Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms. Tirgul 11
|
|
|
- Kelley Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Tirgul 11
2 Multi-Label Classification 2
3 Multilabel Problem: Example Mapping Apps to smart folders: Assign an installed app to one or more folders Candy Crush Saga 3
4 Goal Given A, an installed app: Farm Story Assign it to y Y the set of relevant folders: Where Y is the set of all folders: Games Social Social Music Games Photography Shopping 4
5 Multilabel Classification A variant of the classification problem: Multiple target labels must by assigned to each instance. Setting: There are k different possible labels: Y = 1,, k. Every instance x i is associated with a set of relevant labels y i. Special case: There is a single relevant label for each instance: multiclass (single-label) classification. 5
6 Multilabel Classification Other usage: Text categorization: x i represents a document. y i is the set of topics which are relevant to the document Chosen from a predefined collection of topics. E.g.: A text might be about any of religion, politics, finance or education at the same time or none of these. 6
7 Task Assign user s installed applications to one ore more smart folders in an automatic way 7
8 Task Training set of examples: Each example (A i, y i ) contains an application and a set of one or more smart folders: Farm Story Games Social 8
9 Model Find a function y = f w A with parameters w that assigns a set of folders y to an installed app A. 9
10 Model and Inference y = f w A = argsort y w φ(a, y) weight vectors feature maps 10
11 Feature maps TF-IDF of title Google Play s category TF-IDF of description Representation of related apps
12 Inference y i = argsort y w φ(a i, y) Algorithm s output upon receiving an instance x i : A score for each of the k labels in Y. x i = Farm Story Y = Social Music Games Photography Shopping 0.6, 0.3, 0.7, 0.1,
13 y = argsort y w φ(a, y) Inference The algorithm s prediction is a vector in R k where each element in the vector corresponds to the score assigned to the respective label. This form of prediction is often referred to as label ranking. Y = Social Music Games Photography Shopping 0.6, 0.3, 0.7, 0.1, 0.01 R k 13
14 Inference For a pair of labels r, s Y: If score r > score(s): Label r is ranked higher than label s. Goal of Algorithm: Rank every relevant label above every irrelevant label. Social Music Games Photography Shopping 14
15 The Margin Example: A i, y i =,. Games After making predictions y i, the algorithm receives the correct set y i. 1. Find the least probable correct folder: Social Social Music Games Games 2. Find the most probable wrong folder: Shopping Music max Photography 15
16 Iterate over examples Example: A i, y i =,. Games After making predictions y i, the algorithm receives the correct set y i. Social Social Music Games max Update: Shopping Photography 16
17 The Margin We define the margin attained by the algorithm on round i for example x i, y i, Social Music γ w i, x i, y i = min r y i w i φ x i, r max s y i w i φ x i, s. Games Shopping Photography 17
18 The Margin The margin is positive if all relevant labels are ranked higher than all irrelevant labels. We are not satisfied with only a positive margin; we require the margin of every prediction to be at least 1. γ w i, x i, y i = min r y i w i φ x i, r max s y i w i φ x i, s. 18
19 The Loss l min r y i w i φ x i,r max s y i w i φ x i,s <0 γ w i, x i, y i = min r y i w i φ x i, r max s y i w i φ x i, s. Define a hinge loss: l w i, x i, y i = 0 γ w i, x i, y i 1 1 γ w i, x i, y i otherwise 19
20 The Loss l w i, x i, y i = 0 γ w i, x i, y i 1 1 γ w i, x i, y i otherwise Could also be written as follows: where a + = max(0, a) l w i, x i, y i = 1 γ w i, x i, y i + 20
21 Learning First approach: Goal : 21
22 Multilabel PA Optimization Problem An alternative approach: r i = argmin r yi w i φ(x i, r) s i = argmax s yi w i φ(x i, s) w i+1 = argmin w 1 2 w w i 2 s. t. l w, x i, y i = 1 γ w, x i, y i + = 0 i.e., the margin is greater than 1. γ w i, x i, y i = w i φ x i, r i w i φ x i, s i 22
23 Passive Aggressive (PA) The algorithm is passive whenever the hinge-loss is zero: l i = 0 w i+1 = w i When the loss is positive, the algorithm aggressively forces w i+1 to satisfy the constraint l w i, x i, y i = 0, regardless of the step size required. 23
24 Passive Aggressive Solving with Lagrange Multipliers, we get the following update rule: w i+1 = w i + τ i φ x i, r i φ x i, s i τ i = l i φ x i, r i φ x i, s i 2 24
25 Passive Aggressive The updated vector w i+1 will classify example x i with l w, x i, y i = 0. 25
26 Ranking 26
27 Ranking Problem: Example A Prediction Bar: Predict the apps the user is most likely to use at any given time and location. 27
28 assume the user is at a context. 12:47 at the office today is Wednesday. the most likely app the 4th likely app
29 Goal Find a function f that gets as input the current context x and predicts the apps the user is likely to click at a given context. 29
30 Features time of day day of week location
31 Discriminative Model Parameters w A R d of app A Context x R d Prediction:. 31
32 New Evaluation The performance of the prediction system is measured by Receiver operating Characteristics (ROC) curve. true positive rate= app was in the prediction bar and was clicked total contexts where was clicked app false positive rate= was in the prediction bar and wasn t clicked total contexts where wasn t clicked
33 Maximizing AUC By definition of the AUC (Bamber, 1975; Hanley and McNeil,1982): AUC 33
34 Pairwise Dataset For an application define two sets of context: Waze Waze 34
35 Maximizing AUC By definition of the AUC (Bamber, 1975; Hanley and McNeil,1982): 35
36
37 Solve using PA Set the next w i to be the minimizer of the following optimization problem min w R d,ξ w w i 1 2 s. t. f w x i +, A i f w x i, A i 1 37
38 Implementation Online algorithm to solve the optimization problem efficiency on huge data. Theoretical guarantees of convergence. 38
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
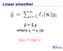 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms
 Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms Jean-Baptiste Behuet 28/11/2007 Tutor: Eneldo Loza Mencía Seminar aus Maschinellem Lernen WS07/08 Overview Online algorithms Online Binary Classification Problem Perceptron
Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms Jean-Baptiste Behuet 28/11/2007 Tutor: Eneldo Loza Mencía Seminar aus Maschinellem Lernen WS07/08 Overview Online algorithms Online Binary Classification Problem Perceptron
Statistical Machine Learning Theory. From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction. Hisashi Kashima.
 http://goo.gl/xilnmn Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
http://goo.gl/xilnmn Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
Statistical Machine Learning Theory. From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction. Hisashi Kashima.
 http://goo.gl/jv7vj9 Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
http://goo.gl/jv7vj9 Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
Online Bayesian Passive-Aggressive Learning
 Online Bayesian Passive-Aggressive Learning Full Journal Version: http://qr.net/b1rd Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu ICML 2014 T. Shi, J. Zhu (Tsinghua) BayesPA ICML 2014 1 / 35 Outline Introduction Motivation Framework
Online Bayesian Passive-Aggressive Learning Full Journal Version: http://qr.net/b1rd Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu ICML 2014 T. Shi, J. Zhu (Tsinghua) BayesPA ICML 2014 1 / 35 Outline Introduction Motivation Framework
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification
 Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Outline
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
COMS F18 Homework 3 (due October 29, 2018)
 COMS 477-2 F8 Homework 3 (due October 29, 208) Instructions Submit your write-up on Gradescope as a neatly typeset (not scanned nor handwritten) PDF document by :59 PM of the due date. On Gradescope, be
COMS 477-2 F8 Homework 3 (due October 29, 208) Instructions Submit your write-up on Gradescope as a neatly typeset (not scanned nor handwritten) PDF document by :59 PM of the due date. On Gradescope, be
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms
 Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Joseph Keshet Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University Jerusalem, 91904, Israel CRAMMER@CIS.UPENN.EDU
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Joseph Keshet Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University Jerusalem, 91904, Israel CRAMMER@CIS.UPENN.EDU
Classification and Pattern Recognition
 Classification and Pattern Recognition Léon Bottou NEC Labs America COS 424 2/23/2010 The machine learning mix and match Goals Representation Capacity Control Operational Considerations Computational Considerations
Classification and Pattern Recognition Léon Bottou NEC Labs America COS 424 2/23/2010 The machine learning mix and match Goals Representation Capacity Control Operational Considerations Computational Considerations
CS-E4830 Kernel Methods in Machine Learning
 CS-E4830 Kernel Methods in Machine Learning Lecture 5: Multi-class and preference learning Juho Rousu 11. October, 2017 Juho Rousu 11. October, 2017 1 / 37 Agenda from now on: This week s theme: going
CS-E4830 Kernel Methods in Machine Learning Lecture 5: Multi-class and preference learning Juho Rousu 11. October, 2017 Juho Rousu 11. October, 2017 1 / 37 Agenda from now on: This week s theme: going
Brief Introduction of Machine Learning Techniques for Content Analysis
 1 Brief Introduction of Machine Learning Techniques for Content Analysis Wei-Ta Chu 2008/11/20 Outline 2 Overview Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) Hidden Markov Model (HMM) Support Vector Machine (SVM) Overview
1 Brief Introduction of Machine Learning Techniques for Content Analysis Wei-Ta Chu 2008/11/20 Outline 2 Overview Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) Hidden Markov Model (HMM) Support Vector Machine (SVM) Overview
CS6375: Machine Learning Gautam Kunapuli. Support Vector Machines
 Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Support Vector Machines. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes
 CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi 1 Boosting We have seen so far how to solve classification (and other) problems when we have a data representation already chosen. We now talk about a procedure,
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi 1 Boosting We have seen so far how to solve classification (and other) problems when we have a data representation already chosen. We now talk about a procedure,
Support Vector and Kernel Methods
 SIGIR 2003 Tutorial Support Vector and Kernel Methods Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Computer Science Department tj@cs.cornell.edu http://www.joachims.org 0 Linear Classifiers Rules of the Form:
SIGIR 2003 Tutorial Support Vector and Kernel Methods Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Computer Science Department tj@cs.cornell.edu http://www.joachims.org 0 Linear Classifiers Rules of the Form:
The Perceptron algorithm
 The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization John Duchi, Elad Hanzan, Yoram Singer
 Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization John Duchi, Elad Hanzan, Yoram Singer Vicente L. Malave February 23, 2011 Outline Notation minimize a number of functions φ
Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization John Duchi, Elad Hanzan, Yoram Singer Vicente L. Malave February 23, 2011 Outline Notation minimize a number of functions φ
Learning by constraints and SVMs (2)
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#14 (Wednesday ctober 17) Learning by constraints and SVMs (2) Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Albert Wu 1 1 Support Vector Ranking Machine pening
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#14 (Wednesday ctober 17) Learning by constraints and SVMs (2) Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Albert Wu 1 1 Support Vector Ranking Machine pening
Introduction to Machine Learning
 1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms
 Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science & Engineering The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel {kobics,oferd,shais,singer}@cs.huji.ac.il
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science & Engineering The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel {kobics,oferd,shais,singer}@cs.huji.ac.il
Support Vector Machine & Its Applications
 Support Vector Machine & Its Applications A portion (1/3) of the slides are taken from Prof. Andrew Moore s SVM tutorial at http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials Mingyue Tan The University of British Columbia
Support Vector Machine & Its Applications A portion (1/3) of the slides are taken from Prof. Andrew Moore s SVM tutorial at http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials Mingyue Tan The University of British Columbia
Midterms. PAC Learning SVM Kernels+Boost Decision Trees. MultiClass CS446 Spring 17
 Midterms PAC Learning SVM Kernels+Boost Decision Trees 1 Grades are on a curve Midterms Will be available at the TA sessions this week Projects feedback has been sent. Recall that this is 25% of your grade!
Midterms PAC Learning SVM Kernels+Boost Decision Trees 1 Grades are on a curve Midterms Will be available at the TA sessions this week Projects feedback has been sent. Recall that this is 25% of your grade!
Lecture 11. Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines
 CS142: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Lecture 11 Instructor: Pedro Felzenszwalb Scribes: Dan Xiang, Tyler Dae Devlin Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines We continue our discussion of linear soft margin
CS142: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Lecture 11 Instructor: Pedro Felzenszwalb Scribes: Dan Xiang, Tyler Dae Devlin Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines We continue our discussion of linear soft margin
COMP 875 Announcements
 Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Algorithms other than SGD. CS6787 Lecture 10 Fall 2017
 Algorithms other than SGD CS6787 Lecture 10 Fall 2017 Machine learning is not just SGD Once a model is trained, we need to use it to classify new examples This inference task is not computed with SGD There
Algorithms other than SGD CS6787 Lecture 10 Fall 2017 Machine learning is not just SGD Once a model is trained, we need to use it to classify new examples This inference task is not computed with SGD There
Multiclass Classification
 Multiclass Classification David Rosenberg New York University March 7, 2017 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 March 7, 2017 1 / 52 Introduction Introduction David Rosenberg (New York University)
Multiclass Classification David Rosenberg New York University March 7, 2017 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 March 7, 2017 1 / 52 Introduction Introduction David Rosenberg (New York University)
1 [15 points] Frequent Itemsets Generation With Map-Reduce
![1 [15 points] Frequent Itemsets Generation With Map-Reduce 1 [15 points] Frequent Itemsets Generation With Map-Reduce](/thumbs/72/67172903.jpg) Data Mining Learning from Large Data Sets Final Exam Date: 15 August 2013 Time limit: 120 minutes Number of pages: 11 Maximum score: 100 points You can use the back of the pages if you run out of space.
Data Mining Learning from Large Data Sets Final Exam Date: 15 August 2013 Time limit: 120 minutes Number of pages: 11 Maximum score: 100 points You can use the back of the pages if you run out of space.
Soft-margin SVM can address linearly separable problems with outliers
 Non-linear Support Vector Machines Non-linearly separable problems Hard-margin SVM can address linearly separable problems Soft-margin SVM can address linearly separable problems with outliers Non-linearly
Non-linear Support Vector Machines Non-linearly separable problems Hard-margin SVM can address linearly separable problems Soft-margin SVM can address linearly separable problems with outliers Non-linearly
SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION
 SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION 1 Outline Basic terminology Features Training and validation Model selection Error and loss measures Statistical comparison Evaluation measures 2 Terminology
SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION 1 Outline Basic terminology Features Training and validation Model selection Error and loss measures Statistical comparison Evaluation measures 2 Terminology
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA
 Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 13, 2017 1 / 21 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP (Y X). Then, given an input x 0, we
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 13, 2017 1 / 21 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP (Y X). Then, given an input x 0, we
CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 2013
 CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 0. Personal info: Name: Student ID: E-mail address:. There should be 5 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet).. You can use any material you brought: any book,
CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 0. Personal info: Name: Student ID: E-mail address:. There should be 5 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet).. You can use any material you brought: any book,
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA
 Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 13, 2017 1 / 21 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP (Y X). Then, given an input x 0, we
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 13, 2017 1 / 21 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP (Y X). Then, given an input x 0, we
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 13. Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research
 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 13 Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research mohri@cims.nyu.edu Multi-Class Classification Mehryar Mohri - Introduction to Machine Learning page 2 Motivation
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 13 Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research mohri@cims.nyu.edu Multi-Class Classification Mehryar Mohri - Introduction to Machine Learning page 2 Motivation
10-701/ Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010
 10-701/15-781 Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam
10-701/15-781 Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam
Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent Léon Bottou leon@bottou.org Microsoft (since June) Summary i. Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. ii. The Tradeoffs of Large Scale Learning.
Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent Léon Bottou leon@bottou.org Microsoft (since June) Summary i. Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. ii. The Tradeoffs of Large Scale Learning.
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities. Kakade Announcements: Project Proposals: due this Friday!
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
2018 EE448, Big Data Mining, Lecture 4. (Part I) Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 2018 EE448, Big Data Mining, Lecture 4 Supervised Learning (Part I) Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://wnzhang.net http://wnzhang.net/teaching/ee448/index.html Content of Supervised Learning
2018 EE448, Big Data Mining, Lecture 4 Supervised Learning (Part I) Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://wnzhang.net http://wnzhang.net/teaching/ee448/index.html Content of Supervised Learning
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis
 Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 2 2013 Optional reading: ISL 4.1, 4.2, 4.4, ESL 4.1 4.3 1 Classification
Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 2 2013 Optional reading: ISL 4.1, 4.2, 4.4, ESL 4.1 4.3 1 Classification
Loss Functions, Decision Theory, and Linear Models
 Loss Functions, Decision Theory, and Linear Models CMSC 678 UMBC January 31 st, 2018 Some slides adapted from Hamed Pirsiavash Logistics Recap Piazza (ask & answer questions): https://piazza.com/umbc/spring2018/cmsc678
Loss Functions, Decision Theory, and Linear Models CMSC 678 UMBC January 31 st, 2018 Some slides adapted from Hamed Pirsiavash Logistics Recap Piazza (ask & answer questions): https://piazza.com/umbc/spring2018/cmsc678
Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning
 Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning International Conference on Machine Learning, 2014 Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu Tsinghua University, China 21 August 2015 Presented by: Kyle Ulrich Introduction Online
Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning International Conference on Machine Learning, 2014 Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu Tsinghua University, China 21 August 2015 Presented by: Kyle Ulrich Introduction Online
Exploiting Primal and Dual Sparsity for Extreme Classification 1
 Exploiting Primal and Dual Sparsity for Extreme Classification 1 Ian E.H. Yen Joint work with Xiangru Huang, Kai Zhong, Pradeep Ravikumar and Inderjit Dhillon Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon
Exploiting Primal and Dual Sparsity for Extreme Classification 1 Ian E.H. Yen Joint work with Xiangru Huang, Kai Zhong, Pradeep Ravikumar and Inderjit Dhillon Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon
Lecture #11: Classification & Logistic Regression
 Lecture #11: Classification & Logistic Regression CS 109A, STAT 121A, AC 209A: Data Science Weiwei Pan, Pavlos Protopapas, Kevin Rader Fall 2016 Harvard University 1 Announcements Midterm: will be graded
Lecture #11: Classification & Logistic Regression CS 109A, STAT 121A, AC 209A: Data Science Weiwei Pan, Pavlos Protopapas, Kevin Rader Fall 2016 Harvard University 1 Announcements Midterm: will be graded
Statistical Methods for NLP
 Statistical Methods for NLP Text Categorization, Support Vector Machines Sameer Maskey Announcement Reading Assignments Will be posted online tonight Homework 1 Assigned and available from the course website
Statistical Methods for NLP Text Categorization, Support Vector Machines Sameer Maskey Announcement Reading Assignments Will be posted online tonight Homework 1 Assigned and available from the course website
Efficient Bandit Algorithms for Online Multiclass Prediction
 Efficient Bandit Algorithms for Online Multiclass Prediction Sham Kakade, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Ambuj Tewari Presented By: Nakul Verma Motivation In many learning applications, true class labels are
Efficient Bandit Algorithms for Online Multiclass Prediction Sham Kakade, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Ambuj Tewari Presented By: Nakul Verma Motivation In many learning applications, true class labels are
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick
 SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning. Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
Factor Modeling for Advertisement Targeting
 Ye Chen 1, Michael Kapralov 2, Dmitry Pavlov 3, John F. Canny 4 1 ebay Inc, 2 Stanford University, 3 Yandex Labs, 4 UC Berkeley NIPS-2009 Presented by Miao Liu May 27, 2010 Introduction GaP model Sponsored
Ye Chen 1, Michael Kapralov 2, Dmitry Pavlov 3, John F. Canny 4 1 ebay Inc, 2 Stanford University, 3 Yandex Labs, 4 UC Berkeley NIPS-2009 Presented by Miao Liu May 27, 2010 Introduction GaP model Sponsored
2017 Fall ECE 692/599: Binary Representation Learning for Large Scale Visual Data
 2017 Fall ECE 692/599: Binary Representation Learning for Large Scale Visual Data Liu Liu Instructor: Dr. Hairong Qi University of Tennessee, Knoxville lliu25@vols.utk.edu September 21, 2017 Liu Liu (UTK)
2017 Fall ECE 692/599: Binary Representation Learning for Large Scale Visual Data Liu Liu Instructor: Dr. Hairong Qi University of Tennessee, Knoxville lliu25@vols.utk.edu September 21, 2017 Liu Liu (UTK)
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms
 Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms Tirgul 2 Part I November 2016 Reminder Domain set, X : the set of objects that we wish to label. Label set, Y : the set of possible labels. A prediction rule, h:
Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms Tirgul 2 Part I November 2016 Reminder Domain set, X : the set of objects that we wish to label. Label set, Y : the set of possible labels. A prediction rule, h:
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Machine Learning. Ludovic Samper. September 1st, Antidot. Ludovic Samper (Antidot) Machine Learning September 1st, / 77
 Machine Learning Ludovic Samper Antidot September 1st, 2015 Ludovic Samper (Antidot) Machine Learning September 1st, 2015 1 / 77 Antidot Software vendor since 1999 Paris, Lyon, Aix-en-Provence 45 employees
Machine Learning Ludovic Samper Antidot September 1st, 2015 Ludovic Samper (Antidot) Machine Learning September 1st, 2015 1 / 77 Antidot Software vendor since 1999 Paris, Lyon, Aix-en-Provence 45 employees
LIBOL: A Library for Online Learning Algorithms
 LIBOL: A Library for Online Learning Algorithms Version 0.3.0 Steven C.H. Hoi Other contributors: Jialei Wang, Peilin Zhao, Ji Wan School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore
LIBOL: A Library for Online Learning Algorithms Version 0.3.0 Steven C.H. Hoi Other contributors: Jialei Wang, Peilin Zhao, Ji Wan School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019)
 CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
Administration. CSCI567 Machine Learning (Fall 2018) Outline. Outline. HW5 is available, due on 11/18. Practice final will also be available soon.
 Administration CSCI567 Machine Learning Fall 2018 Prof. Haipeng Luo U of Southern California Nov 7, 2018 HW5 is available, due on 11/18. Practice final will also be available soon. Remaining weeks: 11/14,
Administration CSCI567 Machine Learning Fall 2018 Prof. Haipeng Luo U of Southern California Nov 7, 2018 HW5 is available, due on 11/18. Practice final will also be available soon. Remaining weeks: 11/14,
ML4NLP Multiclass Classification
 ML4NLP Multiclass Classification CS 590NLP Dan Goldwasser Purdue University dgoldwas@purdue.edu Social NLP Last week we discussed the speed-dates paper. Interesting perspective on NLP problems- Can we
ML4NLP Multiclass Classification CS 590NLP Dan Goldwasser Purdue University dgoldwas@purdue.edu Social NLP Last week we discussed the speed-dates paper. Interesting perspective on NLP problems- Can we
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
Conditional Random Field
 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions Corso di Elaborazione del Linguaggio Naturale Pisa, May, 2011 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions
Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions Corso di Elaborazione del Linguaggio Naturale Pisa, May, 2011 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions
A Unified Algorithmic Approach for Efficient Online Label Ranking
 A Unified Algorithmic Approach for Efficient Online Label Ranking Shai Shalev-Shwartz 1 and Yoram Singer 1,2 1 School of Computer Sci. & Eng., The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel 2 Google Inc.,
A Unified Algorithmic Approach for Efficient Online Label Ranking Shai Shalev-Shwartz 1 and Yoram Singer 1,2 1 School of Computer Sci. & Eng., The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel 2 Google Inc.,
Machine Learning, Fall 2012 Homework 2
 0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 202 Homework 2 Instructors: Tom Mitchell, Ziv Bar-Joseph TA in charge: Selen Uguroglu email: sugurogl@cs.cmu.edu SOLUTIONS Naive Bayes, 20 points Problem. Basic concepts, 0
0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 202 Homework 2 Instructors: Tom Mitchell, Ziv Bar-Joseph TA in charge: Selen Uguroglu email: sugurogl@cs.cmu.edu SOLUTIONS Naive Bayes, 20 points Problem. Basic concepts, 0
Non-linear Support Vector Machines
 Non-linear Support Vector Machines Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Non-linear Support Vector Machines Non-linearly separable problems Hard-margin SVM can address linearly separable
Non-linear Support Vector Machines Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Non-linear Support Vector Machines Non-linearly separable problems Hard-margin SVM can address linearly separable
Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference
 Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder December 12-14, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Unsupervised Naïve Bayes Last week
Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder December 12-14, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Unsupervised Naïve Bayes Last week
Training the linear classifier
 215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
Natural Language Processing (CSEP 517): Text Classification
 Natural Language Processing (CSEP 517): Text Classification Noah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu April 10, 2017 1 / 71 To-Do List Online quiz: due Sunday Read: Jurafsky
Natural Language Processing (CSEP 517): Text Classification Noah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu April 10, 2017 1 / 71 To-Do List Online quiz: due Sunday Read: Jurafsky
Text Mining. Dr. Yanjun Li. Associate Professor. Department of Computer and Information Sciences Fordham University
 Text Mining Dr. Yanjun Li Associate Professor Department of Computer and Information Sciences Fordham University Outline Introduction: Data Mining Part One: Text Mining Part Two: Preprocessing Text Data
Text Mining Dr. Yanjun Li Associate Professor Department of Computer and Information Sciences Fordham University Outline Introduction: Data Mining Part One: Text Mining Part Two: Preprocessing Text Data
Logistic Regression. Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor
 Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Gaussian Models
 Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA
 Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor, 10/12 Slide credits: Sergio Bacallado 1 / 1 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP
Lecture 9: Classification, LDA Reading: Chapter 4 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor, 10/12 Slide credits: Sergio Bacallado 1 / 1 Review: Main strategy in Chapter 4 Find an estimate ˆP
Asaf Bar Zvi Adi Hayat. Semantic Segmentation
 Asaf Bar Zvi Adi Hayat Semantic Segmentation Today s Topics Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN) (CVPR 2015) Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks (ICCV 2015) Gaussian Conditional random
Asaf Bar Zvi Adi Hayat Semantic Segmentation Today s Topics Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN) (CVPR 2015) Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks (ICCV 2015) Gaussian Conditional random
6.036: Midterm, Spring Solutions
 6.036: Midterm, Spring 2018 Solutions This is a closed book exam. Calculators not permitted. The problems are not necessarily in any order of difficulty. Record all your answers in the places provided.
6.036: Midterm, Spring 2018 Solutions This is a closed book exam. Calculators not permitted. The problems are not necessarily in any order of difficulty. Record all your answers in the places provided.
Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP
 CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms
 Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science & Engineering The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel {kobics,oferd,shais,singer}@cs.huji.ac.il
Online Passive-Aggressive Algorithms Koby Crammer Ofer Dekel Shai Shalev-Shwartz Yoram Singer School of Computer Science & Engineering The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904, Israel {kobics,oferd,shais,singer}@cs.huji.ac.il
Model Accuracy Measures
 Model Accuracy Measures Master in Bioinformatics UPF 2017-2018 Eduardo Eyras Computational Genomics Pompeu Fabra University - ICREA Barcelona, Spain Variables What we can measure (attributes) Hypotheses
Model Accuracy Measures Master in Bioinformatics UPF 2017-2018 Eduardo Eyras Computational Genomics Pompeu Fabra University - ICREA Barcelona, Spain Variables What we can measure (attributes) Hypotheses
Maximum Margin Matrix Factorization for Collaborative Ranking
 Maximum Margin Matrix Factorization for Collaborative Ranking Joint work with Quoc Le, Alexandros Karatzoglou and Markus Weimer Alexander J. Smola sml.nicta.com.au Statistical Machine Learning Program
Maximum Margin Matrix Factorization for Collaborative Ranking Joint work with Quoc Le, Alexandros Karatzoglou and Markus Weimer Alexander J. Smola sml.nicta.com.au Statistical Machine Learning Program
4.1 Online Convex Optimization
 CS/CNS/EE 53: Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Topic: Online Convex Optimization and Online SVM Lecturer: Daniel Golovin Scribe: Xiaodi Hou Date: Jan 3, 4. Online Convex Optimization Definition 4..
CS/CNS/EE 53: Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Topic: Online Convex Optimization and Online SVM Lecturer: Daniel Golovin Scribe: Xiaodi Hou Date: Jan 3, 4. Online Convex Optimization Definition 4..
Linear Classifiers IV
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Linear Classifiers IV Blaine Nelson, Tobias Scheffer Contents Classification Problem Bayesian Classifier Decision Linear Classifiers, MAP Models Logistic
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Linear Classifiers IV Blaine Nelson, Tobias Scheffer Contents Classification Problem Bayesian Classifier Decision Linear Classifiers, MAP Models Logistic
Support Vector Machines. CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Support Vector Machines CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Support Vector Machines CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
Classification: Analyzing Sentiment
 Classification: Analyzing Sentiment STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 17, 2018 Predicting sentiment by topic: An intelligent restaurant review system 1 4/16/18 It
Classification: Analyzing Sentiment STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 17, 2018 Predicting sentiment by topic: An intelligent restaurant review system 1 4/16/18 It
Errors, and What to Do. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall What to Do About Errors. Later On. Some (Simplified) Biology
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
Mark your answers ON THE EXAM ITSELF. If you are not sure of your answer you may wish to provide a brief explanation.
 CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds
 Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds 1 Introduction December 11, 2009 Steven Wu RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is a family of data formats used to publish frequently updated works. RSS
Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds 1 Introduction December 11, 2009 Steven Wu RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is a family of data formats used to publish frequently updated works. RSS
6.036 midterm review. Wednesday, March 18, 15
 6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
Multi-Class Confidence Weighted Algorithms
 Multi-Class Confidence Weighted Algorithms Koby Crammer Department of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 19104 Mark Dredze Alex Kulesza Human Language Technology
Multi-Class Confidence Weighted Algorithms Koby Crammer Department of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 19104 Mark Dredze Alex Kulesza Human Language Technology
Statistics and learning: Big Data
 Statistics and learning: Big Data Learning Decision Trees and an Introduction to Boosting Sébastien Gadat Toulouse School of Economics February 2017 S. Gadat (TSE) SAD 2013 1 / 30 Keywords Decision trees
Statistics and learning: Big Data Learning Decision Trees and an Introduction to Boosting Sébastien Gadat Toulouse School of Economics February 2017 S. Gadat (TSE) SAD 2013 1 / 30 Keywords Decision trees
Logistic Regression. Advanced Methods for Data Analysis (36-402/36-608) Spring 2014
 Logistic Regression Advanced Methods for Data Analysis (36-402/36-608 Spring 204 Classification. Introduction to classification Classification, like regression, is a predictive task, but one in which the
Logistic Regression Advanced Methods for Data Analysis (36-402/36-608 Spring 204 Classification. Introduction to classification Classification, like regression, is a predictive task, but one in which the
Text Classification. Jason Rennie
 Text Classification Jason Rennie jrennie@ai.mit.edu 1 Text Classification Assign text document a label based on content. Examples: E-mail filtering Knowedge-base creation E-commerce Question Answering
Text Classification Jason Rennie jrennie@ai.mit.edu 1 Text Classification Assign text document a label based on content. Examples: E-mail filtering Knowedge-base creation E-commerce Question Answering
OPTIMIZING SEARCH ENGINES USING CLICKTHROUGH DATA. Paper By: Thorsten Joachims (Cornell University) Presented By: Roy Levin (Technion)
 OPTIMIZING SEARCH ENGINES USING CLICKTHROUGH DATA Paper By: Thorsten Joachims (Cornell University) Presented By: Roy Levin (Technion) Outline The idea The model Learning a ranking function Experimental
OPTIMIZING SEARCH ENGINES USING CLICKTHROUGH DATA Paper By: Thorsten Joachims (Cornell University) Presented By: Roy Levin (Technion) Outline The idea The model Learning a ranking function Experimental
