Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei
|
|
|
- Candice Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei Eric Bonnet (GANIL) for the INDRA and ALADIN collaboration IWM 09, Catania
2 Outline First order phase transition in finite system Definition and related signals starting from microcanonical entropy Canonical ensemble and Quasi Projectile fragmentation data Study of the bimodal distribution of the charge of the biggest fragment (Z1) in Au+Au reactions. Trace back the density of states of Gold nuclei Starting from the experimental 2D distribution Z1 E* (Excitation energy) Derive the equivalent canonical distribution Constrain canonical ensemble using comparison with data Extract properties for the hot nuclei de excitation
3 First order phase transition in finite system : Definition Presence of a residual convex intruder in the entropy S(X) of the mixed system. 2 X S(X) >0 define the spinodal zone X : order parameter (X) = X S : conjugate variable
4 First order phase transition in finite system : Consequences Bimodal canonical distribution of an order parameter 2 X S(X) >0 define the spinodal zone P can (X) = exp (S(X) X) What information can we get? Boundaries of the coexistence zone P X can (X) = 0 latent heat
5 First order phase transition in finite system : Consequences Bimodal canonical distribution of an order parameter 2 X S(X) >0 define the spinodal zone P can (X) = exp (S(X) X) What information can we get? Boundaries of the coexistence zone P X can (X) = 0 latent heat Boundaries of the spinodal zone 2 P X can (X) > 0
6 First order phase transition in finite system : Consequences Negative heat capacity (C) Experimental evidence of abnormal fluctuations of configurational energies P. Chomaz et al, NPA 647 (1999) 2 X S(X) >0 define the spinodal zone 2 E S = 1/CT2 >0 C < 0 Boundaries of the spinodal zone
7 First order phase transition in finite system : Results Negative heat capacity (C) Experimental evidence of abnormal fluctuations of configurational energies Le Neindre et al, NPA 795 (2007) INDRA M. Bruno et al, NPA 807 (2008) M. D'Agostino et al, PLB 473 (2000) Multics Miniball Au+Au 35 A MeV C k = canonical heat capacity k = configurational energies fluctuations Ck > As k /T 2 C < 0
8 First order phase transition in finite system : Results Negative heat capacity (C) Experimental evidence of abnormal fluctuations of configurational energies Le Neindre et al, NPA 795 (2007) INDRA M. Bruno et al, NPA 807 (2008) M. D'Agostino et al, PLB 473 (2000) Multics Miniball Au+Au 35 A MeV Deduce boundaries for the spinodal region Liquid side = MeV/A Gas side = MeV/A
9 First order phase transition in finite system : Guideline Canonical ensemble allows to make a direct link between finite size system which passed through a phase transition and the bimodal distribution of an order parameter Take as a guideline for analysis bimodality observed in the QP fragmentation data. Which experimental observable? Charge of the biggest fragment (Z1) as a reliable order parameter F. Gulminelli et al, PRC 71 (2005) What have we studied? Well defined QP of Gold sources produced in semi peripheral collisions Au+Au@80, 100 MeV/A INDRA@GSI Two data selection method : M. Pichon et al, NPA 779 (2006) E. Bonnet et al, NPA 807 (2009)
10 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data? First attempt... Au+Au 80 A MeV Canonical ensemble = Target "temperature" as control parameter System in contact with thermal bath M. Pichon et al, NPA 779 (2006) M. Bruno et al, NPA 807 (2008) Target "temperature" as control parameter Localize the transition region Bimodality observed in Z1 vs (Z1 Z2)/(Z1+Z2) In this region, «coexistence» of events with two excitation energies at the same canonical temperature? In this approach, an other interpretation is given in A. LeFèvre et al, PRC 80 (2009) (see Arnaud poster)
11 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) Au+Au Selected QP events in the Z1 E* plane and projections Most events with low E* > Dominated by most peripheral collisions P (exp) (E*,Z1) W(E*,Z1) g (exp) (E*) It has been checked that only P (exp) (E*) is biased by experimental conditions. E. Bonnet et al, PRL103 (2009) For a given E*, the Z1 distribution seems to reflect intrinsic density of states W(E*,Z1). How to trace back W(E*,Z1)?
12 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) How to trace back W(E*,Z1)? In canonical ensemble: Start with a system with a given density of states W(E*,Z1) Describe hot nuclei
13 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) How to trace back W(E*,Z1)? In canonical ensemble: Start with a system with a given density of states W(E*,Z1) Derive the canonical probability Describe hot nuclei P (can) (E*,Z1) = W(E*,Z1) exp ( E*) Z -1 -Boltzmann factor exp ( E*) Partition sum Z
14 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) How to trace back W(E*,Z1)? In canonical ensemble: Start with a system with a given density of states W(E*,Z1) Derive the canonical probability Describe hot nuclei P (can) (E*,Z1) = W(E*,Z1) exp ( E*) Z -1 -Boltzmann factor exp ( E*) Partition sum Z Experimental ensemble : P (exp) (E*,Z1) W(E*,Z1) g (exp) (E*) Get rid of experimental bias
15 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) How to trace back W(E*,Z1)? In canonical ensemble: Start with a system with a given density of states W(E*,Z1) Derive the canonical probability Describe hot nuclei P (can) (E*,Z1) = W(E*,Z1) exp ( E*) Z -1 -Boltzmann factor exp ( E*) Partition sum Z Experimental ensemble : P (exp) (E*,Z1) W(E*,Z1) g (exp) (E*) Get rid of experimental bias Renormalization of 2D distributions in order to have equiprobable E* distribution
16 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) How to trace back W(E*,Z1)? In canonical ensemble: Start with a system with a given density of states W(E*,Z1) Derive the canonical probability Describe hot nuclei P (can) (E*,Z1) = W(E*,Z1) exp ( E*) Z -1 -Boltzmann factor exp ( E*) Partition sum Z Experimental ensemble : P (exp) (E*,Z1) W(E*,Z1) g (exp) (E*) Renormalization of 2D distributions in order to have equiprobable E* distribution P (exp) (E*) = P (exp) (E*,Z1) dz1 = W(E*) g (exp) (E*) P (exp) (E*,Z1) = P (exp) (E*,Z1)/P (exp) (E*) = W(E*,Z1)/W(E*) Get rid of experimental bias Renormalization prescription Focus on the density of states
17 How to deal with canonical ensemble in QP fragmentation data?... going to the next step, F. Gulminelli, NPA 791 (2007) To compare directly canonical / experimental distributions, derive an analytic expression P (can) (E*,Z1) = W(E*,Z1) exp ( E*) Z -1 W(E*,Z1) = exp ( S(E*,Z) ) + double saddle point approximation for entropy P can 1 E, Z1 = i =l, g N i exp 1 det i 2 x i 1 i x i Double gaussian function : 11 parameters 4 parameters for each phase correlation factor Population of the 2 phases Nl, Ng
18 Renormalization and comparison between experimental and canonical P(E,Z1) distributions Au+Au P (exp) (E*,Z1)
19 Renormalization and comparison between experimental and canonical P(E,Z1) distributions Au+Au P (exp) (E*,Z1) (exp) (E) = ( P (exp) (E*,Z1) dz1) 1
20 Renormalization and comparison between experimental and canonical P(E,Z1) distributions Au+Au P (exp) (E*,Z1) (exp) (E) P (exp) (E*,Z1) (exp) (E) = ( P (exp) (E*,Z1) dz1) 1
21 Renormalization and comparison between experimental and canonical P(E,Z1) distributions Au+Au P (exp) (E*,Z1) P (can) (E*,Z1) (exp) (E) (can) (E) P (exp) (E*,Z1) P (can) (E*,Z1) (exp) (E) = ( P (exp) (E*,Z1) dz1) 1 (can) (E) = ( P (can) (E*,Z1) dz1) 1
22 Renormalization and comparison between experimental and canonical P(E,Z1) distributions Au+Au P (exp) (E*,Z1) P (can) (E*,Z1) The two distributions can be compared directly W(E*,Z1)/W(E*)
23 Results: Fitting procedure Projection Mean Value Standard Deviation Fitting procedure has been used to obtain best reproduction of experimental distribution by canonical distributions Fit range E* = [2,7] MeV/A. Assuming that canonical distribution is derived at transition temperature. 4 sets of data have been taken into account : 2 incident bombarding energies 2 QP event selections P (exp) (E*,Z1) P (can) (E*,Z1) The two distributions can be compared directly W(E*,Z1)/W(E*)
24 Results: Fitting procedure : One solution Au+Au@80 A.MeV Projection Mean Value Standard Deviation Experimental ensemble to be reproduced Canonical ensemble fit result Adequacy of the fit
25 Results: Fitting procedure : One solution Au+Au@80 A.MeV Projection Mean Value Standard Deviation Canonical Data Experimental ensemble to be reproduced Canonical ensemble fit result Adequacy of the fit
26 Results: P can 1 E, Z1 = i =l, g N i exp 1 det i 2 x i 1 i x i E. Bonnet et al, PRL103 (2009) Extraction of the latent heat
27 Results: Fitting procedure : One solution Au+Au@80 A.MeV
28 Preliminary Results: Boundaries of the coexistence zone El = MeV/A Eg = MeV/A Boundaries of the spinodal zone 2 P > 0 E MeV/A for liquid side MeV/A for gas side Negative heat capacity signal MeV/A MeV/A M. Bruno et al, NPA 807 (2008) Le Neindre et al, NPA 795 (2007) M. D'Agostino et al, PLB 473 (2000)
29 Conclusion: A system passing through a first order phase transition described in the canonical ensemble seems to be a good tool to understand the decay hot nuclei. The bimodality of the charge of the biggest (Z1) can be related to an evidence of such phase transition. Using a renormalisation prescription for experimental and canonical 2D distributions, we can get rid of experimental bias on the experimental energy distribution. From the comparison of the renormalized 2D distributions, we have extracted parameters related to 2 phases and deduce the latent heat for Gold nuclei. We confirm results obtained from negative heat capacity, and show that the spinodal zone is entirely within the coexistence region.
30 Perspective: Widen this analysis to address the effect of system size on properties like latent heat and spinodal zone. 65, 80 and 100 MeV/A (INDRA@GSI) and study of Xe Quasi Projectile is running An heavier system like U+U@100 MeV/A would be a good tool to bring also some information on the role plays by coulomb. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!
31
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010](/thumbs/94/120296745.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models
 Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
hal , version 1-5 Mar 2010
 Author manuscript, published in "International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics in Heavy-Ion Reactions and the Symmetry Energy (IWND29, Shanghai : Chine (29" DOI :.42/S285928 March 5, 2 5: WSPC/INSTRUCTION
Author manuscript, published in "International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics in Heavy-Ion Reactions and the Symmetry Energy (IWND29, Shanghai : Chine (29" DOI :.42/S285928 March 5, 2 5: WSPC/INSTRUCTION
Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process
 REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model
 Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model A. Wielocha, J. Brzychczyka, J. Łukasikb, P. Pawłowskib, T. Pietrzaka, W. Trautmannc a M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, Reymonta
Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model A. Wielocha, J. Brzychczyka, J. Łukasikb, P. Pawłowskib, T. Pietrzaka, W. Trautmannc a M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, Reymonta
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Oct 2003
 1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources. A. Chbihi GANIL
 Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun
 Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun Multifragmentation is phenomenon in which nuclear system decays to a final configuration
Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun Multifragmentation is phenomenon in which nuclear system decays to a final configuration
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
Fluctuations of fragment observables
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Fluctuations of fragment observables F. Gulminelli 1 and M.D Agostino 2 1 LPC Caen (IN2P3-CNRS/Ensicaen et Université), F-14050 Caen Cédex, France 2
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Fluctuations of fragment observables F. Gulminelli 1 and M.D Agostino 2 1 LPC Caen (IN2P3-CNRS/Ensicaen et Université), F-14050 Caen Cédex, France 2
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions.
 Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV)
 Search for alpha-particle condensation with CHIMERA 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV) De-excitation of quasi-projectiles (primary and secondary products) C.R. Badita, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre,
Search for alpha-particle condensation with CHIMERA 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV ( 40 Ca+ 40 Ca, 25 AMeV) De-excitation of quasi-projectiles (primary and secondary products) C.R. Badita, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre,
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
AMD. Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/ / 22
 2009 3 25 26 AMD Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/25 26 1 / 22 (?) ( ) 2009/03/25 26 2 / 22 Nuclear Matter in Nuclear Collisions and Neutron Stars 0 60 E sym [MeV] 40 20 0 0 NL3 ChPT DBHF DD ρδ DD TW var AV18+ δ V+3
2009 3 25 26 AMD Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/25 26 1 / 22 (?) ( ) 2009/03/25 26 2 / 22 Nuclear Matter in Nuclear Collisions and Neutron Stars 0 60 E sym [MeV] 40 20 0 0 NL3 ChPT DBHF DD ρδ DD TW var AV18+ δ V+3
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems:
 Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Thermodynamics of the nucleus
 Thermodynamics of the nucleus Hilde-Therese Nyhus 1. October, 8 Hilde-Therese Nyhus Thermodynamics of the nucleus Owerview 1 Link between level density and thermodynamics Definition of level density Level
Thermodynamics of the nucleus Hilde-Therese Nyhus 1. October, 8 Hilde-Therese Nyhus Thermodynamics of the nucleus Owerview 1 Link between level density and thermodynamics Definition of level density Level
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation
 Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve
 Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure
 Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies
 Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Understanding Molecular Simulation 2009 Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamics in different ensembles. Srikanth Sastry
 JNCASR August 20, 21 2009 Understanding Molecular Simulation 2009 Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamics in different ensembles Srikanth Sastry Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bangalore
JNCASR August 20, 21 2009 Understanding Molecular Simulation 2009 Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamics in different ensembles Srikanth Sastry Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bangalore
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004
 Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group
 Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group Permamentstaff : R. Bougault, N. Le Neindre, O. Lopez, E. Vient PhD Student: M. Kabtoul, E. Legouée Collaborations: LPC: F.Gulminelli (Théorie), D.Durand(Théorie),
Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group Permamentstaff : R. Bougault, N. Le Neindre, O. Lopez, E. Vient PhD Student: M. Kabtoul, E. Legouée Collaborations: LPC: F.Gulminelli (Théorie), D.Durand(Théorie),
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Particle-number projection in finite-temperature mean-field approximations to level densities
 Particle-number projection in finite-temperature mean-field approximations to level densities Paul Fanto (Yale University) Motivation Finite-temperature mean-field theory for level densities Particle-number
Particle-number projection in finite-temperature mean-field approximations to level densities Paul Fanto (Yale University) Motivation Finite-temperature mean-field theory for level densities Particle-number
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR. Yvonne Leifels GSI
 Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions
 Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
New experiments on low-energy fission. Methods and results
 New experiments on low-energy fission Methods and results Karl-Heinz Schmidt Contribution to the meeting of the WPEG subgroup Improved Fission product yield evaluation methodologies May 22, 2013 Issy-les-Moulineaux,
New experiments on low-energy fission Methods and results Karl-Heinz Schmidt Contribution to the meeting of the WPEG subgroup Improved Fission product yield evaluation methodologies May 22, 2013 Issy-les-Moulineaux,
Spectroscopic Quadrupole Moment in 96,98 Sr : Shape coexistence at N=60. E.Clément-GANIL IS451 Collaboration
 Spectroscopic Quadrupole Moment in 96,98 Sr : Shape coexistence at N=60 E.Clément-GANIL IS451 Collaboration Shape Transition at N=60 P. Campbell, I.D. Moore, M.R. Pearson Progress in Particle and Nuclear
Spectroscopic Quadrupole Moment in 96,98 Sr : Shape coexistence at N=60 E.Clément-GANIL IS451 Collaboration Shape Transition at N=60 P. Campbell, I.D. Moore, M.R. Pearson Progress in Particle and Nuclear
Challenges of finite systems stat. phys.
 Challenges of finite systems stat. phys. Ph. Chomaz, Caen France Connections to other chapters Finite systems Boundary condition problem Statistical descriptions Gibbs ensembles - Ergodicity Inequivalence,
Challenges of finite systems stat. phys. Ph. Chomaz, Caen France Connections to other chapters Finite systems Boundary condition problem Statistical descriptions Gibbs ensembles - Ergodicity Inequivalence,
Dissipative nuclear dynamics
 Dissipative nuclear dynamics Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter universitario de Fisica Nuclear Universidad de Santiago de Compostela March 2009 Karl Heinz Schmidt Collective dynamical properties
Dissipative nuclear dynamics Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter universitario de Fisica Nuclear Universidad de Santiago de Compostela March 2009 Karl Heinz Schmidt Collective dynamical properties
Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion collisions
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies
 Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies Critical Point and Onset of Deconfinement 2016, Wrocław. Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, P. M. Hohler, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies Critical Point and Onset of Deconfinement 2016, Wrocław. Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, P. M. Hohler, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
Cluster Dscay of the High-lying Excited States in 14 C
 Cluster Dscay of the High-lying Excited States in 14 C Yanlin Ye School of Physics and State Key Lab of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University INPC2016, Sept. 11-16, 2016, Adelaide, Australia
Cluster Dscay of the High-lying Excited States in 14 C Yanlin Ye School of Physics and State Key Lab of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University INPC2016, Sept. 11-16, 2016, Adelaide, Australia
Molecular Structures in Slow Nuclear Collisions
 Molecular Structures in Slow Nuclear Collisions ALEXIS DIAZ-TORRES European Centre for Theoretical Studies in Nuclear Physics and Related Areas Trento, Italy Nuclear Structure Reaction Dynamics FAIR Nuclear
Molecular Structures in Slow Nuclear Collisions ALEXIS DIAZ-TORRES European Centre for Theoretical Studies in Nuclear Physics and Related Areas Trento, Italy Nuclear Structure Reaction Dynamics FAIR Nuclear
1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter
 1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter Intensive: independent of the amount of substance, e.g. temperature,pressure. Extensive: depends on the amount of substance, e.g. internal energy, enthalpy.
1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter Intensive: independent of the amount of substance, e.g. temperature,pressure. Extensive: depends on the amount of substance, e.g. internal energy, enthalpy.
nuclear states nuclear stability
 nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
(# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble
 Recall from before: Internal energy (or Entropy): &, *, - (# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble & = /01Ω maximized Ω: fundamental statistical quantity
Recall from before: Internal energy (or Entropy): &, *, - (# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble & = /01Ω maximized Ω: fundamental statistical quantity
Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay
 LOI @ Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay S.Pirrone (INFN Catania), J.P.Wieleczko (GANIL- Caen), M.La Commara (Univ.& INFN Napoli), A.Pagano (INFN-Catania), G.Politi (Univ. &INFN
LOI @ Isospin dependence of compound nuclear formation and decay S.Pirrone (INFN Catania), J.P.Wieleczko (GANIL- Caen), M.La Commara (Univ.& INFN Napoli), A.Pagano (INFN-Catania), G.Politi (Univ. &INFN
Noncentral collisions
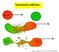 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes
 Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes T. Marchi (IKS, KU Leuven) XX Colloque GANIL, Amboise 15-20 October 2017 Motivation and outline Fast processes in fusion reactions Competition
Reaction dynamics and exotic systems: a focus on fast processes T. Marchi (IKS, KU Leuven) XX Colloque GANIL, Amboise 15-20 October 2017 Motivation and outline Fast processes in fusion reactions Competition
Single particle degrees of freedom in fission
 Single particle degrees of freedom in fission Heloise Goutte SPhN division CEA Saclay CEA-Saclay/DSM/Irfu Service de Physique Nucléaire PND2 PAGE 1 Non exhaustive Focused on: - Fission fragment yields
Single particle degrees of freedom in fission Heloise Goutte SPhN division CEA Saclay CEA-Saclay/DSM/Irfu Service de Physique Nucléaire PND2 PAGE 1 Non exhaustive Focused on: - Fission fragment yields
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Giovanni Casini Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Sezione di Firenze SUMMARY. Some Physics at the Fermi regime.
 Fast emission processes in peripheral heavy ion reactions and their impact on reaction dynamics Giovanni Casini Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Sezione di Firenze SUMMARY Some Physics at the Fermi
Fast emission processes in peripheral heavy ion reactions and their impact on reaction dynamics Giovanni Casini Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Sezione di Firenze SUMMARY Some Physics at the Fermi
Coulomb Correction to Density and Temperature of Fermions and Bosons from Quantum Fluctuations
 Coulomb Correction to Density and Temperature of Fermions and Bosons from Quantum Fluctuations Hua Zheng a, Gianluca Giuliani a and Aldo Bonasera a,b! a)cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University! b)lns-infn,
Coulomb Correction to Density and Temperature of Fermions and Bosons from Quantum Fluctuations Hua Zheng a, Gianluca Giuliani a and Aldo Bonasera a,b! a)cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University! b)lns-infn,
Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy
 Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy Alexandra Gade National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy at Michigan State University, East
Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy Alexandra Gade National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy at Michigan State University, East
The nuclear many- body problem: an open quantum systems perspec6ve. Denis Lacroix GANIL- Caen
 The nuclear many- body problem: an open quantum systems perspec6ve Denis Lacroix GANIL- Caen Coll: M. Assié, S. Ayik, Ph. Chomaz, G. Hupin, K. Washiyama Trento, Decoherence -April 2010 The nuclear many-
The nuclear many- body problem: an open quantum systems perspec6ve Denis Lacroix GANIL- Caen Coll: M. Assié, S. Ayik, Ph. Chomaz, G. Hupin, K. Washiyama Trento, Decoherence -April 2010 The nuclear many-
Energy Dependence of Multiplicity Fluctuations in Heavy Ion Collisions. Benjamin Lungwitz, IKF Universität Frankfurt for the NA49 collaboration
 Energy Dependence of Multiplicity Fluctuations in Heavy Ion Collisions Benjamin Lungwitz, IKF Universität Frankfurt for the NA49 collaboration Outline Introduction Analysis of energy dependence Energy
Energy Dependence of Multiplicity Fluctuations in Heavy Ion Collisions Benjamin Lungwitz, IKF Universität Frankfurt for the NA49 collaboration Outline Introduction Analysis of energy dependence Energy
Multiplicity Fluctuations in Statistical Models
 Multiplicity Fluctuations in Statistical Models Michael Hauer Outline Introduction Particle Anti Particle Gas Hadron Gas Comparison with Data Summary 1 Statistical Ensembles Grand Canonical Canonical Microcanonical
Multiplicity Fluctuations in Statistical Models Michael Hauer Outline Introduction Particle Anti Particle Gas Hadron Gas Comparison with Data Summary 1 Statistical Ensembles Grand Canonical Canonical Microcanonical
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania)
 Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams
 Angela Bonaccorso The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams G Blanchon, DM Brink, F Carstoiu, A Garcia-Camacho, R Kumar, JMargueron, N Vinh Mau JAPAN-ITALY EFES Workshop on Correlations in
Angela Bonaccorso The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams G Blanchon, DM Brink, F Carstoiu, A Garcia-Camacho, R Kumar, JMargueron, N Vinh Mau JAPAN-ITALY EFES Workshop on Correlations in
Monte Carlo. Lecture 15 4/9/18. Harvard SEAS AP 275 Atomistic Modeling of Materials Boris Kozinsky
 Monte Carlo Lecture 15 4/9/18 1 Sampling with dynamics In Molecular Dynamics we simulate evolution of a system over time according to Newton s equations, conserving energy Averages (thermodynamic properties)
Monte Carlo Lecture 15 4/9/18 1 Sampling with dynamics In Molecular Dynamics we simulate evolution of a system over time according to Newton s equations, conserving energy Averages (thermodynamic properties)
Dynamics of the scattering of 11 Li on 208 Pb at energies around the Coulomb barrier
 Dynamics of the scattering of 11 Li on 208 Pb at energies around the Coulomb barrier J. A. Lay Departamento de Física Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear; Universidad de Sevilla University of Surrey, 9 th November
Dynamics of the scattering of 11 Li on 208 Pb at energies around the Coulomb barrier J. A. Lay Departamento de Física Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear; Universidad de Sevilla University of Surrey, 9 th November
SMR/ International Workshop on QCD at Cosmic Energies III. 28 May - 1 June, Lecture Notes. E. Zabrodin University of Oslo Oslo, Norway
 SMR/1842-26 International Workshop on QCD at Cosmic Energies III 28 May - 1 June, 2007 Lecture Notes E. Zabrodin University of Oslo Oslo, Norway Open questions of the statistical approach to or little
SMR/1842-26 International Workshop on QCD at Cosmic Energies III 28 May - 1 June, 2007 Lecture Notes E. Zabrodin University of Oslo Oslo, Norway Open questions of the statistical approach to or little
An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning
 An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning Chang Liu Tsinghua University June 1, 2016 1 / 22 What is covered What is Statistical mechanics developed for? What
An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning Chang Liu Tsinghua University June 1, 2016 1 / 22 What is covered What is Statistical mechanics developed for? What
Statistical description of nuclear break-up
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017](/thumbs/90/103449438.jpg) A new 3D Calorimetry of hot nuclei arxiv:179.7396v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 217 E. Vient, 1, L. Manduci, 2, 1 E. Legouée, 1 L. Augey, 1 E. Bonnet, 3 B. Borderie, 4 R. Bougault, 1 A. Chbihi, 5 D. Dell
A new 3D Calorimetry of hot nuclei arxiv:179.7396v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 217 E. Vient, 1, L. Manduci, 2, 1 E. Legouée, 1 L. Augey, 1 E. Bonnet, 3 B. Borderie, 4 R. Bougault, 1 A. Chbihi, 5 D. Dell
Investigation of Pygmy Dipole Resonance in neutron rich exotic nuclei
 Investigation of Pygmy Dipole Resonance in neutron rich exotic nuclei R.Avigo 1,2, O.Wieland 1, A.Bracco 1,2, F.Camera 1,2 on behalf of the AGATA and DALI2 collaborations 1 INFN, sezione di Milano 2 Università
Investigation of Pygmy Dipole Resonance in neutron rich exotic nuclei R.Avigo 1,2, O.Wieland 1, A.Bracco 1,2, F.Camera 1,2 on behalf of the AGATA and DALI2 collaborations 1 INFN, sezione di Milano 2 Università
Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter. Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta
 Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta LPC Caen, France IFIN Bucharest Supernova remnant and neutron star in Puppis A (ROSAT x-ray) χ 1/2 Τ 10 12 Κ Motivation:
Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta LPC Caen, France IFIN Bucharest Supernova remnant and neutron star in Puppis A (ROSAT x-ray) χ 1/2 Τ 10 12 Κ Motivation:
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
PHASE TRANSITIONS. A. Budzanowski
 PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
Statistical properties of nuclei by the shell model Monte Carlo method
 Statistical properties of nuclei by the shell model Monte Carlo method Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Shell model Monte Carlo (SMMC) method Circumventing the odd particle-number sign problem
Statistical properties of nuclei by the shell model Monte Carlo method Introduction Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Shell model Monte Carlo (SMMC) method Circumventing the odd particle-number sign problem
CURRICULUM VITAE. Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest, POB-MG 6, Romania
 CURRICULUM VITAE SURNAME: Raduta FIRST NAME(S): Alexandru Horia Date of birth: 9 June 1970 Place of birth: Fagaras, Romania Nationality: Romanian Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear
CURRICULUM VITAE SURNAME: Raduta FIRST NAME(S): Alexandru Horia Date of birth: 9 June 1970 Place of birth: Fagaras, Romania Nationality: Romanian Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 12 Jun 2000
 Microcanonical Lattice Gas Model for Nuclear Disassembly C. B. Das 1, S. Das Gupta 1 and S. K. Samaddar 2 1 Physics Department, McGill University, 3600 University St., Montréal, Québec Canada H3A 2T8 2
Microcanonical Lattice Gas Model for Nuclear Disassembly C. B. Das 1, S. Das Gupta 1 and S. K. Samaddar 2 1 Physics Department, McGill University, 3600 University St., Montréal, Québec Canada H3A 2T8 2
Jet Physics with ALICE
 Jet Physics with ALICE Oliver Busch for the ALICE collaboration Oliver Busch Tsukuba 2014 /03/13 1 Outline introduction results from pp jets in heavy-ion collisions results from Pb-Pb collisions jets in
Jet Physics with ALICE Oliver Busch for the ALICE collaboration Oliver Busch Tsukuba 2014 /03/13 1 Outline introduction results from pp jets in heavy-ion collisions results from Pb-Pb collisions jets in
Nuclear Science Research Group
 UR-NCUR 05-12 THE UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Nuclear Science Research Group ROCHESTER, NEW YORK 14267-0216, USA Compound Nucleus with Surface Entropy; A Unified Phenomenology of Particle Evaporation, Fission,
UR-NCUR 05-12 THE UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Nuclear Science Research Group ROCHESTER, NEW YORK 14267-0216, USA Compound Nucleus with Surface Entropy; A Unified Phenomenology of Particle Evaporation, Fission,
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Table of Contents [ttc]
![Table of Contents [ttc] Table of Contents [ttc]](/thumbs/89/97960614.jpg) Table of Contents [ttc] 1. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Thermodynamics overview. [tln2] Preliminary list of state variables. [tln1] Physical constants. [tsl47] Equations of state. [tln78]
Table of Contents [ttc] 1. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Thermodynamics overview. [tln2] Preliminary list of state variables. [tln1] Physical constants. [tsl47] Equations of state. [tln78]
Nuclear Science Research Group
 Triad Nancy Jurs UR-NCUR 10-26 THE UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Nuclear Science Research Group ROCHESTER, NEW YORK 14267-0216, USA Surface Boiling a New Type of Instability of Highly Excited Atomic Nuclei J.
Triad Nancy Jurs UR-NCUR 10-26 THE UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Nuclear Science Research Group ROCHESTER, NEW YORK 14267-0216, USA Surface Boiling a New Type of Instability of Highly Excited Atomic Nuclei J.
Silvia M. Lenzi University of Padova and INFN. Silvia Lenzi, 10th Int. Spring Seminar on Nuclear Physics, Vietri sul Mare, May 21-25, 2010
 Structure of Neutron-Rich Nuclei near N=40 Silvia M. Lenzi University of Padova and INFN 10th International Spring Seminar on Nuclear Physics Vietri sul Mare, May 21-25, 2010 Collaboration Theory: F. Nowacki,
Structure of Neutron-Rich Nuclei near N=40 Silvia M. Lenzi University of Padova and INFN 10th International Spring Seminar on Nuclear Physics Vietri sul Mare, May 21-25, 2010 Collaboration Theory: F. Nowacki,
Nuclear Physics from Lattice Effective Field Theory
 Nuclear Physics from Lattice Effective Field Theory Dean Lee (NCSU/Bonn) work done in collaboration with Evgeny Epelbaum (Bochum) Hermann Krebs (Bochum) Ulf-G. Meißner (Bonn/Jülich) Buḡra Borasoy (now
Nuclear Physics from Lattice Effective Field Theory Dean Lee (NCSU/Bonn) work done in collaboration with Evgeny Epelbaum (Bochum) Hermann Krebs (Bochum) Ulf-G. Meißner (Bonn/Jülich) Buḡra Borasoy (now
Van der Waals equation: event-by-event fluctuations, quantum statistics and nuclear matter
 Van der Waals equation: event-by-event fluctuations, quantum statistics and nuclear matter Volodymyr Vovchenko In collaboration with Dmitry Anchishkin, Mark Gorenstein, and Roman Poberezhnyuk based on:
Van der Waals equation: event-by-event fluctuations, quantum statistics and nuclear matter Volodymyr Vovchenko In collaboration with Dmitry Anchishkin, Mark Gorenstein, and Roman Poberezhnyuk based on:
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation
 Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Self-Consistent Equation of State for Hot Dense Matter: A Work in Progress
 Self-Consistent Equation of State for Hot Dense Matter: A Work in Progress W.G.Newton 1, J.R.Stone 1,2 1 University of Oxford, UK 2 Physics Division, ORNL, Oak Ridge, TN Outline Aim Self-consistent EOS
Self-Consistent Equation of State for Hot Dense Matter: A Work in Progress W.G.Newton 1, J.R.Stone 1,2 1 University of Oxford, UK 2 Physics Division, ORNL, Oak Ridge, TN Outline Aim Self-consistent EOS
Recent results from the NA61/SHINE experiment
 Recent results from the NA6/SHINE experiment Emil Kaptur for the NA6/SHINE collaboration University of Silesia October 7, 5 of 5 Outline NA6/SHINE experiment Selected results from energy scan (,,, 8, 58
Recent results from the NA6/SHINE experiment Emil Kaptur for the NA6/SHINE collaboration University of Silesia October 7, 5 of 5 Outline NA6/SHINE experiment Selected results from energy scan (,,, 8, 58
The shell model Monte Carlo approach to level densities: recent developments and perspectives
 The shell model Monte Carlo approach to level densities: recent developments and perspectives Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Introduction: the shell model Monte Carlo (SMMC) approach Level density in
The shell model Monte Carlo approach to level densities: recent developments and perspectives Yoram Alhassid (Yale University) Introduction: the shell model Monte Carlo (SMMC) approach Level density in
Mapping Low-Energy Fission with RIBs (in the lead region)
 Mapping Low-Energy Fission with RIBs (in the lead region) Andrei Andreyev University of York, UK Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Tokai, Japan Low-energy fission in the new regions of the Nuclear Chart
Mapping Low-Energy Fission with RIBs (in the lead region) Andrei Andreyev University of York, UK Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Tokai, Japan Low-energy fission in the new regions of the Nuclear Chart
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter. Matthias Hempel, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel,
 Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements
 Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
THE SPY MODEL: HOW A MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION OF THE NUCLEUS CAN SHED SOME LIGHT ON FISSION
 THE SPY MODEL: HOW A MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION OF THE NUCLEUS CAN SHED SOME LIGHT ON FISSION S. Panebianco, N. Dubray, S. Hilaire, J-F. Lemaître, J-L. Sida CEA - Irfu/SPhN, Saclay, France CEA DIF, Arpajon,
THE SPY MODEL: HOW A MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION OF THE NUCLEUS CAN SHED SOME LIGHT ON FISSION S. Panebianco, N. Dubray, S. Hilaire, J-F. Lemaître, J-L. Sida CEA - Irfu/SPhN, Saclay, France CEA DIF, Arpajon,
pt-inclusive 2-particle correlations; p-p, Cu-Cu, Au-Au BES
 pt-inclusive 2-particle correlations; p-p, Cu-Cu, Au-Au BES Duncan May 7, 2012 1 Agenda Review of Methods Minimum-bias Jets in pp - the reference system Review 200, 62 GeV Au-Au Compare Cu-Cu to Au-Au
pt-inclusive 2-particle correlations; p-p, Cu-Cu, Au-Au BES Duncan May 7, 2012 1 Agenda Review of Methods Minimum-bias Jets in pp - the reference system Review 200, 62 GeV Au-Au Compare Cu-Cu to Au-Au
Cluster-gas-like states and monopole excitations. T. Yamada
 Cluster-gas-like states and monopole excitations T. Yamada Cluster-gas-like states and monopole excitations Isoscalar monopole excitations in light nuclei Cluster-gas-likes states: C, 16 O, 11 B, 13 C
Cluster-gas-like states and monopole excitations T. Yamada Cluster-gas-like states and monopole excitations Isoscalar monopole excitations in light nuclei Cluster-gas-likes states: C, 16 O, 11 B, 13 C
Nuclear spectroscopy with fast exotic beams. Alexandra Gade Professor of Physics NSCL and Michigan State University
 Nuclear spectroscopy with fast exotic beams Alexandra Gade Professor of Physics NSCL and Michigan State University or puzzles in the region around N=28 from 48 Ca over 46 Ar to 42 Si Alexandra Gade Professor
Nuclear spectroscopy with fast exotic beams Alexandra Gade Professor of Physics NSCL and Michigan State University or puzzles in the region around N=28 from 48 Ca over 46 Ar to 42 Si Alexandra Gade Professor
Slow dynamics in systems with long-range interactions
 Slow dynamics in systems with long-range interactions STEFANO RUFFO Dipartimento di Energetica S. Stecco and INFN Center for the Study of Complex Dynamics, Firenze Newton Institute Workshop on Relaxation
Slow dynamics in systems with long-range interactions STEFANO RUFFO Dipartimento di Energetica S. Stecco and INFN Center for the Study of Complex Dynamics, Firenze Newton Institute Workshop on Relaxation
Appendix C extra - Partition function Cextra4-1
 Appendix C extra - Partition function Cextra4-1 Appendix C extra - Partition function his section introduces the partition function Z, a very useful tool for calculations in statistical mechanics. here
Appendix C extra - Partition function Cextra4-1 Appendix C extra - Partition function his section introduces the partition function Z, a very useful tool for calculations in statistical mechanics. here
Contents. 1 Introduction and guide for this text 1. 2 Equilibrium and entropy 6. 3 Energy and how the microscopic world works 21
 Preface Reference tables Table A Counting and combinatorics formulae Table B Useful integrals, expansions, and approximations Table C Extensive thermodynamic potentials Table D Intensive per-particle thermodynamic
Preface Reference tables Table A Counting and combinatorics formulae Table B Useful integrals, expansions, and approximations Table C Extensive thermodynamic potentials Table D Intensive per-particle thermodynamic
Baryon number distribution in Lattice QCD
 Baryon number distribution in Lattice QCD Keitaro Nagata KEK KN, S. Motoki, Y. Nakagawa, A. Nakamura, T. Saito [PTEP01A103(2012)] A. Nakamura, KN [arxiv:1305.0760] KN, K. Kashiwa, A. Nakamura, S. M. Nishigaki
Baryon number distribution in Lattice QCD Keitaro Nagata KEK KN, S. Motoki, Y. Nakagawa, A. Nakamura, T. Saito [PTEP01A103(2012)] A. Nakamura, KN [arxiv:1305.0760] KN, K. Kashiwa, A. Nakamura, S. M. Nishigaki
SPY: a microscopic statistical scission-point model to predict fission fragment distributions
 CEA Irfu Service de Physique Nucléaire SPY: a microscopic statistical scission-point model to predict fission fragment distributions S. Panebianco 1, J.-L. Sida 1, J.-F. Lemaitre 1, S. Heinrich 2*, S.
CEA Irfu Service de Physique Nucléaire SPY: a microscopic statistical scission-point model to predict fission fragment distributions S. Panebianco 1, J.-L. Sida 1, J.-F. Lemaitre 1, S. Heinrich 2*, S.
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics
 The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
