Error Analysis in Laser Vibrometer Measurements of Lamb Waves
|
|
|
- Johnathan Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - Th.3.D.4 More info about this article: Error Analysis in Laser Vibrometer Measurements of Lamb Waves M. N. NEUMANN and R. LAMMERING ABSTRACT Lamb waves are widely employed for structural health monitoring in thin plate structures by interpreting their interaction with damages. For the observation of Lamb waves, scanning laser vibrometry is a common technique providing spatial and temporal information on the wave field. One-dimensional scanning vibrometry, due to its lower costs, is more spread than 3D vibrometry, but generates systematic errors uring oblique-angled vibrations. This is owing to the physical principle of the technique: The directly ured value is the projection of the actual vibration velocity vector to the laser beam containing no information on the direction, hence, any angle other than ero between beam and velocity vector produces a significant error, which, with knowledge of the angle, may be corrected afterwards. Measuring lamb wave fields, the velocity vector rotates with the angular frequency of the excitation. For transient experiments on finite-sie plates, the actual angle is undetermined. Thus, the induced error is not correctable. In addition to the error in amplitude, the association of phase and vibration direction induces an error concerning the observed phase velocity and hence a seeming phase shift. The quantity of both, amplitude and phase error is shown and a workaround to avoid them is deduced. Three-dimensional data sets are, of course, free of the mentioned errors, so a method to perform 3D-Scans employing D-hardware is deduced and presented. INTRODUCTION Ultrasonic Lamb waves are a promising phenomenon for Structural Health Monitoring purposes for their visible interaction with discontinuities in thin-walled structures. After excitation by, for example, a pieoceramic wafer under alternating Mirko Nikolaj Neumann, Rolf Lammering Helmut-Schmidt-Universität, Universität der Bundeswehr Hamburg Fakultät für Maschinenbau, Institut für Mechanik Holstenhofweg 85, D-43 Hamburg mirko.neumann@hsu-hh.de License:
2 current, the wavefield is disturbed at locations of structural inhomogeneities, as damages. A common method for quasi-continuous observation in both time and space is scanning laser vibrometry, quickly providing experimental results without retroaction to the structure. For many applications, like vibrations of two-dimensional structures, one-dimensionally working equipment does fine. Three-dimensional devices come along with vastly higher costs, why most researchers are bound to employ standard-, one-dimensional vibrometers. The severe disadvantage is that the trajectories of Lamb waves are no straight oscillations but the material points move in ellipses. These are far from comparability to straight, thus correct information on particle motion and the resulting wave fields can only be obtained performing 3D-experiments. This work deduces the caused errors both in time and phase quantitavely and presents a workaround to obtained three-dimensional information employing onedimensional equipment. ONE-DIMENSIONAL OBSERVATION OF OBLIQUE-ANGLED MOTION Laser vibrometry Laser (Doppler-) vibrometry ures oscillation velocities along the laser beam by means of the optical Doppler shift. The split up laser beam is partly projected to the object and recombined with the reference beam on an interferometer. The resulting beat frequency is ured and directly proportional to the signless oscillation velocity. The sign is reproduced by shifting the reference beam s frequency through a bragg cell, cf. []. Scanning vibrometers repeat the urement at all defined grid points. At each point the experiment is repeated with unchanged parameters and all single time series are combined to a video-like representation of the data, discretised by sampling frequency and grid increments. Axis-parallel oscillation Conventional (D-) scanning vibrometers work under the assumption of motion parallel to the non-deflected urement beam, which may be considered the -axis. This way, the only component of an oscillator s velocity vector is v v v. Since vibrometers generally ure the velocity component in the beam direction the projection of the velocity vector to the beam (angle α) the caused error can be compensated via v d v cos, cf. Figure, left.
3 Figure : Axis-parallel (left) and oblique-angled oscillation (right, angle β) under observation by a deflected urement beam (angle α) Oblique-angled oscillation For oscillations not parallel, but under some arbitrary angle to the -axis (angle β, see figure right), the above mentioned error compensation cannot work properly. Again, the ured velocity is the projection of the velocity vector to the beam, i.e. v vcos. The angle compensation of the used vibrometry software gives the value v, v cos, while the correct out-of-plane velocity is v vcos. ind This yields the relative error factor vind, cos tan tan. () v coscos Clearly for at least one angle equal ero, either vertical laser beam or oscillation, there is no error. For any angle equal 9, the error becomes infinite. For technical reasons, α can not be 9, whereas β, in the case of elliptic trajectories of particle motion, reaches ±9 twice every period. The error may be decreased by deactivating angle-compensating ures, then it becomes v cos () v cos This results in a somewhat smaller error, which is nevertheless of inacceptable quantity making the results unsuitable for quantitative evaluation. OBSERVATION OF LAMB WAVES USING D-VIBROMETRY With the oscillators (material points) travelling along the mentioned elliptic trajectories, the angle β (movement direction) is no longer constant but time-variant. Lamb waves, simplified plate wave approach To keep things short, Lamb waves deduced from mathematics of continuum mechanics will be skipped here. See, e.g., [3] for detailed explanations. 3
4 Not considering the investigated structure as a three-dimensional continuum but modeling it as a (Kirchhoff-) plate for flexural waves (analogue to A Lamb waves) and as a plate under plane stress for pressure waves (analogue to S Lamb waves) simplifies the proceeding significantly. The simplification gives very good results for low frequencies, which are the technically most relevant ones. Phase velocities of the flexural waves c F and of the pressure wave c P are then determined by cf E 4 h and E cp (5) with plate thickness h, Young s modulus E, density ρ and the Poisson ratio ν at an angular frequency ω. Detailed derivations of (5) may be found e.g. in [4]. The displacement (u and w for for displacements in x- and -direction, cf. Figure ) field of such waves (travelling in positive x-direction) at the upper (urable) plate surface is described by uf hw F kcost kx, (6) wf w Fsint kx, (7) up upcost kx and (8) wp h k up sin t kx. (9) Figure : Elliptical trajectory of particle motion for orthogonal and oblique-angled urement The ratios of out-of-plane- to in-plane-amplitude, i.e., the ellipses shapes, can so be determined as w hk and () u F w u hk P. () Phase shift errors in D vibrometer scans The displacement velocity vector field of plate waves is the time derivative of equations (6-9): uf t hkw F sin t kx, () The negative sign for equation (9) results from the clockwise spin direction of symmetric Lamb waves here. 4
5 wf t w F cost kx, (3) u t u t kx and (4) P P sin wp t hk u P cos t kx. (5) The ured signal reaches ero when oscillation and laser beam are orthogonal to each other: vl ( ). Here, u t sin v and l, (6) w t cos where, after normaliing both vectors to vx / v sin ev and el, (7) v / cos v orthogonality is expressed as negative, reciprocal slope, e x el. e e (8) lx ωt is separated from one scalar component of (8). The conclusion t t (see Figure ) yields the shift in phase of actual to ured out-of-plane displacement (velocity) field x t arccos cos cos t phase Knowing that allows the more illustrative expression w u xphase cos arccos 4 cos w u.. (9) () Figure 3: Relative phase (left) and amplitude error (right) wrongly observed with D scanning vibrometry plotted over scanning angle α. Solid: Symmetric modes, dash-dotted: antisymmetric modes. Grey: Active software-sided angle compensation. 5
6 The relative phase shift () is plotted over the scanning angle α in Figure 3 left. It is obvious that ured symmetric waves are weighted by enormous phase errors (up to about a quarter wavelength), while the influence on antisymmetric wave observation is relatively small within the technically relevant angles (up to about 5 ). Amplitude errors observing Lamb waves with D-vibrometry The error quantity of out-of-plane oscillations ured with an oblique-angled laser beam is described by (), respectively (). With the rotating oscillation vector of waves, this error reaches infinity twice per period and is hence not very useful for a description in this matter. A comparison of the actual amplitude ˆv and the ured amplitude v ˆ of the velocities is more helpful. The ured quantity is the projection of the displacement velocity vector to the laser beam: v ve () l u sin t sin cos cos w t () u sin tsin wcostcos (3) The sought extremum is found at the root of both partial derivatives v t u costsin w sin tcos and (4) v u sin tcos w costsin (5) yielding ωt=α. Hence, the ured amplitude ˆv v t (6) u sin wcos. (7) The error factor is the quotient of (7) and the actual out-of-plane velocity v ˆ : u w converging to for α=9 vˆ u vˆ w sin cos, (8) Figure 3, right hand side, depicts the relative amplitude error plotted over the scanning angle α, evincing the enlarged error quantity diverging to infinity with active vibrometer-sided angle compensation described by Vibrometric area scans vˆ,ind u vˆ cos sin cos w (9) The most common application for scanning vibrometry is the scanning of areal surfaces. In this case the waves are not generally travelling towards or away from the point of normality between surface and laser beam. The distribution of phase- and amplitude errors for a specific experiment is shown in figure 4. The experiment was repeated with identical parameters: Transient excitation of waves at the center of a quadratic plate. 6
7 The first urement (right) was made with a vertically mounted scanning head the error is distributed uniformly outwards from the wave source and hence not visible. The second urement was performed with the scanning head on a tripod, the nondeflected laser beam at a degree of about 45 to the plate surface. The amplitude error is larger and clearly variable with respect to the area. The phase shift is large and changes sign at the black sketched lines, where the influence of the in-plane velocity component on the ured signal vanishes: v e, cf. eqs. () to (3). l Figure 4: Out-of-plane velocity field from D urement of transiently excited Lamb waves in a plate. Left: Undeflected laser beam orthogonal to plate surface. Right: Undeflected beam 45 to plate surface. AVOIDANCE OF SYSTEMATIC ERRORS OBSERVING OBLIQUE- ANGLED OSCILLATIONS The formerly discussed errors can be critical, when quantitative data is needed for runtime urements, comparison to computationally obtained data and other purposes. One option to obtain correct data is single-point-uring with a vertical urement beam, not allowing area scans. 3D scanning vibrometry avoids the problems by producing data in a cartesian system, clearly separating the components in different spatial directions. Because commercial 3D vibrometer systems are connected to about triple the costs of standard D systems, many researchers are bound to the latter. An approach requiring a higher time effort but keeping the investment in equipment short, is the combination of three independent D scans from different directions into the sought 3D wave field. A comprehensive description of such a technique is given in [5]. Figure 5 shows the actual fields of view of three D scans, all of them observing the same, repeated experiment from different directions. Figure 5: Views of a scanned area from different uring directions 7
8 Surface plots of the separate Cartesian components resulting from the transformation of these urements are given in Figure 6. Figure 6: Snapshots of x-, y- and displacement field of Lamb waves after transient excitation. CONCLUSIONS The paper shows systematic urement errors, which generally occur in observation of oblique-angled oscillations with D scanning laser vibrometry. The errors were quantified and, with special focus on Lamb waves, different error qualities for amplitude and phase, deduced and also determined in sie. Knowledge about these error influences on experimentally obtained data can help understanding deviations between simulation and experiment. Subjective errors in past comparisons of both can possibly be neglected afterwards. For future wave or oscillation in general observation a deliberate decision whether the precision of 3D scanning is necessary or not, can be made and, if so, a workaround for 3D scanning with D equipment (see[5]) can be employed. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The financial support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft is gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES. Axel Donges and Reinhard Noll. Lasermeßtechnik: Grundlagen und Anwendungen. Hüthig Buch Verlag GmbH, Heidelberg, Horace Lamb. On waves in an elastic plate. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, Vol. XCIII, pages 4 8, Karl F. Graff. Wave Motion in Elastic Solids. Oxford University Press, 975. Dover edition, Dover Publications, Inc., New York, Victor Giurgiutiu. Structural health monitoring with pieoelectric wafer active sensors. Elsevier Inc., Burlington, USA, Mirko Nikolaj Neumann, Bianca Hennings, and Rolf Lammering (). Identification and avoidance of systematic urement errors in Lamb wave observation with d scanning laser vibrometry. Manuscript submitted for publication. 8
QUASI-CONTINUOUS MODE CONVERSION OF LAMB WAVES IN CFRP PLATES DUE TO INHOMOGENEITY ON MICRO AND MESO SCALE
 7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 8-11, 2014. La Cité, Nantes, France More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17216 QUASI-CONTINUOUS MODE CONVERSION OF LAMB WAVES IN
7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 8-11, 2014. La Cité, Nantes, France More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17216 QUASI-CONTINUOUS MODE CONVERSION OF LAMB WAVES IN
Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Testing Identifying Defects per Scanning Laser Vibrometry Application Note
 Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Testing Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Testing Identifying Defects per Scanning Laser Vibrometry Application Note 2 Structural Damage in Components
Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Testing Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Testing Identifying Defects per Scanning Laser Vibrometry Application Note 2 Structural Damage in Components
ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE DETECTION USING THE TIME REVERSAL PRINCIPLE ON DISPERSIVE WAVES IN BEAMS
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE DETECTION USING THE TIME REVERSAL PRINCIPLE ON DISPERSIVE WAVES IN BEAMS ERNST ROBERT 1,DUAL JURG 1 1 Institute of Mechanical Systems, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, ETH
ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE DETECTION USING THE TIME REVERSAL PRINCIPLE ON DISPERSIVE WAVES IN BEAMS ERNST ROBERT 1,DUAL JURG 1 1 Institute of Mechanical Systems, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, ETH
Lamb Wave Propagation Modeling Using Cellular Automata
 6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - We.3.E.2 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=14171 Lamb Wave Propagation Modeling Using Cellular Automata P. KLUSKA 1, W. J. STASZEWSKI
6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - We.3.E.2 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=14171 Lamb Wave Propagation Modeling Using Cellular Automata P. KLUSKA 1, W. J. STASZEWSKI
Simulation of Piezoelectric Induced Lamb Waves in Plates
 Simulation of Piezoelectric Induced Lamb Waves in Plates C. WILLBERG, J. M. VIVAR-PEREZ, Z. AHMAD and U. GABBERT ABSTRACT The use of Lamb waves for damage detection and non-destructive evaluation have
Simulation of Piezoelectric Induced Lamb Waves in Plates C. WILLBERG, J. M. VIVAR-PEREZ, Z. AHMAD and U. GABBERT ABSTRACT The use of Lamb waves for damage detection and non-destructive evaluation have
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
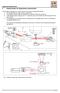 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia
 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia August 2007 Written Comprehensive Exam Day 1 This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. You may use a calculator, but only for arithmetic functions
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia August 2007 Written Comprehensive Exam Day 1 This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. You may use a calculator, but only for arithmetic functions
7.2.1 Seismic waves. Waves in a mass- spring system
 7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
Analytically based time-reversal technique for damage localization and characterization in laminate composite structures
 8th European Workshop On Structural Health Monitoring (EWSHM 2016), 5-8 July 2016, Spain, Bilbao www.ndt.net/app.ewshm2016 Analytically based time-reversal technique for damage localization and characterization
8th European Workshop On Structural Health Monitoring (EWSHM 2016), 5-8 July 2016, Spain, Bilbao www.ndt.net/app.ewshm2016 Analytically based time-reversal technique for damage localization and characterization
Physical and Biological Properties of Agricultural Products Acoustic, Electrical and Optical Properties and Biochemical Property
 Physical and Biological Properties of Agricultural Products Acoustic, Electrical and Optical Properties and Biochemical Property 1. Acoustic and Vibrational Properties 1.1 Acoustics and Vibration Engineering
Physical and Biological Properties of Agricultural Products Acoustic, Electrical and Optical Properties and Biochemical Property 1. Acoustic and Vibrational Properties 1.1 Acoustics and Vibration Engineering
(Refer Slide Time: 1: 19)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations
 An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University November 3, 2015 1 Introduction Ideally, the atoms in a crystal are positioned in a regular manner following
An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University November 3, 2015 1 Introduction Ideally, the atoms in a crystal are positioned in a regular manner following
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Physics Letters A.
 Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS OF A HIGH POWER ULTRASONIC SYSTEM USED IN ELECTRODISCHARGE MACHINING
 Nonconventional Technologies Review Romania, March, 2012 2012 Romanian Association of Nonconventional Technologies DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS OF A HIGH POWER ULTRASONIC SYSTEM USED IN ELECTRODISCHARGE MACHINING
Nonconventional Technologies Review Romania, March, 2012 2012 Romanian Association of Nonconventional Technologies DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS OF A HIGH POWER ULTRASONIC SYSTEM USED IN ELECTRODISCHARGE MACHINING
Compensation-based non-destructive automatic quality control using acoustic methods
 Compensation-based non-destructive automatic quality control using acoustic methods Abstract Keywords Ingolf Hertlin RTE Akustik + Prüftechnik GmbH Gewerbestr. 26, D-76327 Pfinztal, Germany www.rte.de
Compensation-based non-destructive automatic quality control using acoustic methods Abstract Keywords Ingolf Hertlin RTE Akustik + Prüftechnik GmbH Gewerbestr. 26, D-76327 Pfinztal, Germany www.rte.de
Characterization of MEMS Devices
 MEMS: Characterization Characterization of MEMS Devices Prasanna S. Gandhi Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, Recap Fabrication of MEMS Conventional
MEMS: Characterization Characterization of MEMS Devices Prasanna S. Gandhi Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, Recap Fabrication of MEMS Conventional
 J. Luis Deán, José L. Fernández, Ángel F. Doval and Cristina Trillo, "Measurement of Lamb waves dispersion curves under narrowband monomode excitation using TV holography," Proc. SPIE 6341, "Speckle06:
J. Luis Deán, José L. Fernández, Ángel F. Doval and Cristina Trillo, "Measurement of Lamb waves dispersion curves under narrowband monomode excitation using TV holography," Proc. SPIE 6341, "Speckle06:
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Table of Contents. Preface... 13
 Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave
 433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems
 Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics
 Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
Lamb Wave Behavior in Bridge Girder Geometries
 Lamb Wave Behavior in Bridge Girder Geometries I. J. Oppenheim a*, D. W. Greve b, N. L. Tyson a a Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 b Dept.
Lamb Wave Behavior in Bridge Girder Geometries I. J. Oppenheim a*, D. W. Greve b, N. L. Tyson a a Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 b Dept.
Using the irrotational part of the structural intensity to identify sources of vibrational energy
 Sound Intensity and Inverse Methods in Acoustics: Paper ICA-8 Using the irrotational part of the structural intensity to identify sources of vibrational energy N.B. Roozen (a), C. Glorieux (a), J.-L. Guyader
Sound Intensity and Inverse Methods in Acoustics: Paper ICA-8 Using the irrotational part of the structural intensity to identify sources of vibrational energy N.B. Roozen (a), C. Glorieux (a), J.-L. Guyader
CFRP Bonds Evaluation Using Piezoelectric Transducer
 4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Th.1.B.2 CFRP Bonds Evaluation Using Piezoelectric Transducer Paweł MALINOWSKI*, Łukasz SKARBEK*, Tomasz WANDOWSKI*, Wiesław OSTACHOWICZ* * Institute
4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Th.1.B.2 CFRP Bonds Evaluation Using Piezoelectric Transducer Paweł MALINOWSKI*, Łukasz SKARBEK*, Tomasz WANDOWSKI*, Wiesław OSTACHOWICZ* * Institute
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS WAVES IN THE OCEANS. Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany
 WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
Physics I Keystone Institute Technology & Management Unit-II
 Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
2 u 1-D: 3-D: x + 2 u
 c 2013 C.S. Casari - Politecnico di Milano - Introduction to Nanoscience 2013-14 Onde 1 1 Waves 1.1 wave propagation 1.1.1 field Field: a physical quantity (measurable, at least in principle) function
c 2013 C.S. Casari - Politecnico di Milano - Introduction to Nanoscience 2013-14 Onde 1 1 Waves 1.1 wave propagation 1.1.1 field Field: a physical quantity (measurable, at least in principle) function
Characterization of MEMS Devices
 MEMS: Characterization Characterization of MEMS Devices Prasanna S. Gandhi Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, Recap Characterization of MEMS
MEMS: Characterization Characterization of MEMS Devices Prasanna S. Gandhi Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, Recap Characterization of MEMS
and the radiation from source 2 has the form. The vector r points from the origin to the point P. What will the net electric field be at point P?
 Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation)
 Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation) P.E.G. Baird MT2011 Electro-optic modulation of light An electro-optic crystal is essentially a variable phase plate and as such can be used either
Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation) P.E.G. Baird MT2011 Electro-optic modulation of light An electro-optic crystal is essentially a variable phase plate and as such can be used either
Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures
 Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures Zacarias E. Fabrim PGCIMAT, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Wang Chong, Manoel Martín Pérez Reimbold DeTec, UNIJUI, Ijuí, RS, Brazil Abstract This
Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures Zacarias E. Fabrim PGCIMAT, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Wang Chong, Manoel Martín Pérez Reimbold DeTec, UNIJUI, Ijuí, RS, Brazil Abstract This
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
Electromechanical Impedance Technique and Scanning Vibrometry for Structure Characterization
 6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - Tu.2.C.4 Electromechanical Impedance Technique and Scanning Vibrometry for Structure Characterization L. SKARBEK, T. WANDOWSKI, S. OPOKA, P. MALINOWSKI
6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - Tu.2.C.4 Electromechanical Impedance Technique and Scanning Vibrometry for Structure Characterization L. SKARBEK, T. WANDOWSKI, S. OPOKA, P. MALINOWSKI
Multiple Defect Detection by Applying the Time Reversal Principle on Dispersive Waves in Beams
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Multiple Defect Detection by Applying the Time Reversal Principle on Dispersive Waves in Beams Robert ERNST 1, Mario
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Multiple Defect Detection by Applying the Time Reversal Principle on Dispersive Waves in Beams Robert ERNST 1, Mario
Lecture 5: Polarization. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Outline
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring
 Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring F. Dreier, P. Günther, T. Pfister, J. Czarske, Technische Universität Dresden, Laboratory for Measuring and
Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring F. Dreier, P. Günther, T. Pfister, J. Czarske, Technische Universität Dresden, Laboratory for Measuring and
TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
 Paths of Discovery Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Acta 18, Vatican City 2006 www.pas.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/acta18/acta18-moshinsky.pdf TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
Paths of Discovery Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Acta 18, Vatican City 2006 www.pas.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/acta18/acta18-moshinsky.pdf TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
Scale factor characteristics of laser gyroscopes of different sizes
 Scale factor characteristics of laser gyroscopes of different sizes Zhenfang Fan, Guangfeng Lu, Shomin Hu, Zhiguo Wang and Hui Luo a) National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, Hunan 410073,
Scale factor characteristics of laser gyroscopes of different sizes Zhenfang Fan, Guangfeng Lu, Shomin Hu, Zhiguo Wang and Hui Luo a) National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, Hunan 410073,
Influence of the cover plate thickness on the Lamb wave propagation in honeycomb sandwich panels
 CEA Aeronaut J (2013) 4:69 76 DOI 10.1007/s13272-012-0054-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Influence of the cover plate thickness on the Lamb wave propagation in honeycomb sandwich panels. M. H. Hosseini U. Gabbert R.
CEA Aeronaut J (2013) 4:69 76 DOI 10.1007/s13272-012-0054-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Influence of the cover plate thickness on the Lamb wave propagation in honeycomb sandwich panels. M. H. Hosseini U. Gabbert R.
Dispersion Relations in Plate Structures Studied with a Scanning Laser Vibrometer
 ECNDT 2006 - Mo.2.1.4 Dispersion Relations in Plate Structures Studied with a Scanning Laser Vibrometer Bernd KÖHLER, Fraunhofer Institute for Non-Destructive Testing, Dresden, Germany Abstract. Scanning
ECNDT 2006 - Mo.2.1.4 Dispersion Relations in Plate Structures Studied with a Scanning Laser Vibrometer Bernd KÖHLER, Fraunhofer Institute for Non-Destructive Testing, Dresden, Germany Abstract. Scanning
AN ANALYSIS OF ULTRASONIC WAVE GENERATED BY OBLIQUE INCIDENCE OF LASER
 International Symposium on Structural Health Monitoring and Nondestructive Testing 4-5 October 2018, Saarbruecken, Germany More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23511 http://www.ndt.net/?id=23551
International Symposium on Structural Health Monitoring and Nondestructive Testing 4-5 October 2018, Saarbruecken, Germany More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23511 http://www.ndt.net/?id=23551
CALCULATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD IN THE END WINDING REGION OF UNSATURATED ELECTRICAL MACHINES WITH SMALL AIR-GAP
 ISEF 2005 - XII International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering Baiona, Spain, September 15-17, 2005 CALCULATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD IN THE END
ISEF 2005 - XII International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering Baiona, Spain, September 15-17, 2005 CALCULATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD IN THE END
Nanoscale shift of the intensity distribution of dipole radiation
 Shu et al. Vol. 26, No. 2/ February 2009/ J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 395 Nanoscale shift of the intensity distribution of dipole radiation Jie Shu, Xin Li, and Henk F. Arnoldus* Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Shu et al. Vol. 26, No. 2/ February 2009/ J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 395 Nanoscale shift of the intensity distribution of dipole radiation Jie Shu, Xin Li, and Henk F. Arnoldus* Department of Physics and Astronomy,
THE REFLECTION PHENOMENA OF SV-WAVES IN A GENERALIZED THERMOELASTIC MEDIUM
 Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. Vol., No. 8 () 59 56 S67 Hindawi Publishing Corp. THE REFLECTION PHENOMENA OF SV-WAVES IN A GENERALIZED THERMOELASTIC MEDIUM ABO-EL-NOUR N. ABD-ALLA and AMIRA A. S. AL-DAWY
Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. Vol., No. 8 () 59 56 S67 Hindawi Publishing Corp. THE REFLECTION PHENOMENA OF SV-WAVES IN A GENERALIZED THERMOELASTIC MEDIUM ABO-EL-NOUR N. ABD-ALLA and AMIRA A. S. AL-DAWY
Application of Normal Mode Expansion to AE Waves in Finite Plates1
 Application of Normal Mode Expansion to AE Waves in Finite Plates1 M. R. Gorman2 and W. H. Prosser3 INTRODUCTION Breckenridge et al. (1975), Hsu (1985) and Pao (1978) adapted approaches from seismology
Application of Normal Mode Expansion to AE Waves in Finite Plates1 M. R. Gorman2 and W. H. Prosser3 INTRODUCTION Breckenridge et al. (1975), Hsu (1985) and Pao (1978) adapted approaches from seismology
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 09 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Inhomogeneous Plasma (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Today, I
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 09 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Inhomogeneous Plasma (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Today, I
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION
 17 Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION 3.1 Fundamental Poisson Equation The simplest version of the frictionless laminated model was originally introduced in 1961 by Salamon, and more recently explored
17 Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION 3.1 Fundamental Poisson Equation The simplest version of the frictionless laminated model was originally introduced in 1961 by Salamon, and more recently explored
Studies of Sound Radiation From Beams with Acoustic Black Holes
 Studies of Sound Radiation From Beams with Acoustic Black Holes Chenhui Zhao 1, M.G. Prasad 2 Stevens Institute of Technology Abstract: Recently, Acoustic Black Holes (), a new passive structural modification
Studies of Sound Radiation From Beams with Acoustic Black Holes Chenhui Zhao 1, M.G. Prasad 2 Stevens Institute of Technology Abstract: Recently, Acoustic Black Holes (), a new passive structural modification
General elastic beam with an elastic foundation
 General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
Lamb Waves in Plate Girder Geometries
 Lamb Waves in Plate Girder Geometries D.W. Greve, 1 N. L. Tyson 2, and I.J. Oppenheim 2 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 15213 2 Civil and Environmental
Lamb Waves in Plate Girder Geometries D.W. Greve, 1 N. L. Tyson 2, and I.J. Oppenheim 2 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 15213 2 Civil and Environmental
Acoustic Emission Source Identification in Pipes Using Finite Element Analysis
 31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Fr.3.B.2 Acoustic Emission Source Identification in Pipes Using Finite Element Analysis Judith ABOLLE OKOYEAGU*, Javier PALACIO
31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Fr.3.B.2 Acoustic Emission Source Identification in Pipes Using Finite Element Analysis Judith ABOLLE OKOYEAGU*, Javier PALACIO
Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis
 Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis M-F. Dandine a, D. Necsulescu b LPMI Laboratoire M.I., ENSAM, 2 bd du Ronceray, 49035 Angers, France a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis M-F. Dandine a, D. Necsulescu b LPMI Laboratoire M.I., ENSAM, 2 bd du Ronceray, 49035 Angers, France a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem
 Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem F. F. Mende http://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.html mende_fedor@mail.ru Abstract Huygens principle is the basic postulate of geometric
Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem F. F. Mende http://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.html mende_fedor@mail.ru Abstract Huygens principle is the basic postulate of geometric
ON THE FREE VIBRATION OF PLATES
 ON THE FREE VIBRATION OF PLATES PACS REFERENCE: 4.40.Dx Nieves, F.J. 1 ; Bayón, A. ; Gascón, F. 1) ETS de Arquitectura, niversidad de Sevilla, Reina Mercedes,, 4101 Sevilla, Spain. Tel 4 95455667, Fax
ON THE FREE VIBRATION OF PLATES PACS REFERENCE: 4.40.Dx Nieves, F.J. 1 ; Bayón, A. ; Gascón, F. 1) ETS de Arquitectura, niversidad de Sevilla, Reina Mercedes,, 4101 Sevilla, Spain. Tel 4 95455667, Fax
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity. We ll start with optics. The one-dimensional wave equation. What is a wave? Optional optics texts: f(x)
 We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation
 Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation By Jennifer Hay, Nanomechanics, Inc. Abstract This application note teaches the theory and practice of measuring the complex modulus
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation By Jennifer Hay, Nanomechanics, Inc. Abstract This application note teaches the theory and practice of measuring the complex modulus
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
NV-TECH-Design: Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for structural dynamics testing
 NV-TECH-Design: Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for structural dynamics testing NV-TECH-Design Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) für structural testing. Patent number: DE 10 2015 110 597.7 Description
NV-TECH-Design: Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for structural dynamics testing NV-TECH-Design Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) für structural testing. Patent number: DE 10 2015 110 597.7 Description
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics for Aerodynamics B-: Flow Field Representations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics for Aerodynamics B-: Flow Field Representations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis
ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL PROTOTYPING IN ANSYS: A VERIFICATION EXPERIMENT
 ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL PROTOTYPING IN ANSYS: A VERIFICATION EXPERIMENT Ing. Gergely TAKÁCS, PhD.* * Institute of Automation, Measurement and Applied Informatics Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Slovak
ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL PROTOTYPING IN ANSYS: A VERIFICATION EXPERIMENT Ing. Gergely TAKÁCS, PhD.* * Institute of Automation, Measurement and Applied Informatics Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Slovak
NORMAL MODES, WAVE MOTION AND THE WAVE EQUATION. Professor G.G.Ross. Oxford University Hilary Term 2009
 NORMAL MODES, WAVE MOTION AND THE WAVE EQUATION Professor G.G.Ross Oxford University Hilary Term 009 This course of twelve lectures covers material for the paper CP4: Differential Equations, Waves and
NORMAL MODES, WAVE MOTION AND THE WAVE EQUATION Professor G.G.Ross Oxford University Hilary Term 009 This course of twelve lectures covers material for the paper CP4: Differential Equations, Waves and
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS
 INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS J. Frieden, J. Cugnoni, J. Botsis, Th. Gmür, D. Coric Laboratoire de Mécanique appliquée et d Analyse de Fiabilité
INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS J. Frieden, J. Cugnoni, J. Botsis, Th. Gmür, D. Coric Laboratoire de Mécanique appliquée et d Analyse de Fiabilité
Radiated sound power estimates of building elements by means of laser Doppler vibrometry
 Radiated sound power estimates of building elements by means of laser Doppler vibrometry N.B. Roozen, L. Labelle, M. Rychtáriková,2, C. Glorieux, D. Urbán 3, P. Za tko 3, H. Mullner 4 Laboratory of Acoustics,
Radiated sound power estimates of building elements by means of laser Doppler vibrometry N.B. Roozen, L. Labelle, M. Rychtáriková,2, C. Glorieux, D. Urbán 3, P. Za tko 3, H. Mullner 4 Laboratory of Acoustics,
Methods Based on the Phenomenon of Elastic Wave Propagation (Guided Waves) Interaction with Damage
 Propagation (Guided Waves) Interaction with Damage Wieslaw Ostachowicz Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Fluid Flow Machinery Department of Mechanics of Intelligent Structures 14 Fiszera Street 80231
Propagation (Guided Waves) Interaction with Damage Wieslaw Ostachowicz Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Fluid Flow Machinery Department of Mechanics of Intelligent Structures 14 Fiszera Street 80231
Harmonic balance approach for a degenerate torus of a nonlinear jerk equation
 Harmonic balance approach for a degenerate torus of a nonlinear jerk equation Author Gottlieb, Hans Published 2009 Journal Title Journal of Sound and Vibration DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.11.035
Harmonic balance approach for a degenerate torus of a nonlinear jerk equation Author Gottlieb, Hans Published 2009 Journal Title Journal of Sound and Vibration DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.11.035
Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
 C H A P T E R Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) 5 A PDE is an equation that contains one or more partial derivatives of an unknown function that depends on at least two variables. Usually one of these
C H A P T E R Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) 5 A PDE is an equation that contains one or more partial derivatives of an unknown function that depends on at least two variables. Usually one of these
Virtual distortions applied to structural modelling and sensitivity analysis. Damage identification testing example
 AMAS Workshop on Smart Materials and Structures SMART 03 (pp.313 324) Jadwisin, September 2-5, 2003 Virtual distortions applied to structural modelling and sensitivity analysis. Damage identification testing
AMAS Workshop on Smart Materials and Structures SMART 03 (pp.313 324) Jadwisin, September 2-5, 2003 Virtual distortions applied to structural modelling and sensitivity analysis. Damage identification testing
Chapter 9. Reflection, Refraction and Polarization
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Measurement of Structural Intensity Using an Angular Rate Sensor
 Measurement of Structural Intensity Using an Angular Rate Sensor Nobuaki OMATA 1 ; Hiroki NAKAMURA ; Yoshiyuki WAKI 3 ; Atsushi KITAHARA 4 and Toru YAMAZAKI 5 1,, 5 Kanagawa University, Japan 3, 4 BRIDGESTONE,
Measurement of Structural Intensity Using an Angular Rate Sensor Nobuaki OMATA 1 ; Hiroki NAKAMURA ; Yoshiyuki WAKI 3 ; Atsushi KITAHARA 4 and Toru YAMAZAKI 5 1,, 5 Kanagawa University, Japan 3, 4 BRIDGESTONE,
FEA Based Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic and Orthotropic Media
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 016 FEA Based Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic and Orthotropic Media Debasis DATTA 1 1 Indian Institute of Engineering Science and
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 016 FEA Based Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic and Orthotropic Media Debasis DATTA 1 1 Indian Institute of Engineering Science and
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light
 1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
An Investigation of the use of Spatial Derivatives in Active Structural Acoustic Control
 An Investigation of the use of Spatial Derivatives in Active Structural Acoustic Control Brigham Young University Abstract-- A ne parameter as recently developed by Jeffery M. Fisher (M.S.) for use in
An Investigation of the use of Spatial Derivatives in Active Structural Acoustic Control Brigham Young University Abstract-- A ne parameter as recently developed by Jeffery M. Fisher (M.S.) for use in
EF 152 Exam 2 - Spring, 2017 Page 1 Copy 223
 EF 152 Exam 2 - Spring, 2017 Page 1 Copy 223 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Do not leave if there is less than 5 minutes to go in the exam. When time is called, immediately
EF 152 Exam 2 - Spring, 2017 Page 1 Copy 223 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Do not leave if there is less than 5 minutes to go in the exam. When time is called, immediately
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Canonical Transformations-1
 1 Introduction Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics Canonical Transformations The choice of generalized coordinates used to describe a physical system is completely arbitrary, but the Lagrangian is invariant
1 Introduction Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics Canonical Transformations The choice of generalized coordinates used to describe a physical system is completely arbitrary, but the Lagrangian is invariant
Electromagnetic Waves
 May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
Computing the uncertain vibrations of plates with spatially-extended random excitation using the image source method
 Computing the uncertain vibrations of plates with spatially-extended random excitation using the image source method J. Cuenca, M. Kurowski,2, B. Peeters Siemens Industry Software NV Interleuvenlaan 68,
Computing the uncertain vibrations of plates with spatially-extended random excitation using the image source method J. Cuenca, M. Kurowski,2, B. Peeters Siemens Industry Software NV Interleuvenlaan 68,
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
Longitudinal Waves. waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation
 Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Advanced Vibrations. Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian
 Advanced Vibrations Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions Relation between Discrete and Distributed
Advanced Vibrations Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions Relation between Discrete and Distributed
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components
 Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
ANALYSIS OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES OF DISC-LIKE STRUCTURES IN WATER ENVIRONMENT BY COUPLED FLUID-STRUCTURE-INTERACTION SIMULATION
 6 th IAHR International Meeting of the Workgroup on Cavitation and Dynamic Problems in Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, September 9-11, 15, Ljubljana, Slovenia ANALYSIS O NATURAL REQUENCIES O DISC-LIKE
6 th IAHR International Meeting of the Workgroup on Cavitation and Dynamic Problems in Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, September 9-11, 15, Ljubljana, Slovenia ANALYSIS O NATURAL REQUENCIES O DISC-LIKE
ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam
 ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam Objectives: 1. To find the natural frequencies and mode shapes of a tapered beam using FEA.. To compare the FE solution to analytical solutions of the vibratory
ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam Objectives: 1. To find the natural frequencies and mode shapes of a tapered beam using FEA.. To compare the FE solution to analytical solutions of the vibratory
COMPARISON OF DEFECT DETECTION IN ALUMINUM AND STEEL PLATES USING AN ELECTROMAGNETIC ACOUSTIC TRANSDUCER
 The 12 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering September 4-6, 2013, Portorož, Slovenia COMPARISON
The 12 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering September 4-6, 2013, Portorož, Slovenia COMPARISON
ENGI Second Order Linear ODEs Page Second Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 ENGI 344 - Second Order Linear ODEs age -01. Second Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations The general second order linear ordinary differential equation is of the form d y dy x Q x y Rx dx dx Of
ENGI 344 - Second Order Linear ODEs age -01. Second Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations The general second order linear ordinary differential equation is of the form d y dy x Q x y Rx dx dx Of
ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT HELSINKI UNIVERSITE DE TECHNOLOGIE D HELSINKI A posteriori error analysis for the Morley plate element Jarkko Niiranen Department of Structural
ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT HELSINKI UNIVERSITE DE TECHNOLOGIE D HELSINKI A posteriori error analysis for the Morley plate element Jarkko Niiranen Department of Structural
Characterization of particle impacts using acoustic emission
 Characterization of particle impacts using acoustic emission More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23588 Lorenzo CARRILLO 1, Eric SERRIS 1 1 Mines Saint-Etienne, SPIN EMSE, CNRS UMR 5307,
Characterization of particle impacts using acoustic emission More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23588 Lorenzo CARRILLO 1, Eric SERRIS 1 1 Mines Saint-Etienne, SPIN EMSE, CNRS UMR 5307,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
Phase Space Study of the Synchrotron Oscillation and Radiation Damping of the Longitudinal and Transverse Oscillations
 ScienceAsia 28 (2002 : 393-400 Phase Space Study of the Synchrotron Oscillation and Radiation Damping of the Longitudinal and Transverse Oscillations Balabhadrapatruni Harita*, Masumi Sugawara, Takehiko
ScienceAsia 28 (2002 : 393-400 Phase Space Study of the Synchrotron Oscillation and Radiation Damping of the Longitudinal and Transverse Oscillations Balabhadrapatruni Harita*, Masumi Sugawara, Takehiko
