Classical Approach to the Theory of Elementary Particles
|
|
|
- Jesse Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based only on lassial piniples that wee developed befoe the intodution of quantum theoy) to the theoy of elementay patiles. In physis, dualism efes to media with popeties that an be assoiated with the mehanis of two diffeent phenomena. Beause these two phenomena's mehanis ae mutually exlusive, both ae needed in ode to desibe the possible behavios. (Retieved fom " Usually, dualism in physis is explained by the example: wave / patile. This stated with a lassial eletomagneti wave / quantum photon example fo light and poeeded with a lassial patile / quantum wave fo massive patiles. I want to peeive this dualism altogethe as lassial / quantum appoah to the physial objet. This sounds plausible (but we have to emembe that these two appoahes ae "mutually exlusive" and neve intemix them). Taking the idea of lassial appoah to the elementay patiles seiously, we an see that the existing lassial eletodynamis (CED) has to be modified in ways:. Many things wee intodued in CED duing the "quantum ea" in ode to naow the gap between CED and Quantum theoy and also in ode to make CED a sevant of Quantum theoy. Aoding to the lassial piniples that wee established befoe the ise of Quantum theoy, only the eletomagneti field and the field of uent density wee to epesent the physial eality. The potential was not unique and was teated only as a mathematial tool. The Lagangian was also thought of as the unique physial quantity that an not be expessed though potential. Hee I mean the so alled "inteation tems" in the Lagangian that wee intodued to ease the bidge between CED and the Quantum petubation theoy. The CED as we have it now is atually a pat of Quantum theoy. This should be undone (intelligently) to make CED a eal altenative to Quantum theoy (we expet that both theoies will enjoy a patial expeimental onfimation).. The CED (as it was in old times and is now) ontains "singulaities" as models fo the elementay patiles whih deem to be "pointlike". I do not think that infinite quantities exist in physial eality. The tue lassial appoah would be to eplae these singulaities by some extended field stutues. Theefoe CED has to be adially modified. But the way to modify CED will not be the easy one as one may expet. So let us stat with the simplest possible Lagangian:
2 ab d ab g g FaFbd g j a jb () 6 k whee F ik is the eletomagneti field, j k is the field of uent density, and k will be the new onstant of the theoy. We suggest that the onnetion between the fields (also an be alled inteation ) is given by Maxwell's equations with uents (half of Maxwell's system): i ik 4 j F k dive j oth E 4,, j () 4 whih is given as a peliminay ondition befoe any vaiation. The inteation ondition () is an auxiliay ondition with espet to the Lagangian (). The () also povides the onsevation of hage: j a a= (the antisymmety of the eletomagneti field is also a peliminay ondition). The othe half of Maxwell's equations is: * * F, F e F, divh, ote ik ik iklm lm H k (a) This will be the esult of the vaiation poedue late on. Befoe we stat with the vaiation of fields, let us find the enegy-momentum tenso that oesponds to the Lagangian (). The meti tenso in lassial 4-spae is g ik =diag[,-,-,-] (we assume =). Let us onside an abitay vaiation of a meti tenso but on the ondition that this vaiation does not intodue any uvatue in spae. This vaiation is: (3) g ik i k k i whee k is an abitay but small veto. One has to use the mathematial appaatus of Geneal Relativity to hek it with the vaiation (3) the Riemann uvatue tenso emains zeo in the fist ode. Assuming that the ovaiant omponents of the physial fields ae kept onstant (then the ontavaiant omponents will be vaied as a esult of the vaiation of the meti tenso, but we do not use them -- see ()) we an alulate the vaiation of the ation. The vaiation of the squae oot of the deteminant of the meti tenso is: i k g gg ik g (this esult an be found in textbooks on Theoy of Field). The vaiation of the ation beomes: i k i k S g gd T gd ik ik ik g 4 T g F F F F g j j j j g ab ab a ik ia kb ab ik i k a ik 4 6 k k (4) ik The integal in (4) an be tansfomed to the fom T ki gd if we onside that the integal ove some emote losed sufae tuns to zeo due to the smallness of T ik and the integal ove 3-d volume at t and t tuns to zeo due to the assumption: i = at these times. Sine i ae abitay small funtions (between t and t), the equiement S= yields:
3 T (5) ia a We have found the unique definition of the enegy-momentum tenso (4). If we want ation to be minimum with espet to the abitay vaiation of the meti tenso in flat spae then (5) should be satisfied. Let us ewite the enegy-momentum tenso in 3-d fom: T ( E H ) [( j ) ( j) ] 8 k T ( E H E H ) [( j ) ( j) ( j ) ] 8 k 4 T ( E H E H ) j j k 4 T ( E E H H ) j j 4 k Notie, that we did not used Maxwell's o any othe field equations so fa. Substituting (4) in (5) and using the Maxwell's equation () and antisymmety of F ik, we obtain: (4a) a k k k j Fai ja i ji a, j E j & j j H otj (6) A new Dynamis The equation (6) we an all a Dynamis Equation. It is nonlinea equation. It an be shown that any 3-d hypesufae that is eveywhee tangent to the veto J k is a haateisti of the equation (6). The equation (6) is automatially satisfied in vauum (J k =). An anothe possibility (J k ) will be the inside egion of the elementay patile. The bounday between these egions will be a haateisti sufae. Inside the elementay patile the dynamis equation (6) desibes, as we all it, Mateial Continuum. A Mateial Continuum an not be divided into a system of mateial points. The Relativisti (o Newton's) Dynamis Equation of CED, that desibes behavio of the patile as a whole, ompletely disappeas inside the elementay patile. Thee is no foe, no veloity o aeleation inside the patile. A kinemati state of the Mateial Continuum is defined by the field of uent density j k. A wold line of uent j k is not a wold line of a mateial point. That allows us to deny any ausal onnetion between the points on this line. In a onsequene j k an be spae-like as well as time-like. That is in no ontadition with the fat that the bounday of the patile an not exeed the speed of light. If N k is a nomal to the bounday of a patile then N k j k = should be satisfied eveywhee on this bounday. The sala multipliation of N k and (6) gives: 3
4 k F N a j b b a a a ab j j N a b N, j j a a 4 It is lealy seen that the left pat of this equation is definite on the bounday of the patile. So should be and the ight pat. That means that on the bounday with vauum the invaiant density of hage should be zeo. By the equation (6) we have gotten something vey impotant, but we ae just on the beginning of a diffiult and unetain jouney. Let us etae some ou steps.. Ideal Patile (IP) The fist question was: is thee a stati solution to the system of equations (6) plus Maxwell's equations (), (a)? The solution was found: k j R ( z), z n ; j, n z ; j (7) 4 n E kr ( z), z n ; E ( ) kn / z, n z ; H whee z = k o, R o (z)=sin (z)/z, R (z)=sin (z)/z -os (z)/z - the spheial Bessel funtions, is an abitay onstant. The full hage of IP is: n e 4 j d ( ) n (8) k To find the mass we should integate T ove the volume: 8 k m T sin( ) dd d [ E ( j ) ] d k 6 z (9) dz { [ R ( z) R ( z)] z dz ( n) } n k z k z. The seond question was: is thee a stati solution that poses a spin? Afte a long seies of unsuessful attempts it was poven (see Appendix) the theoem that stati spin is impossible with any enegy-momentum tenso if its divegene vanishes eveywhee and it is good on a emote sphee (stati spin is possible in a stati extenal magneti field but the oesponding enegy-momentum tenso is not good at infinity). The seah fo a dependent of time solution with spin gave no esults. Afte these unsuessful attempts it was ealized that the main esult of the equation (6) is the bounday of the patile (haateisti of the oesponding PDE system). We did not expet it duing the deivation of (6). We did not ask fo touble, so to speak, but we got it. The mee existene of the bounday of the elementay patile is a vey impotant hange in ou mathematial appaatus and it equies all possible attention. Now, even befoe we an get the onsevation equation (5) o pefom any othe vaiation, we have to take ae of the bounday of the patile. We have: k i k k i k i k i S T gd T T d T gd T gd i k i i in k i k i k in Sine k is abitay, we ae oming to the onsevation (5) inside and side sepaately, and an additional equiement on the sufae of disuption : ia T Na ontinuous (5a) 4
5 whee N k is a nomal to the sufae. Let us ewite (5a) in 3-d fom. Suppose the bounday of the patile is given in the fom: f(t,y,z)-x =. The ovaiant nomal to this sufae will be (f, t - f, y f, z ). The (5a) podues 4 onditions: 6 E H ( )., ( ) ( ) f& E H n ont j j k 6 ( E H ) f& E H n ( E n) E ( H n) H ont. k (5b) Now we an vay the physial fields J k and F ik keeping in mind that the spae is divided at least in two pats by some disuption sufae. Fo that eason we have to apply a vaiation poedue sepaately fo eah egion. We laim that the peliminay ondition () holds in both these egions, but now we even not sue if it should hold on the bounday itself. In ou system we have unknown independent funtions (4 funtions in J k and 6 funtions in F ik ). These funtions aleady have to satisfy to 8 equations (4 equations in () and 4 equations in (6)). We have only degees of feedom left. We an not vaiate neithe J k no F ik by the staight fowad poedue. Let us employ hee the Lagange method of indefinite fatos. Let us intodue a modified Lagangian: a b ' A ja Fab () 4 whee A k ae 4 indefinite Lagange fatos. Now we have +4=6 degees of feedom and we use them to vay F ik. The vaiation of the field F ik we have to keep zeo on the bounday sine the deivatives of the field ae pesent in (). The Eule's equation gives: Fik Ak i Ai k () inside. The Maxwell's equation (a) follows fom (). We ae not able to vey J k sine thee ae no degees of feedom left, but we aleady have (6) as a dynamis equation. If we do not keep the vaiation of field zeo on the bounday then we will get, in addition to (), the sufae integal: i kl k il A g A g Fikd l 4 Ñ () in whih we want to get id of ( is the bounday sufae of the patile). Let us onside the vauum aound the patile. If we use the same modified Lagangian () in vauum and vay the eletomagneti field in vauum inluding the bounday of the patile, then in addition to the extension of () into the vauum (still, it is not definite whethe () holds on the bounday itself), we will get the sufae integal: i kl k il A g A g Fikd l 4 Ñ (3) Both integals will annihilate if the tangent omponents of a veto potential A k ae ontinuous aoss the patile bounday. The omponent of potential that is pependiula to the bounday of the patile an have a jump. The potential Ak should be hosen so that it satisfies the peliminay ondition (). Using () and (), and not assuming any gauge, we get: 5
6 A A 4 j inside, A A vauum (4) k a a k k k a a k a a a a In addition, as we leaned above, the tangent omponents of potential have to be ontinuous aoss the bounday of the patile. The potential futhe eveals its stange natue. Notie, that the above deivation does not pelude a failue of Maxwell's equations () o (a) on the bounday of the patile. We ame at a vey unusual aangement:. The equations (6), (), and (a) define the solution fo the eleti, magneti, and uent density fields inside the patile.. The same equations define the solution fo the eleti and magneti fields in vauum. 3. Thee ae no diet equiements on the omponents of eletomagneti field and 3 omponents of a uent density on the bounday of the patile (only the omponent of uent nomal to the bounday should be zeo). Instead, we have the 4 nonlinea algebai onditions (5b) on eletomagneti field and uents, and the 3 diet onditions on the tangent omponents of potential (we do not ae ab the omponent of potential that is nomal to the bounday). That means that with the potential we an not solve the physial poblem. Still, the potential is only a mathematial tool (it does not epesent any physial eality in a point of spae (ontay to the eletomagneti field and the field of uent density)). This was the one of the lassial piniples befoe the quantum theoy. Compaison of the two appoahes Above we developed the two possible ways in whih CED an be modified (extended) in ode to appoah the elementay patiles fom the pue lassial point of view:. The "bounday last" appoah. We equested that the "inteation" between the eletomagneti field and the field of uent (expessed by the Maxwell's equation ()) should be the peliminay ondition tue in all the spae. We did not expet any disuption sufae befoe the vaiation. We obtaind the system (), (a), (6) with the onseving enegy-momentum tenso (4), (4a). This system is unlinea due to the equation (6). The haateistis of the system allow a sufae of disuption in a solution. We obtained the stati solution of this system (IP). The whole set of the solutions of the system was investigated puely, but I would like to say that having only Ideal Patile one an not explain muh in the eal wold. The fist eage was to do away with the quantization of the adius of IP. The oesponding patile was alled IP+ and, shue enougth, IP+ violates the enegy-momentum onsevation. I am 9% sue that if we want to ontinue with the "bounday last" appoah, we have to live with this unonsevation. But we ae not questioning the validity of the Maxwell's equations hee. It was mentioned above that IP+ violates the enegy-momentum onsevation. What does it mean? Let us onside two oodinate systems: K the oodinate system in whih the solution IP+ is given, and K' that moves with a speed V in x dietion (we assume =). Using Loentz tansfomation we obtain image of the IP+ solution in K'. If we alulate by integation a global (meaning not onneted to any point of spae) 6
7 onseving linea momentum veto: k k P T d3v t (5) in oodinates K, then we find only time omponent (enegy) is diffeent fom zeo: P. The oesponding integation in K' (ove t'=) will give anothe veto Q k ' with Q ' and Q ' diffeent fom zeo. Now by Loentz tansfomation we an tansfom P k fom K to K' obtaining P k ' (with omponents diffeent fom zeo). If the solution satisfies the onsevation equiements, then we should get: P k '=Q k ' in K'. Let us see what we get fo IP+. m P m z R ( z)os( z), P ; P ' m m V, P ' mv; k m m Q ' ( m mv ) m V, Q ' V ( m m ), m z R ( z ) 3 6k (6) If z=nπ then m=; m stays positive almost at all z; the appoximation is given fo a small V. Fo IP+ it looks like the unonsevation is playing games with the mass.. The "bounday fist" appoah. We state the existene of the bounday fom the vey beginning. We laim that the inteation () is valid inside and side the patile sepaately. We obtained that (), (a), (6) ae valid inside the patile, and (), (a) with a zeo uent ae valid in vauum. We do not question the enegy-momentum onsevation hee. It bings us, in addition, the bounday onditions fo the fields and uents (5a), (5b) whih ae unlinea in natue. In addition, we have the unknown in onventional CED equiement on the tangent omponents of potential on the patile bounday and on infinity. In this appoah the Maxwell's equations an fail on the bounday of the patile (the eletomagneti field and uents an have a jump). IP: Let us obtain a simplest stati solution in the "boundat fist" appoah with eleti hage and eleti field only. We have: k A R ( z) R ( z) bz, z z; j R ( z); 4 z A b, z z ; b R ( z) R ( z); z (7) z E kr ( z), z z; E kb, z z ; z 3 3 m z R ( z) z R ( z) z R ( z) R ( z) ; k Now the position of the bounday z is abitay. In geneal, the eleti field has a jump on the bounday of IP. Aodingly, the total hage has diffeent atual and effetive values (the effetive hage is the one that oesponds to the vauum field of the patile). If z is equal to nπ then the jump disappeas and IP tuns to IP. The IP fully satisfies to the enegy-momentum onsevation law (5), (5a), (5b). The potential A 7
8 is a tangent omponent, so, it should be ontinuous ove the patile's bounday, and should have a easonable value at infinity. If we want the integal () taken ove the infinitely emote sphee to be zeo then the potential has to deease as - o faste. Fo that eason we an always onside two patiles with opposite hages that is vey fa one fom anothe so that the inteation an be negleted, but still, they will make a pope dependene of the potential at infinity. The ontinuity of potential bings up a vey inteesting question: Two patiles does not inteat but the stutue of the one an influene the stutue of the othe though the potential at infinity. Suppose ou patile has a spin dieted along z-axis. Then anothe patile of the simila stutue but with untipaallel spin should exist somewhee in spae (fa, o lose does not matte) in ode to anel the potential at infinity. Magnifient Patile (MP) Hee we dissuss "the bounday fist" appoah. Above we saw the eleti stati solution (IP) that violates Maxwell's equations on the bounday, but (and this is impotant) does not violate the pinipal of minimum ation. We tied to obtain a magneti stati solution (stati spin), but again, it was unsuesslull. Now we ae ompelled that a spin should be looked fo in a steady-state osillating solution. Waning: The MP is not an atual igoous solution (beause we mange to to satisfy the unlinea bounday ondition (5b) only in aveage ove the peiod of osillation) but an inteesting lose shot on it. Sine the potential satisfies the linea equations (4) and the stait fowad bounday onditions (tangent omponents should be ontinuous), it follows that the sum of two solutions of the equations (4) is also a solution (pinipal of supeposition). The touble aises when it omes to the unlinea bounday ondition (5b) fo the eletomagneti field and uents. We will dissuss a solution that ontains 3 pats (we assume that the uents inside the patile ae expessed though the potential k k k j A 4 with exeption of the stati eleti pat; also we assume the Loentz gauge):. A stati eleti pat: e k e A R ( k) R ( k ), j R ( k) in; A k 4 k (8) A is a tangent omponent at the infinitely emote sphee. To anel the potential thee (and make it deease as - ) we have to have anothe patile with α'e'=- αe somewhee befoe the infinity. The oesponding eleti field is:. A stati magneti pat: e E k R ( k ) in; E k (8a) 8
9 A R ( k)sin in; A R ( k ) sin (9) We may do not need to anel this at infinity beause we aleady have a good deease ate. The oesponding magneti field is: H R ( k)os in; H R 3 ( k )os H R ( k) kr ( k) sin in; H R 3 ( k )sin 3. And an osillating pat: (9a) h sin( t), h os( t), z k, k k y ( ) R ( ) Q ( ), y ( ) R ( ) Q ( ) A h R ( z)sin in; A h y ( )sin k A h ( ) R ( z) R ( z) sin in, A h y ( ) y( ) sin k z k k A h ( ) R ( z) R ( z) os in, A h y( ) os k z k k A h ( ) R ( z) R ( z) in, A h y( ) k z () whee Q (x) =-os(x)/x, Q (x)=-os(x)/x^-sin(x)/x ae the seond kind spheial Bessel funtions. The potentials () satisfy (4) and the onsevation ondition: A k k= inside. The (8) and (9) ae witten so that the bounday onditions at aleady satisfied. To satisfy the bounday onditions fo () we have to equest: k k R ( z) y( ); ( ) R R y( ) k z R ; Ri Ri ( z); z k ( zr R ) () The onstant γ is obtained as a esult of the fist two bounday onditions. On this onditions A, A θ, and A φ will be ontinuous (A is not ontinuous but we do not ae ab that). We have to anel the osillating potential at infinity beause the spheial Bessel funtions of both kinds deease as - (not good enough) at infinity. So we have to have anothe patile with δ '=-δ and δ '=-δ (also will be δ'=-δ) with the same oientation of z-axis. Note, that the funtions h(φ-ωt) and h(φ-ωt) should be the same. If we hange the sign of ω then it will be anothe solution. Let us alulate the 9
10 eletomagneti field that oesponds to the osillating potentials (): k E h ( ) R ( z) R ( z) sin in, E k z k E h R ( z) ( ) R ( z) os in, E k z k E h R ( z) ( ) R ( z) in, E k z k H in, H ; H h R ( z) in, H k H h R ( z)os in, H (a) The amazing thing ab this osillating field is: The osillating eletomagneti field inside the patile is pesent, but thee ae no osillating eletomagneti fields in vauum while the osillating potential is pesent. The expession fo γ (see ()) indiates that thee exist the esonane fequenies that oespond to: z= , , ,... (if k and ae given then only fequeny defines z) at whih γ (and the whole solution) beomes infinite. k j A The investigation of the adial uent 4 (see ()) on the bounday shows that it has minimums at z that satisfies the equation: R ( z ) zr ( z) 3 () the solutions of whih ae: z= , , ,.... If we take z satisfying () then fom () we find γ= (the eason why we do not equie j = on the patile bounday will be explained late). We will seek the solution as a supeposition of all the above 3 pats. But ou bounday of the patile is too simplified (it is a stati in time sphee of adius ). We found that we ae not able to satisfy the bounday onditions (5b) on the stati sphee. We think that the eal bounday has to be not a sphee (but lose to it) and has to depend on time. Bound by the spheial oodinate system we wee not able to find the eal bounday (and so the atual solution). Still, we an hope that if we satisfy the bounday onditions (5b) on ou sphee in aveage ove a one peiod of the osillation, then the eal solution should exist somewhee not fa fom ou appoximation. These ae also the easons why we ae seeking the adial uent to be only a minimum on the sphee. Let us take a lose look at the onditions (5b). We have the nomal in spheial oodinates:, t =, n =-, n θ =, n φ =. The time omponent of the ondition (5b) is satisfied beause ( E H n). The phi omponent of (5b) is ontinuous in aveage. The time aveage of the theta omponent of (5b) (the diffeene inside minus vauum) is
11 popotional to: R ( k ) R ( k )sin os Let us take k =π (whih tuns the above expession to zeo) and z= Then k/k.948, ω/k.773. The k still emains indefinite. At these values the adial uent is vey small ompae to its neighboing tems. The time aveage of the adial omponent of the ondition (5b) will be of the fom: A+Bsin θ. Fom A= we will get: α (-e /k / ) δ.688, and fom B= we will get: β δ.954. These onditions will define α and β (we still have the option to hoose the sign of α and β as we like). Afte that we an alulate the effetive hage and magneti moment, and, afte the integation ove 3-spae, the mass and the spin. All these values will be expessed though δ, k, and. These 3 onstants won't allow us to make the esult looking as an eleton o poton (beause it equies 4 onstants). On the top of that the values of the atual solution that satisfies (5b) an shift signifiantly. Still we only hope that this atual solution (MP) does exist, but this peliminay attempt looks pomising. Sine the solution has esonane fequenies we need to intodue a powe dissipation to make a moe ealisti solution. Conlusion: I want to attat attention to the hange of the vaiation poedue: instead of keeping the inteation tem in the Lagangian and vaiating potential (onventional poedue) we define inteation () as an auxiliay ondition befoe the vaiation. Then, vaiating the eletomagneti field itself (not a potential), we use the Lagange method of indefinite fatos with the modified Lagangian (). The impotant esult of this hange of the vaiation poedue is the ontinuity of tangent omponents of the potential (and, onsequently, definite value of them at infinity) is valid in the onventional eletodynamis also. Appendix: The Spin of a Classial Physial System with Continuous (Inluding Fist Deivatives) and "Good" Behaving at Infinity Enegy-Momentum Tenso in Statis is Zeo The flat spae of eal 4-dimensional independent vaiable x k with Loentz meti is assumed. If we have a lassial physial system desibed in that spae and the enegymomentum tenso of that system obeys the onsevation law, and if:. This enegy-momentum tenso is ontinuous in 4-spae and has ontinuous fist deivatives eveywhee in 4-spae (it an have a bake of the seond deivative on some losed 3-d sufae in that spae).. This enegy-momentum tenso is good at teestial infinity (so that the sufae integal ove a 3-sphee of a big adius an be negleted). 3. The enegy-momentum tenso does not depend on time. Then the angula momentum of this system (spin) is zeo.
12 To pove this theoem let us fist onside a onseving veto j k k=. Applying 4-d Gauss theoem sepaately to 4 volume inside and side 3-d losed sufae we an pove that the integal: e j d3v (.a) t does not depend on time. The integation in () goes ove the hypesufae x =. In diffeent oodinates it will be diffeent hypesufae but the integal will have still the same value. It is a good example of a global thing. Let us elaboate on the meaning of a good global. Let us onside two etilinea oodinate systems K and K whih ae onneted by the Loentz tansfomation: We have: e x x' ( x' Vx' ), ( x Vx ), x ( x' Vx' ) x' ( x Vx j' dx' j dx j' ( x', x' ) Vj' ( x', x' ) x' x x ) dx (.a) Hee the integation ove dx and dx 3 supposed to be pefomed but not indiated fo simpliity. In the last integal we just expessed j aoding to the tansfomation of a ontavaiant veto whih tansfoms the same way as oodinates do. Instead of integating ove dx in the last integal we an integate ove dx but we have to fulfill the ondition x =, o x =-Vx and dx = γdx sine we keep x =. We have: e j' (, x' ) dx' j' ( Vx', x' ) Vj' ( Vx', x' ) x' x' Vx' Now suppose that ou distibution of uents does not depend on time x in oodinates K. Sine V is abitay and the Loentz tansfomation (boost) an involve any of the oodinates x,x,x 3 we should onlude that in this ase the integal: j k ' d 3V ' if k,,3 dx' (3.a) This integal diffes fom zeo only if k=. Taking the enegy-momentum tenso we have to be aeful beause the Gauss theoem only applies to a veto. To edue a tenso to a veto we have to intodue a onstant veto e k (fou linea independent onstant vetos an be intodued in a flat spae). Using the onseving veto G k =e i T ik and using the same logi we an pove that if T ik does not depend on time in oodinates K then the integal: T ' ik d3v ' if i k only (4.a) diffes fom zeo only if i=k=. The same way we an pove that in statis the integal: l mn M ' e x' T ' d 3V ' if n only (5.a) ik iklm Now using (4) and (5) we an pove that in statis: i k x T ' d V if i, k, i k ' 3 (6.a) The onsequene of (6) is that M k (spin) equals to zeo in statis. The final onlusion is: An independent of time solution that has a onseving (T ik k=) eveywhee enegy-momentum tenso that is "good" at infinity an not have angula
13 momentum diffeent fom zeo. Refeenes:. Yui Keilman, Phys. Essays,, # p.34, (998). Idem, Phys. Essays, 5, #3, (3) 3
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
E(r,t) = e 3. r 3. (b) Show that the transverse current, J t,is 3n(n e 3 ) e 3
 Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Reflectance spectra for Si
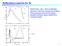 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Mass- and light-horizons, black holes' radii, the Schwartzschild metric and the Kerr metric
 006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Physics 161 Fall 2011 Extra Credit 2 Investigating Black Holes - Solutions The Following is Worth 50 Points!!!
 Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ion-sound waves (electrostatic low frequency waves)
 OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
2. Equation of generalized Dynamics. Let rectangular right hand coordinate triple is fixed in three-dimensional Euclidian space.
 Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
A Relativistic BCS Theory of S-Wave Superconductivity
 A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Chapter 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Physics 2B Chapter 22 Notes - Magnetic Field Spring 2018
 Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
A Theory of the Podkletnov Effect based on General Relativity: Anti-Gravity Force due to the Perturbed Non-Holonomic Background of Space
 July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Laplace Potential Distribution and Earnshaw s Theorem
 Laplae Potential Distibution and Eanshaw s Theoem Fits F.M. de Mul Laplae and Eanshaw Pesentations: Eletomagnetism: Histoy Eletomagnetism: Elet. topis Eletomagnetism: Magn. topis Eletomagnetism: Waves
Laplae Potential Distibution and Eanshaw s Theoem Fits F.M. de Mul Laplae and Eanshaw Pesentations: Eletomagnetism: Histoy Eletomagnetism: Elet. topis Eletomagnetism: Magn. topis Eletomagnetism: Waves
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH 1. INTRODUCTION
 DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Are Singularity and Dark Energy Consequences of Vacuum Solution of Field Equations?
 Intenational Jounal of New Tehnology and Reseah (IJNTR) ISSN:5-116 Volume- Issue-11 Novembe 017 Pages 7-55 Ae Singulaity and Dak Enegy Consequenes of Vauum Solution of Field Equations? Banko M Novakovi
Intenational Jounal of New Tehnology and Reseah (IJNTR) ISSN:5-116 Volume- Issue-11 Novembe 017 Pages 7-55 Ae Singulaity and Dak Enegy Consequenes of Vauum Solution of Field Equations? Banko M Novakovi
On the indirect e ect in the Stokes±Helmert method of geoid determination
 Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theorem that relates to it
 Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
The Kerr-metric, mass- and light-horizons, and black holes' radii.
 006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.
![( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx. ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.](/thumbs/90/103689049.jpg) 9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
Study of the Endface Friction of the Revolving Vane Mechanism
 Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
The Radii of Baryons
 Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
Journal of Theoretics
 Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
AN ELECTROMAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTEM FOR UAVs
 Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
Lorentz-invariant theory of gravitation
 oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (summay) Alexande G. Kyiakos * Annotation This atile is a summay of the non-geometial oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (IGT) (efeenes and itations hee allow to familiaize
oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (summay) Alexande G. Kyiakos * Annotation This atile is a summay of the non-geometial oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (IGT) (efeenes and itations hee allow to familiaize
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Recitation PHYS 131. must be one-half of T 2
 Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
e sin cos i sin sin j cos k [2 POINTS] (c) Hence, determine expressions for sin sin i sin cos j sin e
![e sin cos i sin sin j cos k [2 POINTS] (c) Hence, determine expressions for sin sin i sin cos j sin e e sin cos i sin sin j cos k [2 POINTS] (c) Hence, determine expressions for sin sin i sin cos j sin e](/thumbs/84/89549943.jpg) EN: Continuum Mehanis Homewok : Kinematis Due : noon Fiday Febuay 4th Shool of Engineeing Bown Univesity. To analyze the defomation of a onial membane, it is poposed to use a two-dimensional onial-pola
EN: Continuum Mehanis Homewok : Kinematis Due : noon Fiday Febuay 4th Shool of Engineeing Bown Univesity. To analyze the defomation of a onial membane, it is poposed to use a two-dimensional onial-pola
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Gravitational waves generation
 Chapte 4 Gavitational waves geneation In this hapte we will intodue the quadupole fomalism whih allows to estimate the gavitational enegy and the wavefoms emitted by an evolving physial system desibed
Chapte 4 Gavitational waves geneation In this hapte we will intodue the quadupole fomalism whih allows to estimate the gavitational enegy and the wavefoms emitted by an evolving physial system desibed
Planck Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gravitation
 Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 21 Sep 1999
 Mon. Not. R. Aston. So. 000, 000 000 (0000) Pinted 18 Apil 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Magnetosphee of Osillating Neuton Sta. Nonvauum Teatment. A.N. Timokhin, 1,2,3 G.S. Bisnovatyi-Kogan, 2 H.C. Spuit
Mon. Not. R. Aston. So. 000, 000 000 (0000) Pinted 18 Apil 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Magnetosphee of Osillating Neuton Sta. Nonvauum Teatment. A.N. Timokhin, 1,2,3 G.S. Bisnovatyi-Kogan, 2 H.C. Spuit
Generalized Vapor Pressure Prediction Consistent with Cubic Equations of State
 Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Circular Motion Problem Solving
 iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
Scattering in Three Dimensions
 Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD
 Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
Homework 7 Solutions
 Homewok 7 olutions Phys 4 Octobe 3, 208. Let s talk about a space monkey. As the space monkey is oiginally obiting in a cicula obit and is massive, its tajectoy satisfies m mon 2 G m mon + L 2 2m mon 2
Homewok 7 olutions Phys 4 Octobe 3, 208. Let s talk about a space monkey. As the space monkey is oiginally obiting in a cicula obit and is massive, its tajectoy satisfies m mon 2 G m mon + L 2 2m mon 2
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS
 6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
13. Adiabatic Invariants and Action-Angle Variables Michael Fowler
 3 Adiabatic Invaiants and Action-Angle Vaiables Michael Fowle Adiabatic Invaiants Imagine a paticle in one dimension oscillating back and foth in some potential he potential doesn t have to be hamonic,
3 Adiabatic Invaiants and Action-Angle Vaiables Michael Fowle Adiabatic Invaiants Imagine a paticle in one dimension oscillating back and foth in some potential he potential doesn t have to be hamonic,
Classical Mechanics Homework set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions
 Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
CHAPTER 25 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
 CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
you of a spring. The potential energy for a spring is given by the parabola U( x)
 Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustausch)
 Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1.2 Differential cross section
 .2. DIFFERENTIAL CROSS SECTION Febuay 9, 205 Lectue VIII.2 Diffeential coss section We found that the solution to the Schodinge equation has the fom e ik x ψ 2π 3/2 fk, k + e ik x and that fk, k = 2 m
.2. DIFFERENTIAL CROSS SECTION Febuay 9, 205 Lectue VIII.2 Diffeential coss section We found that the solution to the Schodinge equation has the fom e ik x ψ 2π 3/2 fk, k + e ik x and that fk, k = 2 m
The Substring Search Problem
 The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
3/19/2018. PHY 712 Electrodynamics 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 105
 PHY 7 Eletodynamis 9-9:5 A WF Olin 5 Plan fo Letue 4: Complete eading of Chap. 9 & A. Supeposition of adiation B. Satteed adiation PHY 7 Sping 8 -- Letue 4 PHY 7 Sping 8 -- Letue 4 Eletomagneti waves fom
PHY 7 Eletodynamis 9-9:5 A WF Olin 5 Plan fo Letue 4: Complete eading of Chap. 9 & A. Supeposition of adiation B. Satteed adiation PHY 7 Sping 8 -- Letue 4 PHY 7 Sping 8 -- Letue 4 Eletomagneti waves fom
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Correspondence Analysis & Related Methods
 Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
The electrified interface.
 Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Electric Anisotropy, Magnetic Anisotropy, Uniaxial and Biaxial Materials, Bianisotropic Media (Definitions)
 leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Systems
 Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II September 15, 2012 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
INFN School on Electron Accelerators. Beam Acceleration Cavity Field and Concepts
 INFN Shool on leton Aeleatos -4 Septembe 7, INFN Sezione di Pisa Letue b Beam Aeleation Cavity Field and Conepts Calo Pagani Univesity of Milano INFN Milano-LASA & GD Linea Collide Coneptual Sheme Final
INFN Shool on leton Aeleatos -4 Septembe 7, INFN Sezione di Pisa Letue b Beam Aeleation Cavity Field and Conepts Calo Pagani Univesity of Milano INFN Milano-LASA & GD Linea Collide Coneptual Sheme Final
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW)
 PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
Lecture 7: Angular Momentum, Hydrogen Atom
 Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Numerical Integration
 MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
The Poisson bracket and magnetic monopoles
 FYST420 Advanced electodynamics Olli Aleksante Koskivaaa Final poject ollikoskivaaa@gmail.com The Poisson backet and magnetic monopoles Abstact: In this wok magnetic monopoles ae studied using the Poisson
FYST420 Advanced electodynamics Olli Aleksante Koskivaaa Final poject ollikoskivaaa@gmail.com The Poisson backet and magnetic monopoles Abstact: In this wok magnetic monopoles ae studied using the Poisson
