Nuclear Physics - 1
 2358-19 Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Nuclear Structure Decay Data: Theory and Evaluation 6-17 August 2012 Introduction to Nuclear Physics - 1 P. Van Isacker GANIL, Grand Accelerateur National d'ions Lourds
2358-19 Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Nuclear Structure Decay Data: Theory and Evaluation 6-17 August 2012 Introduction to Nuclear Physics - 1 P. Van Isacker GANIL, Grand Accelerateur National d'ions Lourds
Electric dipole moments of Hg, Xe, Rn, Ra, Pu, and TlF induced. by the nuclear Schiff moment and limits on time-reversal. violating interactions
 Electric dipole moments of Hg, Xe, Rn, Ra, Pu, and TlF induced by the nuclear Schiff moment and limits on time-reversal violating interactions V.A. Dzuba, V.V. Flambaum, and J.S.M. Ginges School of Physics,
Electric dipole moments of Hg, Xe, Rn, Ra, Pu, and TlF induced by the nuclear Schiff moment and limits on time-reversal violating interactions V.A. Dzuba, V.V. Flambaum, and J.S.M. Ginges School of Physics,
- Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions).
 170 LIGHT wavelength Diffraction frequency = wavelengths / time = - Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions). - Einstein noted that viewing light as a particle
170 LIGHT wavelength Diffraction frequency = wavelengths / time = - Light has properties of WAVES such as DIFFRACTION (it bends around small obstructions). - Einstein noted that viewing light as a particle
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics. Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments Nuclear models
 PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments Nuclear models eigenfunctions & eigenvalues: Classical: L = r p; Spherical Harmonics: Orbital angular momentum Orbital
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments Nuclear models eigenfunctions & eigenvalues: Classical: L = r p; Spherical Harmonics: Orbital angular momentum Orbital
RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties
 RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 2 Nuclear Properties Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 1 Introduction, Chapter 2 Atomic Nuclei Nuclear properties Masses
RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 2 Nuclear Properties Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 1 Introduction, Chapter 2 Atomic Nuclei Nuclear properties Masses
Particle Physics. experimental insight. Paula Eerola Division of High Energy Physics 2005 Spring Semester Based on lectures by O. Smirnova spring 2002
 experimental insight e + e - W + W - µνqq Paula Eerola Division of High Energy Physics 2005 Spring Semester Based on lectures by O. Smirnova spring 2002 Lund University I. Basic concepts Particle physics
experimental insight e + e - W + W - µνqq Paula Eerola Division of High Energy Physics 2005 Spring Semester Based on lectures by O. Smirnova spring 2002 Lund University I. Basic concepts Particle physics
( ) ( ) Last Time. 3-D particle in box: summary. Modified Bohr model. 3-dimensional Hydrogen atom. Orbital magnetic dipole moment
 Last Time 3-dimensional quantum states and wave functions Decreasing particle size Quantum dots (particle in box) Course evaluations Thursday, Dec. 10 in class Last HW assignment available : for practice
Last Time 3-dimensional quantum states and wave functions Decreasing particle size Quantum dots (particle in box) Course evaluations Thursday, Dec. 10 in class Last HW assignment available : for practice
ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT OF THE ELECTRON AND ITS COSMOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS
 ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT OF THE ELECTRON AND ITS COSMOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS H S NATARAJ Under the Supervision of Prof. B P DAS Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore
ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT OF THE ELECTRON AND ITS COSMOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS H S NATARAJ Under the Supervision of Prof. B P DAS Non-Accelerator Particle Physics Group Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bangalore
Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 468 472 Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 2, August 15, 2008 Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron YANG Jian-Hui, 1 LI Ping, 2, ZHANG Jian-Ping,
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 468 472 Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 2, August 15, 2008 Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron YANG Jian-Hui, 1 LI Ping, 2, ZHANG Jian-Ping,
Energy level structure of Er 3+ free ion and Er 3+ ion in Er 2 O 3 crystal
 Energy level structure of Er 3+ free ion and Er 3+ ion in Er 2 O 3 crystal G. Gaigalas a,b, D. Kato a, P. Jönsson c, P. Rynkun b, L. Radžiūtė b a National Institute for Fusion Science, 322-6 Oroshi-cho,
Energy level structure of Er 3+ free ion and Er 3+ ion in Er 2 O 3 crystal G. Gaigalas a,b, D. Kato a, P. Jönsson c, P. Rynkun b, L. Radžiūtė b a National Institute for Fusion Science, 322-6 Oroshi-cho,
Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field
 Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field δε = j A j0 (nfjl) Fm F j0 Fm F Clebsch-Gordan coefficients n principal quantum number n F hydrogen total angular momentum
Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field δε = j A j0 (nfjl) Fm F j0 Fm F Clebsch-Gordan coefficients n principal quantum number n F hydrogen total angular momentum
Development of atomic theory
 Development of atomic theory The chapter presents the fundamentals needed to explain and atomic & molecular structures in qualitative or semiquantitative terms. Li B B C N O F Ne Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni
Development of atomic theory The chapter presents the fundamentals needed to explain and atomic & molecular structures in qualitative or semiquantitative terms. Li B B C N O F Ne Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni
Instead, the probability to find an electron is given by a 3D standing wave.
 Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
Space-Time Symmetries
 Space-Time Symmetries Outline Translation and rotation Parity Charge Conjugation Positronium T violation J. Brau Physics 661, Space-Time Symmetries 1 Conservation Rules Interaction Conserved quantity strong
Space-Time Symmetries Outline Translation and rotation Parity Charge Conjugation Positronium T violation J. Brau Physics 661, Space-Time Symmetries 1 Conservation Rules Interaction Conserved quantity strong
EDM. Spin. ν e. β - Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics
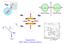 T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
Mean field studies of odd mass nuclei and quasiparticle excitations. Luis M. Robledo Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Spain
 Mean field studies of odd mass nuclei and quasiparticle excitations Luis M. Robledo Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Spain Odd nuclei and multiquasiparticle excitations(motivation) Nuclei with odd number
Mean field studies of odd mass nuclei and quasiparticle excitations Luis M. Robledo Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Spain Odd nuclei and multiquasiparticle excitations(motivation) Nuclei with odd number
Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra
 Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra I. Ahmad, K. Bailey, J. Guest, R. J. Holt, Z.-T. Lu, T. O Connor, D. H. Potterveld, N. D. Scielzo Roy Holt Lepton Moments 2006 Cape Cod Outline Why is an EDM interesting?
Status of the Search for an EDM of 225 Ra I. Ahmad, K. Bailey, J. Guest, R. J. Holt, Z.-T. Lu, T. O Connor, D. H. Potterveld, N. D. Scielzo Roy Holt Lepton Moments 2006 Cape Cod Outline Why is an EDM interesting?
Democritus s ideas don t explain chemical behavior & lacked experimental support.
 A1: Atomic Structure Worksheet Key (Goals 1 3, Chapter 4) 1. Democritus, who lived in Greece during the 4 th century B.C., suggested that matter is made up of tiny particles that cannot be divided. He
A1: Atomic Structure Worksheet Key (Goals 1 3, Chapter 4) 1. Democritus, who lived in Greece during the 4 th century B.C., suggested that matter is made up of tiny particles that cannot be divided. He
RFSS: Lecture 8 Nuclear Force, Structure and Models Part 1 Readings: Nuclear Force Nuclear and Radiochemistry:
 RFSS: Lecture 8 Nuclear Force, Structure and Models Part 1 Readings: Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 10 (Nuclear Models) Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 5 (Nuclear Forces) and Chapter 6 (Nuclear
RFSS: Lecture 8 Nuclear Force, Structure and Models Part 1 Readings: Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 10 (Nuclear Models) Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 5 (Nuclear Forces) and Chapter 6 (Nuclear
INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS
 DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
The Proper)es of Nuclei. Nucleons
 The Proper)es of Nuclei Z N Nucleons The nucleus is made of neutrons and protons. The nucleons have spin ½ and (individually) obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Protons p 938.3 MeV 2.79µ N Neutrons n
The Proper)es of Nuclei Z N Nucleons The nucleus is made of neutrons and protons. The nucleons have spin ½ and (individually) obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Protons p 938.3 MeV 2.79µ N Neutrons n
Optical frequency comb and precision spectroscopy. Fundamental constants. Are fundamental constants constant? Precision spectroscopy
 27.01.2015 Optical frequency comb and precision spectroscopy Fundamental constants Are fundamental constants constant? Precision spectroscopy Frequency comb Drift of fine structure constant Fundamental
27.01.2015 Optical frequency comb and precision spectroscopy Fundamental constants Are fundamental constants constant? Precision spectroscopy Frequency comb Drift of fine structure constant Fundamental
ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION
 ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION OUTLINE Overview of the Atomic Parity Violation Theory: How to calculate APV amplitude? Analysis of Cs experiment and implications for search for physics beyond the Standard Model
ATOMIC PARITY VIOLATION OUTLINE Overview of the Atomic Parity Violation Theory: How to calculate APV amplitude? Analysis of Cs experiment and implications for search for physics beyond the Standard Model
" = Y(#,$) % R(r) = 1 4& % " = Y(#,$) % R(r) = Recitation Problems: Week 4. a. 5 B, b. 6. , Ne Mg + 15 P 2+ c. 23 V,
 Recitation Problems: Week 4 1. Which of the following combinations of quantum numbers are allowed for an electron in a one-electron atom: n l m l m s 2 2 1! 3 1 0 -! 5 1 2! 4-1 0! 3 2 1 0 2 0 0 -! 7 2-2!
Recitation Problems: Week 4 1. Which of the following combinations of quantum numbers are allowed for an electron in a one-electron atom: n l m l m s 2 2 1! 3 1 0 -! 5 1 2! 4-1 0! 3 2 1 0 2 0 0 -! 7 2-2!
I.B. Khriplovich Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia
 HISTORY AND PERSPECTIVES OF P AND T VIOLATION IN ATOMS I.B. Khriplovich Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia I. HISTORY Historically, good reasons to start just with /P, /T effects.
HISTORY AND PERSPECTIVES OF P AND T VIOLATION IN ATOMS I.B. Khriplovich Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia I. HISTORY Historically, good reasons to start just with /P, /T effects.
-"l" also contributes ENERGY. Higher values for "l" mean the electron has higher energy.
 170 - Giving the four parameters will uniquely identify an electron around an atom. No two electrons in the same atom can share all four. These parameters are called QUANTUM NUMBERS. PRINCIPAL QUANTUM
170 - Giving the four parameters will uniquely identify an electron around an atom. No two electrons in the same atom can share all four. These parameters are called QUANTUM NUMBERS. PRINCIPAL QUANTUM
13. Basic Nuclear Properties
 13. Basic Nuclear Properties Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 13. Basic Nuclear Properties 1 In this section... Motivation for study The strong nuclear force Stable nuclei Binding
13. Basic Nuclear Properties Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 13. Basic Nuclear Properties 1 In this section... Motivation for study The strong nuclear force Stable nuclei Binding
Chapter 7. Characteristics of Atoms. 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation. Chapter 7 1. The Quantum Mechanical Atom. Atoms: How do we study atoms?
 Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Atom 1 Characteristics of Atoms Atoms: possess mass contain positive nuclei contain electrons occupy volume have various properties attract one another combine to form
Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Atom 1 Characteristics of Atoms Atoms: possess mass contain positive nuclei contain electrons occupy volume have various properties attract one another combine to form
Ab-initio Calculations for Forbidden M1/E2 Decay Rates in Ti XIX ion
 EJTP 3, No. 11 (2006) 111 122 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Ab-initio Calculations for Forbidden M1/E2 Decay Rates in Ti XIX ion A. Farrag Physics Department,Faculty of Science, Cairo University,
EJTP 3, No. 11 (2006) 111 122 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Ab-initio Calculations for Forbidden M1/E2 Decay Rates in Ti XIX ion A. Farrag Physics Department,Faculty of Science, Cairo University,
Klaus Jungmann 2006 EDM Experiments
 Klaus Jungmann 2006 EDM Experiments Heavy Quarks and Leptons16.10-20.10.2006 Munich, Germany Fundamental Symmetries and Forces Discrete Symmetries Fundamental Fermions Models Beyond Standard Theory Precision
Klaus Jungmann 2006 EDM Experiments Heavy Quarks and Leptons16.10-20.10.2006 Munich, Germany Fundamental Symmetries and Forces Discrete Symmetries Fundamental Fermions Models Beyond Standard Theory Precision
Physics 1C Lecture 29B
 Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY
 Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS
 QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS Outline I Introduction II Correlation Static correlation effects MC methods DFT III Relativity Generalities From 4 to 1 components Effective core potential Outline
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS Outline I Introduction II Correlation Static correlation effects MC methods DFT III Relativity Generalities From 4 to 1 components Effective core potential Outline
Unit 1 Part 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Introduction to Atomic Structure UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC STRUCTURE Contents 1. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons 2. Early Models of the Atom 3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4. Atoms and Ions
Search for temporal variations of fundamental constants
 Schladming School 2010: Masses and Constants Lecture II Search for temporal variations of fundamental constants Ekkehard Peik Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Time and Frequency Department Braunschweig,
Schladming School 2010: Masses and Constants Lecture II Search for temporal variations of fundamental constants Ekkehard Peik Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Time and Frequency Department Braunschweig,
 Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS. ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are...
 Atomic Structure THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Atomic Structure THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Chemistry 3502/4502. Final Exam Part I. May 14, 2005
 Advocacy chit Chemistry 350/450 Final Exam Part I May 4, 005. For which of the below systems is = where H is the Hamiltonian operator and T is the kinetic-energy operator? (a) The free particle
Advocacy chit Chemistry 350/450 Final Exam Part I May 4, 005. For which of the below systems is = where H is the Hamiltonian operator and T is the kinetic-energy operator? (a) The free particle
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman. Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION
 P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
Glenn T. Seaborg and the Modern Periodic Table of Elements. V. Pershina GSI, Darmstadt, Germany
 Glenn T. Seaborg and the Modern Periodic Table of Elements V. Pershina GSI, Darmstadt, Germany Glenn T. Seaborg (1912-1999) 1997 [www.allperiodictables.com] Periodic Table of Dimitri I. Mendeleev Dimitri
Glenn T. Seaborg and the Modern Periodic Table of Elements V. Pershina GSI, Darmstadt, Germany Glenn T. Seaborg (1912-1999) 1997 [www.allperiodictables.com] Periodic Table of Dimitri I. Mendeleev Dimitri
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms
 Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms Hyperfine effects in atomic physics are due to the interaction of the atomic electrons with the electric and magnetic multipole
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 21 Hyperfine Structure in Hydrogen and Alkali Atoms Hyperfine effects in atomic physics are due to the interaction of the atomic electrons with the electric and magnetic multipole
