Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis: a method for PSA in dynamic process system
|
|
|
- Shanon Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis: a method for PSA in dynamic process system M. Demichela & N. Piccinini Centro Studi su Sicurezza Affidabilità e Rischi, Dipartimento di Scienza dei Materiali e Ingegneria Chimica, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi, Torino, Italia One of the important issues still under investigations in order to increase the confidence in the results obtained in the PSA of technological systems is the physical modelling of the process. Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis provides a full representation of the plant states, as well as all the possible occurrences patterns, expressed in a set of mutually self-excluding sequences. Availability of the full set of alternatives allows the complete spectrum of possible probability-consequence conditions to be used as a basis for decisions in risk reduction. Furthermore it is possible to interface with the logicprobabilistic model a process simulator, in order to assess the status of each relevant process variable with reference to the failure sequence identified, allowing the mutual interactions of the hardware components and the physical evolution of the plant to be taken into account. This approach is here described through a simple case study taken from literature. 1. Introduction In the present work, through the application to a simple exercise taken from literature, the capabilities of dealing with the risk assessment of dynamic system of IDDA (Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis) methodology were investigated. IDDA is based on an enhanced form of dynamic event tree. Starting from a description, reflecting the level of knowledge that the analyst has about the system, IDDA is able to develop all the sequences of events compatible with the description received, from the point of view both of the logical construction, as of the probabilistic coherence. The system description has the form a binary chart, where the real logical and chronological sequence of the events is described; the direction of each branch is characterised by a probability of occurrence that can be modified by the boundary conditions, and in particular by the same development of the events themselves (probabilities conditioned by the events dynamic). As a matter of fact, in a dynamic cause-consequence logic, in addition to the direct logical interactions characterising it, each event can influence the subsequent events, depending on deterministic cause-consequence relations or stochastic dependences. At the end of the analysis, the full set of the possible alternatives in which the system could evolve is obtained. These alternatives represent a partition since they are mutually exclusive; they are all and the sole possible alternatives, this allowing the method to guarantee the completeness and the coherence of the analysis. The above logical-probabilistic model can be interfaced with a phenomenological model of the system, in order to obtain, for each alternative sequence:
2 Probability of occurrence; Trend of the significant physical variable; Consequences entity. The analysis of the alternatives in terms of logical congruence and correspondence with the knowledge of the plant is made easier by their representation as concatenations of events, placed along a well-defined time-trajectory. Once the model has been defined, all the information worked out by the software are made available to the analyst as results (Piccinini et al., 1996; Galvagni & Demichela, 2003). 2. The Case Study The case study is taken from Marseguerra & Zio (1996). In particular, the system object of the study (Fig. 1) is a tank containing a liquid. Its level is controlled discontinuously by three independent units, made of three level transmitters, all measuring the level in the main tank, each activating respectively two feed systems (U1 and U2) and one extraction system (U3). The liquid supply takes place through two pumps, fed by different tanks, with a flow rate able to maintain a constant level variation of 0,6 m/h each pump. The extraction system is made of a on-off valve with a flow rate able to bring to a level reduction of 0,6 m/h. At time t=0, the system is in its nominal configuration, with the units U1 and U3 operating and the U2 component in stand-by. In this case, the net flow rate is zero and the level is constant, until the first stochastic modification of the component status occurs. The system components can assume 4 status, whose transitions follow to an exponential law: 1. operating (on) 2. stand-by (off) 3. stuck on 4. stuck off Figure 1. The tank object of the analysis. The mean time between failures is respectively: U1: 219 h U2: 175 h U3: 320 h
3 The probability over time of main tank overfilling or dry out has been assessed over a mission time of 1000 h, in different conditions as described below. 3. Non Repairable Components The first stage of the analysis is the construction of the logical-probabilistic model of the system, using the IDDA syntax. Each line consists in a question that can have multiple possible answers, each one characterised by an expectation degree. Every question is a level in the IDDA syntax and a branch point in an event tree. Each branch is characterised by a probability of occurrence, its uncertainty degree and a series of addresses, that define the logical path depending on the answer to the analyst question. The alternatives are mutually exclusive. In the present case, the transition rates do not change if the component is operating and fails stuck-on, or if it is in stand-by and fails stuck-off, thus the process control system intervention, activating or deactivating the components, as a matter of fact have not any influence on the occurrence probability of a failure. At this stage no probabilities were introduced in the model, but only conventional values 0.5. This indicating that the real probabilities will be provided by an external file, that from failure rates and mission times calculates the probabilities for each branch. IDDA combines the answers to the analyst questions in all the possible ways, in order to obtain the partition made of all the possible alternative sequences of events, to which a probability of occurrence in associated. The sequences are of immediate reading and understanding. They show, step by step, the chosen paths, the associated probabilities and the modification on the logical status and on the probability of each event included in the sequence. The reading of the alternatives immediately reveals possible incongruence and omissions in the logical representation of the problem. In the present case, only a sequence can bring to the dry-out of the tank, as detailed in Table 1. The possible alternative sequences rise to 5 if the events bringing to overflow are considered: their single and cumulative probabilities are shown in Table 2. Table 1. Dry out constituent. CONSTITUENT Number : 1 10 U1 Fails E U1 S. Off E U2 Fails E U2 S. Off E U3 Fails E U3 S. On E Exit Dry out E-01 CONSTITUENT PROBABILITY: E-01 Table 2. Overflow constituents COSTIT. N. PROBABILITY E E E E E CUMULATE PROB E-01
4 Figure 2 shows the results of the input model processing. At each time the probabilities of the four incompatible operating modes (overflow, dry out, no flow and normal operations) add up to 1. The second case investigated through IDDA is the one in which the transition probability to the state 3 (stuck on) is increased of a factor 10 and the one to the state 4 (stuck off) increased of a factor 100: the logical-probabilistic model will undergo substantial modifications 1 0,8 - cpdf - 0,6 0,4 0,2 0 - tempo [h] - Overflow Dry out No flow Normal flow Figure 2. Non repairable components, transition rates invariable with the transition type. In fact, while in the previous case, the event probability was independent on the occurrence order of the components failures, in the following one, the event probability will be strongly dependent on it. As an example, let s consider the first failure of the U1 component (the whole input model will keep into account also the case of a first failure of the U2 or U3 component) in the stuck on failure mode. The subsequent level examines the presence of other failures: if no other failure is present, the model will directly send to a normal operating condition; otherwise it will be investigated what of the other components, U2 or U3, will fail first. Let s consider a failure of U3 component: it could fail stuck on or stuck off. In the case of U3 stuck off, the consequence will be the overflow, independently from the behaviour of U2. With U3 stuck on, instead, the behaviour of U2 will be decisive: if U2 is stuck on, the result will be an overflow, if stuck off, the result will be a normal operating condition. Similarly, let us consider the case of a failure of the U2 component after the U1 component has failed. If U2 is stuck on, the event will result in an overflow, independently from the behaviour of U3; if U2 is stuck off, the whole system performance will depend on the U3 component behaviour: even with U3 stuck on, there will be normal operating conditions, instead U3 stuck off will bring to an overflow. The input model thus includes all the possible evolution path of the system failures. Furthermore, also the complexity of the factors to be included in the probability assessment will increase.
5 The solution of the differential equation system: dpf = λ Pf dt dp g = + λ P f dt Will bring to the following probabilities: Absence of failures p1 = { 1 exp[ Σ T ]} with =λ1+λ2+λ3 sum of the transition rates of the single system components. First failure of U1 Absence of U2 and U3 failures [ 1 exp[ ( λ" + λ ) T ] k2 p 3 = 1 k2 p1 1 k2 λ" 2+ λ3 k2 = where Σ and λ 2 transition rate of U2 modified after a failure of U1 occurred. λ" 2 p4 = λ" Second failure of U2 2+ λ3 PU 1, U 2, U 3 p5 = p U3 operating or failed 1 p2 p3 p4. Hereafter the result obtained are reported: 6 sequences has been identified for the dry out, with a cumulate probability of 8.05E-02; 18 sequences bring to the overflow, with a total cumulate probability of 3.546E-01. Figure 3 shows the results as a diagram. 1 p 2 = λ 1 Σ 0,8 - cpdf - 0,6 0,4 0,2 0 - time [h] - Overflow Dry out No flow Normal flow Figure 3: Non repairable components, transition rates variable with the transition type.
6 0,0E+00 In Figure 4 a comparison between the results of the cases previously discussed is reported, with reference to the main events dry-out (a) and overflow (b). Thick lines represent the case of constant transition rate, while thin ones the case of increased transition rate for stuck on and stuck off conditions. a 3,0E-04 2,5E-04 2,0E-04 1,4E-03 1,2E-03 1,0E-03 - PDDF - 1,5E-04 - PDDF - 8,0E-04 6,0E-04 1,0E-04 4,0E-04 5,0E-05 2,0E-04 0,0E+00 - time [h] - - time [h] - b Figure 4. Comparison between the results of the cases discussed in the first sections. 4,0E-01 3,5E-01 3,0E-01 2,5E-01 - cpdf - 2,0E-01 1,5E-01 1,0E-01 5,0E-02 0,0E+00 - time [h] - Figure 5 Comparison between the case of the failure on demand of the PCS and the previous cases analysed Both the logical-probabilistic model and the calculation tool developed allow taking into consideration the possibility of a failure on demand of the process control system (PCS), with the hypothesis that this failure didn t influence the probability of the subsequent failures. In this case the unavailability on demand of the control system has been taken equivalent to 0.1. In Figure 5 the results in the case of failure on demand (thick lines) are compared with the previously discussed cases of overflow (continuous lines) and dry out (dotted lines) for constant transition rates. Both the top events occurs in shorter times and with higher cumulative probabilities in the case of failure on demand of the PCS.
7 4. Effect of the Temperature on the Reliability of the System In the case a heat source, heating up the content of the main tank, is considered, the effect of the temperature on the reliability of the control units can be assessed, under the hypothesis of an adiabatic behaviour of the system and of an homogeneous distribution of the heat in the whole mass. From a phenomenological point of view, the transient events bringing to a temperature increase in the system are those produced by U3 stuck off, both for a PCS call and for a failure. The difference within them is solely due to the quantity of liquid trapped in the tank, and thus to its thermal capacity. The introduction of the heating source doesn t imply modification in the logical-probabilistic model. In order to assess quantitatively the effect of the temperature on the reliability of the system the following mass and energy balances have been formulated with reference to the tank level. dl() t = Qi () t Qo () t dt dϑ() t 1 = { w Qi () t [ θ () t θi ]} dt L() t with the initial equilibrium conditions: L = 7 0 e ϑ = where: L is the tank level; Qi is the inlet flow rate and Qo the outflow; θ is the temperature of the liquid in the tank, w is the heating source power, with H m C w = 1 ρ A C h, with the following geometric dimensions for the mail tank: A, tank surface, 180 m2; H, level heights: minimum 4 m, maximum 10 m, controlled between 6 and 8 meters; ρ, the density of the liquid and C, its heat capacity. From the balance it is easy to deduce how the significant level transients, all initiated from an equilibrium situation, imply the related temperature transients, that can be computed once for all. The failure rate time development stiffly depends on the above temperature transients. Failure rates dependencies from the temperatures were defined through the correlation represented in Marseguerra & Zio, Since the temperature transient is set by an univocal function T=f(t), also the failure rates λ() T are univocally defined as λ[ f( t) ]. Ultimately, before the thermal transient are started, the failure rates are constant, after they change according to a given function of the time. From the system reliability point of view, at a first time pt ()= exp( λ t), then pt ()= exp[ λ( t) dt]. In order to solve the transients problem, a code able to solve (finite difference solution) the differential equations for the temperature, according to the model described in Marseguerra & Zio (1996) was developed. In Figure 7 the results are shown, both in the case of PCS without unavailability problems (continuous lines), and in the case of PCS failure on demand (FOD) probability of 0.2 (dotted lines), for the main consequences in the system (overflow, thick lines and dry-out, thin lines).
8 6,0E-01 5,0E-01 4,0E-01 - CPDF - 3,0E-01 2,0E-01 1,0E-01 0,0E+00 Time [h] Overflow Dry out Overflow FOD Dry out FOD Figure 7 Results in the case of temperature dependence of the transition rates. 5. Conclusions In the present work a situation where the evolution of the physical variables can have an impact on the reliability and availability of a system was analysed. The tool used to perform the study was IDDA (Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis), that was applied to a simple case taken from the literature. The methodology allows a logical-probabilistic model, similar to an event tree, but based on its own syntax, to be developed, together with a model able to associate to the events described in the first one the parameters characterising them. In the present case, the above parameters are the probabilities, computed as functions of the mission time of the system, using the traditional reliability and availability expressions for components and systems. Those expressions are systematically applied to each event sequence developed by the model processing, these last representing the constituents of a partition. As a matter of fact, the results obtained are realistic and complete, since they derive from the analytical computation of the system behaviour. References Galvagni, R. & Clementel, S., 1989 Risk Analysis as an instrument of design, in Safety Design Criteria for Industrial Plant, M. Cumo and A. Naviglio (eds.), CRC Press, Boca Raton. Galvagni R. and Demichela M., 2003 IDDA (Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis) - Metodologia per la valutazione di sicurezza con alberi decisionali, Proc. convegno nazionale la protezione dell ambiente, l affidabilita dei sistemi e la sicurezza industriale: da 20 anni di esperienze alle prospettive future, Alghero: Marseguerra M. and Zio E., 1996 Monte Carlo approach to PSA for dynamic process systems, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 52: Piccinini, N., Scataglini, L., Fiorentini, C. and De Vecchi F Logical and physical simulation of a gas drying plant for safety management Chemputers Europe III Frankfurt, Germany.
MODELLING DYNAMIC RELIABILITY VIA FLUID PETRI NETS
 MODELLING DYNAMIC RELIABILITY VIA FLUID PETRI NETS Daniele Codetta-Raiteri, Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Torino, Italy Andrea Bobbio, Dipartimento di Informatica, Università del Piemonte
MODELLING DYNAMIC RELIABILITY VIA FLUID PETRI NETS Daniele Codetta-Raiteri, Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Torino, Italy Andrea Bobbio, Dipartimento di Informatica, Università del Piemonte
Reliability of Technical Systems
 Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method
 Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method Sunghyon Jang, and Akira Yamaguchi Department of Nuclear Engineering and Management, The University of
Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method Sunghyon Jang, and Akira Yamaguchi Department of Nuclear Engineering and Management, The University of
Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis. Markov Processes
 Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis Firma convenzione Politecnico Part II: Continuous di Milano e Time Veneranda Discrete Fabbrica State del Duomo di Milano Markov Processes Aula Magna Rettorato
Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis Firma convenzione Politecnico Part II: Continuous di Milano e Time Veneranda Discrete Fabbrica State del Duomo di Milano Markov Processes Aula Magna Rettorato
Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum
 Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum Pavel Krcal a,b and Ola Bäckström a a Lloyd's Register Consulting, Stockholm, Sweden b Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Abstract:
Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum Pavel Krcal a,b and Ola Bäckström a a Lloyd's Register Consulting, Stockholm, Sweden b Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Abstract:
However, reliability analysis is not limited to calculation of the probability of failure.
 Probabilistic Analysis probabilistic analysis methods, including the first and second-order reliability methods, Monte Carlo simulation, Importance sampling, Latin Hypercube sampling, and stochastic expansions
Probabilistic Analysis probabilistic analysis methods, including the first and second-order reliability methods, Monte Carlo simulation, Importance sampling, Latin Hypercube sampling, and stochastic expansions
Application of the Stress-Strength Interference Model to the Design of a Thermal- Hydraulic Passive System for Advanced Reactors
 Application of the Stress-Strength Interference Model to the Design of a Thermal- Hydraulic Passive System for Advanced Reactors Luciano Burgazzi Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and
Application of the Stress-Strength Interference Model to the Design of a Thermal- Hydraulic Passive System for Advanced Reactors Luciano Burgazzi Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and
Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems
 Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems RA II: Methods (FTA, ETA) Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Problem description It is not possible to analyse complicated, highly-reliable or novel systems as black box
Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems RA II: Methods (FTA, ETA) Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Problem description It is not possible to analyse complicated, highly-reliable or novel systems as black box
System Reliability Analysis. CS6323 Networks and Systems
 System Reliability Analysis CS6323 Networks and Systems Topics Combinatorial Models for reliability Topology-based (structured) methods for Series Systems Parallel Systems Reliability analysis for arbitrary
System Reliability Analysis CS6323 Networks and Systems Topics Combinatorial Models for reliability Topology-based (structured) methods for Series Systems Parallel Systems Reliability analysis for arbitrary
Failures in Process Industries
 Fault Tree Analysis Failures in Process Industries Single Component Failure Data for failure rates are compiled by industry Single component or single action Multiple Component Failure Failures resulting
Fault Tree Analysis Failures in Process Industries Single Component Failure Data for failure rates are compiled by industry Single component or single action Multiple Component Failure Failures resulting
12 - The Tie Set Method
 12 - The Tie Set Method Definitions: A tie set V is a set of components whose success results in system success, i.e. the presence of all components in any tie set connects the input to the output in the
12 - The Tie Set Method Definitions: A tie set V is a set of components whose success results in system success, i.e. the presence of all components in any tie set connects the input to the output in the
UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY ABSTRACT
 (Vol.2) 29, December UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY R. Briš Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Ostrava, Czech Republic
(Vol.2) 29, December UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY R. Briš Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Ostrava, Czech Republic
A MONTE CARLO SIMULATION APPROACH TO THE PRODUCTION AVAILABILITY EVALUATION OF AN OFFSHORE INSTALLATION WITH OPERATIONAL LOOPS
 A MONTE CARLO SIMULATION APPROACH TO THE PRODUCTION AVAILABILITY EVALUATION OF AN OFFSHORE INSTALLATION WITH OPERATIONAL LOOPS ENRICO ZIO, PIERO BARALDI, AND EDOARDO PATELLI Dipartimento Ingegneria Nucleare
A MONTE CARLO SIMULATION APPROACH TO THE PRODUCTION AVAILABILITY EVALUATION OF AN OFFSHORE INSTALLATION WITH OPERATIONAL LOOPS ENRICO ZIO, PIERO BARALDI, AND EDOARDO PATELLI Dipartimento Ingegneria Nucleare
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability
 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
LOCAL FUSION OF AN ENSEMBLE OF SEMI-SUPERVISED SELF ORGANIZING MAPS FOR POST-PROCESSING ACCIDENTAL SCENARIOS
 LOCAL FUSION OF AN ENSEMBLE OF SEMI-SUPERVISED SELF ORGANIZING MAPS FOR POST-PROCESSING ACCIDENTAL SCENARIOS Francesco Di Maio 1, Roberta Rossetti 1, Enrico Zio 1,2 1 Energy Department, Politecnico di
LOCAL FUSION OF AN ENSEMBLE OF SEMI-SUPERVISED SELF ORGANIZING MAPS FOR POST-PROCESSING ACCIDENTAL SCENARIOS Francesco Di Maio 1, Roberta Rossetti 1, Enrico Zio 1,2 1 Energy Department, Politecnico di
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems
 (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Fault Tree Analysis Mathematical Background and Algorithms Prof. Dr. Liggesmeyer, 0 Content Definitions of Terms Introduction to Combinatorics General
(Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Fault Tree Analysis Mathematical Background and Algorithms Prof. Dr. Liggesmeyer, 0 Content Definitions of Terms Introduction to Combinatorics General
Reliability of Technical Systems
 Main Topics 1. Introduction, Key Terms, Framing the Problem 2. Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 3. Some Important Reliability Distributions 4. Component Reliability 5. Software
Main Topics 1. Introduction, Key Terms, Framing the Problem 2. Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 3. Some Important Reliability Distributions 4. Component Reliability 5. Software
arxiv: v2 [math.oc] 28 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.oc] 28 Feb 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.oc] 28 Feb 2013](/thumbs/91/107402029.jpg) Predictive maintenance for the heated hold-up tank Benoîte de Saporta Huilong Zhang arxiv:127.4866v2 [math.oc] 28 Feb 213 Abstract We present a numerical method to compute an optimal maintenance date for
Predictive maintenance for the heated hold-up tank Benoîte de Saporta Huilong Zhang arxiv:127.4866v2 [math.oc] 28 Feb 213 Abstract We present a numerical method to compute an optimal maintenance date for
BEST ESTIMATE PLUS UNCERTAINTY SAFETY STUDIES AT THE CONCEPTUAL DESIGN PHASE OF THE ASTRID DEMONSTRATOR
 BEST ESTIMATE PLUS UNCERTAINTY SAFETY STUDIES AT THE CONCEPTUAL DESIGN PHASE OF THE ASTRID DEMONSTRATOR M. Marquès CEA, DEN, DER F-13108, Saint-Paul-lez-Durance, France Advanced simulation in support to
BEST ESTIMATE PLUS UNCERTAINTY SAFETY STUDIES AT THE CONCEPTUAL DESIGN PHASE OF THE ASTRID DEMONSTRATOR M. Marquès CEA, DEN, DER F-13108, Saint-Paul-lez-Durance, France Advanced simulation in support to
RESPONSE SURFACE METHODS FOR STOCHASTIC STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION
 Meccanica dei Materiali e delle Strutture Vol. VI (2016), no.1, pp. 99-106 ISSN: 2035-679X Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale, Aerospaziale, Dei Materiali DICAM RESPONSE SURFACE METHODS FOR
Meccanica dei Materiali e delle Strutture Vol. VI (2016), no.1, pp. 99-106 ISSN: 2035-679X Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale, Aerospaziale, Dei Materiali DICAM RESPONSE SURFACE METHODS FOR
Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability and Availability analyses
 Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability and Availability analyses Monte Carlo Simulation: Why? 2 Computation of system reliability and availability for industrial systems characterized by: many components
Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability and Availability analyses Monte Carlo Simulation: Why? 2 Computation of system reliability and availability for industrial systems characterized by: many components
RISK AND RELIABILITY IN OPTIMIZATION UNDER UNCERTAINTY
 RISK AND RELIABILITY IN OPTIMIZATION UNDER UNCERTAINTY Terry Rockafellar University of Washington, Seattle AMSI Optimise Melbourne, Australia 18 Jun 2018 Decisions in the Face of Uncertain Outcomes = especially
RISK AND RELIABILITY IN OPTIMIZATION UNDER UNCERTAINTY Terry Rockafellar University of Washington, Seattle AMSI Optimise Melbourne, Australia 18 Jun 2018 Decisions in the Face of Uncertain Outcomes = especially
Nuclear reliability: system reliabilty
 Nuclear reliability: system reliabilty Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) December 3, 203 Goal of these two lectures failures are inevitable: need methods for characterising and quantifying them LAST
Nuclear reliability: system reliabilty Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) December 3, 203 Goal of these two lectures failures are inevitable: need methods for characterising and quantifying them LAST
EE 445 / 850: Final Examination
 EE 445 / 850: Final Examination Date and Time: 3 Dec 0, PM Room: HLTH B6 Exam Duration: 3 hours One formula sheet permitted. - Covers chapters - 5 problems each carrying 0 marks - Must show all calculations
EE 445 / 850: Final Examination Date and Time: 3 Dec 0, PM Room: HLTH B6 Exam Duration: 3 hours One formula sheet permitted. - Covers chapters - 5 problems each carrying 0 marks - Must show all calculations
Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2)
 Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2) Frank Coolen UTOPIAE Training School II, Durham University 3 July 2018 (UTOPIAE) Introduction to Reliability Theory 1 / 21 Outline Statistical issues Software
Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2) Frank Coolen UTOPIAE Training School II, Durham University 3 July 2018 (UTOPIAE) Introduction to Reliability Theory 1 / 21 Outline Statistical issues Software
Introduction to Engineering Reliability
 Introduction to Engineering Reliability Robert C. Patev North Atlantic Division Regional Technical Specialist (978) 318-8394 Topics Reliability Basic Principles of Reliability Analysis Non-Probabilistic
Introduction to Engineering Reliability Robert C. Patev North Atlantic Division Regional Technical Specialist (978) 318-8394 Topics Reliability Basic Principles of Reliability Analysis Non-Probabilistic
Performance Characteristics of Deterministic Leak Detection Systems
 Performance Characteristics of Deterministic Leak Detection Systems Michael Kasch 3S Consult München GmbH Germany Abstract The aim of leak detection and leak location is the limitation of losses and possible
Performance Characteristics of Deterministic Leak Detection Systems Michael Kasch 3S Consult München GmbH Germany Abstract The aim of leak detection and leak location is the limitation of losses and possible
of an algorithm for automated cause-consequence diagram construction.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Development of an algorithm for automated cause-consequence diagram construction. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Development of an algorithm for automated cause-consequence diagram construction. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Basics of Uncertainty Analysis
 Basics of Uncertainty Analysis Chapter Six Basics of Uncertainty Analysis 6.1 Introduction As shown in Fig. 6.1, analysis models are used to predict the performances or behaviors of a product under design.
Basics of Uncertainty Analysis Chapter Six Basics of Uncertainty Analysis 6.1 Introduction As shown in Fig. 6.1, analysis models are used to predict the performances or behaviors of a product under design.
Reliability of Technical Systems
 Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
PSA Quantification. Analysis of Results. Workshop Information IAEA Workshop
 IAEA Training Course on Safety Assessment of NPPs to Assist Decision Making PSA Quantification. Analysis of Results Lecturer Lesson Lesson IV IV 3_7.3 3_7.3 Workshop Information IAEA Workshop City, XX
IAEA Training Course on Safety Assessment of NPPs to Assist Decision Making PSA Quantification. Analysis of Results Lecturer Lesson Lesson IV IV 3_7.3 3_7.3 Workshop Information IAEA Workshop City, XX
Structural Reliability
 Structural Reliability Thuong Van DANG May 28, 2018 1 / 41 2 / 41 Introduction to Structural Reliability Concept of Limit State and Reliability Review of Probability Theory First Order Second Moment Method
Structural Reliability Thuong Van DANG May 28, 2018 1 / 41 2 / 41 Introduction to Structural Reliability Concept of Limit State and Reliability Review of Probability Theory First Order Second Moment Method
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655 Part 1 Introduction C. M. Krishna Fall 2006 ECE655/Krishna Part.1.1 Prerequisites Basic courses in
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655 Part 1 Introduction C. M. Krishna Fall 2006 ECE655/Krishna Part.1.1 Prerequisites Basic courses in
Analysis of the Space Propulsion System Problem Using RAVEN
 Analysis of the Space Propulsion System Problem Using RAVEN Diego Mandelli*, C. Smith, A. Alfonsi, C. Rabiti Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho Falls (ID), USA Abstract: This paper presents a solution of
Analysis of the Space Propulsion System Problem Using RAVEN Diego Mandelli*, C. Smith, A. Alfonsi, C. Rabiti Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho Falls (ID), USA Abstract: This paper presents a solution of
Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) Prof. Enrico Zio
 Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) This lecture Life test (t 1,t 2,...,t n ) Estimate θ of f T t θ For example: λ of f T (t)= λe - λt Classical approach (frequentist
Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) This lecture Life test (t 1,t 2,...,t n ) Estimate θ of f T t θ For example: λ of f T (t)= λe - λt Classical approach (frequentist
Evaluating Safety Integrity Level in presence of uncertainty
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224880564 Evaluating Safety Integrity Level in presence of uncertainty Conference Paper June
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224880564 Evaluating Safety Integrity Level in presence of uncertainty Conference Paper June
Evaluating the Core Damage Frequency of a TRIGA Research Reactor Using Risk Assessment Tool Software
 Evaluating the Core Damage Frequency of a TRIGA Research Reactor Using Risk Assessment Tool Software M. Nematollahi and Sh. Kamyab Abstract After all preventive and mitigative measures considered in the
Evaluating the Core Damage Frequency of a TRIGA Research Reactor Using Risk Assessment Tool Software M. Nematollahi and Sh. Kamyab Abstract After all preventive and mitigative measures considered in the
Introduction to Modelling and Simulation
 Introduction to Modelling and Simulation Prof. Cesar de Prada Dpt. Systems Engineering and Automatic Control EII, University of Valladolid, Spain prada@autom.uva.es Digital simulation Methods and tools
Introduction to Modelling and Simulation Prof. Cesar de Prada Dpt. Systems Engineering and Automatic Control EII, University of Valladolid, Spain prada@autom.uva.es Digital simulation Methods and tools
Control of Hybrid Petri Nets using Max-Plus Algebra
 Control of Hybrid Petri Nets using Max-Plus Algebra FABIO BALDUZZI*, ANGELA DI FEBBRARO*, ALESSANDRO GIUA, SIMONA SACONE^ *Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli
Control of Hybrid Petri Nets using Max-Plus Algebra FABIO BALDUZZI*, ANGELA DI FEBBRARO*, ALESSANDRO GIUA, SIMONA SACONE^ *Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli
Modeling Common Cause Failures in Diverse Components with Fault Tree Applications
 Modeling Common Cause Failures in Diverse s with Fault Tree Applications Joseph R. Belland, Isograph Inc. Key Words: Common Cause Failures, Fault Trees, Beta Factor SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS A common cause
Modeling Common Cause Failures in Diverse s with Fault Tree Applications Joseph R. Belland, Isograph Inc. Key Words: Common Cause Failures, Fault Trees, Beta Factor SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS A common cause
Process Control Hardware Fundamentals
 Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
Issues in Dependency Modeling in Multi- Unit Seismic PRA
 Issues in Dependency Modeling in Multi- Unit Seismic PRA 1 Taotao Zhou Mohammad Modarres Enrique López Droguett Center for Risk and Reliability University of Maryland, College Park Presented at the PSA-2017,
Issues in Dependency Modeling in Multi- Unit Seismic PRA 1 Taotao Zhou Mohammad Modarres Enrique López Droguett Center for Risk and Reliability University of Maryland, College Park Presented at the PSA-2017,
Raven Facing the Problem of assembling Multiple Models to Speed up the Uncertainty Quantification and Probabilistic Risk Assessment Analyses
 13 th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management PSAM 13) Raven Facing the Problem of assembling Multiple Models to Speed up the Uncertainty Quantification and Probabilistic
13 th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management PSAM 13) Raven Facing the Problem of assembling Multiple Models to Speed up the Uncertainty Quantification and Probabilistic
Calculation method for the determination of leak probabilities for complex structural geometries and load conditions
 3 Reactor safety research 3.1 Calculation method for the determination of leak probabilities for complex structural geometries and load conditions Dr. Jürgen Sievers Yan Wang When it comes to assessing
3 Reactor safety research 3.1 Calculation method for the determination of leak probabilities for complex structural geometries and load conditions Dr. Jürgen Sievers Yan Wang When it comes to assessing
AC&ST AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS. Claudio Melchiorri
 C. Melchiorri (DEI) Automatic Control & System Theory 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI)
C. Melchiorri (DEI) Automatic Control & System Theory 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI)
Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen
 Industrial Automation Automation Industrielle Industrielle Automation 9.6 Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen Prof Dr. Hubert Kirrmann & Dr. B. Eschermann
Industrial Automation Automation Industrielle Industrielle Automation 9.6 Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen Prof Dr. Hubert Kirrmann & Dr. B. Eschermann
Design for Reliability and Robustness through probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization In1 Design for Reliability and Robustness through probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY In2
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization In1 Design for Reliability and Robustness through probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY In2
Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Chapter 18 Section 8.5 Fault Trees Analysis (FTA) Don t get caught out on a limb of your fault tree.
 Chapter 18 Section 8.5 Fault Trees Analysis (FTA) Don t get caught out on a limb of your fault tree. C. Ebeling, Intro to Reliability & Maintainability Engineering, 2 nd ed. Waveland Press, Inc. Copyright
Chapter 18 Section 8.5 Fault Trees Analysis (FTA) Don t get caught out on a limb of your fault tree. C. Ebeling, Intro to Reliability & Maintainability Engineering, 2 nd ed. Waveland Press, Inc. Copyright
Key Words: Lifetime Data Analysis (LDA), Probability Density Function (PDF), Goodness of fit methods, Chi-square method.
 Reliability prediction based on lifetime data analysis methodology: The pump case study Abstract: The business case aims to demonstrate the lifetime data analysis methodology application from the historical
Reliability prediction based on lifetime data analysis methodology: The pump case study Abstract: The business case aims to demonstrate the lifetime data analysis methodology application from the historical
Constant speed drive time between overhaul extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet.
 Constant speed drive time between overhaul extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet. Capt. M. Amura¹, Capt. F. De Trane², Maj. L. Aiello¹ Italian Air Force Centro Sperimentale Volo - Airport
Constant speed drive time between overhaul extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet. Capt. M. Amura¹, Capt. F. De Trane², Maj. L. Aiello¹ Italian Air Force Centro Sperimentale Volo - Airport
Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems 5.1 Reliability Quantification with RBDs
 Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems 5.1 Reliability Quantification with RBDs Mary Ann Lundteigen and Marvin Rausand mary.a.lundteigen@ntnu.no &marvin.rausand@ntnu.no RAMS Group Department of Production
Reliability of Safety-Critical Systems 5.1 Reliability Quantification with RBDs Mary Ann Lundteigen and Marvin Rausand mary.a.lundteigen@ntnu.no &marvin.rausand@ntnu.no RAMS Group Department of Production
Reliability Analysis of Hydraulic Steering System with DICLFL Considering Shutdown Correlation Based on GO Methodology
 2015 ICRSE&PHM-Beijing Reliability Analysis of Hydraulic Steering System with DICLFL Considering Shutdown Correlation Based on GO Methodology YI Xiaojian, SHI Jian, MU Huina, DONG Haiping, GUO Shaowei
2015 ICRSE&PHM-Beijing Reliability Analysis of Hydraulic Steering System with DICLFL Considering Shutdown Correlation Based on GO Methodology YI Xiaojian, SHI Jian, MU Huina, DONG Haiping, GUO Shaowei
Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes
 Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury 1 Rationale for Dynamic Models 1. Improve understanding of the process 2. Train Plant operating personnel 3. Develop control strategy
Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury 1 Rationale for Dynamic Models 1. Improve understanding of the process 2. Train Plant operating personnel 3. Develop control strategy
Real-Time Feasibility of Nonlinear Predictive Control for Semi-batch Reactors
 European Symposium on Computer Arded Aided Process Engineering 15 L. Puigjaner and A. Espuña (Editors) 2005 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. Real-Time Feasibility of Nonlinear Predictive Control
European Symposium on Computer Arded Aided Process Engineering 15 L. Puigjaner and A. Espuña (Editors) 2005 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. Real-Time Feasibility of Nonlinear Predictive Control
Lecture 4 The stochastic ingredient
 Lecture 4 The stochastic ingredient Luca Bortolussi 1 Alberto Policriti 2 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste Via Valerio 12/a, 34100 Trieste. luca@dmi.units.it
Lecture 4 The stochastic ingredient Luca Bortolussi 1 Alberto Policriti 2 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste Via Valerio 12/a, 34100 Trieste. luca@dmi.units.it
POLITECNICO DI TORINO
 Dipartimento di Ingegneria del Territorio, dell Ambiente e delle Geotecnologie April, 11 2007 The Scientific Coordinator: (Dott. Paola Marini) REPORT LM/KP_04/07in REPORT ON DETERMINATION OF PHYSICAL AND
Dipartimento di Ingegneria del Territorio, dell Ambiente e delle Geotecnologie April, 11 2007 The Scientific Coordinator: (Dott. Paola Marini) REPORT LM/KP_04/07in REPORT ON DETERMINATION OF PHYSICAL AND
A BAYESIAN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS PRIMER. José M. Bernardo Universitat de València, Spain
 A BAYESIAN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS PRIMER José M. Bernardo Universitat de València, Spain jose.m.bernardo@uv.es Bayesian Statistics is typically taught, if at all, after a prior exposure to frequentist
A BAYESIAN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS PRIMER José M. Bernardo Universitat de València, Spain jose.m.bernardo@uv.es Bayesian Statistics is typically taught, if at all, after a prior exposure to frequentist
Presentation of Common Cause Failures in Fault Tree Structure of Krško PSA: An Historical Overview
 International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2003 Portorož, Slovenia, September 8-11, 2003 http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2003 Presentation of Common Cause Failures in Fault Tree Structure of Krško
International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2003 Portorož, Slovenia, September 8-11, 2003 http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2003 Presentation of Common Cause Failures in Fault Tree Structure of Krško
Using Fuzzy Logic as a Complement to Probabilistic Radioactive Waste Disposal Facilities Safety Assessment -8450
 Using Fuzzy Logic as a Complement to Probabilistic Radioactive Waste Disposal Facilities Safety Assessment -8450 F. L. De Lemos CNEN- National Nuclear Energy Commission; Rua Prof. Mario Werneck, s/n, BH
Using Fuzzy Logic as a Complement to Probabilistic Radioactive Waste Disposal Facilities Safety Assessment -8450 F. L. De Lemos CNEN- National Nuclear Energy Commission; Rua Prof. Mario Werneck, s/n, BH
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS IN BOLTED COMPOSITE JOINTS WITH SHIMMING MATERIAL
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RELIABILITY ANALYSIS IN BOLTED COMPOSITE JOINTS WITH SHIMMING MATERIAL P. Caracciolo, G. Kuhlmann AIRBUS-Germany e-mail: paola.caracciolo@airbus.com
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RELIABILITY ANALYSIS IN BOLTED COMPOSITE JOINTS WITH SHIMMING MATERIAL P. Caracciolo, G. Kuhlmann AIRBUS-Germany e-mail: paola.caracciolo@airbus.com
Complex systems reliability: A complex challenge for reliability analysts
 Complex systems reliability: A complex challenge for reliability analysts Enrico Zio Chair on Systems Science and the Energy Challenge Ecole Centrale Paris and Supelec, EuropeanFoundationforNew Energy-Electricitéde
Complex systems reliability: A complex challenge for reliability analysts Enrico Zio Chair on Systems Science and the Energy Challenge Ecole Centrale Paris and Supelec, EuropeanFoundationforNew Energy-Electricitéde
STUDY OF AGGREGATION IN BARIUM SULPHATE PRECIPITATION
 15 th International Symposium on Industrial Crystallization Sorrento, Italy, 15-18 September 2002 paper 171 STUDY OF AGGREGATION IN BARIUM SULPHATE PRECIPITATION D. L. Marchisio 1, A. A. Barresi, M. Garbero,
15 th International Symposium on Industrial Crystallization Sorrento, Italy, 15-18 September 2002 paper 171 STUDY OF AGGREGATION IN BARIUM SULPHATE PRECIPITATION D. L. Marchisio 1, A. A. Barresi, M. Garbero,
PREDICTING THE PROBABILITY OF FAILURE OF GAS PIPELINES INCLUDING INSPECTION AND REPAIR PROCEDURES
 REDICTING THE ROBABILITY OF FAILURE OF GAS IELINES INCLUDING INSECTION AND REAIR ROCEDURES Zhang, L. 1, Adey, R.A. 2 1 C M BEASY Ltd, Ashurst Lodge, Lyndhurst Road, Southampton, SO40 7AA, UK, lzhang@beasy.com
REDICTING THE ROBABILITY OF FAILURE OF GAS IELINES INCLUDING INSECTION AND REAIR ROCEDURES Zhang, L. 1, Adey, R.A. 2 1 C M BEASY Ltd, Ashurst Lodge, Lyndhurst Road, Southampton, SO40 7AA, UK, lzhang@beasy.com
Authors : Eric CHOJNACKI IRSN/DPAM/SEMIC Jean-Pierre BENOIT IRSN/DSR/ST3C. IRSN : Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire
 WORKSHOP ON THE EVALUATION OF UNCERTAINTIES IN RELATION TO SEVERE ACCIDENTS AND LEVEL II PROBABILISTIC SAFETY ANALYSIS CADARACHE, FRANCE, 7-9 NOVEMBER 2005 TITLE The use of Monte-Carlo simulation and order
WORKSHOP ON THE EVALUATION OF UNCERTAINTIES IN RELATION TO SEVERE ACCIDENTS AND LEVEL II PROBABILISTIC SAFETY ANALYSIS CADARACHE, FRANCE, 7-9 NOVEMBER 2005 TITLE The use of Monte-Carlo simulation and order
Common Cause Failures: Extended Alpha Factor method and its Implementation
 Common Cause Failures: Extended Alpha Factor method and its Implementation Alexandra Sitdikova Reactor Engineering Division, Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Institute of Physics
Common Cause Failures: Extended Alpha Factor method and its Implementation Alexandra Sitdikova Reactor Engineering Division, Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Institute of Physics
Stochastic Dual Dynamic Programming with CVaR Risk Constraints Applied to Hydrothermal Scheduling. ICSP 2013 Bergamo, July 8-12, 2012
 Stochastic Dual Dynamic Programming with CVaR Risk Constraints Applied to Hydrothermal Scheduling Luiz Carlos da Costa Junior Mario V. F. Pereira Sérgio Granville Nora Campodónico Marcia Helena Costa Fampa
Stochastic Dual Dynamic Programming with CVaR Risk Constraints Applied to Hydrothermal Scheduling Luiz Carlos da Costa Junior Mario V. F. Pereira Sérgio Granville Nora Campodónico Marcia Helena Costa Fampa
Basic notions of probability theory
 Basic notions of probability theory Contents o Boolean Logic o Definitions of probability o Probability laws Objectives of This Lecture What do we intend for probability in the context of RAM and risk
Basic notions of probability theory Contents o Boolean Logic o Definitions of probability o Probability laws Objectives of This Lecture What do we intend for probability in the context of RAM and risk
Analysis methods for fault trees that contain secondary failures
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Analysis methods for fault trees that contain secondary failures This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Analysis methods for fault trees that contain secondary failures This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
Availability analysis of nuclear power plant system with the consideration of logical loop structures
 Availability analysis of nuclear power plant system with the consideration of logical loop structures MATSUOKA Takeshi 1, 2 1. Mechanical Systems Engineering, Department of Engineering, Utsunomiya University,
Availability analysis of nuclear power plant system with the consideration of logical loop structures MATSUOKA Takeshi 1, 2 1. Mechanical Systems Engineering, Department of Engineering, Utsunomiya University,
Probabilistic assessment of geotechnical objects by means of MONTE CARLO METHOD. Egidijus R. Vaidogas
 Probabilistic assessment of geotechnical objects by means of MONTE CARLO METHOD Egidijus R. Vaidogas Vilnius Gediminas technical university, Lithuania ERASMUS/SOCRATES program, 2007 What is the principal
Probabilistic assessment of geotechnical objects by means of MONTE CARLO METHOD Egidijus R. Vaidogas Vilnius Gediminas technical university, Lithuania ERASMUS/SOCRATES program, 2007 What is the principal
NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3
 Nuclear Safety and Reliability Dan Meneley Page 1 of 10 NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS - WEEK 1 1. Introduction to Risk Analysis...1 Conditional Probability Matrices for Each Step
Nuclear Safety and Reliability Dan Meneley Page 1 of 10 NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS - WEEK 1 1. Introduction to Risk Analysis...1 Conditional Probability Matrices for Each Step
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
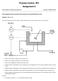 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Bayesian Networks 2:
 1/27 PhD seminar series Probabilistics in Engineering : Bayesian networks and Bayesian hierarchical analysis in engineering Conducted by Prof. Dr. Maes, Prof. Dr. Faber and Dr. Nishijima Bayesian Networks
1/27 PhD seminar series Probabilistics in Engineering : Bayesian networks and Bayesian hierarchical analysis in engineering Conducted by Prof. Dr. Maes, Prof. Dr. Faber and Dr. Nishijima Bayesian Networks
Reliability and Availability Simulation. Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa
 Reliability and Availability Simulation Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa Content BACKGROUND DEFINITIONS SINGLE COMPONENTS MULTI-COMPONENT SYSTEMS AVAILABILITY SIMULATION CONCLUSION
Reliability and Availability Simulation Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa Content BACKGROUND DEFINITIONS SINGLE COMPONENTS MULTI-COMPONENT SYSTEMS AVAILABILITY SIMULATION CONCLUSION
Reliability analysis of geotechnical risks
 Reliability analysis of geotechnical risks Lazhar Belabed*, Hacene Benyaghla* * Department of Civil Engineering and Hydraulics, University of Guelma, Algeria Abstract The evaluation of safety or reliability
Reliability analysis of geotechnical risks Lazhar Belabed*, Hacene Benyaghla* * Department of Civil Engineering and Hydraulics, University of Guelma, Algeria Abstract The evaluation of safety or reliability
Variability within multi-component systems. Bayesian inference in probabilistic risk assessment The current state of the art
 PhD seminar series Probabilistics in Engineering : g Bayesian networks and Bayesian hierarchical analysis in engeering g Conducted by Prof. Dr. Maes, Prof. Dr. Faber and Dr. Nishijima Variability within
PhD seminar series Probabilistics in Engineering : g Bayesian networks and Bayesian hierarchical analysis in engeering g Conducted by Prof. Dr. Maes, Prof. Dr. Faber and Dr. Nishijima Variability within
A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK. Agency for the Environmental Protection, ITALY (
 A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK Roberto W. Romeo 1, Randall W. Jibson 2 & Antonio Pugliese 3 1 University of Urbino, ITALY (e-mail: rwromeo@uniurb.it) 2 U.S. Geological Survey
A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK Roberto W. Romeo 1, Randall W. Jibson 2 & Antonio Pugliese 3 1 University of Urbino, ITALY (e-mail: rwromeo@uniurb.it) 2 U.S. Geological Survey
Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
Time-varying failure rate for system reliability analysis in large-scale railway risk assessment simulation
 Time-varying failure rate for system reliability analysis in large-scale railway risk assessment simulation H. Zhang, E. Cutright & T. Giras Center of Rail Safety-Critical Excellence, University of Virginia,
Time-varying failure rate for system reliability analysis in large-scale railway risk assessment simulation H. Zhang, E. Cutright & T. Giras Center of Rail Safety-Critical Excellence, University of Virginia,
CALCULATION OF A SHEET PILE WALL RELIABILITY INDEX IN ULTIMATE AND SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATES
 Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica, Vol. XXXII, No. 2, 2010 CALCULATION OF A SHEET PILE WALL RELIABILITY INDEX IN ULTIMATE AND SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATES JERZY BAUER Institute of Mining, Wrocław University
Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica, Vol. XXXII, No. 2, 2010 CALCULATION OF A SHEET PILE WALL RELIABILITY INDEX IN ULTIMATE AND SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATES JERZY BAUER Institute of Mining, Wrocław University
Stochastic dominance with imprecise information
 Stochastic dominance with imprecise information Ignacio Montes, Enrique Miranda, Susana Montes University of Oviedo, Dep. of Statistics and Operations Research. Abstract Stochastic dominance, which is
Stochastic dominance with imprecise information Ignacio Montes, Enrique Miranda, Susana Montes University of Oviedo, Dep. of Statistics and Operations Research. Abstract Stochastic dominance, which is
In-Flight Engine Diagnostics and Prognostics Using A Stochastic-Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
 In-Flight Engine Diagnostics and Prognostics Using A Stochastic-Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Dan M. Ghiocel & Joshua Altmann STI Technologies, Rochester, New York, USA Keywords: reliability, stochastic
In-Flight Engine Diagnostics and Prognostics Using A Stochastic-Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Dan M. Ghiocel & Joshua Altmann STI Technologies, Rochester, New York, USA Keywords: reliability, stochastic
A MULTI-STATE PHYSICS MODELING FOR ESTIMATING THE SIZE- AND LOCATION-DEPENDENT LOSS OF COOLANT ACCIDENT INITIATING EVENT PROBABILITY
 MULTI-STTE PHYSICS MODELING FOR ESTIMTING THE SIZE- ND LOCTION-DEPENDENT LOSS OF COOLNT CCIDENT INITITING EVENT PROBBILITY Francesco Di Maio 1, Davide Colli 1, Enrico Zio 1,2, Liu Tao 3, Jiejuan Tong 3
MULTI-STTE PHYSICS MODELING FOR ESTIMTING THE SIZE- ND LOCTION-DEPENDENT LOSS OF COOLNT CCIDENT INITITING EVENT PROBBILITY Francesco Di Maio 1, Davide Colli 1, Enrico Zio 1,2, Liu Tao 3, Jiejuan Tong 3
Module 8. Lecture 5: Reliability analysis
 Lecture 5: Reliability analysis Reliability It is defined as the probability of non-failure, p s, at which the resistance of the system exceeds the load; where P() denotes the probability. The failure
Lecture 5: Reliability analysis Reliability It is defined as the probability of non-failure, p s, at which the resistance of the system exceeds the load; where P() denotes the probability. The failure
Formal Handling of the Level 2 Uncertainty Sources and Their Combination with the Level 1 PSA Uncertainties
 OECD/NEA/CSNI Workshop on Evaluation of Uncertainties in Relation to Severe Accidents and Level 2 Probabilistic Safety Analysis 7-9 November 2005, Aix-en-Provence, France Formal Handling of the Level 2
OECD/NEA/CSNI Workshop on Evaluation of Uncertainties in Relation to Severe Accidents and Level 2 Probabilistic Safety Analysis 7-9 November 2005, Aix-en-Provence, France Formal Handling of the Level 2
Reinforcement Learning
 Reinforcement Learning March May, 2013 Schedule Update Introduction 03/13/2015 (10:15-12:15) Sala conferenze MDPs 03/18/2015 (10:15-12:15) Sala conferenze Solving MDPs 03/20/2015 (10:15-12:15) Aula Alpha
Reinforcement Learning March May, 2013 Schedule Update Introduction 03/13/2015 (10:15-12:15) Sala conferenze MDPs 03/18/2015 (10:15-12:15) Sala conferenze Solving MDPs 03/20/2015 (10:15-12:15) Aula Alpha
Performance based Engineering
 Probability based based Methods in Performance based Engineering Fatemeh Jalayer University of Naples Federico II A RELAXED WORKSHOP ON PERFORMANCE-BASED EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING July 2-4 2009 The characterization
Probability based based Methods in Performance based Engineering Fatemeh Jalayer University of Naples Federico II A RELAXED WORKSHOP ON PERFORMANCE-BASED EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING July 2-4 2009 The characterization
PSA on Extreme Weather Phenomena for NPP Paks
 PSA on Extreme Weather Phenomena for NPP Paks Tamás Siklóssy siklossyt@nubiki.hu WGRISK Technical Discussion on PSA Related to Weather-Induced Hazards Paris, 9 March, 2017 Background Level 1 Seismic PSA
PSA on Extreme Weather Phenomena for NPP Paks Tamás Siklóssy siklossyt@nubiki.hu WGRISK Technical Discussion on PSA Related to Weather-Induced Hazards Paris, 9 March, 2017 Background Level 1 Seismic PSA
Dynamic Event Trees for Probabilistic Safety Analysis
 Dynamic Event Trees for Probabilistic Safety Analysis E. Hofer, M. Kloos, B. Krzykacz-Hausmann, J. Peschke, M. Sonnenkalb (GRS) Abstract: In technical systems like nuclear power plants, an accident sequence
Dynamic Event Trees for Probabilistic Safety Analysis E. Hofer, M. Kloos, B. Krzykacz-Hausmann, J. Peschke, M. Sonnenkalb (GRS) Abstract: In technical systems like nuclear power plants, an accident sequence
Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic BWR: An Approach to Communication and Decision Making
 International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment And Analysis, PSA 2017, September 24-28, 2017. Pittsburgh, PA. Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic
International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment And Analysis, PSA 2017, September 24-28, 2017. Pittsburgh, PA. Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
Use of Simulation in Structural Reliability
 Structures 008: Crossing Borders 008 ASCE Use of Simulation in Structural Reliability Author: abio Biondini, Department of Structural Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, P.za L. Da Vinci 3, 033 Milan,
Structures 008: Crossing Borders 008 ASCE Use of Simulation in Structural Reliability Author: abio Biondini, Department of Structural Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, P.za L. Da Vinci 3, 033 Milan,
Stochastic Simulation.
 Stochastic Simulation. (and Gillespie s algorithm) Alberto Policriti Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Istituto di Genomica Applicata A. Policriti Stochastic Simulation 1/20 Quote of the day D.T.
Stochastic Simulation. (and Gillespie s algorithm) Alberto Policriti Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Istituto di Genomica Applicata A. Policriti Stochastic Simulation 1/20 Quote of the day D.T.
Interactivity-Compatibility. TA Hydronic College Training
 Interactivity-Compatibility TA Hydronic College Training Hydraulic interactivity B Both valves are open. What becomes the flow if one of these valves is closed? p AB A H Head [ft] 140.00 120.00 100.00
Interactivity-Compatibility TA Hydronic College Training Hydraulic interactivity B Both valves are open. What becomes the flow if one of these valves is closed? p AB A H Head [ft] 140.00 120.00 100.00
A Thesis presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School at the University of Missouri-Columbia
 LRFD for Settlement Analyses of Shallow Foundations and Embankments ------ Developed Resistance Factors for Consolidation Settlement Analyses A Thesis presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School at
LRFD for Settlement Analyses of Shallow Foundations and Embankments ------ Developed Resistance Factors for Consolidation Settlement Analyses A Thesis presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School at
Design for Reliability and Robustness through Probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Design for Reliability and Robustness through Probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY The-Quan Pham * 1, Holger Neubert
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Design for Reliability and Robustness through Probabilistic Methods in COMSOL Multiphysics with OptiY The-Quan Pham * 1, Holger Neubert
GOAL-BASED NEW SHIP CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS General principles for structural standards MSC 80/6/6
 GOAL-BASED NEW SHIP CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS General principles for structural standards MSC 80/6/6 Rolf Skjong, Dr Rolf.Skjong@dnv.com IMO MSC 80, Lunch Presentation May 12th, 2005 1 Goal Based Construction
GOAL-BASED NEW SHIP CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS General principles for structural standards MSC 80/6/6 Rolf Skjong, Dr Rolf.Skjong@dnv.com IMO MSC 80, Lunch Presentation May 12th, 2005 1 Goal Based Construction
Bayesian Reliability Analysis: Statistical Challenges from Science-Based Stockpile Stewardship
 : Statistical Challenges from Science-Based Stockpile Stewardship Alyson G. Wilson, Ph.D. agw@lanl.gov Statistical Sciences Group Los Alamos National Laboratory May 22, 28 Acknowledgments Christine Anderson-Cook
: Statistical Challenges from Science-Based Stockpile Stewardship Alyson G. Wilson, Ph.D. agw@lanl.gov Statistical Sciences Group Los Alamos National Laboratory May 22, 28 Acknowledgments Christine Anderson-Cook
PROBABILISTIC APPROACH TO DETERMINE PUMP OPERATING POINT
 Technical Paper Session: 16 1 Session Name: Performing pump systems PROBABILISTIC APPROACH TO DETERMINE PUMP OPERATING POINT Author: Dr. Swaminathan Gopalakrishnan General Manager CAC ELGI Equipments Ltd.
Technical Paper Session: 16 1 Session Name: Performing pump systems PROBABILISTIC APPROACH TO DETERMINE PUMP OPERATING POINT Author: Dr. Swaminathan Gopalakrishnan General Manager CAC ELGI Equipments Ltd.
