Constant speed drive time between overhaul extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet.
|
|
|
- Jessie Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constant speed drive time between overhaul extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet. Capt. M. Amura¹, Capt. F. De Trane², Maj. L. Aiello¹ Italian Air Force Centro Sperimentale Volo - Airport De Bernardi, Pratica di Mare, Pomezia, Rome, Reparto Manutenzione Velivoli Cameri (NO), SS Bellinzago-Cameri, mikael.amura@aeronautica.difesa.it ABSTRACT Scheduled maintenance can be very expensive in economics terms, but also in operational terms. This cost is not sustainable particularly if it is possible to demonstrate that item s life can be extended. In this paper are shown the statistical considerations that the Italian Air Force made to extend the time between overhaul (TBO) of the Control Speed Drive (CSD), the mechanical part of the Tornado s Integrated Drive Generator, the main item generating alternate electric power for the aircraft. Maintenance data are investigated using the General Theory of Reliability, Fault Tree Analysis and Risk Assessment. Results are compared with German and Royal Air Forces maintenance policy for the same item and similar studies on other components..0 INTRODUCTION During the last few years every Air Force Fleets management have become more appreciative of any study or research oriented to saving funds without reducing the combat readiness, with the aim of optimizing any phase of the integrated logistic support []. Moreover the always reducing availability of human and economical resources, makes more important, and in many cases fundamental, such studies. The attention is generally concentrated on managing logistics aspects. However it s not possible to neglect the costs related to the technical management of the aircraft fleet. In this context, the Italian Air Force carried out many studies to identify some items from the Tornado aircraft for whose maintenance policy could be modified, whilst maintaining the same safety standards by adequate Risk Assessment and Risk Management. Because the scheduled maintenance approach is very expensive in economical terms and also in operational terms, the chance to improve the time between overhaul (TBO) operations phasing is highly recommended whenever it is possible to demonstrate that an item s life could be extended. In this paper the case of Constant Speed Drive (CSD) TBO extension will be described; it is the mechanical part of the Tornado s Integrated Drive Generator (IDG), the main item generating alternating electric power on the aircraft. RTO-MP-AVT
2 2.0 AIRCRAFT ELECTRIC SYSTEM: BACKGROUND 2. Short description The Tornado s electric power system is essentially composed by two low fixed-frequency generators (integrated drive generators IDG). These systems, left and right, supply alternate tri-phase electrical power (5V 400Hz) and are actuated by two gearboxes, connected to the engines. If one IDG fails, the other will generate all the electrical power the aircraft needs. Electrical generation is lost only if both IDGs fail (except for the first 20 minutes, for which the electrical power is provided by an Emergency Power System). The IDG is divided into a generator and a rotational speed converter (constant speed drive - CSD): The generator is composed of statoric windings, a rotor with its own windings and a permanent magnet. Rotor is actuated by CSD. The manufacturer s fixed generator s TBO is 200 flight hours. The CSD operates hydro-mechanically and is composed by differential gearing, a clutch, a hydraulic pump, a centrifugal regulator and a RPM transducer. The manufacturer s fixed CSD s TBO is 600 flight hours. The CSD s role is to convert variable rotational speed arriving from gearbox to constant rotational speed, before supplying this motion to the generator; in this way it will produce the right constant alternate electrical power. 2.2 Maintenance The CSD works with the electrical generator, together composing the IDG, but their scheduled TBO lives were different: even if the CSD demonstrated high reliability, its overhaul was fixed by the manufacturer to 600 flight hours despite the generator s fixed to 200 flight hours. This was a heavy recurrent operating cost not only from the direct economic point of view: in fact, there were often many difficulties caused by the non-availability of both items at the same time. 3.0 RELIABILITY S THEORY BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Here are summarised some basic concepts and definitions of the reliability s theory that will be used in the statistical analysis. 3. Reliability The reliability of a product is the probability that this item could be efficient after a period of operational life: With R () t N E = N ( t) N E () t number of efficient items at t time; N total number of the units under test. 8-2 RTO-MP-AVT-57
3 3.2 Unreliability The unreliability of a product is the probability that this item could become inefficient after a period of operational life, so it s the complementary part of the reliability, referring to an unitary space of events: Where, F () t = R() t N F = N ( t) N F () t number of inefficient items to the t time; N total number of items under test. 3.3 Density of Damage probability The previous definitions are all related to the cumulative distributions functions (CDF), but they could be calculated analytically starting from the definition of Density of Damage probability: the probability for a system to become inefficient at the instant t. We can write the previous equations as: consequently, f () t = df dt t F() t = f ()dt t 0 ( t) dr( t) dn ( t) = dt = N F dt 3.4 Failure rate The failure rate, λ, is defined as the probability that, in a well determined time range Δt, the system fails, under the hypothesis of perfect working condition at the starting time. Based on the previous definitions we have, λ = R ( t) R( t + Δt) R t Δt () And, lim RTO-MP-AVT
4 3.5 Parallel and series systems By schematizing systems as block diagrams it is easy to distinguish two particular cases: parallel and series systems. For the series kind, if only one component fails, the serviceability of all the system is lost. We assume that the probabilities of failure of each component are stochastically independent: if a subpart fails, the probability of failure of the other subparts do not change. Therefore the reliability at a generic moment t is the product of the reliabilities of all the subparts: n Figure : Block diagrams - Series System R S In a parallel system all the subparts have to fail to make the whole unserviceable. So the reliability is expressed as the complement to the product of each unreliability. n ( T ) = R ( T ) i... R P ( T ) = F ( T ) n i n Figure 2: Block diagrams - Parallel System 8-4 RTO-MP-AVT-57
5 3.6 Tools 3.6. Exponential distribution In this paper we will assume as the mathematical model the exponential distribution with constant failure rate because: it represents very well random failures on parts; the failure rate tends to become constant even when subparts show reliability curves very different between them. Therefore is possible to specialize the above definitions as: λ = const λt ( ) = e R t F λt ( t) = e f t ( t) = λe λ Fault Tree Analysis The Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a methodology applied in statistics. Whenever an event happens, named the Top Event, it is subordinate to other events, Base Events, related to the previous and related to each other by some equations that identify intermediate events, named Dependent Events. The probability for the Top Event is therefore evaluated starting from the probabilities of the Base Events, assumed as known, using the block diagram s equations. We use the following table: EVENTS Logic Gate Base Event AND And Dependent Event OR Or Not developed event m Vote Call to an other FTA OR Exclusive Or Figure 3: Block diagrams - symbols Using the introduced symbols, the equations for the subsystems should be written in the following way RTO-MP-AVT
6 OR R n = R i Series System AND R = n ( R i ) Parallel System And, assuming constant failure rate: OR λ = n λ i AND n λ = λi 4.0 DATA ANALYSIS Data for this paper, related to CSD and Generators from 998 up to 2005, were provided by the IDG Work Area of IAF Main Depot, RMV, devoted to Italian Tornado Fleet Maintenance. Considering the following maintenance actions: Serviceable after testing in RMV Work Area: RMV has a very limited maintenance capability for IDG items; Sent to Manufacturer for Overhaul (O); Sent to Manufacturer for Overhaul and Modification (OM); Sent to Manufacturer for Overhaul and repair (OR); Sent to Manufacturer for Overhaul, Repair and Modification (ORM); 8-6 RTO-MP-AVT-57
7 CSD TBO extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet. The following table summarizes the data whichh are shown graphically in Figures 4 and 5: TOTALS GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD GEN CSD Serviceable O 0 OM 0 OR 9 ORM TOTALS Table : IDG maintenance data By analyzing the data from the table is possible to obtain the percentages related to the column of totals. In particular, CSD OR and ORM percentage with 600 flight hours of TBO is less than 3% %; Generator OR percentage with 200 flight hours of TBO is about 8%; It s evident there is no relation between defect rate and TBO for Generator and CSD. CSD % ,63% 2,44% Serviceable 32,52% 60,7% OR O OM ORM 0,24% Figure 4: CSD maintenancee data diagram RTO-MP-AVT
8 CSD TBO extension: a case study from Italian Air Force Fleet. Figure 5: Generator maintenance data diagram 4. Failure ratess evaluation The calculation required the total flight hours flown by the Tornadoo Fleet (IDS, ECR and ADV, IDG components are common to any version of the aircraft) from 998 up to 2005: flight hours. Moreover rate is: it s necessary to considerate the system s double redundancy. Therefore CSD average failure λ CS SD = [/flight hour] While the Generator failure rate is: λ G GEN = [/flight hour] Now considering 998, 339 flight hours, we take in account for the worst case: λ MAX _ CSD = [/flight hour] λ M MAX _ GEN = [/flight hour] 8-8 RTO-MP-AVT-57
9 5.0 IDG FAULT TREE ANALYSIS The loss probability of the whole AC generating system will be evaluated, therefore the failure of both the IDGs at the same time is considered. 5. Worst Case Scenario The failure rate of the worst case scenario is evaluated using block diagrams and the maxima failure rates of CSD and Generator. So, Figure 5: FTA worst case scenario RTO-MP-AVT
10 5.2 Normal Failure Rate Scenario We will now consider the average failure rate of CSD and generator to evaluate the normal failure rate of the whole AC generating system. Figure 7: FTA normal case scenario 5.2. Independent total failure rate Using the average values of CSD and Generator failure rate and assuming alternatively one of the two items as an infinite reliability system (λ=0), we can calculate the independent total failure rate: λ F λ F _ =.28 0 CSD 8 _ = GEN 7 [/flight hour] [/flight hour] 8-0 RTO-MP-AVT-57
11 6.0 EVALUATIONS FROM COMPARISONS 6. Crew Escape System Mods Package Before introducing four modifications to the Tornado Crew Escape System BAE Systems developed similar statistical studies: indeed the new parachute diminishes the physical gap between the navigator and canopy. These modifications could lead to a malfunction to the canopy s Plexiglass explosion system with the resultant possibility of crew loss. The manufacturer demonstrated that with the introduction of the modifications, the improvements resulted in a negligible crew loss probability rate, evaluated as.287*0-8 per hour. This rate was shown to be lower than that for the unmodified system. 6.2 CSD maintenance in GAF and RAF It was also interesting to compare different maintenance philosophy for the same item in other Air Forces: CSD s TBO in GAF is 200 flight hours; In RAF CSD is an on condition item; 7.0 RISK MATRIX AND RISK INDEX The failure rates obtained are analyzed using a risk matrix, described in the following tables [4]. These classify the probability of an event happening and its consequences. Table 2: Hazard severity categories RTO-MP-AVT
12 Description Level Individual item Fleet Frequency Frequent Probable Occasional A B C Likely to occur frequently Will occur several time in life time of an item Likely to occur some time in life of an item Continuously experienced Will occur frequently Will occur several times F 0 3 F f 0 F f Remote D Unlikely but possible to occur in life time of an item Unlikely but can reasonably be expected to occur 0 9 F f 0 7 Improbable E So unlikely, it can be assumed occurrence will be not experienced Unlikely to occur but possible 0 Table 3: Hazard frequency categories Therefore we can compose the risk matrix. Each risk index is associated with a corrective action. PROBABILITY SEVERITY I II III IV A B C D E HRI Assessment Action -5 High Risk Unacceptable 6- Moderate Risk Acceptable with review 2-20 Low Risk Acceptable without review Table 4: Hazard risk index (HRI) Considering that Tornado has a back-up system, the Emergency Power System, that guarantees electric power for twenty minutes in case of complete loss of the generating system, it s reasonable to assume a Severity level of III. This value combined with the independent CSD failure rate gives a Risk index of 4. Therefore no corrective actions or checks are needed. 8-2 RTO-MP-AVT-57
13 8.0 CONCLUSIONS 8. Results: Generator s probability of failure is higher than the CSD s; Generator percentage of items sent to the manufacturer, calculated by maintenance data, is nine time higher than the CSD s; In RAF the CSD is an on condition item; Generator had TBO fixed to 200 flight hours, while CSD was 600 flight hours; Complete system failure s rate is in the lower range magnitudes of acceptable risk. 8.2 Considerations: In this paper maintenance data have been used to provide evidence that there is no relation between defect rate and TBO for the generator and CSD. Moreover the statistical analysis highlighted the possibility of extending the CSD s life without safety related problems. Comparisons with GAF and RAF fleet highlighted further the extreme conservatively TBO limit imposed by the manufacturer. 8.3 Subsequent Actions: The studies and results described in this paper were addressed in a technical document to propose an extension to the CSD s TBO from 600 to 200 Flight hours. MoD authorized the TBO extension. 8.4 Consequences for the IAF Tornado fleet: Generator s and CSD s overhauls are performed at the same time; this implies a better maintenance organization and an improved readiness; Economical benefit are attained due to the longer CSD s TBO. Bibliography [] ISO/IEC CD 5288 CD3 System Engineering System Life Cycle Processes Date: ; [2] Pasquale Erto Probabilità e statistica per le scienze e l ingegneria, McGraw-Hill 999; [3] Teoria e metodi dell affidabilità, appunti del corso universitario, Federico II, 2002 [4] 4 Corso Ufficiali Sicurezza Volo, appunti del corso, Istituto Superiore per la Sicurezza del Volo, 2005 RTO-MP-AVT
14 8-4 RTO-MP-AVT-57
Terminology and Concepts
 Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
Chapter 6. a. Open Circuit. Only if both resistors fail open-circuit, i.e. they are in parallel.
 Chapter 6 1. a. Section 6.1. b. Section 6.3, see also Section 6.2. c. Predictions based on most published sources of reliability data tend to underestimate the reliability that is achievable, given that
Chapter 6 1. a. Section 6.1. b. Section 6.3, see also Section 6.2. c. Predictions based on most published sources of reliability data tend to underestimate the reliability that is achievable, given that
Failure rate in the continuous sense. Figure. Exponential failure density functions [f(t)] 1
![Failure rate in the continuous sense. Figure. Exponential failure density functions [f(t)] 1 Failure rate in the continuous sense. Figure. Exponential failure density functions [f(t)] 1](/thumbs/73/68618961.jpg) Failure rate (Updated and Adapted from Notes by Dr. A.K. Nema) Part 1: Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed for example in failures per hour. It is
Failure rate (Updated and Adapted from Notes by Dr. A.K. Nema) Part 1: Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed for example in failures per hour. It is
Key Words: Lifetime Data Analysis (LDA), Probability Density Function (PDF), Goodness of fit methods, Chi-square method.
 Reliability prediction based on lifetime data analysis methodology: The pump case study Abstract: The business case aims to demonstrate the lifetime data analysis methodology application from the historical
Reliability prediction based on lifetime data analysis methodology: The pump case study Abstract: The business case aims to demonstrate the lifetime data analysis methodology application from the historical
Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis:
 Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis: An Overview of Models and Applications Professor and Industrial Research Chair Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis: An Overview of Models and Applications Professor and Industrial Research Chair Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems
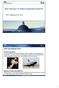 Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems RA II: Methods (FTA, ETA) Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Problem description It is not possible to analyse complicated, highly-reliable or novel systems as black box
Risk Analysis of Highly-integrated Systems RA II: Methods (FTA, ETA) Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Problem description It is not possible to analyse complicated, highly-reliable or novel systems as black box
MINISTRY OF DEFENCE MILITARY AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT SUMMARY
 MINISTRY OF DEFENCE MILITARY AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT SUMMARY AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT TO ROYAL AIR FORCE TORNADO F3 ZG751 AIRCRAFT: RAF Tornado F3 ZG751 DATE: 25 August 2003 LOCATION: PARENT UNIT: CREW: INJURIES: CFB
MINISTRY OF DEFENCE MILITARY AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT SUMMARY AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT TO ROYAL AIR FORCE TORNADO F3 ZG751 AIRCRAFT: RAF Tornado F3 ZG751 DATE: 25 August 2003 LOCATION: PARENT UNIT: CREW: INJURIES: CFB
Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction.
 Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction. Problems & Solutions. Problem 1. Estimate the individual part failure rate given a base failure rate of 0.0333 failure/hour, a quality factor of
Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction. Problems & Solutions. Problem 1. Estimate the individual part failure rate given a base failure rate of 0.0333 failure/hour, a quality factor of
Maintenance free operating period an alternative measure to MTBF and failure rate for specifying reliability?
 Reliability Engineering and System Safety 64 (1999) 127 131 Technical note Maintenance free operating period an alternative measure to MTBF and failure rate for specifying reliability? U. Dinesh Kumar
Reliability Engineering and System Safety 64 (1999) 127 131 Technical note Maintenance free operating period an alternative measure to MTBF and failure rate for specifying reliability? U. Dinesh Kumar
Chapter 4 Availability Analysis by Simulation and Markov Chain
 Chapter 4 Availability Analysis by Simulation and Markov Chain Chapter 4 Availability Analysis by Simulation and Markov Chain 4.1 Introduction: For a perfect design, an engineering systems, component and
Chapter 4 Availability Analysis by Simulation and Markov Chain Chapter 4 Availability Analysis by Simulation and Markov Chain 4.1 Introduction: For a perfect design, an engineering systems, component and
Reliability Engineering I
 Happiness is taking the reliability final exam. Reliability Engineering I ENM/MSC 565 Review for the Final Exam Vital Statistics What R&M concepts covered in the course When Monday April 29 from 4:30 6:00
Happiness is taking the reliability final exam. Reliability Engineering I ENM/MSC 565 Review for the Final Exam Vital Statistics What R&M concepts covered in the course When Monday April 29 from 4:30 6:00
Fault Tolerance. Dealing with Faults
 Fault Tolerance Real-time computing systems must be fault-tolerant: they must be able to continue operating despite the failure of a limited subset of their hardware or software. They must also allow graceful
Fault Tolerance Real-time computing systems must be fault-tolerant: they must be able to continue operating despite the failure of a limited subset of their hardware or software. They must also allow graceful
Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability Analysis of Emergency and Standby Power Systems
 Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability Analysis of Emergency and Standby Power Systems Chanan Singh, Fellow, IEEE Joydeep Mitra, Student Member, IEEE Department of Electrical Engineering Texas A & M University
Monte Carlo Simulation for Reliability Analysis of Emergency and Standby Power Systems Chanan Singh, Fellow, IEEE Joydeep Mitra, Student Member, IEEE Department of Electrical Engineering Texas A & M University
12 - The Tie Set Method
 12 - The Tie Set Method Definitions: A tie set V is a set of components whose success results in system success, i.e. the presence of all components in any tie set connects the input to the output in the
12 - The Tie Set Method Definitions: A tie set V is a set of components whose success results in system success, i.e. the presence of all components in any tie set connects the input to the output in the
ELE 491 Senior Design Project Proposal
 ELE 491 Senior Design Project Proposal These slides are loosely based on the book Design for Electrical and Computer Engineers by Ford and Coulston. I have used the sources referenced in the book freely
ELE 491 Senior Design Project Proposal These slides are loosely based on the book Design for Electrical and Computer Engineers by Ford and Coulston. I have used the sources referenced in the book freely
DESIGN OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SCHEDULING MODEL FOR DETERIORATING SYSTEMS
 DESIGN OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SCHEDULING MODEL FOR DETERIORATING SYSTEMS P.A. Ozor a, S.O. Onyegegbu Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, NIGERIA. a Email: paul.ozor@unn.edu.ng
DESIGN OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SCHEDULING MODEL FOR DETERIORATING SYSTEMS P.A. Ozor a, S.O. Onyegegbu Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, NIGERIA. a Email: paul.ozor@unn.edu.ng
Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method
 Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method Sunghyon Jang, and Akira Yamaguchi Department of Nuclear Engineering and Management, The University of
Development of Multi-Unit Dependency Evaluation Model Using Markov Process and Monte Carlo Method Sunghyon Jang, and Akira Yamaguchi Department of Nuclear Engineering and Management, The University of
NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3
 Nuclear Safety and Reliability Dan Meneley Page 1 of 10 NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS - WEEK 1 1. Introduction to Risk Analysis...1 Conditional Probability Matrices for Each Step
Nuclear Safety and Reliability Dan Meneley Page 1 of 10 NUCLEAR SAFETY AND RELIABILITY WEEK 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS - WEEK 1 1. Introduction to Risk Analysis...1 Conditional Probability Matrices for Each Step
Business Case: UV Facility Backup Generator
 Business Case: UV Facility Backup Generator Eric Brainich December 13, 2010 Background The Portland Water Bureau is currently working on the design for a new Ultra Violet (UV) Treatment Facility and the
Business Case: UV Facility Backup Generator Eric Brainich December 13, 2010 Background The Portland Water Bureau is currently working on the design for a new Ultra Violet (UV) Treatment Facility and the
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Module No. # 03 Lecture No. # 11 Probabilistic risk analysis
 Health, Safety and Environmental Management in Petroleum and offshore Engineering Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #
Health, Safety and Environmental Management in Petroleum and offshore Engineering Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems
 (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Fault Tree Analysis Mathematical Background and Algorithms Prof. Dr. Liggesmeyer, 0 Content Definitions of Terms Introduction to Combinatorics General
(Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Fault Tree Analysis Mathematical Background and Algorithms Prof. Dr. Liggesmeyer, 0 Content Definitions of Terms Introduction to Combinatorics General
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES
 27 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES 3.1 INTRODUCTION The express purpose of this research is to assimilate reliability and its associated probabilistic variables into the Unit
27 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES 3.1 INTRODUCTION The express purpose of this research is to assimilate reliability and its associated probabilistic variables into the Unit
Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590. Topic 2: Discrete Distributions
 Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590 Topic 2: Discrete Distributions Saurabh Bagchi ECE/CS Purdue University Outline Basic probability Conditional probability Independence of events Series-parallel
Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590 Topic 2: Discrete Distributions Saurabh Bagchi ECE/CS Purdue University Outline Basic probability Conditional probability Independence of events Series-parallel
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF E S R C 1400 BUCKET WHEEL EXCAVATORS OPERATING IN OLTENIA LIGNITE OPEN PIT MINES
 RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF E S R C 1400 BUCKET WHEEL EXCAVATORS OPERATING IN OLTENIA LIGNITE OPEN PIT MINES Dumitru Jula 1, Stela Dinescu 2, Ovidiu-Bogdan Tomus 3 1 Ph.D., Assoc. Professor, 2 Ph.D., Lecturer,
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF E S R C 1400 BUCKET WHEEL EXCAVATORS OPERATING IN OLTENIA LIGNITE OPEN PIT MINES Dumitru Jula 1, Stela Dinescu 2, Ovidiu-Bogdan Tomus 3 1 Ph.D., Assoc. Professor, 2 Ph.D., Lecturer,
Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis: a method for PSA in dynamic process system
 Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis: a method for PSA in dynamic process system M. Demichela & N. Piccinini Centro Studi su Sicurezza Affidabilità e Rischi, Dipartimento di Scienza dei Materiali e Ingegneria
Integrated Dynamic Decision Analysis: a method for PSA in dynamic process system M. Demichela & N. Piccinini Centro Studi su Sicurezza Affidabilità e Rischi, Dipartimento di Scienza dei Materiali e Ingegneria
EE 445 / 850: Final Examination
 EE 445 / 850: Final Examination Date and Time: 3 Dec 0, PM Room: HLTH B6 Exam Duration: 3 hours One formula sheet permitted. - Covers chapters - 5 problems each carrying 0 marks - Must show all calculations
EE 445 / 850: Final Examination Date and Time: 3 Dec 0, PM Room: HLTH B6 Exam Duration: 3 hours One formula sheet permitted. - Covers chapters - 5 problems each carrying 0 marks - Must show all calculations
Causal & Frequency Analysis
 Causal & Frequency Analysis Arshad Ahmad arshad@utm.my Fishbone Diagram 2 The Cause and Effect (CE) Diagram (Ishikawa Fishbone) Created in 1943 by Professor Kaoru Ishikawa of Tokyo University Used to investigate
Causal & Frequency Analysis Arshad Ahmad arshad@utm.my Fishbone Diagram 2 The Cause and Effect (CE) Diagram (Ishikawa Fishbone) Created in 1943 by Professor Kaoru Ishikawa of Tokyo University Used to investigate
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability
 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Evaluation and Validation
 Evaluation and Validation Peter Marwedel TU Dortmund, Informatik 12 Germany Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 2011 06 18 These slides use Microsoft clip arts. Microsoft copyright restrictions
Evaluation and Validation Peter Marwedel TU Dortmund, Informatik 12 Germany Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 2011 06 18 These slides use Microsoft clip arts. Microsoft copyright restrictions
Non-observable failure progression
 Non-observable failure progression 1 Age based maintenance policies We consider a situation where we are not able to observe failure progression, or where it is impractical to observe failure progression:
Non-observable failure progression 1 Age based maintenance policies We consider a situation where we are not able to observe failure progression, or where it is impractical to observe failure progression:
Quantitative Reliability Analysis
 Quantitative Reliability Analysis Moosung Jae May 4, 2015 System Reliability Analysis System reliability analysis is conducted in terms of probabilities The probabilities of events can be modelled as logical
Quantitative Reliability Analysis Moosung Jae May 4, 2015 System Reliability Analysis System reliability analysis is conducted in terms of probabilities The probabilities of events can be modelled as logical
Software Reliability & Testing
 Repairable systems Repairable system A reparable system is obtained by glueing individual non-repairable systems each around a single failure To describe this gluing process we need to review the concept
Repairable systems Repairable system A reparable system is obtained by glueing individual non-repairable systems each around a single failure To describe this gluing process we need to review the concept
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability
 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
FAULT - TOLERANT PROCEDURES FOR AIR DATA ELABORATION
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES FAULT - TOLERANT PROCEDURES FOR AIR DATA ELABORATION Alberto Calia, Eugenio Denti, Roberto Galatolo, Francesco Schettini University of Pisa Department
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES FAULT - TOLERANT PROCEDURES FOR AIR DATA ELABORATION Alberto Calia, Eugenio Denti, Roberto Galatolo, Francesco Schettini University of Pisa Department
System Model. Real-Time systems. Giuseppe Lipari. Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa -Italy
 Real-Time systems System Model Giuseppe Lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa -Italy Corso di Sistemi in tempo reale Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria dell Informazione Università di Pisa p. 1/?? Task
Real-Time systems System Model Giuseppe Lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa -Italy Corso di Sistemi in tempo reale Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria dell Informazione Università di Pisa p. 1/?? Task
A new FMECA model for reliability computations in electrical distribution systems
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 6-8, 2006 A new FMECA model for reliability computations in electrical
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 6-8, 2006 A new FMECA model for reliability computations in electrical
Known probability distributions
 Known probability distributions Engineers frequently wor with data that can be modeled as one of several nown probability distributions. Being able to model the data allows us to: model real systems design
Known probability distributions Engineers frequently wor with data that can be modeled as one of several nown probability distributions. Being able to model the data allows us to: model real systems design
Basics of Uncertainty Analysis
 Basics of Uncertainty Analysis Chapter Six Basics of Uncertainty Analysis 6.1 Introduction As shown in Fig. 6.1, analysis models are used to predict the performances or behaviors of a product under design.
Basics of Uncertainty Analysis Chapter Six Basics of Uncertainty Analysis 6.1 Introduction As shown in Fig. 6.1, analysis models are used to predict the performances or behaviors of a product under design.
Application of Common Cause Failure Methodology to Aviation Safety Assessment Model
 Application of Common Cause Failure Methodology to Aviation Safety Assessment Model Seungwon Noh Systems Engineering and Operations Research George Mason University Fairfax, VA, USA snoh2@gmu.edu Abstract
Application of Common Cause Failure Methodology to Aviation Safety Assessment Model Seungwon Noh Systems Engineering and Operations Research George Mason University Fairfax, VA, USA snoh2@gmu.edu Abstract
Improving Electromotor Process in Water Pump by Using Power Spectral Density, Time Signal and Fault Probability Distribution Function
 Improving Electromotor Process in Water Pump by Using Power Spectral Density, Time Signal and Fault Probability Distribution Function Hojjat Ahmadi, Zeinab Khaksar Department of Agricultural Machinery
Improving Electromotor Process in Water Pump by Using Power Spectral Density, Time Signal and Fault Probability Distribution Function Hojjat Ahmadi, Zeinab Khaksar Department of Agricultural Machinery
Reliability and Availability Simulation. Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa
 Reliability and Availability Simulation Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa Content BACKGROUND DEFINITIONS SINGLE COMPONENTS MULTI-COMPONENT SYSTEMS AVAILABILITY SIMULATION CONCLUSION
Reliability and Availability Simulation Krige Visser, Professor, University of Pretoria, South Africa Content BACKGROUND DEFINITIONS SINGLE COMPONENTS MULTI-COMPONENT SYSTEMS AVAILABILITY SIMULATION CONCLUSION
Common Cause Failure (CCF)
 Common Cause Failure (CCF) 건국대학교컴퓨터공학과 UC Lab. 정혁준 & 박경식 amitajung@naver.com, kyeongsik@konkuk.ac.kr Contents Common Cause Failure (CCF) Types of CCF Examples Reducing CCF Common Cause Failure (CCF) Definition
Common Cause Failure (CCF) 건국대학교컴퓨터공학과 UC Lab. 정혁준 & 박경식 amitajung@naver.com, kyeongsik@konkuk.ac.kr Contents Common Cause Failure (CCF) Types of CCF Examples Reducing CCF Common Cause Failure (CCF) Definition
UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY ABSTRACT
 (Vol.2) 29, December UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY R. Briš Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Ostrava, Czech Republic
(Vol.2) 29, December UNAVAILABILITY CALCULATIONS WITHIN THE LIMITS OF COMPUTER ACCURACY R. Briš Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Ostrava, Czech Republic
Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum
 Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum Pavel Krcal a,b and Ola Bäckström a a Lloyd's Register Consulting, Stockholm, Sweden b Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Abstract:
Time Dependent Analysis with Common Cause Failure Events in RiskSpectrum Pavel Krcal a,b and Ola Bäckström a a Lloyd's Register Consulting, Stockholm, Sweden b Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Abstract:
Reliability Assessment of Water Distribution Networks Considering Mechanical-Hydraulic Behavior Using Informational Entropy
 Reliability Assessment of Water Distribution Networks Considering Mechanical-Hydraulic Behavior Using Informational Entropy H. Emamjomeh & M. Hosseini International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Reliability Assessment of Water Distribution Networks Considering Mechanical-Hydraulic Behavior Using Informational Entropy H. Emamjomeh & M. Hosseini International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
SPARE PARTS STOCK LEVEL CALCULATION
 1.0 Objective SPARE PARTS STOCK LEVEL CALCULATION The purpose of this paper is to describe a simple technique to calculate the aircraft spare parts quantity (for fleet size and inventory) taking into account
1.0 Objective SPARE PARTS STOCK LEVEL CALCULATION The purpose of this paper is to describe a simple technique to calculate the aircraft spare parts quantity (for fleet size and inventory) taking into account
RELIABILITY OF FLEET OF AIRCRAFT
 Session 2. Reliability and Maintenance Proceedings of the 12 th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication (RelStat 12), 17 2 October 212, Riga, Latvia, p.
Session 2. Reliability and Maintenance Proceedings of the 12 th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication (RelStat 12), 17 2 October 212, Riga, Latvia, p.
Fault-Tolerant Computing
 Fault-Tolerant Computing Motivation, Background, and Tools Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing) by Behrooz Parhami,
Fault-Tolerant Computing Motivation, Background, and Tools Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing) by Behrooz Parhami,
The Failure-tree Analysis Based on Imprecise Probability and its Application on Tunnel Project
 463 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 59, 2017 Guest Editors: Zhuo Yang, Junjie Ba, Jing Pan Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-49-5; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
463 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 59, 2017 Guest Editors: Zhuo Yang, Junjie Ba, Jing Pan Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-49-5; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Signal Handling & Processing
 Signal Handling & Processing The output signal of the primary transducer may be too small to drive indicating, recording or control elements directly. Or it may be in a form which is not convenient for
Signal Handling & Processing The output signal of the primary transducer may be too small to drive indicating, recording or control elements directly. Or it may be in a form which is not convenient for
SIMULATION OF FTA IN SIMULINK. Alexej Chovanec
 J. ucha,. Chovanec SIMYLTION OF FT IN SIMULINK R&RT # 4 SIMULTION OF FT IN SIMULINK lexej Chovanec Faculty of Special Technology / lexander Dubcek University in Trencin Studentska 1, 911 5 Trencin, Slovak
J. ucha,. Chovanec SIMYLTION OF FT IN SIMULINK R&RT # 4 SIMULTION OF FT IN SIMULINK lexej Chovanec Faculty of Special Technology / lexander Dubcek University in Trencin Studentska 1, 911 5 Trencin, Slovak
Development of Reliability-Based Damage Tolerant Structural Design Methodology
 Development of Reliability-Based Damage Tolerant Structural Design Methodology Presented by Dr. Kuen Y. Lin and Dr. Andrey Styuart Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics University of Washington, Box
Development of Reliability-Based Damage Tolerant Structural Design Methodology Presented by Dr. Kuen Y. Lin and Dr. Andrey Styuart Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics University of Washington, Box
Cyber Physical Power Systems Power in Communications
 1 Cyber Physical Power Systems Power in Communications Information and Communications Tech. Power Supply 2 ICT systems represent a noticeable (about 5 % of total t demand d in U.S.) fast increasing load.
1 Cyber Physical Power Systems Power in Communications Information and Communications Tech. Power Supply 2 ICT systems represent a noticeable (about 5 % of total t demand d in U.S.) fast increasing load.
Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Assessing system reliability through binary decision diagrams using bayesian techniques. This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Integrating Quality and Inspection for the Optimal Lot-sizing Problem with Rework, Minimal Repair and Inspection Time
 Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, January 22 24, 2011 Integrating Quality and Inspection for the Optimal Lot-sizing
Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, January 22 24, 2011 Integrating Quality and Inspection for the Optimal Lot-sizing
Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection
 J Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Original Research Paper Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection alip Singh
J Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Original Research Paper Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection alip Singh
This Capstone Project will address the analysis and diagnosis of the Steam Turbo-Generator (STG) machine vibration problems in Thermal Power Plant
 This Capstone Project will address the analysis and diagnosis of the Steam Turbo-Generator (STG) machine vibration problems in Thermal Power Plant (TPP) Kosova-B that are degrading the normal operations
This Capstone Project will address the analysis and diagnosis of the Steam Turbo-Generator (STG) machine vibration problems in Thermal Power Plant (TPP) Kosova-B that are degrading the normal operations
A comparison of modelling approaches for the time-limited dispatch (TLD) of aircraft
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository A comparison of modelling approaches for the time-limited dispatch (TLD) of aircraft This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository A comparison of modelling approaches for the time-limited dispatch (TLD) of aircraft This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance actions: Optimizing by monte carlo simulation
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp. 230-236 A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp. 230-236 A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance
49th European Organization for Quality Congress. Topic: Quality Improvement. Service Reliability in Electrical Distribution Networks
 49th European Organization for Quality Congress Topic: Quality Improvement Service Reliability in Electrical Distribution Networks José Mendonça Dias, Rogério Puga Leal and Zulema Lopes Pereira Department
49th European Organization for Quality Congress Topic: Quality Improvement Service Reliability in Electrical Distribution Networks José Mendonça Dias, Rogério Puga Leal and Zulema Lopes Pereira Department
Risk and Safety in Civil, Surveying and Environmental Engineering
 Risk and Safety in Civil, Surveying and Environmental Engineering Prof. Dr. Michael Havbro Faber ETH Zurich, Switzerland Contents of Today's Lecture Introduction to structural systems reliability General
Risk and Safety in Civil, Surveying and Environmental Engineering Prof. Dr. Michael Havbro Faber ETH Zurich, Switzerland Contents of Today's Lecture Introduction to structural systems reliability General
Monitoring Radar Mechanical Drive Systems FAA's choice of monitoring solutions
 Monitoring Radar Mechanical Drive Systems FAA's choice of monitoring solutions Mission-critical Ask the public to name mission-critical systems, and air traffic control radar will be at the top of the
Monitoring Radar Mechanical Drive Systems FAA's choice of monitoring solutions Mission-critical Ask the public to name mission-critical systems, and air traffic control radar will be at the top of the
AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING. Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008
 VAWG/5-DP/18 25/6/08 AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008 Agenda Item 11: Any other business NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR HIGH PRECISION PAPI
VAWG/5-DP/18 25/6/08 AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008 Agenda Item 11: Any other business NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR HIGH PRECISION PAPI
Introduction to Engineering Reliability
 Introduction to Engineering Reliability Robert C. Patev North Atlantic Division Regional Technical Specialist (978) 318-8394 Topics Reliability Basic Principles of Reliability Analysis Non-Probabilistic
Introduction to Engineering Reliability Robert C. Patev North Atlantic Division Regional Technical Specialist (978) 318-8394 Topics Reliability Basic Principles of Reliability Analysis Non-Probabilistic
Chap 4. Software Reliability
 Chap 4. Software Reliability 4.2 Reliability Growth 1. Introduction 2. Reliability Growth Models 3. The Basic Execution Model 4. Calendar Time Computation 5. Reliability Demonstration Testing 1. Introduction
Chap 4. Software Reliability 4.2 Reliability Growth 1. Introduction 2. Reliability Growth Models 3. The Basic Execution Model 4. Calendar Time Computation 5. Reliability Demonstration Testing 1. Introduction
Probability Distribution
 Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.98 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.98 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
Hazard Function, Failure Rate, and A Rule of Thumb for Calculating Empirical Hazard Function of Continuous-Time Failure Data
 Hazard Function, Failure Rate, and A Rule of Thumb for Calculating Empirical Hazard Function of Continuous-Time Failure Data Feng-feng Li,2, Gang Xie,2, Yong Sun,2, Lin Ma,2 CRC for Infrastructure and
Hazard Function, Failure Rate, and A Rule of Thumb for Calculating Empirical Hazard Function of Continuous-Time Failure Data Feng-feng Li,2, Gang Xie,2, Yong Sun,2, Lin Ma,2 CRC for Infrastructure and
Chapter 2. Theory of Errors and Basic Adjustment Principles
 Chapter 2 Theory of Errors and Basic Adjustment Principles 2.1. Introduction Measurement is an observation carried out to determine the values of quantities (distances, angles, directions, temperature
Chapter 2 Theory of Errors and Basic Adjustment Principles 2.1. Introduction Measurement is an observation carried out to determine the values of quantities (distances, angles, directions, temperature
B.H. Far
 SENG 521 Software Reliability & Software Quality Chapter 8: System Reliability Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Calgary B.H. Far (far@ucalgary.ca) http://www.enel.ucalgary.ca/people/far/lectures/seng521
SENG 521 Software Reliability & Software Quality Chapter 8: System Reliability Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Calgary B.H. Far (far@ucalgary.ca) http://www.enel.ucalgary.ca/people/far/lectures/seng521
Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2)
 Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2) Frank Coolen UTOPIAE Training School II, Durham University 3 July 2018 (UTOPIAE) Introduction to Reliability Theory 1 / 21 Outline Statistical issues Software
Introduction to Reliability Theory (part 2) Frank Coolen UTOPIAE Training School II, Durham University 3 July 2018 (UTOPIAE) Introduction to Reliability Theory 1 / 21 Outline Statistical issues Software
Aviation Infrastructure Economics
 Aviation Short Course Aviation Infrastructure Economics October 14-15, 15, 2004 The Aerospace Center Building 901 D St. SW, Suite 850 Washington, DC 20024 Lecture BWI/Andrews Conference Rooms Instructor:
Aviation Short Course Aviation Infrastructure Economics October 14-15, 15, 2004 The Aerospace Center Building 901 D St. SW, Suite 850 Washington, DC 20024 Lecture BWI/Andrews Conference Rooms Instructor:
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Lecture 5 Probability
 Lecture 5 Probability Dr. V.G. Snell Nuclear Reactor Safety Course McMaster University vgs 1 Probability Basic Ideas P(A)/probability of event A 'lim n64 ( x n ) (1) (Axiom #1) 0 # P(A) #1 (1) (Axiom #2):
Lecture 5 Probability Dr. V.G. Snell Nuclear Reactor Safety Course McMaster University vgs 1 Probability Basic Ideas P(A)/probability of event A 'lim n64 ( x n ) (1) (Axiom #1) 0 # P(A) #1 (1) (Axiom #2):
Complementary Use of Airborne Wx Radar & Datalink Graphical Wx
 Complementary Use of Airborne Wx Radar & Datalink Graphical Wx What if to What next? Cheri Haynes XCELAR Friends/Partners in Aviation Weather Forum October 31, 2012 What if to What next? Today there are
Complementary Use of Airborne Wx Radar & Datalink Graphical Wx What if to What next? Cheri Haynes XCELAR Friends/Partners in Aviation Weather Forum October 31, 2012 What if to What next? Today there are
Markov Models for Reliability Modeling
 Markov Models for Reliability Modeling Prof. Naga Kandasamy ECE Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 904 Many complex systems cannot be easily modeled in a combinatorial fashion. The corresponding
Markov Models for Reliability Modeling Prof. Naga Kandasamy ECE Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 904 Many complex systems cannot be easily modeled in a combinatorial fashion. The corresponding
Mean fault time for estimation of average probability of failure on demand.
 Mean fault time for estimation of average probability of failure on demand. Isshi KOYATA a *, Koichi SUYAMA b, and Yoshinobu SATO c a The University of Marine Science and Technology Doctoral Course, Course
Mean fault time for estimation of average probability of failure on demand. Isshi KOYATA a *, Koichi SUYAMA b, and Yoshinobu SATO c a The University of Marine Science and Technology Doctoral Course, Course
Reliability of Technical Systems
 Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
Reliability of Technical Systems Main Topics 1. Short Introduction, Reliability Parameters: Failure Rate, Failure Probability, etc. 2. Some Important Reliability Distributions 3. Component Reliability
Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko. FSD3020xxx-x_01-00
 Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko FSD3020xxx-x_01-00 1 Content Introduction Vibration problems in EDGs Sources of excitation 2 Introduction Goal of this
Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko FSD3020xxx-x_01-00 1 Content Introduction Vibration problems in EDGs Sources of excitation 2 Introduction Goal of this
Contents Introduction Purpose Background What is a hazardous chemical? What is the GHS?...
 CHEMICAL LABELLING SAFETY HEALTH & WELLBEING CONTENTS Contents... 1 1 Introduction... 3 2 Purpose... 3 3 Background... 3 3.1 What is a hazardous chemical?... 3 3.2 What is the GHS?... 3 4 Standard labelling
CHEMICAL LABELLING SAFETY HEALTH & WELLBEING CONTENTS Contents... 1 1 Introduction... 3 2 Purpose... 3 3 Background... 3 3.1 What is a hazardous chemical?... 3 3.2 What is the GHS?... 3 4 Standard labelling
The random counting variable. Barbara Russo
 The random counting variable Barbara Russo Counting Random Variable } Until now we have seen the point process through two sets of random variables } T i } X i } We introduce a new random variable the
The random counting variable Barbara Russo Counting Random Variable } Until now we have seen the point process through two sets of random variables } T i } X i } We introduce a new random variable the
6. STRUCTURAL SAFETY
 6.1 RELIABILITY 6. STRUCTURAL SAFETY Igor Kokcharov Dependability is the ability of a structure to maintain its working parameters in given ranges for a stated period of time. Dependability is a collective
6.1 RELIABILITY 6. STRUCTURAL SAFETY Igor Kokcharov Dependability is the ability of a structure to maintain its working parameters in given ranges for a stated period of time. Dependability is a collective
Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen
 Industrial Automation Automation Industrielle Industrielle Automation 9.6 Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen Prof Dr. Hubert Kirrmann & Dr. B. Eschermann
Industrial Automation Automation Industrielle Industrielle Automation 9.6 Safety analysis and standards Analyse de sécurité et normes Sicherheitsanalyse und Normen Prof Dr. Hubert Kirrmann & Dr. B. Eschermann
9.4 Life Sensitivity for Stress Effects
 9.4 Life Sensitivity for Stress Effects The fatigue crack growth life of structural components is significantly affected by the level of applied (repeating) stress and the initial crack size. This section
9.4 Life Sensitivity for Stress Effects The fatigue crack growth life of structural components is significantly affected by the level of applied (repeating) stress and the initial crack size. This section
Evaluation and Validation
 Evaluation and Validation Jian-Jia Chen (slides are based on Peter Marwedel) TU Dortmund, Informatik 12 Germany Springer, 2010 2018 年 01 月 17 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts. Microsoft copyright
Evaluation and Validation Jian-Jia Chen (slides are based on Peter Marwedel) TU Dortmund, Informatik 12 Germany Springer, 2010 2018 年 01 月 17 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts. Microsoft copyright
System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models
 System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr March 20, 2012 Introduction Introduction The world of the model-builder
System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr March 20, 2012 Introduction Introduction The world of the model-builder
A binary decision diagram method for phased mission analysis of non-repairable systems
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository binary decision diagram method for phased mission analysis of non-repairable systems This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository binary decision diagram method for phased mission analysis of non-repairable systems This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Probability and Statistics for Engineers
 Probability and Statistics for Engineers Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Ruochen Liu Ruochenliu@xidian.edu.cn Institute of Intelligent Information Processing, Xidian University Outline Random variables
Probability and Statistics for Engineers Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Ruochen Liu Ruochenliu@xidian.edu.cn Institute of Intelligent Information Processing, Xidian University Outline Random variables
arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 25 Feb 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 25 Feb 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 25 Feb 2008](/thumbs/91/104903128.jpg) A Note on Walking Versus Waiting Anthony B. Morton February 28 arxiv:82.3653v [math.ho] 25 Feb 28 To what extent is a traveller called Justin, say) better off to wait for a bus rather than just start walking
A Note on Walking Versus Waiting Anthony B. Morton February 28 arxiv:82.3653v [math.ho] 25 Feb 28 To what extent is a traveller called Justin, say) better off to wait for a bus rather than just start walking
However, reliability analysis is not limited to calculation of the probability of failure.
 Probabilistic Analysis probabilistic analysis methods, including the first and second-order reliability methods, Monte Carlo simulation, Importance sampling, Latin Hypercube sampling, and stochastic expansions
Probabilistic Analysis probabilistic analysis methods, including the first and second-order reliability methods, Monte Carlo simulation, Importance sampling, Latin Hypercube sampling, and stochastic expansions
Peterborough Distribution Inc Ashburnham Drive, PO Box 4125, Station Main Peterborough ON K9J 6Z5
 Peterborough Distribution Inc. 1867 Ashburnham Drive, PO Box 4125, Station Main Peterborough ON K9J 6Z5 November 15, 2017 Ontario Energy Board PO Box 2319 27 th Floor, 2300 Yonge St Toronto ON M4P 1E4
Peterborough Distribution Inc. 1867 Ashburnham Drive, PO Box 4125, Station Main Peterborough ON K9J 6Z5 November 15, 2017 Ontario Energy Board PO Box 2319 27 th Floor, 2300 Yonge St Toronto ON M4P 1E4
Fault-tolerant Control of a Wind Turbine with a Squirrel-cage Induction Generator and Rotor Bar Defects
 Fault-tolerant Control of a Wind Turbine with a Squirrel-cage Induction Generator and Rotor Bar Defects V. Lešić 1, M. Vašak 1, N. Perić 1, T. Wolbank 2 and G. Joksimović 3 vinko.lesic@fer.hr 1 University
Fault-tolerant Control of a Wind Turbine with a Squirrel-cage Induction Generator and Rotor Bar Defects V. Lešić 1, M. Vašak 1, N. Perić 1, T. Wolbank 2 and G. Joksimović 3 vinko.lesic@fer.hr 1 University
Predicting flight on-time performance
 1 Predicting flight on-time performance Arjun Mathur, Aaron Nagao, Kenny Ng I. INTRODUCTION Time is money, and delayed flights are a frequent cause of frustration for both travellers and airline companies.
1 Predicting flight on-time performance Arjun Mathur, Aaron Nagao, Kenny Ng I. INTRODUCTION Time is money, and delayed flights are a frequent cause of frustration for both travellers and airline companies.
Risk Analysis for Assessment of Vegetation Impact on Outages in Electric Power Systems. T. DOKIC, P.-C. CHEN, M. KEZUNOVIC Texas A&M University USA
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2016 Grid of the Future Symposium Risk Analysis for Assessment of Vegetation Impact on Outages in Electric Power Systems
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2016 Grid of the Future Symposium Risk Analysis for Assessment of Vegetation Impact on Outages in Electric Power Systems
IoT Network Quality/Reliability
 IoT Network Quality/Reliability IEEE PHM June 19, 2017 Byung K. Yi, Dr. of Sci. Executive V.P. & CTO, InterDigital Communications, Inc Louis Kerofsky, PhD. Director of Partner Development InterDigital
IoT Network Quality/Reliability IEEE PHM June 19, 2017 Byung K. Yi, Dr. of Sci. Executive V.P. & CTO, InterDigital Communications, Inc Louis Kerofsky, PhD. Director of Partner Development InterDigital
9. Reliability theory
 Material based on original slides by Tuomas Tirronen ELEC-C720 Modeling and analysis of communication networks Contents Introduction Structural system models Reliability of structures of independent repairable
Material based on original slides by Tuomas Tirronen ELEC-C720 Modeling and analysis of communication networks Contents Introduction Structural system models Reliability of structures of independent repairable
PROBABILISTIC AND POSSIBILISTIC FAULT TREE ANALYSIS
 PROBABILISTIC AD POSSIBILISTIC FAULT TREE AALYSIS M. Ragheb 12/28/2017 ITRODUCTIO In the design of nuclear power plants, it is important to analyze the probable and possible mechanisms of failure. Fault
PROBABILISTIC AD POSSIBILISTIC FAULT TREE AALYSIS M. Ragheb 12/28/2017 ITRODUCTIO In the design of nuclear power plants, it is important to analyze the probable and possible mechanisms of failure. Fault
Power System Research Group Electrical Engineering Dept., University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon, Canada
 Abstract Failure Bunching Phenomena in Electric Power Transmission Systems Roy Billinton Gagan Singh Janak Acharya Power System Research Group Electrical Engineering Dept., University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon,
Abstract Failure Bunching Phenomena in Electric Power Transmission Systems Roy Billinton Gagan Singh Janak Acharya Power System Research Group Electrical Engineering Dept., University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon,
