arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007
|
|
|
- Tiffany Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 28 Nov 2007 N/Z DEPENDENCE OF PROJECTILE FRAGMENTATION W. TRAUTMANN, 1 P. ADRICH, 1 T. AUMANN, 1 C.O. BACRI, 2 T. BARCZYK, 3 R. BASSINI, 4 S. BIANCHIN, 1 C. BOIANO, 4 A.S. BOTVINA, 1,11 A. BOUDARD, 5 J. BRZYCHCZYK, 3 A. CHBIHI, 6 J. CIBOR, 7 B. CZECH, 7 M. DE NAPOLI, 8 J.-É. DUCRET,5 H. EMLING, 1 J.D. FRANKLAND, 6 M. HELLSTRÖM,1 D. HENZLOVA, 1 G. IMMÈ,8 I. IORI, 4 H. JOHANSSON, 1 K. KEZZAR, 1 A. LAFRIAKH, 2 A. LE FÈVRE,1 E. LE GENTIL, 5 Y. LEIFELS, 1 J. LÜHNING,1 J. LUKASIK, 1,7 W.G. LYNCH, 9 U. LYNEN, 1 Z. MAJKA, 3 M. MOCKO, 9 W.F.J. MÜLLER,1 A. MYKULYAK, 10 H. ORTH, 1 A.N. OTTE 1 R. PALIT, 1 P. PAW LOWSKI, 7 A. PULLIA, 4 G. RACITI, 8, E. RAPISARDA, 8 H. SANN, 1, C. SCHWARZ, 1 C. SFIENTI, 1 H. SIMON, 1 K. SÜMMERER,1 M.B. TSANG, 9 G. VERDE, 9 C. VOLANT, 5 M. WALLACE, 9 H. WEICK, 1 J. WIECHULA, 1 A. WIELOCH, 3 and B. ZWIEGLIŃSKI10 1 Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbh, Planckstr. 1, D Darmstadt, Germany 2 Institut de Physique Nucléaire, IN2P3-CNRS et Université, F Orsay, France 3 M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, Pl Kraków, Poland 4 Istituto di Scienze Fisiche, Università degli Studi and INFN, I Milano, Italy 5 DAPNIA/SPhN, CEA/Saclay, F Gif-sur-Yvette, France 6 GANIL, CEA et IN2P3-CNRS, F Caen, France 7 IFJ-PAN, Pl Kraków, Poland 8 Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia dell Università and INFN-LNS and Sez. CT, I Catania, Italy 9 Department of Physics and Astronomy and NSCL, MSU, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 10 A. So ltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Pl Warsaw, Poland 11 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Science, Ru Moscow, Russia deceased THE ALADIN 2000 COLLABORATION Received (received date) Revised (revised date) The N/Z dependence of projectile fragmentation at relativistic energies has been studied in a recent experiment at the GSI laboratory with the ALADiN forward spectrometer coupled to the LAND neutron detector. Besides a primary beam of 124 Sn, also secondary beams of 124 La and 107 Sn delivered by the FRS fragment separator have been used in order to extend the range of isotopic compositions of the produced spectator sources. With the achieved mass resolution of A/A 1.5%, lighter isotopes with atomic numbers Z 10 are individually resolved. The presently ongoing analyses of the measured isotope yields focus on isoscaling and its relation to the properties of hot fragments at freeze-out and on the derivation of chemical freeze-out temperatures which are found to be independent of the isotopic composition of the studied systems. The latter result is at variance with the predictions for limiting temperatures as obtained with finitetemperature Hartree-Fock calculations. w.trautmann@gsi.de 1
2 2 W. Trautmann et al. 1. Introduction The present interest in isotopic effects in nuclear multifragmentation is partly motivated by the importance of the nuclear equation of state for astrophysical processes. Supernova simulations or neutron star models require inputs for the nuclear equation of state at extreme values of density and asymmetry for which the predictions differ widely. 1 5 Fragmentation reactions are of interest here because they permit the production of nuclear systems with subnuclear densities and temperatures which, e.g., largely overlap with those expected for the explosion stages of corecollapse supernovae. 6 Laboratory studies of the properties of nuclear matter in the hot environment, similar to the astrophysical situation, are thus becoming feasible, and an active search for suitable observables is presently underway. Of particular interest is the density-dependent strength of the symmetry term which is essential for the description of neutron-rich objects up to the extremes encountered in neutron stars (refs. 3,7 9 and contributions to this workshop). Here, new results from a recent experiment performed with the ALADIN spectrometer at the GSI laboratory will be discussed in which the possibility of using secondary beams for reaction studies at relativistic energies has been explored. Beams of 107 Sn, 124 Sn, 124 La, and 197 Au as well as Sn and Au targets were used to investigate the mass and isospin dependence of projectile fragmentation at 600 MeV per nucleon. The neutron-poor radioactive projectiles 107 Sn and 124 La were produced at the Fragment Separator FRS by fragmentation of a primary beam of 142 Nd and delivered to the ALADIN experiment. The results presented in the following, after a brief discussion of global observables, will be restricted to quantities deduced from the measured yields of resolved isotopes. They will, in particular, include isoscaling and its relation to the properties of hot fragments at the low-density freeze-out, as well as chemical temperatures deduced from double ratios of isotopic yields and the consequences for the limitingtemperature concept in multifragmentation. Preliminary results from the present experiments have been presented previously N/Z dependence of global fragmentation observables The dependence on the isotopic composition of the system is rather small for global observables of the studied reactions. This is shown in Fig. 1 for the multiplicity of the produced intermediate-mass fragments and for Z max, both as a function of Z bound. Here Z max denotes the largest atomic number Z within a partition while the sorting variable Z bound = ΣZ i with Z i 2 is related to the impact parameter and inversely correlated with the degree of excitation of the produced spectator system. The multiplicities exhibit the universal rise and fall of fragment production 13 (Fig. 1, left panel), and only a slightly steeper slope in the rise section distinguishes the neutron-rich case of 124 Sn from the other two systems. As confirmed by statistical model calculations, this difference is related to the evaporation properties of excited heavy nuclei. 10 Neutron emission prevails for neutron-rich nuclei which leads to a
3 N/Z Dependence of Projectile Fragmentation 3 <M IMF > Sn 124 La 107 Sn Z bound <Z max >/<Z proj > Sn 124 La 107 Sn Z bound /Z proj Fig. 1. Mean multiplicity <M IMF > of intermediate-mass fragments 3 Z 20 produced in the fragmentation of 107,124 Sn and 124 La at 600 A MeV as a function of Z bound (left panel). The right panel shows the correlations of the mean Z of the largest fragment with Z bound with both quantities being normalized with respect to the projectile Z. concentration of the residue channels, with small associated fragment multiplicities, in a somewhat narrower range of large Z bound than in the case of the neutron-poor systems. The evaporation of protons reduces Z bound since protons are not counted therein. This effect is, nevertheless, small and nearly invisible in the correlation of <Z max > with Z bound (Fig. 1, right panel). There, the transition from predominantly residue production to multifragmentation becomes apparent as a reduction of <Z max > with respect to Z bound which occurs between Z bound /Z proj = 0.6 and 0.8. The range of isotopic compositions of the studied nuclei N/Z = 1.14 to 1.48 is not large enough for significant variations of the reaction mechanism to appear. A shrinking of the coexistence zone in the temperature-density plane is predicted for neutron-rich matter but observable consequences can only be expected for asymmetries far beyond those presently available for laboratory studies. 14,15 This fact, on the other hand, has the important consequence that the basic reaction process is the same for all the present systems, a prerequisite for the interpretation of isoscaling and its relation with the symmetry energy. This point will be further quantified in the section on temperatures. 3. N/Z dependence of light fragment production The mass resolution obtained for projectile fragments entering into the acceptance of the ALADIN spectrometer is about 3% for fragments with Z 3 and decreases to 1.5% for Z 6. Masses are thus individually resolved for fragments with atomic number Z 10. The elements are resolved over the full range of atomic numbers up to the projectile Z with a resolution of Z 0.2 obtained with the TP-MUSIC IV detector. 10
4 4 W. Trautmann et al. Fig. 2. Inclusive mean values <N>/Z of light fragments with 3 Z 9 produced in the fragmentation of 107,124 Sn (600 A MeV, ALADIN), 56 Fe and 238 U (both 1 A GeV, FRS, from refs. 16,18 ) as a function of the fragment Z (left panel). The right panel shows the results for Z = 8 as a function of the N/Z value of the projectile. The lines represent the trend of the data (full line) and <N>/Z = (N/Z) proj (dashed). The inclusive mean neutron-to-proton ratio <N >/Z of light fragments in the range 3 Z 9 is presented in Fig. 2. The values for Z = 4 have been corrected for the missing yield of unstable 8 Be by including an estimate for it obtained from a smooth interpolation over the identified yields of 7,9 11 Be. This correction has a negligible effect for the case of 107 Sn because <N>/Z of the detected beryllium isotopes is close to 1 already. For 124 Sn the value of <N>/Z for Z = 4 is lowered from 1.24 to 1.18 which makes the systematic odd-even variation more clearly visible in the neutron rich case. The odd-even staggering is, however, much more pronounced in the case of the neutron-poor 107 Sn. The strongly bound even-even nuclei attract a large fraction of the product yields during the secondary evaporation stage. 16 This effect is, apparently, larger if the hot fragments are already close to symmetry, as it is expected for the fragmentation of 107 Sn. 17 Inclusive data 16,18 obtained with the FRS fragment separator at GSI for 238 U and 56 Fe fragmentations on titanium targets at 1 A GeV bombarding energy confirm that the observed patterns are very systematic (Fig. 2, left panel). Nuclear structure effects characteristic for the isotopes produced combine with significant memory effects of the isotopic composition of the excited system by which they are emitted. This has the consequence that, because of its strong variation with Z, averaged neutron-to-proton ratios <N >/Z for unspecified ranges of Z are not very useful for studying nuclear matter properties. For this purpose, techniques will have to be used which cause the nuclear structure effects to cancel out. Selecting a particular element, e.g. Z = 8, is already sufficient to reveal the linear correlation of <N >/Z with the N/Z of the projectile (Fig. 2, right panel). According to the Statistical Fragmentation Model (SMM 19 ), the correlation should be much stronger for the excited fragments at the breakup stage and, in fact, not deviate much from the
5 N/Z Dependence of Projectile Fragmentation 5 dashed <N>/Z = (N/Z) proj line in the figure. 17 The reduction is due to sequential decay and its tendency of directing the isotope distributions closer to the valley of stability. For a quantitative analysis, a precise modeling of these secondary processes will, therefore, be required Z /Z bound proj ( ] ( ] ( ] ( ] [ ] S(N) 10 Z S(N) Z peripheral mid-central central 300 MeV peripheral mid-central central 600 MeV N N Fig. 3. Scaled isotopic ratios S(N) for Li to O isotopes from the fragmentation of 124 Sn and 107 Sn projectiles at 600 A MeV (ALADIN, left panel) and for H to B isotopes from 12 C + 112,124 Sn at E/A = 300 and 600 MeV (INDRA, right panel, from ref. 25 ) as a function of the neutron number N. The centrality selection was obtained with Z bound (ALADIN, left panel, five bins as indicated) and according to charged particle multiplicity as measured with the full detector (INDRA, right panel, three bins with central indicating b/b max 0.4). The dashed lines in both panels are the results of exponential fits according to Eq. (1). Only statistical errors are displayed; note also the offset factors of multiples of three in the right panel. 4. Isoscaling The phenomenon of isoscaling has been shown to be common to many different types of heavy-ion reactions It is observed by comparing product yields Y i from reactions which differ only in the isotopic composition of the projectiles or targets or both. Isoscaling refers to an exponential dependence of the measured yield ratios R 21 (N, Z) on the neutron number N and proton number Z of the detected products. The scaling expression R 21 (N, Z) = Y 2 (N, Z)/Y 1 (N, Z) = C exp(αn + βz) (1) describes rather well the measured ratios over a wide range of complex particles and light fragments. 24 The accuracy with which the isoscaling relation is
6 6 W. Trautmann et al. obeyed is conveniently judged by regarding the scaled isotopic ratios S(N) = R 21 (N, Z)/exp(βZ), obtained by dividing out the common Z dependence after fitting according to eq. (1). Isoscaling means that all the scaled yield ratios will follow the same exponential dependence on the neutron number N. The results for the pair of reactions with 124 Sn and 107 Sn projectiles, sorted into five bins of Z bound are shown in Fig. 3, left panel. Alternatively, one may also regard the behavior of the exponential slopes α(z) of the yield ratios for individual elements or β(n) for individual chains of isotones. As demonstrated in Fig. 4 for the inclusive yields from the same pair of reactions, the deviations from the common mean value are impressively small. Besides the precision with which isoscaling is observed in the range of fragments from Li to Ne, also the monotonic decrease of the slope of S(N) with centrality represents a remarkable observation. Qualitatively, it resembles that observed for the reactions 12 C + 112,124 Sn at 300 and 600 MeV per nucleon, studied with INDRA at GSI (ref. 25, right panels of Fig. 3) α = ± α(z) β(n) β = ± Z or N Fig. 4. Isoscaling parameters α(z) and β(n) obtained by individually fitting the N and Z dependences of isotopes and isotones, respectively, for inclusive yields from the fragmentation of 124 Sn and 107 Sn projectiles at 600 A MeV. The dashed lines represent the mean values for isotopes with Z from 3 to 10 and isotones with N from 3 to 12. Only statistical errors are displayed. The statistical model offers a simple physical explanation for the appearance of isoscaling in finite systems. Charge distributions of fragments with fixed mass numbers A, as well as mass distributions for fixed Z, are approximately Gaussian with average values and variances which are connected with the temperature, the symmetry-term coefficient, and other parameters. (Here the symmetry-energy term, E sym = γ(a 2Z) 2 /A with the coefficient γ, is that of the liquid-drop description of the nascent fragments at freeze-out and γ = 25 MeV is normally used. 19 ) The mean values of the fragment distributions depend on the total mass and charge of the systems, e.g. via the chemical potentials in the grand-canonical approximation, while the variances depend mainly on the physical conditions reached, the temper-
7 N/Z Dependence of Projectile Fragmentation 7 ature, the density and possibly other variables. For example, the charge variance σ Z (AT/8γ) obtained for fragments with a given mass number A is only a function of the temperature and of the symmetry-term coefficient since the Coulomb contribution is very small. 26 This relation of isoscaling with the symmetry energy has attracted considerable interest recently. 21,22,25,27,28 In the grand-canonical approximation, assuming that the temperature T is about the same (see below), the scaling parameters α and β are given by the differences of the neutron and proton chemical potentials for the two systems divided by the temperature, α = µ n /T and β = µ p /T. The proportionality of µ n and thus of the isoscaling parameters with the coefficient γ of the symmetry-energy term has been obtained from the statistical interpretation of isoscaling within the SMM 21 and Expanding-Emitting-Source Model 24 and confirmed by an analysis of reaction dynamics. 27 The relation is µ n = µ n,2 µ n,1 4γ( Z2 1 A 2 1 Z2 2 A 2 ) = 4γ (Z 2 /A 2 ) (2) 2 where Z 1,A 1 and Z 2,A 2 are the charges and mass numbers of the neutron-poor and neutron-rich systems, respectively, at breakup. The difference of the chemical potentials depends essentially only on the coefficient γ of the symmetry term and on the isotopic compositions. A proportionality of α and 1/T, with T derived from double isotope ratios, has been observed for light-ion (p, d, α) induced reactions at bombarding energies in the GeV range. 21 Also the symmetry-term coefficient γ 22.5 MeV, deduced according to eq. (2), supported the statistical approach. These data were inclusive and a value close to the standard value was to be expected because the fragment multiplicities are small in this case. 29 The present reactions studied with ALADIN cover the full rise and fall of fragment production while the 12 C induced reactions studied with INDRA cover mainly the rise up to Z bound Z proj /2 with multiple fragment production being dominant in central collisions. 13 In both cases, the measured temperatures rise slightly with increasing centrality but not sufficiently fast in order to compensate for the decrease of the isoscaling parameter α. The product µ n = α T, therefore, decreases. With the assumption that the isotopic compositions remain close to those of the original 112,124 Sn targets, the evolution of the apparent symmetry-term coefficient γ app, i.e. without corrections for the effects of sequential decay, was followed into the regime of multifragmentation with the 12 C induced data measured with INDRA. 25 It was again found to be close to the normal-density coefficient γ 25 MeV for peripheral collisions, associated with small fragment multiplicities, but dropped to lower values of 15 to 17 MeV for the central impact parameters leading to multifragmentation. This result is confirmed by the preliminary analysis of the new data for projectile fragmentation measured with ALADIN. The product α T drops by about 20% through the rise of fragment production but then remains fairly constant once the regime of multifragmentation has been reached (Z bound /Z proj 0.5).
8 8 W. Trautmann et al. Fig. 5. Apparent temperatures T HeLi (left panel) and T BeLi (right panel) as a function of Z bound for the three reaction systems produced with 107,124 Sn and 124 La projectiles. Only statistical errors are displayed. 5. N/Z dependence of the nuclear caloric curve Two examples of double-isotope temperatures deduced from the measured isotope yields are shown in Fig. 5 as a function of Z bound. Besides the frequently used T HeLi (left panel), determined from 3,4 He and 6,7 Li yields also the results for T BeLi are displayed (right panel). For T BeLi the isotope pairs of 7,9 Be and 6,8 Li are used which each differ by two neutrons. The double difference of their binding energies amounts to 11.3 MeV and is nearly as large as the 13.3 MeV in the T HeLi case. The apparent temperatures are displayed, i.e. no corrections for secondary decays feeding the ground states of these nuclei are applied. Both temperature observables show the same smooth rise with increasing centrality that was observed earlier in a study of 197 Au fragmentations. 30 According to T BeLi, the temperatures at the chemical freeze-out are identical for all three reaction systems and have the same dependence on Z bound. This is not equally visible in T HeLi which exhibits slightly larger values for the neutron rich case of 124 Sn. Inspection of the single isotope ratios shows, however, that the 3,4 He ratio represents an exception in that it varies much less than the other ratios with the neutron-richness of the system. A possible explanation is offered by the observations shown in Fig. 2. The strong population of even-n-even-z nuclei, evident from the behavior of <N>/Z, suggests that also 4 He nuclei are abundantly produced. The effect is stronger in the neutron-poor cases for which the apparent T HeLi will be accordingly lower. Taking this nuclear-structure effect into account is likely to reduce the differences between systems also for this thermometer. The observed invariance of the breakup temperature with the isotopic composition of the system is of interest because it is opposite to what is expected according
9 N/Z Dependence of Projectile Fragmentation 9 to the finite-temperature Hartree-Fock calculations of Besprosvany and Levit. 31 The limiting temperatures obtained for the stability of excited nuclei are strongly dependent on the Coulomb pressure generated by the protons they contain. Along isobars, the limiting temperatures decrease rapidly toward the proton rich side and, along the valley of stability, they decrease with increasing mass because the effect of the increasing Z dominates over that of the decreasing Z/A. For the nuclei studied here, a difference of about 2 MeV is predicted between the limiting temperature of 124 Sn and those for the proton rich 107 Sn and 124 La or for the heavier 197 Au. 31 A difference of this magnitude is clearly not seen in the data (Fig. 5). Neither does a comparison with the apparent temperatures measured for 197 Au fragmentations (Fig. 7 in ref. 30 ) provide evidence for the predicted mass dependence. The temperatures are the same, within errors, when regarded as a function of the scaled quantity Z bound /Z proj. This, however, is suggested by the Z bound scaling of fragmentation observables if a comparison of sources of different mass but equal excitation is intended to be made Discussion It is one of the basic assumptions of isotopic reaction studies that the mechanism as such remains unchanged and that effects related to the asymmetry dependence of the nuclear forces can be isolated by changing nothing but the isotopic composition of the system. This view is supported by the observed invariance of the chemical breakup temperatures, here for the case of spectator fragmentation. The interpretation of the breakup temperatures as a manifestation of the limiting temperatures predicted by the Hartree-Fock model, 31 on the other hand, is not equally supported. This interpretation was derived from the Z bound dependence of the temperature which suggested a mass dependence because of the changing mass of the spectator system. 32 Later on, the predicted mass dependence was found to be confirmed in a compilation of chemical break-up temperatures from several experiments, 33 including the earlier ALADIN data, which led to their use as a general reference for testing predictions of nuclear stability with respect to temperature (see ref. 34 for references). The new data for the A 120 region and their comparison with 197 Au fragmentations suggest that the observed variation with decreasing Z bound is more related to the increasing excitation energy than to the decreasing mass of the produced spectator system. Breakup temperatures fairly independent of the isotopic composition or mass of the system are, e.g., predicted by the statistical fragmentation models which are based on the concept of a phase-space driven instability. 35 The discussion of the isoscaling results has focussed on mainly three topics, among them primarily the effects of sequential decay for the isoscaling parameters and for the symmetry term, as well as the role of the surface term in the symmetry energy. Surface terms gain in importance as the mean mass of the produced fragments decreases in multi-fragment decays. Thirdly, also a possible modification of the source N/Z due to preequilibrium emissions prior to breakup will affect and
10 10 W. Trautmann et al. most probably reduce the isoscaling parameters. So far, however, none of these mechanisms has been identified as providing an obvious explanation for the large drop that is observed. Calculations with the microcanonical Markov-chain version of the SMM, 36 even show that sequential decay will cause the isoscaling coefficients to increase if the symmetry term governing the mass distributions of the hot fragments is reduced. 25 Transport models predict that the isotopic composition at breakup should not deviate by more than a few percent from the original value. 37 New experimental results, furthermore, indicate that the isotopic dependence of the surface term is reduced, with respect to that needed to describe ground-state masses, as the excitation of the system increases. 38 This is also expected theoretically. 27 A decrease of the isoscaling parameter α with increasing violence of the collision, beyond that expected from the simultaneous increase of the temperature, has also been observed for reactions at intermediate energy (refs. 28,39 and references therein) and a systematics is emerging. A very recent interpretation of these results arrives at the conclusion that the reduced density, rather than the elevated temperature, causes the symmetry term to be smaller than the standard value. 40 This analysis uses a temperature independent potential part of the symmetry term and a kinetic part in the form of a Fermi gas, and it is argued that the isoscaling phenomenon itself is evidence for the fact that properties of the considered homogeneous nuclear matter are observable in fragmentation reactions. In the Statistical Multifragmentation Model, 19 normal-density fragments statistically distributed within an expanded volume are considered. Here a reduction of the symmetry term in their liquid-drop description can be imagined to be caused by fragment modifications in the hot environment, including deformations or the effects of nuclear interactions between them. The neglect of such effects in the actual codes should probably be regarded as an idealization as the assumption of equilibrium at the final freeze-out stage requires nuclear interactions in order to achieve it. The consequences of a reduced symmetry term for predicted global fragment observables, as e.g. multiplicity, are rather small for this class of models. The partitioning is predominantly driven by the surface term in the fragment description while a variation of the symmetry term affects mainly the isotopic distributions. 17,35,38 Further studies will be needed in order to put some of the assumptions on a firmer basis and to quantitatively establish the reduction of the symmetry term in multi-fragment breakups. The sequential decay corrections are obviously important but also the evolution of the isotopic compositions during the reaction process deserves attention. It will have to be explored whether an experimental reconstruction of the neutron-to-proton ratio of the detected spectator systems will be feasible using the coincident neutron data measured with the LAND detector. 41 This work has been supported by the European Community under contract No. HPRI-CT , by the Polish State Committee for Scientific Research (KBN) under contract No. 2P03B11023, and by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education under Contracts No. 1 P03B ( ) and N /4308 ( ).
11 N/Z Dependence of Projectile Fragmentation 11 References 1. J.M. Lattimer and M. Prakash, Phys. Rep. 333 (2000) U. Lombardo and W. Zuo, in Isospin Physics in Heavy-Ion Collisions at Intermediate Energies, ed. B.-A. Li and W.U. Schröder, Nova Science, New York, 2001, p I. Bombaci, ibid., p A.S. Botvina and I.N. Mishustin, Phys. Lett. B 584 (2004) for reviews see, e.g., Dynamics and Thermodynamics with Nuclear Degrees of Freedom, ed. Ph. Chomaz et al. (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 2006), and Eur. Phys. J. A 30 (2006). 6. A.S. Botvina and I.N. Mishustin, Phys. Rev. C 72 (2005) Bao-An Li, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (2002) V. Greco et al., Phys. Lett. B 562 (2003) Lie-Wen Chen et al., preprint arxiv: (2007). 10. C. Sfienti et al., Nucl. Phys. A 749 (2005) 83c. 11. W. Trautmann et al., Nucl. Phys. A 787 (2007) 575c. 12. C. Sfienti et al., Nucl. Phys. A 787 (2007) 627c. 13. A. Schüttauf et al., Nucl. Phys. A 607 (1996) H. Müller and B.D. Serot, Phys. Rev. C 52 (1995) S.J. Lee and A.Z. Mekjian, Phys. Rev. C 63 (2001) M.V. Ricciardi et al., Nucl. Phys. A 733 (2004) N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, A.S. Botvina, Eur. Phys. J. A 25 (2005) P. Napolitani et al., Phys. Rev. C 70 (2004) J.P. Bondorf et al., Phys. Rep. 257 (1995) M.B. Tsang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 (2001) A.S. Botvina, O.V. Lozhkin, W. Trautmann, Phys. Rev. C 65 (2002) G.A. Souliotis et al., Phys. Rev. C 68 (2003) W.A. Friedman, Phys. Rev. C 69 (2004) (R). 24. M.B. Tsang et al., Phys. Rev. C 64 (2001) A. Le Fèvre et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 (2005) A.S. Botvina, A.S. Iljinov, I.N. Mishustin, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 42 (1985) A. Ono et al., Phys. Rev. C 68 (2003) (R). 28. D.V. Shetty et al., Phys. Rev. C 76 (2007) L. Beaulieu et al., Phys. Lett. B 463 (1999) 159 and Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 (2000) W. Trautmann et al., preprint arxiv: [nucl-ex]. 31. J. Besprosvany and S. Levit, Phys. Lett. B 217 (1989) J.B. Natowitz et al., Phys. Rev. C 52 (1995) R J.B. Natowitz et al., Phys. Rev. C 65 (2002) A. Kelić, J.B. Natowitz, K.-H. Schmidt, Eur. Phys. J. A 30, 203 (2006). 35. R. Ogul and A.S. Botvina, Phys. Rev. C 66 (2002) A.S. Botvina and I.N. Mishustin, Phys. Rev. C 63 (2001) (R). 37. T. Gaitanos et al., Nucl. Phys. A 732 (2004) 24 and private communication. 38. A.S. Botvina et al., Phys. Rev. C 74 (2006) G.A. Souliotis et al., Phys. Rev. C 73 (2006) Bao-An Li and Lie-Wen Chen, Phys. Rev. C 74 (2006) W. Trautmann et al., in Proceedings of the IWM2005 International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics, Catania, Italy, 2005, edited by R. Bougault et al., Conf. Proc., Vol. 91 (Italian Physical Society, Bologna, 2006) p. 157; preprint nucl-ex/
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 2010](/thumbs/88/114600668.jpg) arxiv:13.8v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 1 Tracing a phase transition with fluctuations of the largest fragment size: Statistical multifragmentation models and the ALADIN S54 data T. Pietrzak 1, P. Adrich, T. Aumann,
arxiv:13.8v1 [nucl-ex] 14 Mar 1 Tracing a phase transition with fluctuations of the largest fragment size: Statistical multifragmentation models and the ALADIN S54 data T. Pietrzak 1, P. Adrich, T. Aumann,
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve
 Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Isotopic Dependence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt 9/17/2008 W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt, Erice 2008 1 Isotopic Independence of the Caloric Curve W. Trautmann, GSI Darmstadt I. II. III.
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions
 Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear. Fragmentation Experiments. Abstract
 Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009](/thumbs/79/80008332.jpg) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
Symmetry energy of dilute warm nuclear matter
 Symmetry energy of dilute warm nuclear matter J. B. Natowitz, G. Röpke, 1 S. Typel, 2,3 D. Blaschke, 4, 5 A. Bonasera, 6 K. Hagel, T. Klähn, 4, 7 S. Kowalski, L. Qin, S. Shlomo, R. Wada, and H. H. Wolter
Symmetry energy of dilute warm nuclear matter J. B. Natowitz, G. Röpke, 1 S. Typel, 2,3 D. Blaschke, 4, 5 A. Bonasera, 6 K. Hagel, T. Klähn, 4, 7 S. Kowalski, L. Qin, S. Shlomo, R. Wada, and H. H. Wolter
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast
 Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions
 CNR*11 Third International Workshop on Compound Nuclear Reactions and Related Topics September 19-23, 2011 Prague Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions 78 Kr+ 40
CNR*11 Third International Workshop on Compound Nuclear Reactions and Related Topics September 19-23, 2011 Prague Study and comparison of the decay modes of the systems formed in the reactions 78 Kr+ 40
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ at 15 MeV/nucleon
 Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions K.-H. Schmidt 1 for the
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions K.-H. Schmidt 1 for the
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Oct 2003
 1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 3 Apr 1997
 Emission temperatures and freeze out densities from light particle correlation functions in Au+Au collisions at A GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/974v 3 Apr 997 S.Fritz for the ALADiN collaboration: R. Bassini, () M.
Emission temperatures and freeze out densities from light particle correlation functions in Au+Au collisions at A GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/974v 3 Apr 997 S.Fritz for the ALADiN collaboration: R. Bassini, () M.
S. YOKOYAMA 1;2. Abstract. Light particle-unstable nuclei were studied along the neutron. B is a possible candidate for neutron
 Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
PHASE TRANSITIONS. A. Budzanowski
 PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction 136 Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV
 Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV J.A Alcántara-Núñez 1), J. Benlliure 1), D. Perez Loureiro 1) and the S184 Collaboration 1) Universidade de
Investigating the intra-nuclear cascade process using the reaction Xe on deuterium at 500 AMeV J.A Alcántara-Núñez 1), J. Benlliure 1), D. Perez Loureiro 1) and the S184 Collaboration 1) Universidade de
Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. Abstract
 Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University
 Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Projectile Fragmentation at the Fragment Separator
 Projectile Fragmentation at the Fragment Separator Andreas Heinz Wright Nuclear Structure Laboratory, Yale University for the CHARMS Collaboration Symposium on 30 Years of Projectile Fragmentation, ACS
Projectile Fragmentation at the Fragment Separator Andreas Heinz Wright Nuclear Structure Laboratory, Yale University for the CHARMS Collaboration Symposium on 30 Years of Projectile Fragmentation, ACS
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation
 Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Spinodal decomposition, nuclear fog and two characteristic volumes in thermal multifragmentation V.A.Karnaukhov 1,*, H.Oeschler, S.P.Avdeyev 1, V.K.Rodionov 1, V.V.Kirakosyan 1, A.V.Simonenko 1, P.A.Rukoyatkin
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective
 Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
Invited. New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions. 1 Introduction. 2 Installations of GSI
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07720 Invited New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07720 Invited New generation of measurements and model developments on nuclide production in spallation reactions
Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model
 Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model A. Wielocha, J. Brzychczyka, J. Łukasikb, P. Pawłowskib, T. Pietrzaka, W. Trautmannc a M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, Reymonta
Critical like behavior in the lattice gas model A. Wielocha, J. Brzychczyka, J. Łukasikb, P. Pawłowskib, T. Pietrzaka, W. Trautmannc a M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, Reymonta
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters
 Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 55, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1997 Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions M. B. Tsang, C. Williams, M. J. Huang, W. G. Lynch, L. Phair,* D. R. Bowman,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 55, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1997 Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions M. B. Tsang, C. Williams, M. J. Huang, W. G. Lynch, L. Phair,* D. R. Bowman,
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS
 Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon
 IWM 2011 Int. Work. Multifrag. Rel. Topics Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dip. di Scienze Fisiche,
IWM 2011 Int. Work. Multifrag. Rel. Topics Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare N/Z effects on 40,48 Ca+ 40,48 Ca reactions at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dip. di Scienze Fisiche,
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production
 On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 Mar 2005
 Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, (2012) DOI: / epjconf/ C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012
 EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS
 ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
N/Z influence on the level density parameter
 EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
CURRICULUM VITAE. Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest, POB-MG 6, Romania
 CURRICULUM VITAE SURNAME: Raduta FIRST NAME(S): Alexandru Horia Date of birth: 9 June 1970 Place of birth: Fagaras, Romania Nationality: Romanian Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear
CURRICULUM VITAE SURNAME: Raduta FIRST NAME(S): Alexandru Horia Date of birth: 9 June 1970 Place of birth: Fagaras, Romania Nationality: Romanian Affiliation: National Institute of Physics and Nuclear
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 27 Feb 2003
 Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy
 Nuclear Science and echniques 24 (2013) 050501 IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy WADA Roy 1,* HUANG Meirong 1 LIN Weiping 1,2 LIU Xingquan 1,2 ZHAO Minghui 1,2
Nuclear Science and echniques 24 (2013) 050501 IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy WADA Roy 1,* HUANG Meirong 1 LIN Weiping 1,2 LIU Xingquan 1,2 ZHAO Minghui 1,2
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004
 Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation
 July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities
 Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities J. Benlliure Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Spain The role of fission 260 < A < 320 spontaneous fission n-induced fission
Fission and the r-process: experimental achievements and future possibilities J. Benlliure Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Spain The role of fission 260 < A < 320 spontaneous fission n-induced fission
Noncentral collisions
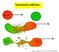 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve
 How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models
 Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems:
 Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics
 The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy
 Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy Alexandra Gade National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy at Michigan State University, East
Probing the evolution of shell structure with in-beam spectroscopy Alexandra Gade National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy at Michigan State University, East
Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation. Ca + Be. Betty Tsang March 27, 2008
 Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation 48 Ca + Be Betty Tsang March 27, 2008 Acknowledgement Collaborators: Michal Mocko (thesis) M. Andronenko, L. Andronenko, N. Aoi, J. Cook, F. Delaunay,
Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation 48 Ca + Be Betty Tsang March 27, 2008 Acknowledgement Collaborators: Michal Mocko (thesis) M. Andronenko, L. Andronenko, N. Aoi, J. Cook, F. Delaunay,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009](/thumbs/90/103476070.jpg) Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Statistical description of nuclear break-up
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Statistical description of nuclear break-up A.S. Botvina 1 and I.N. Mishustin 2 1 Institute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117312
Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion collisions
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons?
 How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams
 Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter
 T-REX Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter J. Natowitz et al. T-REX [ TAMU Reaccelerated EXotics] The Symmetry Energy Problem Density Dependence? Constraining the density
T-REX Clusterization and the Symmetry Energy in Low Density Nuclear Matter J. Natowitz et al. T-REX [ TAMU Reaccelerated EXotics] The Symmetry Energy Problem Density Dependence? Constraining the density
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010](/thumbs/94/120296745.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
ASY-EOS experiment at GSI: constraining the symmetry energy with neutron and proton elliptic flows
 Società Italiana di Fisica XCVI Congresso Nazionale Bologna, 20-24 Settembre, 2010 ASY-EOS experiment at GSI: constraining the symmetry energy with neutron and proton elliptic flows Amorini F., Boiano
Società Italiana di Fisica XCVI Congresso Nazionale Bologna, 20-24 Settembre, 2010 ASY-EOS experiment at GSI: constraining the symmetry energy with neutron and proton elliptic flows Amorini F., Boiano
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process
 REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
Caloric curve of 8 GeVÕc À, p 197 Au reactions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 66, 044603 2002 Caloric curve of 8 GeVÕc À, p 197 Au reactions A. Ruangma,* R. Laforest, E. Martin, E. Ramakrishnan, D. J. Rowland, M. Veselsky, E. M. Winchester, and S. J. Yennello Cyclotron
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 66, 044603 2002 Caloric curve of 8 GeVÕc À, p 197 Au reactions A. Ruangma,* R. Laforest, E. Martin, E. Ramakrishnan, D. J. Rowland, M. Veselsky, E. M. Winchester, and S. J. Yennello Cyclotron
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence. Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University. Wako, Japan
 Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Neutron multiplicity. Total radioactivity (Ci) Time after beam cut. Target A s 1min 1h 1d 1m 1y 10y 100y
 0 proton 000 MeV proton 500 MeV pronto 200 MeV 0-0 25 50 75 00 25 50 75 200 225 250 Target A ' data and Mote Carlo simulations on spallation New relevant for the design of ADS reactions J.Benlliure University
0 proton 000 MeV proton 500 MeV pronto 200 MeV 0-0 25 50 75 00 25 50 75 200 225 250 Target A ' data and Mote Carlo simulations on spallation New relevant for the design of ADS reactions J.Benlliure University
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter
 An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012](/thumbs/72/67186430.jpg) Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter. Matthias Hempel, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel,
 Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars
 1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity. Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University
 Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.6.13-18@NuSym2016 Outline 1. Cluster radioactivity: brief review and our recent
Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.6.13-18@NuSym2016 Outline 1. Cluster radioactivity: brief review and our recent
NN th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy
 NN 2015 12 th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Isospin influence on the decay modes of systems produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca reactions at 10AMeV
NN 2015 12 th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISSIONS June 21-26, 2015, Catania, Italy Isospin influence on the decay modes of systems produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca reactions at 10AMeV
Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 63, 034608 Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation Scott Pratt, Wolfgang Bauer, Christopher Morling, and Patrick Underhill* Department of Physics and Astronomy
PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 63, 034608 Rare isotope production in statistical multifragmentation Scott Pratt, Wolfgang Bauer, Christopher Morling, and Patrick Underhill* Department of Physics and Astronomy
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti*
 3 rd year of PhD Admission Exam Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti* Magda Cicerchia Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Padova Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro INFN Outline Clustering
3 rd year of PhD Admission Exam Pre-equilibrium Emission in formation of 46 Ti* Magda Cicerchia Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Padova Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro INFN Outline Clustering
which escape from the nucleus cool down the residue and thermal equilibrium cannot be maintained. In order to avoid these diculties, in the present si
 The nuclear liquid{gas phase transition within Fermionic Molecular Dynamics J. Schnack 1 and H. Feldmeier 2 Gesellschaft fur Schwerionenforschung mbh, Postfach 110 552, D-64220 Darmstadt & Technische Hochschule
The nuclear liquid{gas phase transition within Fermionic Molecular Dynamics J. Schnack 1 and H. Feldmeier 2 Gesellschaft fur Schwerionenforschung mbh, Postfach 110 552, D-64220 Darmstadt & Technische Hochschule
Structure of Sn isotopes beyond N =82
 Structure of Sn isotopes beyond N =8 L. Coraggio, A. Covello, A. Gargano, and N. Itaco Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli Federico II, and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Complesso
Structure of Sn isotopes beyond N =8 L. Coraggio, A. Covello, A. Gargano, and N. Itaco Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli Federico II, and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Complesso
Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 65, 014612 Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei B. A. Brown and S. Typel Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 65, 014612 Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei B. A. Brown and S. Typel Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions.
 Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction
 The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction R. Spartà 1, M. La Cognata 1, C. Spitaleri 1,2, S. Cherubini
The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction R. Spartà 1, M. La Cognata 1, C. Spitaleri 1,2, S. Cherubini
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission
 Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
Chapter VIII: Nuclear fission 1 Summary 1. General remarks 2. Spontaneous and induced fissions 3. Nucleus deformation 4. Mass distribution of fragments 5. Number of emitted electrons 6. Radioactive decay
3 rd International Symposium NuSym. Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration)
 3 rd International Symposium NuSym Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Isospin effects in medium mass nuclear systems at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dipartimento di Fisica,
3 rd International Symposium NuSym Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Isospin effects in medium mass nuclear systems at 25 MeV/nucleon Ivano Lombardo (EXOCHIM Collaboration) Dipartimento di Fisica,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013](/thumbs/83/87477490.jpg) PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
