Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
|
|
|
- Lorin Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, (2012) DOI: / epjconf/ C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models E. Legouée, E. Vient and D. Durand LPC Caen, Université, ENSICAEN, CNRS/IN2P3, F Caen cedex, France Abstract The characterization of hot quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric or quasi-symmetric reactions (Au + Au, Xe + Sn, Ni + Ni, Ar + KCl) at different incident energies are estimated by means of two different procedures. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are analyzed on the basis of simulations using events produced by two slightly different models: HIPSE and ELIE. 1 Introduction Nuclear reactions around the Fermi energy produce hot species by means of energy and/or mass transfers between the two partners of the collision. Of particular interest is the production of hot projectile-like nuclei because, due to favourable kinematical conditions, they can be accurately detected by large multidetectors such as INDRA [1]. The thermodynamics of such hot species is a key topic of nuclear physics since it allows to address, for instance, the existence of a liquid-gas phase transition in nuclear matter. The precise measurement of the amount of excitation energy deposited in hot nuclei (calorimetry) is a prerequisite in such studies. The complexity of nuclear reactions makes such measurements rather difficult and requires This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Article available at or
2 EPJ Web of Conferences accurate and well-controlled methods. These latter use event selections and kinematical cuts based on the angular distributions of all detected charged particles. The aim of the present work is to discuss optimal procedures for nuclear calorimetry. For this, computer simulations modeling nuclear reactions can be helpfull. Here, we have used the events generated by two models: HIPSE (Heavy Ion Phase Space Exploration) [2] and ELIE [3]. 2 Brief description of the events generators and comparison with selected data The two event generators are based on a two-step scenario of the reaction: an entrance channel phase ending with the formation (for finite impact parameters) of excited PLF (projectile-like fragment), TLF (target-like fragment) and participants. a second phase considering secondary decay and propagation towards the detectors. In the ELIE model, the mass numbers of the PLF, TLF and participants are obtained by considering the geometrical overlap of the nuclei for each impact parameter according to the high energy participant-spectator picture while in the HIPSE case, it is governed by the minimum distance of approach obtained with a trajectory calculation based on a realistic interaction potential. To build the kinematics of the projectile-like, the target-like and the partition of the participants, the following hypothesis are assumed: 1. The momentum distribution of the incoming nucleons inside the two partners is supposed to have no time to relax on a time scale comparable with the reaction time. This is a frozen approximation: only a few hard nucleon-nucleon collisions can occur and those latter are governed by a single parameter: the mean free path. 2. In the ELIE model, the partition of the participants is generated by a random process in momentum space. The mass number A of each species (including A=1 free nucleons) is sequentially chosen at random by picking A nucleons from the nucleon momentum distribution. For IMF s (A 4), the excitation energy, E, is obtained by summing the center-of-mass kinetic energy of all nucleons belonging to the fragment. If E is larger than a maximum value associated with a maximum p.2
3 IWM2011 Figure 1: Particle multiplicities cross-sections(from protons to IMF as indicated in each panel) for Xe + Sn central collisions at 50 A.MeV. Black points are INDRA data while the histograms are for ELIE data (Colour online). temperature T max, the fragment is rejected and a new try is made until all nucleons have been assigned. In the following, it turns out that a value of T max = 5.5 MeV allows to reproduce the experimental data (with a level density parameter equal to A/10, E = 3 MeV/u). 3. In the HIPSE approach, an aggregation algorithm based on cuts in momentum and real space is applied to build the fragments and constitute the partition. In a second step, the partition is propagated in space-time and secondary decays are considered. This is done using a standard evaporation code: the SIMON event generator [4]. The essential difference between the two models lies in the excitation energy distribution in the fragments since in the ELIE case, the limiting temperature (5.5 MeV) limits E* to around 3 MeV/u while for HIPSE, the amount of excitation energy can extend to much larger values (see blue histograms in fig.3) (colour online) p.3
4 EPJ Web of Conferences Figure 1 shows a comparison of the multiplicity cross-sections from protons to IMF s between INDRA data and ELIE data for Xe+Sn central collisions at 50 A.MeV. For that purpose, a selection of the events has been made using the total light charged particle transverse energy, E tr12,normalized to the CM available energy. Assuming that this latter is correlated to the impact parameter, central collisions have been defined by keeping only the 50 mbarn cross-section associated with the largest E tr12 values. For such central collisions, particle multiplicities are correctly reproduced by the model. Other observables have been considered and a general good agreement has been reached between INDRA data and ELIE data. Same conclusions can be reached as far as HIPSE is concerned. These models are therefore sufficiently realistic to allow a check of the calorimetric methods described in the following. 3 Data analysis and calorimetries PLF s characteristics (mass, charge and excitation energy) are measured by considering fragments and light charged particles on an event by event basis. The question of the undetected neutrons is discussed later. A completion criterium is first applied to the data by imposing that most of the charged particles (around 80 percent at the forward of the center of mass) emitted in the reaction be detected. This ensures that no major biases are introduced in the final retained event sample. Then, two different methods are used: a standard calorimetry and the so-called 3D calorimetry. The projectilelike frame [5] in which all kinematical quantities are calculated is built by adding all fragments (charge larger than 2) which are located in the forward hemisphere of the center of mass of the reaction (for symetric systems this corresponds to positive CM velocities). Considering the standard calorimetry, all particles emitted in the forward hemisphere of the PLF frame are assumed to be emitted by the PLF and as such are taken into account in the reconstruction of the excitation energy and mass. In order to cover the whole 4π-space, this contribution is doubled on an event by event basis. Note that in this case, no attempt is made to consider non-equilibrium effects. Such effects are tentitatively taken into account in the 3D calorimetry by first assuming that PLF evaporation is cylindrically symmetric around the perpendicular axis of the reaction plane, as shown in fig.2. It is then assumed that all particles emitted in the angular domain ϕ [0, 60 ] result from the evaporation of the PLF, and, as such, the evaporation probability in this angular range prob ref (i) of species i (proton, deuteron, triton,...) p.4
5 IWM2011 Figure 2: Angular domains with respect to the reaction plane and beam direction chosen to determine the probability of emission of particles by the PLF. is equal to 1 whatever the kinetic energy (E ci ) distribution, called W ref (i). In other angular regions covering the same solid angle, other processes of emission can occur so that the evaporation probability can take values lower than 1. The probability p j (i) in this region labelled j is then obtained by dividing the kinetic energy distribution W j (i) byw ref (i) for each energy bin E c (i). Thus, with this method, the probability of evaporation is a function of the species (proton, deuteron, triton,...), the kinetic energy and the angle of emission of the particle. The probability of evaporation hereafter labelled prob i for particle labelled i is used for the reconstruction of the hot PLF : in mass (A PLF ), charge (Z PLF ), and excitation energy E PLF according to the following equations: E PLF = A PLF = multot i=1 multot i=1 Z PLF = prob i A i + N neutron (1) multot i=1 prob i Z i (2) prob i E ci + N neutron E c p+α ΔQ (3) p.5
6 EPJ Web of Conferences Figure 3: <E PLF > (MeV/u) as a function of E tr12 for Ni+Ni at 52 A.MeV. Left, ELIE data. Right: HIPSE data, both compared with INDRA data (red crosses and open points)(colour online). The number of neutrons is obtained by imposing the conservation of the (A/Z) of the projectile. The mass number of fragments when not measured is obtained from the measured atomic number following the Charity prescription [6]. Figure 3 shows preliminary results concerning the correlation between E tr12 and the mean PLF excitation energy per nucleon E A for ELIE data (left) and HIPSE data (right). In both cases, the INDRA data have been superimposed for a sake of comparison. Results of the studies are rather contrasted. None of the methods can reproduce the excitation energy values given by the ELIE model and a strong over-estimation is obtained especially for the most central collisions. This is due to the fact that, in the ELIE case, even in the reference angular domain, most of emitted particles do not originate from a slow equilibrated process. However, for excitation energies lower than 2 MeV/u, the 3D method gives good results. As for HIPSE, the 3D calorimetry reproduces the excitation energy distribution while the standard method leads to a systematic overestimation. It is worth noted that, whatever the method, the methods applied to INDRA data lead to very high excitation energies: a point which remains to be understood p.6
7 IWM Summary and perspectives Two different methods for the characterization of projectile-like fragments in nuclear reactions have been discussed. Tests of the procedures using data generated by two models, ELIE and HIPSE, have been shown. Results are contrasted. However, work is still in progress to improve the 3D calorimetry. This could help extract, by subtraction of the evaporation component, the non-equilibrium processes associated with the first instants of the reaction. References [1] J. Pouthas et al., Nucl. Inst. Meth. Phys. Res. A 369 (1996) 222. [2] D. Lacroix, A. Van Lauwe, D. Durand, Phys. Rev. C 69 (2004) [3] D. Durand, ELIE a minimal dynamical model, IWM2007 Proceedings p [4] A. Van Lauwe, D. Lacroix, D. Durand, IWM2003 International Workshop on Multifragmentation and Related Topics (IWM2003) (2004) [5] D. Durand, E. Suraud, and B. Tamain, Nuclear Dynamics in the Nucleonic Regime (IOP Publishing, Bristol, UK, and Philadelphia, 2001). [6] R. J. Charity, Phys. Rev. C 58 (1998) p.7
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Noncentral collisions
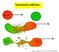 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, (2012) DOI: / epjconf/ C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012
 EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 00037 (0) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 030037 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 0 The elusiveness of multifragmentation footprints in -GeV proton-nucleus reactions
N/Z influence on the level density parameter
 EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources. A. Chbihi GANIL
 Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Correlation functions and characterization of emitting sources A. Chbihi GANIL Outline Intensity interferometry Directional correlations : size-lifetime Angle-averaged correlation functions Imaging, model
Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process?
 arxiv:nucl-ex/0203017v1 25 Mar 2002 Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process? A. Van Lauwe a, D. Durand a, G. Auger b, N. Bellaize a, B. Bouriquet b, A.M. Buta
arxiv:nucl-ex/0203017v1 25 Mar 2002 Multifragmentation in central collisions at intermediate energies: a fast process? A. Van Lauwe a, D. Durand a, G. Auger b, N. Bellaize a, B. Bouriquet b, A.M. Buta
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013](/thumbs/83/87477490.jpg) PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
PJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by DP Sciences, 2014 arxiv:1308.6470v1 [nucl-ex] 29 Aug 2013 Nuclear stopping for
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Fission Fragment characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS
 EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group
 Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group Permamentstaff : R. Bougault, N. Le Neindre, O. Lopez, E. Vient PhD Student: M. Kabtoul, E. Legouée Collaborations: LPC: F.Gulminelli (Théorie), D.Durand(Théorie),
Nucleardynamicsand thermodynamics INDRA FAZIA group Permamentstaff : R. Bougault, N. Le Neindre, O. Lopez, E. Vient PhD Student: M. Kabtoul, E. Legouée Collaborations: LPC: F.Gulminelli (Théorie), D.Durand(Théorie),
Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 76, 6161(R) (7) Distinctive features of Coulomb-related emissions in peripheral heavy ion collisions at Fermi energies S. Piantelli, 1 P. R. Maurenzig, A. Olmi, 1,* L. Bardelli, M. Bini,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault. In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of
 CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
CALORIMETRY V.E. Viola and R. Bougault In any attempt to describe a system in terms of thermodynamic variables, a knowledge of heat content is fundamental. For hot nuclei, this energetic factor is usually
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 2017](/thumbs/90/103449438.jpg) A new 3D Calorimetry of hot nuclei arxiv:179.7396v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 217 E. Vient, 1, L. Manduci, 2, 1 E. Legouée, 1 L. Augey, 1 E. Bonnet, 3 B. Borderie, 4 R. Bougault, 1 A. Chbihi, 5 D. Dell
A new 3D Calorimetry of hot nuclei arxiv:179.7396v1 [physics.data-an] 21 Sep 217 E. Vient, 1, L. Manduci, 2, 1 E. Legouée, 1 L. Augey, 1 E. Bonnet, 3 B. Borderie, 4 R. Bougault, 1 A. Chbihi, 5 D. Dell
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models
 Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Bimodalities: a survey of experimental data and models O. Lopez Λ and M. F. Rivet y Λ Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire, IN2P3-CNRS/ENSICAEN /Université, F-14050 Caen cedex, France y Institut de Physique
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ at 15 MeV/nucleon
 Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Neutron-rich rare isotope production with stable and radioactive beams in the mass range A ~ 40-60 at 15 MeV/nucleon A. Papageorgiou 1, G.A. Soulotis 1, M. Veselsky 2, A. Bonasera 3,4 1 Laboratory of Physical
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies*
 Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Isotopic compositions in projectile fragmentation at Fermi energies* Nihal Buyukcizmeci 1, A. Ergun 1, H. Imal 1, R. Ogul 1, A.S. Botvina 2,3 1 Selcuk University, Department of Physics, 42079, Campus,
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process
 REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
REVISTA MEXICANA DE FÍSICA S 52 (4) 109 114 NOVIEMBRE 2006 Dynamical and thermodynamical features in the fragmentation process J.P. Wieleczko a, R. Bougault b, A. Chbihi a, D. Durand b, C. Escano Rodriguez
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Citation EPJ Web of Conferences (2014), provided the original work is prope
 TitleStudy of heavy-ion induced fission Nishio, K.; Ikezoe, H.; Hofmann, S. Ackermann, D.; Antalic, S.; Aritomo Düllman, Ch.E.; Gorshkov, A.; Graeg Author(s) J.A.; Hirose, K.; Khuyagbaatar, J.; Lommel,
TitleStudy of heavy-ion induced fission Nishio, K.; Ikezoe, H.; Hofmann, S. Ackermann, D.; Antalic, S.; Aritomo Düllman, Ch.E.; Gorshkov, A.; Graeg Author(s) J.A.; Hirose, K.; Khuyagbaatar, J.; Lommel,
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions.
 Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Fragment properties of fragmenting heavy nuclei produced in central and semi-peripheral collisions. E. Bonnet, Bernard Borderie, N. Le Neindre, Marie-France Rivet, R. Bougault, A. Chbihi, R. Dayras, J.D.
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation
 Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
(Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S Pb
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve
 How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
How Much Cooler Would It Be With Some More Neutrons? Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University 1 Asymmetry Dependence of the Nuclear Caloric Curve Nuclear Caloric
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons?
 How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
How much cooler would it be with some more neutrons? The Influence of Neutron-Proton Asymmetry on Nuclear Temperature Alan McIntosh Texas A&M University International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics and Thermodynamics
Use of fragmentation beams at LNS with CHIMERA detector
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00036 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100036 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Use of fragmentation beams at LNS with CHIMERA detector G. Cardella
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00036 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100036 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Use of fragmentation beams at LNS with CHIMERA detector G. Cardella
Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 031601(R) (2004) Interplay of initial deformation and Coulomb proximity on nuclear decay S. Hudan, R. Alfaro, L. Beaulieu, B. Davin, Y. Larochelle, T. Lefort, V. E. Viola, H. Xu,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 14 Oct 2004
 Critical Behavior in Light Nuclear Systems: (I) Experimental Aspects arxiv:nucl-ex/48 v 4 Oct 24 Y. G. Ma,,2 J. B. Natowitz, R. Wada, K. Hagel, J. Wang, T. Keutgen, 3 Z. Majka, 4 M. Murray, 5 L. Qin, P.
Critical Behavior in Light Nuclear Systems: (I) Experimental Aspects arxiv:nucl-ex/48 v 4 Oct 24 Y. G. Ma,,2 J. B. Natowitz, R. Wada, K. Hagel, J. Wang, T. Keutgen, 3 Z. Majka, 4 M. Murray, 5 L. Qin, P.
Small Collision Systems at RHIC
 EPJ Web of Conferences 7, (8) SQM 7 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/87 Small Collision Systems at RHIC Norbert Novitzky, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 79, USA
EPJ Web of Conferences 7, (8) SQM 7 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/87 Small Collision Systems at RHIC Norbert Novitzky, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 79, USA
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC
 Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
Topics of interest for Must2 in HIC 1. Density dependence of the symmetry energy: peripheral and central collisions 2. particle-particle correlations a. Imaging of emitting sources: space-time properties
2 Give the compound nucleus resulting from 6-MeV protons bombarding a target of. my notes in the part 3 reading room or on the WEB.
 Lecture 15 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3 direct reactions 11.11 13.11/12 ch 14 Admixed Wave functions residual interaction 5.1-4 Admixed Wave functions
Lecture 15 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3 direct reactions 11.11 13.11/12 ch 14 Admixed Wave functions residual interaction 5.1-4 Admixed Wave functions
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei
 Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei Eric Bonnet (GANIL) for the INDRA and ALADIN collaboration IWM 09, Catania Outline First order phase transition in finite system Definition and related signals
Bimodality and latent heat of gold nuclei Eric Bonnet (GANIL) for the INDRA and ALADIN collaboration IWM 09, Catania Outline First order phase transition in finite system Definition and related signals
What is Spallation???
 What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
Author(s) Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki. Citation Physics Procedia (2015), 64:
 Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 22 Mar 2010](/thumbs/94/120296745.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:3.45v [nucl-ex] 22 Mar THE PROMINENT ROLE OF THE HEAVIEST FRAGMENT IN MULTIFRAGMENTATION AND PHASE TRANSITION FOR HOT
Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions
 Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter-universitario de Física Nuclear Universidade de Santiago de Compostela March 2008 Contents Elements of
Deexcitation mechanisms in compound nucleus reactions Curso de Reacciones Nucleares Programa Inter-universitario de Física Nuclear Universidade de Santiago de Compostela March 2008 Contents Elements of
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 Mar 2005
 Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Size and asymmetry of the reaction entrance channel: influence on the probability of neck production arxiv:nucl-ex/0503005v1 10 Mar 2005 P.M.Milazzo a, G.Vannini b, C.Agodi c, R.Alba c, G.Bellia c, N.Colonna
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI
 THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
Transverse momentum of ionized atoms and diatomic molecules acquired in collisions with fast highly-charged heavy ion. V. Horvat and R. L.
 Transverse momentum of ionized atoms and diatomic molecules acquired in collisions with fast highly-charged heavy ion V. Horvat and R. L. Watson The momenta of ions and electrons emerging from collisions
Transverse momentum of ionized atoms and diatomic molecules acquired in collisions with fast highly-charged heavy ion V. Horvat and R. L. Watson The momenta of ions and electrons emerging from collisions
Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Bimodal pattern in the fragmentation of Au quasi-projectiles M. Bruno 1, F. Gulminelli 2a, F. Cannata 1, M. D Agostino 1, F. Gramegna 3, G. Vannini 1
Neutron capture and fission reactions on. sections, -ratios and prompt -ray emission from fission. 1 Introduction and Motivation
 EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01002 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Neutron capture and fission reactions on 235 U : cross sections, -ratios
EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01002 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Neutron capture and fission reactions on 235 U : cross sections, -ratios
INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION MODELS IN GEANT4
 Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 24 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 24 Jun 2016 arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 24 Jun 2016](/thumbs/79/80286264.jpg) Using LHC Forward Proton Detectors to Tag Nuclear Debris Rafa l Staszewski and Janusz J. Chwastowski Institute of Nuclear Physics Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland
Using LHC Forward Proton Detectors to Tag Nuclear Debris Rafa l Staszewski and Janusz J. Chwastowski Institute of Nuclear Physics Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland
Fission-yield data. Karl-Heinz Schmidt
 Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions
 New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems:
 Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Thermodynamical coordinates of excited nuclear systems: 4,48 Ca + 58,64 Ni and 4 Ca + 58 Fe reactions M. Bruno, F. Cannata, M.D Agostino, J. De Sanctis, S. Fabbri, E.Geraci, B. Guiot, G.Vannini Department
Velocity-dependent transverse momentum distribution of projectilelike fragments at 95 MeV/u. Sadao MOMOTA Kochi University of Technology
 5th International Conference on Nuclear ragmentation Oct./-/5, Kemer, Turkey Velocity-dependent transverse momentum distribution of projectilelike fragments at 95 MeV/u Sadao MOMOTA Kochi University of
5th International Conference on Nuclear ragmentation Oct./-/5, Kemer, Turkey Velocity-dependent transverse momentum distribution of projectilelike fragments at 95 MeV/u Sadao MOMOTA Kochi University of
Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
In-medium Properties of Hadrons
 EPJ Web of Conferences 37, 5 () DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 375 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, In-medium Properties of Hadrons Volker Metag a II. Physikalisches Institut, University of Giessen,
EPJ Web of Conferences 37, 5 () DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 375 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, In-medium Properties of Hadrons Volker Metag a II. Physikalisches Institut, University of Giessen,
hal , version 1-5 Mar 2010
 Author manuscript, published in "International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics in Heavy-Ion Reactions and the Symmetry Energy (IWND29, Shanghai : Chine (29" DOI :.42/S285928 March 5, 2 5: WSPC/INSTRUCTION
Author manuscript, published in "International Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics in Heavy-Ion Reactions and the Symmetry Energy (IWND29, Shanghai : Chine (29" DOI :.42/S285928 March 5, 2 5: WSPC/INSTRUCTION
Evidence for dynamical proton emission in peripheral Xe+Sn. collisions at 50 MeV/u.
 Evidence for dynamical proton emission in peripheral Xe+Sn collisions at 50 MeV/u. M. Germain a;1 D. Gourio b, Ph. Eudes a, J.L. Laville a;c, T. Reposeur a, D. Ardouin a, M. Assenard a, G. Auger c, C.
Evidence for dynamical proton emission in peripheral Xe+Sn collisions at 50 MeV/u. M. Germain a;1 D. Gourio b, Ph. Eudes a, J.L. Laville a;c, T. Reposeur a, D. Ardouin a, M. Assenard a, G. Auger c, C.
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS
 Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
Systematic study of spallation reactions in inverse kinematics at the FRS M. Valentina Ricciardi GSI A campaign of measurements and studies started at GSI in 1996 in collaboration with other institutes:
Dynamics of light clusters in fragmentation reactions
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 390 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16390-x Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Dynamics of light clusters in fragmentation reactions Akira Ono Department of Physics, Tohoku University - Sendai 980-8578,
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 390 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16390-x Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Dynamics of light clusters in fragmentation reactions Akira Ono Department of Physics, Tohoku University - Sendai 980-8578,
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions
 The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Annax-I. Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in
 Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
JRPR. Measurement of Neutron Production Doubledifferential Cross-sections on Carbon Bombarded with 430 MeV/Nucleon Carbon Ions.
 Journal of Radiation Protection and Research 2016;41(4):344-349 pissn 2508-1888 eissn 2466-2461 Measurement of Neutron Production Doubledifferential Cross-sections on Carbon Bombarded with 430 MeV/Nucleon
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research 2016;41(4):344-349 pissn 2508-1888 eissn 2466-2461 Measurement of Neutron Production Doubledifferential Cross-sections on Carbon Bombarded with 430 MeV/Nucleon
FIRST STEPS IN PHYSICAL TREATING OF THE COLLINEAR CLUSTER TRI-PARTITION MECHANISM
 FIRST STEPS IN PHYSICAL TREATING OF THE COLLINEAR CLUSTER TRI-PARTITION MECHANISM Yu.V. Pyatkov 1,2, D.V. Kamanin 1, W. von Oertzen 3, A.A. Alexandrov 1, I.A. Alexandrova 1, N.A. Kondratyev 1, E.A. Kuznetsova
FIRST STEPS IN PHYSICAL TREATING OF THE COLLINEAR CLUSTER TRI-PARTITION MECHANISM Yu.V. Pyatkov 1,2, D.V. Kamanin 1, W. von Oertzen 3, A.A. Alexandrov 1, I.A. Alexandrova 1, N.A. Kondratyev 1, E.A. Kuznetsova
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects
 Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Proximity Decay and Tidal Effects A. B. McIntosh,S. Hudan, C.J. Metelko, N. Peters, J. Black, RdS Dept of Chemistry and IUCF, Indiana University July 16 22 1994: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/sl9/ Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact
 Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Jagiellonian University
 Jagiellonian University THE FACULTY OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY, AND APPLIED COMPUTER SCIENCE MARIAN SMOLUCHOWSKI INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS Model Description of Proton Induced Fragmentation of Atomic Nuclei Małgorzata
Jagiellonian University THE FACULTY OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY, AND APPLIED COMPUTER SCIENCE MARIAN SMOLUCHOWSKI INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS Model Description of Proton Induced Fragmentation of Atomic Nuclei Małgorzata
Recent experiments in inverse kinematics with the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA
 Recent experiments in inverse kinematics with the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA E. Fioretto 1,L.Corradi 1, D. Montanari 2,S.Szilner 3, G. Pollarolo 4,F.Galtarossa 1,5,D.Ackermann 6, G. Montagnoli 7,F.Scarlassara
Recent experiments in inverse kinematics with the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA E. Fioretto 1,L.Corradi 1, D. Montanari 2,S.Szilner 3, G. Pollarolo 4,F.Galtarossa 1,5,D.Ackermann 6, G. Montagnoli 7,F.Scarlassara
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production
 On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch /2 7.5 Reaction dynamics /4 Reaction cross sections 11.
 Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch 13 7.1/2 7.5 Reaction dynamics 11.2 13.2 7.3/4 Reaction cross sections 11.4 2.10 Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3
Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch 13 7.1/2 7.5 Reaction dynamics 11.2 13.2 7.3/4 Reaction cross sections 11.4 2.10 Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3
On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield
 EPJ Web of Conferences 53, 10001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20135310001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination
EPJ Web of Conferences 53, 10001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20135310001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination
Evaluation of inclusive breakup cross sections in reactions induced by weakly-bound nuclei within a three-body model
 Evaluation of inclusive breakup cross sections in reactions induced by weakly-bound nuclei within a three-body model Jin Lei, Antonio M. Moro Departamento de FAMN, Universidad de Sevilla, Apartado 165,
Evaluation of inclusive breakup cross sections in reactions induced by weakly-bound nuclei within a three-body model Jin Lei, Antonio M. Moro Departamento de FAMN, Universidad de Sevilla, Apartado 165,
NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 70 Zn MeV/nucleon)
 NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 7 Zn+ 7 Zn @ 35 MeV/nucleon) Dr. 1 1Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, TAMU DNP 218, Kona 1 Systems studied: 7 Zn+
NZ equilibration in two and three bodies dynamically deformed nuclear systems ( 7 Zn+ 7 Zn @ 35 MeV/nucleon) Dr. 1 1Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, TAMU DNP 218, Kona 1 Systems studied: 7 Zn+
Measurements of the electron-positron continuum in ALICE
 EPJ Web of Conferences 6, 0000 (01) DOI:.1/ epjconf/ 0160000 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 01 Measurements of the electron-positron continuum in ALICE Christoph Baumann a for the ALICE
EPJ Web of Conferences 6, 0000 (01) DOI:.1/ epjconf/ 0160000 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 01 Measurements of the electron-positron continuum in ALICE Christoph Baumann a for the ALICE
Coherent photo-production of ρ 0 mesons in ultra-peripheral Pb-Pb collisions at the LHC measured by ALICE
 EPJ Web of Conferences 8, 4) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 4 8 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 4 Coherent photo-production of ρ mesons in ultra-peripheral Pb-Pb collisions at the LHC measured by
EPJ Web of Conferences 8, 4) DOI:.5/ epjconf/ 4 8 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 4 Coherent photo-production of ρ mesons in ultra-peripheral Pb-Pb collisions at the LHC measured by
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/69624022.jpg) Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 56, NUMBER 2 AUGUST 1997 Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission R. J. Charity, M. Korolija,* D. G. Sarantites, and L. G. Sobotka
PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 56, NUMBER 2 AUGUST 1997 Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission R. J. Charity, M. Korolija,* D. G. Sarantites, and L. G. Sobotka
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Oct 2003
 1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
1 Experimental Signals of Phase Transition M. D Agostino a M. Bruno a, F. Gulminelli b, R. Bougault b, F. Cannata a, Ph. Chomaz c, F. Gramegna d, N. Le Neindre e, A. Moroni f, G. Vannini a arxiv:nucl-ex/3113
Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies Andrey Seryakov for
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies Andrey Seryakov for
Colinear ternary fission and nucleon phase model G. Mouze, S. Hachem and C. Ythier
 1 Colinear ternary fission and nucleon phase model G. Mouze, S. Hachem and C. Ythier Faculté des Sciences, Université de Nice, 06108 Nice cedex 2, France mouze@unice.fr bstract: The colinear ternary fission
1 Colinear ternary fission and nucleon phase model G. Mouze, S. Hachem and C. Ythier Faculté des Sciences, Université de Nice, 06108 Nice cedex 2, France mouze@unice.fr bstract: The colinear ternary fission
Neutron multiplicity. Total radioactivity (Ci) Time after beam cut. Target A s 1min 1h 1d 1m 1y 10y 100y
 0 proton 000 MeV proton 500 MeV pronto 200 MeV 0-0 25 50 75 00 25 50 75 200 225 250 Target A ' data and Mote Carlo simulations on spallation New relevant for the design of ADS reactions J.Benlliure University
0 proton 000 MeV proton 500 MeV pronto 200 MeV 0-0 25 50 75 00 25 50 75 200 225 250 Target A ' data and Mote Carlo simulations on spallation New relevant for the design of ADS reactions J.Benlliure University
Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun
 Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun Multifragmentation is phenomenon in which nuclear system decays to a final configuration
Bimodality and Scaling-Signs of phase transition in Nuclear Multifragmentation? B.Grabez Institute of Physics Zemun Multifragmentation is phenomenon in which nuclear system decays to a final configuration
Measurement of secondary particle production induced by particle therapy ion beams impinging on a PMMA target
 EPJ Web of Conferences 117, Measurement of secondary particle production induced by particle therapy ion beams impinging on a PMMA target M. Toppi 1,G.Battistoni 2, F. Bellini 3,4, F. Collamati 3,4, E.
EPJ Web of Conferences 117, Measurement of secondary particle production induced by particle therapy ion beams impinging on a PMMA target M. Toppi 1,G.Battistoni 2, F. Bellini 3,4, F. Collamati 3,4, E.
Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion collisions
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 01018 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146601018 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Probing the nuclear equation-of-state and the symmetry energy with heavy-ion
Sunday Monday Thursday. Friday
 Nuclear Structure III experiment Sunday Monday Thursday Low-lying excited states Collectivity and the single-particle degrees of freedom Collectivity studied in Coulomb excitation Direct reactions to study
Nuclear Structure III experiment Sunday Monday Thursday Low-lying excited states Collectivity and the single-particle degrees of freedom Collectivity studied in Coulomb excitation Direct reactions to study
Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe Pt for production of exotic nuclei
 16 th ASRC International Workshop Mar. 19, 2014 Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe + 198 Pt for production of exotic nuclei Contents Y.X. Watanabe (KEK) 1. Introduction (MNT reactions
16 th ASRC International Workshop Mar. 19, 2014 Study of multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions of 136 Xe + 198 Pt for production of exotic nuclei Contents Y.X. Watanabe (KEK) 1. Introduction (MNT reactions
Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions
 Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions J A Tostevin Department of Physics, School of Electronics and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, United Kingdom, and Graduate
Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions J A Tostevin Department of Physics, School of Electronics and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, United Kingdom, and Graduate
Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( )
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 110 A, N. 9-10 Settembre-Ottobre 1997 Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( ) A. G. POPEKO Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR - 141980 Dubna,
IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 110 A, N. 9-10 Settembre-Ottobre 1997 Subbarrier cold fusion reactions leading to superheavy elements( ) A. G. POPEKO Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR - 141980 Dubna,
Nuclear lifetime measurements from data with independently varying observation
 44 (216) Heavy Ion Accelerator Symposium 215 DOI: 1.151/ epjconf/21612344 Nuclear lifetime measurements from data with independently varying observation times T. J. Gray 1, M. W. Reed 1,a, G. J. Lane 1,
44 (216) Heavy Ion Accelerator Symposium 215 DOI: 1.151/ epjconf/21612344 Nuclear lifetime measurements from data with independently varying observation times T. J. Gray 1, M. W. Reed 1,a, G. J. Lane 1,
Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 366 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16366-x Colloquia: SEA2016 Isospin influence on the decay modes of compound nuclei produced in the 78,86 Kr + 40,48 Ca at 10 MeV/nucleon S. Pirrone(
Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment
 Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center
 1 Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center M. Mocko 1, G. Muhrer 1, F. Tovesson 1, J. Ullmann 1 1 LANSCE, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos NM 87545,
1 Nuclear Cross-Section Measurements at the Manuel Lujan Jr. Neutron Scattering Center M. Mocko 1, G. Muhrer 1, F. Tovesson 1, J. Ullmann 1 1 LANSCE, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos NM 87545,
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions
 Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Signatures for multifragmentation in spallation reactions Karl-Heinz Schmidt for the CHARMS collaboration * GSI, Planckstr. 1, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract: The traditional theoretical description
Measurement and evaluation of the excitation function in (α,xn) reactions on Au up to energy range 60MeV
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 215, 6(7):199-23 ISSN: 976-861 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Measurement and evaluation of the excitation function in (α,xn)
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 215, 6(7):199-23 ISSN: 976-861 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Measurement and evaluation of the excitation function in (α,xn)
Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies
 Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies Christoph Langer (JINA/NSCL) INT Workshop: Reactions and Structure of Exotic Nuclei March 2015 1 Understanding
Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies Christoph Langer (JINA/NSCL) INT Workshop: Reactions and Structure of Exotic Nuclei March 2015 1 Understanding
