Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
|
|
|
- Esmond Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus, Konya, Turkey 2 Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, J.W. Goethe University, D Frankfurt am Main, Germany 3 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia September 22, 2015 International School of Nuclear Physics/Workshop on Probing Hadron Structure with Lepton and Hadron Beams, September 2015, Erice, ITALY - *This work is supported by Tübitak-113F058 project and Selcuk U. BAP Content 1. Introduction 2. Statistical Multifragmentation Model 3. Angular momentum and Coulomb effects for hot fragments in peripheral HICs at Fermi energies 4. Interpretation of FAZIA[1] experimental data with new approach 5. Conclusions [1]. S. Barlini, S. Piantelli, et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, (2013)
2 Statistical approach in nuclear reactions:conception of equilibrium Experimentally established: 1) few stages of reactions leading to multifragmentation, 2) short time ~100fm/c for primary fragment production, 3) freeze-out density is around 0.1ρ 0-0.6ρ 0, 4) high degree of equilibration at the freeze-out. Intermediate energy collisions Preequlibrium emission + equilibration Compound-nucleus decay channels (sequential evaporation or fission) dominate at low excitation energy of thermal sources E * <2-3 MeV/nucl. At high excitation energy E * >3-4 MeV/nucl there is a simultaneous break-up into many fragments evaporation fission Multifragmentation at freeze-out thermal and chemical equilibrium
3 Probability of channel: mass and charge conservation Free energy of individual fragments: Statistical Multifragmentation Model [2] JP Bondorf, AS Botvina et al., Phys. Rep. 257, mic 1 Wf exp {S f (E0,A, Z)}, with exp {S f (E0,A, Z)} f N. A A, N. Z Z A, Z AZ Ff Energy conservation E0 Ff T f T f Ff entropy of channel S f T f Fragments obey Boltzmann statistics, liquid-drop description of individual fragments, Coulomb interaction in the Wigner-Seitz approximation Z0 e free energy of channel: Ff N AZFAZ 1/3 1/3 5 r A (1 ) F AZ A, Z F b AZ F 0 s AZ 0 F 0 sym AZ A, Z F c c AZ AZ 0 liquid-drop model Bulk term: Surface term: Symmetry energy term: Coulomb term: F F F b AZ s AZ sym AZ c F AZ 2 [ 0 B W 0 Tf / ( A)] A, / 4 2/3 0[( Tc Tf )/( Tc Tf )] A (N Z) Z e 5 r A 2 / A, / [1 (1 ) 3 1/3 c 0 0 ],, W 0 16 MeV B 0 18 MeV T c 18 MeV 25MeV
4 MSU exp.: central collisions of 112,124 Sn+ 112,124 Sn at E/A= 50 MeV. (Liu TX et al 2004 Phys. Rev. C ) The microcanonical Markov-chain SMM calculations assuming the decay of single isolated source. N Buyukcizmeci et al., J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 39 (2012) Predicted charge yields of light fragments (Z 8) emitted from the multifragmentation of the sources, and the comparison with MSU experimental data. Predicted isotope distributions for carbon and oxygen fragments for the both sources. The panels (a) and (b) are for the carbon isotopes, and (c) and (d) for the oxygen isotopes. The dashed lines correspond to the present results for cold fragments at gamma=14 MeV, the circles to the MSU data, full lines CTM results.
5 ALADIN projectile fragmentation of 124 Sn, 107 Sn and 124 La beams at an incident energy of 600 MeV per nucleon studied with ALADIN spectrometer. Z=3-10 SMM Ensemble Calculations R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Atav U., Buyukcizmeci N.,et al., Phys. Rev. C 83, (2011). J. P. Bondorf et al., Phys. Rep. 257, 133 (1995). N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Eur. Phys. J. A (2005).
6 FRS GSI FRS projectile fragmentation of two symetric systems 124 Sn Sn and 112 Sn Sn at an incident beam energy of 1 A GeV measured with high-resolution magnetic spectrometer FRS. (V. Föhr, et al., Phys. Rev. C 84, (2011) ) Symmetry-energy coefficients. Experimental data are well reproduced with statistical calculations in the SMM ensemble. To reproduce the FRS data symmetry energy term is reduced as shown in the table. We have also found a decreasing trend of the symmetry energy with increasing charge number, for the neutron-rich heavy fragments resulting from 124Sn projectile. H. Imal, A.Ergun, N. Buyukcizmeci, R.Ogul, A.S. Botvina, W. Trautmann, C 91, (2015)
7 Angular momentum and Coulomb effects for hot fragments in peripheral HICs at Fermi energies peripheral 84 Kr+ 84 Kr collisions at energy of 35 MeV per nucleon The first source (projectile) is flying along Y -axis. The location of the second (target) source is RY =-10.6 fm and RZ=10.6 fm respective to the first source. The peripheral collision is assumed to take place in the Y-Z plane, therefore, the coordinate in Z-axis is determined by the sizes of colliding nuclei, as well as their possible repulsion after the collision. The X-axis is assumed to be an angular momentum axis.
8 Charge distribution A.Ergun, H. Imal, N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Phys. Rev. C 92, (2015) = 0 /2 = 0 /6 Fig.1: Total charge yield of primary hot fragments, in the cases of without (full circles) and with angular momentum (L) of 80Ћ (open circles), after multifragmentation of the 84 Kr source at the excitation energy of Ex = 5 MeV/nucleon. This projectile source is assumed to be formed in the peripheral 84 Kr+ 84 Kr collision at 35 MeV/nucleon, and its disintegration are affected by the Coulomb field of the partner. Top and bottom panels show results at freeze-out densities = 0/2, and = 0/6, respectively. For comparison, the results of multifragmentation of a single isolated 84 Kr source, at the same excitation energy but without the external Coulomb and without angular momentum, is shown too. An angular momentum (open circles) favors emission of IMF(Z=3-20) with larger charge (mass) numbers since the system in the freeze-out needs to have a large moment of inertia in order to minimize rotational energy and maximize the entropy. From another side a Coulomb interaction (full circles) prevents to emit IMF with large charge number Z.
9 Charge distribution of the first, second and third largest hot fragments A.Ergun, H. Imal, N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Phys. Rev. C 92, (2015) = 0 /2 = 0 /6 L= 0ħ only Coulomb effect L= 80ħ angular momentum + Coulomb effect Fig. 2: The yields of the first, second and third largest hot fragments with the atomic numbers Z max1, Z max2, and Z max3, respectively, for 84 Kr+ 84 Kr reaction at E x =5 MeV/n.
10 <N>/Z distributions The angular momentum leads to increasing N/Z values of IMFs 84 Kr : initial <N>/Z=1.33 Fig.3 :The average neutron-to-proton ratio <N> /Z of hot primary fragments produced in the freeze-out ρ =ρ0/2 (top panel) and ρ =ρ0/6 (bottom panel) for 84Kr+84Kr at Ex=5 MeV/n. Full and empty circles show the distributions in the case of L=0 hbar and including angular momentum L=80 hbar, respectively.
11 Theoretical Calculation of V x And V y Velocity Distributions for 84 Kr+ 84 Kr yield per event V x 84 Kr+ 84 Kr Ex=5 MeV/n hot 10 0 V x without with ang. momentum ang. momentum R YSEC =-10.6=R ZSEC Calculations are done over events for this fig. X angular momentum direction 10-4 yield per event V y V y Zmax1 Zmax2 Zmax3 Y reaction direction velocity (c) velocity (c) Figure 4: Theoretical calculations of V x and V y velocity distributions of 1 st, 2 nd and 3 rd charged hot particles without (left) and with (right) inclusion of angular momentum for 84 Kr+ 84 Kr reaction at E x =5 MeV/n. In the case of inclusion of angular momentum, all these fragments fly predominantly in the plane of rotation. This is seen from the peaked distributions at V x. As a result of Coulomb proximity, the maximum fragments fly predominantly in forward direction, while second and third ones fly in the direction of the target sources. There is an order in emission of these fragments: The largest fragments have the largest V y velocity, and then 2 nd and 3 rd ones (As is seen from V y panel). This effect is consistent with the previous experimental observations [J. Colin et al., Phys. Rev. C 67, (2003).]
12 <N/Z> and yield per event for velocity distribution Vy Z=3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 Figure 5-6 : < N > /Z and yield per event as a function of velocity Vy. Full and open circles show the distributions for L = 0ħ and L = 80ħ, respectively.
13 <Z> and <N>/Z vs velocity Vy L = 0ħ L= 80ħ Fig.7: Average charge <Z> (top) and <N>/Z (bottom) distributions of the first, second and third largest hot fragments with the atomic numbers Z max1, Z max2, and Z max3, respectively, according to the V y for hot primary fragments produced in the freeze-out density = 0 /2 for 84 Kr+ 84 Kr at E x =5 MeV/n. It is in agreement with our previous conclusions on modification of statistical picture. In particular, one can see a trend of increasing < N > /Z toward midrapidity for Z max3 when the angular momentum is included (right bottom panel).
14 Dependence of the fragment characteristics on distances between the sources Fig.8:The total charge yield (top panel) and the mean neutron-to-proton ratios $<N>/Z$ (bottom panel) of all primary fragments produced at the freeze-out density = 0 /2 for 84 Kr+ 84 Kr at E x =5 MeV/n., and at different distances between the sources To clarify the Coulomb contribution, we do not include the angular momentum here. If Ry=-70 fm: The decrease of the external Coulomb field leads to the enhanced IMF production because of a lower Coulomb barrier. The expected distributions are very close to those obtained in the case of isolated sources The neutron richness of these fragments increases slightly and, correspondingly, the neutron content of the largest fragment decreases, in correlation with their more uniform distribution in the coordinate space.
15 Dependence of the fragment characteristics on distances between the sources: yields and <N>/Z vs velocity Vy A.Ergun, H. Imal, N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Phys. Rev. C 92, (2015) Double nuclear system+necklike fragment ( C ) Double nuclear system Fig.9:Yield distribution (top) and mean neutron-to-proton ratios <N>/Z (bottom) of primary fragments with Z=6 as a function of their velocity VY in the source frame, at different distances between the sources. Fig.10:Same as Fig. 9, but RY= 10.6 fm between the sources and with the presence of the neck-like fragment (A = 12, Z = 6) at midrapidity between the sources. L = 80 hbar
16 3.Theoretical interpretation of FAZIA[1] 84 Kr+ 112,124 Sn reactions at an incident beam energy of 35 MeV/n including the Coulomb proximity and angular momentum effects on multifragmentation picture with Markov chain SMM. [1]. S. Barlini, S. Piantelli, et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, (2013) the correlation between excitation energy and velocity of projectile residues for 84 Kr + 112,124 Sn Ex (MeV/n) Zs As(112Sn) As(124Sn) Vs(112Sn) (mm/ns) Vs(124Sn) (mm/ns) Weight Angular Momentum (h-bars) Table 1. Values used for SMM calculations as initial parameters. Vlab=Vs+Vcm While the less excited (Ex=2 MeV/n) projectile sources fly more quickly, the highly excited (Ex=7 MeV/n) projectile sources fly more slowly.
17 We have found velocity of sources from energy and momentum conservation. V1 velocity of projectile V2 velocity of target Velocity of target in projectile system DV=V2-V1 Fig 6: Ex excitation energy vs average velocities of projectile residues for 84 Kr + 112,124 Sn. kinetic energy of the projectile : 35 MeV/n
18 Charge distributions : FAZIA [1] data-smm calculations Inclusive charge distribution of fragments (Z 3) produced in the 84 Kr+ 112 Sn (red solid dots) and 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (black open dots) reactions at 35 MeV/n. The distributions are normalized in the region 18 Z 28. [1] S. Barlini et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, (2013) We have ignored Ex<2 MeV/n cases in SMM calculations. Trends seems similar. (preliminary results) Buyukcizmeci et al. Nuc. Sci. And Tech. 26, S20507 (2015)
19 <N>/Z <N>/Z Distributions: FAZIA[1] data-smm calculations The <N>/Z of the products detected in the n-rich case is systematically higher than the <N>/Z of the n-poor case without angular momentum Kr 84 +Sn 112 Exp. Ex=2-7 Without mom. triangle weighted Z=3-9 =14 Z=10-17 =16 Z=18-20 =19 <N>/Z with angular momentum 84 Kr+ 112 Sn exp. Ex=2-7 with mom. triangle weighted Z=3-9 =14 MeV Z=10-17 =16 MeV Z=18-20 =19 MeV Kr 84 +Sn 124 Exp. 84 Kr+ 124 Sn exp. <N>/Z <N>/Z Col 1 vs Col 2 Col 3 vs Col 12 Z=3-9 =14 MeV Z=10-17 =18 MeV Z=18-20 =19 MeV Z Şekil 8: <N>/Z as a function of Z for the reaction 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (red full stars) and 84 Kr+ 112 Sn (red open stars) at 35 MeV/nucleon [1]. Z
20 Isotopic Distributions: SMM calculations Z=3-9 =14 MeV Z=10-17 =16 MeV Z=18-20 =19 MeV Fig. Predicted isotope distributions for Z =6, 12, 18 fragments for 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (top panels) and 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (bottom panels) reactions. The solid lines correspond to the present results with angular momentum, the dashed lines show results without angular momentum. For our predictions γ =14, 16 and 19 MeV values are used for Z=6, 12 and 18 isotopes, respectively. These γ values are in agreement with our previous predictions in [13].
21 Isotopic Distributions: Comparison FAZIA data-smm calculations Z=3-9 =14 MeV Z=10-17 =16 MeV Z=18-20 =19 MeV Fig. Predicted isotope distributions for Z = 3 20 fragments for 84 Kr+ 112 Sn (left panels) and 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (right panels) reactions. The solid lines correspond to the present results and the stars to the FAZIA data [1].
22 Angular momentum effect is very important to describe the velocities of fragments. <N> / Z 1.4 Z=3 Z= Z=4 Z= Ex=4 MeV/n Ex=6 MeV/n Z=9 without angular momentum Z=9 <N> / Z 1.4 Z=3 Z= Z=4 Z= Ex=2 MeV/n Ex=4 MeV/n Ex=6 MeV/n Z=9 with angular momentum Z=9 The less excited (Ex=2 MeV/n) projectile sources fly more quickly and produces not very neutron rich light fragments. While more excited sources (Ex=4-6 MeV/n) fly slower, and as a result of their decay more neutron rich light fragments are produced =14 MeV Z=10 84 Kr+ 124 Sn 84 Kr+ 112 Sn Z= =14 MeV Z=10 84 Kr+ 124 Sn 84 Kr+ 112 Sn Z=10 We observe a clear increasing <N>/Z of these fragments toward midrapidity. During the evolution of <N>/Z, n-rich system are always above n-poor system V lab (mm/ns) V lab (mm/ns) Figure 4: The evolution of <N>/Z for elements (Z=3, 4, 9, 10) as a function of the laboratory velocity of the fragments for 84 Kr+ 112 Sn (open stars) and 84 Kr+ 124 Sn (full stars) reactions [1]. SMM calculations without (left figures) and with (right figures) the inclusion of angular momentum of sources (see Table 1) for =14 MeV are shown. For light ions <N>/Z rapidly decreases with increasing velocity, while it displays a rather flat behavior for heavier ions.
23 CONCLUSIONS These are our preliminary results. Investigation of the influence of angular momentum and Coulomb proximity on fragment production in heavy-ion collisions at Fermi energies, including the description of FAZIA [1] experimental data, within the statistical approaches [5-13] is very promising. Including an angular momentum and a long-range Coulomb interaction between projectile and target residues leads to new features in the statistical fragmentation picture: It is possible to obtain a correlation of sizes of emited fragments with their velocities and an emission in the reaction plane. [11] The angular momentum may lead to more neutron-rich IMF production and to anisotropic emission respective to the projectile and target sources. Coulomb interaction of the target and projectile-like sources leads to a predominant midrapidity ( neck -like) emission of intermediate mass fragments. We see a significant influence of these effects on the isotope production both in the midrapidity and in the kinematic regions of the projectile/target. This kind of investigations may provide us with inputs to understand the nuclear equation of state and nuclear composition, which are important to determine the properties of nuclear and stellar matter at extreme conditions and their connections to the thermodynamics of stellar matter and astrophysical events.
24 REFERENCES [1] S. Barlini et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, (2013) [2] J. P. Bondorf et al., Phys. Rep. 257, 133 (1995). [3]A.S. Botvina, I.N. Mishustin, Phys. Rev. C 63, (R) (2001). [4] A.S. Botvina, arxiv:nucl-th/ , (2000). [5] N. Buyukcizmeci, H. Imal, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina and I.N. Mishustin, J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 39 (2012) [6] A.S. Botvina, and D.H.E. Gross, Nucl. Phys. A 592 (1995) [7] A.S. Botvina, M. Bruno, M. D'Agostino, and D.H.E. Gross. Phys. Rev. C 59 (1999) [8] A.S. Botvina, and I.N. Mishustin, Phys. Rev. C 63 (2001) (R). [9] M. Jandel, A.S. Botvina, S.J. Yennello, G.A. Souliotis, D.V. Shetty, E. Bell, and A. Keksis. Journal of Physics G:Nucl. Part. Phys. 31 (2005) [10] G.A. Souliotis, A.S. Botvina, D.V. Shetty, A.L. Keksis, M. Jandel, M. Veselsky, S.J. Yennello. Phys. Rev. C 75 (2007) [11] A.Ergun, H. Imal, N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Phys. Rev. C 92, (2015). [12] Buyukcizmeci N., A.Ergun, H. Imal, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Nuc. Sci. And Tech. 26, S20507 (2015) [13] H. Imal, A.Ergun, N. Buyukcizmeci, R.Ogul, A.S. Botvina, W. Trautmann, PRC 91, (2015).
25
Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ at 15 MeV/nucleon
 Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
PHASE TRANSITIONS. A. Budzanowski
 PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions
 Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve
 Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Noncentral collisions
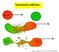 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation
 Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Statistical description of nuclear break-up
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective
 Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009](/thumbs/79/80008332.jpg) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production
 On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University
 Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams
 Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay
 Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V.E. Viola, H. Xu, R. Yanez, and R.T. de Souza Department of
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V.E. Viola, H. Xu, R. Yanez, and R.T. de Souza Department of
Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions
 Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter-universitario de Física Nuclear Universidade de Santiago de Compostela March 2008 Contents Elements of
Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter-universitario de Física Nuclear Universidade de Santiago de Compostela March 2008 Contents Elements of
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004
 Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources. A. Chbihi GANIL
 Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
PoS(NIC XII)250. A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars
 A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars 1, Kohsuke Sumiyoshi 2, Shoichi Yamada 1,3, Hideyuki Suzuki 4 1 Department of Science and Engineering,
A new equation of state with abundances of all nuclei in core collapse simulations of massive stars 1, Kohsuke Sumiyoshi 2, Shoichi Yamada 1,3, Hideyuki Suzuki 4 1 Department of Science and Engineering,
What is Spallation???
 What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions
 Degree of equilibra2on depends on contact 2me and gradient of poten2al driving equilibra2on Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions 112,124 Sn + 112,124
Degree of equilibra2on depends on contact 2me and gradient of poten2al driving equilibra2on Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions 112,124 Sn + 112,124
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jul 2003
 K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve
 How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer
 Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer V. I. Zagrebaev Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reaction, JINR, Dubna, Moscow Region, Russia Received 6 March 2003; published 25 June 2003 From the analysis
Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer V. I. Zagrebaev Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reaction, JINR, Dubna, Moscow Region, Russia Received 6 March 2003; published 25 June 2003 From the analysis
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Oct 2003
 1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons?
 How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS
 Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations
 Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
PHL424: Nuclear fusion
 PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 Mar 2005
 Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS
 ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics
 The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies
 Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission
 Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( )
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 110 A, N. 9-10 Settembre-Ottobre 1997 Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( ) A. G. POPEKO Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR - 141980 Dubna,
IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 110 A, N. 9-10 Settembre-Ottobre 1997 Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( ) A. G. POPEKO Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR - 141980 Dubna,
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions
 New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
Nuclear Binding Energy
 Nuclear Energy Nuclei contain Z number of protons and (A - Z) number of neutrons, with A the number of nucleons (mass number) Isotopes have a common Z and different A The masses of the nucleons and the
Nuclear Energy Nuclei contain Z number of protons and (A - Z) number of neutrons, with A the number of nucleons (mass number) Isotopes have a common Z and different A The masses of the nucleons and the
Dissipative nuclear dynamics
 Dissipative nuclear dynamics Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter universitario de Fisica Nuclear Universidad de Santiago de Compostela March 2009 Karl Heinz Schmidt Collective dynamical properties
Dissipative nuclear dynamics Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter universitario de Fisica Nuclear Universidad de Santiago de Compostela March 2009 Karl Heinz Schmidt Collective dynamical properties
Jagiellonian University
 Jagiellonian University THE FACULTY OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY, AND APPLIED COMPUTER SCIENCE MARIAN SMOLUCHOWSKI INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS Model Description of Proton Induced Fragmentation of Atomic Nuclei Małgorzata
Jagiellonian University THE FACULTY OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY, AND APPLIED COMPUTER SCIENCE MARIAN SMOLUCHOWSKI INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS Model Description of Proton Induced Fragmentation of Atomic Nuclei Małgorzata
Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion
 1 Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion J. Tõke, L. Pieńkowski, M. Houck, and W.U. Schröder Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
1 Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion J. Tõke, L. Pieńkowski, M. Houck, and W.U. Schröder Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
Physics of neutron-rich nuclei
 Physics of neutron-rich nuclei Nuclear Physics: developed for stable nuclei (until the mid 1980 s) saturation, radii, binding energy, magic numbers and independent particle. Physics of neutron-rich nuclei
Physics of neutron-rich nuclei Nuclear Physics: developed for stable nuclei (until the mid 1980 s) saturation, radii, binding energy, magic numbers and independent particle. Physics of neutron-rich nuclei
Pre Equilibrium and Equilibrium decays in Geant4
 CERN/IT-API and U. of Valencia Equilibrium decays in Geant4 Hadronic Working Group CHEP 2000 Padova, Italy 7 Feb. 2000 Abstract Home Page Theoretical Driven Hadronic Models................. 3 2 Pre Equilibirum
CERN/IT-API and U. of Valencia Equilibrium decays in Geant4 Hadronic Working Group CHEP 2000 Padova, Italy 7 Feb. 2000 Abstract Home Page Theoretical Driven Hadronic Models................. 3 2 Pre Equilibirum
The IC electrons are mono-energetic. Their kinetic energy is equal to the energy of the transition minus the binding energy of the electron.
 1 Lecture 3 Nuclear Decay modes, Nuclear Sizes, shapes, and the Liquid drop model Introduction to Decay modes (continued) Gamma Decay Electromagnetic radiation corresponding to transition of nucleus from
1 Lecture 3 Nuclear Decay modes, Nuclear Sizes, shapes, and the Liquid drop model Introduction to Decay modes (continued) Gamma Decay Electromagnetic radiation corresponding to transition of nucleus from
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes. Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2
 Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 2 Jun 2003
 CHEP 2003, La Jolla, California, USA, March 24-28 2003 1 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade implementation in Geant4 Aatos Heikkinen, Nikita Stepanov Helsinki Institute of Physics, P.O. Box 64, FIN-00014 University
CHEP 2003, La Jolla, California, USA, March 24-28 2003 1 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade implementation in Geant4 Aatos Heikkinen, Nikita Stepanov Helsinki Institute of Physics, P.O. Box 64, FIN-00014 University
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, (2012) DOI: / epjconf/ C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012
 EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 63, 034608 Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation Scott Pratt, Wolfgang Bauer, Christopher Morling, and Patrick Underhill* Department of Physics and Astronomy
PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 63, 034608 Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation Scott Pratt, Wolfgang Bauer, Christopher Morling, and Patrick Underhill* Department of Physics and Astronomy
FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds
 9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. Abstract
 Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders
 Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders Akihiko Monnai (KEK, Japan) with Jean-Yves Ollitrault (IPhT Saclay, France) AM and J.-Y. Ollitrault, Phys. Rev. C 96, 044902 (2017) New Frontiers
Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders Akihiko Monnai (KEK, Japan) with Jean-Yves Ollitrault (IPhT Saclay, France) AM and J.-Y. Ollitrault, Phys. Rev. C 96, 044902 (2017) New Frontiers
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007](/thumbs/74/70259022.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:0711.4462v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007 N/Z DEPENDENCE OF PROJECTILE FRAGMENTATION W. TRAUTMANN, 1 P. ADRICH, 1 T. AUMANN,
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:0711.4462v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007 N/Z DEPENDENCE OF PROJECTILE FRAGMENTATION W. TRAUTMANN, 1 P. ADRICH, 1 T. AUMANN,
Heavy Ion Interactions. Beginners FLUKA Course
 Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
The nuclear fragmentation problem and Bormio's contribution to its solution
 The nuclear fragmentation problem and Bormio's contribution to its solution 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory 567 Wilson
The nuclear fragmentation problem and Bormio's contribution to its solution 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory 567 Wilson
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Jan 1997
 Extended Hauser-Feshbach Method for Statistical Binary-Decay of Light-Mass Systems T. Matsuse, C. Beck, R. Nouicer, D. Mahboub Centre de Recherches Nucléaires, Institut National de Physique Nucléaire et
Extended Hauser-Feshbach Method for Statistical Binary-Decay of Light-Mass Systems T. Matsuse, C. Beck, R. Nouicer, D. Mahboub Centre de Recherches Nucléaires, Institut National de Physique Nucléaire et
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010](/thumbs/88/114600668.jpg) arxiv:13.8v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 1 Tracing a phase transition with fluctuations of the largest fragment size: Statistical multifragmentation models and the ALADIN S54 data T. Pietrzak 1, P. Adrich, T. Aumann,
arxiv:13.8v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 1 Tracing a phase transition with fluctuations of the largest fragment size: Statistical multifragmentation models and the ALADIN S54 data T. Pietrzak 1, P. Adrich, T. Aumann,
Instead, the probability to find an electron is given by a 3D standing wave.
 Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
The liquid-gas phase transition and the caloric curve of nuclear matter
 The liquid-gas phase transition and the caloric curve of nuclear matter K. Miyazaki E-mail: miyazakiro@rio.odn.ne.jp Abstract A new relativistic mean- eld model, which reproduces the astronomical observations
The liquid-gas phase transition and the caloric curve of nuclear matter K. Miyazaki E-mail: miyazakiro@rio.odn.ne.jp Abstract A new relativistic mean- eld model, which reproduces the astronomical observations
Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and Its Excitation Energy Dependence
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
Principalities Charged-π Yields, Theory & Expt Incompressibility Conclusions. Pions in pbuu. Pawel Danielewicz
 Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Transport 2017: International Workshop on Transport Simulations for Heavy Ion Collisions under Controlled Conditions FRIB-MSU,
Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Transport 2017: International Workshop on Transport Simulations for Heavy Ion Collisions under Controlled Conditions FRIB-MSU,
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities
 Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities J. Benlliure Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Spain The role of fission 260 < A < 320 spontaneous fission n-induced fission
Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities J. Benlliure Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Spain The role of fission 260 < A < 320 spontaneous fission n-induced fission
Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment
 Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact
 Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Equilibration dynamics in heavy-ion reactions. Yoritaka Iwata (GSI, Darmstadt)
 Equilibration dynamics in heavy-ion reactions Yoritaka Iwata (GSI, Darmstadt) Contents Dynamics via nucleus-nucleus potential [1] Dynamics at the early stage dynamics governed by charge equilibration [2]
Equilibration dynamics in heavy-ion reactions Yoritaka Iwata (GSI, Darmstadt) Contents Dynamics via nucleus-nucleus potential [1] Dynamics at the early stage dynamics governed by charge equilibration [2]
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast
 Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions
 CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 70 Zn MeV/nucleon)
 NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 7 Zn+ 7 Zn @ 35 MeV/nucleon) Dr. 1 1Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, TAMU DNP 218, Kona 1 Systems studied: 7 Zn+
NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 7 Zn+ 7 Zn @ 35 MeV/nucleon) Dr. 1 1Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, TAMU DNP 218, Kona 1 Systems studied: 7 Zn+
Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti*
 3 rd year of PhD Admission Exam Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti* Magda Cicerchia Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Padova Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro INFN Outline Clustering
3 rd year of PhD Admission Exam Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti* Magda Cicerchia Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Padova Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro INFN Outline Clustering
Heavy Ions Interactions. FLUKA Beginner s Course
 Heavy Ions Interactions FLUKA Beginner s Course Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Heavy Ions Interactions FLUKA Beginner s Course Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis
 Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis C. Ishizuka a, A. Ohnishi a and K. Sumiyoshi b a Division of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University,
Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis C. Ishizuka a, A. Ohnishi a and K. Sumiyoshi b a Division of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University,
New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions K.-H. Schmidt 1 for the
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions K.-H. Schmidt 1 for the
Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator
 Vienna meeting on inter-comparison of spallation reactions models Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator K. K. Gudima 1, M. I. Baznat 1 S. G. Mashnik 2, and A. J. Sierk 2 1 Institute of Applied Physics,
Vienna meeting on inter-comparison of spallation reactions models Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator K. K. Gudima 1, M. I. Baznat 1 S. G. Mashnik 2, and A. J. Sierk 2 1 Institute of Applied Physics,
Introduction to Nuclear Physics
 1/3 S.PÉRU The nucleus a complex system? What is the heaviest nucleus? How many nuclei do exist? What about the shapes of the nuclei? I) Some features about the nucleus discovery radius, shape binding
1/3 S.PÉRU The nucleus a complex system? What is the heaviest nucleus? How many nuclei do exist? What about the shapes of the nuclei? I) Some features about the nucleus discovery radius, shape binding
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters
 Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and intermediate energies
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 84, No. 4 journal of April 2015 physics pp. 581 590 Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 84, No. 4 journal of April 2015 physics pp. 581 590 Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and
nuclear states nuclear stability
 nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
