On the indirect e ect in the Stokes±Helmert method of geoid determination
|
|
|
- Ami Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S Stokholm, Sweden sjobeg@geomatis.kth.se; Tel.: ; Fax: eeived: 10 Mah 1998 / Aepted: 16 Novembe 1998 Abstat. The lassial integal fomula fo detemining the indiet e et in onnetion with the Stokes±Helmet method is elated to a plana appoximation of the sea level. A stit integal fomula, as well as some appoximations to it, ae deived. It is onluded that the apsize tunated integal fomulas will su e fom the omission of some long-wavelength ontibutions, of the ode of 50 m in high mountains fo the lassial fomula. This long-wavelength infomation an be epesented by a set of spheial hamoni oe ients of the topogaphy to, say, degee and ode 60. Hene, fo patial use, a ombination of the lassial fomula and a set of spheial hamonis is eommended. Key wods. Geoid Helmet ondensation Indiet e et emove±estoe that they ae limited to the seond o thid powe of elevation. A eent desiption of the Stokes±Helmet method fo geoid detemination was given by VanõÂ ek and Matine (1994). The spei poblem of detemining the indiet e et was teated by Matine and VanõÂ ek (1994), who pointed out that the lassial fomula may be seveely biased. In the pesent pape, we will stat to ompae the fomulas based on plana appoximation with those based on spheial hamonis. Futhe on, a igoous sufae integal fomula fo the indiet e et will be deived (assuming a spheial appoximation of the geoid and onstant topogaphi density). The stit fomula is nally expanded in a Taylo seies fo ompaison with the pevious appoximate solutions. The indiet e et to powe H 1 Intodution Geoid detemination by Stokes' well-known fomula equies that all topogaphi masses ae emoved o edued to a laye on o below the geoid. The e et of estoation of these masses is the indiet e et. The most ommon edution method is Helmet's seond ondensation method, whee the topogaphi masses ae edued to a sufae laye at sea level in a spheial appoximation of the geoid. This lassial method, using a plana appoximation, has been extensively disussed, by, fo example, Heiskanen and Moitz (1967), Wihienhaoen (198), VanõÂ ek and Kleusbeg (1987), Wang and app (1990) and SjoÈ beg (1994). SjoÈ beg (1994, 1995, 1997) and Nahavandhi and SjoÈ beg (1998) used a spheial hamoni appoah to deive the indiet e et. Common to all the above methods is Coespondene to: Las E. SjoÈ beg The lassial fomula (see e.g. Wihienhaoen 198) fo detemining the indiet e et on the geoid fo Helmet's seond ondensation method is N I P lassi ˆ plh P l H HP 6 `0 d 1 whee l ˆ Gq 0, G being the univesal gavitational onstant, and q 0 the density of topogaphy, assumed to be onstant; H; H P =othometi heights of the unning and omputation p points, espetively; ˆ 1 os w ˆ sin w ; = mean Eath sufae adius; = the unit sphee; w = geoenti angle between omputation point P and unning point on the sphee; = mean nomal gavity.
2 88 SjoÈ beg (1994, 1995, 1997) developed the indiet e et in tems of (sufae) spheial hamonis to the powe H, and Nahavandhi and SjoÈ beg (1998) extended this appoah to the powe H. The esults an be summaized as N I P ˆ pl X 1 n 1 n 1 H n P pl X 1 n n 1 n 1 H n P whee Hn m 1 P ˆn H m P n os w d; m ˆ ; 4p and P n os w is Legende's polynomial of ode n. Equation () an be efomulated as an integal simila to Eq. (1). To ahieve this, we st ewite Eq. () as follows: " N I P ˆpl HP H P X1 n 1 H n P X1 n 1 # 1 H n P 4 n 1 whee we have used the notation H m P ˆ X1 Hn m P ; m ˆ ; Inseting Eq. (), and onsideing that X 1 P n os w ˆ and (Heiskanen and Moitz 1967, p. 9) 1 X 1 nhn H P ˆ HP d p `0 we aive at N I P ˆpl HP H d 4p H P HP H H 6p `0 4 d In view of the fat that d ˆ 1 4p we nally obtain N I P ˆpl H P l H HP d 4 l H H P 1 `0 6 `0 4 d Compaing the lassial fomula [Eq. (1)] with the new one [Eq. (9)], we obtain the di eene dn I P ˆN lassi I l 4 NI new o, in view of Eq. (8) dn I P ˆ l 4 o, in spetal fom dn I P ˆ pl whee H m P ˆ X1 ˆ pl H P H H P H H P pl 1 n 1 H m n P d l 8 d l 8 H P H P H H P H H P d d Fomula (1) shows that thee ae some long-wavelength di eenes of powe H between the lassial and new fomulas. (The tems of powe H ae less than a few entimetes, and they an theefoe be negleted in most ases.) The most likely explanation fo this di eene is that the lassial method su es fom the plana appoximation. This an be seen fom the following example. Fo a smooth topogaphy, the st tem on the ight-hand side of Eq. (11) an be appoximated by l 4 H d ˆ: plh P s 0 ˆ: 0:07s 0 H P mm whee s 0 is the maximum pola adius (in km) and H P is also given in km. Fo example, with s 0 ˆ 555 km (oesponding to a geoenti adius of about 5 ) and H P =1 km, this tem beomes 1:5 m, but fo H P ˆ 6 km it anges to 50 m! (Cf. Matine and VanõÂek 1994). Hene dn I in Eq. (1) an be egaded as a oetion to the lassial method, whih leads to the fomula N new I ˆ N lassi I dn I 14 A stit fomula fo the indiet e et At the point P on the sphee of adius, the topogaphi potential at point P an be witten (fo onstant density) Z H V t d P ˆl d 15 ˆ ` p whee ` ˆ t, is the geoenti adius of topogaphi point and t ˆ os w. The oesponding
3 89 potential of a ondensed laye aoding to Helmet's seond ondensation method beomes V P ˆl H d 16 oesponding to a sufae laye of density q 0 H on the sphee of adius. By di eening and dividing by (Buns' fomula), we obtain the indiet geoid e et N I P ˆ1 V t P V P ˆ l f H; t H d 17 whee we have intodued the kenel funtion f H; t ˆ Z H d ` 18 This fomula an be dietly integated to (f. Matine and VanõÂ ek 1994) f H; t ˆ H t ` t H t ` P t ln t 19 o 8 0 if H ˆ 0 >< t f H; t ˆ ` H H ` 0 H` >: P t ln H t ` if H > 0 t 19a Theefoe, Eq. (17), with the funtion f H; t povided by Eq. (19) o Eq. (19a), is a igoous integal fomula fo the indiet e et. 4 Taylo expansion of the stit fomula Fo ompleteness, we now deive the powe seies of N I fom the stit fomula of Eq. (17) above. We stat fom a Taylo expansion of f H; t aound f 0; t : f H; t ˆf 0; t X1 kˆ1 f k 0; t H k k! 0 whee f k is the k-th adial deivative (i.e. with espet to H) off H; t. It follows dietly fom Eq. (18) that f 0; t ˆ0 and f 1 0; t ˆ = Thus we an ewite Eq. (17) as X N I P ˆl 1 f k 0; t H k d kˆ k! Fom (with the notation ˆ H) 1 f 1 H; t ˆ` ˆ X1 we obtain n P n t f H; t ˆ ` ` ˆ X1 n 1 n P n t and f H; t ˆ 4` 5 4 ` ˆ 1 X 1 n n 1 n 1 P n t In the limit H! 0, o equivalently!, we obtain f 0; t ˆ d 1 t ˆ X1 n 1 P n t 4 and fom the last sum of Eq. () X f 0; t ˆ1 1 n n 1 P n t ˆ 1 X 1 n 1 n n 1 P n t ˆ 1 D t d 1 t whee we have intodued the notations d 1 t ˆX1 n 1 P n t and D t ˆX1 n 1 np n t 5 Fom Eq. (6), we obtain HP H d ˆ X1 nhn p `0 P ˆ 1 X 1 n 1 np n t H d 4p ˆ 1 D t H d 6 4p and we also have 1 d 1 t F Q d Q ˆ F P 4p fo any ontinuous funtion F and t ˆ os w PQ, whih de nes the popeties of D t and d 1 t. By inseting Eqs. (4) and (5) into Eq. (1), we nally aive at
4 90 N I P ˆpl H P l H HP d 4 l H HP 1 `0 6 `0 4 d O H 4 i.e. the thid-ode Taylo expansion of the stit fomula of Eq. (17) equals ou pevious fomula Eq. (9). 5 Numeial investigations In ode to numeially investigate the indiet e et, we have applied the lassial and new integals, Eqs. (1) and (7) espetively. We have also applied the lassial fomula oeted with the hamoni expansion of Eq. (14) as well as the stit integal of Eq. (17) with f H; t given by Eq. (19a). The esults of the spheial hamoni appoah ae limited to the thid powe of elevation H. The hamoni oe ients of heights Hn and H n ae detemined fom Eq. (). Fo this, a Digital Teain Model (DTM) is geneated using the Geophysial Exploation Tehnology (GETECH) DTM (GETECH 1995a). This DTM was aveaged using aea weighting. Sine the inteest is in ontinental elevation oe ients, the heights below sea level ae all set to zeo. The spheial hamoni oe ients ae omputed to degee and ode 60. The paamete l ˆ Gq is omputed using G ˆ 6: m kg 1 s and q ˆ 670 kgm. =671 km and = 981 Gal ae also used in the omputations. Stitly, Buns' fomula equies to be omputed fo geodeti latitude /. Howeve, sine N I eahes at most m, is set to a onstant. This appoximation is of the ode of the attening of the ellipsoid ( 0:00), whih is at most 6 mm. Two test aeas of size ae hosen. Both of these test aeas ae in Sweden. The aea A is limited by latitudes 57 and 59 N and longitudes 1 and 15 E, loated in the south of Sweden. The topogaphy in this aea vaies fom 40 to 40 m. The aea B is limited by latitudes 6 and 65 N and longitudes 1 and 15 E, loated in noth-west Sweden. The topogaphy in this aea is moe ugged than in test egion A and vaies fom 76 to 1051 m. Fist, the stit fomula is omputed with a global integation. The integation aea is extended outside the test aeas and limited to ap size (w) of0.a:5 :5 0 DTM (GETECH 1995b) is used inside the ap size of 0. Futhe out, we have applied a DTM. This esult is then used as the `tue' solution to ompae with all othe methods. Figue 1 shows the indiet e et omputed by the stit fomula [Eq. (17)] fo aea B. It anges fom 1:5 to 7.4 m. Fo the lassial and new integal appoahes, a :5 :5 0 DTM (GETECH 1995b) is also used. The integation aea is again extended outside the test aeas, but limited to ap sizes of and 1. Figues ±4 show the indiet e et omputed by the lassial [Eq. (1)] and new integal [Eq. (7)], as well as the lassial fomula oeted with the hamoni expansion [Eq. (14)] methods with 1 integation aea in test egion B. Figues and ae simila in shape with mino diffeenes. The plots ange fom 4:0 to 1.0 m (Fig. ) and :99 to 1.79 m (Fig. ). Both of them inlude the loal ontibutions with pue integal fomulas, but they Fig. 1. The indiet e et omputed by stit method [Eq. (17)] with a global integation in test egion B. Contou inteval is 0. m
5 91 Fig.. The indiet e et omputed by lassial method [Eq. (1)] with 1 integation aea in test egion B. Contou inteval is 0. m Fig.. The indiet e et omputed by new integal method [Eq. (7)] with 1 integation aea in test egion B. Contou inteval is 0. m ae laking the fa-zone ontibution outside the ap of adius 1. Figues 1 (`tue' solution) and 4 (oeted lassial solution) ae simila in shape and only slightly di eent in magnitude. In both these fomulas, the loal infomation and long-wavelength ontibutions ae pesent. Finally, Fig. 5 depits the smooth long-wavelength spheial hamoni epesentation of the indiet e et [Eq. ()], anging fom 4. to 6.96 m. This suggests that the lassial fomula oeted with the hamoni expansion [Eq. (14)] is the best altenative to the stit fomula in this study.
6 9 Fig. 4. The indiet e et omputed by lassial fomula oeted with the hamoni expansion [Eq. (14)] with 1 ap size in test egion B. Contou inteval is 0. m Fig. 5. The indiet e et omputed by the spheial hamoni method [Eq. ()] in test egion B. Contou inteval is 0. m In ode to obtain futhe insight into how the methods di e, the lassial, new integal and hamoni expansion appoahes and the lassial fomula, oeted with the hamoni expansion, ae subtated fom the stit method. These di eenes ae pesented fo the two test aeas using integation aeas of and 1 in Tables 1 and, espetively. These tables show eos of the lassial fomula, Eq. (1), as well as the new integal fomula Eq. (7). We note also that the eos even inease with ap size (see Tables 1 and ), evealing that an integation aea of 1 is too small to aount fo the long-wavelength signal. Also, the pue hamoni ex-
7 9 Table 1. Eo of appoximate fomulas fo indiet e et in test egions A and B with ap size Test egion A Test egion B Eq. (1) Eq. (7) Eq. (14) Eq. () Eq. (1) Eq. (7) Eq. (14) Eq. () Max ) )0.5.1 ).69.5 ) Min ).5 ).8 )1.01 ).1 )4.61 ).85 )1.81 )4.0 Ave ).5 )1. ) ).60 ).14 ) SD Units in m Eq. (1) = lassial fomula; Eq. (7) = new fomula; Eq. (14) = oeted lassial fomula; Eq. () = hamoni expansion Table. Eo of appoximate fomulas fo indiet e et in test egions A and B with 1 ap size Test egion A Test egion B Eq. (1) Eq. (7) Eq. (14) Eq. () Eq. (1) Eq. (7) Eq. (14) Eq. () Max ) ) ) ) Min ).1 ).94 )0.71 ).1 )8.4 )9.75 )1.55 )4.0 Ave ).74 )1.5 ) )6.8 )5.04 ) SD Units in m Eq. (1) = lassial fomula; Eq. (7) = new fomula; Eq. (14) = oeted lassial fomula; Eq. () = hamoni expansion pansion of the indiet e et [Eq. ()] is not a good altenative, beause it laks loal details. In both test egions (A and B), the lassial fomula oeted with the hamoni expansion [Eq. (14)] agees bette with the stit fomula than the othe two methods, espeially when the ap size is ineased fom to 1. Tables 1 and show that the mean of di eenes between two methods deeases fom 1.01 to 0.84 m. This justi es ou belief that the best altenative fo the omputation of the indiet e et is the use of Eqs. (14) and (1). 6 Conlusions The indiet geoid e et is omposed of both loal e ets and long-wavelength ontibutions. This implies that most fomulas studied in this pape may have some numeial poblems in epesenting these di eent signals. Ou stit fomula, Eq. (17), as well as its appoximations, Eqs. (7) and (9), equie that the integation aea oves most of the globe to inlude the long wavelengths. Howeve, a pue set of spheial hamonis, Eq. (), tunated to, say, degee 60 will not ontain the loal details. Fo the test aeas A and B in Sweden, the long-wavelength ontibution fom the hamoni expansion is of about the same signi ane as the shot-wavelength signal of the loal integals. In the lassial fomula, Eq. (1), suh long-wavelength infomation, anging to 50 m, is missing even fo a global integation aea. We onlude that ou Eqs. (14) and (1) may be a suitable ompomise between the loal ontibution [epesented by the lassial fomula of Eq. (1)] and a set of spheial hamonis, Eq. (1), that is subtated to aount fo the long-wavelength signal. Finally, all the sufae integals above ould be slightly genealized fom a onstant to a lateally vaiable topogaphi density (l), simply by putting l inside the integals. Aknowledgement. The authos wish to thank D Huaan Fan, who assisted in omputing the hamoni oe ients H n and H n. efeenes Geophysial Exploation Tehnology (1995a) Global DTM5. Geophysial Exploation Tehnology (GETECH), Univesity of Leeds, Leeds, UK Geophysial Exploation Tehnology (1995b) DTM.5 of Euope. Geophysial Exploation Tehnology (GETECH), Univesity of Leeds, Leeds, UK Heiskanen WA, Moitz H (1967) Physial geodesy. Feeman, San Faniso Matine Z, VanõÂek P (1994) The indiet e et of topogaphy in the Stokes±Helmet tehnique fo a spheial appoximation of the geoid. Manus Geod 19: 1±19 Nahavandhi H, SjoÈ beg LE (1998) Teain oetion to powe H in gavimeti geoid detemination. J Geod 7: 14±15 SjoÈ beg LE (1994) On the teain e ets in geoid and quasigeoid deteminations using Helmet's seond ondensation method. ep 6, Depatment of Geodesy, oyal Institute of Tehnology, Stokholm SjoÈ beg LE (1995) On the quasigeoid to geoid sepaation. Manus Geod 0: 18±19 SjoÈ beg LE (1997) On the downwad ontinuation eo at the Eath's sufae and the geoid of satellite deived geopotential models. To appea in Bull Geol Si A VanõÂek P, Kleusbeg A (1987) The Canadian geoid ± Stokesian appoah. Manus Geod 1: 86±98 VanõÂek P, Matine Z (1994) The Stokes±Helmet sheme fo the evaluation of a peise geoid. Manus Geod 19: 119±18 Wang YM, app H (1990) Teain e ets in geoid undulation omputations Manus Geod 15: ±9 Wihienhaoen C (198) The indiet e ets on the omputation of geoid undulations. ep 6, Depatment of Geodesti Siene and Suveying, The Ohio State Univesity, Columbus
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Generalized Vapor Pressure Prediction Consistent with Cubic Equations of State
 Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B. Calculations for Sample Cross-Section 2
 SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
Chapter 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH 1. INTRODUCTION
 DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Value Distribution of L-Functions with Rational Moving Targets
 Advanes in Pue Mathematis 3 3 79-73 Pulished Online Deeme 3 (http://wwwsipog/jounal/apm) http://dxdoiog/436/apm33998 Value Distiution of -Funtions wh ational Moving agets Matthew Cadwell Zhuan Ye * ntelligent
Advanes in Pue Mathematis 3 3 79-73 Pulished Online Deeme 3 (http://wwwsipog/jounal/apm) http://dxdoiog/436/apm33998 Value Distiution of -Funtions wh ational Moving agets Matthew Cadwell Zhuan Ye * ntelligent
Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Systems
 Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD
 Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
SIO 229 Gravity and Geomagnetism. Lecture 6. J 2 for Earth. J 2 in the solar system. A first look at the geoid.
 SIO 229 Gavity and Geomagnetism Lectue 6. J 2 fo Eath. J 2 in the sola system. A fist look at the geoid. The Thee Big Themes of the Gavity Lectues 1.) An ellipsoidal otating Eath Refeence body (mass +
SIO 229 Gavity and Geomagnetism Lectue 6. J 2 fo Eath. J 2 in the sola system. A fist look at the geoid. The Thee Big Themes of the Gavity Lectues 1.) An ellipsoidal otating Eath Refeence body (mass +
Planck Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gravitation
 Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Absorption Rate into a Small Sphere for a Diffusing Particle Confined in a Large Sphere
 Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW)
 PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
1 Spherical multipole moments
 Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
THE LAPLACE EQUATION. The Laplace (or potential) equation is the equation. u = 0. = 2 x 2. x y 2 in R 2
 THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
What Form of Gravitation Ensures Weakened Kepler s Third Law?
 Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
Math 2263 Solutions for Spring 2003 Final Exam
 Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Dissolution of Solid Particles in Liquids: A Shrinking Core Model
 Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
Problem 1. Part b. Part a. Wayne Witzke ProblemSet #1 PHY 361. Calculate x, the expected value of x, defined by
 Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
B da = 0. Q E da = ε. E da = E dv
 lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
Determine the Stress Calculating Mode of Sliding Failure of Soil Mass under the Push-Extend Multi-under-Reamed Pile
 Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Internet Appendix for A Bayesian Approach to Real Options: The Case of Distinguishing Between Temporary and Permanent Shocks
 Intenet Appendix fo A Bayesian Appoach to Real Options: The Case of Distinguishing Between Tempoay and Pemanent Shocks Steven R. Genadie Gaduate School of Business, Stanfod Univesity Andey Malenko Gaduate
Intenet Appendix fo A Bayesian Appoach to Real Options: The Case of Distinguishing Between Tempoay and Pemanent Shocks Steven R. Genadie Gaduate School of Business, Stanfod Univesity Andey Malenko Gaduate
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
Goodness-of-fit for composite hypotheses.
 Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
Conservative Averaging Method and its Application for One Heat Conduction Problem
 Poceedings of the 4th WSEAS Int. Conf. on HEAT TRANSFER THERMAL ENGINEERING and ENVIRONMENT Elounda Geece August - 6 (pp6-) Consevative Aveaging Method and its Application fo One Heat Conduction Poblem
Poceedings of the 4th WSEAS Int. Conf. on HEAT TRANSFER THERMAL ENGINEERING and ENVIRONMENT Elounda Geece August - 6 (pp6-) Consevative Aveaging Method and its Application fo One Heat Conduction Poblem
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
Scattering in Three Dimensions
 Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Numerical Integration
 MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Physics 111. Ch 12: Gravity. Newton s Universal Gravity. R - hat. the equation. = Gm 1 m 2. F g 2 1. ˆr 2 1. Gravity G =
 ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
A dual-reciprocity boundary element method for axisymmetric thermoelastodynamic deformations in functionally graded solids
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th Decembe, 013, Singapoe A dual-ecipocity bounday element method fo axisymmetic themoelastodynamic defomations in functionally gaded solids *W. T. Ang and B. I. Yun Division of Engineeing
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th Decembe, 013, Singapoe A dual-ecipocity bounday element method fo axisymmetic themoelastodynamic defomations in functionally gaded solids *W. T. Ang and B. I. Yun Division of Engineeing
Determining solar characteristics using planetary data
 Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
(n 1)n(n + 1)(n + 2) + 1 = (n 1)(n + 2)n(n + 1) + 1 = ( (n 2 + n 1) 1 )( (n 2 + n 1) + 1 ) + 1 = (n 2 + n 1) 2.
 Paabola Volume 5, Issue (017) Solutions 151 1540 Q151 Take any fou consecutive whole numbes, multiply them togethe and add 1. Make a conjectue and pove it! The esulting numbe can, fo instance, be expessed
Paabola Volume 5, Issue (017) Solutions 151 1540 Q151 Take any fou consecutive whole numbes, multiply them togethe and add 1. Make a conjectue and pove it! The esulting numbe can, fo instance, be expessed
An analytic calculation method on air gap flux in permanent magnet. brushless DC motor with ironless rotor
 Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.
![( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx. ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.](/thumbs/90/103689049.jpg) 9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Application of Parseval s Theorem on Evaluating Some Definite Integrals
 Tukish Jounal of Analysis and Numbe Theoy, 4, Vol., No., -5 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/tjant/// Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/tjant--- Application of Paseval s Theoem on Evaluating
Tukish Jounal of Analysis and Numbe Theoy, 4, Vol., No., -5 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/tjant/// Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/tjant--- Application of Paseval s Theoem on Evaluating
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS
 6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Σk=1. g r 3/2 z. 2 3-z. g 3 ( 3/2 ) g r 2. = 1 r = 0. () z = ( a ) + Σ. c n () a = ( a) 3-z -a. 3-z. z - + Σ. z 3, 5, 7, z ! = !
 09 Maclauin Seies of Completed Riemann Zeta 9. Maclauin Seies of Lemma 9.. ( Maclauin seies of gamma function ) When is the gamma function, n is the polygamma function and B n,kf, f, ae Bell polynomials,
09 Maclauin Seies of Completed Riemann Zeta 9. Maclauin Seies of Lemma 9.. ( Maclauin seies of gamma function ) When is the gamma function, n is the polygamma function and B n,kf, f, ae Bell polynomials,
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Question Bank. Section A. is skew-hermitian matrix. is diagonalizable. (, ) , Evaluate (, ) 12 about = 1 and = Find, if
 Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Study of the Endface Friction of the Revolving Vane Mechanism
 Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Markscheme May 2017 Calculus Higher level Paper 3
 M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M Makscheme May 07 Calculus Highe level Pape 3 pages M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M This makscheme is the popety of the Intenational Baccalaueate and must not be epoduced o distibuted
M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M Makscheme May 07 Calculus Highe level Pape 3 pages M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M This makscheme is the popety of the Intenational Baccalaueate and must not be epoduced o distibuted
Chapter Eight Notes N P U1C8S4-6
 Chapte Eight Notes N P UC8S-6 Name Peiod Section 8.: Tigonometic Identities An identit is, b definition, an equation that is alwas tue thoughout its domain. B tue thoughout its domain, that is to sa that
Chapte Eight Notes N P UC8S-6 Name Peiod Section 8.: Tigonometic Identities An identit is, b definition, an equation that is alwas tue thoughout its domain. B tue thoughout its domain, that is to sa that
F 12. = G m m 1 2 F 21 = F 12. = G m 1m 2. Review. Physics 201, Lecture 22. Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation
 Physics 201, Lectue 22 Review Today s Topics n Univesal Gavitation (Chapte 13.1-13.3) n Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation n Popeties of Gavitational Foce n Planet Obits; Keple s Laws by Newton s Law
Physics 201, Lectue 22 Review Today s Topics n Univesal Gavitation (Chapte 13.1-13.3) n Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation n Popeties of Gavitational Foce n Planet Obits; Keple s Laws by Newton s Law
MULTILAYER PERCEPTRONS
 Last updated: Nov 26, 2012 MULTILAYER PERCEPTRONS Outline 2 Combining Linea Classifies Leaning Paametes Outline 3 Combining Linea Classifies Leaning Paametes Implementing Logical Relations 4 AND and OR
Last updated: Nov 26, 2012 MULTILAYER PERCEPTRONS Outline 2 Combining Linea Classifies Leaning Paametes Outline 3 Combining Linea Classifies Leaning Paametes Implementing Logical Relations 4 AND and OR
ASTR415: Problem Set #6
 ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
The Millikan Experiment: Determining the Elementary Charge
 LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
Mathematical Model of Magnetometric Resistivity. Sounding for a Conductive Host. with a Bulge Overburden
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 13, no. 7, 335-348 Mathematical Model of Magnetometic Resistivity Sounding fo a Conductive Host with a Bulge Ovebuden Teeasak Chaladgan Depatment of Mathematics Faculty
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 13, no. 7, 335-348 Mathematical Model of Magnetometic Resistivity Sounding fo a Conductive Host with a Bulge Ovebuden Teeasak Chaladgan Depatment of Mathematics Faculty
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY
 Poeedings of the 1998 Paifi Confeene on Manufatuing, August 18-20, 1998, Bisbane, Queensland, Austalia SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY Susanto,S., Kennedy,R.D. and Pie,
Poeedings of the 1998 Paifi Confeene on Manufatuing, August 18-20, 1998, Bisbane, Queensland, Austalia SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY Susanto,S., Kennedy,R.D. and Pie,
Solving Problems of Advance of Mercury s Perihelion and Deflection of. Photon Around the Sun with New Newton s Formula of Gravity
 Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
3.6 Applied Optimization
 .6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
.6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
AY 7A - Fall 2010 Section Worksheet 2 - Solutions Energy and Kepler s Law
 AY 7A - Fall 00 Section Woksheet - Solutions Enegy and Keple s Law. Escape Velocity (a) A planet is obiting aound a sta. What is the total obital enegy of the planet? (i.e. Total Enegy = Potential Enegy
AY 7A - Fall 00 Section Woksheet - Solutions Enegy and Keple s Law. Escape Velocity (a) A planet is obiting aound a sta. What is the total obital enegy of the planet? (i.e. Total Enegy = Potential Enegy
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
APPENDIX D COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR EQUATIONS D.1 THE REDLICH KWONG EQUATION
 AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
Central Force Motion
 Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
Numerical approximation to ζ(2n+1)
 Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
8 Separation of Variables in Other Coordinate Systems
 8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
$ i. !((( dv vol. Physics 8.02 Quiz One Equations Fall q 1 q 2 r 2 C = 2 C! V 2 = Q 2 2C F = 4!" or. r ˆ = points from source q to observer
 Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
( ) ( ) Review of Force. Review of Force. r = =... Example 1. What is the dot product for F r. Solution: Example 2 ( )
 : PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
: PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
LET a random variable x follows the two - parameter
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING ISSN: 2231-5330, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2015 19 Shinkage Bayesian Appoach in Item - Failue Gamma Data In Pesence of Pio Point Guess Value Gyan Pakash
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING ISSN: 2231-5330, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2015 19 Shinkage Bayesian Appoach in Item - Failue Gamma Data In Pesence of Pio Point Guess Value Gyan Pakash
Reflectance spectra for Si
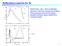 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
A thermodynamic degree of freedom solution to the galaxy cluster problem of MOND. Abstract
 A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
