An introduction to German Syntax. 1. Head directionality: A major source of linguistic divergence
|
|
|
- Mervyn Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An introduction to German Syntax 19 January Head directionality: A major source of linguistic divergence In English, heads uniformly precede their complements: (1) a. [ kiss Mary] a. * [ Mary kiss] b. [ DP the boy] b.* [ DP boy the] c. [ PP with John] c. * [ PP John with] d. [ TP is going home] d.* [ TP going home is] e. [ AP afraid of cats] e. * [ AP of cats afraid] In Turkish, heads uniformly follow their complements: 1 (2) a. [ Hasan öp] a. * [ öp Hasan] Hasan kiss kiss Hasan b. [ PP Deniz ile] b. * [ PP ile Deniz] Deniz with with Deniz c. [ TP Aynur hasta imiş] c. * [ TP imiş Aynur hasta] Aynur sick is is Aynur sick d. [ AP Ali-den memnun] d. * [ AP memnun Ali-den] Ali-from happy happy Ali-from Q: In terms of head-directionality, German is a mixed system: (3) a. [ jemanden etwas fragen] a. * [ fragen jemanden etwas] b. [ DP Nachrichten von mir an dich] b. * [ DP von mir an dich Nachrichten] c. [ PP in das Haus] c. * [ PP das Haus in] 2 d. [ AP den Kindern unangenehm] d. * [ AP unangenehm den Kindern] 1 In comparison with other languages, English has a very strict word-order. Both Turkish and German are less strict in this respect. For the Turkish and German phrases discussed in (2) and (3), the judgements reflect the neutral word order (e.g. in a sentence that initiates a conversation). 2 Some prepositions can also be used as postpositions in German: e.g. entlang, gegenüber 1
2 Conclusions - English is uniformly head-initial - Turkish is uniformly head-final - German is mixed: verbal and adjectival projections are head-final all other phrases are head-initial The German embedded dass-clause: (based on Haider 2010: ch.1) (4) a. die Annahme, dass er sich geirrt habe the assumption that he himself erred has b. (German embedded dass-clause) CP C TP dass T habe DP v er V 1 +v geirrt DP t 1 sich Problem: If German verbal projections (i.e. main verbs, auxiliaries, modals, etc.) are right-branching heads, why aren t all the verbs stacked-up on the right in root clauses and embedded clauses without dass? (5) a. Der Hund hat die Katze gejagt. (the dog has chased the cat) b. die Annahme, der Hund hat die Katze gejagt 2. The V2 property of German Unless C is occupied by a pronounced complementizer, - a finite verb must be the second item in the clause (hence V2 ), which - follows an arbitrary, single, clausal-initial phrase. 2
3 The finite verb undergoes head-movement to occupy C Phrases either undergo A -movement to the Specifier of CP or are base-generated in CP (6) a. [Eine Maus] 1 hat heute t 1 den Käse verschmäht. [A -movement to SpecCP] (a mouse has spurned the cheese today) b. CP (German root clause) DP 2 CP eine Maus hat 1 +C TP t 1 AP heute t 2 v V 3 +v verschmäht DP t 3 den Käse (7) [ CP Es [ C hat 1 [ TP t 1 heute jede Maus den Käse verschmäht]]] [base-generation in C] An important difference between Haider (2010) and our theory: Haider treats head-movement in a simple way. We have been more explicit about headmovement in our description of English, however. One exception to the V2 rule is left-dislocation. Left-dislocation involves an additional element before the finite verb. Left-dislocated phrases are always linked with a pronominal element: (8) [Den Peter] i, den i habe ich gestern gesehen. (Ott 2014) Are sentences like (8) true cases of V3 clauses? 3
4 Ott (2014): Apparent V3 clauses like (8) are actually two separate sentences with ellipsis in the first one. (9) [Den Peter] i habe ich gestern gesehen, den i habe ich gestern gesehen. (Ott 2014) Summary of 2: With regards to head-directionality, German is a mixed system. Verbal and adjectival heads follow their complements (head-final), whereas all other heads precede their complements (head-initial). German exhibits the V2 property: in clauses without a pronounced complementizer, the finite verb moves to C. In such cases, the Specifier of CP must also be occupied by a pronounced element. 3. Haider s (2010:25-30) Head-directionality principle Haider introduces a new constraint on licensing arguments that makes reference to head directionality. Claim 1: Arguments must be in a particular directionality relationship to a verbal head. For languages with head-initial verbal heads (English): every argument A must be preceded by a verbal head H. For languages with head-final verbal heads (German): every argument A must be followed by a verbal head H Claim 2: In addition to this directionality relationship, A and H must minimally, mutually c-command each other. (where X minimally c-commands Y if Y is the sister or first daughter of the sister of X) Together these claims form Haider s Principle of Directional Identification (PDI) 4
5 For German head-final phrases: (10) (German ditransitive verb) subj v V+v obj-a V obj-b t 1 Head following subj = v Head following obj-a = V Head following obj-b = V Subj and v minimally, mutually c-command each other. = subj is licensed Obj-a and V minimally, mutually c-command each other. = obj-a is licensed Obj-b and V minimally, mutually c-command each other. = obj-b is licensed For English head-initial phrases: (11) (English ditransitive verb) subj v V 1 +v obj-a V Head preceding subj = None! Head preceding obj-a = V (or v) Head preceding obj-b = V (trace) t 1 obj-b 5
6 Obj-a and V (or v) minimally, mutually c-command each other. (obj-a c-commands the trace of V, the moved V c-commands obj-a) Obj-b and V minimally, mutually c-command each other. Summary of 3: Haider introduces a new constraint on licensing arguments called the Principle of Directional Interpretation (PDI). Head-final languages such as German satisfy this constraint straightforwardly. Head-initial languages such as English have more trouble satisfying this constraint, and must make use of movement-chains. 4. The German OV properties versus English VO properties 4.1. Difference 1: The EPP property English (and other VO languages) requires a pronounced element to occupy the Specifier of TP. German doesn t require or sometimes doesn t allow a pronounced element to occupy the Specifier of TP. Configurations with unergative verbs (12) a. Today, [a boy] 1 has arrived t 1. (A -movement to Spec, TP) b. Today, there has arrived a boy. 3 (there expletive pronoun) c. * Today, has arrived a boy. (13) a. Heute is ein Junge gekommen. b. * Heute ist es ein Junge gekommen. Cleft configurations (14) a. It has not surprised me that this is so. (it expletive pronoun) b. * Has not surprised me that this is so. (15) Mich hat (es) nicht überrascht, dass das so ist. 3 The configuration exemplified by (12b) is called a postverbal nominative. This construction is archaic in modern English (i.e. it s dying out). Bobaljik & Jonas (1996) provide a useful discussion of how the postverbal DP receives cases in these constructions. 6
7 Intransitive passives (16) Ofte vart det telefonert. [Norwegian] Often was it telephoned (by John) ( John telephoned ) (17) a. Oft wurde telephoniert. b. * Oft wurde es telephoniert Difference 2: Relative order of arguments inside The -internal arguments in English are strictly ordered. The -internal arguments in German are not strictly ordered, however. Haider (2010:13) attributes the variable word-order in German to scrambling: a short instance of movement to the edge of. [NB: We are scheduled to discuss scrambling in more depth in a later seminar.] (18) a. He showed some students this problem. b. * He showed [this problem] 1 some students t 1. (19) a. Er hat einigen Studenten dieses Problem erklärt. b. Er hat [dieses Problem] 1 einigen Studenten t 1 erklärt Difference 3: Compactness English prohibits modifiers between verbs and their complements. German permits modifiers between verbs and their complements, however. (20) a. They will thoroughly investigate something. b. * They will investigate thoroughly something. (21) Sie werden etwas gründlich untersuchen Position of particles in particle verb constructions In English, particles follow the verb, and can split up the non-agentive arguments in double-object constructions. (22) a. The secretary sent out a notice. b. The secretary sent a notice out to the shareholders. 7
8 Unless the verb strands the particle by moving to the Specifier of CP (see 23a), the particle must immediately precede the verb in German: (23) a. [ CP Er 2 wickelt 1 [ TP t 2 es ein t 1 ]]. (he wraps it in) b.... dass er es einwickelt. c. *... dass er es ein gut wickelt. 5. Explaining the VO/VO differences using Haider s framework 5.1. The EPP effect Recall from 3 that the highest argument in the English isn t in a directionality relationship with either v or V: (11) (English ditransitive verb) subj v Problem: How is subj licensed in (11)?? V 1 +v obj-a V t 1 obj-b Haider s solution: if we look higher up in the tree, we see that subj is preceded by another verbal head, namely T: (24) TP (English TP ditransitive verb) T subj v V 1 +v obj-a V t 1 obj-b 8
9 According to Haider s Principle of Directional Identification (PDI), T and subj must minimally, mutually c-command each other. If subj doesn t move, this c-command relationship isn t established. But if subj moves to the Specifier of TP, then this relationship is established! (25) TP (English TP ditransitive verb) subj 2 T T t 2 v V 1 +v - Moved subj c-commands T obj-a V - T c-commands (trace of) subj = minimal, mutual c-command established t 1 obj-b Haider: the EPP condition can actually be reduced to the PDI. Recall from 3 that the highest argument in the is licensed by v in German (see 10, which is repeated below). Therefore, movement to Spec, TP is not required. (10) (German ditransitive verb) subj v V 1 +v obj-a V obj-b t 1 9
10 A question for you to consider in your spare time: Does Haider s account also explain why German doesn t require (and sometimes doesn t allow) expletive pronouns? What would you need to say about the syntax of expletive pronouns in English and German to make his analysis work? 5.2. The relative order of arguments inside the Why does German permit variable word-orders within the, whereas English does not? (18) b. * He showed [this problem] 1 some students t 1. (repeated from 4.2) (19) b. Er has [dieses Problem] 1 einigen Studenten t 1 erklärt. Haider s solution: performing scrambling in English violates the PDI, whereas scrambling in German does not violate the PDI. (26) * TP (English TP ditransitive verb) DP 1 T they T t 1 v V 2 +v showed DP 3 this problem DP V someone t 2 t 3 SCRAMBLING - V precedes someone - someone minimally c-commands V - V minimally doesn t minimally c-command someone (as this problem intervenes) = minimal, mutual c-command not established 10
11 (27) CP (German ditransitive verb) DP 1 C er T 2 +C hat TP t 2 t 1 v V+v erklärt DP 3 dieses problem DP V einigen Studenten t 3 t 4 SCRAMBLING 5.3. Compactness Why does German allow AP modifiers between the main verb and its complement whereas English does not? (20) b. * They will [ investigate thoroughly something]. (repeated from 4.3) (21) Sie werden [ etwas gründlich untersuchen]. Analysis Adverbs such as {thoroughly / gründlich} always branch rightwards. V-to-v movement in German gives the illusion of the modifier being between the main verb and its complement. In English, the adverb still follows the verb when V-to-v movement occurs. The ungrammatical word-order in (20b) is impossible to generate. 11
12 (28) (German transitive verb) DP v Sie V 2 +v untersuchen AP DP t 2 etwas gründlich (29) (English transitive verb) DP v they V 2 +v investigate t 2 AP thoroughly DP something 5.4. Position of particles in particle verb constructions Why does the particle split up arguments in English, but stay next to the verb in German embedded dass-clauses? (22) b. The secretary sent a notice out to the shareholders. (repeated from 4.4) (23) b.... dass er es einwickelt. c. *... dass er es ein gut wickelt. Analysis The particle and verb are generated together, and the verb head-moves to v. 12
13 (30) (English ditransitive verb) DP v the secretary V 1 +v sent DP V a notice V DP to the t 1 V shareholders out (31) (German transitive verb) DP v er V 1 +v wickelt DP V es V t 1 ein A question for you to consider in your spare time: What would we have to say about gut (particularly about the which direction it branches) to account for the unacceptability of (23c)? Is this analysis extensible? 6. Summary of 4-5 Haider s analysis provides an explanation for a number of VO versus OV properties observed in English and German, respectively. 13
14 The EPP condition and English s inability to scramble arguments within the can be explained by appealing to Haider s Principle of Directional Interpretation. The intervening position of modifiers and the distribution of particle verbs can be explained by carefully considering how head-final versus head-initial syntax trees yield very different word orders. References Bobaljik, Jonathan & Dianne Jonas Subject Positions and the Roles of TP. Linguistic Inquiry 27: Haider, Hubert The Syntax of German. Cambridge University Press. Ott, Dennis An Ellipsis Approach to Contrastive Left-Dislocation. Linguistic Inquiry 45:
Other types of Movement
 Other types of Movement So far we seen Wh-movement, which moves certain types of (XP) constituents to the specifier of a CP. Wh-movement is also called A-bar movement. We will look at two more types of
Other types of Movement So far we seen Wh-movement, which moves certain types of (XP) constituents to the specifier of a CP. Wh-movement is also called A-bar movement. We will look at two more types of
CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2000 October 10, 2000 Week 5: Case Theory and θ Theory. θ-theory continued
 CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2000 October 0, 2000 Paul Hagstrom Week 5: Case Theory and θ Theory θ-theory continued From last time: verbs have θ-roles (e.g., Agent, Theme, ) to assign, specified in the lexicon
CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2000 October 0, 2000 Paul Hagstrom Week 5: Case Theory and θ Theory θ-theory continued From last time: verbs have θ-roles (e.g., Agent, Theme, ) to assign, specified in the lexicon
(7) a. [ PP to John], Mary gave the book t [PP]. b. [ VP fix the car], I wonder whether she will t [VP].
![(7) a. [ PP to John], Mary gave the book t [PP]. b. [ VP fix the car], I wonder whether she will t [VP]. (7) a. [ PP to John], Mary gave the book t [PP]. b. [ VP fix the car], I wonder whether she will t [VP].](/thumbs/93/113837834.jpg) CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2000 September 18, 2000 Paul Hagstrom Week 2: Movement Movement Last time, we talked about subcategorization. (1) a. I can solve this problem. b. This problem, I can solve. (2)
CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2000 September 18, 2000 Paul Hagstrom Week 2: Movement Movement Last time, we talked about subcategorization. (1) a. I can solve this problem. b. This problem, I can solve. (2)
Ch. 2: Phrase Structure Syntactic Structure (basic concepts) A tree diagram marks constituents hierarchically
 Ch. 2: Phrase Structure Syntactic Structure (basic concepts) A tree diagram marks constituents hierarchically NP S AUX VP Ali will V NP help D N the man A node is any point in the tree diagram and it can
Ch. 2: Phrase Structure Syntactic Structure (basic concepts) A tree diagram marks constituents hierarchically NP S AUX VP Ali will V NP help D N the man A node is any point in the tree diagram and it can
1. Background. Task: Determine whether a given string of words is a grammatical (well-formed) sentence of language L i or not.
 Constraints in Syntax [1] Phrase Structure and Derivations Düsseldorf LSA/DGfS Summerschool 2002 Gereon Müller (IDS Mannheim) gereon.mueller@ids-mannheim.de 1. Background Task: Determine whether a given
Constraints in Syntax [1] Phrase Structure and Derivations Düsseldorf LSA/DGfS Summerschool 2002 Gereon Müller (IDS Mannheim) gereon.mueller@ids-mannheim.de 1. Background Task: Determine whether a given
Semantics and Generative Grammar. Quantificational DPs, Part 3: Covert Movement vs. Type Shifting 1
 Quantificational DPs, Part 3: Covert Movement vs. Type Shifting 1 1. Introduction Thus far, we ve considered two competing analyses of sentences like those in (1). (1) Sentences Where a Quantificational
Quantificational DPs, Part 3: Covert Movement vs. Type Shifting 1 1. Introduction Thus far, we ve considered two competing analyses of sentences like those in (1). (1) Sentences Where a Quantificational
Raising and Passive. Jean Mark Gawron. Linguistics 522 San Diego State University
 Raising and Passive Jean Mark Gawron Linguistics 522 San Diego State University gawron@mail.sdsu.edu http://www.rohan.sdsu.edu/ gawron Raising and Passive p. 1/20 Sentences Part I Raising and Passive p.
Raising and Passive Jean Mark Gawron Linguistics 522 San Diego State University gawron@mail.sdsu.edu http://www.rohan.sdsu.edu/ gawron Raising and Passive p. 1/20 Sentences Part I Raising and Passive p.
Hierarchical and Linear Constraints on Structure
 Hierarchical and Linear Constraints on Structure Peter Sells Sandbjerg Ph.D. course June 14 16, 2006 Part II 1 OT Evaluations (1) CP XP C C IP Pro/Adv NP Adv I I Adv/Neg/NQ/Pro VP V Pro V NP NP PP V Prt
Hierarchical and Linear Constraints on Structure Peter Sells Sandbjerg Ph.D. course June 14 16, 2006 Part II 1 OT Evaluations (1) CP XP C C IP Pro/Adv NP Adv I I Adv/Neg/NQ/Pro VP V Pro V NP NP PP V Prt
Some binding facts. Binding in HPSG. The three basic principles. Binding theory of Chomsky
 Some binding facts Binding in HPSG Binding theory has to do with constraining referentially dependent elements in terms of what is a possible antecedent, or binder. Introduction to HPSG June, 009 (1) John
Some binding facts Binding in HPSG Binding theory has to do with constraining referentially dependent elements in terms of what is a possible antecedent, or binder. Introduction to HPSG June, 009 (1) John
Andrew Carnie, Structural Relations. The mathematical properties of phrase structure trees
 Structural Relations The mathematical properties of phrase structure trees Important! Important! Even if you have trouble with the formal definitions, try to understand the INTUITIVE idea behind them.
Structural Relations The mathematical properties of phrase structure trees Important! Important! Even if you have trouble with the formal definitions, try to understand the INTUITIVE idea behind them.
Assignment 3. Solution. 1. Give trees showing the derivations of the following sentences; show all movements.
 LIN5317 A, Fall 2015 Dennis Ott Assignment 3 Solution 1. Gie trees showing the deriations of the following sentences; show all moements. (1) a. Who danced? b. I wonder who fell last night. c. Who do you
LIN5317 A, Fall 2015 Dennis Ott Assignment 3 Solution 1. Gie trees showing the deriations of the following sentences; show all moements. (1) a. Who danced? b. I wonder who fell last night. c. Who do you
Ling 98a: The Meaning of Negation (Week 5)
 Yimei Xiang yxiang@fas.harvard.edu 15 October 2013 1 Review Negation in propositional logic, oppositions, term logic of Aristotle Presuppositions Projection and accommodation Three-valued logic External/internal
Yimei Xiang yxiang@fas.harvard.edu 15 October 2013 1 Review Negation in propositional logic, oppositions, term logic of Aristotle Presuppositions Projection and accommodation Three-valued logic External/internal
Introduction to Semantics. The Formalization of Meaning 1
 The Formalization of Meaning 1 1. Obtaining a System That Derives Truth Conditions (1) The Goal of Our Enterprise To develop a system that, for every sentence S of English, derives the truth-conditions
The Formalization of Meaning 1 1. Obtaining a System That Derives Truth Conditions (1) The Goal of Our Enterprise To develop a system that, for every sentence S of English, derives the truth-conditions
2 A not-quite-argument for X-bar structure in noun phrases
 CAS LX 321 / GRS LX 621 Syntax: Introduction to Sentential Structure ovember 16, 2017 1 and pronouns (1) he linguists yodel. (2) We linguists yodel. (3) hey looked at us linguists. (4) hey looked at linguists.
CAS LX 321 / GRS LX 621 Syntax: Introduction to Sentential Structure ovember 16, 2017 1 and pronouns (1) he linguists yodel. (2) We linguists yodel. (3) hey looked at us linguists. (4) hey looked at linguists.
Stepanov 2007: The End of CED? Minimalism and Extraction Domains
 Stepanov (2007) Stepanov 2007: The End of CED? Minimalism and Extraction Domains 1 Introduction In English (and other languages), overt wh-extraction out of subjects or adjuncts (as opposed to objects)
Stepanov (2007) Stepanov 2007: The End of CED? Minimalism and Extraction Domains 1 Introduction In English (and other languages), overt wh-extraction out of subjects or adjuncts (as opposed to objects)
CAS LX 523 Syntax II Spring 2001 March 13, (1) A qp. Kayne, Richard (1995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
 CAS LX 52 Syntax II Spring 200 March, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 7: Antisymmetry Kayne, Richard (995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Koopman, Hilda (2000). The spec-head configuration.
CAS LX 52 Syntax II Spring 200 March, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 7: Antisymmetry Kayne, Richard (995). The antisymmetry of syntax. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Koopman, Hilda (2000). The spec-head configuration.
X-bar theory. X-bar :
 is one of the greatest contributions of generative school in the filed of knowledge system. Besides linguistics, computer science is greatly indebted to Chomsky to have propounded the theory of x-bar.
is one of the greatest contributions of generative school in the filed of knowledge system. Besides linguistics, computer science is greatly indebted to Chomsky to have propounded the theory of x-bar.
Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence
 Ling255: Sem & Cogsci Maribel Romero February 17, 2005 Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence 1. Introduction. We have seen that Determiners express a relation between two sets of individuals
Ling255: Sem & Cogsci Maribel Romero February 17, 2005 Quantification: Quantifiers and the Rest of the Sentence 1. Introduction. We have seen that Determiners express a relation between two sets of individuals
Categories and Transformations 321
 Categories and ransformations 321 4.10 Functional Categories and Formal Features What precedes substantially revises the framework developed in chapters 1 3. But we have not yet subjected functional categories
Categories and ransformations 321 4.10 Functional Categories and Formal Features What precedes substantially revises the framework developed in chapters 1 3. But we have not yet subjected functional categories
Spring 2017 Ling 620. An Introduction to the Semantics of Tense 1
 1. Introducing Evaluation Times An Introduction to the Semantics of Tense 1 (1) Obvious, Fundamental Fact about Sentences of English The truth of some sentences (of English) depends upon the time they
1. Introducing Evaluation Times An Introduction to the Semantics of Tense 1 (1) Obvious, Fundamental Fact about Sentences of English The truth of some sentences (of English) depends upon the time they
HPSG: Binding Theory
 HPSG: Binding Theory Doug Arnold doug@essexacuk Introduction Binding Theory is to do with the syntactic restrictions on the distribution of referentially dependent items and their antecedents: reflexives/reciprocals
HPSG: Binding Theory Doug Arnold doug@essexacuk Introduction Binding Theory is to do with the syntactic restrictions on the distribution of referentially dependent items and their antecedents: reflexives/reciprocals
Time Zones - KET Grammar
 Inventory of grammatical areas Verbs Regular and irregular forms Pages 104-105 (Unit 1 Modals can (ability; requests; permission) could (ability; polite requests) Page 3 (Getting Started) Pages 45-47,
Inventory of grammatical areas Verbs Regular and irregular forms Pages 104-105 (Unit 1 Modals can (ability; requests; permission) could (ability; polite requests) Page 3 (Getting Started) Pages 45-47,
One hint from secondary predication (from Baker 1997 (8) A secondary predicate cannot take the goal argument as subject of predication, wheth
 MIT, Fall 2003 1 The Double Object Construction (Larson 1988, Aoun & Li 1989) MIT, 24.951, Fr 14 Nov 2003 A familiar puzzle The Dative Alternation (1) a. I gave the candy to the children b. I gave the
MIT, Fall 2003 1 The Double Object Construction (Larson 1988, Aoun & Li 1989) MIT, 24.951, Fr 14 Nov 2003 A familiar puzzle The Dative Alternation (1) a. I gave the candy to the children b. I gave the
Recap: Tree geometry, selection, Θ-theory
 Syntax II Seminar 2 Recap: Tree geometry, selection, Θ-theory Dr. James Grifiihs james.grifiihs@uni-konsianz.de Recap: tree geometry terminology M N O D E F H I J Branches 2 Recap: tree geometry terminology
Syntax II Seminar 2 Recap: Tree geometry, selection, Θ-theory Dr. James Grifiihs james.grifiihs@uni-konsianz.de Recap: tree geometry terminology M N O D E F H I J Branches 2 Recap: tree geometry terminology
Ling 240 Lecture #15. Syntax 4
 Ling 240 Lecture #15 Syntax 4 agenda for today Give me homework 3! Language presentation! return Quiz 2 brief review of friday More on transformation Homework 4 A set of Phrase Structure Rules S -> (aux)
Ling 240 Lecture #15 Syntax 4 agenda for today Give me homework 3! Language presentation! return Quiz 2 brief review of friday More on transformation Homework 4 A set of Phrase Structure Rules S -> (aux)
Chapter 5: 1 Reconstruction Effects Revisited
 Chapter 5: 1 Reconstruction Effects Revisited Silke Fischer 1 The Core Data Let us now come back to those data that served as initial motivation for a derivational approach in chapter 3 the reconstruction
Chapter 5: 1 Reconstruction Effects Revisited Silke Fischer 1 The Core Data Let us now come back to those data that served as initial motivation for a derivational approach in chapter 3 the reconstruction
Constituency. Doug Arnold
 Constituency Doug Arnold doug@essex.ac.uk Spose we have a string... xyz..., how can we establish whether xyz is a constituent (i.e. syntactic unit); i.e. whether the representation of... xyz... should
Constituency Doug Arnold doug@essex.ac.uk Spose we have a string... xyz..., how can we establish whether xyz is a constituent (i.e. syntactic unit); i.e. whether the representation of... xyz... should
Ling 5801: Lecture Notes 7 From Programs to Context-Free Grammars
 Ling 5801: Lecture otes 7 From Programs to Context-Free rammars 1. The rules we used to define programs make up a context-free grammar A Context-Free rammar is a tuple C,X,S,R, where: C is a finite set
Ling 5801: Lecture otes 7 From Programs to Context-Free rammars 1. The rules we used to define programs make up a context-free grammar A Context-Free rammar is a tuple C,X,S,R, where: C is a finite set
Feature Stacks and Binding Relations
 Feature Stacks and Binding Relations Silke Fischer (Universität Stuttgart) The Fine Structure of Grammatical Relations, Universität Leipzig December 10, 2010 1. Introduction Background: In Fischer (2004b,
Feature Stacks and Binding Relations Silke Fischer (Universität Stuttgart) The Fine Structure of Grammatical Relations, Universität Leipzig December 10, 2010 1. Introduction Background: In Fischer (2004b,
THE DRAVIDIAN EXPERIENCER CONSTRUCTION AND THE ENGLISH SEEM CONSTRUCTION. K. A. Jayaseelan CIEFL, Hyderabad
 THE DRAVIDIAN EXPERIENCER CONSTRUCTION AND THE ENGLISH SEEM CONSTRUCTION K. A. Jayaseelan CIEFL, Hyderabad 1. Introduction In many languages e.g. Malayalam, Tamil, Hindi, the same verb is used in the Experiencer
THE DRAVIDIAN EXPERIENCER CONSTRUCTION AND THE ENGLISH SEEM CONSTRUCTION K. A. Jayaseelan CIEFL, Hyderabad 1. Introduction In many languages e.g. Malayalam, Tamil, Hindi, the same verb is used in the Experiencer
Control and Tough- Movement
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University February 2, 2012 Control (1/5) We saw that PRO is used for the unrealized subject of nonfinite verbals and predicatives where the subject plays a semantic
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University February 2, 2012 Control (1/5) We saw that PRO is used for the unrealized subject of nonfinite verbals and predicatives where the subject plays a semantic
Towards a Relativized Concept of Cyclic Linearization. Gereon Müller
 Towards a Relativized Concept of Cyclic Linearization Gereon Müller 1 Introduction Suppose that a grammar is an optimal satisfaction of requirements imposed by the interfaces LF and PF (see Chomsky (2000,
Towards a Relativized Concept of Cyclic Linearization Gereon Müller 1 Introduction Suppose that a grammar is an optimal satisfaction of requirements imposed by the interfaces LF and PF (see Chomsky (2000,
Computationele grammatica
 Computationele grammatica Docent: Paola Monachesi Contents First Last Prev Next Contents 1 Unbounded dependency constructions (UDCs)............... 3 2 Some data...............................................
Computationele grammatica Docent: Paola Monachesi Contents First Last Prev Next Contents 1 Unbounded dependency constructions (UDCs)............... 3 2 Some data...............................................
Semantics and Generative Grammar. A Little Bit on Adverbs and Events
 A Little Bit on Adverbs and Events 1. From Adjectives to Adverbs to Events We ve just developed a theory of the semantics of adjectives, under which they denote either functions of type (intersective
A Little Bit on Adverbs and Events 1. From Adjectives to Adverbs to Events We ve just developed a theory of the semantics of adjectives, under which they denote either functions of type (intersective
Grundlagenmodul Semantik All Exercises
 Grundlagenmodul Semantik All Exercises Sommersemester 2014 Exercise 1 Are the following statements correct? Justify your answers in a single short sentence. 1. 11 {x x is a square number} 2. 11 {x {y y
Grundlagenmodul Semantik All Exercises Sommersemester 2014 Exercise 1 Are the following statements correct? Justify your answers in a single short sentence. 1. 11 {x x is a square number} 2. 11 {x {y y
Control and Tough- Movement
 Control and Tough- Movement Carl Pollard February 2, 2012 Control (1/5) We saw that PRO is used for the unrealized subject of nonfinite verbals and predicatives where the subject plays a semantic role
Control and Tough- Movement Carl Pollard February 2, 2012 Control (1/5) We saw that PRO is used for the unrealized subject of nonfinite verbals and predicatives where the subject plays a semantic role
HPSG II: the plot thickens
 Syntactic Models 2/21/06 HPSG II: the plot thickens 1 Passive: a lexical rule that rearranges ARG-ST! (1) Passive Lexical Rule < 1, tv - lxm ARG - ST INDEX i < FPSP 1 a, > part - lxm SYN HEAD FORM pass
Syntactic Models 2/21/06 HPSG II: the plot thickens 1 Passive: a lexical rule that rearranges ARG-ST! (1) Passive Lexical Rule < 1, tv - lxm ARG - ST INDEX i < FPSP 1 a, > part - lxm SYN HEAD FORM pass
Dependency grammar. Recurrent neural networks. Transition-based neural parsing. Word representations. Informs Models
 Dependency grammar Morphology Word order Transition-based neural parsing Word representations Recurrent neural networks Informs Models Dependency grammar Morphology Word order Transition-based neural parsing
Dependency grammar Morphology Word order Transition-based neural parsing Word representations Recurrent neural networks Informs Models Dependency grammar Morphology Word order Transition-based neural parsing
Word Order and the Floating Quantifier in Cebuano
 Word Order and the Floating Quantifier in Cebuano Yumiko Ishikawa 1. Introduction The sentential subject long had been considered to be base-generated in Spec IP and to be assigned nominative Case under
Word Order and the Floating Quantifier in Cebuano Yumiko Ishikawa 1. Introduction The sentential subject long had been considered to be base-generated in Spec IP and to be assigned nominative Case under
A Constraint on Remnant Movement
 To appear in "Towards a Biolinguistic Understanding of Grammar", A. M. di Sciullo (ed.) A Constraint on Remnant Movement Tim Hunter August 31, 2011 1 Introduction The aim of this paper is to begin to assess
To appear in "Towards a Biolinguistic Understanding of Grammar", A. M. di Sciullo (ed.) A Constraint on Remnant Movement Tim Hunter August 31, 2011 1 Introduction The aim of this paper is to begin to assess
IBM Model 1 for Machine Translation
 IBM Model 1 for Machine Translation Micha Elsner March 28, 2014 2 Machine translation A key area of computational linguistics Bar-Hillel points out that human-like translation requires understanding of
IBM Model 1 for Machine Translation Micha Elsner March 28, 2014 2 Machine translation A key area of computational linguistics Bar-Hillel points out that human-like translation requires understanding of
Binding Theory Different types of NPs, constraints on their distribution
 Binding Theory Different types of Ps, constraints on their distribution Ling 322 Read Syntax, Ch. 5 (Lecture notes based on Andrew Carnie s notes) 1 Different Types of Ps R-expressions An P that gets its
Binding Theory Different types of Ps, constraints on their distribution Ling 322 Read Syntax, Ch. 5 (Lecture notes based on Andrew Carnie s notes) 1 Different Types of Ps R-expressions An P that gets its
DEGREE QUANTIFIERS, POSITION OF MERGER EFFECTS WITH THEIR RESTRICTORS, AND CONSERVATIVITY
 DEGREE QUANTIFIERS, POSITION OF MERGER EFFECTS WITH THEIR RESTRICTORS, AND CONSERVATIVITY RAJESH BHATT AND ROUMYANA PANCHEVA University of Texas, Austin bhatt@cs.utexas.edu University of Southern California
DEGREE QUANTIFIERS, POSITION OF MERGER EFFECTS WITH THEIR RESTRICTORS, AND CONSERVATIVITY RAJESH BHATT AND ROUMYANA PANCHEVA University of Texas, Austin bhatt@cs.utexas.edu University of Southern California
Two Types of Remnant Movement. Gereon Müller IDS Mannheim February 10, 2001
 Two Types of Remnant Movement Gereon Müller IDS Mannheim February 10, 2001 1. Introduction This article is concerned with stating and accounting for differences between two types of remnant movement that
Two Types of Remnant Movement Gereon Müller IDS Mannheim February 10, 2001 1. Introduction This article is concerned with stating and accounting for differences between two types of remnant movement that
Holmberg s Generalization and Cyclic Linearization Remarks on Fox and Pesetsky
 Holmberg s Generalization and Cyclic Linearization Remarks on Fox and Pesetsky ELENA ANAGNOSTOPOULOU 0 0 Fox and Pesetsky ( henceforth F&P) propose an architecture for the mapping between syntax and phonology
Holmberg s Generalization and Cyclic Linearization Remarks on Fox and Pesetsky ELENA ANAGNOSTOPOULOU 0 0 Fox and Pesetsky ( henceforth F&P) propose an architecture for the mapping between syntax and phonology
Spring 2018 Ling 620 The Basics of Intensional Semantics, Part 1: The Motivation for Intensions and How to Formalize Them 1
 The Basics of Intensional Semantics, Part 1: The Motivation for Intensions and How to Formalize Them 1 1. The Inadequacies of a Purely Extensional Semantics (1) Extensional Semantics a. The interpretation
The Basics of Intensional Semantics, Part 1: The Motivation for Intensions and How to Formalize Them 1 1. The Inadequacies of a Purely Extensional Semantics (1) Extensional Semantics a. The interpretation
Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization
 Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization Tim Hunter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities NASSLLI, June 2014 Part 1: Grammars and cognitive hypotheses What is a grammar?
Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization Tim Hunter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities NASSLLI, June 2014 Part 1: Grammars and cognitive hypotheses What is a grammar?
Government, Agreement and Minimality Ian Roberts Downing College, University of Cambridge
 1. Introduction 1 Government, Agreement and Minimality Ian Roberts Downing College, University of Cambridge (igr20@cam.ac.uk) Three points: How to define government in bare phrase stcture Government reduces
1. Introduction 1 Government, Agreement and Minimality Ian Roberts Downing College, University of Cambridge (igr20@cam.ac.uk) Three points: How to define government in bare phrase stcture Government reduces
2013 ISSN: JATLaC Journal 8: t 1. t t Chomsky 1993 I Radford (2009) R I t t R I 2. t R t (1) (= R's (15), p. 86) He could have helped
 t 1. tt Chomsky 1993 IRadford (2009) R Itt R I 2. t R t (1) (= R's (15), p. 86) He could have helped her, or [she have helped him]. 2 have I has had I I could ellipsis I gapping R (2) (= R (18), p.88)
t 1. tt Chomsky 1993 IRadford (2009) R Itt R I 2. t R t (1) (= R's (15), p. 86) He could have helped her, or [she have helped him]. 2 have I has had I I could ellipsis I gapping R (2) (= R (18), p.88)
Semantics and Generative Grammar. The Semantics of Adjectival Modification 1. (1) Our Current Assumptions Regarding Adjectives and Common Ns
 The Semantics of Adjectival Modification 1 (1) Our Current Assumptions Regarding Adjectives and Common Ns a. Both adjectives and common nouns denote functions of type (i) [[ male ]] = [ λx : x D
The Semantics of Adjectival Modification 1 (1) Our Current Assumptions Regarding Adjectives and Common Ns a. Both adjectives and common nouns denote functions of type (i) [[ male ]] = [ λx : x D
564 Lecture 25 Nov. 23, Continuing note on presuppositional vs. nonpresuppositional dets.
 564 Lecture 25 Nov. 23, 1999 1 Continuing note on presuppositional vs. nonpresuppositional dets. Here's the argument about the nonpresupp vs. presupp analysis of "every" that I couldn't reconstruct last
564 Lecture 25 Nov. 23, 1999 1 Continuing note on presuppositional vs. nonpresuppositional dets. Here's the argument about the nonpresupp vs. presupp analysis of "every" that I couldn't reconstruct last
Unification. Two Routes to Deep Structure. Unification. Unification Grammar. Martin Kay. Stanford University University of the Saarland
 Two Routes to Deep Structure Derivational! Transformational! Procedural Deep Unidirectional Transformations Surface Stanford University University of the Saarland Constraint-based! Declarative Deep Surface
Two Routes to Deep Structure Derivational! Transformational! Procedural Deep Unidirectional Transformations Surface Stanford University University of the Saarland Constraint-based! Declarative Deep Surface
Semantics 2 Part 1: Relative Clauses and Variables
 Semantics 2 Part 1: Relative Clauses and Variables Sam Alxatib EVELIN 2012 January 17, 2012 Reviewing Adjectives Adjectives are treated as predicates of individuals, i.e. as functions from individuals
Semantics 2 Part 1: Relative Clauses and Variables Sam Alxatib EVELIN 2012 January 17, 2012 Reviewing Adjectives Adjectives are treated as predicates of individuals, i.e. as functions from individuals
Compositionality and Syntactic Structure Marcus Kracht Department of Linguistics UCLA 3125 Campbell Hall 405 Hilgard Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90095
 Compositionality and Syntactic Structure Marcus Kracht Department of Linguistics UCLA 3125 Campbell Hall 405 Hilgard Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90095 1543 kracht@humnet.ucla.edu 1. The Questions ➀ Why does
Compositionality and Syntactic Structure Marcus Kracht Department of Linguistics UCLA 3125 Campbell Hall 405 Hilgard Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90095 1543 kracht@humnet.ucla.edu 1. The Questions ➀ Why does
Proseminar on Semantic Theory Fall 2013 Ling 720 The Proper Treatment of Quantification in Ordinary English, Part 1: The Fragment of English
 The Proper Treatment of Quantification in Ordinary English, Part 1: The Fragment of English We will now explore the analysis of English that Montague puts forth in his seminal paper, PTQ. As we ve already
The Proper Treatment of Quantification in Ordinary English, Part 1: The Fragment of English We will now explore the analysis of English that Montague puts forth in his seminal paper, PTQ. As we ve already
Entropy. Leonoor van der Beek, Department of Alfa-informatica Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. May 2005
 Entropy Leonoor van der Beek, vdbeek@rug.nl Department of Alfa-informatica Rijksuniversiteit Groningen May 2005 What is entropy? Entropy is a measure of uncertainty or surprise or disorder. Entropy was
Entropy Leonoor van der Beek, vdbeek@rug.nl Department of Alfa-informatica Rijksuniversiteit Groningen May 2005 What is entropy? Entropy is a measure of uncertainty or surprise or disorder. Entropy was
CS 188 Introduction to AI Fall 2005 Stuart Russell Final
 NAME: SID#: Section: 1 CS 188 Introduction to AI all 2005 Stuart Russell inal You have 2 hours and 50 minutes. he exam is open-book, open-notes. 100 points total. Panic not. Mark your answers ON HE EXAM
NAME: SID#: Section: 1 CS 188 Introduction to AI all 2005 Stuart Russell inal You have 2 hours and 50 minutes. he exam is open-book, open-notes. 100 points total. Panic not. Mark your answers ON HE EXAM
Wh-movement. CAS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 2001 November 6, 2001
 AS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 200 November 6, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 9: Wh-movement Preliminary tree to remind ourselves: They will bake a cake. () P [ Q] T T VP will P bake they NP a N cake Verb bake needs
AS LX 522 Syntax I Fall 200 November 6, 200 Paul Hagstrom Week 9: Wh-movement Preliminary tree to remind ourselves: They will bake a cake. () P [ Q] T T VP will P bake they NP a N cake Verb bake needs
Künstliche Intelligenz
 Künstliche Intelligenz 4. Wissensrepräsentation Dr. Claudia Schon schon@uni-koblenz.de Institute for Web Science and Technologies 1 Except for some small changes these slides are transparencies from Poole,
Künstliche Intelligenz 4. Wissensrepräsentation Dr. Claudia Schon schon@uni-koblenz.de Institute for Web Science and Technologies 1 Except for some small changes these slides are transparencies from Poole,
Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization
 Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization Tim Hunter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities ESSLLI, August 2015 Part 1: Grammars and cognitive hypotheses What is a grammar?
Sharpening the empirical claims of generative syntax through formalization Tim Hunter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities ESSLLI, August 2015 Part 1: Grammars and cognitive hypotheses What is a grammar?
On Deriving MLC Effects
 On Deriving MLC Effects Gereon Müller Institut für Linguistik Universität Leipzig SoSe 2006 www.uni-leipzig.de/ muellerg Gereon Müller (Institut für Linguistik) Constraints in Syntax 9 July 11, 2006 1
On Deriving MLC Effects Gereon Müller Institut für Linguistik Universität Leipzig SoSe 2006 www.uni-leipzig.de/ muellerg Gereon Müller (Institut für Linguistik) Constraints in Syntax 9 July 11, 2006 1
On Strict Cyclicity and Label: Toward Elimination of Late Merge*
 On Strict Cyclicity and Label: Toward Elimination of Late Merge On Strict Cyclicity and Label: Toward Elimination of Late Merge* Takanori Nakashima Abstract In the Minimalist Program, strict cyclicity
On Strict Cyclicity and Label: Toward Elimination of Late Merge On Strict Cyclicity and Label: Toward Elimination of Late Merge* Takanori Nakashima Abstract In the Minimalist Program, strict cyclicity
7.1 What is it and why should we care?
 Chapter 7 Probability In this section, we go over some simple concepts from probability theory. We integrate these with ideas from formal language theory in the next chapter. 7.1 What is it and why should
Chapter 7 Probability In this section, we go over some simple concepts from probability theory. We integrate these with ideas from formal language theory in the next chapter. 7.1 What is it and why should
Quantifier Scope Constraints in ACD: Implications for the Syntax of Relative Clauses
 Quantifier Scope Constraints in AC: Implications for the Syntax of Relative Clauses Jorie Koster-Moeller and Martin Hackl Pomona College 1. Overview It is widely assumed that restrictive relative clauses
Quantifier Scope Constraints in AC: Implications for the Syntax of Relative Clauses Jorie Koster-Moeller and Martin Hackl Pomona College 1. Overview It is widely assumed that restrictive relative clauses
CAS LX 522 Syntax I. We give trees to ditransitives. We give trees to ditransitives. We give trees to ditransitives. Problems continue * VP
 9 CAS LX 522 Syntax I UTAH (4.3-4.4) You may recall our discussion of θ-theory, where we triumphantly classified erbs as coming in (at least) three types: Intransitie (1 θ-role) Transitie (2 θ-roles) Ditransitie
9 CAS LX 522 Syntax I UTAH (4.3-4.4) You may recall our discussion of θ-theory, where we triumphantly classified erbs as coming in (at least) three types: Intransitie (1 θ-role) Transitie (2 θ-roles) Ditransitie
Syntax-Based Decoding
 Syntax-Based Decoding Philipp Koehn 9 November 2017 1 syntax-based models Synchronous Context Free Grammar Rules 2 Nonterminal rules NP DET 1 2 JJ 3 DET 1 JJ 3 2 Terminal rules N maison house NP la maison
Syntax-Based Decoding Philipp Koehn 9 November 2017 1 syntax-based models Synchronous Context Free Grammar Rules 2 Nonterminal rules NP DET 1 2 JJ 3 DET 1 JJ 3 2 Terminal rules N maison house NP la maison
Structures mathématiques du langage
 tructures mathématiques du langage Alain Lecomte 16 février 2014 1 Heim and Kratzer s theory Montague s grammar was conceived and built during the sixties of the last century, without much attention paid
tructures mathématiques du langage Alain Lecomte 16 février 2014 1 Heim and Kratzer s theory Montague s grammar was conceived and built during the sixties of the last century, without much attention paid
Logical Translations Jean Mark Gawron San Diego State University. 1 Introduction 2
 Logical Translations Jean Mark Gawron San Diego State University Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Truth-Functional Connectives 2 2.1 And................................ 2 2.2 Or.................................
Logical Translations Jean Mark Gawron San Diego State University Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Truth-Functional Connectives 2 2.1 And................................ 2 2.2 Or.................................
a. Rachel is {taller / more intelligent} than Stephanie (is). a. Rachel is the {tallest / most intelligent} (student in my class).
 Degree semantics1 1 Gradability Certain predicates allow us to specify to what extent the predicate holds; we call them gradable. There are many constructions which only apply to gradable predicates. (1)
Degree semantics1 1 Gradability Certain predicates allow us to specify to what extent the predicate holds; we call them gradable. There are many constructions which only apply to gradable predicates. (1)
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web. Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012
 CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
Comparative superlatives in relative clauses
 SynSem, Fall 2017 Comparative superlatives in relative clauses Nico(letta) Loccioni 1 Introduction Languages like Italian and Spanish extensively use relativization as a strategy to form relative interpretations
SynSem, Fall 2017 Comparative superlatives in relative clauses Nico(letta) Loccioni 1 Introduction Languages like Italian and Spanish extensively use relativization as a strategy to form relative interpretations
Creation constructions and frames
 Creation constructions and frames Udo Klein, Marcus Kracht and Ralf Vogel Universität Bielefeld Collaborative Research Centre Alignment in Communication (SFB 673, funded by the German Research Foundation,
Creation constructions and frames Udo Klein, Marcus Kracht and Ralf Vogel Universität Bielefeld Collaborative Research Centre Alignment in Communication (SFB 673, funded by the German Research Foundation,
Infnitives (revisited) / New diagnostics
 Syntax II Seminar 8 Infnitives (revisited) / New diagnostics Dr. James Grifiihs james.grifiihs@uni-konsianz.de 1 Part I: Infnitives (revisited) 2 Recap: Infnitival embedded clauses (from seminar 3) (1)
Syntax II Seminar 8 Infnitives (revisited) / New diagnostics Dr. James Grifiihs james.grifiihs@uni-konsianz.de 1 Part I: Infnitives (revisited) 2 Recap: Infnitival embedded clauses (from seminar 3) (1)
The Semantics of Definite DPs 1. b. Argument Position: (i) [ A politician ] arrived from Washington. (ii) Joe likes [ the politician ].
![The Semantics of Definite DPs 1. b. Argument Position: (i) [ A politician ] arrived from Washington. (ii) Joe likes [ the politician ]. The Semantics of Definite DPs 1. b. Argument Position: (i) [ A politician ] arrived from Washington. (ii) Joe likes [ the politician ].](/thumbs/74/70222443.jpg) The Semantics of Definite DPs 1 Thus far, our semantics is able to interpret common nouns that occupy predicate position (1a). However, the most common position for common nouns to occupy is internal to
The Semantics of Definite DPs 1 Thus far, our semantics is able to interpret common nouns that occupy predicate position (1a). However, the most common position for common nouns to occupy is internal to
Semantics and Generative Grammar. Pronouns and Variable Assignments 1. We ve seen that implicatures are crucially related to context.
 Pronouns and Variable Assignments 1 1. Putting this Unit in Context (1) What We ve Done So Far This Unit Expanded our semantic theory so that it includes (the beginnings of) a theory of how the presuppositions
Pronouns and Variable Assignments 1 1. Putting this Unit in Context (1) What We ve Done So Far This Unit Expanded our semantic theory so that it includes (the beginnings of) a theory of how the presuppositions
Simpler Syntax. Ling : Sign-Based Construction Grammar Instructor: Ivan A. Sag URL:
 Simpler Syntax Ling 7800-065: Sign-Based Construction Grammar Instructor: Ivan A. Sag (sag@stanford.edu) URL: http://lingo.stanford.edu/sag/li11-sbcg 1/ 58 Constructs ] [mtr sign construct : dtrs nelist(sign)
Simpler Syntax Ling 7800-065: Sign-Based Construction Grammar Instructor: Ivan A. Sag (sag@stanford.edu) URL: http://lingo.stanford.edu/sag/li11-sbcg 1/ 58 Constructs ] [mtr sign construct : dtrs nelist(sign)
CS460/626 : Natural Language Processing/Speech, NLP and the Web
 CS460/626 : Natural Language Processing/Speech, NLP and the Web Lecture 23: Binding Theory Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay 8 th Oct, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP
CS460/626 : Natural Language Processing/Speech, NLP and the Web Lecture 23: Binding Theory Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay 8 th Oct, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP
What is a natural syntactic model for frame-semantic composition?
 What is a natural syntactic model for frame-semantic composition? Timm Lichte, Laura Kallmeyer & Rainer Osswald University of Düsseldorf, Germany CTF14, August 26, 214 SFB 991 1 / 26 Overview natural syntax
What is a natural syntactic model for frame-semantic composition? Timm Lichte, Laura Kallmeyer & Rainer Osswald University of Düsseldorf, Germany CTF14, August 26, 214 SFB 991 1 / 26 Overview natural syntax
Semantics and Generative Grammar. Quantificational DPs, Part 2: Quantificational DPs in Non-Subject Position and Pronominal Binding 1
 Quantificational DPs, Part 2: Quantificational DPs in Non-Subject Position and Pronominal Binding 1 1. Introduction (1) Our Current System a. The Ds no, some, and every are type (Quantificational
Quantificational DPs, Part 2: Quantificational DPs in Non-Subject Position and Pronominal Binding 1 1. Introduction (1) Our Current System a. The Ds no, some, and every are type (Quantificational
Linearization. {α,β}= def. α and β aresisters
 Linearization Linguistics 601 3 ecember 2015 Our starting position in thinking about linearization was built upon a view of phrase structure that distinguished maximal projections from intermediary phrases.
Linearization Linguistics 601 3 ecember 2015 Our starting position in thinking about linearization was built upon a view of phrase structure that distinguished maximal projections from intermediary phrases.
Class Notes: Tsujimura (2007), Ch. 5. Syntax (1), pp (3) a. [[akai hon]-no hyooshi] b. [akai [hon-no hyooshi]]
![Class Notes: Tsujimura (2007), Ch. 5. Syntax (1), pp (3) a. [[akai hon]-no hyooshi] b. [akai [hon-no hyooshi]] Class Notes: Tsujimura (2007), Ch. 5. Syntax (1), pp (3) a. [[akai hon]-no hyooshi] b. [akai [hon-no hyooshi]]](/thumbs/80/81815987.jpg) Class otes: Tsujimura (2007), Ch. 5. yntax (1), pp. 206-220 p. 206 What is!ytx"?! n area in linguistics that deals with the REGULRLITY of how words are put together to create grammatical sentences What
Class otes: Tsujimura (2007), Ch. 5. yntax (1), pp. 206-220 p. 206 What is!ytx"?! n area in linguistics that deals with the REGULRLITY of how words are put together to create grammatical sentences What
Features. An argument DP must have been assigned Case by S-structure. A Specifier of IP must have been occupied by something by S-structure.
 Features 26 October 2015 We left with a system that included the following elements. (1) Head Movement onstraint IfanX 0 movestoay 0,therecanbenoZ 0 thatisc-commandedbyy 0 and c-commandsx 0. (2) Like(s)
Features 26 October 2015 We left with a system that included the following elements. (1) Head Movement onstraint IfanX 0 movestoay 0,therecanbenoZ 0 thatisc-commandedbyy 0 and c-commandsx 0. (2) Like(s)
CS1800: Strong Induction. Professor Kevin Gold
 CS1800: Strong Induction Professor Kevin Gold Mini-Primer/Refresher on Unrelated Topic: Limits This is meant to be a problem about reasoning about quantifiers, with a little practice of other skills, too
CS1800: Strong Induction Professor Kevin Gold Mini-Primer/Refresher on Unrelated Topic: Limits This is meant to be a problem about reasoning about quantifiers, with a little practice of other skills, too
Unterspezifikation in der Semantik Scope Semantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars
 in der emantik cope emantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2011/2012 LTAG: The Formalism (1) Tree Adjoining Grammars (TAG): Tree-rewriting
in der emantik cope emantics in Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2011/2012 LTAG: The Formalism (1) Tree Adjoining Grammars (TAG): Tree-rewriting
Lecture 7. Logic. Section1: Statement Logic.
 Ling 726: Mathematical Linguistics, Logic, Section : Statement Logic V. Borschev and B. Partee, October 5, 26 p. Lecture 7. Logic. Section: Statement Logic.. Statement Logic..... Goals..... Syntax of Statement
Ling 726: Mathematical Linguistics, Logic, Section : Statement Logic V. Borschev and B. Partee, October 5, 26 p. Lecture 7. Logic. Section: Statement Logic.. Statement Logic..... Goals..... Syntax of Statement
CAS LX 500 Topics in Linguistics: Questions Spring 2006 March 2, b: Prosody and Japanese wh-questions
 CAS LX 500 Topics in Linguistics: Questions Spring 2006 March 2, 2006 Paul Hagstrom 7b: Prosody and Japanese wh-questions Prosody by phase Prosody and syntax seem to fit quite tightly together. Ishihara,
CAS LX 500 Topics in Linguistics: Questions Spring 2006 March 2, 2006 Paul Hagstrom 7b: Prosody and Japanese wh-questions Prosody by phase Prosody and syntax seem to fit quite tightly together. Ishihara,
The Semantics of Questions Introductory remarks
 MIT, September-October 2012 1 1. Goals for this class The Semantics of Questions Introductory remarks (1) a. Which boy (among John, Bill and Fred) read the book? Uniqueness presupposition (UP): exactly
MIT, September-October 2012 1 1. Goals for this class The Semantics of Questions Introductory remarks (1) a. Which boy (among John, Bill and Fred) read the book? Uniqueness presupposition (UP): exactly
Seminar in Semantics: Gradation & Modality Winter 2014
 1 Subject matter Seminar in Semantics: Gradation & Modality Winter 2014 Dan Lassiter 1/8/14 Handout: Basic Modal Logic and Kratzer (1977) [M]odality is the linguistic phenomenon whereby grammar allows
1 Subject matter Seminar in Semantics: Gradation & Modality Winter 2014 Dan Lassiter 1/8/14 Handout: Basic Modal Logic and Kratzer (1977) [M]odality is the linguistic phenomenon whereby grammar allows
Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features
 Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features Denys Duchier Thi-Bich-Hanh Dao firstname.lastname@univ-orleans.fr Yannick Parmentier Abstract In this paper, we present a model-theoretic description of
Model-Theory of Property Grammars with Features Denys Duchier Thi-Bich-Hanh Dao firstname.lastname@univ-orleans.fr Yannick Parmentier Abstract In this paper, we present a model-theoretic description of
An Alternative Semantics for English Aspectual Particles
 Aspectual Particles 1 of 27 An Alternative Semantics for English Aspectual Particles Alexander Klapheke Harvard University SNEWS November 15, 2014 Aspectual Particles Overview 2 of 27 Overview Previous
Aspectual Particles 1 of 27 An Alternative Semantics for English Aspectual Particles Alexander Klapheke Harvard University SNEWS November 15, 2014 Aspectual Particles Overview 2 of 27 Overview Previous
Moreno Mitrović. The Saarland Lectures on Formal Semantics
 ,, 3 Moreno Mitrović The Saarland Lectures on Formal Semantics λ- λ- λ- ( λ- ) Before we move onto this, let's recall our f -notation for intransitive verbs 1/33 λ- ( λ- ) Before we move onto this, let's
,, 3 Moreno Mitrović The Saarland Lectures on Formal Semantics λ- λ- λ- ( λ- ) Before we move onto this, let's recall our f -notation for intransitive verbs 1/33 λ- ( λ- ) Before we move onto this, let's
Artificial Intelligence
 CS344: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 20-21 Natural Language Parsing Parsing of Sentences Are sentences flat linear structures? Why tree? Is
CS344: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 20-21 Natural Language Parsing Parsing of Sentences Are sentences flat linear structures? Why tree? Is
CAS LX 522 Syntax I. We give trees to ditransitives. We give trees to ditransitives. We give trees to ditransitives. Problems continue UTAH (4.3-4.
 7 CAS LX 522 Syntax I UTAH (4.3-4.4) You may recall our discussion of θ-theory, where we triumphantly classified erbs as coming in (at least) three types: Intransitie (1 θ-role) Transitie (2 θ-roles) Ditransitie
7 CAS LX 522 Syntax I UTAH (4.3-4.4) You may recall our discussion of θ-theory, where we triumphantly classified erbs as coming in (at least) three types: Intransitie (1 θ-role) Transitie (2 θ-roles) Ditransitie
CAS LX 522 Syntax I November 4, 2002 Week 9: Wh-movement, supplement
 CAS LX 522 Syntax I November 4, 2002 Fall 2002 Week 9: Wh-movement, supplement () Italian Tuo fratello ( your brother ), [ CP a cui i [ TP mi domando [ CP che storie i [ TP abbiano raccontato t i t j...
CAS LX 522 Syntax I November 4, 2002 Fall 2002 Week 9: Wh-movement, supplement () Italian Tuo fratello ( your brother ), [ CP a cui i [ TP mi domando [ CP che storie i [ TP abbiano raccontato t i t j...
Agreement is Feature Sharing 1
 Comments, criticisms, remarks, etc. are very welcome. Send email to either author: frampton@neu.edu or sgutm@neu.edu Agreement is Feature Sharing 1 Version 2 John Frampton and Sam Gutmann Northeastern
Comments, criticisms, remarks, etc. are very welcome. Send email to either author: frampton@neu.edu or sgutm@neu.edu Agreement is Feature Sharing 1 Version 2 John Frampton and Sam Gutmann Northeastern
27. THESE SENTENCES CERTAINLY LOOK DIFFERENT
 27 HESE SENENCES CERAINLY LOOK DIEREN comparing expressions versus comparing sentences a motivating example: sentences that LOOK different; but, in a very important way, are the same Whereas the = sign
27 HESE SENENCES CERAINLY LOOK DIEREN comparing expressions versus comparing sentences a motivating example: sentences that LOOK different; but, in a very important way, are the same Whereas the = sign
Ling 510: Lab 2 Ordered Pairs, Relations, and Functions Sept. 16, 2013
 1. What we know about sets A set is a collection of members that are: 1. Not ordered 2. All different from one another Ling 510: Lab 2 Ordered Pairs, Relations, and Functions Sept. 16, 2013 (1) a. A ={Elizabeth,
1. What we know about sets A set is a collection of members that are: 1. Not ordered 2. All different from one another Ling 510: Lab 2 Ordered Pairs, Relations, and Functions Sept. 16, 2013 (1) a. A ={Elizabeth,
Modals and Scope Economy
 Modals and Scope Economy Dominique Blok New Ideas in Semantics and Modelling Universiteit Utrecht 7-8 September 2016 d.blok@uu.nl EHESS, Paris 1 Introduction Scope Economy (Fox, 2000:3): Scope Shifting
Modals and Scope Economy Dominique Blok New Ideas in Semantics and Modelling Universiteit Utrecht 7-8 September 2016 d.blok@uu.nl EHESS, Paris 1 Introduction Scope Economy (Fox, 2000:3): Scope Shifting
The Formal Architecture of. Lexical-Functional Grammar. Ronald M. Kaplan and Mary Dalrymple
 The Formal Architecture of Lexical-Functional Grammar Ronald M. Kaplan and Mary Dalrymple Xerox Palo Alto Research Center 1. Kaplan and Dalrymple, ESSLLI 1995, Barcelona Architectural Issues Representation:
The Formal Architecture of Lexical-Functional Grammar Ronald M. Kaplan and Mary Dalrymple Xerox Palo Alto Research Center 1. Kaplan and Dalrymple, ESSLLI 1995, Barcelona Architectural Issues Representation:
Additional Test Scores. Test Scores Cross Test Scores Subscores Now let's look at what to do next: Areas of Strength
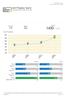 SAT Practice Test D This test scanned: September 22, 2016 Verbal 770 Your Progress 1600 100 Math 660 Total* 130 / 1600 130 1200 1000 910 990 1060 800 600 00 Test A 8//2016 Test B 8/13/2016 Test C 8/27/2016
SAT Practice Test D This test scanned: September 22, 2016 Verbal 770 Your Progress 1600 100 Math 660 Total* 130 / 1600 130 1200 1000 910 990 1060 800 600 00 Test A 8//2016 Test B 8/13/2016 Test C 8/27/2016
