Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group
|
|
|
- Philippa McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group Permamentstaff : R. Bougault, N. Le Neindre, O. Lopez, E. Vient PhD Student: M. Kabtoul, E. Legouée Collaborations: LPC: F.Gulminelli (Théorie), D.Durand(Théorie), M. Parlôg Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay, GANIL Caen, Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers de Paris, Université et INFN de Florence (Italie), Université et INFN, Bologne (Italie), Université et INFN, Naples (Italie), Laboratoire National de Legnaro, LNL-INFN, Legnaro(Italie), Laboratoire National du Sud, LNS-INFN, Catane (Italie), Université et INFN, Catane (Italie), Université Jagiellonian, Institut de Physique, Cracovie (Pologne), InstytutFizykiJądrowejPAN, Cracovie (Pologne), Heavy Ion Laboratory, Université de Varsovie, Varsovie (Pologne), National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucarest(Roumanie), Université de Huelva, Département de Physique Appliquée, Huelva (Espagne) Background The research goal is to study and characterize the nuclear matter equation of state (EOS). The EOS determines the way nuclei respond to external excitations such as those found in nucleus-nucleus collisions or during type-ii supernovæ collapse. Knowledge of this EOS is an important theme of nuclear physics, both for its fundamental character as well as for predicting the evolution of stellar objects such asneutron stars. The meansto achievethisgoalis the study of nucleus-nucleus (heavy ions) collisions around the Fermi energy (E Fermi = 38 MeV/u), which brings experimental constraints concerning the dynamics of the collisions (transport properties) and the thermodynamics of the nuclear systems produced in them (nuclear matter phase diagram). Low energy reactions are also studied to characterize the liquid phase of nuclear matter. The experimental device is the INDRA multi-detector (collaboration between 4 IN2P3 laboratories), using data collected at GANIL (stable and SPIRAL beams) or GSI in Germany. Studies are also carried out in partnership with the CHIMERA collaboration (LNS Catania, Italy). Over the last few years a major effort was committed to research and development for a new detection system using digital techniques: this is the European project FAZIA which is now in the phase of building a demonstrator for SPIRAL2 (Memorandum of Understanding signed by IN2P3, GANIL, Italy, Poland, and Romania). This demonstrator will be coupled with the INDRA array in
2 INDRA and the FAZIA demonstrator Nuclear matter equation of state (EOS) The nuclear matter equation of state characterizes nuclear matter properties under extreme conditions of temperature, T, compression, ρ, and isospin, I=(N-Z)/A. Figure 1 : Nuclear symmetry potential energy E sym as a function of density p. On the left, results obtained with different nuclear models. On the right, the situation for densities close to saturation density p 0 = 0.17 fm -3. The values given in the lefthand figure are the values of E sym calculated with the different models at ρ=ρ 0. The equation of state determines the collective response of nuclei such as their compressibility (via the modulus of incompressibility, K ) and the collective modes of monopole (GMR) or dipole (GDR) oscillations, whether isoscalar (depending only on the density, ρ) or isovector (depending on proton, ρ P, and neutron, ρ N, densities) in nature, the latter bringing in to play the symmetry energy term of the EOS. In addition, the collapse of proto-neutron stars (type-ii supernovæ) as well as the associated cooling phase are intimately linked to the characterization of volume, surface, Coulomb, and symmetry parameters, and their dependence on density, temperature and isospin. Figure 1 presents theoretical predictions [1] for the density-dependence of the isovector part of the equation of state: more precisely, these predictions concern its potential part, as the kinetic part is known. The large spread of the theoretical predictions can be noted, including at low and sub-saturation densities (Fig.1, right). Heavy-ion collisions are one of the experimental tools allowing to constrain this dependence and to study nuclear matter under thermodynamical conditions favoring the determination of the different terms of the equation of state. 22
3 Stopping power of the nuclear matter The stopping power is closely related to transport properties of nuclear matter. Those properties govern the energy dissipation in nuclear collisions, the onset and the dynamics of the large amplitude motions such as expansion, deformation, as well as the competition between reaction mechanisms (deep inelastic, fusion and neck emission). The comparison of experimental data with transport models should allow to better constraint their ingredients at the fundamental level and bring important information about the nuclear equation of state and the in-matter nucleon-nucleon cross section. In the following, we have analysed the quite unique data set obtained with the INDRA 4pi array during the last decades, coming from GANIL and GSI campaigns. These data entangle the largest dataset accumulated so far in the Fermi energy domain with the same array, covering nuclear (mainly symmetric) systems as Ar+KCl, Ni+Ni, Xe+Sn and Au+Au from 10A up to 100A MeV. This systematics in terms of total mass and incident energy allows indeed a complete survey of nuclear reactions properties in the Fermi energy range. Stopping power in central (violent) collisions We have selected central collisions by requiring the highest total multiplicities M tot [2]. Doing so, we have obtained a typical experimental cross-section of about 100mb, which corresponds to an impact parameter of b=2fm. The multiplicity selection has been chosen here in order to avoid strong (self-) correlations between the analysed observable (here the isotropy ratio, see below) and the selection variable. This is thus different from other analyses (thermodynamical studies for example). Figure 2 : Isotropy ratio for central collisions with average values (top) and standard deviations (bottom). Extracted from[2] 23
4 We have then determined the isotropy ratio R E defined as the ratio between the total (among all detected particles, here charged) transverse energy (transverse to the beam axis) over the total longitudinal energy(parallel to the beam axis) for the central collisions selected as indicated above. A large value close to 0 is associated to a complete or quasi-complete stopping while a value close to 1 is associated at variance to a full transparency. The results are presented in Fig. 2 for the whole INDRA dataset for symmetric systems [2]. The different curves correspond to the excitation function of various systems (Ar+KCl, Ni+Ni, Xe+Sn and Au+Au), which encompass as explained before a total mass range between 70 and 400. The dashed curve displays the value of the isotropy ratio if no stopping is present, i.e. full transparency. The top panel corresponds to the mean isotropy ratio R E and the bottom one to the standard deviation. We observe two separate regimes, one associated to a low incident energy range from 10A to 40A MeV (Fermi energy), the second associated to a high incident energy range from 40A to 100A MeV. The first regime (10A- 40A MeV) can be understood as the progressive weakening of the mean-field effects, which are responsible of the fusion process at very low incident energy and to incomplete fusion at higher energies (around and above the Fermi energy). These mechanisms are then associated to a complete toward incomplete stopping power when the incident energy is increasing and correspond to the one-body dissipation by the mean-field. The second regime corresponds on the contrary to the onset of 2-body dissipation effects, because the elastic (hard) nucleon-nucleon (NN) collisions become larger since the Pauli blocking is ineffective at high incident energy (while NN collisions are conversely inhibited at low incident energy). The minimum value is obtained around the Fermi energy (38A MeV), and one could note a slight increase of RE at higher energies due to the increasing number ofnncollisions.itisworthwhiletomentionthattheminimumvalueis always close to the value corresponding to the full transparency, suggesting that the full stopping is far from being achieved in the whole incident energy domain whatever the total system mass is. This result is in itself an important constraint to any transport model aiming to describe nuclear collisions in this energy range. We observe also a mass hierarchy in the isotropy ratio and hence the stopping for the high incident energy part; this is attributed to the increasing number of NN collisions (participants) when looking at heavier systems. At variance, we should observe a relatively small mass dependence of the isotropy ratio for the low incident energy part since this part is mainly governed by mean-field effects which is largely independent on the system size. This behaviour cannot be seen here since only Xe+Sn data are available below 32A MeV. Isospin dependence of the stopping power We have also studied the isospin dependence of the isotropy ratio by looking at selected isospin-defined systems as presented in the table 1. The isotropy ratios are displayed for the seven Xe+Sn systems available with INDRA (some combinations are however missing). The event selection (here central events) is the same as the one discussed above. We can conclude from the values that no strong isospin effect is evidenced, all values being dispatched within 10 %. Once again, this result provides a strong constraint to any kind of transport models. 24
5 Table 1 : Values of R E central for different Xe+Sn systems at 32, 45 and 100 MeV. System N/Z 32 MeV/A 45 MeV/A 100 MeV/A 124 Xe+ 112 Sn 1,27 0,54 0,53 0, Xe+ 112 Sn 1,32 0,6 124 Xe+ 124 Sn 1,38 0,54 0, Xe+ nat Sn 1,38 0,55 0, Xe+ 112 Sn 1,38 0,5 0, Xe+ 124 Sn 1,43 0, Xe+ 124 Sn 1,5 0,49 0,52 Characterization of the anisotropy component The measured isotropy ratio below unity in central collision discussed previously is related to a production of particles in non-equilibrated processes. This pre-equilibrium production is also measured for peripheral reactions and in that case it is superimposed to the evaporation production from the excited Projectile-Like and Target- Like Fragments (PLF and TLF). A previous study allowed us to finalize an experimental method giving the probability for a particle to be emittedbyahotplf.wedecidedtousethisinformationtodetermine the probability not to be evaporated for a particle, produced during a nuclear reaction. We can thus characterize eventually the preequilibrium component or the neck emission, when this contribution exists. We have begun by the study of the system Ni + Ni at different incidental energies 32, 40, 52, 63, 74, 82 A.MeV [3]. For each type of particle, the knowledge of the probability to be evaporated by the PLF or by thetlfallowed usto build different energy spectra, asshown in figure 3. This figure concerns the tritons for Ni + Ni at 52 A.MeV. For the left side of the figure, the kinetic energies are defined in the PLF framewhereastheyaredefinedinthetlfframefortherightside. Figure 3 : Energy spectra of tritons defined in two different frames, according to different origins. The red curves (full) correspond to the total contribution, the green (dash) to the PLF contribution, the blue (dash and dotted) to the TLF contribution. The black curves (dotted) are obtainedby a simple subtraction to the red distribution of the blue and green contributions. The probability distribution of not to be evaporated by the PLF or the TLFcan thusbeobtainedbyasimpledivisionoftheblackcurveby the red curve. 25
6 by a simple subtraction to the red distribution of the blue and green contributions. The probability distribution of not to be evaporated by the PLF or the TLF can thus be obtained by a simple division of the blackcurvebytheredcurve. If the method was perfect, the two histograms should be perfectly identical. It is not exactly true. We observe some small differences, but the results are reasonably compatible. The adequacy between the two histograms is less good for the other light charged particles. For this reason, we have initiated a complementary study. We are using an event generator, like HIPSE, to verify the validity of our method and understand to what extent the experimental set-up breaks the symmetry of the entrance channel and perturbs our measurements. Projectile-Like Fragments produced in symmetric collisions, comparison with models The characterization of hot quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric or quasi-symmetric reactions (Au+Au, Xe+Sn, Ni+Ni, Ar+KCl) at different incident energies are estimated by means of two different procedures. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are analyzed on the basis of simulations using events produced by two slightly different models: HIPSE(Heavy Ion Phase Space Exploration) and ELIE. The essential difference between the two models lies in the excitation energy distribution in the fragments since in the ELIE case, the limiting temperature (5.5 MeV) limits E* to around 3 MeV/u while for HIPSE, the amount of excitation energy can extend to much larger values (see blue histograms in figure 5. Figure 4 : Particle multiplicities cross-sections (from protons to IMF as indicated in each panel) for Xe+Sn central collisions at 50 A.MeV. Black points are INDRA data while the histograms are for ELIE data. For such central collisions, particle multiplicities are correctly reproduced by the model. Other observables have been considered and a general good agreement has been reached between INDRA data and ELIE data. Same conclusions can be reached as far as HIPSE is concerned. These models are therefore sufficiently realistic to allow a check of the calorimetric methods. PLF's characteristics (mass, charge and excitation energy) are measured by two different calorimetric methods: a standard and the so-called3d calorimetry. 26
7 Figure 5 : Mean PLF excitation energy per nucleon (MeV/u) as a function of impact parameter evaluator (large value for central events) for Ni+Ni at 52 A.MeV. Left, ELIE data. Right: HIPSE data, both compared with INDRA data (red crosses and open points). Preliminary results of the studies figure 5 are rather contrasted. None of the methods can reproduce the excitation energy values given by the ELIE model. However, for excitation energies lower than 2 MeV/u, the 3D method gives good results. As for HIPSE, the 3D calorimetry reproduces the excitation energy distribution while the standard method leads to a systematic over-estimation. It is worth to note that, whatever the method applied to INDRA data, very high excitation energies are achieved: a point which remains to be understood. Work is still in progress to improve the 3D calorimetry[3}. INDRA VAMOS Experiment The data reduction concerning INDRA-Vamos experiment is now almost achieved and analyses should start in The aim of this experiment was to study the whole complete de-excitation chain process of fused light system (Ar+Ni Pd at 13.0 A MeV). By mixing different isotopes of projectile Ar and target Ni we were able to register decay events corresponding to Pd allowing to probe isospin effects. Measuring the whole de excitation sequence of all evaporated particles and fragment should allow to constraint de-excitation models and determine how evolves the level density parameter with isospin. This complete measurement has been made possible by the coupling, for the very first time, of a 4π multidetector (INDRA) and a spectrometer (Vamos). The goal is to detect the fusion residue nuclei in Vamos and the corresponding evaporated particles and light fragments with INDRA. Already, analyses about fusion nuclear cross section of those systems have shown that they decrease when isospin decreases, from 914+/-30 mbarn for 34 Ar+ 58 Nito 1691+/-139 mbarnfor 40 Ar+ 64 Ni[4]. Collaboration with CHIMERA(LNS-Catania) The data analysis of the test experiment performed in 2004 in LNS Catania with the CHIMERA multidetector has been achieved. The goal of this experiment was to benefit from the high granularity (1192 telescopes Si-CsI(Tl))of the CHIMERA array to probe for the first time, by fragmentation of quasi projectiles from the nuclear reaction 40 Ca + 12 C at 25 MeV/nucleon, the production of excited states candidates to alpha-particle condensation. The case of the Hoyle state is particularly suggestive, it pleads in favor of a structure, that is a mixture of various pre-formed alphaconfigurations. They are conjectured to be a generic feature of medium-size self-conjugated 4N nuclei whose excitation lies in the vicinity of the N-apha decay threshold. Supposing that equal values of kinetic energy of the emitted alpha-particles represent a sufficient criterion for establishing the existence of alpha-particle condensation, we have found that the complete kinematic characterization of individual decay events reveals that 7.5+/-4.0% of the particle decays 27
8 of the Hoyle state of 12C correspond to direct decays in three equalenergy alpha-particles[5]. The very same study was performed for 16O, but the lack of statistics prevent to any conclusion. Anyway the method is promising and has demonstrated its capabilities. A similar experiment with the same apparatus will be proposed. FAZIA PSA capabilities Two experiments have been achieved in the last two years, Ganil in 2010 and LNS Catania in Those experiments have validated the R&D program and the choices concerning detectors characteristics, electronics and Pulse Shape Analysis (PSA) capabilities. We remember that the goal of the FAZIA collaboration is to construct a new generation multi-detector able to work at low thresholds with very high detection efficiency both in charge Z and Mass A. The low thresholds determination, see figure 6, is achieved via PSA thanks to a severe constraint on silicon detector characteristics, homemade preamplifier of both charge and current signals (PACI) and dedicated low noise digital electronics and sampling [6]. Moreover it allows also a large improvement of the usual DE-E technique see in the following, now allowing isotopic resolution up to Z 22 (instead of Z 4 for INDRA). The recipes are the following, good resistivity homogeneity ( 5%) for ntd-silicon detectors, purposely random cut to appear like an amorphous material for impinging particles (channeling effect), rear side mounting of the silicon detectors (particles enter by the low electric field), dedicated pre-amplifiers for both charge and current with adapted gains (two gains for the first silicon layer to reduce the thresholds and improve isotopic separation) and finally optimization of the digital treatment of the sampled pulse shapes. Figure 6 : Energy thresholds (in energy per nucleon) for Z identification with DE(300µm)-E technique (black triangles) and with PSA technique (energy vs charge rise time: red points rear injection and blue squares front injection ) as a function of atomic number Z. Extended isotopic identification for the FAZIA project The main achievement of the FAZIA project is to realize a unsurpassed isotopic (mass) discrimination by using a full digital electronics (allowing then a powerful -online- pulse shape analysis), and high quality detectors(silicon NTD and highly-doped CsI(Tl)). To fulfil these goals, we need to push to the limit all detection capabilities, not only the detection threshold or the mass(and charge) identification with the pulse shape analysis (see after or above), but also the more traditional and robust identification methods such as the well-known E-DE method. This requires at least a 2-layers telescope, such as those tested for the FAZIA phase 2 program (2 thin Silicon layers followed by a thick CsI crystal). 28
9 Using the formalism developed by M. Parlog [7] which takes into account the carrier recombination (plasma) and the δ-rays (electrons) produced by an impinging nucleus in the detector material (Silicon or CsI), it has been proposed the following formula for the signal L (either light for CsI or electric signal for Si) as a function of the atomic number(z),atomicmass(a)andincidentenergy Eofagivennucleus: where the 4 parameters a G,a R, a n and E d are adjusted to the specific detector (layer) response by a fit to known isotopes. The mass number A and atomic number Z dependence are embedded into the electronic S e and nuclear S n stopping powers. By performing the fit, it is possible to build identification grids which can fit the experimental matrices E-DE, such as the one displayed below for a Silicon-Silicon matrix obtained within the FAZIA project(figure 7). Figure 7 : E-DE (Si-Si) correlation for a FAZIA telescope. The data have been obtained by impinging a 84 Kr beam at 35A MeV on a thin 120 Sn target at the LNS facility (Catania, Italy). The curves represent the identification grid (only one curve per element) and are superimposed to the experimental data (see legend for details). It is then straightforward to get the linearization of the data as displayed in the following figure. As we can see, we are able to achieve the full isotopic identification forelementsrangingfromz=1uptoz= [8] Figure 8 : Particle Identification 8Z+A for the data displayed in the previous figure 29
10 For heavier elements(z>22), it is still possible to have a partial isotopic resolution by estimating the different isotopic contributions as seen in the following figure for iron(z=26) isotopes. Figure 9 : particle Identification 8Z+A for iron isotopes (Z=26). The interest of this identification technique is two-fold. First, it can be implemented in a semi-automatic way, which is indeed mandatory for detection arrays with a large number of telescopes in one wants in order to save time. Second, this allows to assign quite unambiguously the mass number since it relies on a formula which is explicitly depending through the stopping powers on the mass number A. Once the fit is done with some known isotopes, the extrapolation to rare isotopes can safely applied and thus permits to recover those species, even if it is hard to identify them directly on the E-DE matrix because of the smaller statistics(figure for the red-labelled isotopes). Description of current pulses induced by heavy ions in silicon detectors The high frequency sampling of the current or charge signals induced by charged reaction products in silicon detectors gives access to their shape versus time. The signals generated by heavy ions have a longer duration as compared to those corresponding to light particles like protons, due to a slower charge carrier collection - the plasma delay phenomenon. The dependence of this shape on the nature (Z, A, E) of the impinging particlevia thespecificrateofenergy lossbecameoneoftherunways used for the heavy ion identification in the framework of the FAZIA collaboration. The description of the signal shape by realistic simulations will hopefully provide automatic procedures of calibration and nuclear fragment identification in large scale arrays in nuclear physics, provided that the preamplifier transfer function be known. In collaboration with IPN Orsay, we have recently developed a charge carrier collection treatment which considers the progressive extraction of the electrons and holes from the high carrier density zone along the ionizing particle track [9]. This region is assumed to present a supplementary dielectric polarization and consequently a disturbed electric field. The figures 10 & 11 presents the exact coordinate dependence of the modified electric field, inside and outside the 80 MeV 12 C ion range, found as the solution of the one dimensional Maxwell's equation for the electric field in this inhomogeneous medium. The quality of the simulation is illustrated in the following figure, for the signals induced by the same ion impinging ontherear 30
11 or the front side of the same neutron transmutation doped silicon detector. Figure 10 : The distorted electric field strength inside the silicon detector, at different moments, due to the ionized column induced by 80 MeV 12 C ions penetrating on the rear side (left, x = 0 at the rear side contact) and the front side (right, x = 0 at the front side contact) of the detector. The straight dashed line gives in each case the undisturbed electric field. The current signals of 10 different heavy ion species at known energies around 10 AMeV were quite well reproduced by the fit procedure based on this formalism. The two main fit parameters dependofthenatureoftheparticleinapredictableway. Figure 11 : mean experimental current signals induced by 80 MeV 12 C ions impinging on the rear side (left) and on the front side (right) of a silicon detector - full line; the simulation using a distorted electric field - dashed line. Study of the experimental potentiality of the FAZIA detector Within the framework of the collaboration FAZIA, it was developed a program package, called PANFORTE, allowing to simulate the detection of heavy ions by an experimental set-up like INDRA or FAZIA. With the help of the event generator HIPSE, we have made a study to verify to what extent the FAZIA detector is a real improvement to detect and perform the calorimetry of hot nuclei. We present on figure 12, a two-dimension graph of the total detected charge normalized to the total charge of the system as a function of the total parallel detected pseudo-impulse (velocity multiplied by the charge) normalized to the initial value of this quantity. This graph permits to judgethequalityoftheevent detectionforcollisionsxeonsnfrom25 to50a.mev. 31
12 Figure 12 : Graph of the total detected charge normalized to the total charge of the system as a function of the total parallel detected pseudo-impulse (velocity multiplied by the charge) normalized to the initial value of this quantity. Graphs show the proportion of events detected with a quality of 80 % or 90 % as a function of the incidental energy per nucleon for the INDRA detector and FAZIA detector We look at the proportion of events, which are correctly detected by the INDRA detector or by the FAZIA detector in its first geometry. We consider as well detected the events the events falling on the dotted rectangle of the two-dimension graph of the figure(top). This criterion corresponds to a quality of detection of 80 %. We have made the samekindofstudywithaqualityof90%. With this first geometry, the FAZIA detector allows clearly to keep an important cross section, much more than the INDRA detector in spite of strict criteria of quality of detection.[10] [1] M.B. Tsang, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 66 (2011) 400 [2] G. Lehautet al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) [3] E. Legouée, PhD thesis, Université de Caen, in progress [4] P. Marini et al, CNR*09, Second Int. Workshop on Compound Nuclear Reactions, Bordeaux (2009) [5] Ad. Radutaet al, Phys. Lett. B 705 (2011) 65 [6] N. Le Neindreet al, NIM A 701 (2013) 145 [7] M. Parlôget al, NIM A 482 (2002) 674 [8] O. Lopez et al, IWM 09 (2009) [9] H. Hamritaet al, NIM A 642 (2011) 59 [10] P. Napolitaniet al, Phys. Rev. C 89 (2010)
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
N/Z influence on the level density parameter
 EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment
 Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems:
 Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ at 15 MeV/nucleon
 Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Noncentral collisions
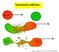 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions
 CNR*11 Third International Workshop on Compound Nuclear Reactions and Related Topics September 19-23, 2011 Prague Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions 78 Kr+ 40
CNR*11 Third International Workshop on Compound Nuclear Reactions and Related Topics September 19-23, 2011 Prague Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions 78 Kr+ 40
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay
 LOI @ Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay S.Pirrone (INFN Catania), J.P.Wieleczko (GANIL- Caen), M.La Commara (Univ.& INFN Napoli), A.Pagano (INFN-Catania), G.Politi (Univ. &INFN
LOI @ Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay S.Pirrone (INFN Catania), J.P.Wieleczko (GANIL- Caen), M.La Commara (Univ.& INFN Napoli), A.Pagano (INFN-Catania), G.Politi (Univ. &INFN
FAZIA detector for isospin φsics: status of the R&D program
 FAZIA detector for isospin φsics: status of the R&D program NEED OF (A,Z) Identification + Coupling LOI 18 «Although many apparatuses are available at present, the new experimental demands require a new
FAZIA detector for isospin φsics: status of the R&D program NEED OF (A,Z) Identification + Coupling LOI 18 «Although many apparatuses are available at present, the new experimental demands require a new
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Oct 2003
 1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013](/thumbs/83/87477490.jpg) PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
Study of the Dynamical Dipole Resonance Mode with the SPES Radioactive Beams
 SPES 2010 International Workshop INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro 15-17 November 2010 Study of the Dynamical Dipole Resonance Mode with the SPES Radioactive Beams D. Pierroutsakou, INFN-Naples LOI
SPES 2010 International Workshop INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro 15-17 November 2010 Study of the Dynamical Dipole Resonance Mode with the SPES Radioactive Beams D. Pierroutsakou, INFN-Naples LOI
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation
 Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV)
 Search for alpha-particle condensation with CHIMERA 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV) De-excitation of quasi-projectiles (primary and secondary products) C.R. Badita, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre,
Search for alpha-particle condensation with CHIMERA 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV) De-excitation of quasi-projectiles (primary and secondary products) C.R. Badita, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre,
Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe Pt for production of exotic nuclei
 16 th ASRC International Workshop Mar. 19, 2014 Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe + 198 Pt for production of exotic nuclei Contents Y.X. Watanabe (KEK) 1. Introduction (MNT reactions
16 th ASRC International Workshop Mar. 19, 2014 Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe + 198 Pt for production of exotic nuclei Contents Y.X. Watanabe (KEK) 1. Introduction (MNT reactions
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment. J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H.
 Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy
 FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy Overview of project and physics inputs Present status (mechanics, electronics) and perspectives for the use with GET electronics G. Cardella, INFN-Catania
FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy Overview of project and physics inputs Present status (mechanics, electronics) and perspectives for the use with GET electronics G. Cardella, INFN-Catania
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies
 two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy
 Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy G. Verde(INFN-CT), A. Chbihi(GANIL), Exochim coll., INFN- CT, LNS, MI, NA - Open collaboration and synergies. Farcosphysics: dynamics & spectroscopy
Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy G. Verde(INFN-CT), A. Chbihi(GANIL), Exochim coll., INFN- CT, LNS, MI, NA - Open collaboration and synergies. Farcosphysics: dynamics & spectroscopy
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector. Alice Mentana
 Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector Alice Mentana The Isospin simmetry Isospin Mixing (breaking of Isospin simmetry) Experimental technique: γ-decay of GDR Experimental apparatus: the PARIS
Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector Alice Mentana The Isospin simmetry Isospin Mixing (breaking of Isospin simmetry) Experimental technique: γ-decay of GDR Experimental apparatus: the PARIS
PoS(ENAS 6)050. Resonances in 19 Ne with relevance to the astrophysically important 18 F(p,α) 15 O reaction
 Resonances in 19 Ne with relevance to the astrophysically important 18 F(p,α) 15 O reaction David Mountford, A.St J. Murphy, T. Davinson, P.J. Woods University of Edinburgh E-mail: d.j.mountford@sms.ed.ac.uk
Resonances in 19 Ne with relevance to the astrophysically important 18 F(p,α) 15 O reaction David Mountford, A.St J. Murphy, T. Davinson, P.J. Woods University of Edinburgh E-mail: d.j.mountford@sms.ed.ac.uk
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model
 High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process
 REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
Progresses in FAZIA detection system and preliminary results from the ISO-FAZIA experiment
 IL UOVO CIMETO 39 C (206) 383 DOI.393/ncc/i206-6383-9 Colloquia: IWM-EC 206 Progresses in FAIA detection system and preliminary results from the ISO-FAIA experiment G. Pastore( )( 2 ), S. Piantelli( 2
IL UOVO CIMETO 39 C (206) 383 DOI.393/ncc/i206-6383-9 Colloquia: IWM-EC 206 Progresses in FAIA detection system and preliminary results from the ISO-FAIA experiment G. Pastore( )( 2 ), S. Piantelli( 2
Testing the shell closure at N=82 via multinucleon transfer reactions at energies around the Coulomb barrier
 Testing the shell closure at N=82 via multinucleon transfer reactions at energies around the Coulomb barrier E. Vardaci 1, E. M. Kozulin 2, D. Quero 1, A. Di Nitto 3, A. Karpov 2, L. Calabretta 4, M. Ashaduzzaman
Testing the shell closure at N=82 via multinucleon transfer reactions at energies around the Coulomb barrier E. Vardaci 1, E. M. Kozulin 2, D. Quero 1, A. Di Nitto 3, A. Karpov 2, L. Calabretta 4, M. Ashaduzzaman
GANIL PROPOSAL FOR EXPERIMENT
 GANIL PROPOSAL FOR EXPERIMENT EXP # : (Do not fill in) Scheduling period : June 2005 May 2006 Dead-line for submission : September 17 th, 2004 If Be or Ni production targets are to be used, indicate the
GANIL PROPOSAL FOR EXPERIMENT EXP # : (Do not fill in) Scheduling period : June 2005 May 2006 Dead-line for submission : September 17 th, 2004 If Be or Ni production targets are to be used, indicate the
N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon
 IWM 2011 Int. Work. Multifrag. Rel. Topics Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dip. di Scienze Fisiche,
IWM 2011 Int. Work. Multifrag. Rel. Topics Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dip. di Scienze Fisiche,
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources. A. Chbihi GANIL
 Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
NN th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy
 NN 2015 12 th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Isospin influence on the decay modes of systems produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca reactions at 10AMeV
NN 2015 12 th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Isospin influence on the decay modes of systems produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca reactions at 10AMeV
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission
 Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Light ion recoil detector
 Light ion recoil detector Overall design The detector for light (target-like) particles is a substantial part of the R3B setup. It allows registration of recoils in coincidence with the heavy fragments,
Light ion recoil detector Overall design The detector for light (target-like) particles is a substantial part of the R3B setup. It allows registration of recoils in coincidence with the heavy fragments,
University of Groningen. Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya
 University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS
 NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics
 The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 Mar 2005
 Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei
 Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei Eric Bonnet (GANIL) for the INDRA and ALADIN collaboration IWM 09, Catania Outline First order phase transition in finite system Definition and related signals
Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei Eric Bonnet (GANIL) for the INDRA and ALADIN collaboration IWM 09, Catania Outline First order phase transition in finite system Definition and related signals
Impact of Terrestrial Facilities on the Structure of the Neutron Star Crust
 Impact of Terrestrial Facilities on the Structure of the Neutron Star Crust Jorge Piekarewicz Florida State University The Neutron Star Crust and Surface (INT - June, 2007) My Collaborators: C.J. Horowitz,
Impact of Terrestrial Facilities on the Structure of the Neutron Star Crust Jorge Piekarewicz Florida State University The Neutron Star Crust and Surface (INT - June, 2007) My Collaborators: C.J. Horowitz,
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models
 Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Status of the TRACE array
 Status of the TRACE array D. Mengoni University of the West of Scotland, Paisley - U.K. INFN - Sezione di Padova, Padova - Italy SPES workshop, LNL - Italy Nov 15 th 17 th, 2010 Outline 1 Introduction
Status of the TRACE array D. Mengoni University of the West of Scotland, Paisley - U.K. INFN - Sezione di Padova, Padova - Italy SPES workshop, LNL - Italy Nov 15 th 17 th, 2010 Outline 1 Introduction
Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive subject not only for nuclear
 First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
(Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S Pb
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, (2012) DOI: / epjconf/ C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012
 EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio
 Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
13 Synthesis of heavier elements. introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1
 13 Synthesis of heavier elements introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1 The triple α Reaction When hydrogen fusion ends, the core of a star collapses and the temperature can reach
13 Synthesis of heavier elements introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1 The triple α Reaction When hydrogen fusion ends, the core of a star collapses and the temperature can reach
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters
 Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
GANIL / SPIRAL1 / SPIRAL2
 Nuclear Structure, Reaction and Dynamics GANIL / SPIRAL1 / SPIRAL2 A huge discovery potential Exotic Nuclei Proton number Z Which force? 3-body, tensor, spin-orbit, Isospin dependence, Continuum coupling
Nuclear Structure, Reaction and Dynamics GANIL / SPIRAL1 / SPIRAL2 A huge discovery potential Exotic Nuclei Proton number Z Which force? 3-body, tensor, spin-orbit, Isospin dependence, Continuum coupling
Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process?
 arxiv:nucl-ex/0203017v1 25 Mar 2002 Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process? A. Van Lauwe a, D. Durand a, G. Auger b, N. Bellaize a, B. Bouriquet b, A.M. Buta
arxiv:nucl-ex/0203017v1 25 Mar 2002 Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process? A. Van Lauwe a, D. Durand a, G. Auger b, N. Bellaize a, B. Bouriquet b, A.M. Buta
Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction 136 Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV
 Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV J.A Alcántara-Núñez 1), J. Benlliure 1), D. Perez Loureiro 1) and the S184 Collaboration 1) Universidade de
Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV J.A Alcántara-Núñez 1), J. Benlliure 1), D. Perez Loureiro 1) and the S184 Collaboration 1) Universidade de
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact
 Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Study of channeling effects in silicon detectors for pulse-shape applications
 Study of channeling effects in silicon detectors for pulse-shape applications Luigi Bardelli for the FAZIA collaboration 1 Outline Introduction to channeling The silicon crystal structure Experimental
Study of channeling effects in silicon detectors for pulse-shape applications Luigi Bardelli for the FAZIA collaboration 1 Outline Introduction to channeling The silicon crystal structure Experimental
14 Supernovae (short overview) introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1
 14 Supernovae (short overview) introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1 The core-collapse of a supernova The core of a pre-supernova is made of nuclei in the iron-mass range A ~
14 Supernovae (short overview) introduc)on to Astrophysics, C. Bertulani, Texas A&M-Commerce 1 The core-collapse of a supernova The core of a pre-supernova is made of nuclei in the iron-mass range A ~
Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes
 Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes T. Marchi (IKS, KU Leuven) XX Colloque GANIL, Amboise 15-20 October 2017 Motivation and outline Fast processes in fusion reactions Competition
Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes T. Marchi (IKS, KU Leuven) XX Colloque GANIL, Amboise 15-20 October 2017 Motivation and outline Fast processes in fusion reactions Competition
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS
 ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
PHL424: Nuclear fusion
 PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes
 High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes Outline: Alain Astier, CSNSM Orsay, France Motivations Experimental conditions
High-spin studies and nuclear structure in three semi-magic regions of the nuclide chart High-seniority states in Sn isotopes Outline: Alain Astier, CSNSM Orsay, France Motivations Experimental conditions
Fission-yield data. Karl-Heinz Schmidt
 Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
GET MEETING 2014 September , Saint-Avit Loisirs, FRANCE. G.Cardella for the FARCOS-EXOCHIM collaboration
 GET MEETING 2014 September 22-25 2014, Saint-Avit Loisirs, FRANCE G.Cardella for the FARCOS-EXOCHIM collaboration Farcos physics cases 1. Dynamics in heavy-ion collision (low and intermediate energies,
GET MEETING 2014 September 22-25 2014, Saint-Avit Loisirs, FRANCE G.Cardella for the FARCOS-EXOCHIM collaboration Farcos physics cases 1. Dynamics in heavy-ion collision (low and intermediate energies,
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter
 An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions
 14 th International Conference on Nuclear Reaction Mechanisms Varenna, June 15-19, 2015 Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions Fabio Crespi Università
14 th International Conference on Nuclear Reaction Mechanisms Varenna, June 15-19, 2015 Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions Fabio Crespi Università
Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter
 T-REX Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter J. Natowitz et al. T-REX [ TAMU Reaccelerated EXotics] The Symmetry Energy Problem Density Dependence? Constraining the density
T-REX Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter J. Natowitz et al. T-REX [ TAMU Reaccelerated EXotics] The Symmetry Energy Problem Density Dependence? Constraining the density
Hypernuclei Production by K at rest
 Hypernuclei Production by K at rest Germano Bonomi 1 Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering via Branze 38, Brescia, ITALY & INFN Pavia via Bassi 6, Pavia, ITALY The creation of a hypernucleus
Hypernuclei Production by K at rest Germano Bonomi 1 Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering via Branze 38, Brescia, ITALY & INFN Pavia via Bassi 6, Pavia, ITALY The creation of a hypernucleus
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions.
 Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
PoS(NIC XII)250. A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars
 A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars 1, Kohsuke Sumiyoshi 2, Shoichi Yamada 1,3, Hideyuki Suzuki 4 1 Department of Science and Engineering,
A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars 1, Kohsuke Sumiyoshi 2, Shoichi Yamada 1,3, Hideyuki Suzuki 4 1 Department of Science and Engineering,
Symmetry Energy. in Structure and in Central and Direct Reactions
 : in Structure and in Central and Direct Reactions Pawel Natl Superconducting Cyclotron Lab, US The 12 th International Conference on Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Bulk Properties
: in Structure and in Central and Direct Reactions Pawel Natl Superconducting Cyclotron Lab, US The 12 th International Conference on Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Bulk Properties
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI
 THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy D.Santonocito 1 and Y.Blumenfeld 2 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy D.Santonocito 1 and Y.Blumenfeld 2 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud,
Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions
 Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions O.B.Tarasov, 1 O.Delaune, 2,a F.Farget, 2 A.M.Amthor, 2,b B.Bastin, 2 D.Bazin, 1 B.Blank, 3 L.Caceres, 2 A.Chbihi, 2 B.Fernandez-Domnguez, 4
Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions O.B.Tarasov, 1 O.Delaune, 2,a F.Farget, 2 A.M.Amthor, 2,b B.Bastin, 2 D.Bazin, 1 B.Blank, 3 L.Caceres, 2 A.Chbihi, 2 B.Fernandez-Domnguez, 4
Annax-I. Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in
 Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION MODELS IN GEANT4
 Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes. Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2
 Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei
 Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
Effect of Λ(1405) on structure of multi-antikaonic nuclei
 12th International Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of the Nucleon, (May 31-June 4, 2010, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia) Session 2B Effect of Λ(1405) on structure
12th International Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of the Nucleon, (May 31-June 4, 2010, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia) Session 2B Effect of Λ(1405) on structure
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Aman Sood, Christoph Hartnack, Elena Bratkovskaya
 What strange particles can tell us about hadronic matter and what hadronic matter tells us about strange particles Aman Sood, Christoph Hartnack, Elena Bratkovskaya Strangeness production at threshold:
What strange particles can tell us about hadronic matter and what hadronic matter tells us about strange particles Aman Sood, Christoph Hartnack, Elena Bratkovskaya Strangeness production at threshold:
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
From few-body to many-body systems
 From few-body to many-body systems Nasser Kalantar-Nayestanaki, KVI-CART, University of Groningen Few-Body Physics: Advances and Prospects in Theory and Experiment 614. WE-Heraeus-Seminar, Bad Honnef April
From few-body to many-body systems Nasser Kalantar-Nayestanaki, KVI-CART, University of Groningen Few-Body Physics: Advances and Prospects in Theory and Experiment 614. WE-Heraeus-Seminar, Bad Honnef April
Nonstatistical fluctuations for deep inelastic processes
 Nonstatistical fluctuations for deep inelastic processes in 27 Al + 27 Al collision Introduction Experimental procedures Cross section excitation functions (EFs) 1. Statistical analysis (a) Energy autocorrelation
Nonstatistical fluctuations for deep inelastic processes in 27 Al + 27 Al collision Introduction Experimental procedures Cross section excitation functions (EFs) 1. Statistical analysis (a) Energy autocorrelation
