ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS
|
|
|
- Rosanna Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA, W.A. Friedman, Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA, L. Beaulieu d, B. Davin, R.T. de Souza, Y. Larochelle e, T. Lefort, R. Yanez, V.E. Viola Jr. Department of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405, USA, R.J. Charity, and L.G. Sobotka, Department of Chemistry, Washington University, St. Louis, MO 63130, USA Using symmetric 112 Sn+ 112 Sn, 124 Sn+ 124 Sn collisions as references, we probe isospin diffusion in peripheral asymmetric 112 Sn+ 124 Sn, 124 Sn+ 112 Sn systems at incident energy of E/A=50 MeV. Isoscaling analyses imply that the quasi-projectile and quasi-target in these collisions do not achieve isospin equilibrium, permitting an assessment of the isospin transport rates. We find that comparisons between isospin sensitive experimental and theoretical observables, using suitably chosen scaled ratios, permit investigation of the density dependence of the asymmetry term of the nuclear equation of state. a Present address: Dept of Physics, Notre Dame University, IN. b Present address: Forschungszentrum Rossendorf e.v., Dresden, Germany. c Present address: Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, Lanzhou, China. d Present address: Université Laval, Quebec City, Canada, G1K-7P4 e Present address: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge TN. 1
2 The nuclear mean field potential binds nuclei, stabilizes neutron stars against gravitational collapse [1] and generates forces that shape the dynamics of nuclear collisions [2-4] and supernova explosions [5]. Many of these environments involve densities or isospin-asymmetries far from those characteristic for stable nuclei [1,5]. Investigations of nucleus-nucleus collisions enable experimental constraints to be placed on the mean field potential and on nuclear equation of state (EOS) at the extremes [2-4,6,7]. Significant constraints have already been placed on the symmetric matter EOS at high densities [2]. In contrast, relatively weak constraints exist on the isospin-asymmetry term of the EOS, which describes the EOS sensitivity to the difference between neutron and proton densities and allows for extrapolations to the neutron-rich matter within neutron stars [1,8]. Comparisons of collisions of neutron-rich to that of neutron-deficient systems provide one means of probing the asymmetry term experimentally [9-11]. A second involves isospin-asymmetric collisions of projectile and target nuclei. In such cases, the asymmetry term of the mean field provides driving forces that propel the system towards isospin equilibrium where anisotropies in the difference between neutron and proton densities are minimized. Investigations of these driving forces require collisions with commensurate collision and isospin-equilibration timescales and observables that reveal isospin equilibration. At low incident energies, deep inelastic collisions have been used to study charge equilibrium leading to conflicting conclusions [12,13]. However at incident energy above E/A=30 MeV, the time scale for fragment emission decreases and anisotropies in the emission patterns may develop [14], which may allow one to measure from the fragments the time scales for charge and mass transport and diffusion during the collision. Here, we show that isotopic distributions near projectile rapidity in peripheral Sn+Sn collisions at E/A=50 MeV allow for investigations of isospin diffusion. Transport calculations suggest that sub-saturation density is achieved in the neck region where isospin diffusion occurs [15]. By comparing the results of measurements and calculations relevant to isospin diffusion, we explore the sensitivity of the diffusion to the density dependence of the asymmetry term of the EOS at sub-saturation densities. The experiment involved bombarding 112 Sn and 124 Sn targets of 5 mg/cm 2 areal density with 50 MeV per nucleon 112 Sn and 124 Sn beams from the K1200 cyclotron at the 2
3 National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory at Michigan State University [11]. Nine telescopes of the Large Area Silicon Strip Array (LASSA) [16] detected isotopically resolved particles with 1 Z 8. Each telescope consists of one 65 µm single-sided silicon strip detector, one 500 µm double-sided silicon strip detector and four 6-cm thick CsI(Tl) scintillators, read out by pin diodes. The strips of the silicon detectors divide the 50mm x 50mm lateral dimensions of each telescope into 256 (3x3 mm 2 ) square pixels, providing an angular resolution of about ±0.43. We placed the center of the LASSA device at the polar angle of θ=32 with respect to the beam axis, covering polar angles of 7 θ 58. Additionally, 188 plastic scintillator - CsI(Tl) phoswich detectors of the Miniball/Miniwall array [17] complemented the LASSA coverage. The combined apparatus covered 80% of the total solid angle. Peripheral collisions were selected by gates on the charged-particle multiplicity yielding the reduced impact parameter range of b/b max = in the sharp cut-off approximation [18]. To minimize contributions from the neck fragments, projectile rapidity fragments were selected by the rapidity gate of y/y beam 0.7, where y and y beam are rapidities of the analyzed particle and beam, respectively. The experimental results are the same within the statistical uncertainty if a more restrictive rapidity gate of y/y beam 0.8 is used instead. Because there are no isospin differences between identical projectiles and targets, the symmetric 112 Sn Sn and 124 Sn Sn collisions are used to establish diffusion-free baseline values for the measured and predicted observables. The asymmetric 124 Sn Sn and 112 Sn Sn collisions, on the other hand, have the large isospin differences needed to explore the isospin diffusion. As experimental observables, we focus on features of the isotopic yields Y i (N,Z) of particles measured for reaction i at y/y beam 0.7. Here, N and Z are the neutron and proton numbers for the detected particles. As in multi-fragmentation [9,10,19], in deep inelastic collisions [10,20] and in statistical evaporation [10], we find that ratios of isotopic yields R 21 (N,Z)=Y 2 (N,Z)/Y 1 (N,Z) for a specific pair of reactions, with a different total isotopic composition, follow the isoscaling relationship [10] R 21 (N,Z)=Y 2 (N,Z)/Y 1 (N,Z)= Cexp(αN+βZ), (1) where α and β are the isoscaling parameters for the chosen reactions pair. 3
4 The left panel of Fig. 1 displays the measured values for R 21 (N,Z) when using 124 Sn Sn collisions as reaction 2 and 112 Sn+ 112 Sn collisions as reaction 1 in Eq. 1. The fits following the right hand side of Eq. 1 are represented by the solid and dashed lines. Fits to the other two systems relative to 112 Sn+ 112 Sn (not shown) are of similar quality. In the right panel of Fig. 1, we plot the best fit values for the isoscaling parameter, α, versus the overall isospin asymmetry of the colliding system: δ O =(N O -Z O)/(N O +Z O), where N O and Z O are the corresponding total neutron and proton numbers. The solid and open points represent data for 124 Sn and 112 Sn projectiles, respectively. In general, the isoscaling parameter α increases with the overall isospin asymmetry δ O. If a linear correlation between α and δ O is assumed [11], then the mixed systems at δ O = should assume an α value midway between that of 124 Sn+ 124 Sn (δ O = 0.193, α=0.57±0.02) and 112 Sn+ 112 Sn (δ O = 0.107, α=0) if isospin is equilibrated across the system. However, the measured value for the 124 Sn projectile (solid point) is much larger than the value for the 112 Sn projectile (open point) at δ O = indicating that isospin equilibrium is not achieved in the asymmetric reaction systems [21]. The upper value of α=0.42±0.02, obtained for 124 Sn+ 112 Sn, represents, in the linear relation, an effective asymmetry of about This value corresponds to roughly half way from the projectile value of to the equilibrium value of The lower value of 0.16±0.02, obtained for 112 Sn+ 124 Sn, has the same interpretation; except here the projectile is 112 Sn and the change in asymmetry is in the opposite direction. The consistency of these results extracted from two independent measurements adds credibility to our approach. Following ref. [22], we define the isospin transport ratio R i as 2x x x R i = (2) x x where x is an isospin sensitive observable, preferably linear in asymmetry. For the two symmetric systems 124 Sn+ 124 Sn and 112 Sn+ 112 Sn, R i is automatically normalized to +1 and 1, respectively, allowing for quantitative comparison of the measured and predicted R i values even if the model calculations use isospin observables that differ from the experimental ones. In the absence of isospin diffusion, preequilibrium emission from the 4
5 projectile should be approximately equal for asymmetric 124 Sn+ 112 Sn ( 112 Sn+ 124 Sn) collisions as for symmetric 124 Sn+ 124 Sn ( 112 Sn+ 112 Sn) collisions. By focusing on differences in isospin observables between mixed and symmetric systems R i (α) largely removes the sensitivity to preequilibrium emission and enhances the sensitivity to diffusion. To represent the experimental data, we chose the neutron isoscaling parameter α because the projectiles and targets for the asymmetric systems differ only in their neutron numbers. Using α for x in Eq. 2, we obtain the isospin transport ratios of the two asymmetric systems shown as the shaded bands in Fig. 2. The observed values, R i ( α ) 0. 5, are consistent with previous discussion that the isospin asymmetry of the projectile remnant is half way between that of the projectile and the equilibration value. We now explore the relationship between isospin diffusion, and the asymmetry term of the EOS within the context of the Boltzmann-Uehling-Uhlenbeck (BUU) [23,24] formalism, which calculates the time evolution of the colliding system using a selfconsistent mean field. The isospin independent part of the mean field in these calculations is momentum independent and described by an incompressibility coefficient of K=210 MeV [15]. The interaction component of the asymmetry term in three sets of calculations provides a contribution to the symmetry energy per nucleon of the form E sym,int /A=C sym (ρ/ρ o ) γ where C sym is set to MeV and γ=2, γ=1 and γ=1/3. Here, smaller values for γ dictate a weaker density dependence for E sym,int. The fourth set of calculations, referred to as SKM, uses an interaction asymmetry term providing E sym,int /A =38.5 (ρ/ρ o ) (ρ/ρ o ) 2 [25] and has the weakest density dependence at ρ ρ o. Calculations were performed for the 124 Sn Sn, 124 Sn Sn, 112 Sn Sn and 112 Sn Sn systems at an impact parameter of b=6 fm [15]. We employed ensembles of 800 test particles per calculation and we followed each calculation for an elapsed time of 216 fm/c. At this late time, the projectile and residues can be cleanly separated. Nonetheless, we require that all nucleons in the assigned regions to have density less than 0.05ρ 0 and velocities more than half of the beam velocity in the center of mass, to be consistent with the experimental gates. To reduce statistical fluctuations in the results, we averaged them over 20 calculations for each system. 5
6 Using the average asymmetry of the projectile-like residue <δ> in the calculation, as the isospin observable, x, in Eq. 2, we plot predictions for R i (δ) as a function of time as bands in Fig. 3 for the stiffest asymmetry term, (ρ 2, top panel) and the softest asymmetry term, (SKM, bottom panel). By construction, R i (δ) describes the evolution of isospin asymmetry for the projectiles ( 112 Sn or 124 Sn) in the mixed reactions relative to that for the symmetric 124 Sn Sn (with R i =1) and 112 Sn Sn (R i =-1) systems. The widths of the bands reflect the statistical uncertainties of the calculated values for R i (δ). Initially, these predictions for R i (δ) represent the isospin of the projectile (R i (δ) =1 for 124 Sn and R i (δ) =- 1 for 112 Sn) nuclei. Subsequent isospin diffusion drives the R i (δ) values towards zero. Even though pre-equilibrium emission from the projectile remnants influences <δ>, R i (δ) is not strongly modified because such pre-equilibrium emission is largely target independent and therefore cancelled in R i (δ) by construction. The influence of the asymmetry term depends on its magnitude at sub-saturation density [24,26]. For the top panel, E sym,int /A =C sym (ρ/ρ o ) 2 decreases rapidly at low density and becomes very small, leading to little isospin diffusion. For the bottom panel, E sym,int /A =38.5 (ρ/ρ o ) (ρ/ρ o ) 2 remains larger at low density, leading to stronger isospin diffusion and driving the residues to approximately the same isospin asymmetry. In both cases, the asymptotic value for R i (δ) is first reached at around 100 fm/c when the two residues separate and cease exchanging nucleons as illustrated by the time evolution images of the collisions for the 124 Sn Sn system in Figure 3. This timescale is comparable to the collision timescale τ coll, which can be roughly (~20%) estimated by τ coll (4R N +d)/v beam 80 fm/c, (3) where R N, v beam and d are the nuclear radius, incident velocity, and the separation distance between the two nuclear surfaces at breakup. Assuming that the experimental isoscaling relationships, shown in Fig. 1, reflect particle emission from the projectile remnants after 100 fm/c and that such emission can be described statistically, the calculated values for R i (δ) may be easily related to the measured ones. In doing so, we take advantage of the nearly linear relationship between α 6
7 and δ that has been shown to be valid for evaporation and for statistical multifragmentation of the remnants that emit the observed particles [27]: δ + 2 δ1 α ( δ ) 1 2 δ1 (4) 2 where δ 1 and δ 2 are the asymmetries for the two systems involved in the isoscaling ratio [27]. Inserting Eq. 4 into the expression for R i (α), one can show ( α ) = ( δ ) ( δ )( ) i δ δ i δ ( δ δ )( [ δ + δ ]/ 2) R. (5) i R i Since the second term is negligible (<4%), we can use asymptotic values of <δ> around 216 fm/c, as x in Eq. 2 to obtain R i (δ) values for these two systems and compare them to the experimental values of R i (α). The calculated values of R i (δ), shown as open points in Fig. 2 in the order of an increasing softness from left to right indicate an increased isospin equilibrium for successively softer asymmetry terms. The diamond shaped points indicate the R i (α) values obtained as in the experiment by decaying the residues obtained in BUU to fragments using the statistical model of ref. [27]. As expected, there is close agreement between the diamonds and the corresponding open points according to Eq. 5. Figure 2 demonstrates the sensitivity of such observables to the asymmetry term of the EOS. The experimental R i (α) values are closest to the predicted R i (δ) values derived from the theoretical predictions for <δ> using the stiffest asymmetry term with E sym,int /A =C sym (ρ/ρ o ) 2. This conclusion depends, however, on the assumption that the measured particles are produced after 100 fm/c when <δ> attains its asymptotic values. If the data include emission from earlier stages when δ is larger, a favorable comparison with calculations using softer asymmetry terms may be possible. Relevant determinations of the emission timescales for the detected particles are being explored [26] and may make the present conclusions regarding the density dependent asymmetry term more definitive. In summary, we have observed the effects of isospin diffusion by investigating heavy ion collisions at E/A=50 MeV with comparable diffusion and collision timescales. Simulations using the BUU transport model predict that the isospin diffusion reflects driving forces arising from the asymmetry term of the EOS. The present comparisons 7
8 suggest a better agreement with the stiff asymmetry term; however, more stringent constraints on the emission timescales for the measured particles are needed. The current version of BUU has no momentum dependence of the mean field which might interplay with the symmetry term. However, at incident energies around 50 MeV/u, few nucleons get accelerated to high momentum so the momentum dependence of the mean field need not be that important. Nonetheless, such effect should be explored in the future. This work is supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant Nos. PHY , PHY , PHY and by the DOE under grant numbers DE- FG02-87ER REFERENCES 1. J.M. Lattimer and M. Prakash, Ap. J., 550, (2001) 426 and refs. therein. 2. Pawel Danielewicz, Roy Lacey and William G. Lynch, Science 298, 1592 (2002). 3. H.H. Gutbrod etal.,. Rep. Prog. Phys. 52, 1267 (1989). 4. C. Sturm et al., PRL 86, 39 (2001). 5. H.A. Bethe, Rev. Mod. Phys. 62, 801 (1990) 6. Bao-An Li, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, (2002) and refs. therein. 7. M. Di Toro et al., Eur. Phys. Jour. A 13, 155 (2002) and refs. therein 8. "Isospin Physics in Heavy-Ion Collisions at Intermediate Energies",Eds. Bao-An Li and W. Udo Schroeder, NOVA Science Publishers, Inc. (New York), (2001). 9. W. P. Tan et al., Phys. Rev. C 64, (R) (2001). 10. M.B. Tsang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5023 (2001). 11. H. Xu et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 716 (2000). 12. B. Gatty et al, Nuc. Phys. A253, 511 (1975). 13. R. Planeta et al Phys. Rev. C 38, 195 (1988), R. Planeta et al., Phys. Rev. C 41, 942 (1990). 14. S. J. Yennello et al., Phys. Lett. B321, 15 (1994). 15. L. Shi, Thesis, Michigan State University, (2003). 16. A. Wagner et. al., Nucl. Instr. & Meth. A456, 290 (2001); B. Davin et al., Nucl. Instr. & Meth. A473, 302 (2001) 17. R.T. de Souza et al. Nucl. Inst. Meth. Phys. Res. A295, 109 (1990). 18. L. Phair et al., Nucl. Phys. A 548, 489 (1992). 19. D.V. Shetty, et al., Phys. Rev. C 68, (2003). 20. G.A. Souliotis, et al., Phys. Rev. C 68, (2003). 21. J. F. Dempsey et al., Phys. Rev, C 54, 1710 (1996) and refs. Therein. 22. F. Rami et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1120 (2000). 23. G. Bertsch and S. Das Gupta, Phys. Rep. 160, 189 (1988). 24. Bao-An Li, et al., Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 7 (1998) 147, and refs. therein. 25. V. Baran, et al., Nucl. Phys. A 632, 287 (1998). 26. L. Shi and P. Danielewicz, nucl-th/ M. B. Tsang et al., Phys. Rev. C 64, (2001) 8
9 Fig. 1: Left panel: Measured values for R 21 (N,Z)= Y (N,Z)/Y (N,Z) (points) and fits with Eq. 1 (solid lines). The solid line and points represent even Z=4,6,8 isotopes while the dash lines and open points represent odd Z=3,5,7 isotopes. Right panel: Best fit values for α as function of δ O. The lines serve to guide the eye. The reactions are labelled next to the data points. Solid points denote 124 Sn as the projectile and open points denote 112 Sn as the projectile. 9
10 Fig.2: Measured (shaded bars) and calculated (open points) values for R i. The labels on the calculated values represent the density dependence of E sym,int /A with increasing softness from left to right. 10
11 Fig. 3: R i (δ ) from BUU calculations are plotted as a function of time for the mixed systems. The symmetric systems are calibrated to +1 and 1 automatically by Eq. 2. The top and bottom panels show the calculated results with E sym,int /A =C sym (ρ/ρ o ) 2 and E sym,int /A =38.5 (ρ/ρ o ) (ρ/ρ o ) 2, respectively. The bands above (below) zero represent the system with 124 Sn ( 112 Sn) as the projectile. The time evolution images of the collisions for the 124 Sn Sn systems are superimposed on the upper panel suggesting that the projectile and target separate around 100 fm/c. 11
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004
 Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
Betty Tsang Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University, Montreal Dec 4, 2004 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Subal Das Gupta Festschrift McGill University,
The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
HIC Observables to probe the ASY-EOS Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University Tests of the ASY-EOS in Heavy Ion Collisions asystiff asysoft Tsang, HW BA
Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. Abstract
 Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy M.B. Tsang( 曾敏兒 ) 1,2*, Yingxun Zhang( 张英逊 ) 1,3, P. Danielewicz 1,2, M. Famiano 4, Zhuxia Li( 李祝霞 ) 3, W.G. Lynch( 連致標 ) 1,2, A. W. Steiner
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay
 Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V.E. Viola, H. Xu, R. Yanez, and R.T. de Souza Department of
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V.E. Viola, H. Xu, R. Yanez, and R.T. de Souza Department of
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective
 Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
Density dependence of the symmetry energy and the nuclear equation of state : A dynamical and statistical model perspective D. V. Shetty, S. J. Yennello, and G. A. Souliotis The density dependence of the
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Overview of Nuclear Science
 Overview of Nuclear Science Nuclear science addresses the quantum quark/gluon and nuclear many body problems. How do we understand nuclei in terms of their fundamental parts and interactions? W. Nazarewicz
Overview of Nuclear Science Nuclear science addresses the quantum quark/gluon and nuclear many body problems. How do we understand nuclei in terms of their fundamental parts and interactions? W. Nazarewicz
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 25 Apr 2005
 A Transport Model for Nuclear Reactions Induced by Radioactive Beams arxiv:nucl-th/5469v1 25 Apr 25 Bao-An Li, Lie-Wen Chen, Champak B. Das 1, Subal Das Gupta, Charles Gale, Che Ming Ko, Gao-Chan Yong
A Transport Model for Nuclear Reactions Induced by Radioactive Beams arxiv:nucl-th/5469v1 25 Apr 25 Bao-An Li, Lie-Wen Chen, Champak B. Das 1, Subal Das Gupta, Charles Gale, Che Ming Ko, Gao-Chan Yong
Isospin dynamics in the nuclear equation of state. The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 Isospin dynamics in the nuclear equation of state Outline: 1. Introduction 2. Experimental signatures from HI collisions a) n/p ratios b) Isotope distributions c) Isospin diffusion at E/A=35 and 50 MeV
Isospin dynamics in the nuclear equation of state Outline: 1. Introduction 2. Experimental signatures from HI collisions a) n/p ratios b) Isotope distributions c) Isospin diffusion at E/A=35 and 50 MeV
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation
 July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter
 Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter William Lynch, NSCL MSU Motivations Sources of constraints on the EOS and symmetry energy. Astrophysics Nuclear experiments Laboratory constraints from nuclear collisions
Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter William Lynch, NSCL MSU Motivations Sources of constraints on the EOS and symmetry energy. Astrophysics Nuclear experiments Laboratory constraints from nuclear collisions
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012](/thumbs/72/67186430.jpg) Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 Dual Nature of Nuclei from Shell model to Isospin Diffusion Shell Model Magic numbers N=20 Liquid Drop Model Fission Process N=10 N=2 Bet t y Tsang, Tohoku Univ ersit y, Sendai, Japan The National Superconducting
Dual Nature of Nuclei from Shell model to Isospin Diffusion Shell Model Magic numbers N=20 Liquid Drop Model Fission Process N=10 N=2 Bet t y Tsang, Tohoku Univ ersit y, Sendai, Japan The National Superconducting
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University
 Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Heavy&ion*collisions:*Direct*and*indirect* probes*of*the*density* and*temperature*dependence*of*e sym * * S. Yennello Texas A&M University Number of ways to measure symmetry energy Direct measurements
Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion
 1 Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion J. Tõke, L. Pieńkowski, M. Houck, and W.U. Schröder Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
1 Retardation of Particle Evaporation from Excited Nuclear Systems Due to Thermal Expansion J. Tõke, L. Pieńkowski, M. Houck, and W.U. Schröder Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion collisions
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics
 The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
The search for the nuclear symmetry energy in reaction dynamics Giuseppe Verde INFN, Sezione di Catania, 64 Via Santa Sofia, I-95123, Catania, Italy E-mail: verde@ct.infn.it ABSTRACT This lecture is devoted
Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 55, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1997 Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions M. B. Tsang, C. Williams, M. J. Huang, W. G. Lynch, L. Phair,* D. R. Bowman,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 55, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1997 Fragment multiplicity dependent charge distributions in heavy ion collisions M. B. Tsang, C. Williams, M. J. Huang, W. G. Lynch, L. Phair,* D. R. Bowman,
HiRA: Science and Design Considerations
 HiRA: Science and Design Considerations Scientific Program: Astrophysics: Transfer reactions Resonance spectroscopy Nuclear Structure: Inelastic scattering Transfer reactions Resonance spectroscopy Breakup
HiRA: Science and Design Considerations Scientific Program: Astrophysics: Transfer reactions Resonance spectroscopy Nuclear Structure: Inelastic scattering Transfer reactions Resonance spectroscopy Breakup
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ at 15 MeV/nucleon
 Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Momentum dependence of symmetry energy
 Momentum dependence of symmetry energy Joint DNP of APS & JPS October 7-11, 2014 Kona, HI, USA 曾敏兒 Betty Tsang, NSCL/MSU Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter E/A (, ) = E/A (,0) + 2 S( ) = (
Momentum dependence of symmetry energy Joint DNP of APS & JPS October 7-11, 2014 Kona, HI, USA 曾敏兒 Betty Tsang, NSCL/MSU Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter E/A (, ) = E/A (,0) + 2 S( ) = (
Inner crust composition and transition densities
 Inner crust composition and transition densities W.G.Newton 1, Bao-An Li 1, J.R.Stone 2,3 M. Gearheart 1, J. Hooker 1 1 Texas A&M University - Commerce 2 University of Oxford, UK 3 Physics Division, ORNL,
Inner crust composition and transition densities W.G.Newton 1, Bao-An Li 1, J.R.Stone 2,3 M. Gearheart 1, J. Hooker 1 1 Texas A&M University - Commerce 2 University of Oxford, UK 3 Physics Division, ORNL,
Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive subject not only for nuclear
 First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
Experimental Observables to study the nuclear symmetry energy with Heavy Ion Collision
 Experimental Observables to study the nuclear symmetry energy with Heavy Ion Collision Heavy Ion Meeting April 13, 212 Pohang, Korea Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan
Experimental Observables to study the nuclear symmetry energy with Heavy Ion Collision Heavy Ion Meeting April 13, 212 Pohang, Korea Betty Tsang The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 27 Feb 2003
 Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 8, 4162(R) (29) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy S. R. Souza, 1,2 M. B. Tsang, 3 B. V. Carlson, 4 R. Donangelo, 1,5 W. G. Lynch, 3 and A. W. Steiner
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve
 How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions
 Degree of equilibra2on depends on contact 2me and gradient of poten2al driving equilibra2on Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions 112,124 Sn + 112,124
Degree of equilibra2on depends on contact 2me and gradient of poten2al driving equilibra2on Velocity damping and fragmenta2on in non- central intermediate energy heavy- ion collisions 112,124 Sn + 112,124
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Jul 2009](/thumbs/79/80008332.jpg) Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
Isospin effects and the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy arxiv:97.1931v1 [nucl-th] 1 Jul 29 S.R. Souza 1,2, M.B. Tsang 3, B.V. Carlson 4, R. Donangelo 1,5, W.G. Lynch 3, and A.W. Steiner
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production
 On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment. J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H.
 Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources. A. Chbihi GANIL
 Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter
 1 Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter Pawel Danielewicz 1, 2, Roy Lacey 3 & William G. Lynch 1 * Nuclear collisions can compress nuclear matter to densities achieved within neutron stars
1 Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter Pawel Danielewicz 1, 2, Roy Lacey 3 & William G. Lynch 1 * Nuclear collisions can compress nuclear matter to densities achieved within neutron stars
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters
 Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation. Ca + Be. Betty Tsang March 27, 2008
 Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation 48 Ca + Be Betty Tsang March 27, 2008 Acknowledgement Collaborators: Michal Mocko (thesis) M. Andronenko, L. Andronenko, N. Aoi, J. Cook, F. Delaunay,
Rare Isotope productions from Projectile Fragmentation 48 Ca + Be Betty Tsang March 27, 2008 Acknowledgement Collaborators: Michal Mocko (thesis) M. Andronenko, L. Andronenko, N. Aoi, J. Cook, F. Delaunay,
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements
 Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and Its Excitation Energy Dependence
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
N/Z influence on the level density parameter
 EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment
 Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 29 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 29 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 29 Jun 2009](/thumbs/86/94712666.jpg) Neutron/proton ratio oucleon emissions as a probe of neutron skin arxiv:0906.5281v1 [nucl-th] 29 Jun 2009 X. Y. Sun a,b, D. Q. Fang a, Y. G. Ma a, X. Z. Cai a, J. G. Chen a, W. Guo a, W. D. Tian a, H.
Neutron/proton ratio oucleon emissions as a probe of neutron skin arxiv:0906.5281v1 [nucl-th] 29 Jun 2009 X. Y. Sun a,b, D. Q. Fang a, Y. G. Ma a, X. Z. Cai a, J. G. Chen a, W. Guo a, W. D. Tian a, H.
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons?
 How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
Overview of Low energy nuclear physics and FRIB
 Overview of Low energy nuclear physics and FRIB William Lynch Low energy physics: not JLAB or RHIC How has the field evolved? What are some of the new scientific objectives? Will not discuss everything.
Overview of Low energy nuclear physics and FRIB William Lynch Low energy physics: not JLAB or RHIC How has the field evolved? What are some of the new scientific objectives? Will not discuss everything.
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast
 Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Principalities Charged-π Yields, Theory & Expt Incompressibility Conclusions. Pions in pbuu. Pawel Danielewicz
 Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Transport 2017: International Workshop on Transport Simulations for Heavy Ion Collisions under Controlled Conditions FRIB-MSU,
Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University Transport 2017: International Workshop on Transport Simulations for Heavy Ion Collisions under Controlled Conditions FRIB-MSU,
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Betty Tsang, NSCL/MSU 曾敏兒. collaboration
 Science of the SpRIT Time Projection Chamber From Earth to Heavens: Femto-scale nuclei to Astrophysical objects SAMURAI International Collaboration Meeting, Sept 8-9, 2014 Sendai, Japan 曾敏兒 for Betty Tsang,
Science of the SpRIT Time Projection Chamber From Earth to Heavens: Femto-scale nuclei to Astrophysical objects SAMURAI International Collaboration Meeting, Sept 8-9, 2014 Sendai, Japan 曾敏兒 for Betty Tsang,
Reaction mechanisms in transport theories: a test of the nuclear effective interaction
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Reaction mechanisms in transport theories: a test of the nuclear effective interaction To cite this article: M Colonna et al 213 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 42 1214 Related
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Reaction mechanisms in transport theories: a test of the nuclear effective interaction To cite this article: M Colonna et al 213 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 42 1214 Related
Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Isospin and symmetry energy effects on nuclear fragment distributions in liquid-gas type phase transition region N. Buyukcizmeci, R. Ogul, and.s. Botvina,
X-ray superburst ~10 42 ergs Annual solar output ~10 41 ergs. Cumming et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 559, L127 (2001) (2)
 Neutron stars, remnant cores following supernova explosions, are highly interesting astrophysical environments In particular, accreting neutron stars presents a unique environment for nuclear reactions
Neutron stars, remnant cores following supernova explosions, are highly interesting astrophysical environments In particular, accreting neutron stars presents a unique environment for nuclear reactions
IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy
 Nuclear Science and echniques 24 (2013) 050501 IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy WADA Roy 1,* HUANG Meirong 1 LIN Weiping 1,2 LIU Xingquan 1,2 ZHAO Minghui 1,2
Nuclear Science and echniques 24 (2013) 050501 IMF production and symmetry energy in heavy ion collisions near Fermi energy WADA Roy 1,* HUANG Meirong 1 LIN Weiping 1,2 LIU Xingquan 1,2 ZHAO Minghui 1,2
The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system To cite this article: F Sammarruca et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 580
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system To cite this article: F Sammarruca et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 580
New experiments on neutron rich r-process Ge Br isotopes at the NSCL
 New experiments on neutron rich r-process Ge Br isotopes at the NSCL M. Quinn* 1,2, A. Aprahamian 1,2, S. Almaraz 1,2, B.B. Skorodumov 1,2, A. Woehr 1,2 1) Institute for Structure and Nuclear Astrophysics
New experiments on neutron rich r-process Ge Br isotopes at the NSCL M. Quinn* 1,2, A. Aprahamian 1,2, S. Almaraz 1,2, B.B. Skorodumov 1,2, A. Woehr 1,2 1) Institute for Structure and Nuclear Astrophysics
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
The National Superconducting Cyclotron State University
 The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University U.S. flagship user facility for rare isotope research and education in nuclear science, astro-nuclear physics, accelerator physics,
The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory @Michigan State University U.S. flagship user facility for rare isotope research and education in nuclear science, astro-nuclear physics, accelerator physics,
Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
Heavy-ion collision theory with momentum-dependent interactions
 PHYSICL REVIEW C VOLUME 3S, NUMBER 5 MY 1987 Heavy-ion collision theory with momentum-dependent interactions C. Gale Physics Department, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455 G. Bertsch
PHYSICL REVIEW C VOLUME 3S, NUMBER 5 MY 1987 Heavy-ion collision theory with momentum-dependent interactions C. Gale Physics Department, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455 G. Bertsch
Noncentral collisions
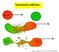 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy
 Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy G. Verde(INFN-CT), A. Chbihi(GANIL), Exochim coll., INFN- CT, LNS, MI, NA - Open collaboration and synergies. Farcosphysics: dynamics & spectroscopy
Farcos FemtoscopeArray for Correlations and Spectroscopy G. Verde(INFN-CT), A. Chbihi(GANIL), Exochim coll., INFN- CT, LNS, MI, NA - Open collaboration and synergies. Farcosphysics: dynamics & spectroscopy
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence. Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University. Wako, Japan
 Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio
 Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds
 9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39
 VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear. Fragmentation Experiments. Abstract
 Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter
 An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
An empirical approach combining nuclear physics and dense nucleonic matter Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, IN2P3-CNRS, Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France E-mail: j.margueron@ipnl.in2p3.fr
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania)
 Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 Mar 2005
 Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
The influence of cluster emission and the symmetry energy on neutron-proton spectral double ratios
 The influence of cluster emission and the symmetry energy on neutron-roton sectral double ratios Yingxun Zhang 1,,3, P. Danielewicz 1,,4, M. Famiano 5, Zhuxia Li 3, W.G. Lynch 1,,4, M.B. Tsang 1,,4* 1
The influence of cluster emission and the symmetry energy on neutron-roton sectral double ratios Yingxun Zhang 1,,3, P. Danielewicz 1,,4, M. Famiano 5, Zhuxia Li 3, W.G. Lynch 1,,4, M.B. Tsang 1,,4* 1
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Introduction to RAON & Detector Systems for Nuclear Physics
 3 rd Japan-Korea PHENIX Collaboration Meeting RIKEN, Japan, 27-28 November 2014 Introduction to RAON & Detector Systems for Nuclear Physics Byungsik Hong (Korea University) Outline - Plan for RAON and
3 rd Japan-Korea PHENIX Collaboration Meeting RIKEN, Japan, 27-28 November 2014 Introduction to RAON & Detector Systems for Nuclear Physics Byungsik Hong (Korea University) Outline - Plan for RAON and
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei
 Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jan 2003
 Probing Transport Theories via Two-Proton Source Imaging G. Verde a, P. Danielewicz a, W.G. Lynch a, D.A. Brown b, C.K. Gelbke a, M.B. Tsang a a National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department
Probing Transport Theories via Two-Proton Source Imaging G. Verde a, P. Danielewicz a, W.G. Lynch a, D.A. Brown b, C.K. Gelbke a, M.B. Tsang a a National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department
Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 65, 014612 Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei B. A. Brown and S. Typel Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C, VOLUME 65, 014612 Interaction cross sections for light neutron-rich nuclei B. A. Brown and S. Typel Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRE-EQUILIBIRUM α-particle EMISSION AS A PROBE TO STUDY α-clustering IN NUCLEI
 Tandem-Alpi proposal: ACLUST-GARFIELD PRE-EQUILIBIRUM α-particle EMISSION AS A PROBE TO STUDY α-clustering IN NUCLEI O.V. Fotina 1, S.A. Goncharov 1, D.O. Eremenko 1, O.A. Yuminov 1, Yu.L. Parfenova 1,
Tandem-Alpi proposal: ACLUST-GARFIELD PRE-EQUILIBIRUM α-particle EMISSION AS A PROBE TO STUDY α-clustering IN NUCLEI O.V. Fotina 1, S.A. Goncharov 1, D.O. Eremenko 1, O.A. Yuminov 1, Yu.L. Parfenova 1,
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Decay of 10 C excited states above the 2 p + 2α threshold and the contribution from democratic two-proton emission
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 75, 534(R) (7) Decay of C excited states above the p + α threshold and the contribution from democratic two-proton emission R. J. Charity, K. Mercurio, L. G. Sobotka,, J. M. Elson, M.
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 75, 534(R) (7) Decay of C excited states above the p + α threshold and the contribution from democratic two-proton emission R. J. Charity, K. Mercurio, L. G. Sobotka,, J. M. Elson, M.
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei
 Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b X. Roca-Maza a,c a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b X. Roca-Maza a,c a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Isospin dependent EoS (Asy-EoS) with Heavy-ion collision probes
 Isospin dependent EoS (Asy-EoS) with Heavy-ion collision probes G. Verde INFN-CT for the Chimera & Farcos group OUTLINE: The Asy-EoS and the density dependence of the symmetry energy Experimental probes
Isospin dependent EoS (Asy-EoS) with Heavy-ion collision probes G. Verde INFN-CT for the Chimera & Farcos group OUTLINE: The Asy-EoS and the density dependence of the symmetry energy Experimental probes
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 12 Nov 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 12 Nov 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 12 Nov 2007](/thumbs/72/66857673.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:0711.1714v1 [nucl-th] 12 Nov 2007 DETERMINING THE DENSITY DEPENDENCE OF THE NUCLEAR SYMMETRY ENERGY USING HEAVY-ION
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:0711.1714v1 [nucl-th] 12 Nov 2007 DETERMINING THE DENSITY DEPENDENCE OF THE NUCLEAR SYMMETRY ENERGY USING HEAVY-ION
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 24 Apr 2001
 Neutron Star Structure and the Neutron Radius of 208 Pb C. J. Horowitz Nuclear Theory Center and Dept. of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 J. Piekarewicz Department of Physics Florida
Neutron Star Structure and the Neutron Radius of 208 Pb C. J. Horowitz Nuclear Theory Center and Dept. of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 J. Piekarewicz Department of Physics Florida
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 May 1996
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei
 Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,c X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,c X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Energy resolution and energy-light response of CsI(Tl) scintillators for charged particle detection
 Energy resolution and energy-light response of CsI(Tl) scintillators for charged particle detection A. Wagner a1, W.P. Tan 1, K. Chalut 1, R.J. Charity 3, B. Davin 2, Y. Larochelle c 2, M.D. Lennek 1,
Energy resolution and energy-light response of CsI(Tl) scintillators for charged particle detection A. Wagner a1, W.P. Tan 1, K. Chalut 1, R.J. Charity 3, B. Davin 2, Y. Larochelle c 2, M.D. Lennek 1,
p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model
 Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
S. YOKOYAMA 1;2. Abstract. Light particle-unstable nuclei were studied along the neutron. B is a possible candidate for neutron
 Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
Correlations between Reaction Product Yields as a Tool for Probing Heavy Ion Reaction Scenarios. Abstract
 Correlations between Reaction Product Yields as a Tool for Probing Heavy Ion Reaction Scenarios W. Gawlikowicz 1,2, D.K. Agnihotri 1, S.A. Baldwin 1, W.U. Schröder 1, J. Tõke 1, R.J. Charity 3, D.G. Sarantites
Correlations between Reaction Product Yields as a Tool for Probing Heavy Ion Reaction Scenarios W. Gawlikowicz 1,2, D.K. Agnihotri 1, S.A. Baldwin 1, W.U. Schröder 1, J. Tõke 1, R.J. Charity 3, D.G. Sarantites
Transport Theory for Energetic Nuclear Reactions
 Transport Theory for Energetic Nuclear Reactions Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University 56 th International Winter Meeting on Nuclear Physics Bormio (Italy), January
Transport Theory for Energetic Nuclear Reactions Pawel National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University 56 th International Winter Meeting on Nuclear Physics Bormio (Italy), January
